Effects of Fe-DTPA on Health and Welfare of the African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and System Maintenance
2.2. Fish Stocking and Feeding
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Blood Smear Analysis and Skin Lesion Documentation
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. RNA Isolation, Primer Design and Multiplex Quantitative PCR
2.7. Ethology Analysis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Water Analyses
3.2. Growth and Mortality
3.3. Fish Behavior
3.4. Leucogram
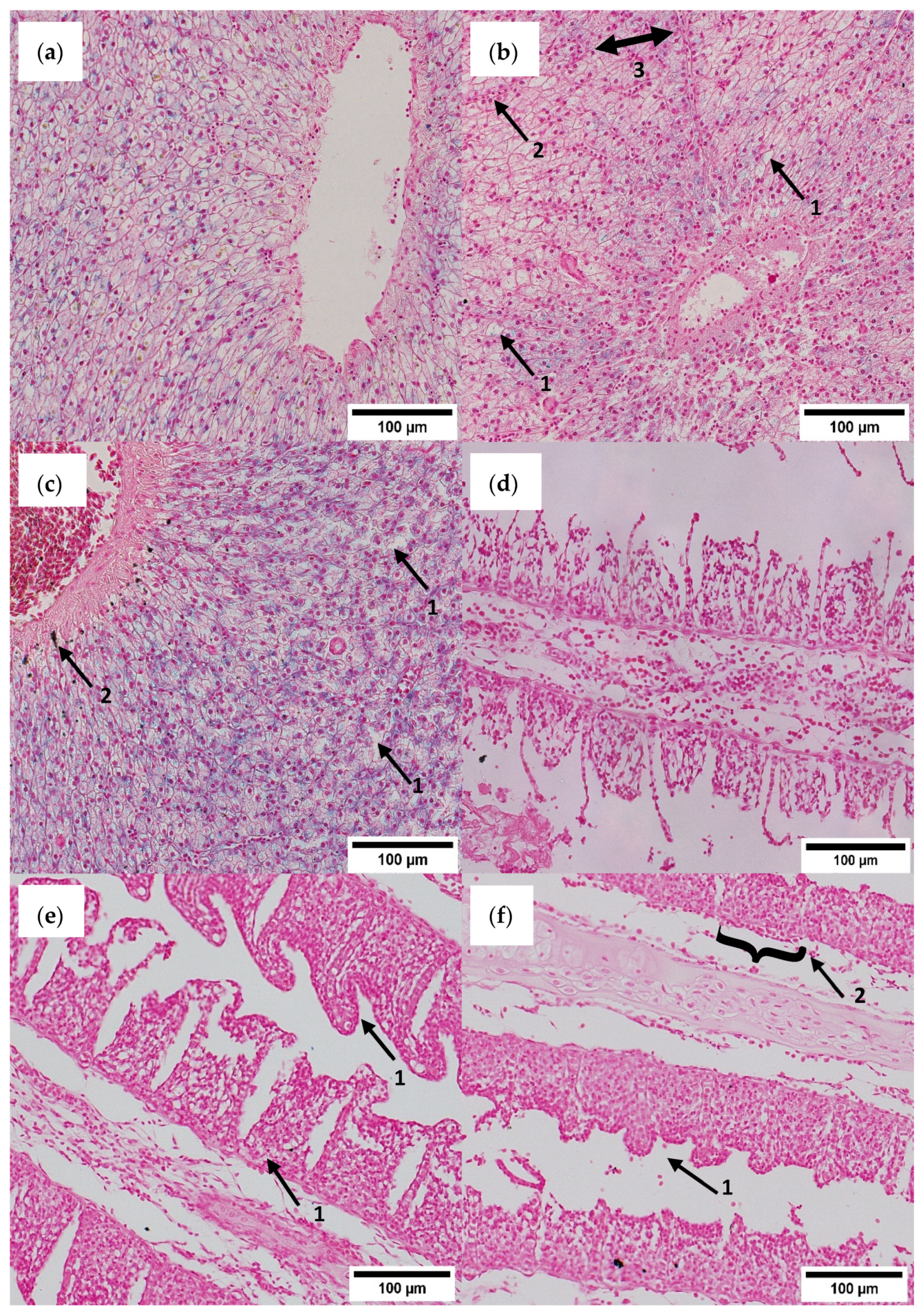
3.5. Histological Assessment
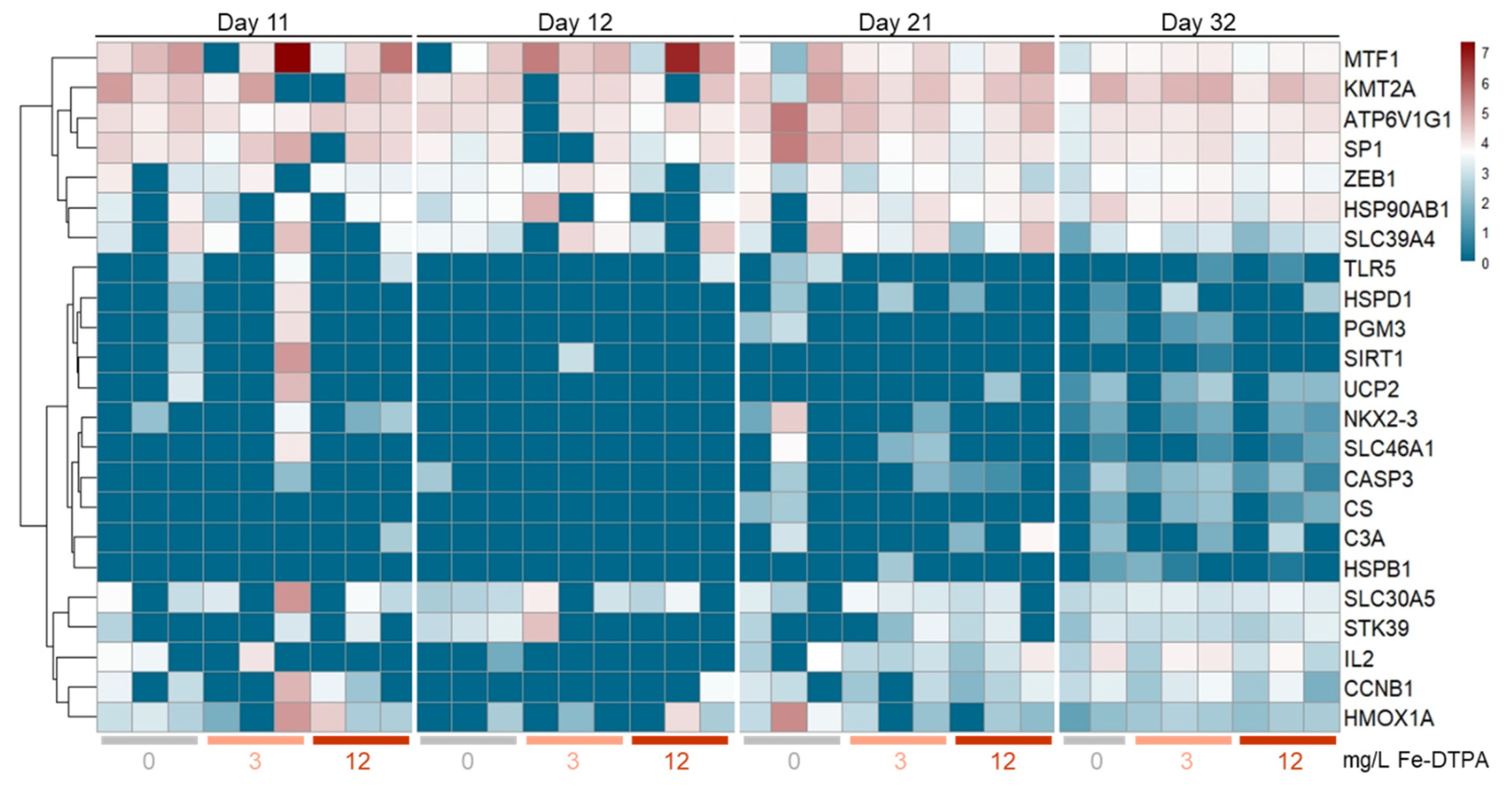
3.6. Gene Expression Profiling
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality
4.2. Growth Performance and Mortality
4.3. Physiological and Behavioral Responses
4.4. Histopathology and Gene Expression Profiling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stathopoulou, P.; Tsoumalakou, E.; Levizou, E.; Vanikiotis, T.; Zaoutsos, S.; Berillis, P. Iron and potassium fertilization improve rocket growth without affecting tilapia growth and histomorphology characteristics in aquaponics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayara, T.; Amarneh, B.; Saleh, T.; Aslan, K.; Abuhanish, R.; Jawabreh, A. Hydroponic and aquaponic systems for sustainable agriculture and environment. Int. J. Plant Sci. Ecol. 2016, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Maneepong, S. Nutrient dynamics of an aquaponic system in Southern Thailand. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Cerozi, B. Fulvic acid increases iron bioavailability in aquaponic systems: Theoretical designs and practical considerations to prevent iron deficiency in plants. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 90, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittsanszky, A.; Uzinger, N.; Gyulai, G.; Mathis, A.; Junge, R.; Villarroel, M.; Kotzen, B.; Kőmíves, T. Nutrient supply of plants in aquaponic systems. Ecocycles 2016, 2, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, V.; Del Río, V.; Pumariño, L.; Igartua, E.; Abadía, J.; Abadía, A. Foliar fertilization of peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) with different iron formulations: Effects on re-greening, iron concentration and mineral composition in treated and untreated leaf surfaces. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 117, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narimani, H.; Rahimi, M.M.; Ahmadikhah, A.; Vaezi, B. Study on the effects of foliar spray of micronutrient on yield and yield components of durum wheat. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 2, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kasozi, N.; Tandlich, R.; Fick, M.; Kaiser, H.; Wilhelmi, B. Iron supplementation and management in aquaponic systems: A review. Aquac. Rep. 2019, 15, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Aquaponic trends and challenges–A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosta, H.R.; Mohsenian, Y. Alleviation of Alkalinity-Induced Fe Deficiency in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) by Foliar Application of Different Fe Sources in Recirculating System. J. Plant Nutr. 2015, 38, 1768–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Potassium and micronutrient fertilizer addition in a mock aquaponic system for drug-type Cannabis sativa L. cultivation. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 101, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqwepu, O.; Salie, K.; Goosen, N. Evaluation of chelated iron and iron sulfate in the diet of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus to enhance iron excretion for application in integrated aquaponics systems. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 1034–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqwepu, O.; Salie, K.; Goosen, N. Evaluation of potassium diformate and potassium chloride in the diet of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus in a recirculating aquaculture system. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuhaimi-Othman, M.; Yakub, N.; Ramle, N.A.; Abas, A. Comparative toxicity of eight metals on freshwater fish. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2015, 31, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajima, M.N.O.; Ogo, O.A.; Akpa, L.E.; Ajaero, I. Biochemical and haematological responses in African catfish Clarias gariepinus following chronic exposure to NPK (15:15:15) fertiliser. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 40, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, L.C.; Strauch, S.M.; Eding, E.; Presas-Basalo, F.X.; Wasenitz, B.; Palm, H.W. Effects of dissolved potassium on growth performance, body composition, and welfare of juvenile african catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fishes 2021, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.M.; Askwith, C.C.; Kaplan, J. Molecular mechanisms of iron uptake in eukaryotes. Physiol. Rev. 1996, 76, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisen, P.; Enns, C.; Wessling-Resnick, M. Chemistry and biology of eukaryotic iron metabolism. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 33, 940–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.A.; Gatlin, D.M., III. Dietary mineral requirements of fish and marine crustaceans. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1996, 4, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O. Accumulation of waterborne iron and expression of ferritin and transferrin in early developmental stages of brown trout (Salmo trutta). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1997, 16, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S. Trace minerals in fish nutrition. Aquaculture 1997, 151, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, N.R.; Grosell, M.; Wood, C.M.; Hogstrand, C.; Wilson, R.W.; Rankin, J.C.; Busk, M.; Lecklin, T.; Jensen, F.B. Intestinal iron uptake in the European flounder (Platichthys flesus). J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, M.S.; Leji, J.; Rejitha, V.; Ignatius, J.; Peter, V.S. Physiological responses of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) to water-borne ferric iron: Effects on thyroidal, metabolic and hydromineral regulations. J. Endocrinol. Reprod. 2008, 12, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.A.; Bury, N.R. The gills as an important uptake route for the essential nutrient iron in freshwater rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter MC, S.; Rejitha, V.; Dilip, D.G. Handling of ferric iron by branchial and intestinal epithelia of climbing perch (Anabas testudineus Bloch). Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 45, 896–900. [Google Scholar]
- Baker RT, M.; Martin, P.; Davies, S.J. Ingestion of sub-lethal levels of iron sulphate by African catfish affects growth and tissue lipid peroxidation. Aquat. Toxicol. 1997, 40, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J.E. Aquaponics: Integrating fish and plant culture. Aquac. Prod. Syst. 2012, 1, 343–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.L.; Waite, T.D. Kinetic model for Fe (II) oxidation in seawater in the absence and presence of natural organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelme, R.P.; Oyserman, B.O.; Blom, J.E.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Newton, R.J. Stripping away the soil: Plant growth promoting microbiology opportunities in aquaponics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radzki, W.; Gutierrez Mañero, F.J.; Algar, E.; Lucas García, J.A.; García-Villaraco, A.; Ramos Solano, B. Bacterial siderophores efficiently provide iron to iron-starved tomato plants in hydroponics culture. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.; Mankasingh, U.