Value of Spatially Distributed Rainfall Design Events—Creating Basin-Scale Stochastic Design Storm Ensembles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Radar Data and Rainfall Event Selection
2.3. Rainfall Simulation Model
2.4. Parameter Estimation
2.5. Ensemble Variation of Simulated Rainfall Events
2.6. Comparison of Rainfall from Areal and Gauge Estimates
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
3.2. Ensemble Variation of Cumulative Areal Rainfall across Spatial Scales
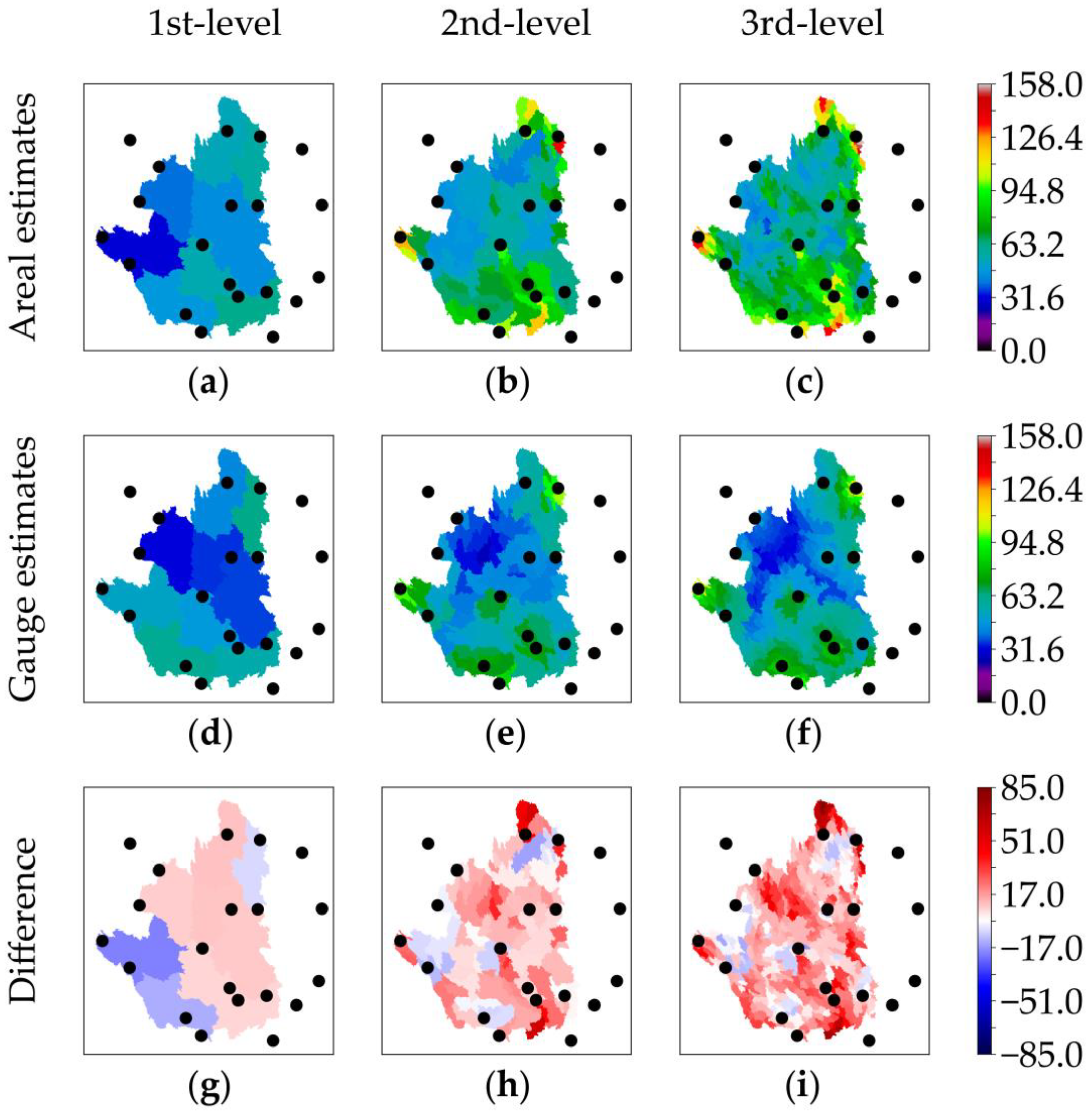
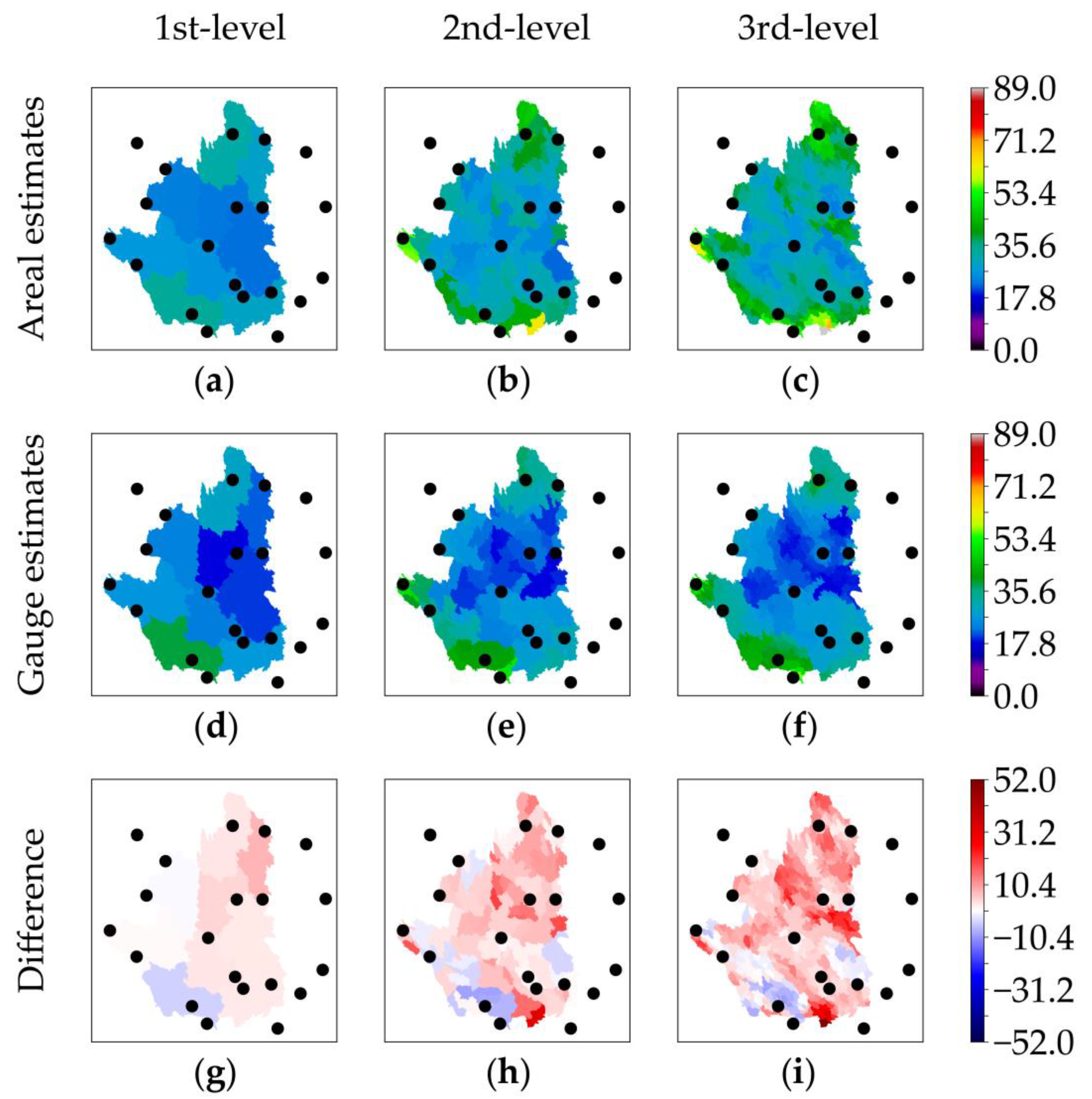
3.3. Variability in Total Event Rainfalls between Areal and Gauge Estimates
4. Discussion
4.1. Benefits of Spatial Rainfall Data and Ensemble Simulations
4.2. Skill of the Model
4.3. Limitations of the Model
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Notaro, V.; Fontanazza, C.M.; Freni, G.; Puleo, V. Impact of Rainfall Data Resolution in Time and Space on the Urban Flooding Evaluation. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 1984–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, T.J.; Warsta, L.; Taka, M.; Hickman, B.; Pulkkinen, S.; Krebs, G.; Moisseev, D.N.; Koivusalo, H.; Kokkonen, T. Applicability of Open Rainfall Data to Event-Scale Urban Rainfall-Runoff Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.B.; Smith, J.A.; Villarini, G.; Baeck, M. Applications of Radar-Based Rainfall Estimates to Urban Flood Studies. J. Water Manag. Model. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorndahl, S.; Einfalt, T.; Willems, P.; Nielsen, J.E.; ten Veldhuis, M.-C.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Rasmussen, M.R.; Molnar, P. Weather Radar Rainfall Data in Urban Hydrology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1359–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peura, M. Anomaly Detection and Removal in Radar Images (AnDRe)—Final Project Report; Finnish Meteorological Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Giangrande, S.E.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Estimation of Rainfall Based on the Results of Polarimetric Echo Classification. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 2445–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, T.; Ritvanen, J.; Pulkkinen, S.; Weisshaupt, N.; Koistinen, J. Bayesian Classification of Nonmeteorological Targets in Polarimetric Doppler Radar Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2022, 39, 1561–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, G.; Reinoso, R.; van de Giesen, N.C.; Clemens, F.H.L.R.; ten Veldhuis, J.A.E. On the Sensitivity of Urban Hydrodynamic Modelling to Rainfall Spatial and Temporal Resolution. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, N.E.; Pierce, C.E.; Seed, A.W. STEPS: A Probabilistic Precipitation Forecasting Scheme Which Merges an Extrapolation Nowcast with Downscaled NWP. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 2127–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalis, A.; Molnar, P.; Fatichi, S.; Burlando, P. A Stochastic Model for High-Resolution Space-Time Precipitation Simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 8400–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Fatichi, S.; Paschalis, A.; Molnar, P.; Burlando, P. An Advanced Stochastic Weather Generator for Simulating 2-D High-Resolution Climate Variables. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 1595–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.B.; Michaelides, K.; Hobley, D.E.J. STORM 1.0: A Simple, Flexible, and Parsimonious Stochastic Rainfall Generator for Simulating Climate and Climate Change. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 3713–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, T.J.; Kokkonen, T.; Seed, A.W. A Simple and Effective Method for Quantifying Spatial Anisotropy of Time Series of Precipitation Fields. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5906–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortis, A.; Puente, C.E.; Sivakumar, B. Encoding Hydrologic Information via a Fractal Geometric Approach and Its Extensions. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2010, 24, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsalek, J.; Watt, W.E. Design Storms for Urban Drainage Design. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1984, 11, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, M.; Špačková, O.; Straub, D. Probabilistic Design Storm Method for Improved Flood Estimation in Ungauged Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 10701–10722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onof, C.; Chandler, R.E.; Kakou, A.; Northrop, P.; Wheater, H.S.; Isham, V. Rainfall Modelling Using Poisson-Cluster Processes: A Review of Developments. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2000, 14, 384–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazanescu, S.; Cazanescu, R.A. New Hydrological Approach for Environmental Protection and Floods Management. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj-Napoca. Agric. 2009, 66, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimene, C.A.; Campos, J.N.B. The Design Flood under Two Approaches: Synthetic Storm Hyetograph and Observed Storm Hyetograph. J. Appl. Water Eng. Res. 2020, 8, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overeem, A.; Holleman, I.; Buishand, A. Derivation of a 10-Year Radar-Based Climatology of Rainfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1448–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segond, M.-L.; Wheater, H.S.; Onof, C. The Significance of Spatial Rainfall Representation for Flood Runoff Estimation: A Numerical Evaluation Based on the Lee Catchment, UK. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Blumensaat, F.; Molnar, P.; Fatichi, S.; Burlando, P. Partitioning the Impacts of Spatial and Climatological Rainfall Variability in Urban Drainage Modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PySteps Developers. Pysteps Reference, Release 1.5.1; 2021. Available online: https://pysteps.readthedocs.io/_/downloads/en/v1.5.1/pdf/ (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Pulkkinen, S.; Nerini, D.; Pérez Hortal, A.A.; Velasco-Forero, C.; Seed, A.; Germann, U.; Foresti, L. Pysteps: An Open-Source Python Library for Probabilistic Precipitation Nowcasting (v1.0). Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 4185–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, T.J.