Effects of Terrain near Taiwan Island on Typhoons with Different Tracks and Typhoon Waves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
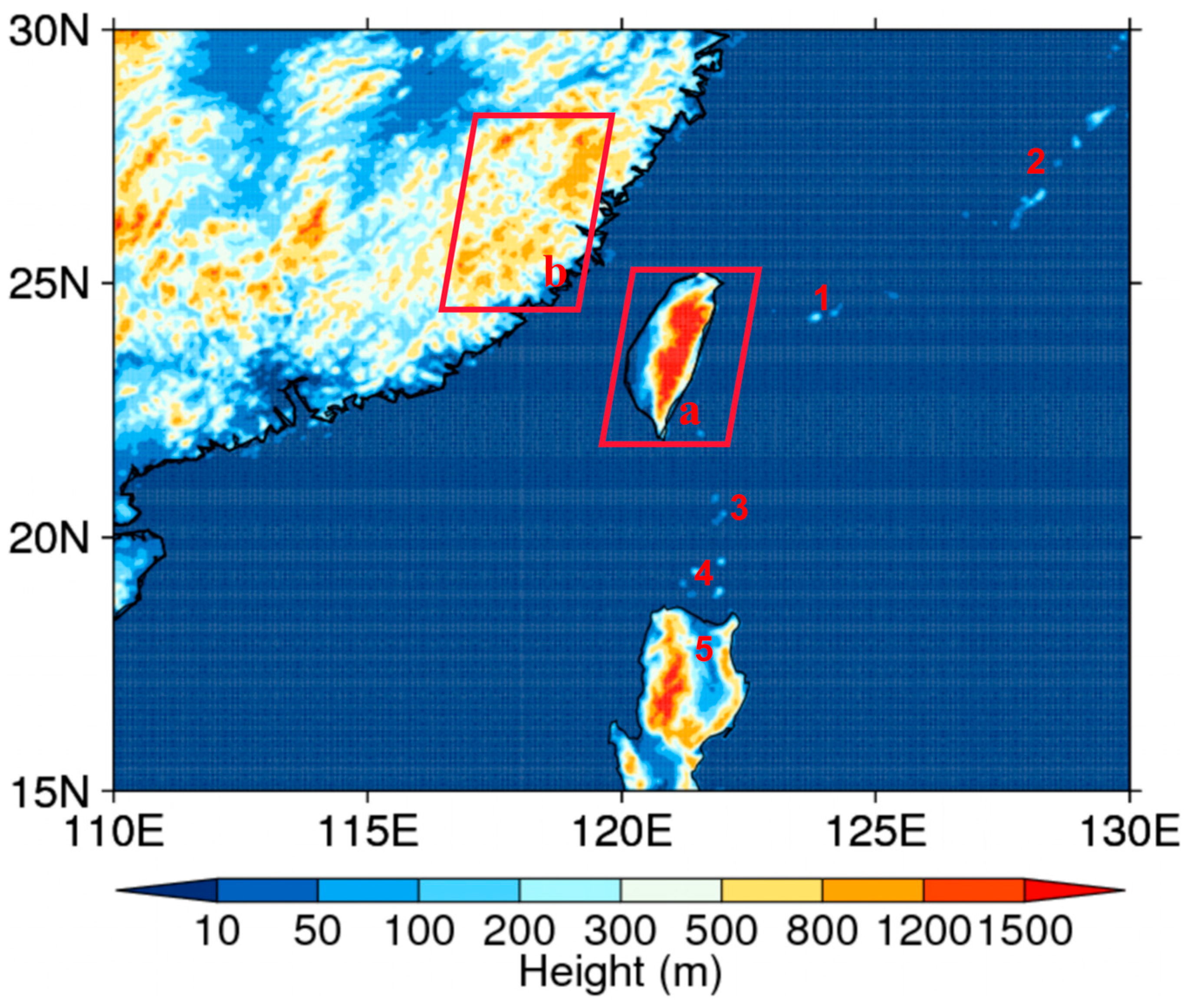
2.1. Region and Parameters
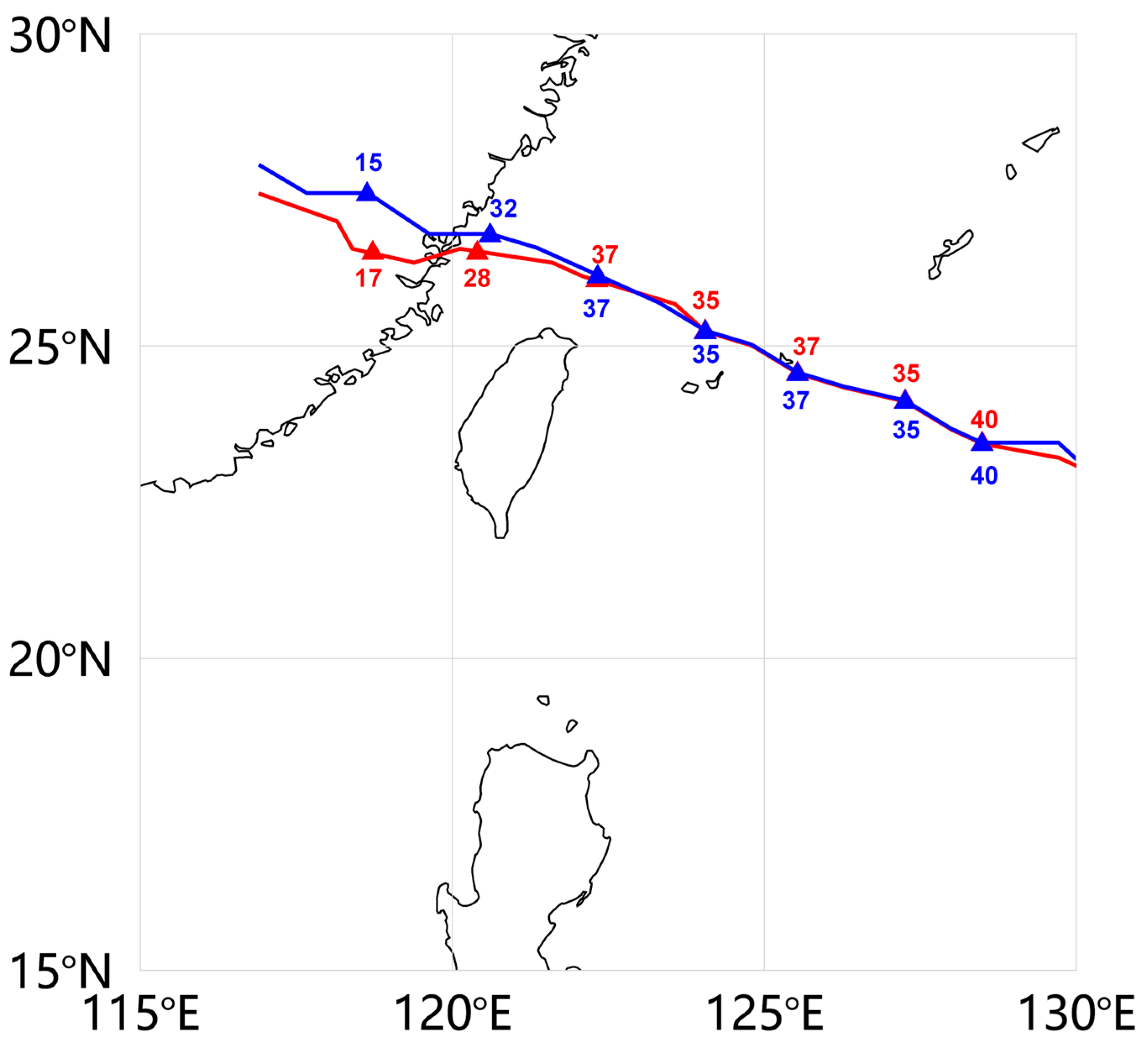
2.2. Typhoon Classification and Typhoon Events
2.3. WRF-SWAN Model
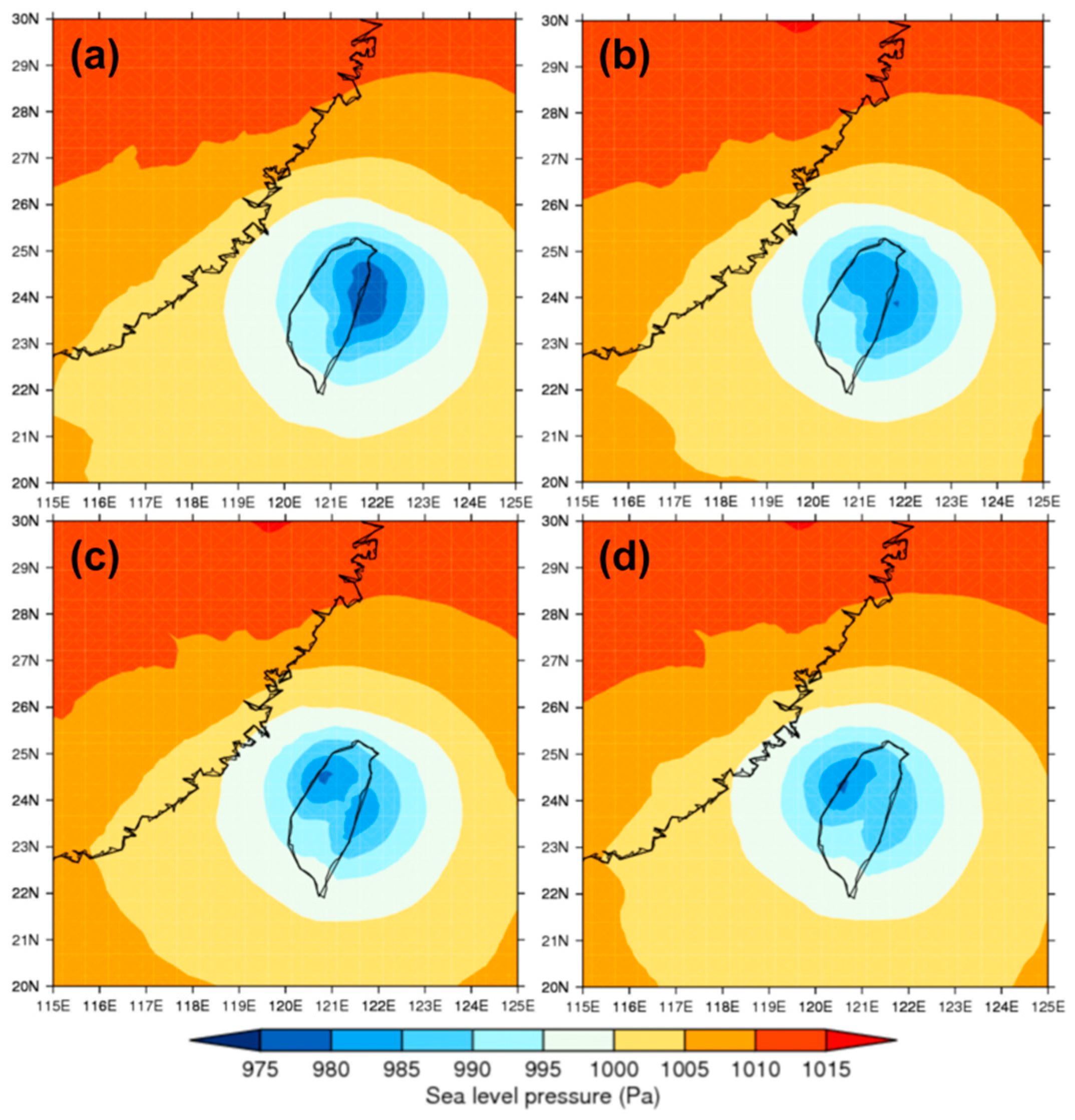
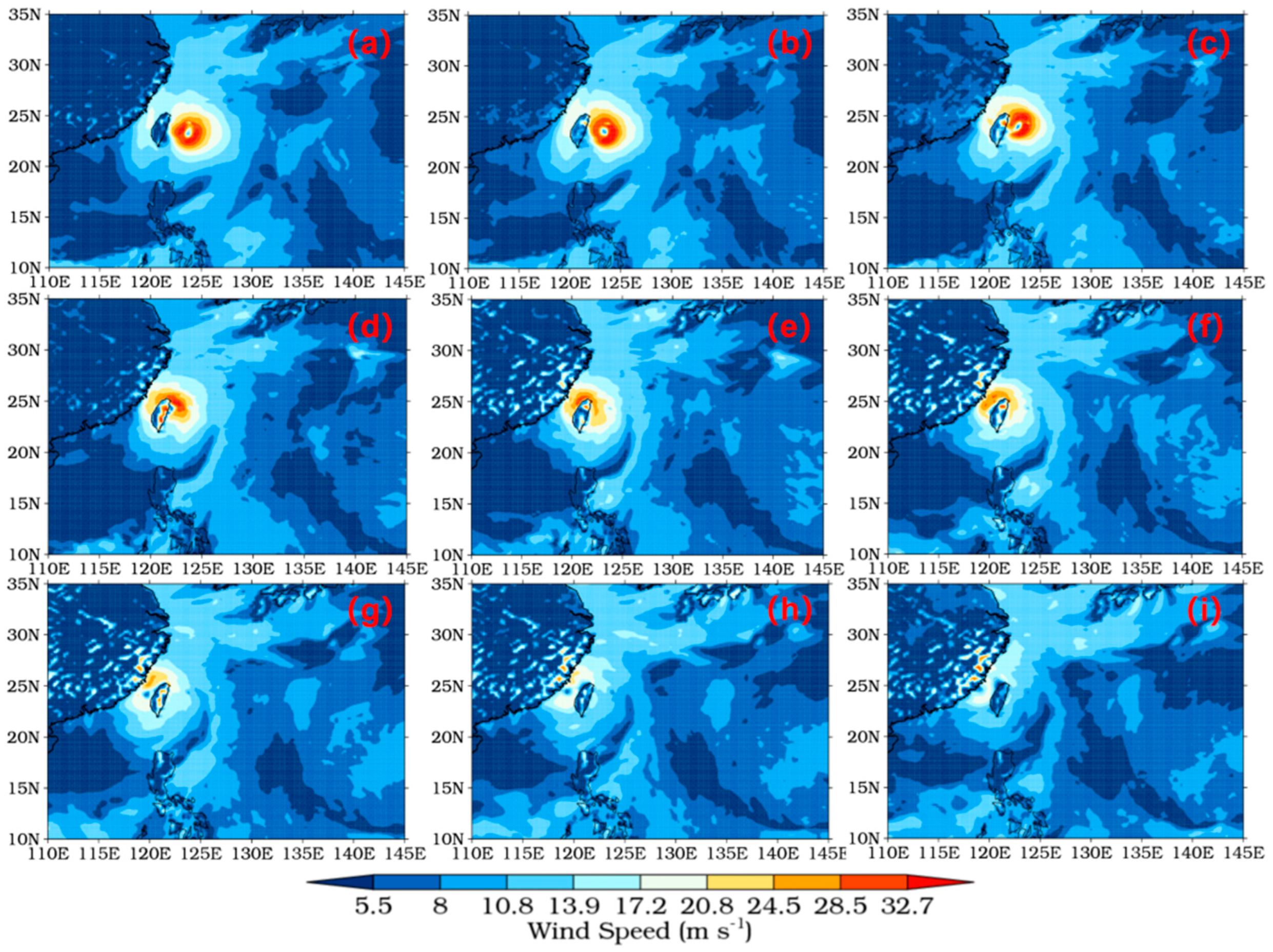
2.4. Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Maria Results
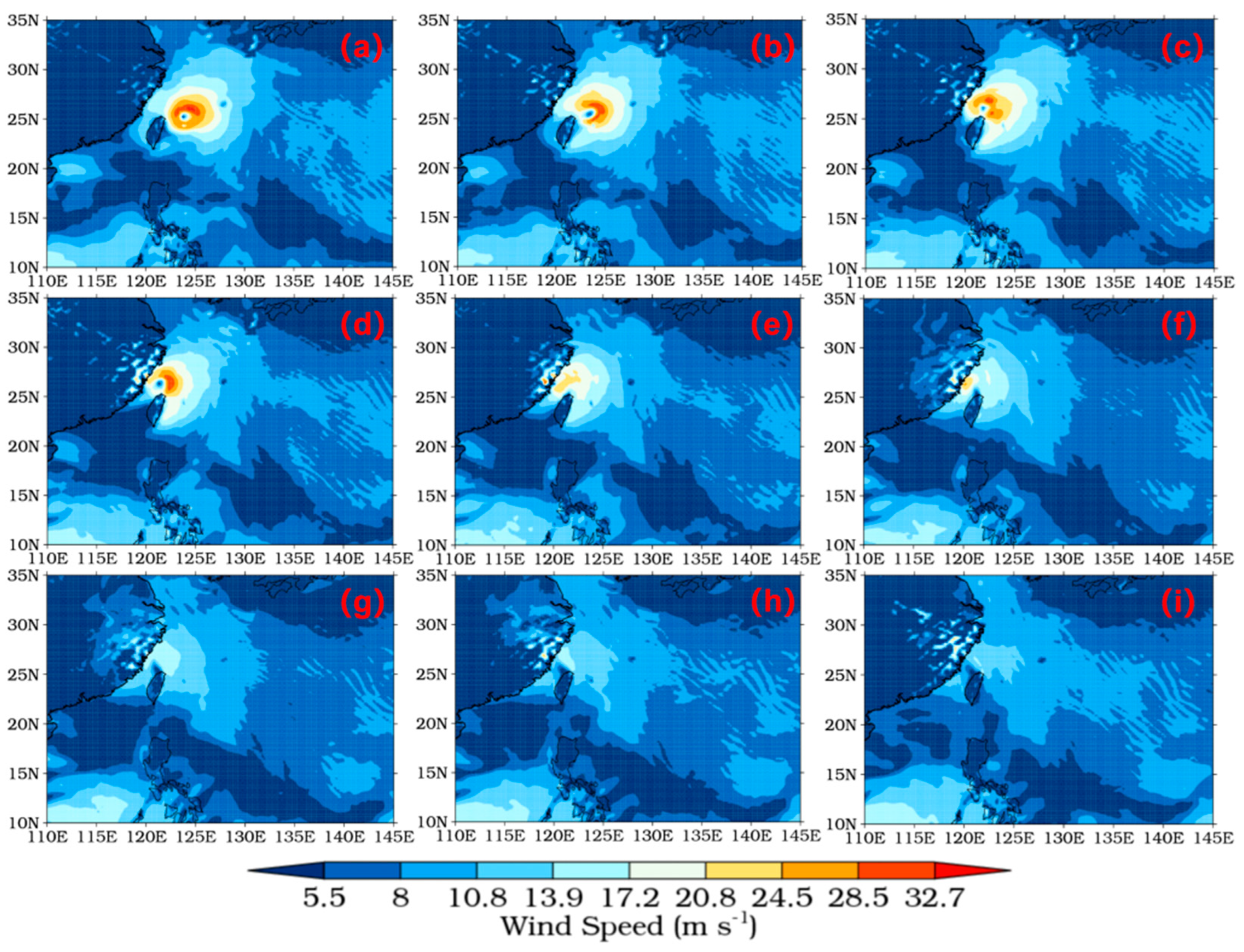
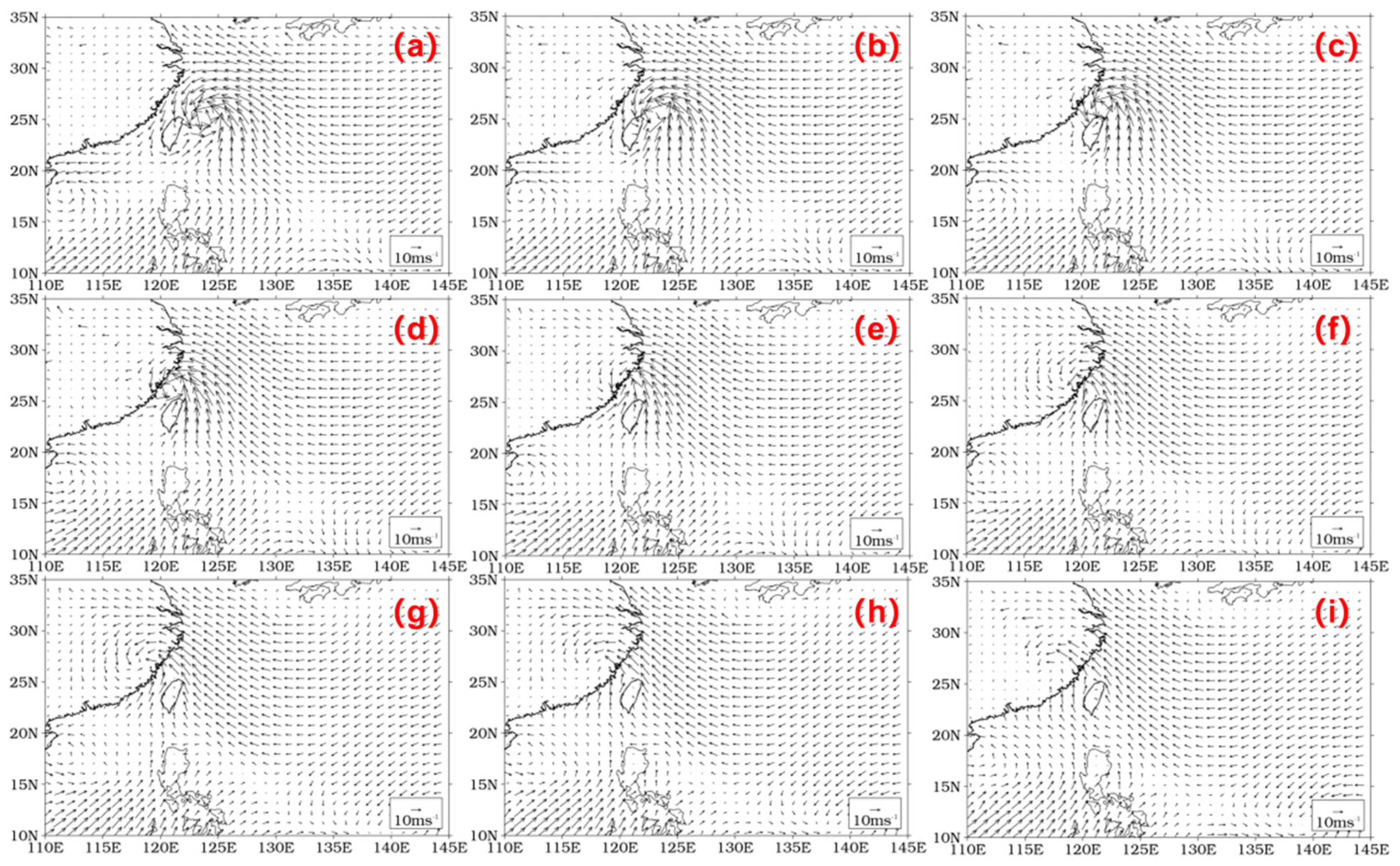
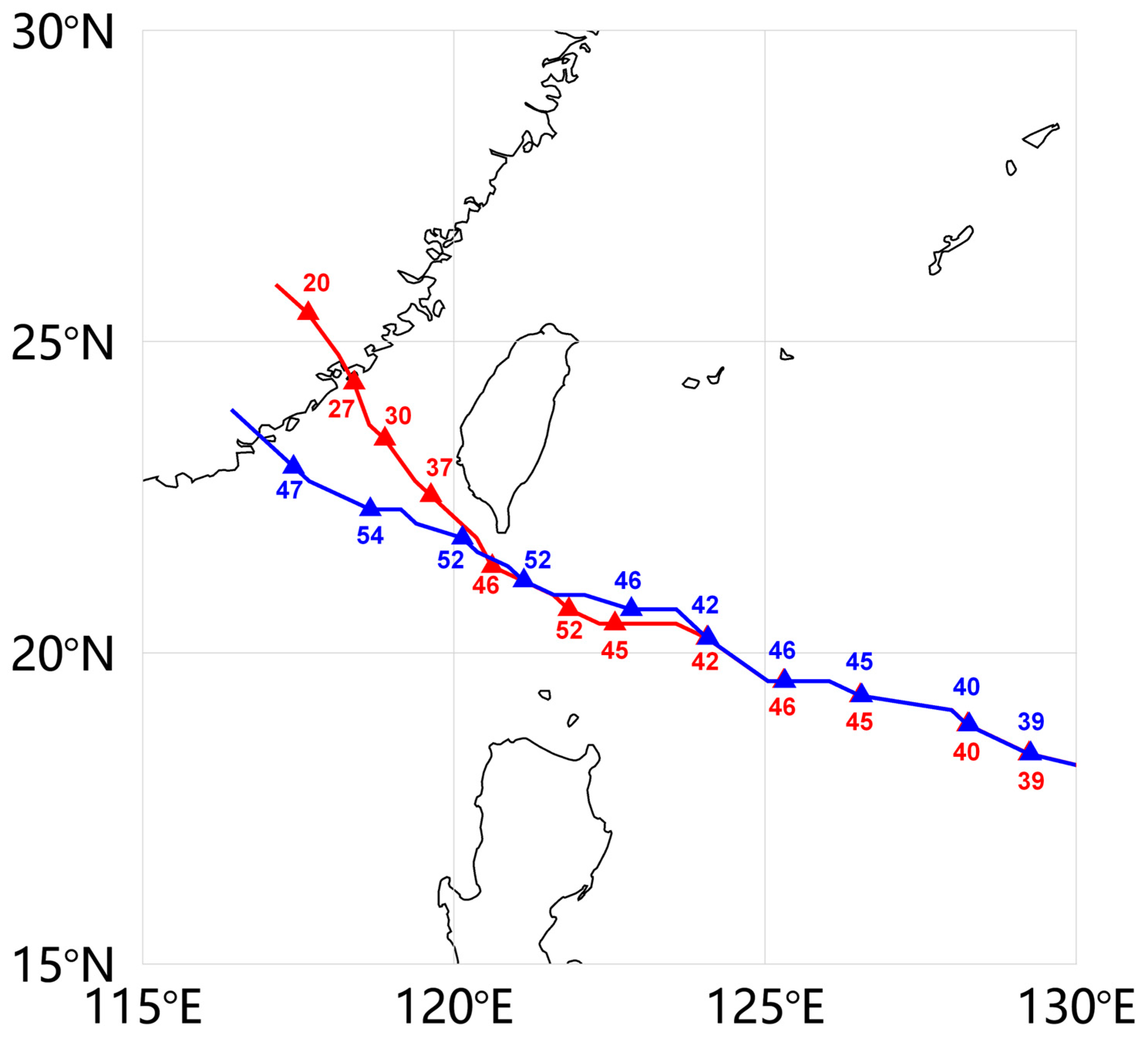
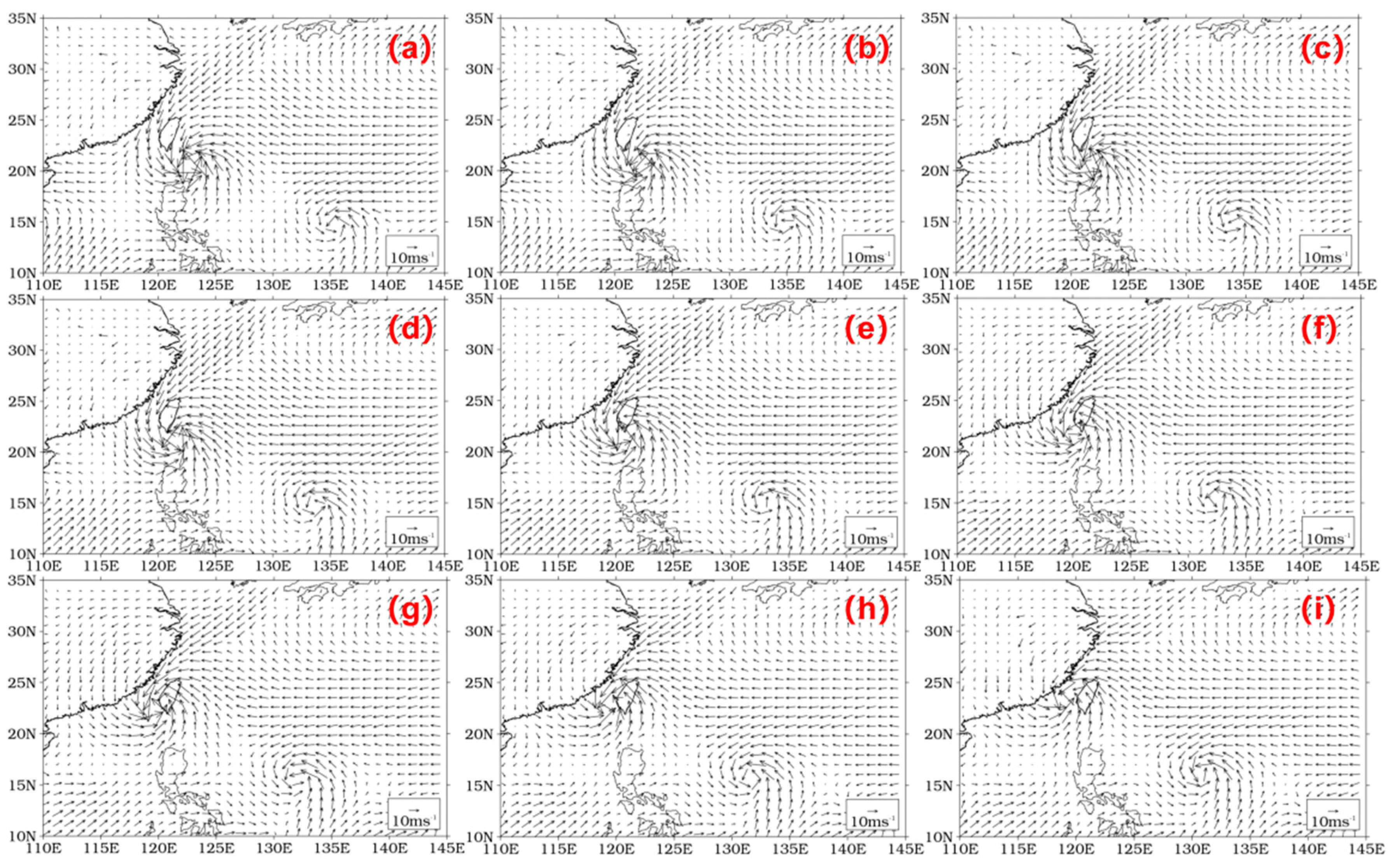
3.1.1. Terrain Effect and Typhoon Characteristics
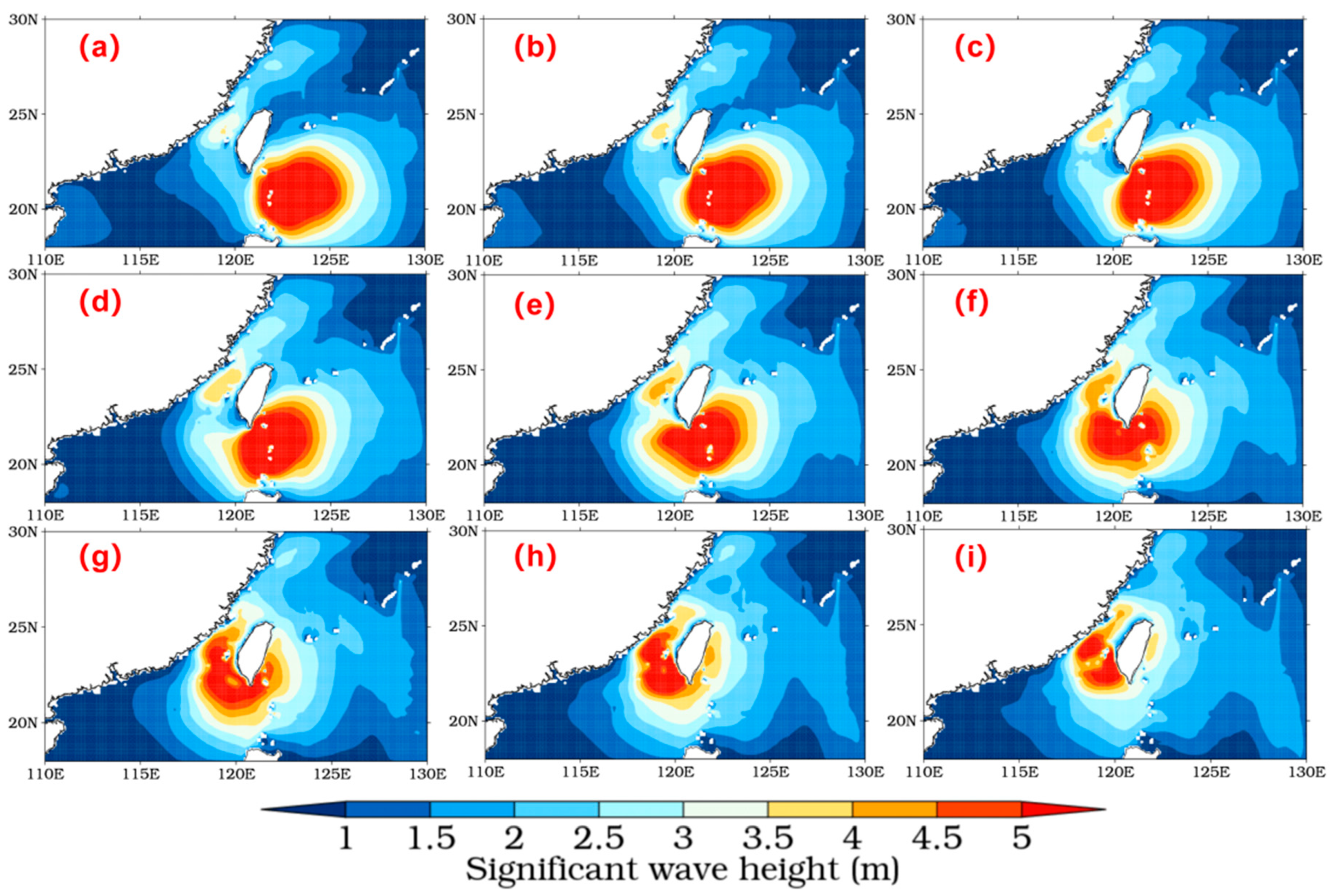
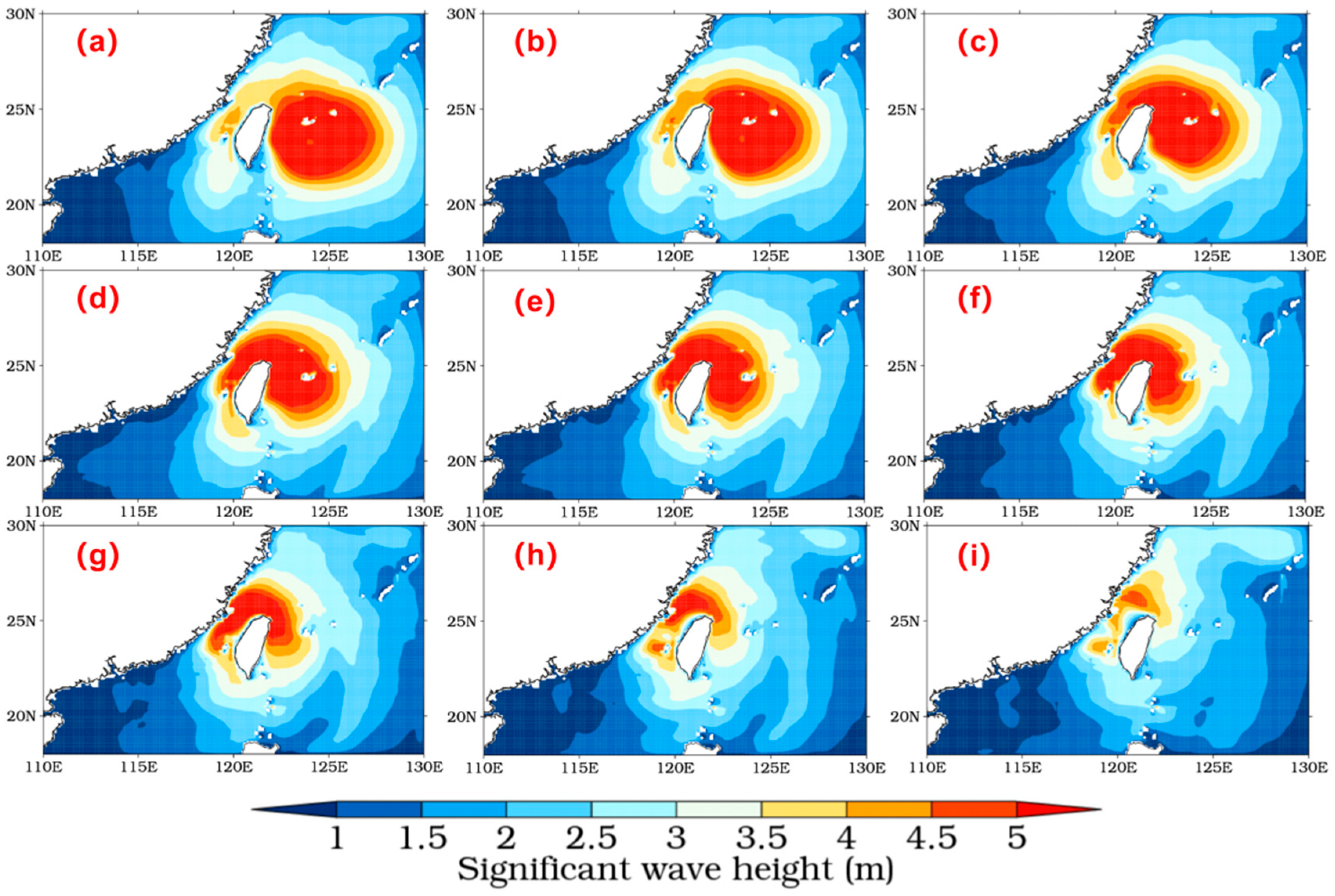
3.1.2. Relationship between Wind and Waves
3.1.3. Summary
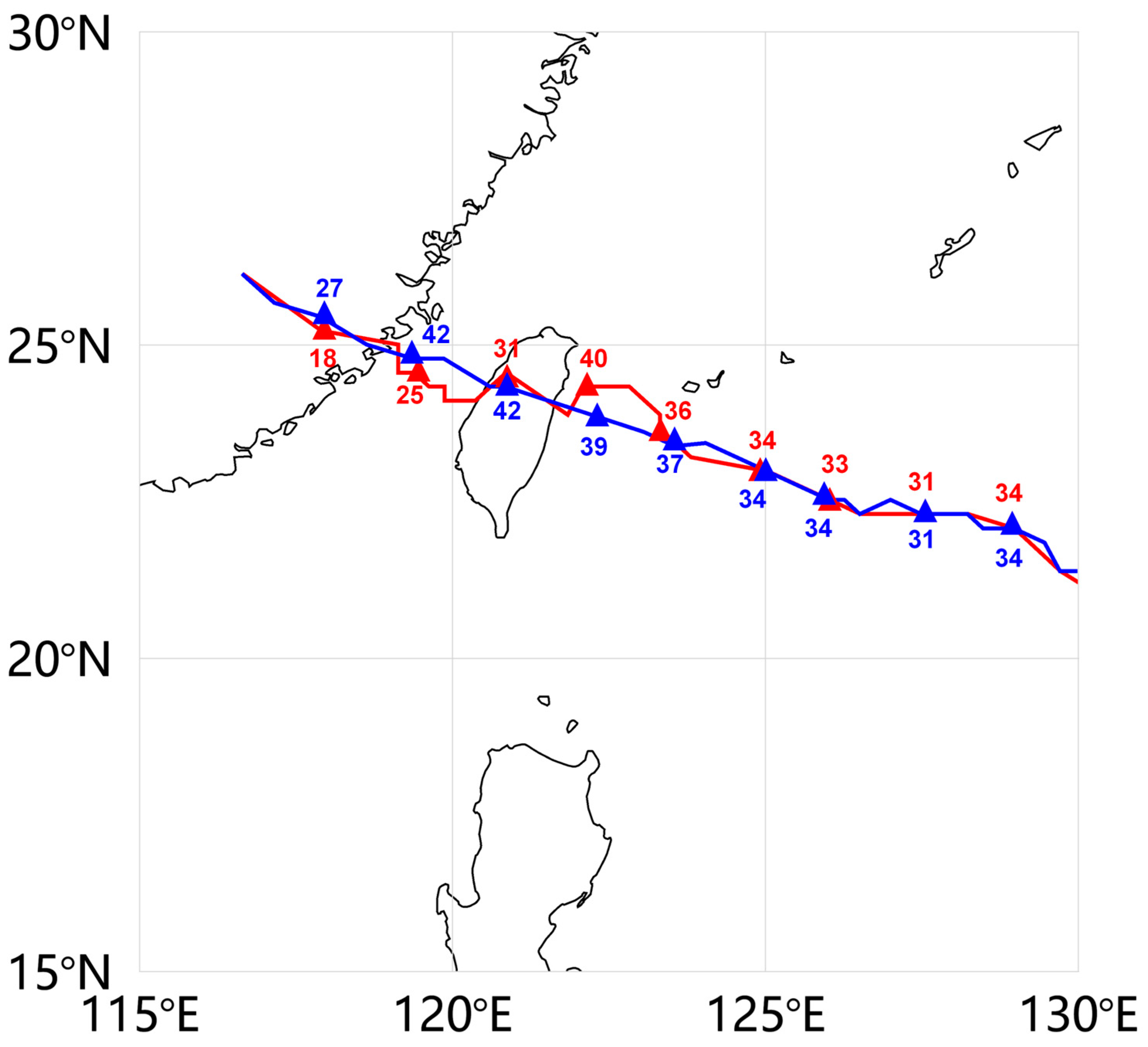
3.2. Meranti Results
3.2.1. Terrain Effect and Typhoon Characteristics
3.2.2. Relationship between Wind and Waves
3.2.3. Summary
3.3. Dujuan Results
3.3.1. Terrain Effect and Typhoon Characteristics
3.3.2. Relationship between Wind and Waves
3.3.3. Summary
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Jia, H.; Du, E.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Yang, A. Spatiotemporal Variations and Risk Analysis of Chinese Typhoon Disasters. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, R.J.; Hall, J.W.; Bates, P.D.; Nicholls, R.J. Quantified Analysis of the Probability of Flooding in the Thames Estuary under Imaginable Worst-case Sea Level Rise Scenarios. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2005, 21, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Hou, Y.; Hu, P.; Wang, K. Effects of Typhoon Paths on Storm Surge and Coastal Inundation in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S.; Stewart, R.W. Radiation stress and mass