Analysis of the Source Tracing and Pollution Characteristics of Rainfall Runoff in Adjacent New and Old Urban Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
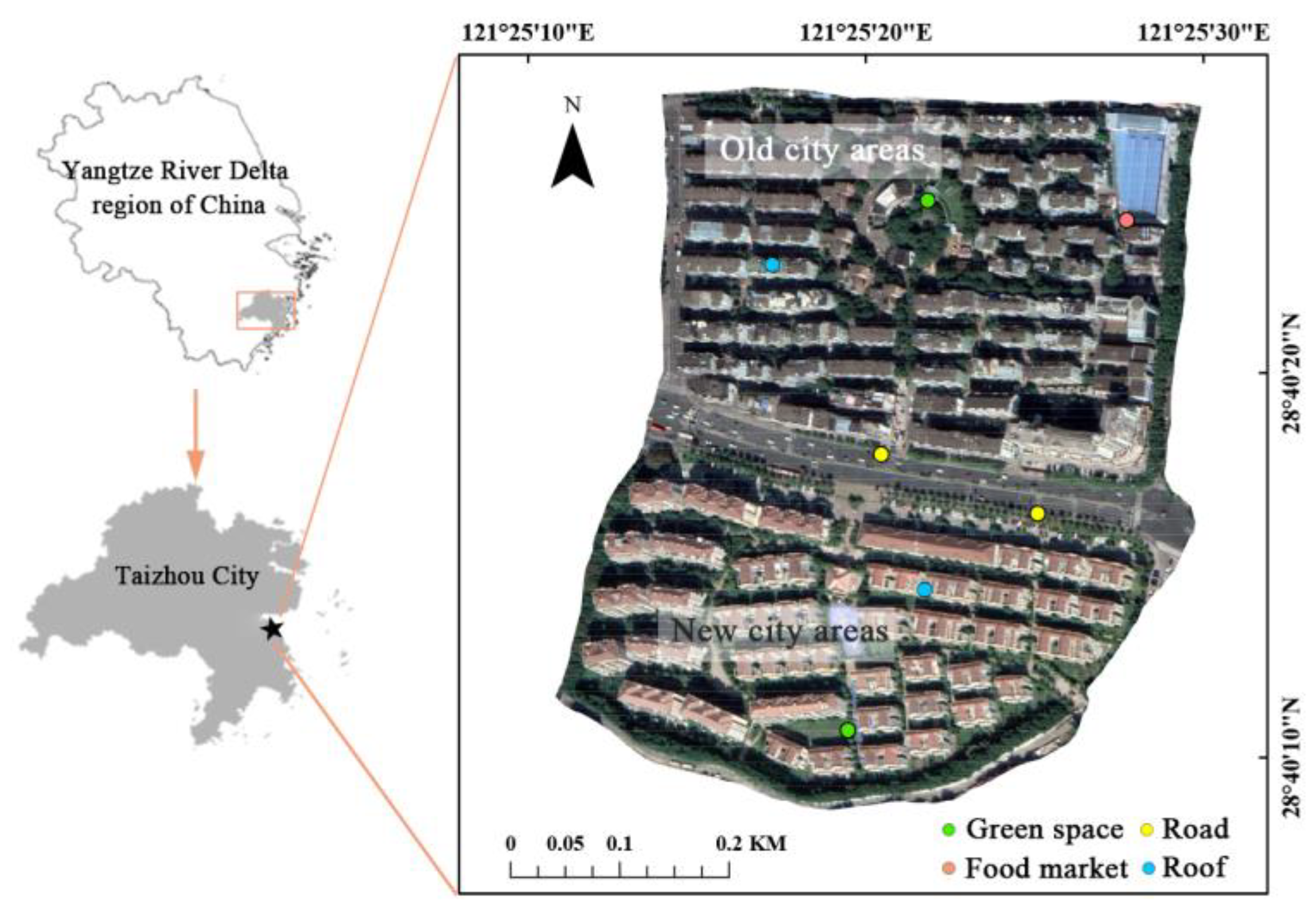
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Rainfall-Runoff Monitoring and Sample Detection
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. The Average Concentration of Pollutants in Each Rainfall
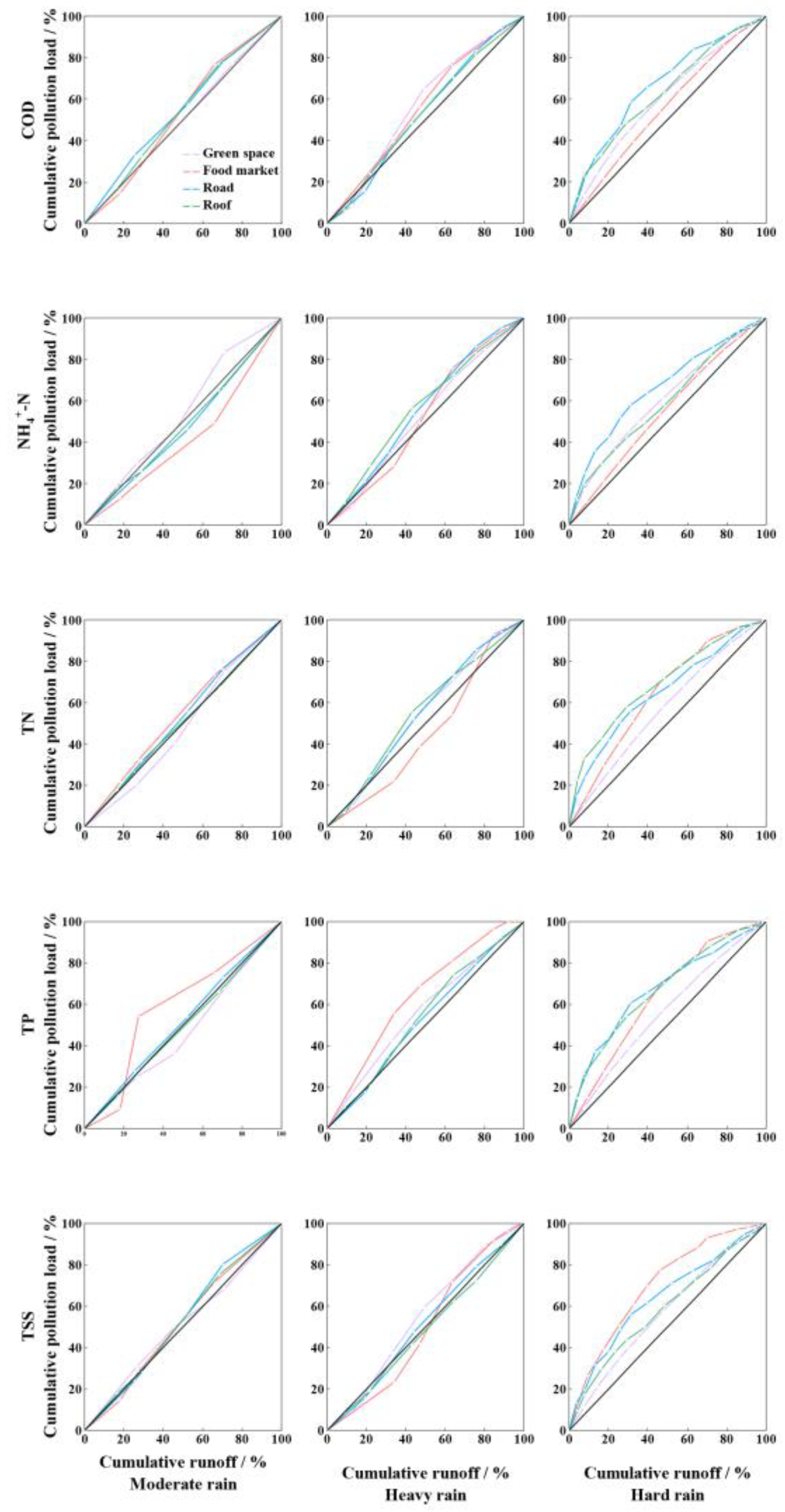
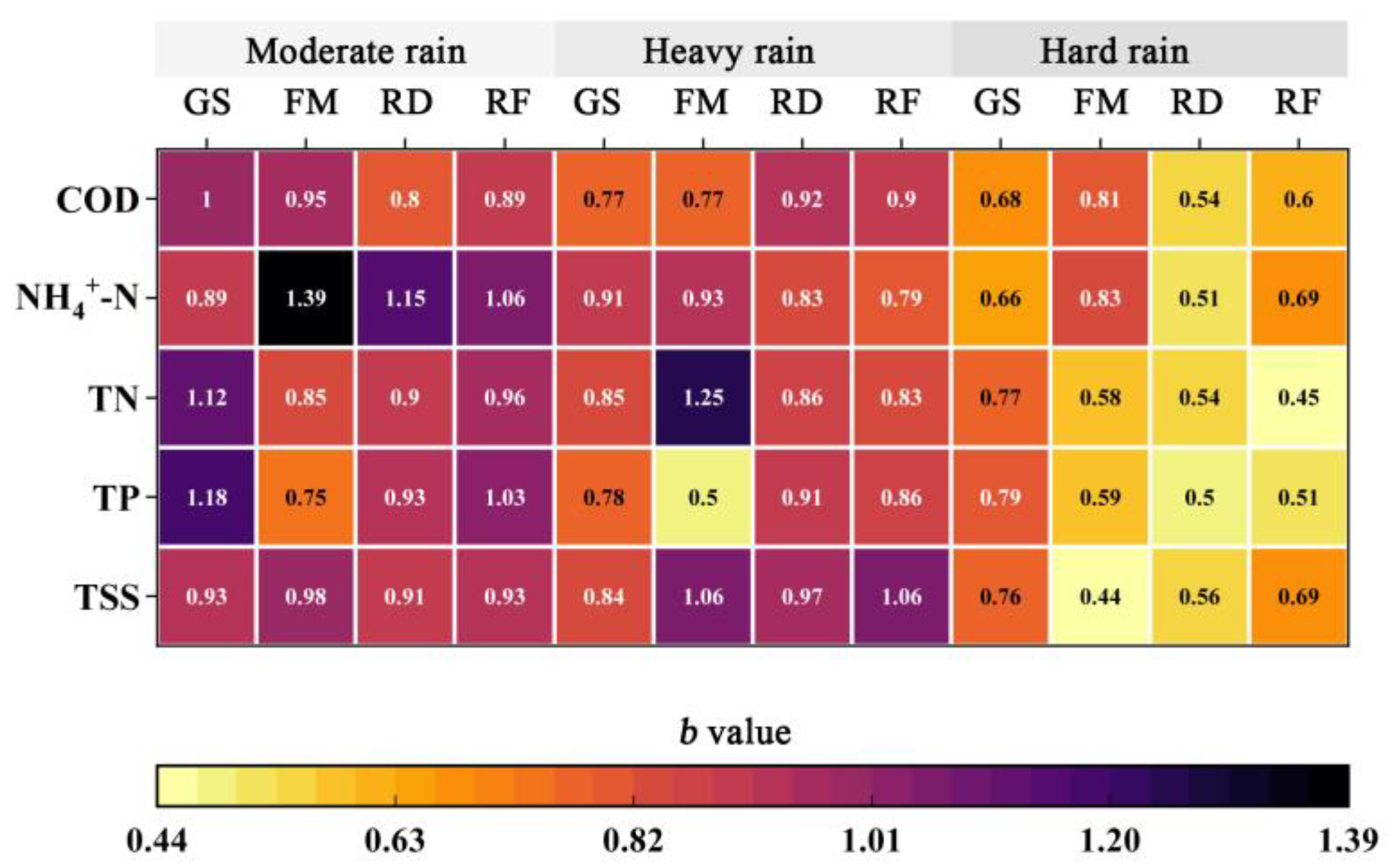
2.3.2. Determination of the Initial Scouring Effect
2.3.3. Rainfall-Runoff Pollution Load
2.3.4. Percentage Difference of Rainfall-Runoff Pollution Load
2.3.5. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Rainfall-Runoff Water Quality on Each Underlying Surface
3.2. Analysis of the Initial Scouring Effect of Rainfall Runoff
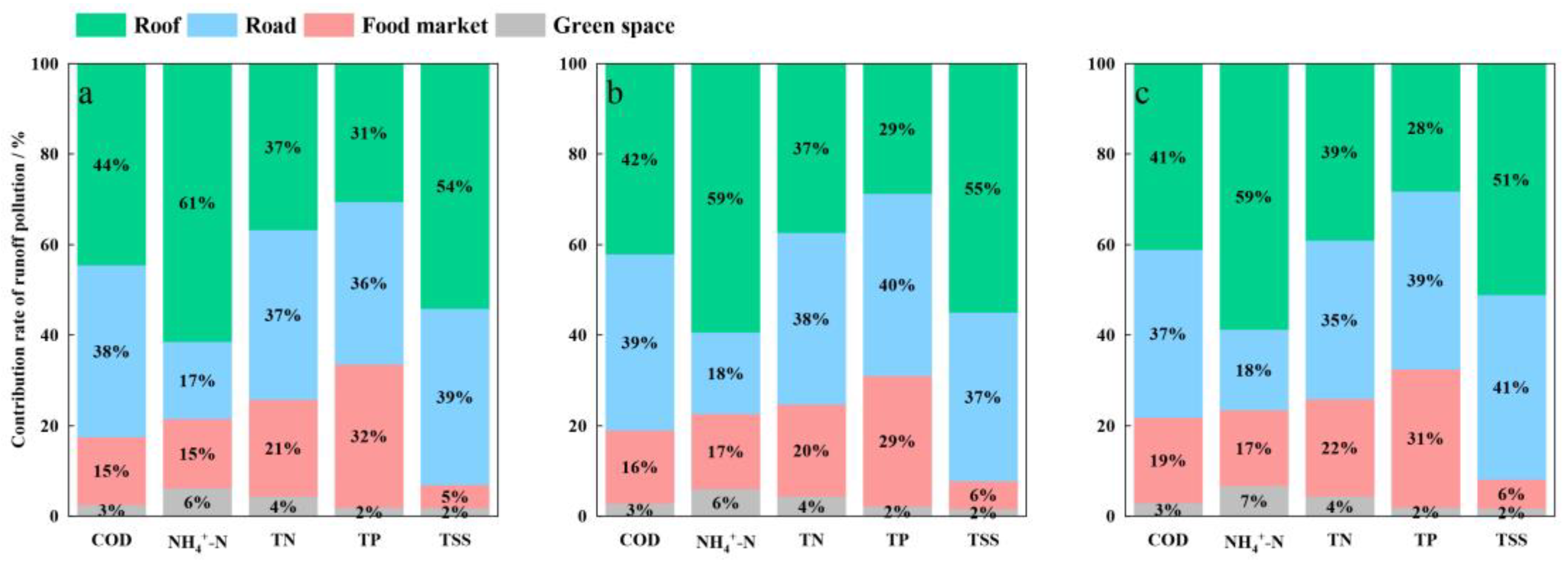
3.3. Traceability of Rainfall-Runoff Pollution
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Variability of Rainfall-Runoff Quality Characteristics
4.2. Identification of Factors Influencing the Initial Scouring Effect of Rainfall Runoff
4.3. Reason for Selecting the Food Market as an Underlying Surface
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, K.; Luo, J. Migration and transformation of nitrogen in bioretention system during rainfall runoff. Chemosphere 2019, 232, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.C.N.; de Andrade, E.M.; Medeiros, P.H.A.; Guerreiro, M.J.S.; Palácio, H.A.d.Q. Effect of Rainfall Characteristics on Runoff and Water Erosion for Different Land Uses in a Tropical Semiarid Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 31, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, F.; Liu, L.; Chen, M.; Sun, D.; Nan, J. How do urban rainfall-runoff pollution control technologies develop in China? A systematic review based on bibliometric analysis and literature summary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, N.; Redfern, T.; Miller, J.; Kjeldsen, T. Understanding the impact of the built environment mosaic on rainfall-runoff behaviour. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, C.; Qi, Y.; Kang, A.; Hu, H.; Wu, X. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of runoff-pollutants from three types of urban pavements. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 125885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Yu, H.; Gong, X.; Chen, J. Study on pollution characteristics of urban pavement runoff. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Ge, X.; Tian, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Z. Variations of Concentration Characteristics of Rainfall Runoff Pollutants in Typical Urban Living Areas. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Hui, C.; Dong, N.; Jing, Z. Study on hydrodynamic characteristics and influence factors of asphalt pavement runoff. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3928–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wei, T.; Jia, Z.; Feng, J.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y. The influence of rainfall and catchment characteristics on runoff generation in urban catchments—A case study in Hebi City of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charters, F.J.; Cochrane, T.A.; O’Sullivan, A.D. The influence of urban surface type and characteristics on runoff water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tu, Z.; Du, P.; Li, Q.; Lin, J. Analysis of rainfall runoff characteristics from a subtropical urban lawn catchment in South-east China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2011, 6, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lim, J.; Ra, K. Heavy metal pollution by road-deposited sediments and its contribution to total suspended solids in rainfall runoff from intensive industrial areas. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Ma, J.; He, F.; Wei, G. Response Model for Urban Area Source Pollution and Water Environmental Quality in a River Network Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, T.; McGree, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Jinadasa, K.; Goonetilleke, A. Catchment based estimation of pollutant event mean concentration (EMC) and implications for first flush assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.M.R.; Sandoval, S.; Aubin, J.-B.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; Xuyong, L.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Vezzaro, L. Classifying pollutant flush signals in stormwater using functional data analysis on TSS MV curves. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Dong, J.; Shen, Z.; Chen, L.; Lai, X.; Qiu, J.; Wei, G.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X. Intra- and inter-event characteristics and controlling factors of agricultural nonpoint source pollution under different types of rainfall-runoff events. Catena 2019, 182, 104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, T.; McGree, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Jinadasa, K.; Goonetilleke, A. Taxonomy