Groundwater Contamination and Risk Assessment in Greater Palm Springs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Collection and Analysis of Groundwater Samples
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Geochemical Modeling
2.3.2. Human Health Risk Assessment Model (HHRAM)
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Coachella Valley Groundwater
3.2. Concentration of Dissolved Components
3.3. PTE Distribution in Coachella Valley Groundwater
3.4. Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater
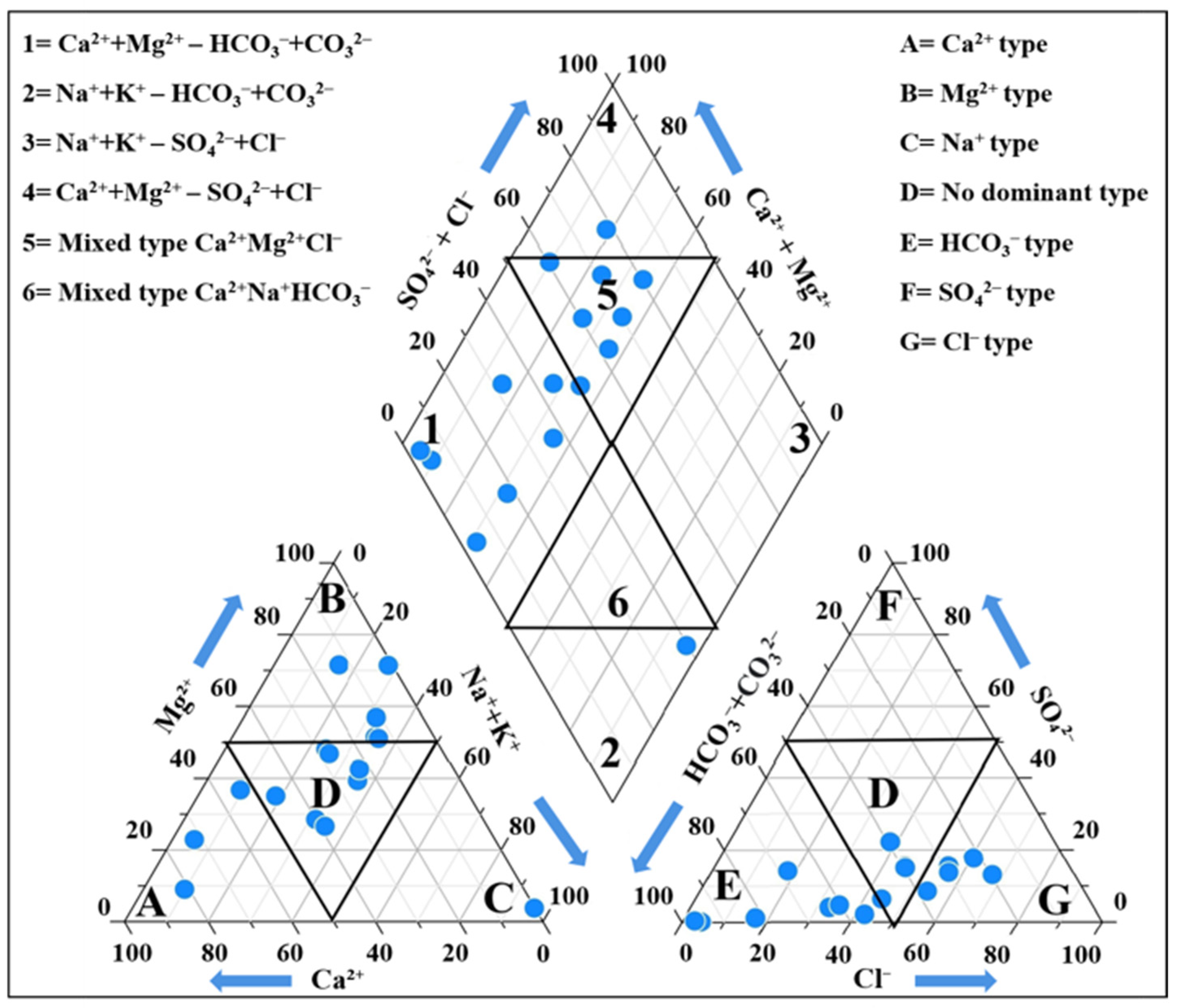
3.4.1. Geochemical Facies of Groundwater
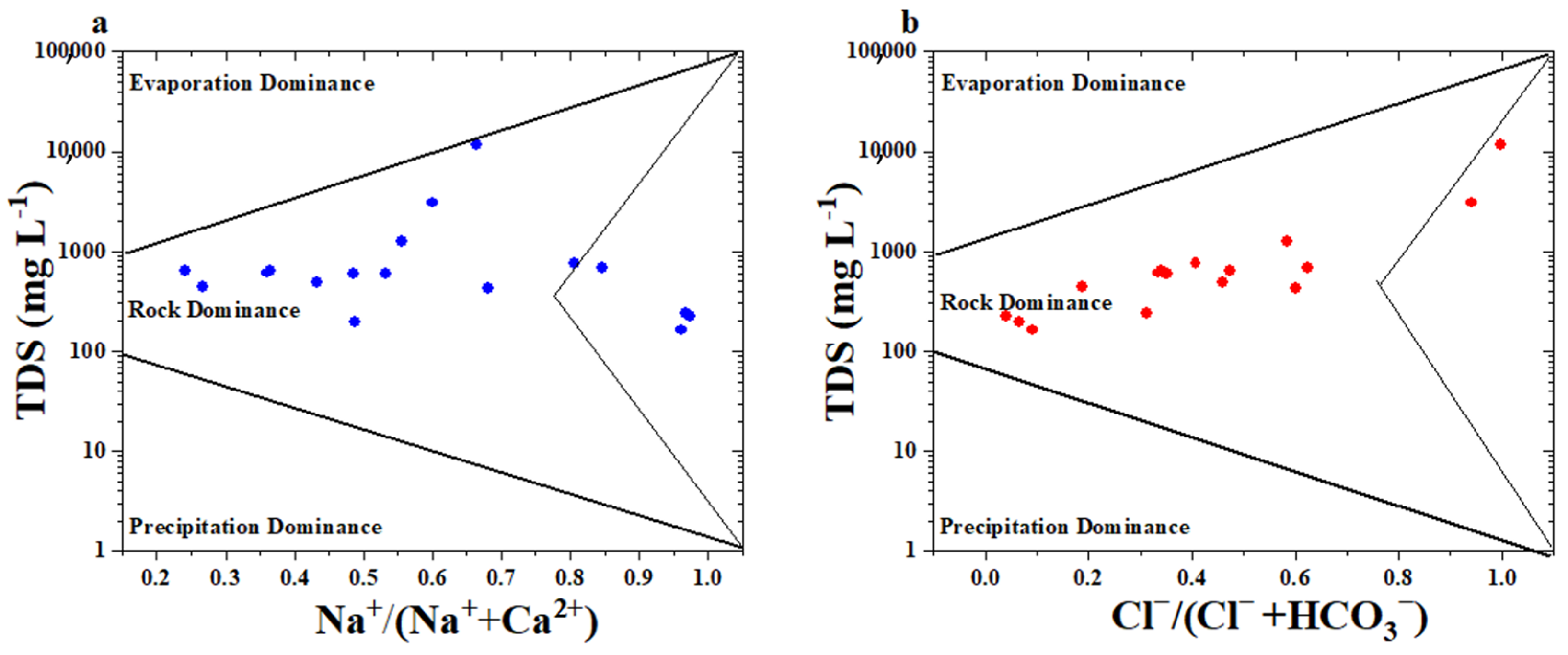
3.4.2. Hydrogeochemical Processes
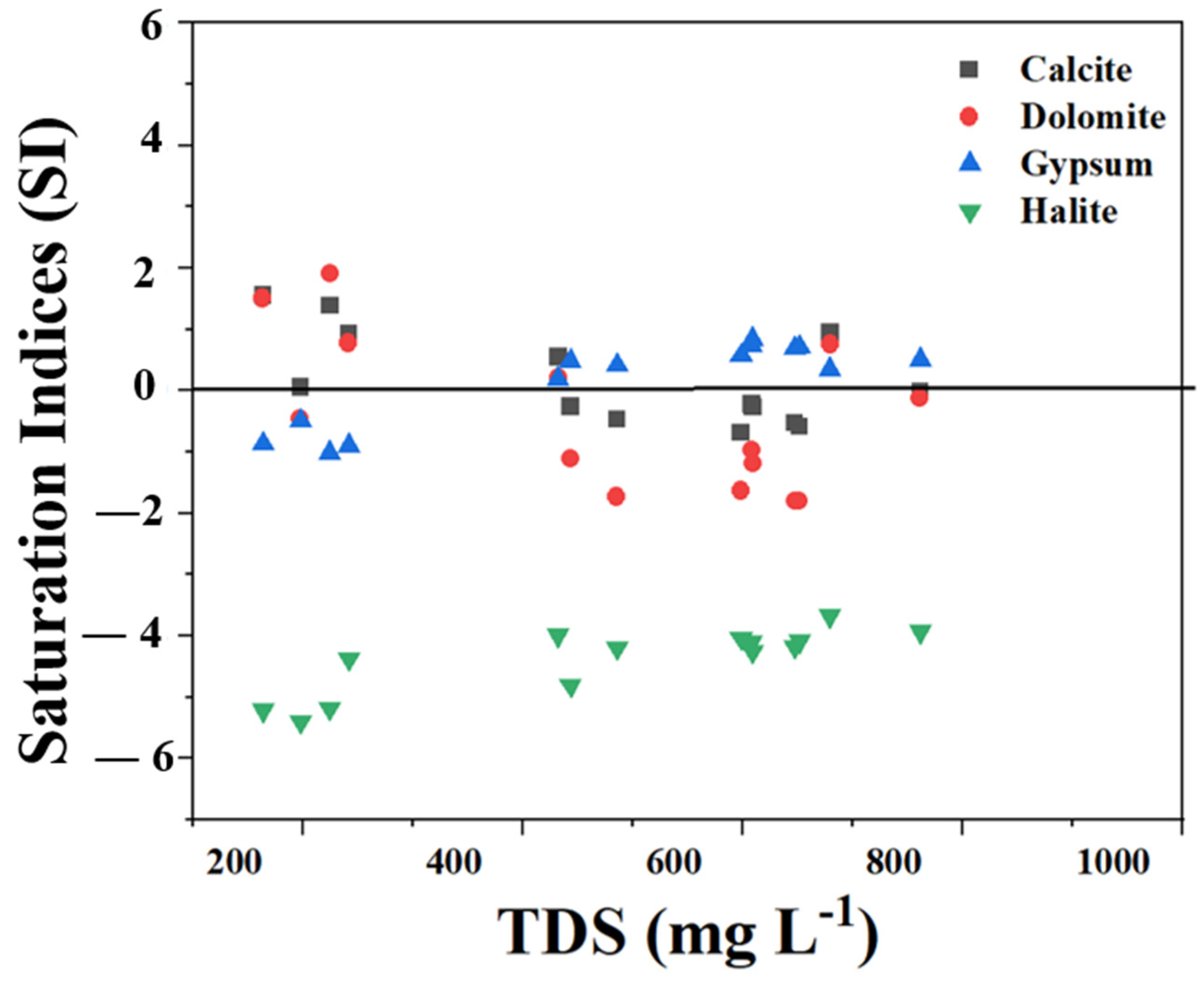
3.4.3. Mineral Saturation Index
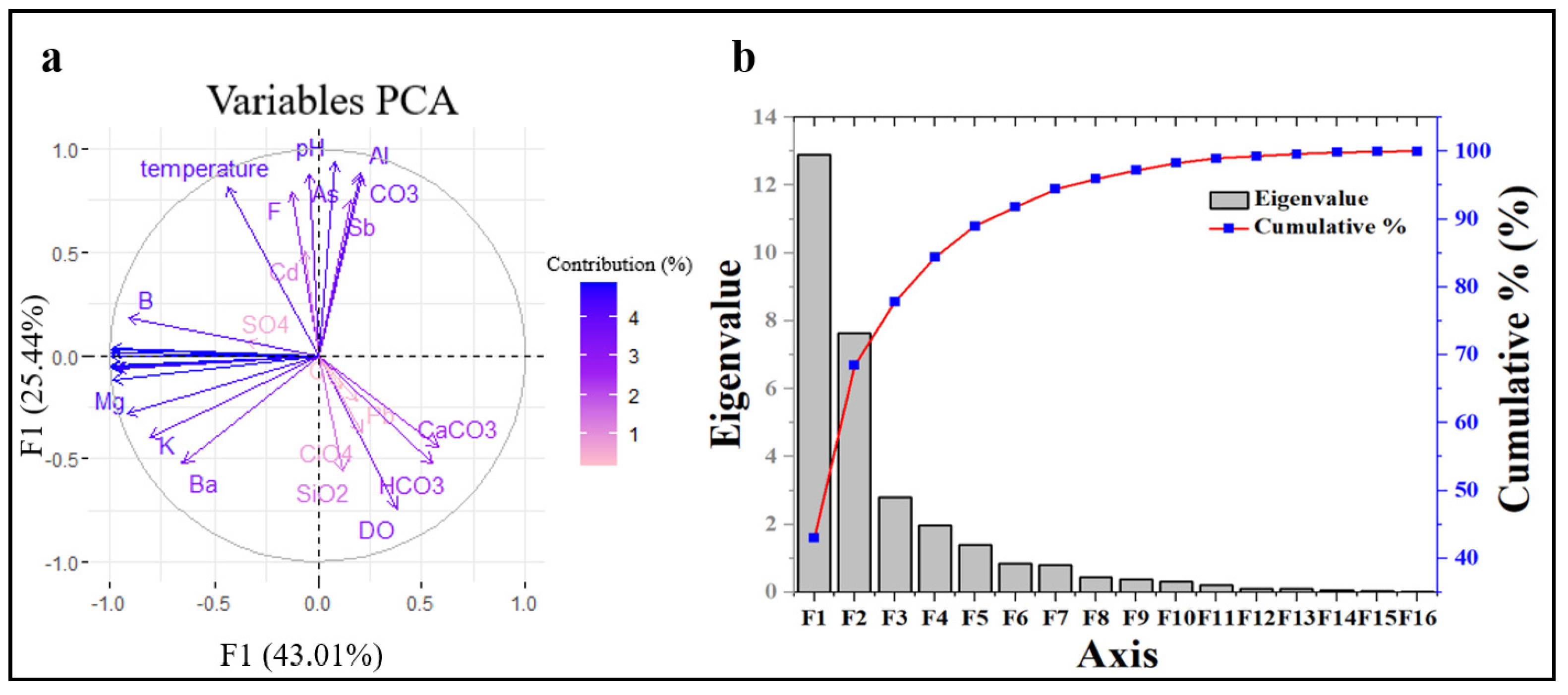
3.5. Principal Component Analysis and Pearson Correlation Analysis
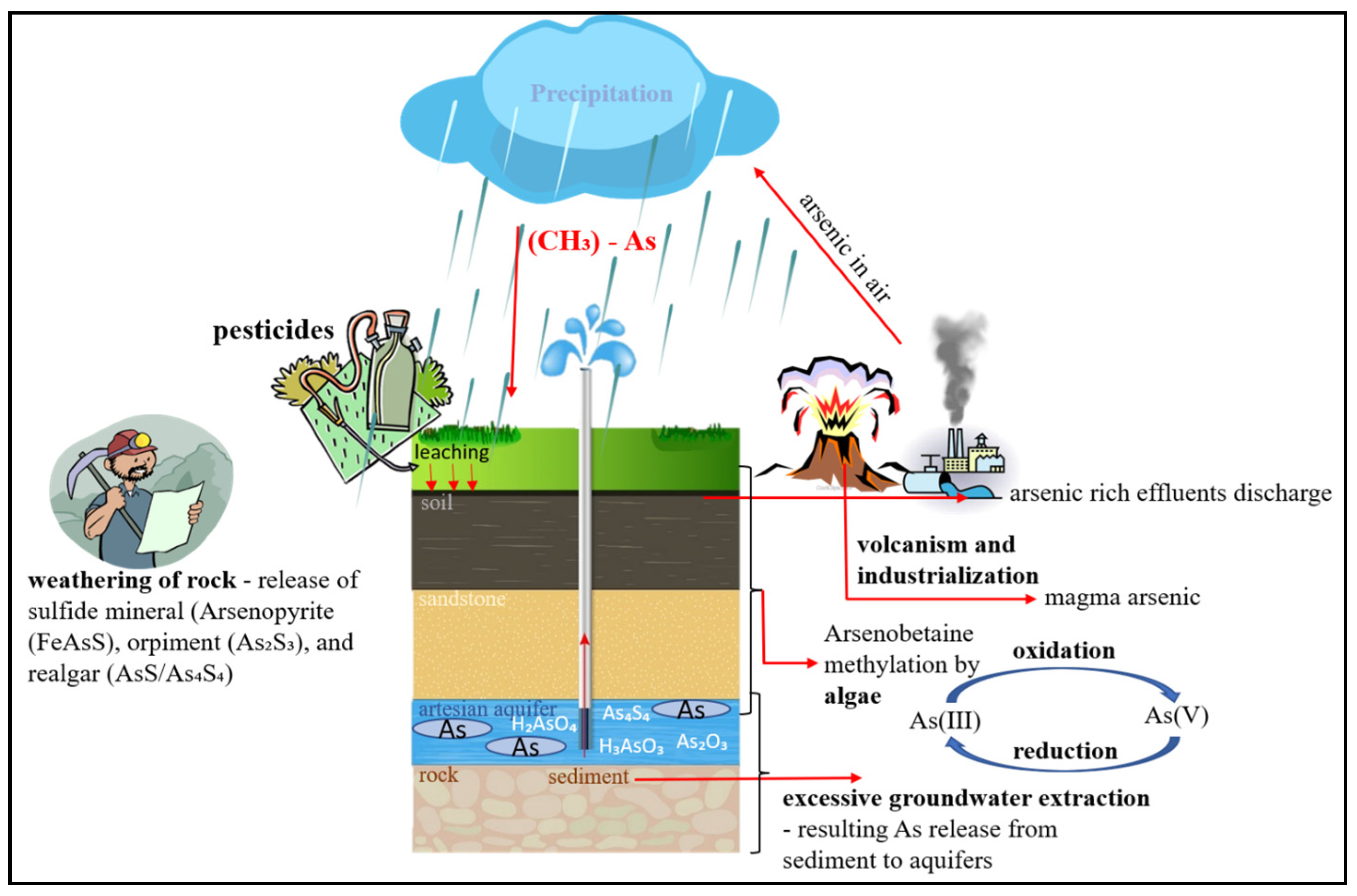
3.6. Arsenic Mechanism in Groundwater
3.7. Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Chai, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z.; Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Silva, L.F.; Zhang, D. Physiological characteristics, geochemical properties and hydrological variables influencing pathogen migration in subsurface system: What we know or not? Geosci. Front. 2022, 1, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Xiu, W.; Wu, S.; Chai, J.; Ma, J.; Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Sun, S.; Yang, Y. Migration risk of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in unsaturated porous media in response to different colloid types and compositions. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, M.J. Visualizing Arsenic Groundwater Contamination in Coachella Valley, California Through Spatial Analysis and Modeling. Master’s Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Su, C.; Talpur, S.A.; Iqbal, J.; Bajwa, K.J.; Jo, E.S. Arsenic Removal from Groundwater Using Iron Pyrite: Influence Factors and Removal Mechanism. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 34, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Ali, S.; Basit, I.; Jamil, A.; Farmonov, N.; Khorrami, B.; Khan, M.M.; Sadri, S.; Baloch, M.Y.J.; Islam, F.; et al. Terrestrial and groundwater storage characteristics and their quantification in the Chitral (Pakistan) and Kabul (Afghanistan) river basins using GRACE/GRACE-FO satellite data. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 100990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, R.; Liang, Z.; Xu, W.; Jat Baloch, M.Y. Health risk assessment during in situ remediation of Cr (VI)-contaminated groundwater by permeable reactive barriers: A field-scale study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, P.; Lyu, Q.; Ren, X.; He, S. Groundwater Contamination Risk Assessment Using a Modified DRATICL Model and Pollution Loading: A Case Study in the Guanzhong Basin of China. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, G.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Cary, L.; Hirata, R.; Montenegro, S.; Paiva, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Coelho, V.; Almeida, C. Delineating Groundwater Contamination Risks in Southern Coastal Metropoles through Implementation of Geochemical and Socio-Environmental Data in Decision-Tree and Geographical Information System. Water Res. 2022, 209, 117877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazotos, P. Potentially Toxic Elements in Groundwater: A Hotspot Research Topic in Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47825–47837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Hernández, J.R.; Green-Ruiz, C.R.; Pelling-Salazar, L.E.; Flegal, A.R. Monitoring of As, Cd, Cr, and Pb in Groundwater of Mexico’s Agriculture Mocorito River Aquifer: Implications for Risks to Human Health. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Liu, H.; Men, B.; Hao, Z.; Qian, P.; Yan, H.; Hao, Q.; Niu, Y.; et al. Impact of Long-Term Reclaimed Water Irrigation on the Distribution of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil: An In-Situ Experiment Study in the North China Plain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Manne, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, H. Appraisal of Vulnerable Zones of Non-Carcinogenic and Carcinogenic Causing Health Risks Associated with Exposure of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of India: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2022, 202, 111674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, S.; Venkatramanan, S.; Singaraja, C. A GIS-Based Assessment of Water Quality Pollution Indices for Heavy Metal Contamination in Tuticorin Corporation, Tamilnadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 10611–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.S.; Ordens, C.M.; Condesso de Melo, M.T.; Inácio, M.; Almeida, A.; Pinto, E.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. An Inter-Disciplinary Approach to Evaluate Human Health Risks Due to Long-Term Exposure to Contaminated Groundwater Near a Chemical Complex. Expo. Health 2019, 12, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Diyabalanage, S.; Dissanayake, C.B. Geogenic Fluoride and Arsenic in Groundwater of Sri Lanka and Its Implications to Community Health. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh (Nath), S.; Debsarkar, A.; Dutta, A. Technology Alternatives for Decontamination of Arsenic-Rich Groundwater—A Critical Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 13, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Gutiérrez, M. Geogenic Arsenic in Groundwater: Challenges, Gaps, and Future Directions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 27, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, N.; Chidambaram, S.; Panda, B.; Thivya, C.; Tirumalesh, K.; Thilagavathi, R. Determination of Anthropogenic Sources in the Groundwater Chemistry Along KT Boundary of South India. In Emerging Issues in the Water Environment during Anthropocene; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uugwanga, M.N.; Kgabi, N.A.; Knoeller, K.; Motsei, L. Isotopic Composition of Water Bodies in the Kuiseb and Cuvelai-Etosha Basin, Namibia. Namib. J. Res. Sci. Technol. 2018, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J.; Su, F. Surface Water Quality and Health Risk Assessment in Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province (China). Expo. Health 2022, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Groundwater and Surface Water Data for a Regional Assessment of Groundwater Salinity Variations and Sources in the Indio Subbasin of the Coachella Valley, California. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/data/groundwater-and-surface-water-data-a-regional-assessment-groundwater-salinity-variations-and (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; ISBN 978 92 4 154815 1. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-Analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C. User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2) (Equations on which the program is based). Water-Resour. Investig. Rep. 1999, 99, 4259. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, A.; Ayub, M.; Khan, S.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, L.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Kaushik, P.; Rasool, A. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Carcinogenic and Non-Carcinogenic Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Elements in Aquifers of the Hindukush Ranges, Pakistan: Insights from groundwater pollution indexing, GIS-based, and multivariate statistical approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75744–75768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Sahakyan, L.; Chemosphere, N.M. Identification of Spatial Patterns, Geochemical Associations and Assessment of Origin-Specific Health Risk of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Armavir Region, Armenia. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Al Shoumik, B.A.; Iqbal, J.; Li, S.; Chai, J.; Farooq, M.A.; Parkash, A. Evolution mechanism of arsenic enrichment in groundwater and associated health risks in southern Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvaiz, A.; Khattak, J.A.; Hussain, I.; Masood, N.; Javed, T.; Farooqi, A. Salinity Enrichment, Sources and Its Contribution to Elevated Groundwater Arsenic and Fluoride Levels in Rachna Doab, Punjab Pakistan: Stable Isotope (Δ2H and Δ18O) Approach as an Evidence. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaño-Sánchez, A.; Hose, G.C.; Reboleira, A.S.P.S. Salinity and Temperature Increase Impact Groundwater Crustaceans. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpur, S.A.; Noonari, T.M.; Rashid, A.; Ahmed, A.; Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Talpur, H.A.; Soomro, M.H. Hydrogeochemical signatures and suitability assessment of groundwater with elevated fluoride in unconfined aquifers Badin District, Sindh, Pakistan. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Sultana, T.; Akram, M.; Al Shoumik, B.A.; Khan, M.Z.; Farooq, M.A.J.E.T. Utilization of sewage sludge to manage saline-alkali soil and increase crop production: Is it safe or not? Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Geochemistry, T.M.-A. Isotope and Minor Element Geochemistry of High Arsenic Groundwater from Hangjinhouqi, the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brima, E.I. Physicochemical Properties and the Concentration of Anions, Major and Trace Elements in Groundwater, Treated Drinking Water and Bottled Drinking Water in Najran Area, KSA. Appl. Water Sci. 2014, 7, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, S.N.; Syed, T.H.; Kumar, A.; Sinha, D. Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in Parts of Southern Gangetic Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanidhi, D.; Aravinthasamy, P.; Deepali, M.; Subramani, T.; Shankar, K. Groundwater Pollution and Human Health Risks in an Industrialized Region of Southern India: Impacts of the COVID-19 Lockdown and the Monsoon Seasonal Cycles. Arch Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Su, C.; Wang, M.; Abbas, H.; Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Ghani, J.; Ullah, Z.; Huq, M.E. Groundwater fluoride and nitrate contamination and associated human health risk assessment in South Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 61606–61625. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Xie, C.; Liang, J.; Ma, H. Risk assessment of groundwater hydrochemistry for irrigation suitability in Ordos Basin, China. Nat. Hazards 2020, 101, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Chai, J.; Li, S.; Alqurashi, M.; Rehman, G.; Tariq, A.; Talpur, S.A.; Iqbal, J.; Munir, M.; et al. Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Its Suitability Analysis for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes. Water 2021, 13, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Su, C.; Rashid, A.; Yang, N.; Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Talpur, S.A.; Ullah, Z.; Rahman, G.; Rahman, N.U.; Sajjad, M.M.; et al. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater and Suitability Analysis for Domestic and Agricultural Utility in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Qian, H.; Health, Y.G.-E. Assessing Nitrate and Fluoride Contaminants in Drinking Water and Their Health Risk of Rural Residents Living in a Semiarid Region of Northwest China. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Shoumik, B.A.A.; Nigar, A.; Elhassan, A.A.M.; Elshekh, A.E.A.; Bashir, M.O.; Mohamed Salih Ebrahim, A.F.; Adam Mohamed, K.a.; Iqbal, J. Hydrogeochemical Mechanism Associated with Land Use Land Cover Indices Using Geospatial, Remote Sensing Techniques, and Health Risks Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Ayub, M.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, A.; Khattak, S.A.; Ali, L.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; Khan, S.; El-Serehy, H.A.; et al. Geochemical Modeling Source Provenance, Public Health Exposure, and Evaluating Potentially Harmful Elements in Groundwater: Statistical and Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Rivera, D.M.; Escobedo-Urías, D.C.; Jonathan, M.P.; Sujitha, S.B.; Chidambaram, S. Evidence of Natural and Anthropogenic Impacts on Rainwater Trace Metal Geochemistry in Central Mexico: A Statistical Approach. Water 2020, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Mangi, S.H. Treatment of synthetic greywater by using banana, orange and 2021sapodilla peels as a low cost activated carbon. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2019, 10, 966–986. [Google Scholar]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Talpur, S.A.; Talpur, H.A.; Iqbal, J.; Mangi, S.H.; Memon, S. Effects of Arsenic Toxicity on the Environment and Its Remediation Techniques: A Review. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2020, 18, 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- Shaji, E.; Santosh, M.; Sarath, K.V.; Prakash, P.; Deepchand, V.; Divya, B.V. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater: A Global Synopsis with Focus on the Indian Peninsula. Geosci. Front. 2020, 12, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Baars, O.; Guo, D.; Whitham, J.; Srivastava, S.; Dong, H. Mineral-Bound Trace Metals as Cofactors for Anaerobic Biological Nitrogen Fixation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7206–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natural Organic Matter Influences Arsenic Release into Groundwater. PressPacs. 11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.acs.org/pressroom/presspacs/2020/acs-presspac-march-11-2020/natural-organic-matter-influences-arsenic-release-into-groundwater.html (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Mazumder, P.; Sharma, S.K.; Taki, K.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Kumar, M. Microbes Involved in Arsenic Mobilization and Respiration: A Review on Isolation, Identification, Isolates and Implications. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3443–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Bundschuh, J.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, W.; Pa, Z. Occurrence and Behavior of Arsenic in Groundwater-Aquifer System of Irrigated Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-W.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Núñez Delgado, A.; Cui, H.-L.; Duan, G.-L.; Rosen, B.P.; Zhu, Y.-G. Fundamentals and Application in Phytoremediation of an Efficient Arsenate Reducing Bacterium Pseudomonas Putida ARS1. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 137, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS): Part A. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/risk-assessment-guidance-superfund-rags-part (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Guadie, A.; Yesigat, A.; Gatew, S.; Worku, A.; Liu, W.; Ajibade, F.O.; Wang, A. Evaluating the Health Risks of Heavy Metals from Vegetables Grown on Soil Irrigated with Untreated and Treated Wastewater in Arba Minch, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. Chemical Contaminant Rules. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/dwreginfo/chemical-contaminant-rules (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Ghani, J.; Nawab, J.; Faiq, M.E.; Ullah, S.; Alam, A.