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; Kokkonen, T.; Hoang, T.M.T.; Seed, A.W. Role of Spatial Anisotropy in Design Storm Generation: Experiment and Interpretation. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekholm, M. Suomen Vesistöalueet. In Vesi-ja Ympäristöhallinnon Julkaisuja—Sarja A 126; Vesi-ja Ympäristöhallitus: Helsinki, Finland, 1993; ISBN 951-37-1087-4. [Google Scholar]
- Finnish Environment Institute Catchment Areas. Available online: https://ckan.ymparisto.fi/dataset/%7B44394B13-85D7-4998-BD06-8ADC77C7455C%7D (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Schleiss, M.; Olsson, J.; Berg, P.; Niemi, T.; Kokkonen, T.; Thorndahl, S.; Nielsen, R.; Ellerbæk Nielsen, J.; Bozhinova, D.; Pulkkinen, S. The Accuracy of Weather Radar in Heavy Rain: A Comparative Study for Denmark, the Netherlands, Finland and Sweden. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 3157–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnish Meteorological Institute. Download Observations. Available online: https://en.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/download-observations (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Finnish Meteorological Institute. Precipitation Return Levels in Finland. Available online: https://www.climateguide.fi/articles/precipitation-return-levels-in-finland/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The Distribution of Raindrops with Size. J. Atmos. Sci. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, J.; Moisseev, D.; Leskinen, M.; Petersen, W.A. A Climatology of Disdrometer Measurements of Rainfall in Finland over Five Years with Implications for Global Radar Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, A.W.; Srikanthan, R.; Menabde, M. A Space and Time Model for Design Storm Rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31623–31630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, A. Modelling and Forecasting Rainfall in Space and Time. In Scales in Hydrology and Water Management; Tchiguirinskaia, I., Hubert, P., Bonell, M., Eds.; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 137–152. ISBN 1901502627. [Google Scholar]