transport in gravity waves, with application to ‘surf beats’. J. Fluid Mech. 1962, 13, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Analysis of the causes of typhoon damage in the Weitou Port of Quanzhou and its restoration. Ocean Eng. 2007, 25, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Ying, L.P.; Liu, Y.L. Storm surge disaster and its impact on coastal wetlands in Yellow River Delta. J. Nat. Disasters 2006, 15, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, K. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 2005, 436, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nie, B. Storm surge prediction: Present status and future challenges. Procedia IUTAM 2017, 25, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, H.; Shih, H.; Chang, C.; Hsiao, S.; Chen, W.; Lin, L. Assessing the Potential Highest Storm Tide Hazard in Taiwan Based on 40-Year Historical Typhoon Surge Hindcasting. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ping, F.; Wang, X.; Li, M. Topographic Influence of Taiwan Island on Typhoon “Matmo”. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 41, 1037–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Xue, M.; Min, J. A comparison of limited-area 3DVAR and ETKFEn3DVAR data assimilation using radar observations at convective scale for the prediction of Typhoon Saomai (2006). Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Huang, L.A.; Gao, W. Assimilation of atmospheric infrared sounder radiances with WRF-GSI for improving typhoon forecast. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.N.; Brown, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Hinkel, J.; Shi, X.W.; Shi, P.J. Spatial-temporal changes of coastal and marine disasters risks and impacts in mainland China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 139, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes of Typhoon in Fujian Province. J. Catastrophol. 