Quantifying the Impact of Organic Fertilizers on Soil Quality under Varied Irrigation Water Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Description
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.3. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.4. SQI Evaluation Method
2.5. Data Processing Method
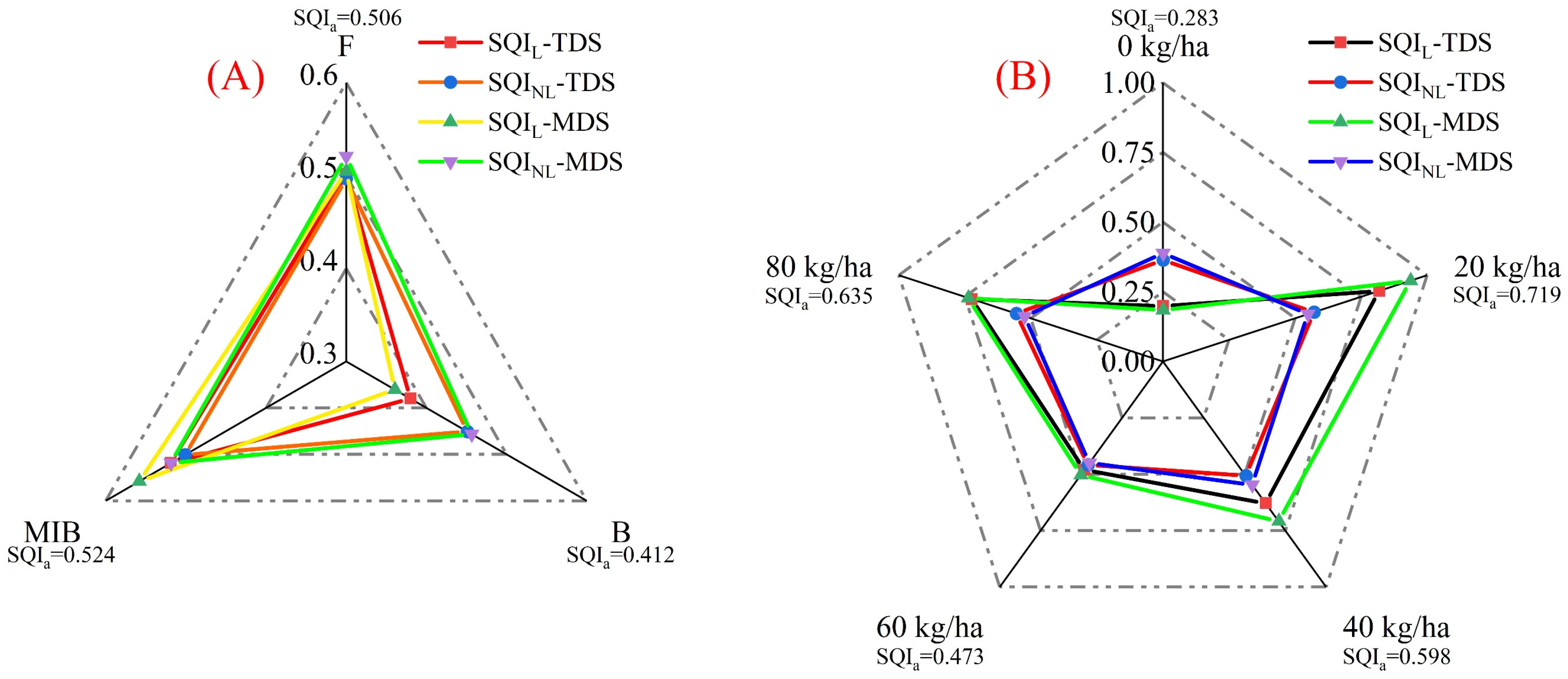
3. Results
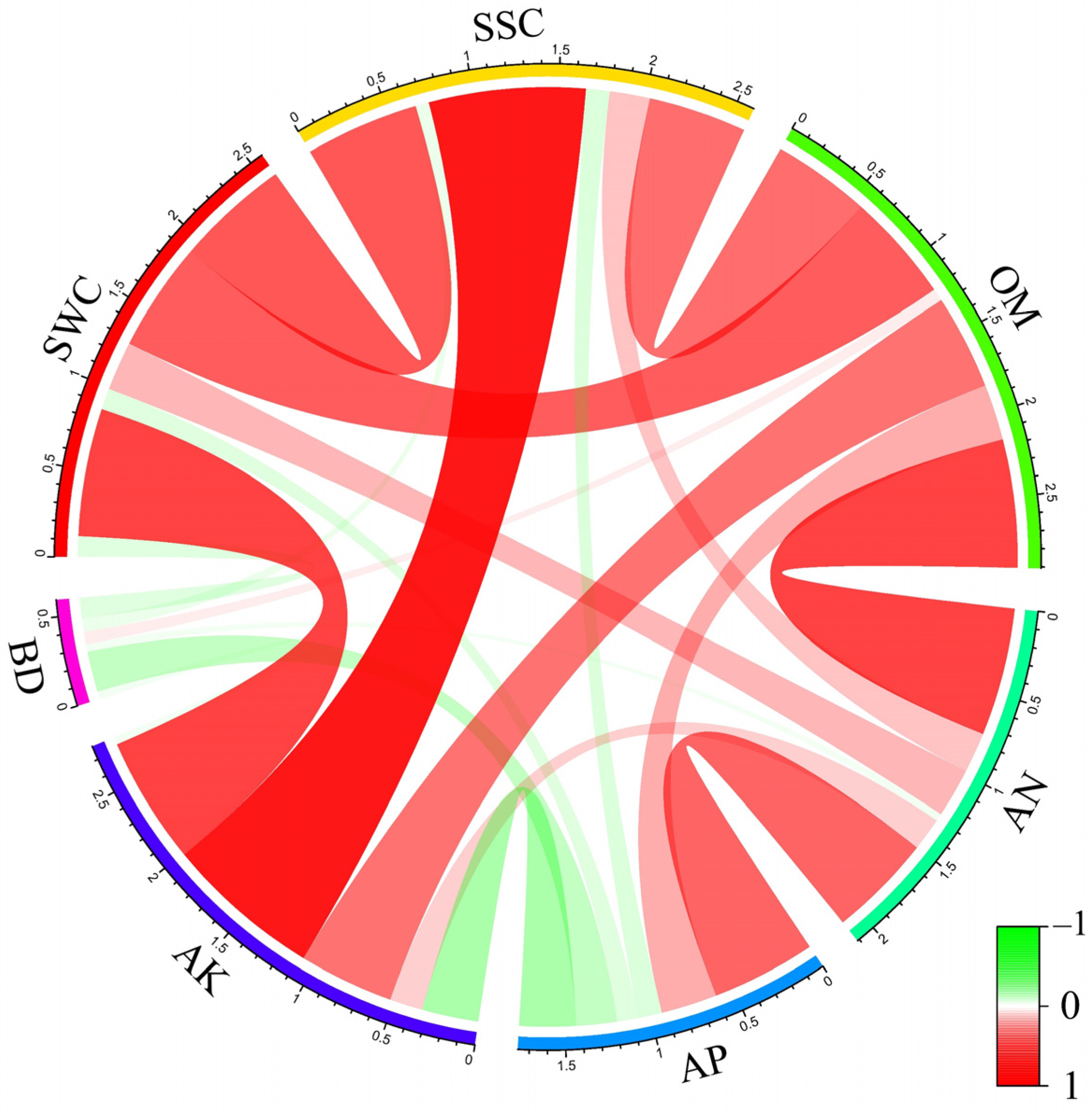
3.1. Statistical Characteristics of Soil Property Indexes
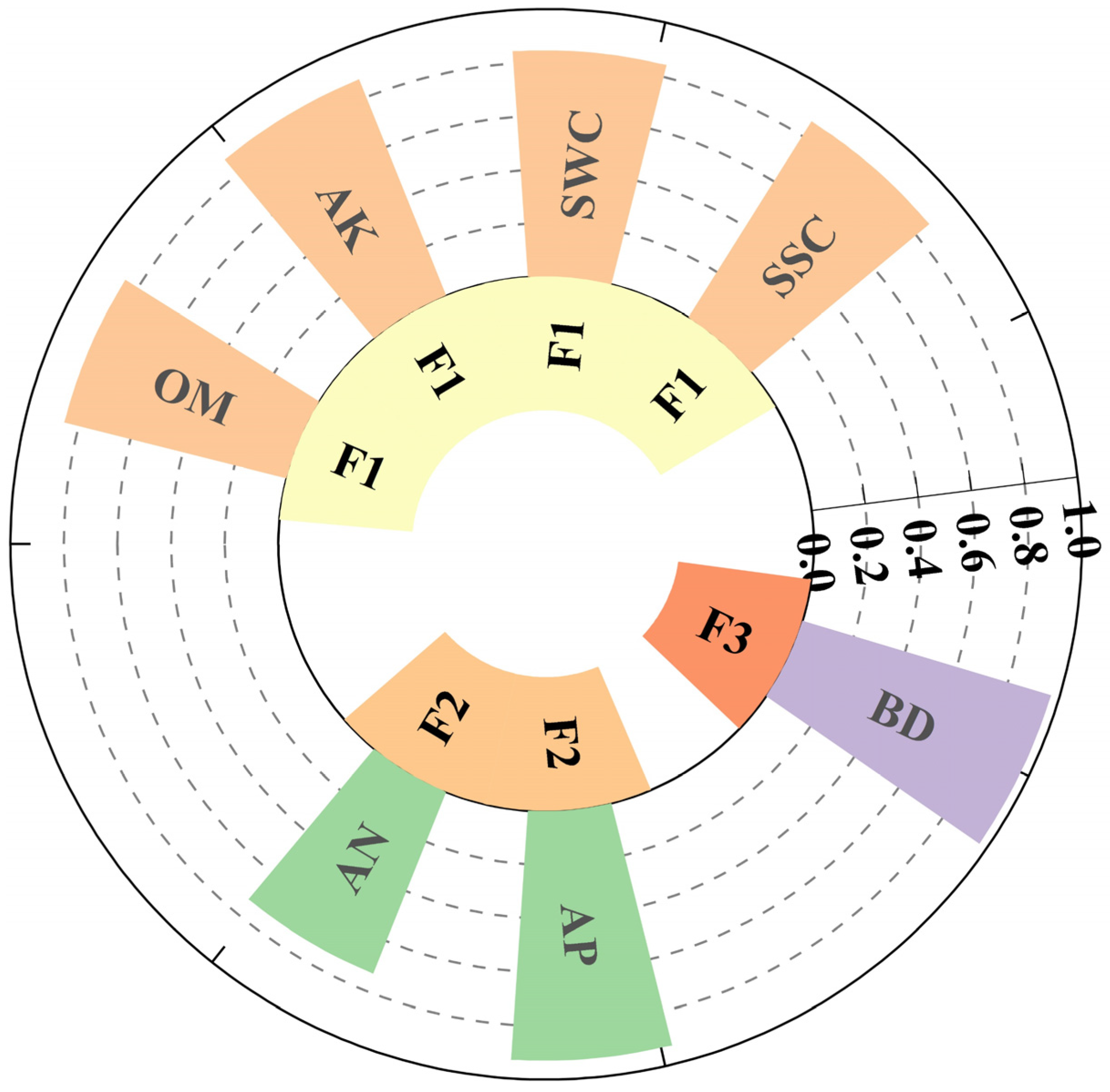
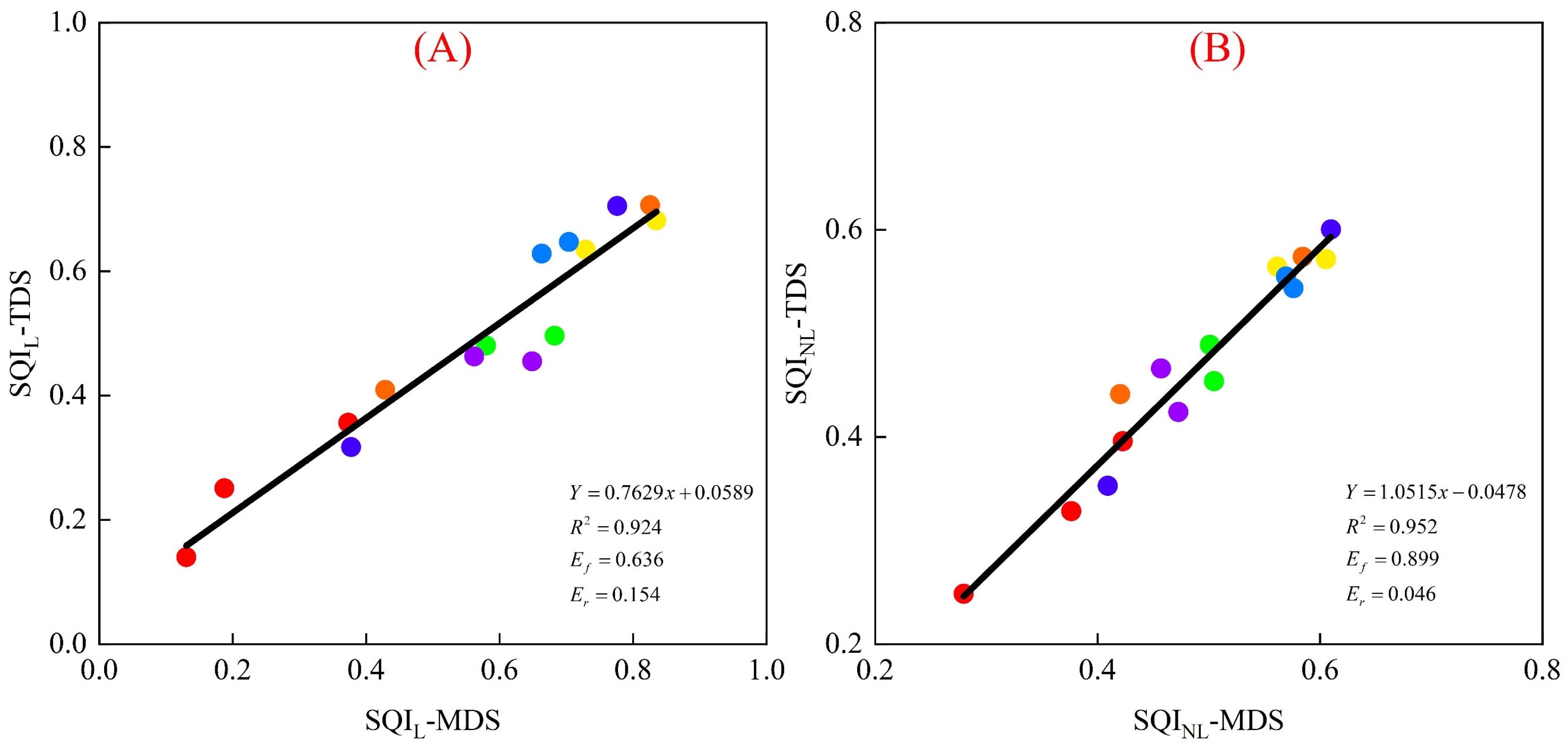
3.2. Establishment and Accuracy Verification of MDS Indexes
3.3. Evaluation of SQI for Irrigation and Fertilization
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Quality Evaluation Methods
4.2. Effects of Irrigation and Fertilization on Soil Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obade, V.; Lal, R. A standardized soil quality index for diverse field conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 541, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.S.; Liu, G.H.; Huang, C.; Liu, Q.S. Soil quality assessment in Yellow River Delta: Establishing a minimum data set and fuzzy logic model. Geoderma 2019, 334, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, F.; Zhao, L.L.; Yao, H.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, H.L. Influences of different land use types on soil characteristics and availability in Karst Area, Guizhou Province. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2014, 22, 1007–1013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, S. Assessment of groundwater and soil quality for agricultural purposes in kopruoren basin, Kutahya, Turkey. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ding, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Soil quality evaluation for navel orange production systems in central subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Deng, H.J.; Du, K.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Fisher, L.; Wu, C.Z.; Hong, T.; Zhang, G.S. Soil quality assessment in different climate zones of China’s Wenchuan earthquake affected region. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Jia, L.Z.; Yang, L.Y.; Guo, Z.H.; Sang, W.G.; Lu, L.; Xiao, C.W. Assessment of the effects of fencing enclosure on soil quality based on minimum data set in Biru County of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, N.; Gu, Y.; Li, D.Z.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, J.C.; Liu, J.Z.; Ren, J.; Cai, H.G. Soil quality evaluation in topsoil layer of black soil in Jilin Province based on minimum data set. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 91–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rahmanipour, F.; Marzaioli, R.; Bahrami, H.A.; Fereidouni, Z.; Bandarabadi, S.R. Assessment of soil quality indices in agricultural lands of Qazvin Province, Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.F.; Shi, D.M.; Lou, Y.B.; Zhang, J.L.; Ye, Q.; Jiang, N. Evaluation of the quality of cultivated-layer soil based on different degrees of erosion in sloping farmland with purple soil in China. Catena 2020, 198, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xu, H.N.; Xiao, F.M. Grey relation analysis of soil quality of Phyllostachys edulis stands at different fertilization. South China For. Sci. 2018, 46, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shiklomanov, I.A. Appraisal and assessment of world water resources. Water Int. 2000, 25, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Z. Towards water and food security in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2014, 8, 880–885. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yermiyahu, U.; Tal, A.; Ben-Gal, A.; Tarchitzky, J.; Lahav, O. Rethinking desalinated water quality and agriculture. Science 2007, 318, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, M.C.; Dadkhah, A.A. On reduction in the surface tension of water due to magnetic treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 278, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.R.; Zhao, Y.J.; Chen, F.L.; Chen, J.Z.; Duan, S.X. Magnetization mechanism of magnetized water. Acta Phys. Sin. 2011, 60, 432–439. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeilnezhad, E.; Choi, H.J.; Schaffie, M.; Gholizadeh, M.; Ranjbar, M. Characteristics and applications of magnetized water as a green technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 908–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, M.H.; El Fakhrani, Y.M.; Mabrouk, S.S.; Ebead, B.M. Effect of magnetic treated irrigation water on salt removal from a sandy soil and on the availability of certain nutrients. Int. J. Eng. 2013, 2, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, A.; Homaee, M.; Afzalinia, S.; Ruhipour, H.; Basirat, S. Organic resource management: Impacts on soil aggregate stability and other soil physico-chemical properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 148, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.J.; Tian, Y.; He, M.