Changes in Nutrient Concentrations and Limitations of Poyang Lake Associated with Socioeconomic Development in the Watershed from 1978 to 2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
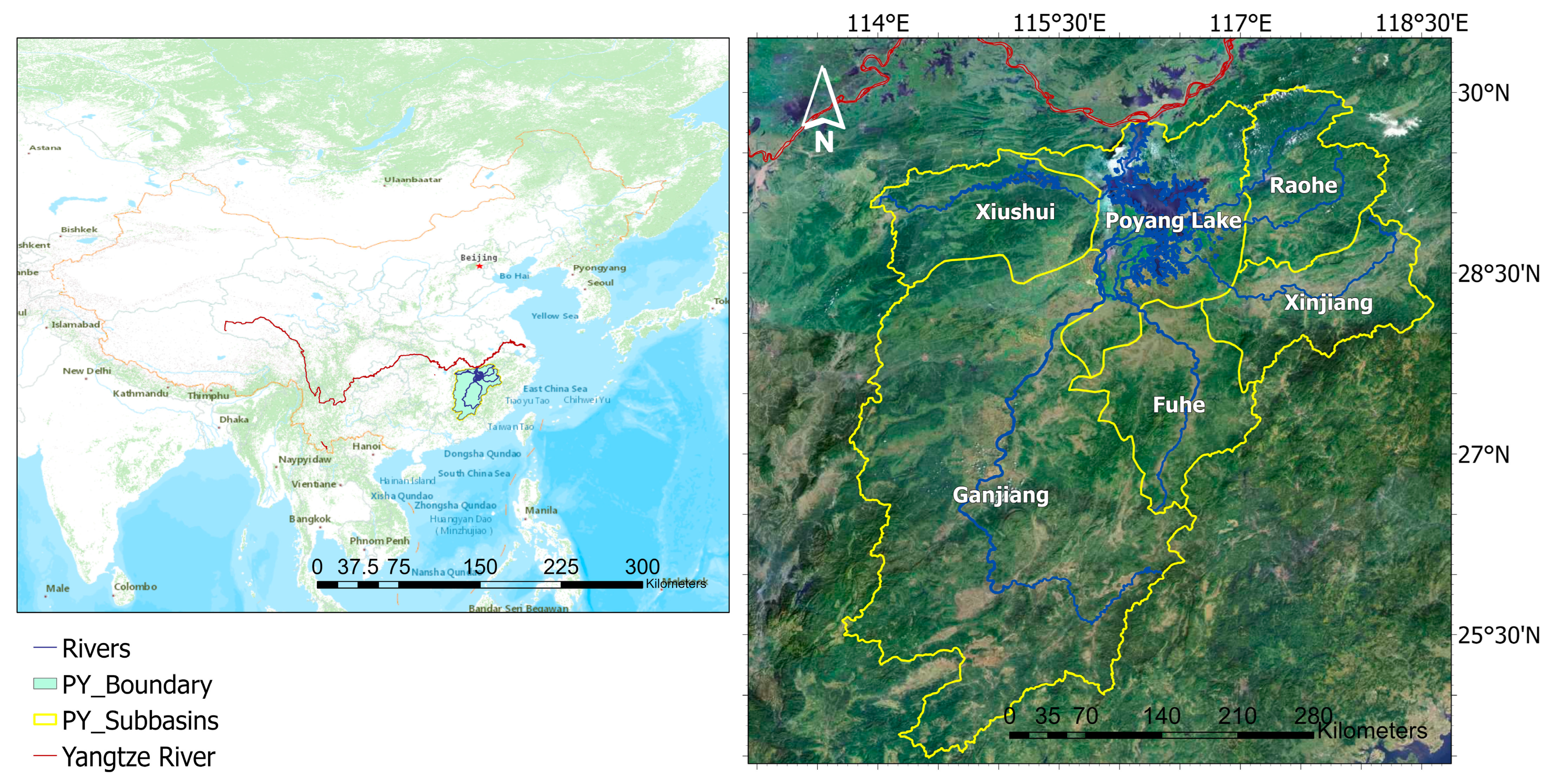
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Statistics
3. Results
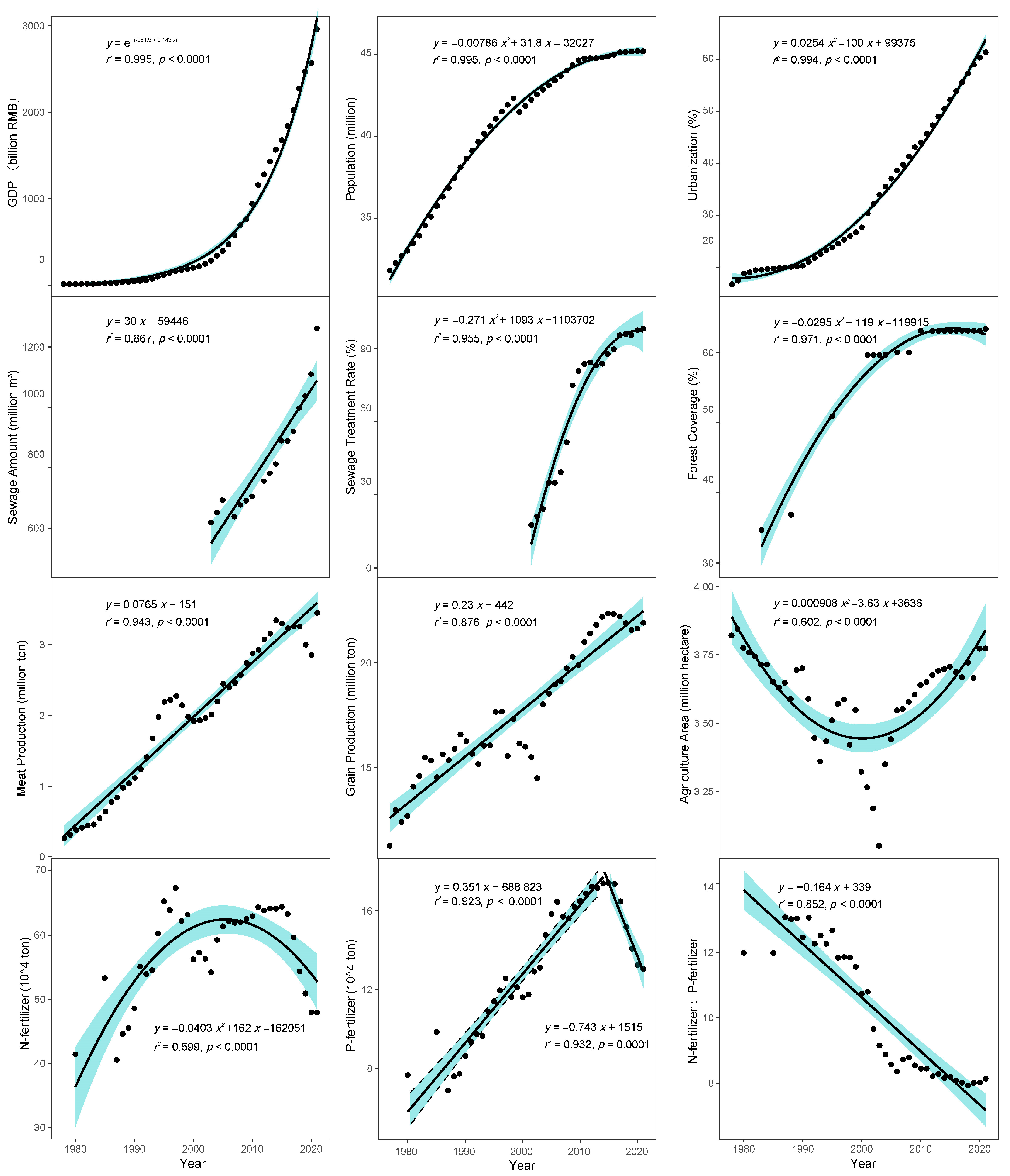
3.1. Socioeconomic Indexes
3.2. Nutrient Concentration and Nutrient Limitation
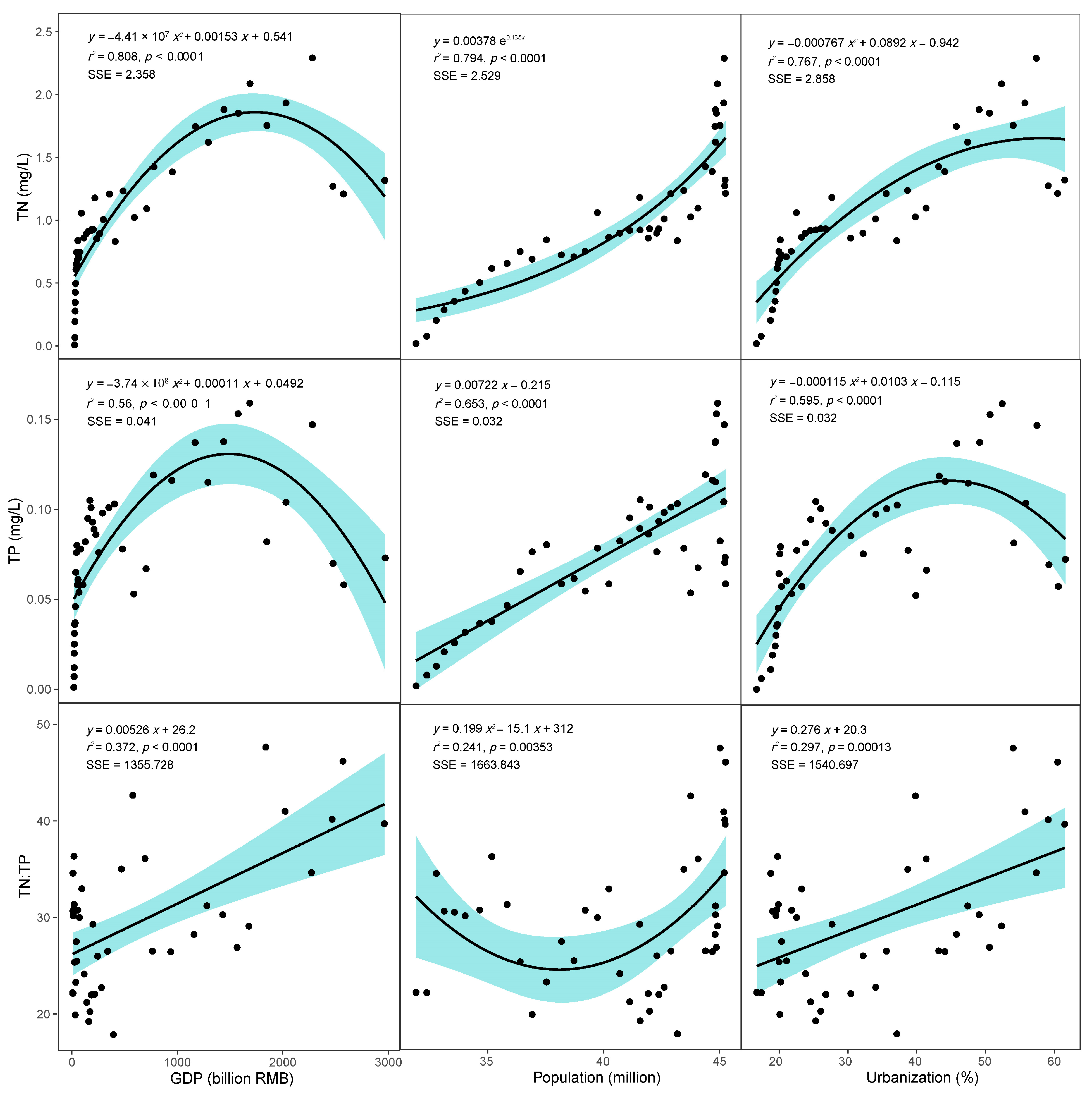
3.3. Lake Nutrients and Society Development
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrient Changes and Eutrophication
4.2. Lake Nutrients Driven by Socioeconomic Development
4.3. Implications for Eutrophication Control
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nixon, S.W. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 1995, 41, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.; Scholes, R.J.; Boyle, E.; Canadell, J.; Canfield, D.; Elser, J.J.; Gruber, N.; Hibbard, K.; Hogberg, P.; Linder, S.; et al. The global carbon cycle: A test of our knowledge of earth as a system. Science 2000, 290, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.R.D. Society × Nature—Anthropocene and Limits of Balance on Earth. In Global Environmental Changes, Desertification and Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melillo, J.M. Disruption of the global nitrogen cycle: A grand challenge for the twenty-first century. Ambio 2021, 50, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F. Human impact on erodable phosphorus and eutrophication: A global pespective. Bioscience 2001, 51, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.; Leavitt, P.R.; Elmgren, R. Effects of land use, urbanization, and climate variability on coastal eutrophication in the Baltic Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. WIREs Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E. Eutrophication: More nitrogen data needed. Science 2009, 324, 721–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakade, A.; Salama, E.; Han, H.; Zheng, Y.; Kulshrestha, S.; Jalalah, M.; Harraz, F.A.; Alsareii, S.A.; Li, X. World eutrophic pollution of lake and river: Biotreatment potential and future perspectives. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N. Nitrogen in aquatic ecosystems. Ambio 2002, 31, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetahi, T. Eutrophication of Ethiopian water bodies, a serious threat to water quality, biodiversity and public health. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 44, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, S. A theoretical basis for the environmental Kuznets Curve. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 53, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koondhar, M.A.; Shahbaz, M.; Memon, K.A.; Ozturk, I.; Kong, R. A visualization review analysis of the last two decades for environmental Kuznets Curve “EKC” based on co-citation analysis theory and pathfinder network scaling algorithms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16690–16706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. Natl. Bur. Econ. Res. 1991, w3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Feridun, M. The impact of growth, energy and financial development on the environment in China: A cointegration analysis. Energy Econ. 2011, 33, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, M.; Giri, A.K.; Mohapatra, G. The impact of financial development, economic growth and energy consumption on environmental degradation: Evidence from India. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2015, 26, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Chandravanshi, P.; Chandravanshi, A.; Jaiswal, K. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on aquatic ecosystem. IOSR J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2016, 9, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Niu, D.; Ma, P.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Elser, J.J. Cascading influences of grassland degradation on nutrient limitation in a high mountain lake and its inflow streams. Ecology 2019, 100, e02755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzai, D.; Terrer, C.; Pellegrini, A.F.A.; Ahlstrom, A.; van Lissa, C.J.; Xia, Z.; Nan, X.; Xinhui, W.; Jackson, R.B. Global patterns of terrestrial nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication and recovery in experimental lakes: Implications for lake management. Science 1974, 184, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterner, R.W. On the phosphorus limitation paradigm for lakes. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. A comparison of cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in freshwater, estuarine and marine environments. Phycologia 1996, 35, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater-marine continuum: Dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuaries Coasts 2009, 32, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.M.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Control of lacustrine phytoplankton by nutrients: Erosion of the phosphorus paradigm. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhou, J.; Elser, J.J.; Gardner, W.S.; Deng, J.; Brookes, J.D. Water depth underpins the relative roles and fates of nitrogen and phosphorus in lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3191–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by blue-green algae in Lake Phytoplankton. Science 1983, 221, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacnik, R.; Andersen, T.; Tamminen, T. Performance of the redfield ratio and a family of nutrient limitation indicators as thresholds for phytoplankton N vs. P limitation. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Andersen, T.; Baron, J.S.; Bergstroem, A.; Jansson, M.; Kyle, M.; Nydick, K.R.; Steger, L.; Hessen, D.O. Shifts in lake N: P stoichiometry and nutrient limitation driven by atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Science 2009, 326, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guildford, S.J.; Hecky, R.E. Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Responses of estuarine and coastal marine phytoplankton to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Resource Competition and Community Structure; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Interlandi, S.J.; Kilham, S.S. Limiting resources and the regulation of diversity in phytoplankton communities. Ecology 2001, 82, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prater, C.; Bullard, J.E.; Osburn, C.L.; Martin, S.L.; Watts, M.J.; Anderson, N.J. Landscape controls on nutrient stoichiometry regulate lake primary production at the margin of the greenland ice sheet. Ecosystems 2022, 25, 931–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, J.P. Resource Competition; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R. Phosphorus