Enhanced Effect of Mining Dust Diffusion on Melting of the Adjacent Glacier: A Case Study in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Plan
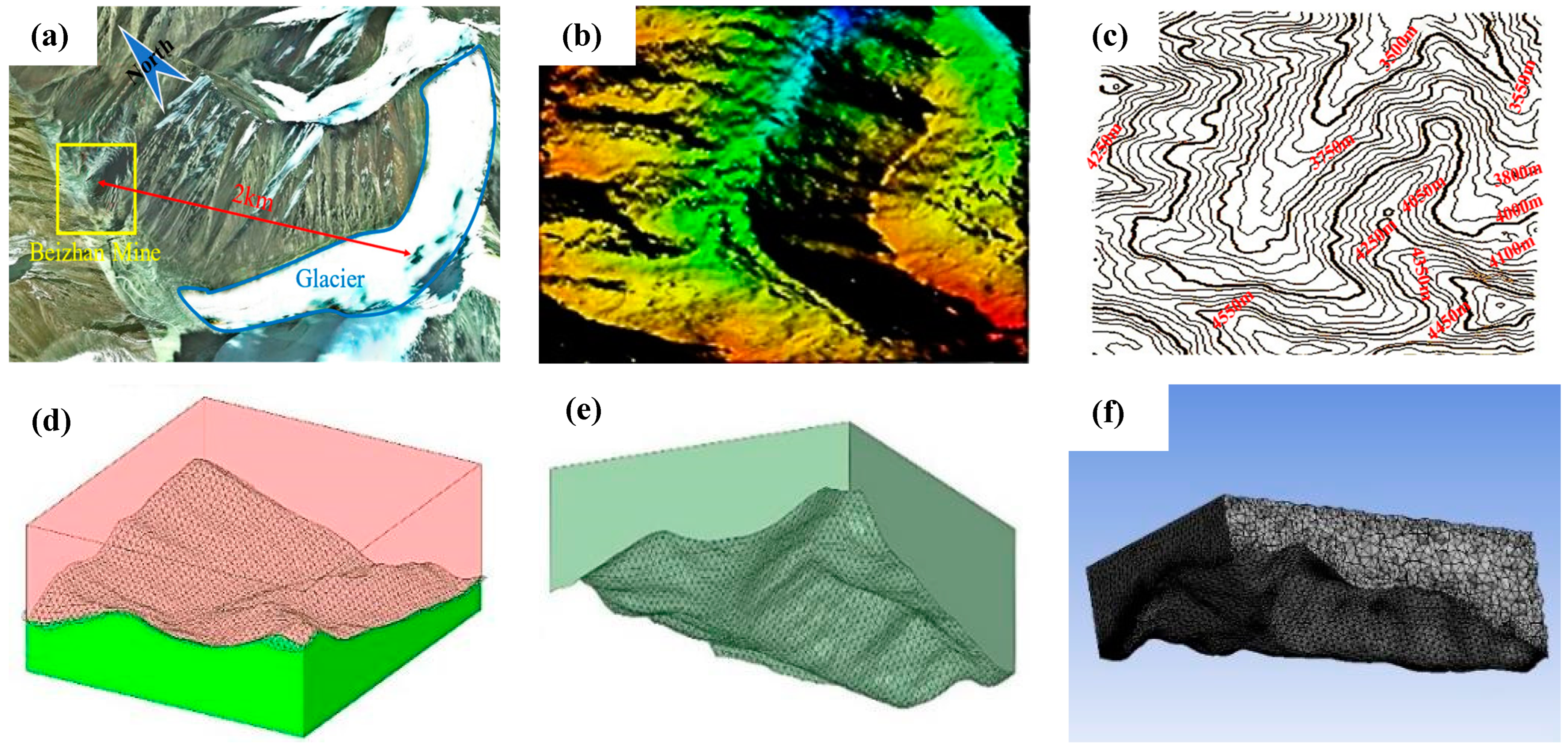
2.1. Research Object
2.2. Research Materials and Methods
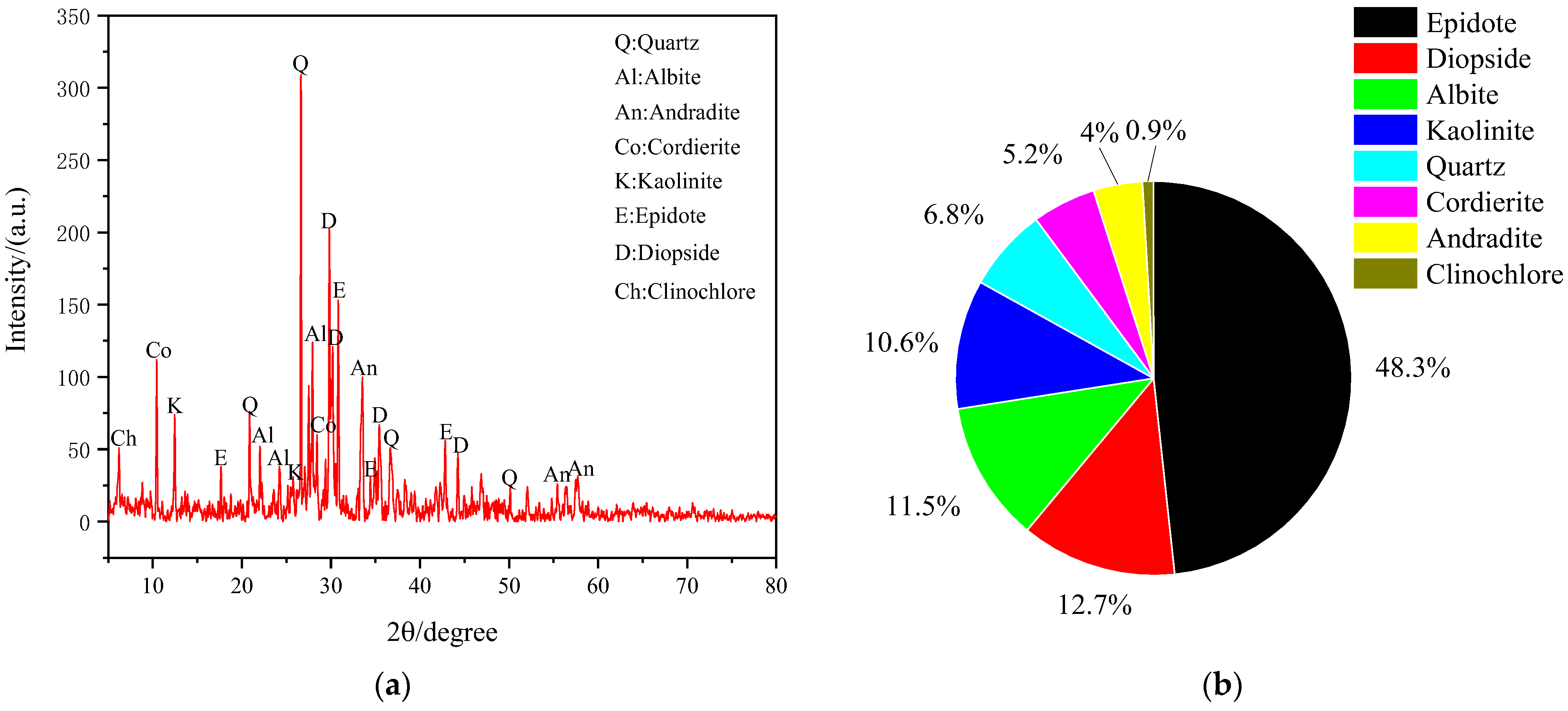