2007, 22, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.H.; He, X.; Ding, C.M. Super Typhoon Defence Scheme of Zhejiang Provinee and Research on Typhoon Hazards. Sci-Tech Inf. Dev. Econ. 2010, 20, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.Z.; Feng, W.C.; Sun, X.G. Characteristics of landfall typhoon in Fujian Province and its defending research. Mar. Sci. 2006, 11, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, L. Effect of the Orography of Taiwan Island on Typhoon Tracks. Sci. Atmos. Sin. 1995, 19, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Hou, Q.F.; Wang, H.D.; Wu, X.D. A numerical study of the effect of Taiwan Island terrain on typhoon Haitang (0505) track. Trop. Meteorol. 2008, 14, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Lin, L.; Jang, J.; Chang, C. Simulation of Typhoon-Induced Storm Tides and Wind Waves for the Northeastern Coast of Taiwan Using a Tide-Surge-Wave Coupled Model. Water 2017, 9, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, D. An observational study of the inner core structure of Typhoon Meranti (2016) near landfall. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, e962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Juan, T.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Chen, J. Track Deflection of Typhoon Maria (2018) during a Westbound Passage Offshore of Northern Taiwan: Topographic Influence. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2020, 148, 4519–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C. Statistics of heavy rainfall occurrences in Taiwan. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 981–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, L.X.; Xu, Y.L. Impacts of upper-level cold vortex on the rapid change of intensity and motion of Typhoon Meranti (2010). J. Trop. Meteorol. 