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Lyu, Q.; Xie, R.J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Deng, L.; Yi, S.L. Effects of chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer application on soil properties, citrus growth physiology, and yield. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Li, J.C.; Jiang, J.J.; Waheed, A.; Wang, S.G.; Rasheed, S.M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.P. Effects of organic fertilizer supply on soil properties, tomato yield, and fruit quality: A Global Meta-Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, S.L. Organic fertilizer increases soil organic carbon and crop yield in four-year tillage and crop rotations on the loess plateau, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 4271–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, L.R.; Lou, Y.S.; Fan, X.R.; Ren, L.X.; Xu, G.H. Watermelon responds to organic fertilizer by enhancing root-associated acid phosphatase activity to improve organic phosphorus utilization. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 279, 153838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, L.C.Z.; Queiroz, H.M.; Cherubin, M.R.; Ferreira, T.O. Applying the soil management assessment framework (SMAF) to assess mangrove soil quality. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.B.; Xu, L.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Shen, X.S.; Xu, H.F.; Jiao, J.G.; Li, H.X.; Hu, F. Crop yield-soil quality balance in double cropping in China’s upland by organic amendments: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.S.; Holden, N.M. Indices for quantitative evaluation of soil quality under grassland management. Geoderma 2014, 230, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Moreno, J.L.; Hernández, T.; García, C. Microbiological degradation index of soils in a semiarid climate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3463–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.B. A comparison of soil qualities of different revegetation types in the Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil 2011, 347, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models. Part 1: A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chen, X.W.; Yao, H.X. Evaluating the use of nash-sutcliffe efficiency coefficient in goodness-of-fit measures for daily runoff simulation with SWAT. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2017, 22, 05017023.1–05017023.