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; Jijakli, H.; Thorarinsdottir, R. Challenges of sustainable and commercial aquaponics. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4199–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, T.S.; De Villiers, D.; Timmons, M.B. Growth and tissue elemental composition response of butterhead lettuce (Lactuca sativa, cv. Flandria) to hydroponic and aquaponic conditions. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, S.M.; Wenzel, L.C.; Bischoff, A.; Dellwig, O.; Klein, J.; Schüch, A.; Wasenitz, B.; Palm, H.W. Commercial African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) recirculating aquaculture systems: Assessment of element and energy pathways with special focus on the phosphorus cycle. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latimer, J.G. The Basics of Fertilizer Calculations for Greenhouse Crops. VCE Publ. 2015, 430. [Google Scholar]
- Ricker, W.E. Linear regressions in fishery research. J. Fish. Board Can. 1973, 30, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulisch, M. Präparation für die konventionelle Rasterelektronenmikroskopie (REM). In Romeis-Mikroskopische Technik; Springer Spektrum: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2015; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rümke, C.L.; Klein, Z. Statistische Betrachtungen über die Genauigkeit der Differenzierung und der Zählung von Leukozyten. Z. Klin. Med. 1987, 42, 173. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, A.J. Fish granulocytes: Morphology, distribution, and function. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1992, 2, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, T.M.; Dove, A.D.; Arnold, J.E. Hematologic disorders of fish. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2008, 11, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomker, J.D. The haematology and histology of the haemopoietic organs of South African freshwater fish. III. The leucocytes, plasma cells and macrophages of Clarias gariepinus and Sarotherodon mossambicus. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1981, 48, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.; Wolf, J.; Braunbeck, T. OECD Guidance Document for the Diagnosis of Endocrine-Related Histopathology of Fish Gonads; OECD: Paris, France, 2009; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, J.R.; Waldenström, J. With reference-to-reference genes: A systematic review of endogenous controls in gene expression studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swirplies, F.; Wuertz, S.; Baßmann, B.; Orban, A.; Schäfer, N.; Brunner, R.M.; Hadlich, F.; Goldammer, T.; Rebl, A. Identification of molecular stress indicators in pikeperch Sander lucioperca correlating with rising water temperatures. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Nieuwegiessen, P.G.; Boerlage, A.S.; Verreth, J.A.; Schrama, J.W. Assessing the effects of a chronic stressor, stocking density, on welfare indicators of juvenile African catfish, Clarias gariepinus Burchell. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 115, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perls, M. Nachweis von Eisenoxyd in gewissen Pigmenten. Arch. Pathol. Anat. Physiol. Klin. Med. 1867, 39, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păpuc, T.; Petrescu-Mag, I.V.; Gavriloaie, C.; Botha, M.; Kovacs, E.; Coroian, C.O. Swimming in the mud-a short review of environmental parameter ranges tolerated by Clarias gariepinus. Extrem. Life Biospeology Astrobiol. 2019, 11, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tyson, R.V.; Simonne, E.H.; White, J.M.; Lamb, E.M. Reconciling water quality parameters impacting nitrification in aquaponics: The pH levels. In Proceedings of the Florida State Horticultural Society, Sanford, FL, USA, 6–8 June 2004; Volume 117, pp. 