- Seed, A.W.; Draper, C.; Srikanthan, R.; Menabde, M. A Multiplicative Broken-Line Model for Time Series of Mean Areal Rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2395–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; Sapozhnikov, V. Evidence of Dynamic Scaling in Space-Time Rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31599–31610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegram, G.G.S.; Clothier, A.N. High Resolution Space–Time Modelling of Rainfall: The “String of Beads” Model. J. Hydrol. 2001, 241, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldvogel, A.; Federer, B.; Grimm, P. Criteria for the Detection of Hail Cells. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1979, 18, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltikoff, E.; Tuovinen, J.P.; Kotro, J.; Kuitunen, T.; Hohti, H. A Climatological Comparison of Radar and Ground Observations of Hail in Finland. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, A.; Jordan, P.; Pierce, C.; Leonard, M.; Nathan, R.; Kordomenidi, E. Stochastic Simulation of Space-Time Rainfall Patterns for the Brisbane River Catchment. In Hydrology and Water Resources Symposium 2014; Engineers Australia: Barton, ACT, Australia, 2014; pp. 1026–1039. ISBN 9781922107190. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, T.; Jakkila, J.; Veijalainen, N.; Backman, L.; Kaurola, J.; Vehviläinen, B. Impacts of Climate Change on Temperature, Precipitation and Hydrology in Finland—Studies Using Bias Corrected Regional Climate Model Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 12, 2657–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, V.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; Räsänen, T.A.; Jakkila, J.; Veijalainen, N.; Kummu, M. Spatiotemporal Hydroclimate Variability in Finland: Past Trends. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1765–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnish Meteorological Institute Observation Stations. Available online: https://www.