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Veum, K.S.; Sudduth, K.A.; Obrycki, J.F. Soil health assessment: Past accomplishments, current activities, and future opportunities. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.J.; Wu, K.N.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, X.L. Advancement and revelation of the research on soil quality assessment on large spatial scales. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 565–578. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.H.; Yu, T.; Xu, Z.T.; Liu, H.Y.; Cai, Q.R. Distribution and probabilistic integrated ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface water of Poyang Lake, China. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Han, D.L.; Liu, S.W.; Wen, X.; Huang, Y.X.; Jia, H.T. Soil quality assessment under different land uses in an alpine grassland. Catena 2018, 171, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Tao, W.U.; Yan, X.U. Assessment of soil quality in coastal tidal flat reclamation areas based on MDS-TOPSIS model. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 5484–5492. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, N.; Yang, B.; Tian, P.; Jiang, Y.; Sui, P.X.; Sun, D.Q.; Zhang, Z.P.; Qi, H. Using a modified soil quality index to evaluate densely tilled soils with different yields in Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 13867–13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.H.; Il Kwak, J.; Chae, Y.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.W.; An, Y.J. In situ determination of crop productivity in metal- contaminated, remediated, and reclaimed soils: Significance of ecotoxicological data on assessing soil quality. Environ. Eng. Res. 2023, 28, 220785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xi, M.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J. Soil quality assessment of coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta of China based on the minimum data set. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.A.; Nicholas, M.H. Quantitative soil quality indexing of temperate arable management systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Bakhshandeh, E.; Hosseini, M.; Alavi, S.M. Assessing the effects of deforestation and intensive agriculture on the soil quality through digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, W.; Pierce, F.J. The dynamics of soil quality as a measure of sustainable management. In Defining Soil Quality for Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Coleman, D.C., Bezedick, D.