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Baßmann, B.; Harbach, H.; Weißbach, S.; Palm, H.W. Effect of plant density in coupled aquaponics on the welfare status of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanika, S.; Kramer, B. Electrosensory prey detection in the African sharptooth catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Clariidae), of a weakly electric mormyrid fish, the bulldog (Marcusenius macrolepidotus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2000, 48, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baßmann, B.; Brenner, M.; Palm, H.W. Stress and welfare of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822) in a coupled aquaponic system. Water 2017, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schram, E.; Roques, J.A.; Abbink, W.; Spanings, T.; De Vries, P.; Bierman, S.; van de Vis, H.; Flik, G. The impact of elevated water ammonia concentration on physiology, growth and feed intake of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Aquaculture 2010, 306, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, E.; Roques, J.A.; Abbink, W.; Yokohama, Y.; Spanings, T.; de Vries, P.; Bierman, S.; van de Vis, H.; Flik, G. The impact of elevated water nitrate concentration on physiology, growth and feed intake of African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell 1822). Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, U.; Wenzel, L.C.; Appelbaum, S.; Palm, H.W. Aquaponics (sl) Production of spearmint (Mentha spicata) with African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) in Northern Germany. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, U.; Palm, H.W. Effects of the fish species choice on vegetables in aquaponics under spring-summer conditions in northern Germany (Mecklenburg Western Pomerania). Aquaculture 2017, 473, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homoki, D.; Minya, D.; Kovács, L.; Molnár, Á.; Balogh, K.; Bársony, P.; Fehér, M.; Kövics, G.; Stündl, L. Comparison of the technological background of aquaponic systems. Acta Agrar. Debr. 2020, 1, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Lewis, D.; Sinet, P.M. Oxygen consumption during the fenton-type reaction between hydrogen peroxide and a ferrous-chelate (Fe2+-DTPA). J. Inorg. Biochem. 1981, 15, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.E.; Maxwell, S.C.; Naughton, D.P. Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide suppression by metal ions and their EDTA complexes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.I.; Aanyu, M.; Schrama, J.W.; Verreth, J.A. Size distribution in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) affects feeding behaviour but not growth. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewolu, M.A.; Adeniji, C.A.; Adejobi, A.B. Feed utilization, growth and survival of Clarias gariepinus (Burchell 1822) fingerlings cultured under different photoperiods. Aquaculture 2008, 283, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, K.; Umah, R.; Muralikrishnan, S.; Xavier, R.; Kathiresan, S. Effect of different feed application rate on growth, survival and cannibalism of african catfish, Clarias gariepinus fingerlings. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2011, 23, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Nieuwegiessen, P.G.; Olwo, J.; Khong, S.; Verreth, J.A.; Schrama, J.W. Effects of age and stocking density on the welfare of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus Burchell. Aquaculture 2009, 288, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, U.U.; Ezeri GN, O.; Opabunmi, O.O. Influence of sex, source, health status and acclimation on the haematology of Clarias gariepinus (Burch, 1822). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.S.; Olaifa, F.E.; Emikpe, B.O. Haematological and blood biochemical changes in African catfish, Clarias gariepinus fed walnut (Tetracarpidium conophorum Mull Arg) leaf and onion (Allium cepa Linn) bulb supplemented diets. Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2014, 4, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.I.; Schrama, J.W.; Verreth, J.A. The effect of group composition on the welfare of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2006, 97, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tort, L. Stress and immune modulation in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomen, R.A.; Hutchings, J.A. Transcriptomic responses to environmental change in fishes: Insights from RNA sequencing. Facets 2017, 2, 610–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.T.; Kadri, S.; Köllner, B.; Rebl, A.; Korytář, T. RNA-Seq of Single Fish Cells–Seeking Out the Leukocytes Mediating Immunity in Teleost Fishes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 798712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Symbol | Gene Product | Function | Sense Primer (5′→3′), Antisense Primer (5′→3′) | Source (Species; Accession Code) | Fragment Length (bp) | PSQ Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference genes: | ||||||
| rna18s | 18S ribosomal RNA | Structure of eukaryotic ribosomes | CTCTGCTGGACGATGGCTTAC, TCGATGAAGAACGCAGCCAGC | C. gariepinus; GQ465239 | 94 | 100 |
| actb | Actin-beta | Cell structure and motility, intercellular signaling | ACCACCACAGCCGAGAGAGAA, CTTCCAGCCATCTTTCCTTGGT | C. gariepinus; EU527191 | 204 | 86 |
| gapdh | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Carbohydrate metabolism | TATGAAGCCCGCTGAGATCCC, GCCTCTTCTCACTTGCAGGGT | C. gariepinus; AF323693 | 106 | 99 |
| rpl | Ribosomal protein, large subunit | Structure of eukaryotic ribosomes | ACTAAATAGCAACTGATCCCTATC, GAATATCTGACCACTAAGATCCG | C. gariepinus; MW080924 | 134 | 96 |
| Target genes: | ||||||
| atp6v1g1 | ATPase H+ transporting v1 subunit g1 | Intercellular Fe homeostasis | CGGAAAAACCGCCGCTTGAAG, GACCAAGGAAGCCGCGGCAC | P. hypophthalmus; XM_026922532 | 106 | 84 |
| c3a | Complement component 3, variant a | Bacteria opsonization and destruction | ATGTCTTTCGATGTCACGGTTTAT, TCGAACCAAGAGTAACGGCATG | I. punctatus; XM_017457024 | 114 | 93 |
| casp3 | Caspase 3 | Apoptosis | CTCTTTATCATTCAGGCTTGTCG, GTACTCTACTGCTCCAGGTTATT | I. punctatus; XM_017473312 | 139 | 95 |
| casp8 | Caspase 8 | Apoptosis | GTTATCAGCCGAAGCCGCTCA, ATCCAGAGCTATGATGTGTCCG | Cyprinus carpio; XM_042730675 | 157 | 91 |
| ccnb1 | Cyclin b1 | Control of the G2/M transition phase of the cell cycle | TCAAAAATCGGAGAGGTTACAGC, TGCACTTTGCTCCCTCTCTGG | I. punctatus; NC_030443 | 103 | 91 |
| cp | Ceruloplasmin | Copper transportation, oxidation of iron (Fe2+ to Fe3+) | CCACAACGTTCTAGAAGAATCATA, CTAAGAATGGAGGTCCAACTAAAA | I. punctatus; JF914943 | 155 | 87 |
| cs | Citrate synthase | Aerobic metabolism | GGTGGTGAAGTGTCCGATGAAA, GCTATGGGCATGCTGTCCTGA | I. punctatus; XM_017487510 | 94 | 94 |
| hmox1a | Heme oxygenase 1 | Cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus | GATTCTTCTGTGTTCCCTGTATG, CCATCTACTTCCCTCAGGAGC | I. punctatus; XM_017491622 | 104 | 95 |
| hsf | Heat-shock transcription factor 1 | ERK signaling, stress response | GTGCAGTCCATCAACTTTGATTC, CTATTCAGGAGTTGCTGTCAGAA | I. punctatus; XM_017455240 | 111 | 93 |
| hsp90ab1 | Heat-shock protein 90 alpha family class b member 1 | Chaperone function, stress response | GAACATCAAGCTGGGCATCCAT, TTACTACATCACTGGTGAGAGCA | I. punctatus; XM_017456214 | 167 | 87 |
| hspb1 | Heat-shock protein family b (small) member 1 | Differentiation of cell types, stress response | ACAGGACAACTGGAAGGTGAAC, GATTATCGGAAACCATGAGGAGA | Clarias batrachus; KT359728 | 107 | 97 |
| hspd1 | Heat shock protein family d (hsp60) member 1 | Chaperone function, stress response | GCACGCTTGTCCTCAACAGGTT, AGACATGGCGATTGCTACTGGA | I. punctatus; XM_017469365 | 113 | 91 |
| igf1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 | Anabolism, growth | CGCCCAAAACACCAAAGAAACC, AGTGACGAGAAGAGGAGAGCG | I. punctatus; NM_001200295 | 164 | 100 |
