Selenium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using a Low-Cost Functional Ceramic Membrane Derived from Waste Cast Iron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of LFCM
2.3. Selenium Removal Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
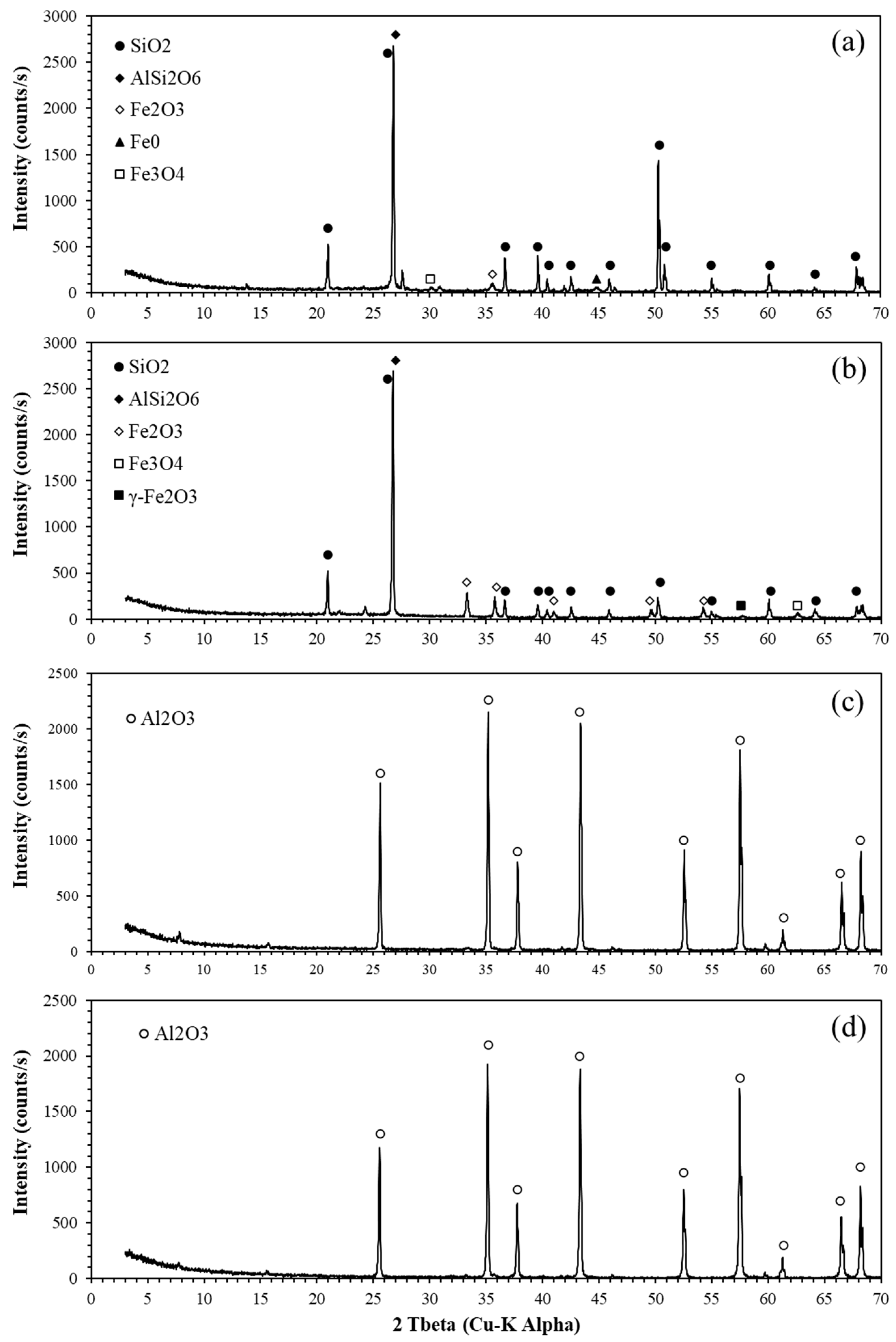
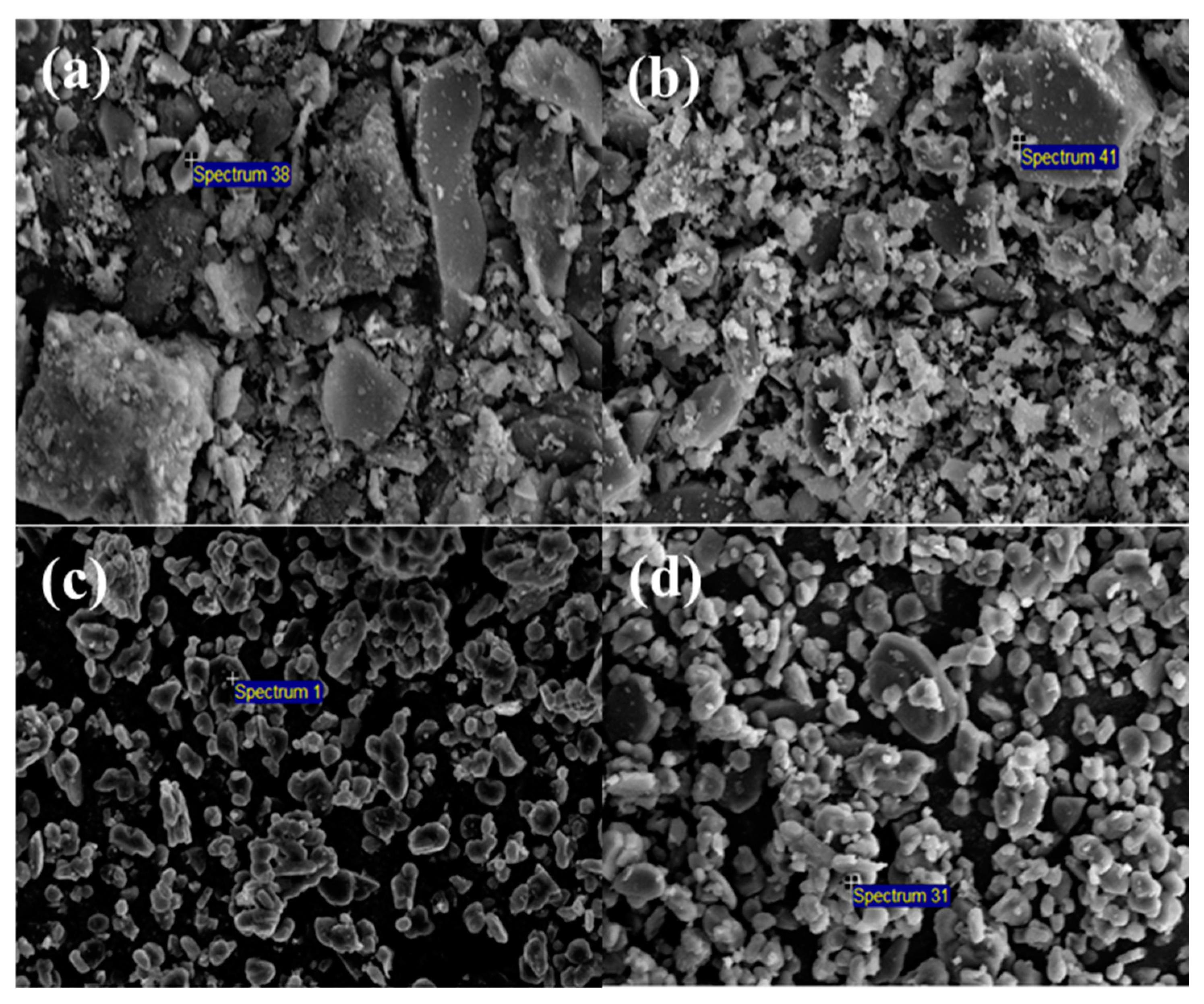
3.1. Characterization of Raw Materials
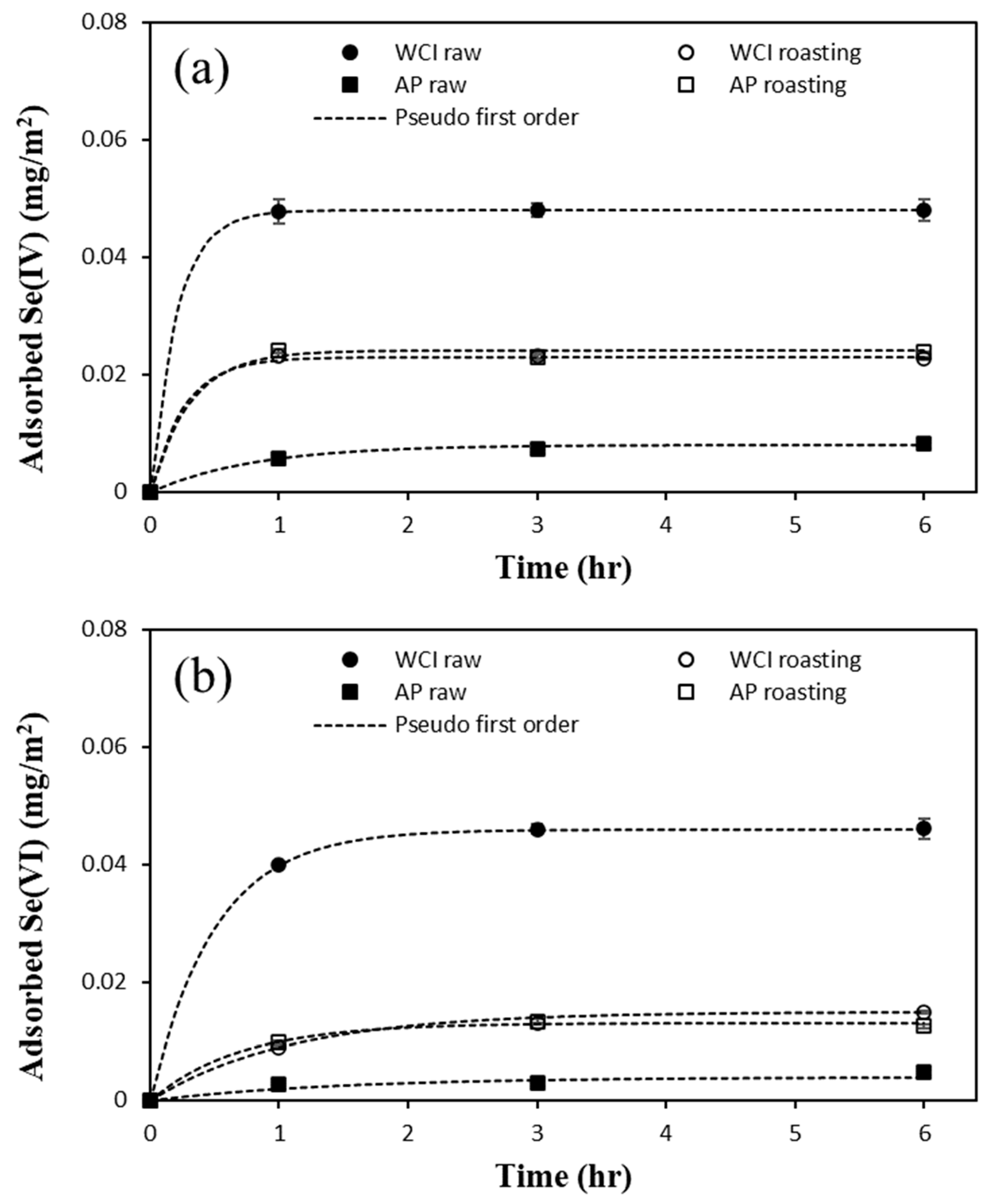
3.2. Se(IV) and Se(VI) Removal Using Raw Materials
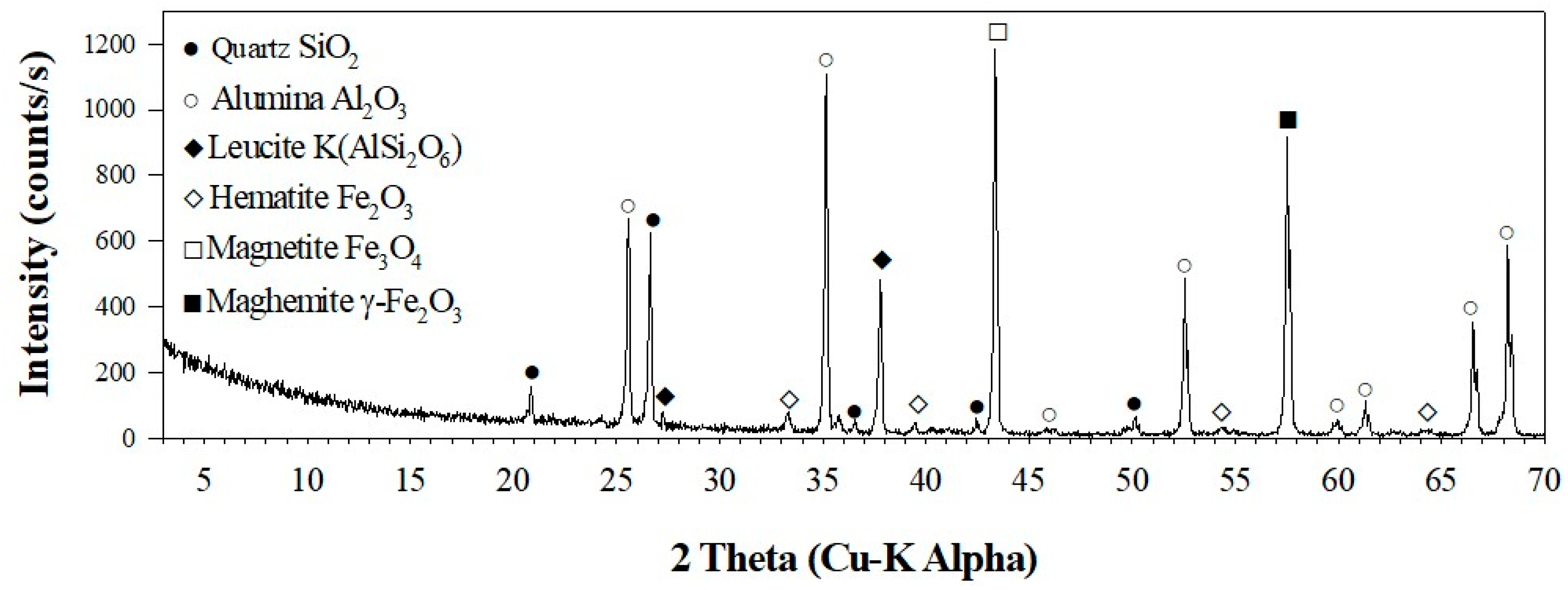
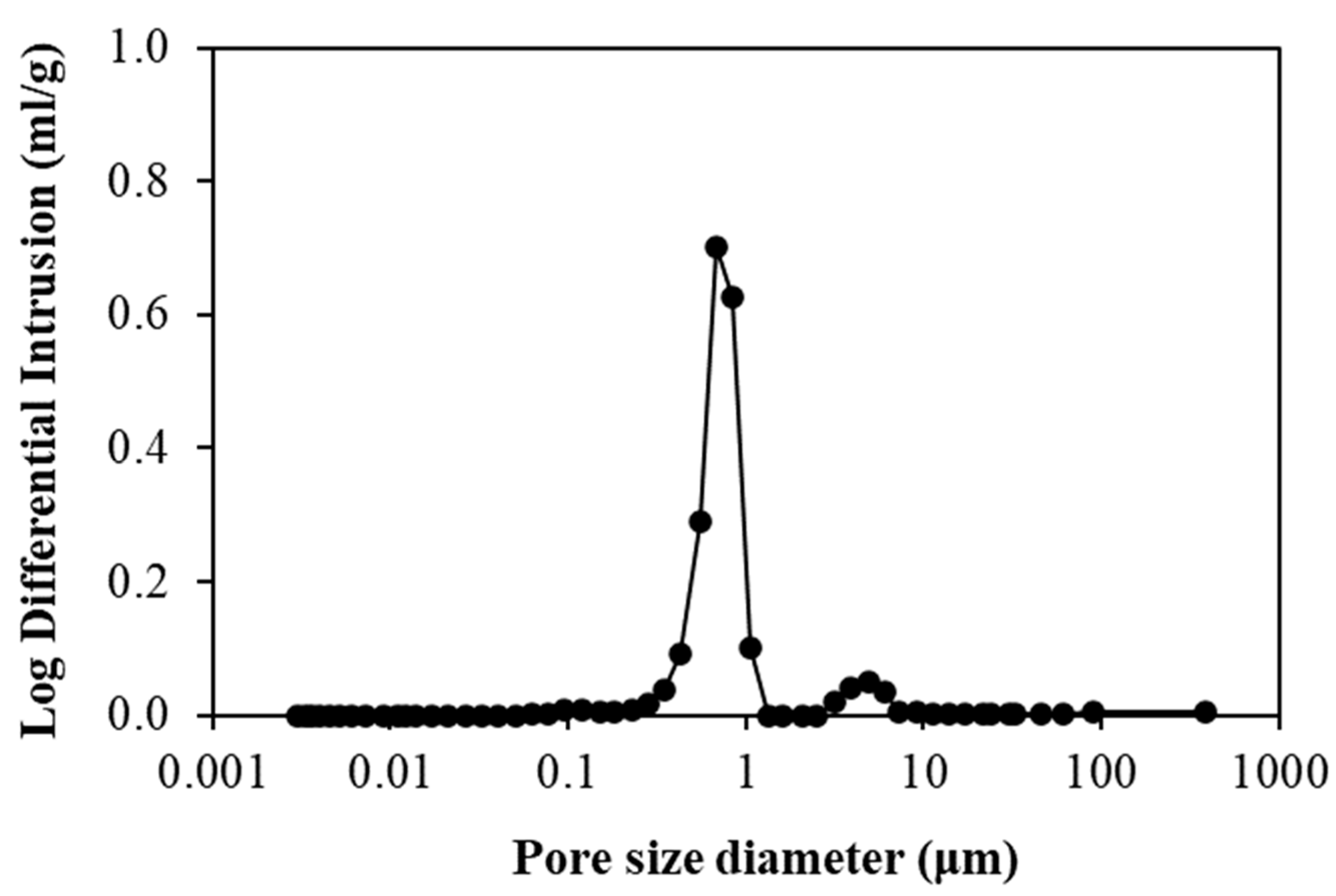
3.3. Characterization of LFCM
3.4. Se(IV) and Se(VI) Removal by LFCM
3.5. Simultaneous Removal of Turbidity-Causing Particles and Se(IV) in the LFCM Filtration System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, S.H.; Lyonga, F.N.; Kang, J.K.; Seo, E.J.; Lee, C.G.; Jeong, S.; Hong, S.G.; Park, S.J. Synthesis of Fe-impregnated biochar from food waste for Selenium (VI) removal from aqueous solution through adsorption: Process optimization and assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.F. Selenium, an antioxidant nutrient. Nutr. Clin. Care 2002, 5, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojadadi, A.; Au, A.; Salah, W.; Witting, P.; Ahmad, G. Role for Selenium in Metabolic Homeostasis and Human Reproduction. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, C.G.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J. Conversion of cattle manure into functional material to remove selenate from wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, M.; Pal, M.; Pal, P. A response surface optimized nanofiltration-based system for efficient removal of selenium from drinking Water. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 33, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.; Ramires, P.F.; Gironés, M.C.R.; Rubio Armendáriz, M.d.C.; Montelongo, S.P.; Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; da Silva Junior, F.M.R. Multiple exposure pathways and health risk assessment of selenium for children in a coal mining area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 13562–13569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Kim, S.-B. Removal of arsenic and selenium from aqueous solutions using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle/multi-walled carbon nanotube adsorbents. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 28323–28339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.B.; Gu, F.X. Emerging nanomaterials for the application of selenium removal for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtfouse, E.; Morin-Crini, N.; Bradu, C.; Boussouga, Y.-A.; Aliaskari, M.; Schäfer, A.I.; Das, S.; Wilson, L.D.; Ike, M.; Inoue, D. Technologies to remove selenium from water and wastewater. In Emerging Contaminants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 207–304. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.B.; Zhang, Z. Ceramic membrane technology for water and wastewater treatment: A critical review of performance, full-scale applications, membrane fouling and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, G.; Chung, T.-S. Novel thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes consisting of a zwitterionic co-polymer for selenium and arsenic removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroufchi Benis, K.; McPhedran, K.N.; Soltan, J. Selenium removal from water using adsorbents: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.C.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, S.O.; Lee, J.W.; Park, J.B. Removal of arsenate and arsenite from aqueous solution by waste cast iron. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazam, E.R.; Breault, R.W.; Siriwardane, R. Kinetics of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Oxidation to Hematite (Fe2O3) in Air for Chemical Looping Combustion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 13320–13328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Mao, Y.; Wang, H.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N. Comparison of biochar- and activated carbon-supported zerovalent iron for the removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI): Influence of pH, ionic strength, and natural organic matter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 21609–21618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-K.; Park, J.-A.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Kim, S.-B. Surface functionalization of mesoporous silica MCM-41 with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane for dye removal: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 7066–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilani, V.; Lee, J.