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, S.W.; Khan, S.; Ahmad, I.; Muhammad, A.; et al. Multi-Geostatistical Analyses of the Spatial Distribution and Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Urban Children’s Park Soils in Pakistan: A Risk Assessment Study. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Field Parameters | Range | Mean ± SD | WHO (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (feet) | 215–1475 | 567.06 ± 358 | - |
| pH | 7.3–9.3 | 8 ± 0.6 | 6.5–9.2 |
| TDS (mg L−1) | 163–11,800 | 1250.1 ± 2634.1 | 1000 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 0.2–13.1 | 5.3 ± 4.1 | |
| Temperature (°C) | 10.6–31 | 24.8 ± 5.1 | 20–50 |
| SC (µS cm−1) | 283–18,800 | 1929.3 ± 4169.5 | 400,000 |
| Parameter | Range * | Mean ± SD | WHO (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2⁺ | 2.1–1350 | 161.1 ± 319.2 | 100 |
| Mg2⁺ | 0.04–107 | 16.5 ± 24.7 | 50 |
| K⁺ | 0.5–21.9 | 6.2 ± 5.2 | 12 |
| SiO2 | 12.1–25.6 | 18 ± 4.1 | - |
| Na⁺ | 28.1–2670 | 268.2 ± 631.8 | 200 |
| Br− | 0.02–8.5 | 0.6 ± 2 | 0.01 |
| Cl− | 5.9–6840 | 497.7 ± 1637.7 | >250 |
| F− | 0.1–6.8 | 1.3 ± 1.7 | 1.5 |
| I− | 0.001–1.3 | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 1 |
| SO42− | 13.6–1570 | 268.6 ± 360 | 500 |
| Al | 9–45 | 9 ± 16.6 | 900 |
| Sb | 0.123–0.4 | 0.04 ± 0.1 | 0.02 |
| Ba | 1.6–248 | 65.3 ± 64.7 | 0.7 |
| B | 22–940 | 184.4 ± 251.1 | 2.4 |
| Fe | 5.1–334 | 29.9 ± 80.5 | 300 |
| ClO4− | 0.15–4.4 | 1 ± 1.4 | - |
| CaCO3 | 18.9–194 | 99.6 ± 47.2 | 40 |
| HCO3− | 22.9–236 | 118.2 ± 58.2 | - |
| CO32− | 0.1–8.1 | 1.5 ± 2.6 | - |
| NO3− | 0.4–16.8 | 4.14 ± 5.9 | 50 |
| Heavy Metal | Range * | Mean ± SD | WHO (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As | 0.1–125 | 21.3 ± 39.4 | 0.01 |
| Cd | 0.033–0.32 | 0.05 ± 0.08 | 0.05 |
| Cr(VI) | 0.05–37.1 | 5.40 ± 9.05 | 50 |
| Pb | 0.02–0.75 | 0.12 ± 0.21 | 10 |
| Parameters | F1 | F2 | F3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.065 | 0.934 | −0.046 |
| TDS | 0.994 | −0.073 | −0.070 |
| DO | −0.391 | −0.722 | −0.071 |
| Temperature | 0.453 | 0.796 | 0.115 |
| SC | 0.991 | −0.079 | −0.105 |
| Ca2⁺ | 0.982 | −0.138 | −0.085 |
| Mg2⁺ | 0.911 | −0.299 | −0.187 |
| K⁺ | 0.804 | −0.409 | 0.125 |
| SiO2 | −0.133 | −0.564 | −0.392 |
| Na⁺ | 0.993 | −0.025 | −0.096 |
| Br− | 0.963 | −0.085 | −0.229 |
| Cl− | 0.970 | −0.077 | −0.214 |
| F− | 0.142 | 0.790 | −0.021 |
| I− | 0.989 | 0.014 | −0.131 |
| SO42− | 0.351 | 0.063 | 0.776 |
| Al | −0.188 | 0.884 | −0.377 |
| Sb | −0.141 | 0.755 | −0.377 |
| As | 0.059 | 0.875 | −0.445 |
| Ba | 0.639 | −0.537 | −0.361 |
| B | 0.915 | 0.171 | 0.237 |