2.2.1. Mineral Dust Sample
2.2.2. Numerical Simulation
2.2.3. Parameter Settings
2.2.4. Physical Simulation
3. Results and Analysis
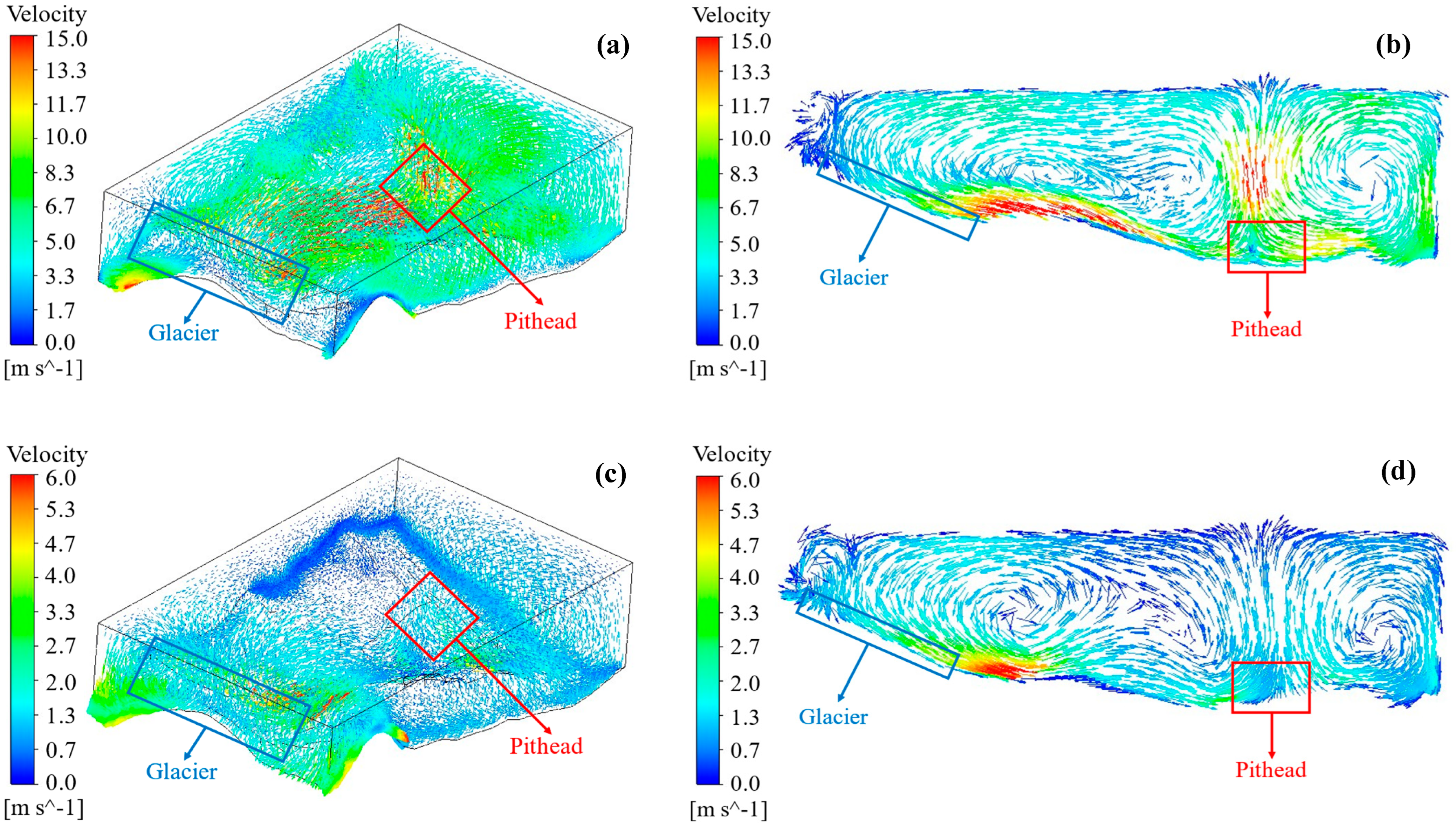
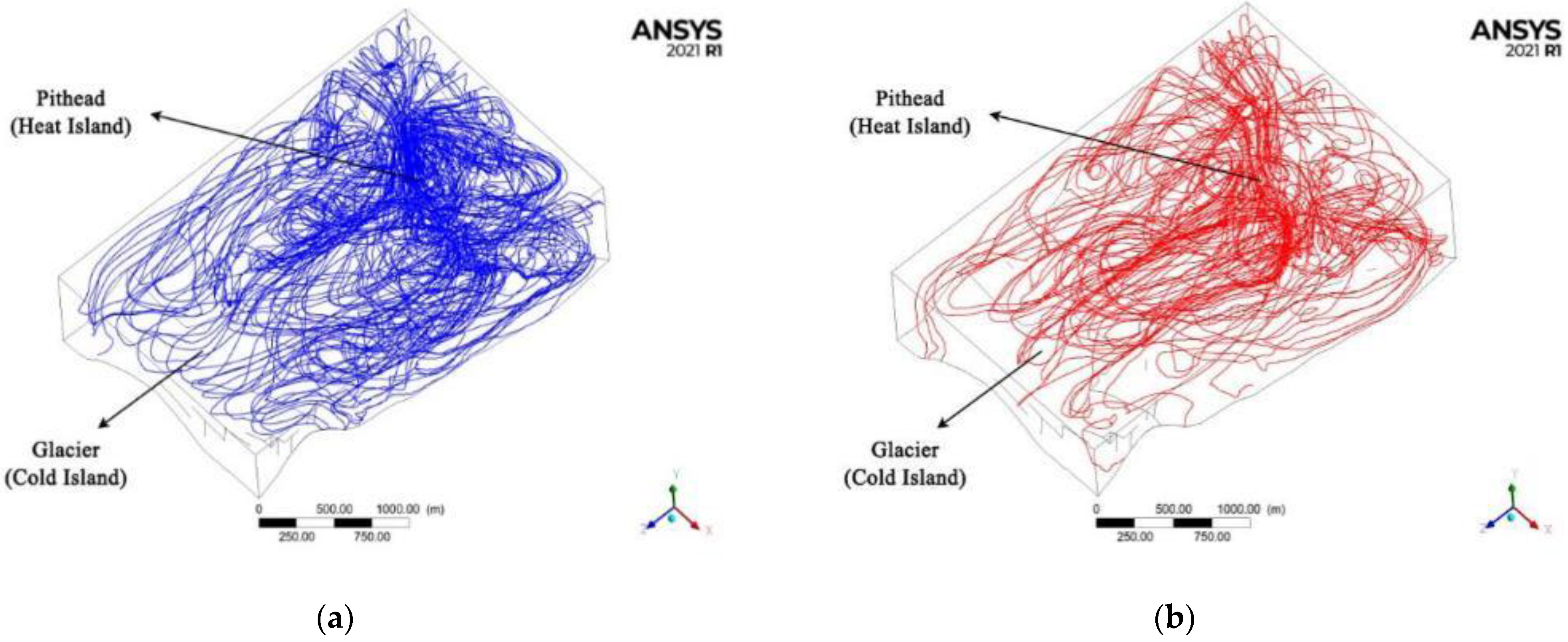
3.1. Local Wind Field in the Alpine Mining Area
3.1.1. Numerical Simulation Results