-I.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, C.-G.; Jeong, S.; Park, S.-J. Application of aluminum-modified food waste biochar as adsorbent of fluoride in aqueous solutions and optimization of production using response surface methodology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 312, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.R.; Jeon, H.G.; Moon, D.H. Sorption of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd from a Contaminated Aqueous Solution Using Starfish (Asterina pectinifera) Derived Biochar. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2021, 43, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, J.-A.; Kang, J.-K.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, C.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, J.-W. Phosphate sorption to quintinite in aqueous solutions: Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium analyses. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 20, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonji, S.O.; Dominic, J.A.; Pernitsky, D.; Achari, G. Removal and recovery of selenium species from wastewater: Adsorption kinetics and co-precipitation mechanisms. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Pan, W.; Wang, F.; Xu, N. Removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) by MFe2O4 nanoparticles from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyonga, F.N.; Hong, S.-H.; Cho, E.-J.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. As (III) adsorption onto Fe-impregnated food waste biochar: Experimental investigation, modeling, and optimization using response surface methodology. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3303–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.-C.; Cho, K.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, C.-G. A Hybrid Ion-Exchange Fabric/Ceramic Membrane System to Remove As(V), Zn(II), and Turbidity from Wastewater. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, J.H.; Kang, J.K.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.G. Application of the anion-exchange resin as a complementary technique to remove residual cyanide complexes in industrial plating wastewater after conventional treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 41688–41701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Ndingwan, A.M.; Yoo, S.C.; Lee, C.G.; Park, S.J. Use of calcined sepiolite in removing phosphate from water and returning phosphate to soil as phosphorus fertilizer. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Component | wt.% |
|---|---|
| Alumina | 58 |
| WCI | 13 |
| Clay | 3 |
| Feldspar | 3 |
| Silica | 3 |
| Binder | 5 |
| Water | 13 |
| Glycerin | 2 |
| Total | 100 |
| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|
| Raw WCI | 2.040 |
| WCI after roasting | 4.303 |
| Raw α-alumina | 1.595 |
| α-alumina after roasting | 1.096 |
| Se(IV) | Se(VI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/m2) | K (1/h) | R2 | qe (mg/m2) | K (1/h) | R2 | |
| WCI raw | 0.048 | 4.875 | 1.000 | 0.046 | 2.016 | 1.000 |