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/havaintoasemat (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Vehviläinen, B.; Huttunen, M.; Huttunen, I. Hydrological Forecasting and Real Time Monitoring in Finland: The Watershed Simulation and Forecasting System (WSFS). In Proceedings of the Innovation, Advances and Implementation of Flood Forecasting Technology, Tromsø, Norway, 17–19 October 2005; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Veijalainen, N. Estimation of Climate Change Impacts on Hydrology and Floods in Finland; Aalto University: Helsinki, Finland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Paschalis, A.; Fatichi, S.; Molnar, P.; Rimkus, S.; Burlando, P. On the Effects of Small Scale Space–Time Variability of Rainfall on Basin Flood Response. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belachsen, I.; Marra, F.; Peleg, N.; Morin, E. Convective Rainfall in a Dry Climate: Relations with Synoptic Systems and Flash-Flood Generation in the Dead Sea Region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5165–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Skinner, C.; Fatichi, S.; Molnar, P. Temperature Effects on the Spatial Structure of Heavy Rainfall Modify Catchment Hydro-Morphological Response. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2020, 8, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Ban, N.; Gibson, M.J.; Chen, A.S.; Paschalis, A.; Burlando, P.; Leitão, J.P. Mapping Storm Spatial Profiles for Flood Impact Assessments. Adv. Water Resour. 2022, 166, 104258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirmbach, M.; Schultz, G.A. Comparison of Rain Gauge and Radar Data as Input to an Urban Rainfall-Runoff Model. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Mein, R.G.; Keenan, T.D.; Elliott, J.F. Flood Estimation Using Radar and Raingauge Data. J. Hydrol. 2000, 239, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengfeld, K.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Fowler, H.J.; Yu, J.; Becker, A.; Flamig, Z.; Gourley, J. Use of Radar Data for Characterizing Extreme Precipitation at Fine Scales and Short Durations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 085003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Paschalis, A.; Peleg, N.; Molnar, P.; Rimkus, S.; Kim, J.; Burlando, P.; Caporali, E. Uncertainty Partition Challenges the Predictability of Vital Details of Climate Change. Earth’s Futur. 