Methods of Removal of Hormones in Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Remediation or Removal
2.1.1. Biological Processes
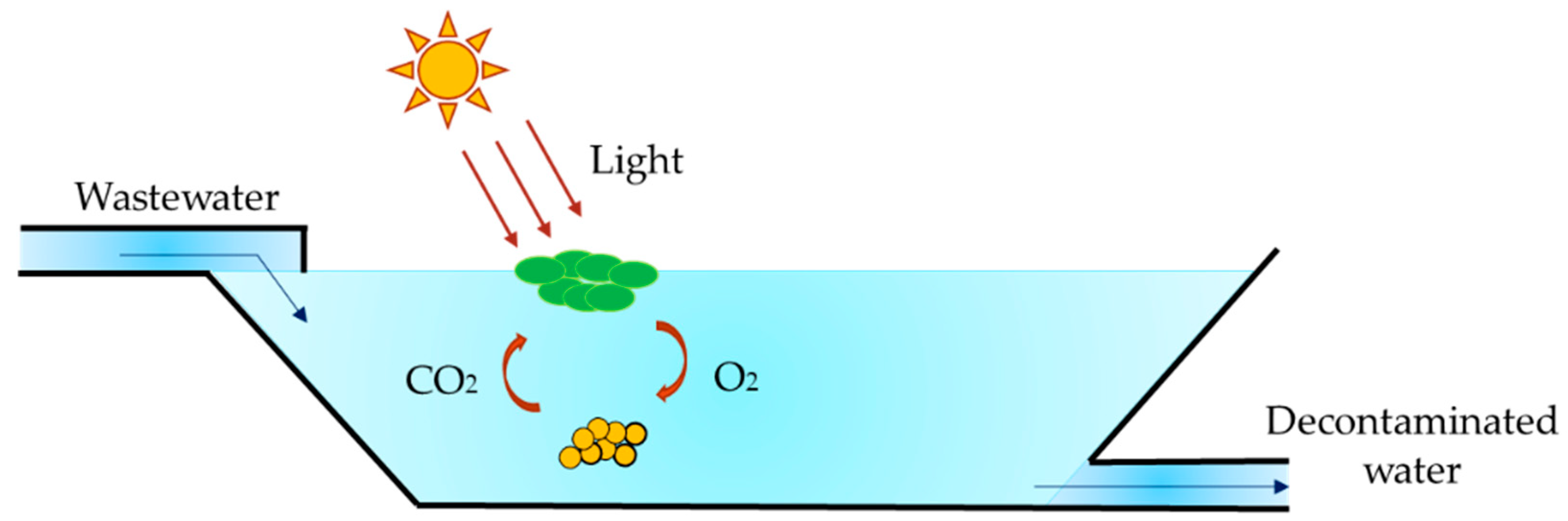
Algae and Microalgae
Rotating Biodisc Contactor (RBC)
2.1.2. Physical Processes
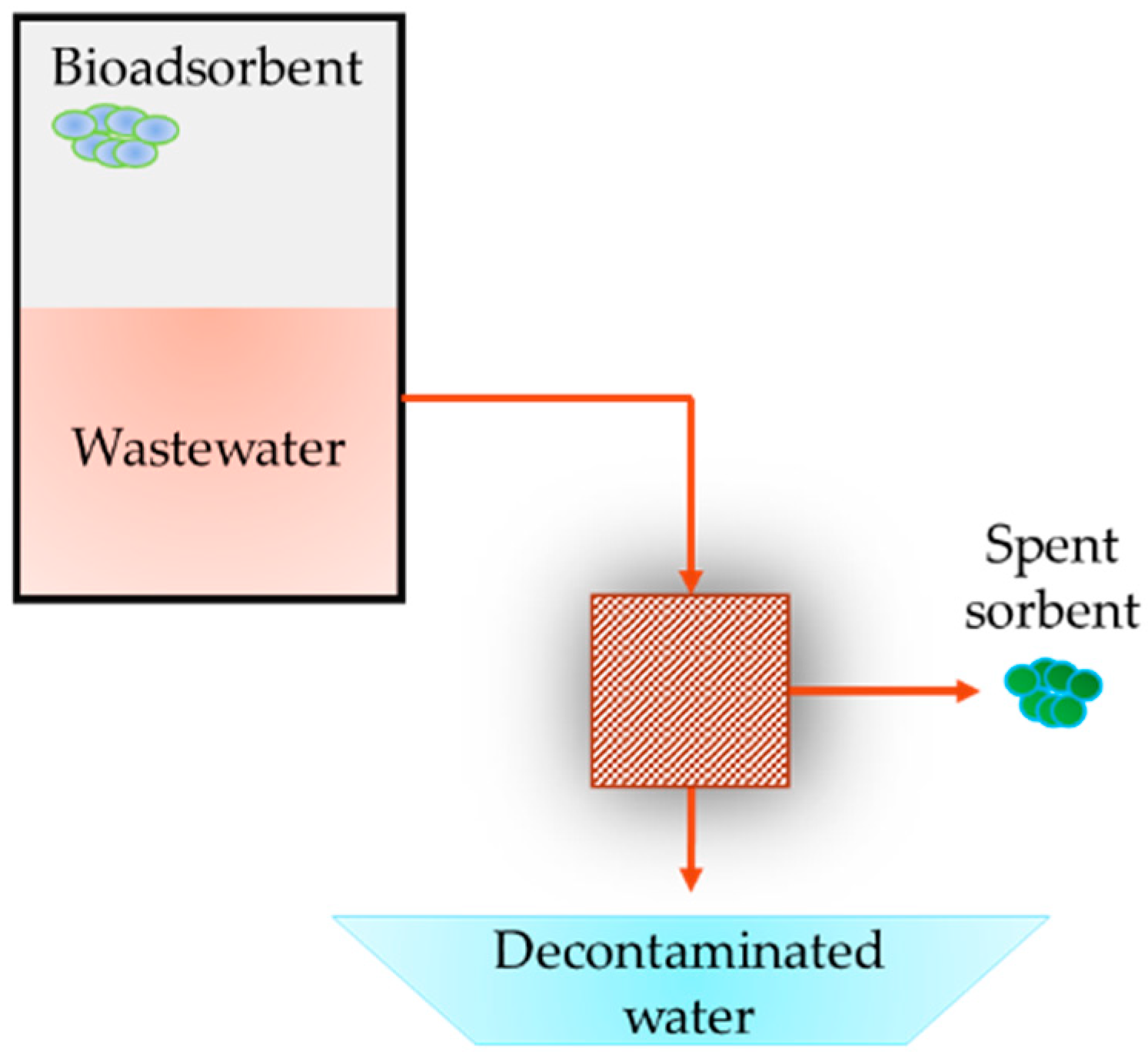
Organic Adsorbents
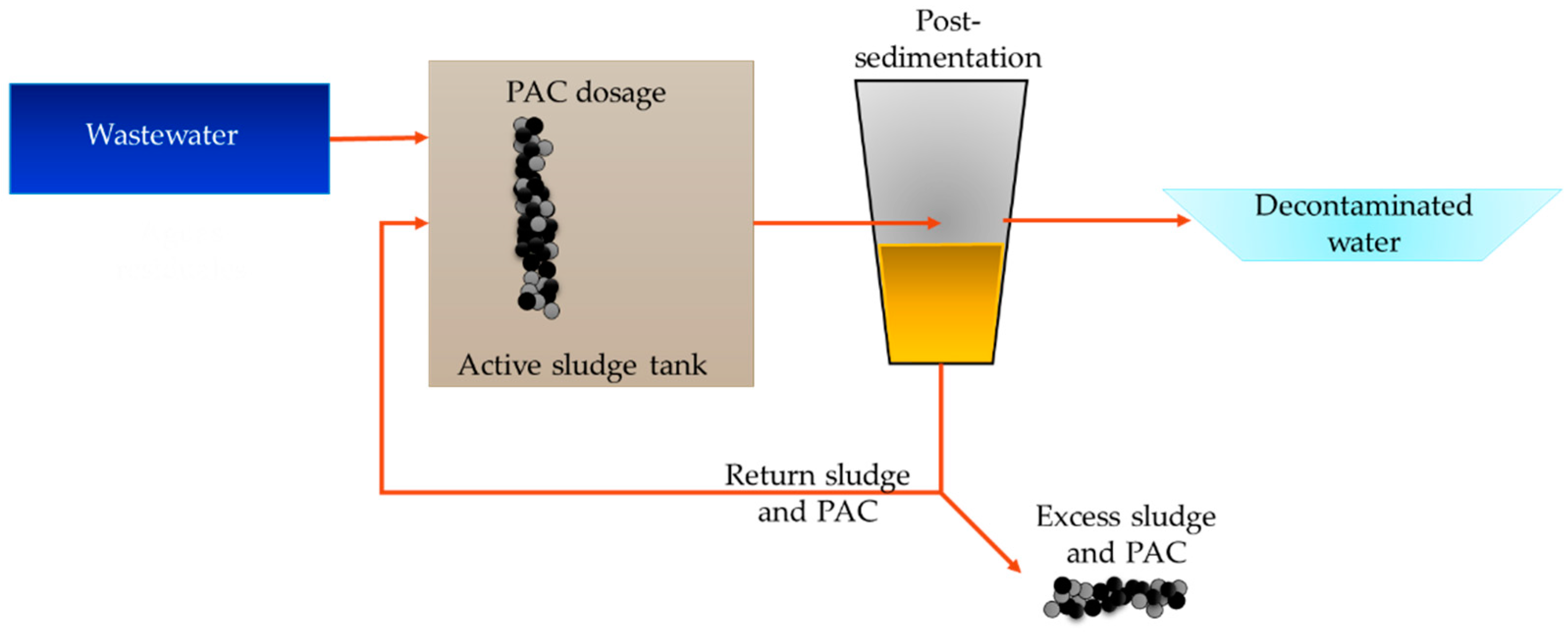
Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) and Granular Activated Carbon (GAC)
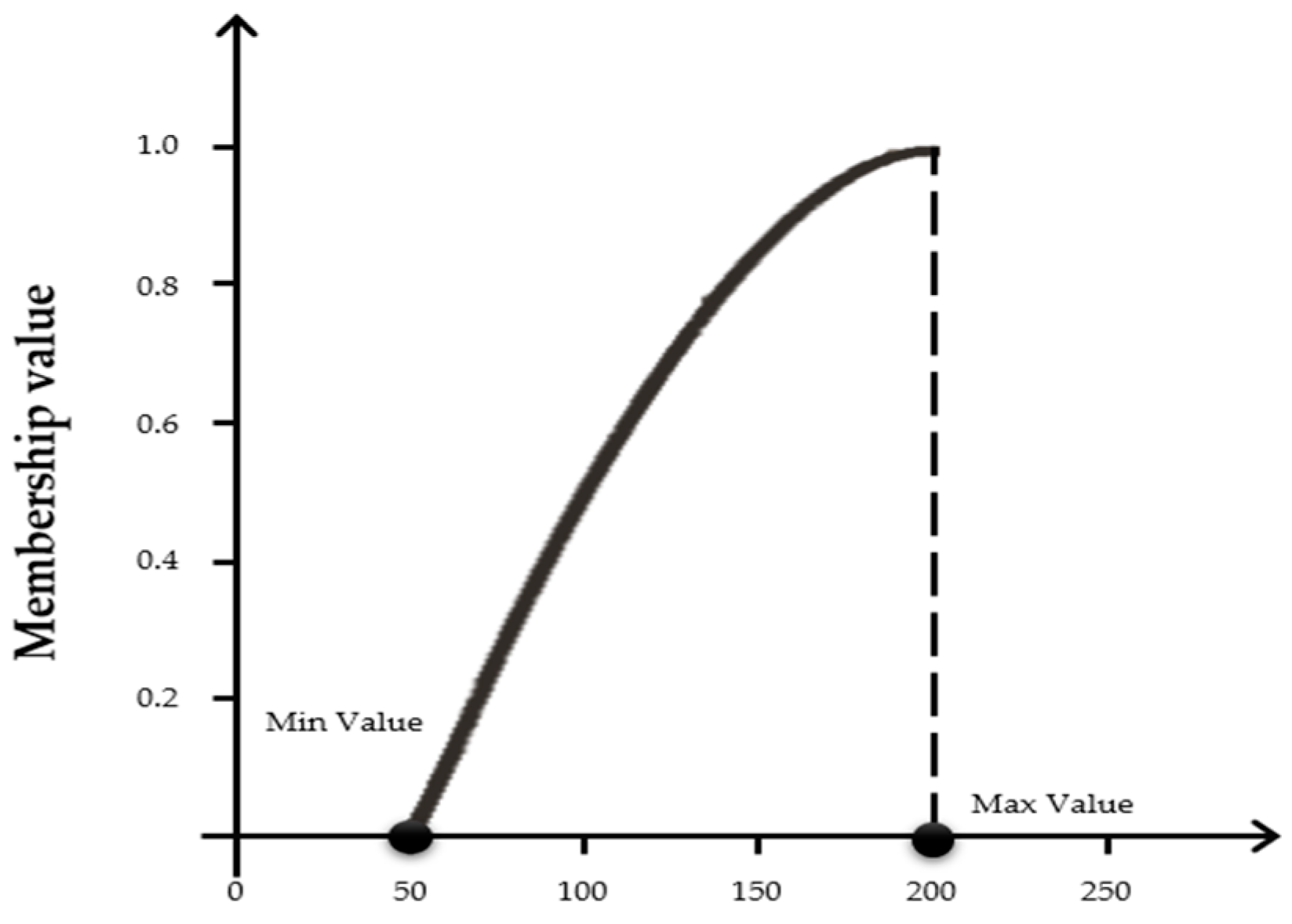
2.2. AHP and FAHP
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHP | Analytical hierarchy processes |
| AOP | Advanced oxidation process |
| Ci | Weight factor for variables |
| E1 | Estrone |
| E2 | 17β-estradiol |
| EC | Emerging pollutants |
| EDC | Endocrine disruptors |
| EE2 | 17-α-ethinyl estradiol |
| EI | Environmental impact |
| EV | Estradiol valerate |
| FAHP | Fuzzy analytical hierarchy or Modified Saaty |
| FTIR | Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy |
| GAC | Granular activated carbon |
| li | Consistency level |
| MC | Maintenance cost |
| n | Number of variables |
| N | Variable normalization |
| PAC | Powdered activated carbon |
| pj | Sum of the weighting of each variable |
| PRO | Progesterone |
| RBC | Rotating biodisc contactor |
| RE | Removal efficiency |
| RT | Removal time |
| SD | Stage of development |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| UF | Ultrafiltration processes |
| Vmáx | Maximum value |
| Vmin | Minimum value |
| Vo | Original value |
| wi | Weight |
| WW | Waste waters |
| WWTP | Wastewater treatment plants |
| μA | Evaluation of the criterion |
References
- Codd, G.A. Cyanobacterial toxins, the perception of water quality, and the prioritisation of eutrophication control. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 16, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water management: Current and future challenges and research directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolund, P.; Hunhammar, S. Ecosystem services in urban areas. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, J.T.A.; Arheimer, B.; Yin, C.; Hefting, M.M. Regional and global concerns over wetlands and water quality. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Tanaka, M. Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: A review and synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 624–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia-R, M.; Layedra-Almeida, A.P.; Torres, Y.; Toulkeridis, T. Evaluation of a Microbial Consortium and Selection of a Support in an Anaerobic Reactor Directed to the Bio-Treatment of Wastewater of the Textile Industry. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.W.; Lipp, E.K.; McLaughlin, M.R.; Rose, J.B. Marine Recreation and Public Health Microbiology: Quest for the Ideal Indicator. Bioscience 2001, 51, 817–825. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/bioscience/article/51/10/817/245219 (accessed on 6 October 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, T.-T.; Lipp, E.K. Enteric Viruses of Humans and Animals in Aquatic Environments: Health Risks, Detection, and Potential Water Quality Assessment Tools. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brito, I.D.A.; Garcia, J.R.E.; Salaroli, A.B.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Martins, C.D.C.; Neto, A.C.; Gusso-Choueri, P.K.; Choueri, R.B.; Araujo, S.B.L.; Ribeiro, C.A.D.O. Embryo toxicity assay in the fish species Rhamdia quelen (Teleostei, Heptaridae) to assess water quality in the Upper Iguaçu basin (Parana, Brazil). Chemosphere 2018, 208, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sonone, S.S.; Jadhav, S.; Sankhla, M.S.; Kumar, R. Water Contamination by Heavy Metals and their Toxic Effect on Aquaculture and Human Health through Food Chain. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2020, 10, 2148–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsalve, E.R.; Prado, P.J.; Ortiz, J.M.; Toulkeridis, T. Differences in Fish Abundance in Rivers under the Influence of Open-Pit Gold Mining in the Santiago-Cayapas Watershed, Esmeraldas, Ecuador. Water 2022, 14, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; He, B.; Zhao, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T. Which type of pollutants need to be controlled with priority in wastewater treatment plants: Traditional or emerging pollutants? Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Wei, D. A critical review on antibiotics and hormones in swine wastewater: Water pollution problems and control approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 387, 121682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Alda, M.J.L.; Díaz-Cruz, S.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Liquid chromatography–(tandem) mass spectrometry of selected emerging pollutants (steroid sex hormones, drugs and alkylphenolic surfactants) in the aquatic environment. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1000, 503–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merritt, R.L.; Foran, C.M. Influence of Persistent Contaminants and Steroid Hormones on Glioblastoma Cell Growth. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 70, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-M.; Albrecht, M.; Fromme, H.; Schramm, K.-W.; De Angelis, M. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Human Breast Milk and Associations with Maternal Thyroid Hormone Homeostasis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Rimaviciute, E.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.P.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V. Processes for the elimination of estrogenic steroid hormones from water: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 165, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, P.; Helmreich, B.; Skrbic, B.; Carballa, M.; Papa, M.; Pastore, C.; Emre, Z.; Oehmen, A.; Langenhoff, A.; Molinos, M.; et al. Status of hormones and painkillers in wastewater effluents across several European states—Considerations for the EU watch list concerning estradiols and diclofenac. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12835–12866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, E.; González-Fuentes, M.A.; Rebollar-Perez, G.; Méndez-Albores, A.; Torres, E. Emerging pollutant treatments in wastewater: Cases of antibiotics and hormones. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 52, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Odaini, N.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yaziz, M.I.; Surif, S. Multi-residue analytical method for human pharmaceuticals and synthetic hormones in river water and sewage effluents by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6791–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Sexual hormones in a coastal river adjacent to the Bohai Sea: Characteristic pollutants and dominantly influencing factors. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furgal, K.M.; Meyer, R.L.; Bester, K. Removing selected steroid hormones, biocides and pharmaceuticals from water by means of biogenic manganese oxide nanoparticles in situ at ppb levels. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, G.R.; Mourikes, V.E.; Neff, A.M.; Brehm, E.; Flaws, J.A. Mechanisms of action of agrochemicals acting as endocrine disrupting chemicals. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 502, 110680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surana, D.; Gupta, J.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, S.; Ghosh, P. A review on advances in removal of endocrine disrupting compounds from aquatic matrices: Future perspectives on utilization of agri-waste based adsorbents. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, S.Y.; Aris, A.Z. Endocrine disrupting compounds in drinking water supply system and human health risk implication. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, E.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Rahman, I. A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigsby, R.; Chapin, R.E.; Daston, G.P.; Davis, B.J.; Gorski, J.; Gray, L.E.; Howdeshell, K.L.; Zoeller, R.T.; Saal, F.S.V. Evaluating the effects of endocrine disruptors on endocrine function during development. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, G.H.; Bolt, H.M. Endocrine disruptors: Update on xenoestrogens. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2000, 73, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monneret, C. What is an endocrine disruptor? C. R. Biol. 2017, 340, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, C.L.S.; Bassin, J.P.; Peixoto, R.S. Water contamination by endocrine disruptors: Impacts, microbiological aspects and trends for environmental protection. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurício, R.; Semedo, F.; Dias, R.; Noronha, J.P.; Amaral, L.; Daam, M.; Mano, A.P.; Diniz, M. Efficacy assessment of peracetic acid in the removal of synthetic 17α-ethinyl estradiol contraceptive hormone in wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 89, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Francis, D.; Yang, Y. Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumond, I.; Arsenault, P.; Marchand, S. Specificity of female and male sex hormones on excitatory and inhibitory phases of formalin-induced nociceptive responses. Brain Res. 2005, 1052, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Hur, H.; Thole, H.H.; Mashiah, A.; Insler, V.; Berman, V.; Shezen, E.; Elias, D.; Zuckerman, A.; Ornoy, A. Estrogen, progesterone and testosterone receptors in human fetal cartilaginous tissue: Immunohistochemical studies. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1997, 60, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, P.S.; Mesa, A.M.; Sirohi, V.K.; Levin, E.R. Role of nuclear and membrane estrogen signaling pathways in the male and female reproductive tract. Differentiation 2020, 118, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, G.P.; de Souza, N.C.; Vidal, C.B.; Alves, J.A.; Firmino, P.I.M.; Nascimento, R.F.; dos Santos, A.B. Occurrence and removal of estrogens in Brazilian wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, S.S.; Arnold, R.G. Removal of natural and xeno-estrogens during conventional wastewater treatment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2008, 7, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet-Giraud, V.; Miege, C.; Choubert, J.-M.; Ruel, S.M.; Coquery, M. Occurrence and removal of estrogens and beta blockers by various processes in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4257–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, H.; Eskicioglu, C. Fate of estrogenic hormones in wastewater and sludge treatment: A review of properties and analytical detection techniques in sludge matrix. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5813–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdulska, A.; Kowalik, R. ESTROGEN REMOVAL FROM WASTEWATER. Struct. Environ. 2020, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, U.; Chatterjee, S.; Mondal, N.K. Isolation and characterization of arsenic-resistant bacteria and possible application in bioremediation. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koh, Y.K.K.; Chiu, T.Y.; Boobis, A.; Scrimshaw, M.; Bagnall, J.P.; Soares, A.; Pollard, S.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J.N. Influence of Operating Parameters on the Biodegradation of Steroid Estrogens and Nonylphenolic Compounds during Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6646–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, X.; Yang, X.; Xie, B.; Jiao, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, Z.; Lin, H.; Chen, W.; et al. Sorption and desorption of sex hormones in soil- and sediment-water systems: A review. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J. Endocrine System 7: Ovaries and Testes, Placenta (Pregnancy). Nurs. Times 2021, 54–58. Available online: https://www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-archive/long-term-conditions/endocrine-system-7-ovaries-and-testes-placenta-pregnancy-25-10-2021/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Singh, A.R.; Bajaj, V.K.; Shekhawat, P.S.; Singh, K. Screening of potential male contraceptive drugs from natural resources: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 1654–1668. Available online: https://ijpsr.com/bft-article/screening-of-potential-male-contraceptive-drugs-from-natural-resources-an-overview/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Vulliet, E.; Cren-Olivé, C. Screening of pharmaceuticals and hormones at the regional scale, in surface and groundwaters intended to human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2929–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibambe, M.G.; Momba, M.N.; Daso, A.; Van Zijl, M.; Coetzee, M.A. Efficiency of selected wastewater treatment processes in removing estrogen compounds and reducing estrogenic activity using the T47D-KBLUC reporter gene assay. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellet, L.; Molinos-Senante, M. Efficiency assessment of wastewater treatment plants: A data envelopment analysis approach integrating technical, economic, and environmental issues. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 167, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-Q.; Zhou, Z.; Sharma, V. Occurrence, transportation, monitoring and treatment of emerging micro-pollutants in waste water—A review from global views. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.L.; Pramanik, B.K.; Shah, K.; Roychand, R. Pathway, classification and removal efficiency of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Rodríguez, L.; Oller, I.; Klamerth, N.; Agüera, A.; Rodríguez, E.; Malato, S. Application of solar AOPs and ozonation for elimination of micropollutants in municipal wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Farré, M.; Pérez, S.; Kantiani, L.; Barceló, D. Fate and toxicity of emerging pollutants, their metabolites and transformation products in the aquatic environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Xu, L.J. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Formation of Hydroxyl Radical and Application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 251–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeeli, F.; Gorbanian, S.A.; Moazezi, N. Removal of Estradiol Valerate and Progesterone using Powdered and Granular Activated Carbon from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes in reclaimed water reuse system with integrated membrane process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 382, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.; Westerhoff, P. Spatial and Temporal Variation in De Facto Wastewater Reuse in Drinking Water Systems across the U.S.A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.; Wei, S.T.; Wang, P.; Wu, P.; Yu, C. Microbial degradation of steroid sex hormones: Implications for environmental and ecological studies. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 13, 926–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olatunde, O.C.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Photo enhanced degradation of contaminants of emerging concern in waste water. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, D.; Almeida, O.P.; Morales, B.; Toulkeridis, T. Smart City Planning Based on Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Fuzzy Logic and Multi-criteria Evaluation Techniques in the City of Quito, Ecuador. In Doctoral Symposium on Information and Communication Technologies—DSICT; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Berrezueta, S., Abad, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 846, pp. 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavini, M.; Weidler, P.G.; Njel, C.; Pohl, J.; Richter, D.; Böhringer, B.; Schäfer, A.I. Polymer-based spherical activated carbon—Ultrafiltration (UF-PBSAC) for the adsorption of steroid hormones from water: Material characteristics and process configuration. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Beyer, R.; Harm, S. Effective Removal of Estrogens from Drinking Water and Wastewater by Adsorption Technology. Environ. Process. 2014, 1, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, M.J.d.C.; da Silva, J.R.P.; Borges, C.P.; da Fonseca, F.V. Ethinylestradiol removal of membrane bioreactor effluent by reverse osmosis and UV/H2O2: A technical and economic assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Reemtsma, T. Membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment—A viable option to reduce the amount of polar pollutants discharged into surface waters? Water Res. 2008, 42, 3837–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahani, N. Application of hybrid SWOT-AHP-FuzzyAHP model for formulation and prioritization of ecotourism strategies in Western Himalaya, India. Int. J. Geoherit. Park. 2021, 9, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapostolou, A.; Karakosta, C.; Apostolidis, G.; Doukas, H. An AHP-SWOT-Fuzzy TOPSIS Approach for Achieving a Cross-Border RES Cooperation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornejo-Vásconez, D.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, F.; Guasumba, A.; Toulkeridis, T. Contrasting Effects of Air Pollution Assessment in two Areas of the Quito Metropolitan District, Ecuador. La Granja 2022, 36, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefeslioglu, H.; Sezer, E.A.; Gokceoglu, C.; Ayas, Z. A modified analytical hierarchy process (M-AHP) approach for decision support systems in natural hazard assessments. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božanić, D.; Pamučar, D.; Bojanić, D. Modification of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) method using fuzzy logic: Fuzzy AHP approach as a support to the decision-making process concerning engagement of the group for additional hindering. Serbian J. Manag. 2015, 10, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orejuela, I.P.; Toulkeridis, T. Evaluation of the susceptibility to landslides through diffuse logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) between Macas and Riobamba in Central Ecuador. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on eDemocracy and eGovernment, ICEDEG, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 22–24 April 2020; pp. 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidnia, M.H.; Alesheikh, A.; Alimohammadi, A. Fuzzy analytical hierarchy process in GIS application. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 593–596. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228406167 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chang, S.; Nguyen, D.; Bui, X.; Zhang, X. Bioprocessing for elimination antibiotics and hormones from swine wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1664–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasulochana, P.; Preethy, V. Comparison on efficiency of various techniques in treatment of waste and sewage water—A comprehensive review. Resour. Technol. 2016, 2, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, W.; Cai, Q.; Li, R.; Jothinathan, L.; Lee, B.; Ng, O.; Guo, J.; Ong, S.; Hu, J. Reverse osmosis concentrate treatment by microbubble ozonation-biological activated carbon process: Organics removal performance and environmental impact assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenaar, A.; Ismail, A.; Bux, F. Comparative evaluation of the microbial community in biological processes treating industrial and domestic wastewaters. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 104, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrin, A.; Neidel, T.L.; Damgaard, A.; Bhander, G.S.; Møller, J.; Christensen, T.H. Modelling of environmental impacts from biological treatment of organic municipal waste in EASEWASTE. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J. Removal of steroid hormones from mariculture system using seaweed Caulerpa lentillifera. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutzu, G.A.; Ciurli, A.; Chiellini, C.; Di Caprio, F.; Concas, A.; Dunford, N.T. Latest developments in wastewater treatment and biopolymer production by microalgae. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 9, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Lee, D.-J.; Varjani, S.; Lam, S.S.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Chang, J.-S. Microalgae-based wastewater treatment—Microalgae-bacteria consortia, multi-omics approaches and algal stress response. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.; Shanmugam, S.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Kumar, D.; Mathimani, T.; Brindhadevi, K.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Rajendran, K. Mechanism and challenges behind algae as a wastewater treatment choice for bioenergy production and beyond. Fuel 2020, 285, 119093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, S.; Sathishkumar, R.; Li, H.-Y. Biotechnological perspectives to augment the synthesis of valuable biomolecules from microalgae by employing wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 39, 101713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Dong, S.; Nghiem, L.D.; Gao, L.; Chaves, A.V.; Zamyadi, A.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. A review on microalgae-mediated biotechnology for removing pharmaceutical contaminants in aqueous environments: Occurrence, fate, and removal mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueñas-Muñoz, D.; Guevara, O.; Oviedo, G.-R.; Crisanto-Perrazo, T.; Toulkeridis, T. Sustainable Treatment Techniques for Emerging Pollutants—The Case of Personal Hygiene Products. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurício, R.; Dias, R.; Ribeiro, V.; Fernandes, S.; Vicente, A.C.; Pinto, M.I.; Noronha, J.P.; Amaral, L.; Coelho, P.; Mano, A.P. 17α-Ethinylestradiol and 17β-estradiol removal from a secondary urban wastewater using an RBC treatment system. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiron, O.; Bumbac, C.; Manea, E.; Stefanescu, M.; Lazar, M.N. Overcoming Microalgae Harvesting Barrier by Activated Algae Granules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassard, F.; Biddle, J.; Cartmell, E.; Jefferson, B.; Tyrrel, S.; Stephenson, T. Rotating biological contactors for wastewater treatment—A review. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kargi, F. Empirical models for biological treatment of saline wastewater in rotating biodisc contactor. Process. Biochem. 2002, 38, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Ravenelle, R.M.; Crittenden, J.C. Treatment of Antibiotic Pharmaceutical Wastewater Using a Rotating Biological Contactor. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 705275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kargi, F.; Uygur, A. Biological treatment of saline wastewater in a rotating biodisc contactor by using halophilic organisms. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 1997, 17, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargi, F.; Dinçer, A.R. Saline Wastewater Treatment by Halophile-Supplemented Activated Sludge Culture in an Aerated Rotating Biodisc Contactor. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1998, 22, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Peng, L.; Wang, D.; Ni, B. The roles of free ammonia (FA) in biological wastewater treatment processes: A review. Environ. Int. 2018, 123, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez, P.; Gutiérrez, M.; Toledo, M.; Alhama, J.; Michán, C.; Martín, M. Activated sludge process versus rotating biological contactors in WWTPs: Evaluating the influence of operation and sludge bacterial content on their odor impact. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorio, J.F.; Veit, M.T.; Tavares, C.R.G. Alternative adsorbents applied to the removal of natural hormones from pig farming effluents and characterization of the biofertilizer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 28429–28435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares-Cisneros, M.G.; Valerio-Cárdenas, C.; de la Cruz-Burelo, P.; Melgoza-Alemán, R.M. Adsorbentes no-convencionales, alternativas sustentables para el tratamiento de aguas residuales. Rev. Ing. Univ. Med. 2017, 16, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.; Sousa, D.; Bernardo, M.; Matos, I.; Fonseca, I.; Cardoso, V.; Carneiro, R.; Silva, S.; Fontes, P.; Daam, M.; et al. Study of the Potential of Water Treatment Sludges in the Removal of Emerging Pollutants. Molecules 2021, 26, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, O. Fundamento Teórico para Modelización de Variables Ambientales Mediante Operadores Difusos. 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274062719_FUNDAMENTO_TEORICO_PARA_MODELIZACION_DE_VARIABLES_AMBIENTALES_MEDIANTE_OPERADORES_DIFUSOS (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Evers, M.; Lange, R.-L.; Heinz, E.; Wichern, M. Simultaneous powdered activated carbon dosage for micropollutant removal on a municipal wastewater treatment plant compared to the efficiency of a post treatment stage. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 47, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Šopík, T.; Ali, H.; Sedlařík, V. Electrospun polyurethane nanofibers coated with polyaniline/polyvinyl alcohol as ultrafiltration membranes for the removal of ethinylestradiol hormone micropollutant from aqueous phase. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, W. Simultaneous coupling of fluidized granular activated carbon (GAC) and powdered activated carbon (PAC) with ultrafiltration process: A promising synergistic alternative for water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 282, 120085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, X.; Duan, S.; Li, S. Optimizing the inclined plate settler for a high-rate microaerobic activated sludge process for domestic wastewater treatment: A theoretical model and experimental validation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 154, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Eckert, C.M.; Earl, C. A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikodzi, D. Spatial Modelling of Malaria Risk Zones Using Environmental, Anthropogenic Variables and GeograPhical Information Systems Techniques. J. Geosci. Geomat. 2013, 1, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Arguello, M.; Abad-Sarango, V.; Crisanto-Perrazo, T.; Toulkeridis, T. Removal of METH through Tertiary or Advanced Treatment in a WWTP. Water 2022, 14, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | RE | MC | SD | EI | RT | Ci | wi | λi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE | 1.00 | 0.56 | 5.00 | 1.67 | 0.71 | 1.27 | 0.20 | 1.00 |
| MC | 1.80 | 1.00 | 9.00 | 3.00 | 1.29 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 1.00 |
| SD | 0.20 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 1.00 |
| EI | 0.60 | 0.33 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.76 | 0.12 | 1.00 |
| RT | 1.40 | 0.78 | 7.00 | 2.33 | 1.00 | 1.78 | 0.28 | 1.00 |
| ∑ | 5.00 | 2.78 | 25.00 | 8.33 | 3.57 | 6.35 | 1.00 | 5.00 |
| Removal Efficiency (%) | Removal Time (h) | Stage of Development | Maintenance Cost | Environmental Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algae and microalgae | 90 | 12 | Laboratory | Low | Low |
| Rotating biodisc contactor | 66 | 4.33 | Pilot | Low | Low |
| Organic adsorbents | 80 | 4 | Pilot | Low | Low |
| Powdered activated carbon and granular activated carbon | 98 | 8 | Laboratory | Low | Medium |
| Method = | W1 × RE | + | W2 × MC | + | W3 × SD | + | W4 × EI | + | W5 × RT | = | RESULT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algae and microalgae | 0.14 | + | 0.00 | + | 0.00 | + | 0.00 | + | 0.28 | = | 0.42 |
| RBC | 0.00 | + | 0.00 | + | 0.03 | + | 0.00 | + | 0.14 | = | 0.17 |
| Organic adsorbents | 0.08 | + | 0.36 | + | 0.03 | + | 0.12 | + | 0.00 | = | 0.58 |
| PAC and GAC | 0.20 | + | 0.00 | + | 0.00 | + | 0.12 | + | 0.24 | = | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guerrero-Gualan, D.; Valdez-Castillo, E.; Crisanto-Perrazo, T.; Toulkeridis, T. Methods of Removal of Hormones in Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020353
Guerrero-Gualan D, Valdez-Castillo E, Crisanto-Perrazo T, Toulkeridis T. Methods of Removal of Hormones in Wastewater. Water. 2023; 15(2):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020353
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuerrero-Gualan, Daniela, Eduardo Valdez-Castillo, Tania Crisanto-Perrazo, and Theofilos Toulkeridis. 2023. "Methods of Removal of Hormones in Wastewater" Water 15, no. 2: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020353
APA StyleGuerrero-Gualan, D., Valdez-Castillo, E., Crisanto-Perrazo, T., & Toulkeridis, T. (2023). Methods of Removal of Hormones in Wastewater. Water, 15(2), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020353