| WCI roasting | 0.023 | 3.817 | 1.000 | 0.015 | 0.921 | 0.995 |
| AP raw | 0.008 | 1.251 | 0.993 | 0.004 | 0.688 | 0.874 |
| AP roasting | 0.024 | 3.234 | 0.999 | 0.013 | 1.439 | 0.995 |
| LFCM | 0.032 | 3.636 | 1.000 | 0.031 | 0.566 | 0.926 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.; Cho, K.-H.; Kim, M.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, C.-G.; Choi, N.-C. Selenium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using a Low-Cost Functional Ceramic Membrane Derived from Waste Cast Iron. Water 2023, 15, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020312
Yoon S, Cho K-H, Kim M, Park S-J, Lee C-G, Choi N-C. Selenium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using a Low-Cost Functional Ceramic Membrane Derived from Waste Cast Iron. Water. 2023; 15(2):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020312
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Sungmoon, Kang-Hee Cho, Minsung Kim, Seong-Jik Park, Chang-Gu Lee, and Nag-Choul Choi. 2023. "Selenium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using a Low-Cost Functional Ceramic Membrane Derived from Waste Cast Iron" Water 15, no. 2: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020312
APA StyleYoon, S., Cho, K.-H., Kim, M., Park, S.-J., Lee, C.-G., & Choi, N.-C. (2023). Selenium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using a Low-Cost Functional Ceramic Membrane Derived from Waste Cast Iron. Water, 15(2), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020312