| il2 | Interleukin-2 | Activation and proliferation of lymphocytes | GTCGGCCTGGGAAAAAGCCAAT, TTATGTGTTTGCACCAGACAACG | I. punctatus; XM_017474923 | 162 | 95 |
| il4 | Interleukin-4 | Activation and proliferation of leucocytes | ATGAATCCTTGTGGAAGATTAGAG, GGAGTATTTGGTGAGAGAGGTAA | P. hypophthalmus; XM_026924084 | 108 | 86 |
| il6 | Interleukin-6 | Acute-phase response | GCAGTTGAAACGGGACTTCCCA, TGTACCAAGCTTACCTGCCCTA | I. punctatus; XM_017455306 | 162 | 96 |
| kmt2a | Lysine-specific methyltransferase 2a | Regulation of early development and hematopoiesis | ATTGGGTCGAAATCGTGCTGTAT, ATGATAAGTCTTCAGTGGCAGGT | I. punctatus; XM_017490460 | 121 | 90 |
| mtf1 | Metal regulatory transcription factor 1 | Catabolic regulation of cartilages | GTAGGAGGGCATTCAGGGAAC, AGTCAGAACGCTGCCCCCTC | I. punctatus; XM_017475296 | 146 | 90 |
| nkx2-3 | NK2 homeobox 3 | Cell differentiation | TACAGGACAACCTGGTGGAAAG, ACAACTCTTGGTTTCCTGCTCTT | I. punctatus; XM_017464595 | 119 | 89 |
| nr3c1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group c, member 1, glucocorticoid receptor | Stress response | TGTAGAAGGCCAACACAACTATC, GAACCTAGAAGCACGCAAAAACA | I. punctatus; XM_017492397 | 137 | 94 |
| oser1 | Oxidative stress-responsive serine-rich protein 1 | Oxidative stress | AACTGGCATGGATGCAGTCGAA, ACCTACTGTAGCTCTAAAATGCAA | I. punctatus; NM_001200453 | 120 | 93 |
| osgin2 | Oxidative stress growth inhibitor | Oxidative stress | AGGAGCCTGGCATGCAATGGA, GTGACCAATGACCGGGCCAC | I. punctatus; XM_017467887 | 129 | 91 |
| pgm3 | Phosphoglucomutase 3 | Carbohydrate metabolism | GACACAGGCAGGGCTGAATCT, CTTCGTACAGCACACTGTAACC | I. punctatus; XM_017494096 | 112 | 94 |
| sirt1 | Sirtuin 1 | Oxidative stress | AGTGAGGTGCTAGGGTTAATGG, TTGGTTCTTATCGCTTTATTCAGC | I. punctatus; XM_017461869 | 148 | 91 |
| slc30a5 | Solute carrier family 30, member 5 | Zinc transportation | AATAGTCACCAAAAGACAGTGGAT, CATCGTTGTGCTCGAACAACAG | I. punctatus; XM_017459891 | 134 | 90 |
| slc39a8 | Solute carrier family 39, member 8 | Cellular zinc uptake, protection from inflammation-related injury and death | TTTAACCTGATCTCAGCCATGTC, TATGTTCCCTGAGATGAATGCCA | I. punctatus; XM_017489708 | 151 | 93 |
| slc46a1 | Solute carrier family 46, member 1 | Folate transportation | AATGGCGACATGCACAAGGGTAT, AGAACAGCCTTGCCCCAGGG | I. punctatus; XM_017491375 | 129 | 88 |
| sp1 | SP1 transcription factor | Cell growth, apoptosis, differentiation and immune responses | AGCACAGCAGGTGATCAGGGA, GAGAAGCGTGCACATGTCCATA | I. punctatus; XM_017450095 | 119 | 91 |
| st8sia4 | St8 alpha-n-acetyl-neuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase | Synthesis of polysialic acid for cell adhesion molecule | GGTTCATGCAGTCAGAGGGTAC, CTTCTGCGATGAGATCCACTTG | C. gariepinus; PRJNA820763 | 112 | 85 |
| stk39 | Serine/threonine kinase 39 | Stress response | TGTAGTTGTTGCTGCTAACCTTC, AGATCCCTGACGAGGTGAAGC | I. punctatus; XM_017469076 | 116 | 89 |
| tlr5 | Toll-like receptor 5 | Detection of bacteria | GGCAGCATGGGAAAGGGAGTT, GTTAAGGCTCTGGATCTGTCCA | I. punctatus; NM_001200229 | 103 | 96 |
| tnf | Tumor necrosis factor alpha | Immune/acute-phase response | AAACCAGACGAGACCCAAGAAAT, TCTATGCAGTGGTTCGACAACG | I. punctatus; NM_001200172 | 130 | 96 |
| ucp2 | Uncoupling protein 2 | Regulation of production of reactive oxygen species, function of mitochondria | GGCTCCAGATCCAAGGGGAGA, CCACGTAGTCTCTACAACGGG | I. punctatus; XM_017489367 | 131 | 92 |
| zeb1 | Zinc finger e-box binding homeobox 1 | Repression of interleukin-2 function | GCAGAGACCAGCGGCATGTAA, ATACGAGTGCCCCAACTGTAAAA | I. punctatus; XM_017483097 | 156 | 89 |
| Behavioral Element | Definition |
|---|---|
| Agonistic behavior | Chasing or biting a fish or being chased by or bitten by another fish. |
| Air breathing | The fish moves to the water surface and takes a gulp of air. This was checked by escaping air from the gills of the fish when it was swimming back to the bottom of the tank. |