control is critical to mitigating eutrophication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11039–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelske, C.L. Eutrophication: Focus on phosphorus. Science 2009, 324, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Havens, K.E.; Xu, H.; Zhu, G.; Mccarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Scott, J.T.; Hall, N.S.; Otten, T.G.; Qin, B. Mitigating eutrophication and toxic cyanobacterial blooms in large lakes: The evolution of a dual nutrient (N and P) reduction paradigm. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 4359–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Fargione, J.; Wolff, B.; D’Antonio, C.; Dobson, A.; Howarth, R.; Schindler, D.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Simberloff, D.; Swackhamer, D. Forecasting agriculturally driven global environmental change. Science 2001, 292, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehto, L.L.P.; Hill, B.H. The effect of catchment urbanization on nutrient uptake and biofilm enzyme activity in Lake Superior (USA) tributary streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 713, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juma, D.W.; Wang, H.; Li, F. Impacts of population growth and economic development on water quality of a lake: Case study of Lake Victoria Kenya water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5737–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Kang, S.; Apip Zhou, M.; Lyu, J.; Aisyah, S.; Binaya, M.; Regmi, R.K.; Nover, D. Water quality trend assessment in Jakarta: A rapidly growing Asian megacity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokal, M.; Bai, Z.; Franssen, W.H.P.; Hofstra, N.; Koelmans, A.A.; Ludwig, F.; Ma, L. Urbanization: An Increasing Source of Multiple Pollutants to Rivers in the 21st Century. NPJ Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhang, R.; Yu, Y.; Wu, D.; et al. Strategy for cost-effective BMPs of non-point source pollution in the small agricultural watershed of Poyang Lake: A case study of the Zhuxi River. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.R.; Kang, Q.; Chen, B.; Ye, X. Chapter four—Fate and transport modelling of emerging pollutants from watersheds to oceans: A review. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2018, 81, 97–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.I.; Leavitt, P.R.; Quinlan, R.; Dixit, A.S.; Smol, J.P. Effects of agriculture, urbanization, and climate on water quality in the northern Great Plains. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, B. The Chinese Economy: Transition and Growth; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Weerasooriya, R.R.; Liyanage, L.P.K.; Rathnappriya, R.H.K.; Bandara, W.B.M.A.C.; Perera, T.A.N.T.; Gunarathna, M.H.J.P.; Jayasinghe, G.Y. Industrial water conservation by water footprint and sustainable development goals: A review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 12661–12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, G.; Rao, Z.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y. Deciphering spatial pattern of groundwater chemis try and nitrogen pollution in Poyang Lake Basin (eastern China) using self-organizing map and multivariate statistics. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, G.