3.1.2. Theoretical Analysis of the Simulated Results
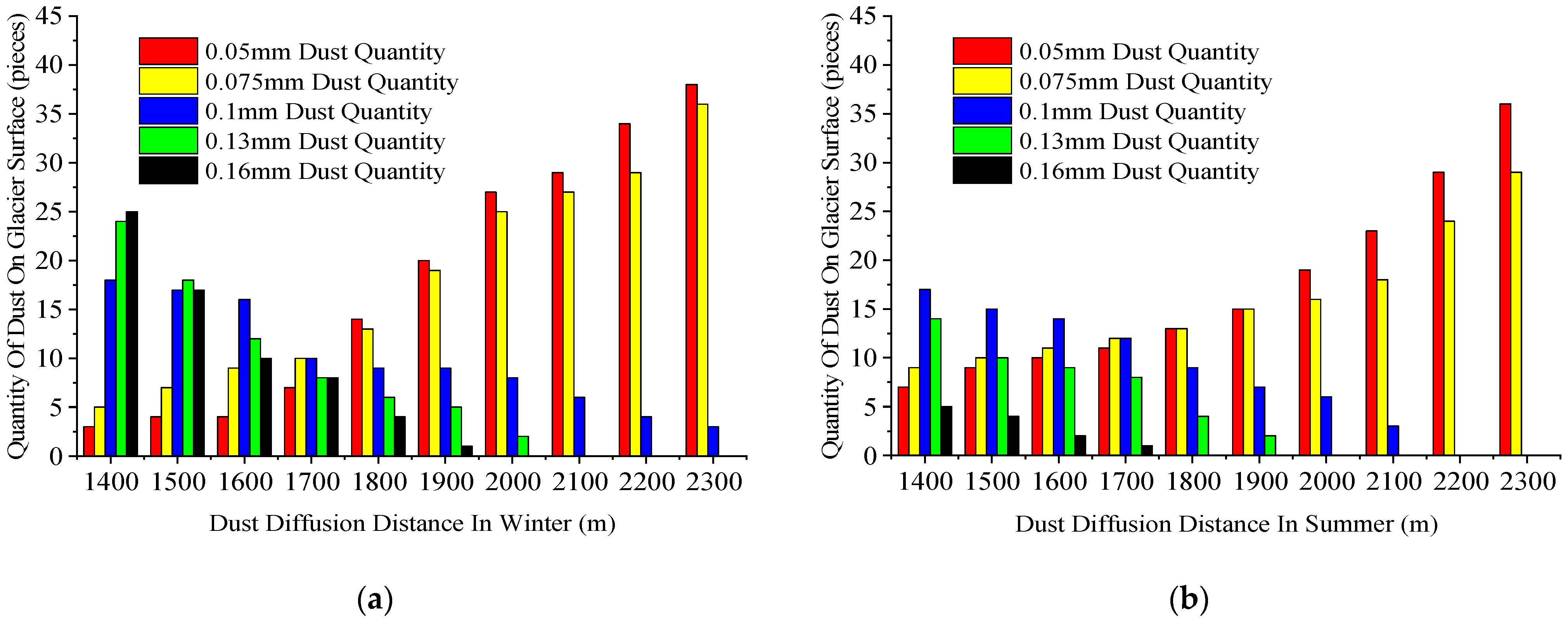
3.2. Dust Diffusion in the Alpine Mining Area
3.2.1. Numerical Simulation Results
3.2.2. Theoretical Analysis of the Simulated Results
- (1)
- Horizontal force and velocity of dust
- (2)
- Vertical force and velocity of dust
3.3. Grading of the Dust Particles on the Glacier Surface
3.4. Effect of Mining Dust on Accelerated Glacier Ablation
3.4.1. Physical Experiment Results
- (1)
- Influence of dust coverage on the ice-melting rate
- (2)
- Influence of temperature on the ice-melting rate
3.4.2. Theoretical Analysis of the Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The combined effects of the mine (heat island) and glacier (cold island) lead to local atmospheric circulation in alpine areas.
- (2)
- The local atmospheric circulation results in the spread of mining dust to the glacier surface.