2016, 4, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraga, J.S.; Peleg, N.; Fatichi, S.; Molnar, P.; Burlando, P. Revealing the Impacts of Climate Change on Mountainous Catchments through High-Resolution Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Habib, E.; Bárdossy, A. Modeling Radar Rainfall Estimation Uncertainties: Random Error Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 15, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Wang, L.P.; Willems, P.; Onof, C. A Review of Radar-Rain Gauge Data Merging Methods and Their Potential for Urban Hydrological Applications. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6356–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartke, S.H.; Wright, D.B.; Li, Z.; Maggioni, V.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Khan, S. Ensemble Representation of Satellite Precipitation Uncertainty Using a Nonstationary, Anisotropic Autocorrelation Model. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

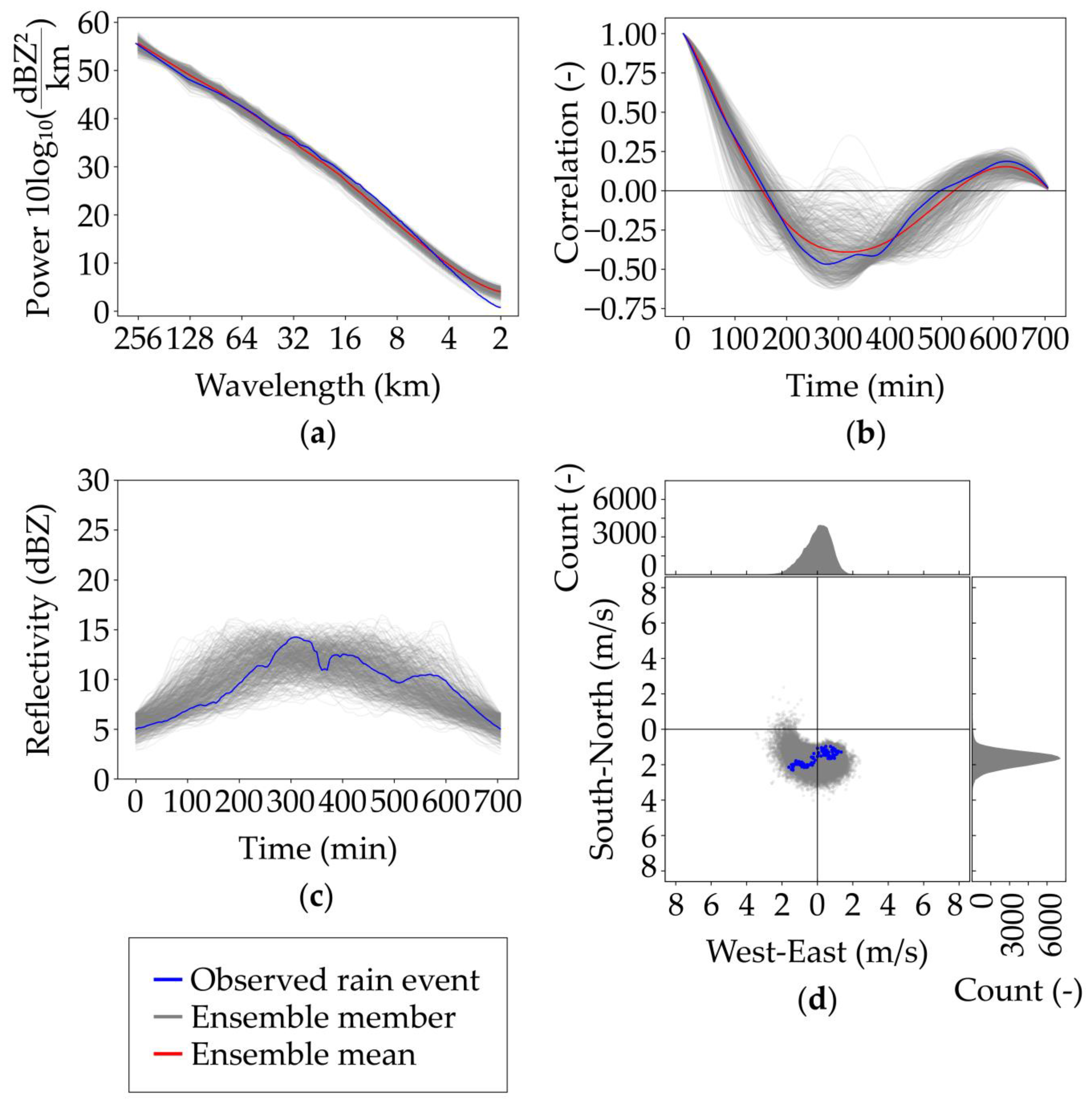
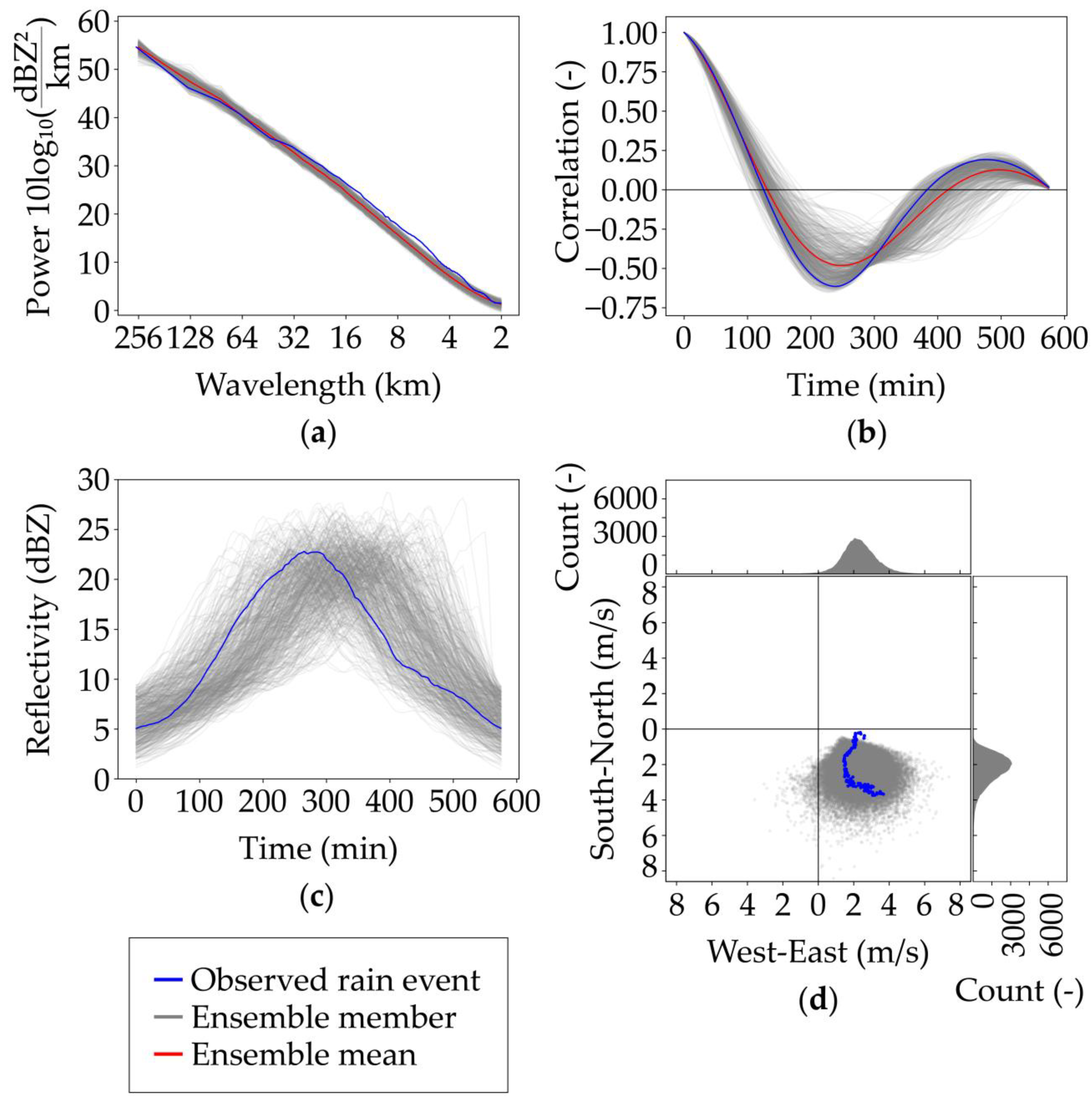
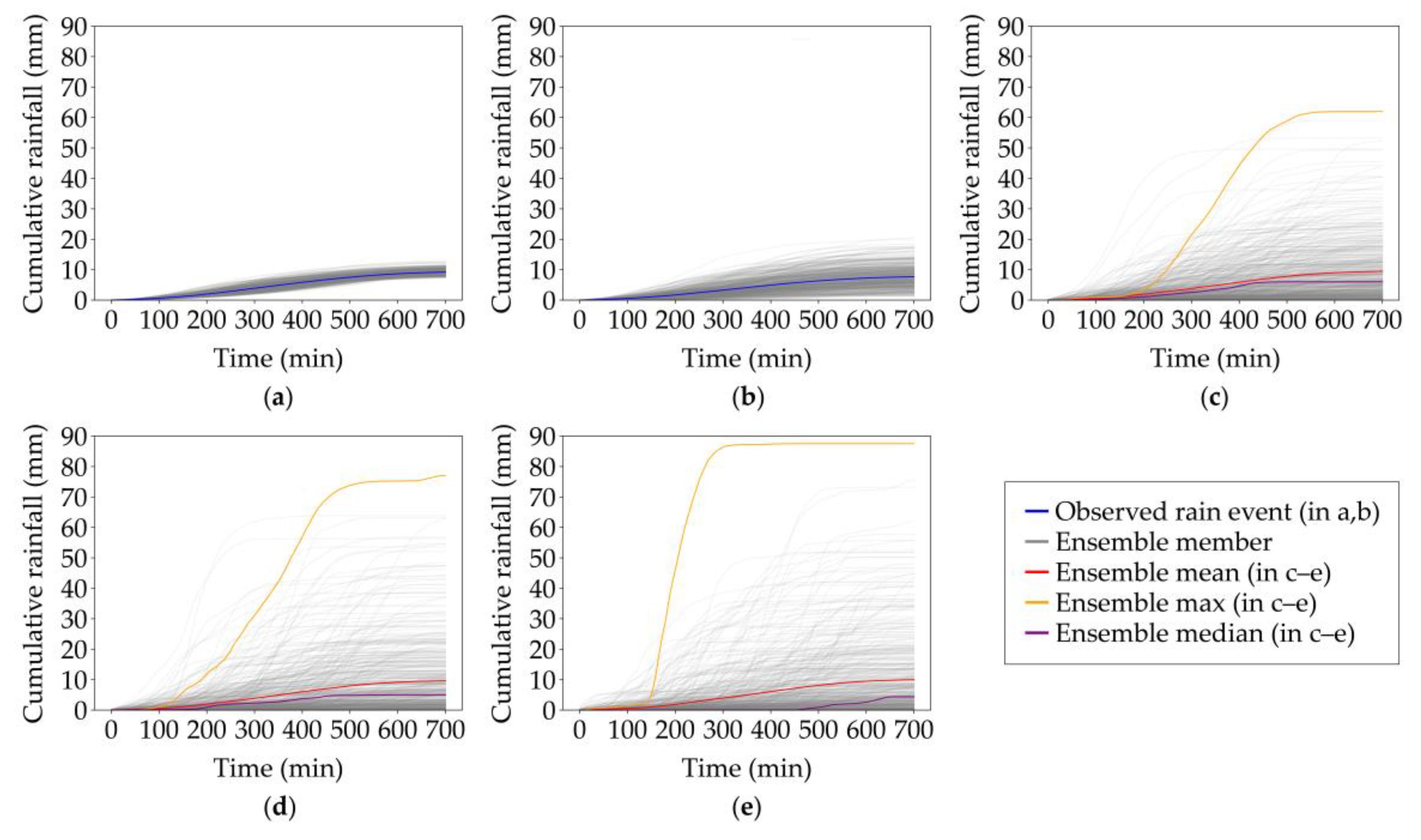
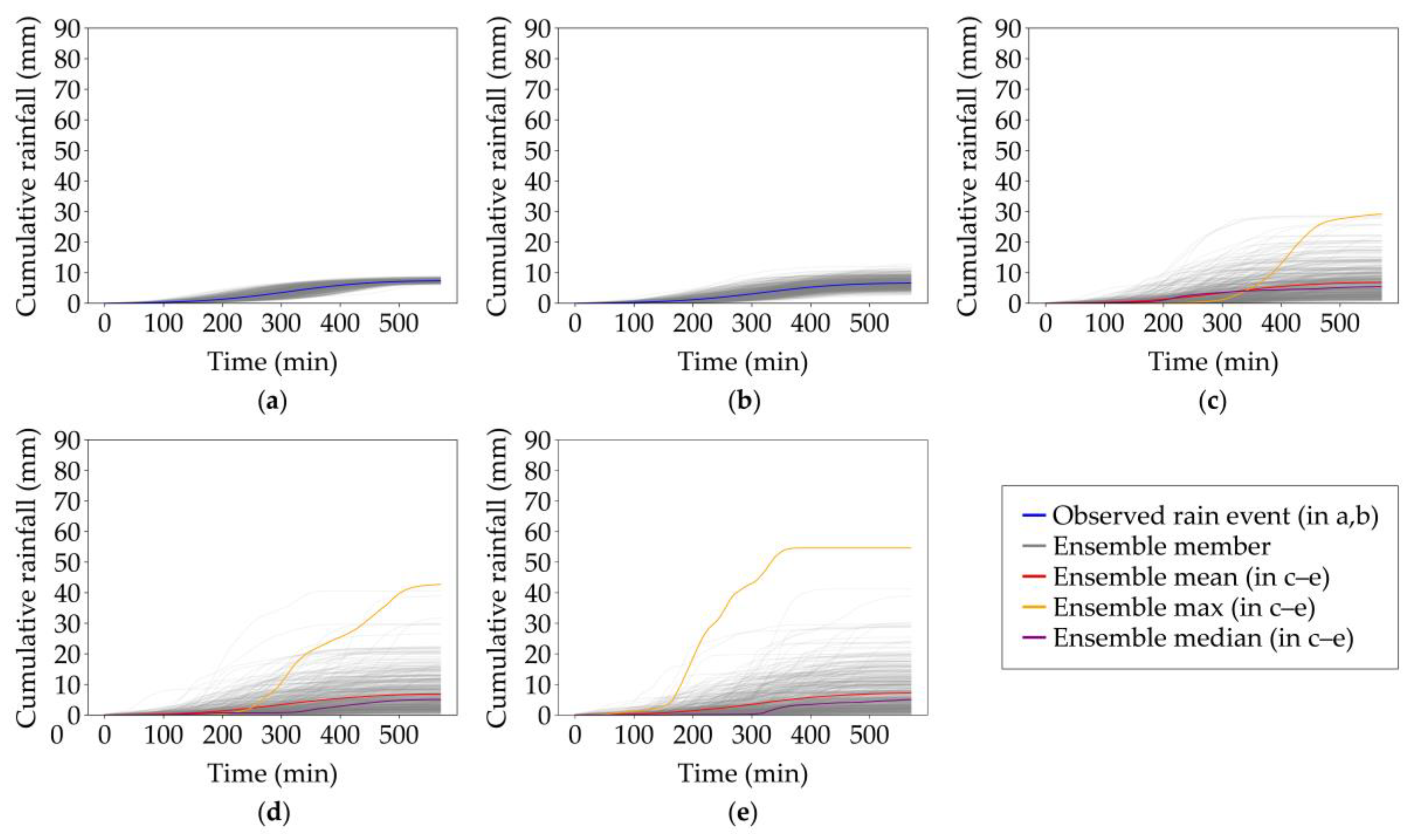
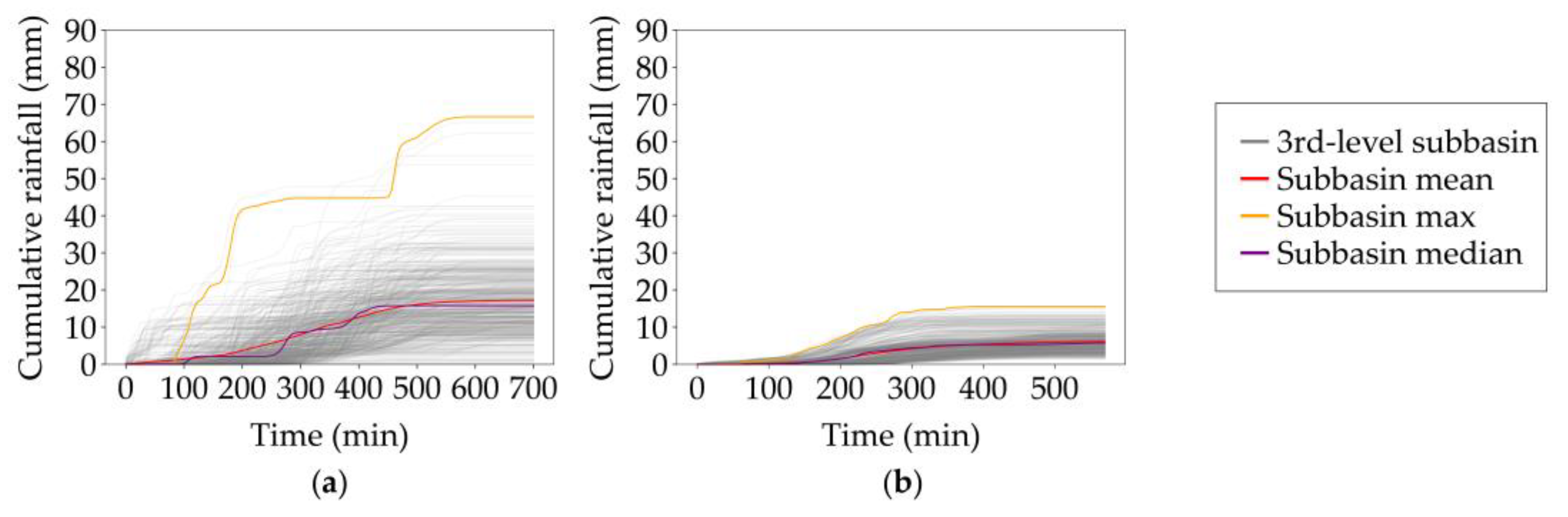
| Event | Start and End Time | Duration (h:mm) | Average (Peak) μ (mm/h) | Average (Maximum) WAR (%) | Cumulative Mean Areal Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event 1 | 27 June 2013, 08:10– 27 June 2013, 19:55 | 11:45 | 1.11 (2.17) | 30 (49) | 12.28 |
| Event 2 | 28 October 2013, 18:10– 29 October 2013, 03:45 | 9:35 | 0.68 (1.73) | 55 (91) | 6.16 |
| Spatial Scale | Max (mm) | Min (mm) | Mean (mm) | Median (mm) | Std (mm) | CV (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radar field | 13.05 (8.83) | 7.19 (6.00) | 9.22 (7.36) | 9.06 (7.34) | 0.99 (0.48) | 0.11 (0.07) |
| Kokemäenjoki river basin | 20.53 (12.67) | 1.19 (2.73) | 7.72 (6.62) | 7.33 (6.42) | 3.58 (1.73) | 0.46 (0.26) |
| 1st-level | 62.00 (29.20) | 0.02 (0.68) | 9.50 (6.86) | 6.02 (5.50) | 10.20 (5.24) | 1.07 (0.76) |