| Cd | 0.082 | 0.523 | 0.592 |
| Cr | −0.113 | −0.159 | 0.454 |
| Fe | 0.992 | −0.012 | −0.102 |
| Pb | −0.200 | −0.248 | −0.123 |
| ClO4− | −0.222 | −0.386 | 0.073 |
| HCO3− | −0.560 | −0.505 | −0.428 |
| CO32− | −0.191 | 0.871 | −0.397 |
| CaCO3 | −0.585 | −0.427 | −0.470 |
| NO3− | −0.247 | −0.466 | −0.091 |
| Eigenvalue | 12.905 | 7.634 | 2.802 |
| Variability (%) | 43.017 | 25.446 | 9.339 |
| Cumulative (%) | 43.017 | 68.463 | 77.802 |
| Ingestion | RfD | CSF | Non-Carcinogenic Risk | Carcinogenic Risk | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ (Child) | HQ (Adult) | HI (Child) | HI (Adult) | Risk (Child) | Risk (Adult) | |||
| As-cancer | 3.00 × 10−4 | 1.50 × 100 | - | - | - | - | 8.00 × 10−7 | 9.55 × 10−7 |
| As-non | - | - | 1.78 × 10−3 | 2.12 × 10−3 | 3.02 × 10−2 | 3.61 × 10−2 | - | - |
| Cd-cancer | 5.00 × 10−4 | 1.00 × 10−3 | - | - | - | - | 1.37 × 10−12 | 1.64 × 10−12 |
| Cd-non | - | - | 2.75 × 10−6 | 3.28 × 10−6 | 4.67 × 10−5 | 5.58 × 10−5 | - | - |
| Cr-cancer | 1.50 × 100 | 5.00 × 10−1 | - | - | - | - | 6.75 × 10−8 | 8.06 × 10−8 |
| Cr-non | - | - | 9.01 × 10−8 | 1.08 × 10−7 | 1.53 × 10−6 | 1.83 × 10−6 | - | - |
| Pb-cancer | 3.60 × 10−2 | 8.50 × 10−3 | - | - | - | - | 2.72 × 10−11 | 3.25 × 10−11 |
| Pb-non | - | - | 8.88 × 10−8 | 1.06 × 10−7 | 1.51 × 10−6 | 1.80 × 10−6 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalid, W.; Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Ali, A.; Ngata, M.R.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Rashid, A.; Ilić, P.; Almutairi, M.H.; Siddique, J. Groundwater Contamination and Risk Assessment in Greater Palm Springs. Water 2023, 15, 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173099
Khalid W, Jat Baloch MY, Ali A, Ngata MR, Alrefaei AF, Rashid A, Ilić P, Almutairi MH, Siddique J. Groundwater Contamination and Risk Assessment in Greater Palm Springs. Water. 2023; 15(17):3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalid, Warda, Muhammad Yousuf Jat Baloch, Asmat Ali, Mbega Ramadhani Ngata, Abdulwahed Fahad Alrefaei, Abdur Rashid, Predrag Ilić, Mikhlid H. Almutairi, and Jamil Siddique. 2023. "Groundwater Contamination and Risk Assessment in Greater Palm Springs" Water 15, no. 17: 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173099
APA StyleKhalid, W., Jat Baloch, M. Y., Ali, A., Ngata, M. R., Alrefaei, A. F., Rashid, A., Ilić, P., Almutairi, M. H., & Siddique, J. (2023). Groundwater Contamination and Risk Assessment in Greater Palm Springs. Water, 15(17), 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173099