| Escape attempts | The fish moves to the water surface and its head emerges from the water surface past its gill cover. |
| Resting | Moving passively through the water or lying still at the bottom of the tank. |
| Stereotypic behavior | Continuous and compulsive swimming in a fixed, repetitive pattern. |
| Swimming | Displacement of the body, while browsing, moving, eating and air-breathing. |
| Parameters | Exp. A | Exp. B | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeDTPA-0 | ±SD | FeDTPA-0.75 | ±SD | FeDTPA-3 | ±SD | FeDTPA-0 | ±SD | FeDTPA-3 | ±SD | FeDTPA-12 | ±SD | ||
| Temp. | (°C) | 29.80 | 1.06 | 29.70 | 0.78 | 29.50 | 1.00 | 29.00 | 1.10 | 28.00 | 0.61 | 28.90 | 0.76 |
| DO | (mg/L) | 8.20 | 0.27 | 8.10 | 0.18 | 8.10 | 0.19 | 7.10 | 0.39 | 6.80 | 0.52 | 6.90 | 0.36 |
| EC | (µS/cm) | 523.80 a | 21.70 | 534.00 a | 21.86 | 545.30 b | 39.35 | 986.80 a | 86.69 | 958.70 a | 77.87 | 1058.20 b | 129.11 |
| Redox | (mV) | 190.00 a | 15.89 | 151.80 b | 32.56 | 122.90 c | 51.21 | 169.00 a | 15.12 | 126.50 b | 27.69 | 128.80 b | 28.12 |
| pH | 8.70 | 0.07 | 8.70 | 0.10 | 8.70 | 0.08 | 6.40 a | 0.74 | 7.00 b | 0.50 | 6.70 c | 0.65 | |
| NO3− | (mg/L) | 12.31 | 2.63 | 13.02 | 3.72 | 13.92 | 3.95 | 201.60 | 78.74 | 174.95 | 79.09 | 185.92 | 78.13 |
| NO2− | (mg/L) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.49 | 0.48 |
| PO42− | (mg/L) | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.58 | 0.13 | 0.65 | 0.36 | 6.78 | 3.37 | 4.72 | 2.39 | 5.84 | 2.58 |
| NH4+ | (mg/L) | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 2.03 a | 1.92 | 0.39 b | 0.60 | 0.84 c | 0.94 |
| Fe3+ | (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Fe2+ | (mg/L) | 0.06 a | 0.03 | 0.58 b | 0.22 | 2.36 c | 0.98 | 0.07 a | 0.03 | 2.24 a | 1.21 | 9.00 b | 4.94 |
| Fe total | (mg/L) | 0.08 a | 0.02 | 0.59 b | 0.22 | 2.37 c | 0.99 | 0.09 a | 0.01 | 2.25 b | 1.18 | 8.99 c | 4.90 |
| Exp. A | Exp. B | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeDTPA-0 | FeDTPA-0.75 | FeDTPA-3 | FeDTPA-0 | FeDTPA-3 | FeDTPA-12 | |
| Initial weight (g) | 0.229 ± 0.04 | 0.217 ± 0.03 | 0.171 ± 0.04 | 271.43 ± 12.75 | 272.82 ± 20.21 | 256.87 ± 19.57 |
| Final weight (g) | 2.318 ± 0.98 | 2.558 ± 1.03 | 2.931 ± 0.83 | 270.40 ± 56.80 | 315.88 ± 70.93 | 286.31 ± 45.54 |
| Initial length (cm) | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 30.5 ± 1.8 | 32.67 ± 0.5 | 30.8 ± 2.8 |
| Final length (cm) | 6.3 ± 1.3 | 6.6 ± 1.3 | 7.0 ± 0.7 | 33.7 ± 1.8 | 33.5 ± 2.2 | 33.3 ± 2.3 |
| Total feed input (kg) | 0.03907 | 0.03987 | 0.04702 | 2.022 | 2.038 | 1.971 |
| Condition factor | 0.79 ± 0.03 | 0.84 ± 0.03 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | 0.81 ± 0.11 | 0.77 ± 0.05 | 0.8 ± 0.05 |
| Mortality in % (n) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 11.1 (2) | 5.5 (1) | 5.5 (1) |
| Video and Direct Observations | Exp. A | Exp. B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeDTPA-0 | FeDTPA-0.75 | FeDTPA-3 | FeDTPA-0 | FeDTPA-3 | FeDTPA-12 | |
| Swimming activity (Mean %) day 8 | 70.70 ± 9.66 | 62.22 ± 24.11 | 77.38 ± 6.48 | 77.67 ± 8.52 | 74.88 ± 7.73 | 75.53 ± 5.03 |
| Swimming activity (Mean %) day 18 | 68.47 ± 16.82 | 75.34 ± 2.93 | 78.40 ± 6.00 | 82.40 ± 4.50 | 74.09 ± 14.70 | 83.42 ± 5.04 |
| Swimming activity (Mean %) day 28 | 69.99 ± 12.67 | 80.35 ± 11.28 | 74.42 ± 12.73 | 78.80 ± 12.65 | 79.69 ± 17.74 | 86.82 ± 13.94 |
| Escape attempts (Total frequency) day 8 | 1 ± 0.60 | 0 ± 0.00 | 1 ± 0.60 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 |
| Escape attempts (Total frequency) day 18 | 1 ± 0.60 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 |
| Escape attempts (Total frequency) day 28 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 2 ± 1.20 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 1 ± 0.60 |