- (3)
- Mining dust coverage leads to accelerated ablation of the adjacent glacier.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, W.M.; Zhao, S.M. Study of the Spatial Distribution Pattern of the Digital Glacial Geomorphology in China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2009, 31, 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, D.H. Glossary of Cryospheric Science; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.P.; Li, P.H.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Xu, C.H. Advances in research on changes and effects of glaciers in Xinjiang mountains. Adv. Water Sci. 2020, 31, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, Z.; Tian, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, H. Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of Glacier Resources in Xinjiang over the Past 50 Years. Water 2022, 14, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.P.; Ran, L.K.; Cao, J. Diagnosis and Analysis of Vertical Motion during Complex Topographical Heavy Snowfall. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 45, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yu, S.; Shang, H. An Analysis of Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions Based on Isotopic Data from the Kaidu River Basin, South Tianshan Mountain. Water 2022, 14, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tian, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Kang, Z.; Wang, T.; Gao, Y.; Yu, F.; et al. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Glacier Mass Balance on the Northern and Southern Slopes of the Central Tianshan Mountains, China. Water 2022, 14, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Yue, X. Glaciers in Xinjiang, China: Past Changes and Current Status. Water 2020, 12, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saydi, M.; Tang, G.; Fang, H. Major Controls on Streamflow of the Glacierized Urumqi River Basin in the Arid Region of Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Jin, S.; Xu, C.; Deng, H.; Zhang, M. Runoff Changes from Urumqi Glacier No. 1 over the Past 60 Years, Eastern Tianshan, Central Asia. Water 2020, 12, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Gao, T.G.; Kang, S.C. Albedo reduction as an important driver for glacier melting in Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding areas. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.Y. Area Changes and Mass Balance of Glaciers in KangzhagRi of the Tibetan Plateau from 1970 to 2016 Derived from Remote Sensing Data. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.R.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.H. Vulnerability of glacier change in the Tianshan Mountains region of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.P.; Li, M.; Tan, C.P.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, S.J. Public perception and selections of adaptation measures against glacier change and its impacts: Taking the Hexi inland river basin as an example. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2015, 37, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaiMa, Y.Z.; La, Z.; ZhaXi, Y.Z. Responses of lakes and glaciers of Tibet to climate change from 1973 to 2020. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2021, 41, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Han, H.; Kang, S. Modeling Glacier Mass Balance and Runoff in the Koxkar River Basin on the South Slope of the Tianshan Mountains, China, from 1959 to 2009. Water 2017, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Li, H.M.; Pan, Z.S.; Che, D.; Zhao, T. The present situation of national mineral resources conditions investigation and appraisal (NMRCIA) and its supporting technological systems in the new development stage, China. Adv. Water Sci. China Min. Mag. 2022, 31, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Q. Analysis on the types and characteristics of mineral resources in Xinjiang. World Nonferrous Met. 2018, 33, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.F.; Shi, J.F.; Chen, X.F.; Ye, J.H. Distribution characteristic and potential analysis of important solid mineral resources in “Belt and Road” area. China Min. Mag. 2017, 26, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. An analysis of the situation of mineral resources exploration and development and supply and demand in Western China. World Nonferrous Met. 2020, 4, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. A Study of the Coupling Relation between Mineral Resources Exploitation and Ecological Environment: Evidence from the Grassland of Inner Mongolia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 811, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Q.; Yang, Q.; Mao, W.Y.; Xu, X.B.; Liu, Z.H. Evaluation of the impacts of climate change and human activities on the hydrological environment in Central Asia. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2016, 38, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.Q.; Mu, J.X.; He, H.D. Impact of the Glacier Change on Water Resources in the Kuytun River Basin, Tianshan Mountains During Recent 50 Years. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2017, 37, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Nüsser, M.; Schmidt, S. Glacier changes on the Nanga Parbat 1856–2020: A multi-source retrospective analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Sun, X.J.; Li, S.N.; Zhang, Q.G. Advances on inorganic hydrochemistry of glacial meltwater runoff in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its surrounding areas. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2020, 42, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.J.; Cai, Q.X. Dust distribution in open-pit mines based on monitoring data and fluent simulation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Jia, M.T.; Ren, J.Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, F.; Lu, Z.Y. Study on diffusion law of blasting toxic and harmful gas and dust in roadway blasting. Mod. Min. 2021, 37, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Song, Y.; Zeng, Q. Study on the Ablation of the Glacier Covered by Mineral Dust in Alpine Regions. Water 2022, 14, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, K.R.; Mayewski, P.A.; Hubbard, M.; Broad, K.; Clifford, H.; Napper, I.; Gajurel, A.; Jaskolski, C.; Li, W.; Potocki, M.; et al. A Perspective of the Cumulative Risks from Climate Change on Mt. Everest: Findings from the 2019 Expedition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.B.; Ji, W.Q.; Xu, L.J.; Wang, S.T. Deformation Time Series and Driving-Force Analysis of Glaciers in the Eastern Tienshan Mountains Using the SBAS InSAR Method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, L.B. Climate Change and Its Impact on the Eco-Environment of the Three-Rivers Headwater Region on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12057–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Gui, X.Y.; Meng, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.L. Research on stressed analysis and moving trace on dust particles in air flow of screening shop. Coal Eng. 2008, 8, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q. Research on the variation of dust transport velocity rules under effect of two forces. Miner. Eng. Res. 2014, 29, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.W.; Guo, H.X.; Wang, R.S. Analysis on Variation Law and Influencing Factors of Dust Migration Velocity in High Inclination-angle Full-mechanized Top-coal Caving Face. World SCI-Tech. RD 2015, 37, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Fang, B.J. Stress Analysis and Movement Study on Construction Tunnel Dust. Coal Technol. 2016, 35, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Cheng, X.J. Mechanical analysis of blasting dust particles in movement. J. Hebei Inst. Technol. 1996, 4, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.J.; Yao, T.D. Progress in Studies on Insoluble Microparticle in Ice Cores. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2005, 27, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, J.E.; Rotstayn, L.D. Indirect aerosol forcing. Science 2000, 290, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idso, S.B. Thermal blanketing: A case for aerosol-induced climatic alteration. Science 1974, 186, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, V. Mineralogy of atmospheric microparticles deposited along the Greenland Ice Core Project ice core. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 26725–26734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Cai, S.Z.; Zou, H. Effect of Rare Earth Ce on Thermal Performance of Al-Mg-Ce Alloy Fuels. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar]











| Particle Size Range (mm) | 0.05–0.09 | 0.09–0.12 | 0.12–0.16 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of particle size (%) | 50 | 40 | 10 |
| Area | Temperature in Winter/°C | Temperature in Summer/°C |
|---|---|---|
| Air Fluid | 0 | 15 |
| Ground | 10 | 20 |
| Glacier Surface | −20 | 0 |
| Mine | 20 | 30 |
| The Injection Parameters | Parameter Settings |
|---|---|
| Dust Density (kg/m3) | 2100 |
| Minimum Diameter (m) | 0.00005 |
| Maximum Diameter (m) | 0.00016 |
| Injection Speed /(m/s) | X = 0; Y = 1; Z = 0 |
| Area | Type | Speed/(m/s) | Boundary Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glacier Surface | Wall | — | Trap |
| Mine | Inlet | 1 | Escape |
| Ground | Wall | — | Reflect |
| Glacier–Mine Wall | Wall | — | Trap |
| Other Wall | Wall | — | Reflect |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Xu, X.; Hou, D. Enhanced Effect of Mining Dust Diffusion on Melting of the Adjacent Glacier: A Case Study in Xinjiang, China. Water 2023, 15, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020224
Zhang Z, Song Y, Xu X, Hou D. Enhanced Effect of Mining Dust Diffusion on Melting of the Adjacent Glacier: A Case Study in Xinjiang, China. Water. 2023; 15(2):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020224
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiyi, Yongze Song, Xinyi Xu, and Dazhong Hou. 2023. "Enhanced Effect of Mining Dust Diffusion on Melting of the Adjacent Glacier: A Case Study in Xinjiang, China" Water 15, no. 2: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020224
APA StyleZhang, Z., Song, Y., Xu, X., & Hou, D. (2023). Enhanced Effect of Mining Dust Diffusion on Melting of the Adjacent Glacier: A Case Study in Xinjiang, China. Water, 15(2), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020224