2012, 18, 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, M.A.; Tuleya, R.E.; Kurihara, Y. A numerical study of the effect of island terrain on tropical cyclones. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1987, 115, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C. Numerical simulation of typhoon Gladys (1994) and its interaction with Taiwan terrain using the GFDL hurricane model. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2001, 129, 1533–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Qian, Q. Influence of Taiwan Island on the intensity of landed typhoons. J. Mar. Meteorol. 2018, 38, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.K.; Chan, J.C.L. Idealized simulations of the effect of Taiwan and Philippines topographies on tropical cyclone tracks. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. A Numerical Study of the Track Deflection of Supertyphoon Haitang (2005) Prior to Its Landfall in Taiwan. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2008, 136, 598–615. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.K.; Chan, J.C.L. Idealized simulations of the effect of Taiwan topography on the tracks of tropical cyclones with different steering flow strengths. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 3211–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.S.; Chai, F.; Zhang, C.Y.; Huang, B.Q.; Jiang, Y.W.; Hu, J.Y. An overview of physical and biogeochemical processes and ecosystem dynamics in the Taiwan Strait. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.J.; Zhang, D.L.; Tang, X.D. A modeling study of typhoon Nari (2001) at landfall: 2. Structural changes and terrain-induced asymmetries. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D09112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Numerical Simulation of Wind Waves and Typhoon Air-Sea Interaction Process. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of Taiwan topography on the rapid intensification of typhoon Meranti (1010) passing by the Taiwan Strait. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 39, 789–801. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Duan, H.; Yan, L. Numerical simulation of rapid intensification change of super typhoon Saomai (2006) over the coastal water of China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 32, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y. Study on Molave typhoon wave in South China Sea based on SWAN model. J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 35, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, D.J.; Gray, W.M. The hurricane’s inner core region. I. Symmetric and asymmetric structure. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 1544–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, P.J.; MacAfee, A.W. The theory of trapped-fetch waves with tropical cyclones—An operational perspective. Weather Forecast. 2005, 20, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.L.; Chen, Q. Directional spectra of hurricane-generated waves in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L19608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.B.; Shemdin, O.H. Radar observation of hurricane wave directions. Int. Conf. Coast. Eng. 1978, 8, 209–226. [Google Scholar]
- Young, I.R. A review of the sea state generated by hurricanes. Mar. Struct. 2003, 16, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booij, N.; Ris, R.C.; Holthuijsen, L.H. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: Model description and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 7649–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Shi, F.Y.; Hong, H.S.; Shang, S.P.; Kirby, J.T. Tide-surge Interaction Intensified by the Taiwan Strait. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C06012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, W.B. Modeling the interaction between tides and storm surges for the Taiwan coast. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 721–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Study on the characteristics of typhoon waves under three typical paths in Taiwan Strait. Mar. Forecast. 2018, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.C.; Li, T.H.; Huang, Y.H. Influence of Mesoscale Topography on Tropical Cyclone Tracks: Further Examination of the Channeling Effect. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 72, 3032–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.; Elsberry, R.L. Interaction of Typhoons with the Taiwan Orography. Part II: Continuous and Discontinuous Tracks across the Island. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 121, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.K.; Chan, J.C.L. Idealized simulations of the effect of local and remote topographies on tropical cyclone tracks. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2045–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, W.; Sheng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Z.; Qu, W.; Li, X.; Hai, S. Influence of polluted dust on chlorophyll-a concentration and particulate organic carbon in the subarctic North Pacific Ocean based on satellite observation and the WRF-Chem simulation. Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, C.; Sheng, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. Effects of biomass burning on chlorophyll-a concentration and particulate organic carbon in the subarctic North Pacific Ocean based on satellite observations and WRF-Chem model simulations: A case study. Atmos. Res. 2021, 254, 105526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the aer radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.; Gettelman, A. A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and Numerical Tests. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3642–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Dezs, D. A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 38-1–38-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, B.; Seyed, M.S.; Mahyar, M.N. Skill assessment of SWAN model in the red sea using different wind data. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 30, 100714. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, A.; Adem, A.; Nour, E.I.B.; Recep, E.C.; Fouzia, H. Evaluation of a high-resolution wave hindcast model SWAN for the West Mediterranean basin. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2019, 84, 225–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, B.; Seyed, M.S.; Marzieh, H.D. Calibration and skill assessment of two input and dissipation parameterizations in WAVEWATCH-III model forced with ERA5 winds with application to Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 219, 108445. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.S.; Zhao, W.; Donelan, M.A.; Tolman, H.L. Directional Wind-Wave Coupling in Fully Coupled Atmosphere-Wave-Ocean Models: Results from CBLAST-Hurricane. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 3198–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarrieta, M.; Warner, J.C.; Armstrong, B.; Zambon, J.B.; He, R. Ocean-atmosphere dynamics during Hurricane Ida and Nor’Ida: An application of the coupled ocean-atmosphere-wave-sediment transport (COAWST) modeling system. Ocean Model. 2012, 43, 112–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, R.; Mostafa, B.; Seyed, M.S.; Mohammad, N.A. Simulating Meteorological and Water Wave Characteristics of Cyclone Shaheen. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 533. [Google Scholar]