| 2nd-level | 77.09 (42.76) | 0.01 (0.07) | 9.65 (6.90) | 5.03 (5.05) | 12.39 (6.12) | 1.28 (0.89) |
| 3rd-level | 87.53 (54.64) | 0.00 (0.04) | 10.01 (7.14) | 4.39 (5.04) | 13.39 (6.67) | 1.34 (0.93) |
| Spatial Scale | Statistic | Areal Estimate | Gauge Estimate | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st-level | Max (mm) | 61.98 (33.47) | 63.31 (38.24) | −1.33 (−4.77) |
| 1st-level | Mean (mm) | 48.24 (27.10) | 47.12 (25.24) | 1.12 (1.86) |
| 1st-level | Median (mm) | 47.35 (26.74) | 47.74 (23.95) | −0.39 (2.80) |
| 1st-level | Std (mm) | 9.19 (3.86) | 10.93 (5.66) | −1.74 (−1.80) |
| 1st-level | CV (-) | 0.19 (0.14) | 0.23 (0.22) | −0.04 (−0.08) |
| 2nd-level | Max (mm) | 137.87 (62.89) | 100.76 (50.10) | 37.11 (12.79) |
| 2nd-level | Mean (mm) | 68.81 (32.99) | 54.88 (27.61) | 13.93 (5.38) |
| 2nd-level | Median (mm) | 62.73 (31.51) | 54.48 (26.61) | 8.25 (4.90) |
| 2nd-level | Std (mm) | 20.90 (7.11) | 15.72 (7.01) | 5.18 (0.10) |
| 2nd-level | CV (-) | 0.30 (0.22) | 0.29 (0.25) | 0.02 (−0.04) |
| 3rd-level | Max (mm) | 157.09 (88.94) | 119.46 (58.55) | 37.64 (30.39) |
| 3rd-level | Mean (mm) | 72.97 (35.15) | 55.46 (28.11) | 17.51 (7.05) |
| 3rd-level | Median (mm) | 68.23 (33.79) | 55.12 (27.07) | 13.11 (6.72) |
| 3rd-level | Std (mm) | 21.05 (7.75) | 16.70 (7.47) | 4.35 (0.28) |
| 3rd-level | CV (-) | 0.29 (0.22) | 0.30 (0.27) | −0.01 (−0.05) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lindgren, V.; Niemi, T.; Koivusalo, H.; Kokkonen, T. Value of Spatially Distributed Rainfall Design Events—Creating Basin-Scale Stochastic Design Storm Ensembles. Water 2023, 15, 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173066
Lindgren V, Niemi T, Koivusalo H, Kokkonen T. Value of Spatially Distributed Rainfall Design Events—Creating Basin-Scale Stochastic Design Storm Ensembles. Water. 2023; 15(17):3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLindgren, Ville, Tero Niemi, Harri Koivusalo, and Teemu Kokkonen. 2023. "Value of Spatially Distributed Rainfall Design Events—Creating Basin-Scale Stochastic Design Storm Ensembles" Water 15, no. 17: 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173066