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, A.C.R.; Brussaard, L.; Totola, M.R.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; Goede, R.G.M.D. A functional evaluation of three indicator sets for assessing soil quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 64, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.N.; Feng, T.J.; Wang, P.; Wu, X.D. Effects of long-term artificial forest restoration on soil moisture and nutrient characteristics in the Loess Area of Western Shanxi Province, China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 228–237. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.G.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Yue, X.L.; Liang, J.P.; Yang, Q.L.; Li, J.; Li, N. Micro-moistening irrigation combined with bio-organic fertilizer: An adaptive irrigation and fertilization strategy to improve soil environment, edible Rose yield, and nutritional quality. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 196, 116487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Z.; Yang, S.H.; Xu, J.Z.; Luo, Y.F.; Hou, H.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching losses from paddy fields with different water and nitrogen managements. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Z. Store grain in water and technology-development of highly-efficient agricultural water use for ensuring national food security. China Water Resour. 2022, 13, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Tian, L.; Lou, B.Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.T.; Dong, X.L.; Guo, K.; Liu, X.J. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil quality and crop production: A review. Chin. J. Eco Agric. 2023, 31, 354–363. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cao, C.Y.; Zheng, C.L.; Dang, H.K.; Guo, L.; Ma, J.Y. Salinity threshold of long-term saline water irrigation for winter wheat in Hebei Lowland Plain. Chin. J. Eco Agric. 2016, 24, 643–651. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Sun, H.Y.; Dong, X.L.; Chen, P.; Zhang, X.J.; Tian, L.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, J.T. Did manure improve saline water irrigation threshold of winter wheat? A 3-year field investigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.W.; Kong, S.Q.; Liu, R.Q. A review of brackish water for agricultural safe irrigation. Water Sav. Irrig. 2020, 10, 91–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.Q.; She, D.L. Influence of water quality on soil saturated hydraulic conductivity and infiltration properties. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 108–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.N.; Hou, Z.A. Effect of drip irrigation with saline water on soil nitrous oxide emissions in cotton field. J. Shihezi Univ. Nat. Sci. 2016, 34, 301–308. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.B.; Li, L.J.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q.L. Desalination characteristics and efficiency of high saline soil leached by brackish water and Yellow River water. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhao, G.Q.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.J. Advances in the application of activated water irrigation. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2019, 36, 403–411. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.J.; Sun, Y.; Ning, S.R.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhou, B.B.; Su, L.J.; Shan, Y.Y. Effects of activated irrigation water on soil physicochemical properties and crop growth and analysis of the probable pathway. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 660–670. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.J.; Xie, J.B.; Zhang, J.H.; Wei, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.Y. Effects of magnetic field strength on magnetized water infiltration and soil water and salt movement. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 292–298. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.X.; Zhou, X. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of chemical fertilizer application intensity of vegetable planting in China. J. China Agric. Univ. 2022, 27, 248–263. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.L.; Wang, J.P.; Su, T.M.; Li, H.G.; Tan, B.S.; Yang, W.J. Effects of partial substitution of chemical fertilizers by organic fertilizers on lettuce growth and soil environment. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 44, 41–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Hu, C.S.; Dong, W.X.; Li, X.X.; Liu, X.P.; Zhang, L.J.; Wen, H.D. Effects of long-term nutrient recycling pathways on soil nutrient dynamics and fertility effect in farmland. J. China Ecol. Agric. 2022, 30, 937–951. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.W.; Xie, Y.H.; Li, T.L.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Q.R.; Cao, J.; Shao, J.L. Effects of different organic substitutes on soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions and winter wheat yield in dryland of loess plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 286–293. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Reardon, C.L.; Klein, A.M.; Melle, C.J.; Hagerty, C.H.; Klarer, E.R.; Machado, S.; Paulitz, T.; Pritchett, L.; Schlatter, D.; Smith, S.F.; et al. Enzyme activities distinguish long-term fertilizer effects under different soil storage methods. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 177, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; Li, Y.Q.; Lin, Z.A.; Zhao, B.Q. Crop yield and soil fertility response to commercial organic fertilizer substituting chemical fertilizer. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 2136–2142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Guo, A.Q.; Cui, Z.T.; Shi, W.J. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction and organic fertilizer application on soil quality, eggplant yield and quality in solar greenhouse. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2023, 38, 188–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Jin, N.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.D.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S.L.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J.H. Changes in the microbial structure of the root soil and the yield of Chinese Baby Cabbage by chemical fertilizer reduction with bio-organic fertilizer application. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01215-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.X.; Feng, J.N.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, Z.B.; Shao, X.D.; Xia, T.Y. Coupling amendment of microbial and compound fertilizers increases fungal necromass carbon and soil organic carbon by regulating microbial activity in flue-cured tobacco-planted field. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2023, 117, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jia, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, R. Effects of bio-organic fertilizers on oat production and soil fertility in alpine region of Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2019, 27, 1759–1765. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Depth (cm) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Mechanical Composition (%) | Alkali-Hydrolyzed Nitrogen (mg/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) | Organic Matter (g/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Silt | Sand | ||||||
| 0–20 | 1.45 | 5.3 | 52.5 | 42.2 | 24.34 | 41.37 | 240 | 8.10 |