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, B.; Yan, X. Geochemical evolution of groundwater under the influence of human activities: A case study in the southwest of Poyang Lake Basin. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 140, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrommati, G.; Baustian, M.M.; Dreelin, E.A. Coupling socioeconomic and lake systems for sustainability: A conceptual analysis using Lake St. Clair region as a case study. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2014, 43, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Vadde, K.K.; Tonkin, J.D.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; McCarthy, A.J.; Sekar, R. Urbanization impacts the physicochemical characteristics and abundance of fecal markers and bacterial pathogens in surface water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Structural changes and economic growth in China over the past 40 years of reform and opening-up. China Political Econ. 2020, 3, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBSC. National Bureau of Statistics of China: China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y. Environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms in Chinese inland waters. Harmful Algae 2021, 110, 102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Eutrophication control of large shallow lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Cao, X.; Bai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, E.; Li, Y.; Ran, Y. Spatial and temporal variations of chlorophyll-a concentration from 2009 to 2012 in Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4063–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Jia, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Shi, K.; Gao, Y. Changes in chlorophyll-a and its response to nitrogen and phosphorus characteristics over the past three decades in Poyang Lake. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Jin, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Spatial–temporal variations of total nitrogen and phosphorus in Poyang, Dongting and Taihu Lakes from landsat-8 data. Water 2021, 13, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Nover, D.N.; Yang, G.; Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Zou, S.; Liu, C. Water quality assessment and pollution source identification of the eastern Poyang Lake basin using multivariate statistical methods. Sustainability 2016, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Liang, Q.L. Landscape changes and increasing flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region. Prof. Geogr. 2003, 55, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, T. Distribution characteristics of phosphorus in the sediments and overlying water of Poyang Lake. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e125859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Gong, P. Modelling spatial-temporal change of Poyang Lake using multitemporal landsat imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5767–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zeng, N.; Wang, Y.; Gong, P.; Xu, B.; Bao, S. Analysis on the waterbirds community survey of Poyang Lake in winter. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2007, 13, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhen, L.; Wang, C.; Yan, B.; Cao, X.; Wu, R. Impacts of ecological restoration and human activities on habitat of overwintering migratory birds in the wetland of Poyang Lake, Jiangxi Province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chen, L. Aggravation of reactive nitrogen flow driven by human production and consumption in Guangzhou City China. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Feng, G.; Swaney, D.P.; Dentener, F.; Koeble, R.; Ouyang, Y.; Gao, W. Global and regional estimation of net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs (NANI). Geoderma 2020, 361, 114066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenon, G.; Singh, B.; De Sena, A.; Madramootoo, C.A.; von Sperber, C.; Goyal, M.K.; Zhang, T. Phosphorus fate, transport and management on subsurface drained agricultural organic soils: A review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Xu, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, R.; Wu, D.; Xie, X. Role of phosphite in the environmental phosphorus cycle. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, J.; Alahuhta, J.; Bini, L.M.; Cai, Y.; Heiskanen, A.S.; Hellsten, S.; Kortelainen, P.; Kotamaki, N.; Tolonen, K.T.; Vihervaara, P.; et al. Lakes in the era of global change: Moving beyond single-lake thinking in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem services. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Zhang, S.; Qin, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on chlorophyll a in lakes of China: A meta-analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 74038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Steinman, A.D.; Oudsema, M.; Hassett, M.; Xie, L. The influence of nutrients limitation on phytoplankton growth and microcystins production in Spring Lake, USA. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratt, A.R.; Finlay, J.C.; Welter, J.R.; Vculek, B.A.; Van Allen, R.E. Co-limitation by N and P characterizes phytoplankton communities across nutrient availability and land use. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, J.; Han, B.; Naselli-Flores, L. The effects of absolute and relative nutrient concentrations (N/P) on phytoplankton in a subtropical reservoir. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, Z.V.; Beardall, J.; Flynn, K.J.; Quigg, A.; Rees, T.A.V.; Raven, J.A. Phytoplankton in a changing world: Cell size and elemental stoichiometry. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, M.; Koussoroplis, A.M.; Hillebrand, H.; Striebel, M. Phytoplankton community responses to temperature fluctuations under different nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry. Ecology 2019, 100, e02834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, M.D.; Venkataramana, V.; Sarma, V.V.S.S. Phytoplankton community structure is governed by salinity gradient and nutrient composition in the tropical estuarine system. Cont. Shelf Res. 2022, 234, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normile, D. China’s living laboratory in urbanization. Science 2008, 319, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, G.P.; Guan, D.; Hubacek, K.; Minx, J.C.; Weber, C.L. Effects of China’s economic growth. Science 2010, 328, 824–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Vitousek, P. An experiment for the world. Nature 2013, 497, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Gibson, V.; Cui, S.; Yu, C.; Chen, S.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, Y. Managing urban nutrient biogeochemistry for sustainable urbanization. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Kong, X.; Hu, S.; Li, Y. Land use transitions under rapid urbanization: A perspective from developing China. Land 2021, 10, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcel, A. New insights into the environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis in developing and transition economies: A literature survey. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2020, 22, 585–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.A.; Zhang, Q.; Asmi, F.; Hussain, N.; Plantinga, A.; Zafar, M.W.; Sinha, A. Global perspectives on environmental kuznets curve: A bibliometric review. Gondwana Res. 2022, 103, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Asghar, M.M.; Malik, M.N.; Nawaz, K. Moving towards a sustainable environment: The dynamic linkage between natural resources, human capital, urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint in China. Resour. Policy 2020, 67, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Elser, J.J. Intensification of phosphorus cycling in China since the 1600s. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.T. Urbanization and the natural environment: An environmental sociological review and synthesis. Organ. Environ. 2010, 23, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Shi, Y.; Groffman, P.M.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Zhu, Y. Centennial-scale analysis of the creation and fate of reactive nitrogen in China (1910–2010). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2052–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, T. How urbanization and ecological conditions affect urban diet-linked GHG emissions: New evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J. China’s rapid urbanization. Science 2013, 342, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, T.; Qu, Y. Do decaying rural communities have an incentive to maintain large-scale farming? A comparative analysis of farming systems for peri—Urban agriculture in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Guo, Q.; Wei, R.; Tian, L. Human-driven spatiotemporal distribution of phosphorus flux in the environment of a mega river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the three gorges dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, G.; Wang, R. Multidecadal water quality deterioration in the largest freshwater lake in China (Poyang Lake): Implications on eutrophication management. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Q. Influence of the three gorges dam on total suspended matters in the Yangtze estuary and its adjacent coastal waters: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, L.; Peng, D.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, Z. Net anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs in the Yangtze River economic belt: Spatiotemporal dynamics, attribution analysis, and diversity management. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; Findlay, D.L.; Stainton, M.P.; Parker, B.R.; Paterson, M.J.; Beaty, K.G.; Lyng, M.; Kasian, S.E.M. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.E.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.T.; Foy, B.; et al. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading—An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhou, W. Phosphorus forms and distribution in the sediments of Poyang Lake, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.R.; Deng, X.Z.; Jin, Q.; Zheng, X.Q. Relationships between Economic Growth and Emissions of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Poyang Lake Basin. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 2169–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.L.; Xiao, Y.T.; Liang, Y.X. Evaluation of Poyang Lake’s Water Quality and Control Measures. J. Anhui Agri. Sci. 2013, 41, 12129–12131. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.M.; Li, C.C.; Peng, C.L. Primary Studies on Community Ecology of Floating Algae in Poyang Lake. Jiangxi Sci. 2000, 18, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.H.; Zhang, B. Poyang Lake—Hydrology, Biology, Sedimentation, Wetland, Development and Remediation; University of Science and Technology of China Press: Hefei, China, 1997; pp. 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.J. Status Quo and Trend of Water Quality in Poyang Lake. J. Lake Sci. 1994, 6, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.J. Investigation of Poyang Lake water pollution by eutrphication. J. Lake Sci. 1996, 8, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.Z. Research on the Present Situation of Water Pollution and the Forecast and Planning for Water Quality in Poyang Lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Val. 1996, 5, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.X.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhong, X.L.; Yao, J. Evaluaion Method of Eutrophication in Poyang Lake and Its Leading Factors. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2009, 21, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.B.; Yan, W.W. Evaluation Methods Application in and Probing into Eutrophication of Poyang Lake Area. J. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2007, 31, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.L.; Hu, C.H.; Zhou, W.B. Concentration Variations of N and P in Poyang Lake during High Water Period with Analysis on their Sources. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2008, 17, 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.L.; Zhou, W.B.; Hu, C.H. Status of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Waters of Lake Poyang Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 334–338. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.L.; Zhou, W.B. Spatial-Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Inorganic Nitrogen in Poyang Lake. Yangtze River 2010, 41, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.H.; Zhou, W.B.; Wang, M.L.; Wei, Z.W. Inorganic Nitrogen and Phosphate and Potential Eutrophication Assessment in Lake Poyang. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 723–728. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, H. Retrieval of Total Phosphorus Concentration in the Surface Waters of Poyang Lake Based on Remote Sensing and Analysis of its Spatial-Temporal Characteristics. Nat. Resour. J. 2013, 28, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, M.L.; Zhou, W.B.; Hu, C.H. Chlorophyll-a’s Spatial Distribution and Relationship with Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Poyang Lake. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2012, 21, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.H.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, S.M.; Zhou, W.B. The Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Different Species Nitrogen in Poyang Lake. J. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 36, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.C.; Hu, W.; Ge, G.; Xiong, Y.; Lai, J.H.; Wu, L. Contents of Nutrients and Heavy Metals in the Poyang Lake During Dry Season. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.C.; Yu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Ge, G.; Wu, L. Water Quality Variations in Poyang Lake. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.J.; Zhou, W.B.; Li, M.T.; Tong, L.; Hu, C.H. Research on the of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on the Phytoplankton Community in Poyang Lake. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2013, 3, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.Q.; Lu, J.Z. Distribution Characteristic of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Lake Poyang during High Water Period. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.G.; Chen, Y.W. Spatial Distribution of Chlorophyll a in Poyang Lake during Wet Season and its Relationship with Environmental Factors. Wetl. Sci. 2014, 12, 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.Q.; Zhang, P. Spatial Distribution of Water quality and its Impacting Factor in the Wet Season of Poyang Lake using the Hydro-geomorphological Partitions. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 2637–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, Z.X. Content Analysis of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Different Sediment Types During Wet Season in Lake Poyang. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, G.F.; Zhang, W.; Peng, N.Y.; Lou, Q.; Zhong, J.Y. Study on Distribution of N and P Pollution and Risk of Cyanobacteria Bloom in Poyang Lake and Waters around the Lake during Drought Periods. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 838–844. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.T.; Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, M.L. Study on the Eutrophication Status in Poyang Lake during Lower Water Period. J. Nanchang Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2014, 38, 596–599. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, B.F.; Zhou, Z.; Su, H.; Zhuo, H.H. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Key Indicators of Nutritional Level and Control Standards in Lake Poyang. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 897–908. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Su, G.; Li, X. Changes in Nutrient Concentrations and Limitations of Poyang Lake Associated with Socioeconomic Development in the Watershed from 1978 to 2021. Water 2023, 15, 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183304
Zhang C, Su G, Li X. Changes in Nutrient Concentrations and Limitations of Poyang Lake Associated with Socioeconomic Development in the Watershed from 1978 to 2021. Water. 2023; 15(18):3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183304
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cheng, Guodong Su, and Xia Li. 2023. "Changes in Nutrient Concentrations and Limitations of Poyang Lake Associated with Socioeconomic Development in the Watershed from 1978 to 2021" Water 15, no. 18: 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183304
APA StyleZhang, C., Su, G., & Li, X. (2023). Changes in Nutrient Concentrations and Limitations of Poyang Lake Associated with Socioeconomic Development in the Watershed from 1978 to 2021. Water, 15(18), 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183304