| Typhoon Dujuan | Typhoon Meranti | Typhoon Maria | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | AE | d | r | AE | d | r | AE | d | |
| Wind speed (m/s) | 0.76 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 0.77 | −0.02 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.03 | 0.93 |
| Wind direction (°) | 0.95 | 0.3 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.45 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.37 | 0.94 |
| Significant wave height (m) | 0.79 | −0.04 | 0.87 | 0.81 | −0.11 | 0.86 | 0.84 | −0.06 | 0.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, C.; Shang, S.; Xie, Y.; He, Z.; Wei, G.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Effects of Terrain near Taiwan Island on Typhoons with Different Tracks and Typhoon Waves. Water 2023, 15, 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203661
Luo C, Shang S, Xie Y, He Z, Wei G, Zhang F, Wang L, Li X. Effects of Terrain near Taiwan Island on Typhoons with Different Tracks and Typhoon Waves. Water. 2023; 15(20):3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203661
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Chenghan, Shaoping Shang, Yanshuang Xie, Zhigang He, Guomei Wei, Feng Zhang, Lei Wang, and Xueding Li. 2023. "Effects of Terrain near Taiwan Island on Typhoons with Different Tracks and Typhoon Waves" Water 15, no. 20: 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203661
APA StyleLuo, C., Shang, S., Xie, Y., He, Z., Wei, G., Zhang, F., Wang, L., & Li, X. (2023). Effects of Terrain near Taiwan Island on Typhoons with Different Tracks and Typhoon Waves. Water, 15(20), 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203661