| 20–40 | 1.37 | 3.3 | 32.9 | 63.8 | 13.83 | 8.79 | 144 | 5.10 |
| Soil Index | Max | Min | Mean | SD | Cv | Skewness | Kurtosis | K-S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD (g/cm3) | 1.385 a | 1.345 c | 1.365 b | 0.011 | 0.008 | −0.116 | −0.663 | 0.998 |
| SWC (cm3/cm3) | 0.213 a | 0.064 b | 0.120 ab | 0.034 | 0.284 | 1.191 | 2.657 | 0.565 |
| SSC (g/kg) | 8.622 a | 2.357 a | 4.614 a | 1.883 | 0.408 | 1.074 | 0.120 | 0.309 |
| AN (mg/kg) | 24.898 a | 9.406 c | 18.332 b | 4.765 | 0.260 | −0.237 | −1.292 | 0.720 |
| AP (mg/kg) | 30.085 a | 2.834 b | 10.455 ab | 8.125 | 0.777 | 1.522 | 1.694 | 0.503 |
| AK (mg/kg) | 786.000 a | 98.000 a | 270.733 a | 224.342 | 0.829 | 1.500 | 0.793 | 0.072 |
| OM (g/kg) | 7.276 a | 3.374 b | 5.759 a | 1.163 | 0.202 | −0.240 | −0.863 | 0.863 |
| Soil Index | PCA | Norm Value | Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | TDS | MDS | ||
| BD (g/cm3) | −0.081 | −0.184 | 0.970 | 0.416 | 0.063 | 0.302 |
| SWC (cm3/cm3) | 0.846 | −0.192 | −0.102 | 2.310 | 0.122 | |
| SSC (g/kg) | 0.866 | −0.293 | −0.089 | 2.200 | 0.113 | |
| AN (mg/kg) | 0.565 | 0.731 | 0.167 | 3.398 | 0.231 | 0.326 |
| AP (mg/kg) | 0.057 | 0.932 | −0.105 | 1.819 | 0.133 | |
| AK (mg/kg) | 0.871 | −0.426 | −0.056 | 2.003 | 0.098 | |
| OM (g/kg) | 0.854 | 0.358 | 0.236 | 3.722 | 0.240 | 0.372 |
| Principal component eigenvalue | 3.282 | 1.870 | 1.058 | – | – | – |
| Contribution rate (%) | 46.886 | 26.715 | 15.112 | – | – | – |
| Accumulating contribution rate (%) | 43.826 | 73.293 | 88.713 | – | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Lei, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Su, L.; Wang, Q.; Tao, W.; Deng, M. Quantifying the Impact of Organic Fertilizers on Soil Quality under Varied Irrigation Water Sources. Water 2023, 15, 3618. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203618
Lin S, Lei Q, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Su L, Wang Q, Tao W, Deng M. Quantifying the Impact of Organic Fertilizers on Soil Quality under Varied Irrigation Water Sources. Water. 2023; 15(20):3618. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203618
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shudong, Qingyuan Lei, Yun Liu, Yimei Zhao, Lijun Su, Quanjiu Wang, Wanghai Tao, and Mingjiang Deng. 2023. "Quantifying the Impact of Organic Fertilizers on Soil Quality under Varied Irrigation Water Sources" Water 15, no. 20: 3618. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203618