| Air breathing Index (Total frequency) day 8 | 0.81 ± 0.43 | 0.52 ±0.50 | 0.74 ± 0.25 | 6.31 ± 0.34 | 5.39 ± 0.42 | 6.30 ± 1.14 |
| Air breathing Index (Total frequency) day 18 | 1.36 ± 0.31 | 1.14 ± 0.49 | 1.48 ± 0.90 | 5.70 ± 1.18 | 7.33 ± 1.18 | 5.69 ± 1.28 |
| Air breathing Index (Total frequency) day 28 | 2.02 ± 0.43 | 4.52 ± 1.69 | 1.69 ± 1.49 | 5.48 ± 1.63 | 8.49 ± 1.81 | 6.48 ± 1.46 |
| Agonistic behavior Index (Total frequency) day 8 | 1.55 ± 0.18 | 1.02 ± 0.23 a | 1.62 ± 0.25 b | 0.15 ± 0.21 | 0.11 ± 0.15 | 0.11 ± 0.15 |
| Agonistic behavior Index (Total frequency) day 18 | 2.90 ± 1.03 | 2.43 ± 0.58 | 2.40 ± 0.57 | 0.29 ± 0.32 | 0.29 ± 0.31 | 0.44 ± 0.60 |
| Agonistic behavior Index (Total frequency) day 28 | 2.69 ± 0.61 | 2.50 ± 0.31 a | 1.74 ± 0.35 b | 0.78 ± 0.84 | 0.67 ± 0.70 | 0.39 ± 0.67 |
| Stereotypical behavior (Total frequency) day 8 | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 |
| Stereotypical behavior (Total frequency) day 18 | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 |
| Stereotypical behavior (Total frequency) day 28 | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0.00 |
| Skin lesions (n) day 11 | n.g. | n.g. | n.g. | 5 A | 0 A | 3 A |
| Skin lesions (n) day 21 | n.g. | n.g. | n.g. | 3 A | 13 B | 6 A |
| Skin lesions (n) day 32 | n.g. | n.g. | n.g. | 11 A | 29 B | 3 A |
| Skin lesion area (cm2) day 11 | n.g. | n.g. | n.g. | 0.43 ± 0.92 A | 0.00 ± 0.00 A | 0.33 ± 0.66 A |
| Skin lesion area (cm2) day 21 | n.g. | n.g. | n.g. | 0.30 ± 0.75 A | 0.65 ± 0.56 B | 0.60 ± 1.14 A |
| Skin lesion area (cm2) day 32 | n.g. | n.g. | n.g. | 0.70 ± 1.06 A | 1.55 ± 1.81 B | 0.15 ± 0.41 A |
| Cell Types (%) | Day 11 (after 24 h) | Day 21 | Day 32 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeDTPA-0 | FeDTPA-3 | FeDTPA-12 | FeDTPA-0 | FeDTPA-3 | FeDTPA-12 | FeDTPA-0 | FeDTPA-3 | FeDTPA-12 | |
| Lymphocytes | 52.28 ± 1.73 A | 52.91 ± 2.17 A | 48.92 ± 3.27 A | 58.78 ± 2.48 a | 73.63 ± 2.65 b | 58.41 ± 10.93 | 65.27 ± 7.39 B | 65.09 ± 4.50 B | 57.60 ± 8.77 B |
| Monocytes | 19.59 ± 2.84 | 17.22 ± 7.18 | 19.53 ± 2.82 | 20.86 ± 7.81 | 14.35 ± 1.49 | 20.32 ± 7.12 | 26.40 ± 6.62 | 23.12 ± 1.00 | 28.11 ± 3.52 |
| Mature neutrophils | 22.35 ± 1.12 aA | 24.78 ± 7.96 A | 26.63 ± 0.64 bA | 16.90 ± 4.74 | 9.03 ± 2.44 | 17.85 ± 5.72 | 6.17 ± 1.39 B | 7.53 ± 2.51 B | 5.54 ± 1.12 B |
| Neutrophile meta-granulocyte | 3.22 ± 0.53 A | 2.56 ± 1.93 A | 2.74 ± 0.09 A | 0.86 ± 0.55 B | 1.09 ± 0.63 B | 1.22 ± 0.20 B | 0.49 ± 0.28 B | 0.64 ± 0.44 B | 0.63 ± 0.49 B |
| Neutrophile meso-granulocyte | 2.48 ± 0.21 A | 2.64 ± 1.18 A | 2.16 ± 0.96 A | 2.39 ± 1.39 | 1.80 ± 1.09 | 2.14 ± 0.85 | 1.12 ± 0.34 B | 1.81 ± 0.58 B | 1.58 ± 0.71 B |
| Eosinophils | n.g. | n.g. | n.g. | 0.19 ± 0.33 | 0.06 ± 0.10 | n.g. | 0.48 ± 0.52 | 1.79 ± 2.03 | 0.37 ± 0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hildebrand, M.-C.; Rebl, A.; Nguinkal, J.A.; Palm, H.W.; Baßmann, B. Effects of Fe-DTPA on Health and Welfare of the African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Water 2023, 15, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020299
Hildebrand M-C, Rebl A, Nguinkal JA, Palm HW, Baßmann B. Effects of Fe-DTPA on Health and Welfare of the African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Water. 2023; 15(2):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020299
Chicago/Turabian StyleHildebrand, Marc-Christopher, Alexander Rebl, Julien Alban Nguinkal, Harry Wilhelm Palm, and Björn Baßmann. 2023. "Effects of Fe-DTPA on Health and Welfare of the African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822)" Water 15, no. 2: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020299
APA StyleHildebrand, M.-C., Rebl, A., Nguinkal, J. A., Palm, H. W., & Baßmann, B. (2023). Effects of Fe-DTPA on Health and Welfare of the African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Water, 15(2), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020299