of influential factors for predicting pollutant first flush in urban stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Fang, X.; Yin, D.; Xie, P.; Nie, L. Factors affecting the ability of extensive green roofs to reduce nutrient pollutants in rainfall runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Gong, J.; Sun, F.; Xu, Y. Characterization and first flush analysis in road and roof runoff in Shenyang, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, C.; Ma, B.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, L. The characteristics of rainfall runoff pollution and its driving factors in Northwest semiarid region of China—A case study of Xi’an. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, Q.; Ai, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Pollutant concentrations and pollution loads in stormwater runoff from different land uses in Chongqing. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lin, W.; Qi, Y.; Long, J.; et al. Analysis of the Migration Characteristics of Stormwater Runoff Pollutants on Different Underlying Surfaces in Guangzhou, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 554588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Q.; Yu, Z. The influence of traffic density on heavy metals distribution in urban road runoff in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qianqian, Z.; Liping, M.; Huiwei, W.; Long, W. Analysis of the effect of green roof substrate amended with biochar on water quality and quantity of rainfall runoff. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Bang, K.; Ketchum, L.; Choe, J.; Yu, M. First flush analysis of urban storm runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Dai, M. Influence of rainfall characteristics on pollutant wash-off for road catchments in urban Shanghai. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z. Transport and sources of nitrogen in stormwater runoff at the urban catchment scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Quan, F.; Hu, S.; Wu, Q.; Luo, M.; Gu, Y.; Tang, S.; Jiang, J. Road runoff as a significant nonpoint source of parabens and their metabolites in urban rivers. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wei, W.; Xu, Y. Does the spatial location of green roofs affects runoff mitigation in small urbanized catchments? J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillefalk, M.; Tetzlaff, D.; Hinkelmann, R.; Kuhlemann, L.-M.; Smith, A.; Meier, F.; Maneta, M.P.; Soulsby, C. Quantifying the effects of urban green space on water partitioning and ages using an isotope-based ecohydrological model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3635–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Serial No | Date/ YYYY-MM-DD | Rainfall/mm | Rainfall Type | Rainfall Duration /h | Average Rainfall in Tensity /(mm/h) | Early Drought Time /h | Background Concentrations of the Pollutants/(mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | NH4+-N | TN | TP | TSS | |||||||
| 1 | 2018-4-30 | 69 | Hard rain | 7 | 9.9 | 20 | 19.1 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.08 | 21 |
| 2 | 2018-5-1 | 5 | Moderate rain | 2 | 2.5 | 16 | 23.6 | 0.30 | 0.71 | 0.05 | 19 |
| 3 | 2018-5-7 | 22 | Heavy rain | 2 | 11.0 | 133 | 25.1 | 0.28 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 33 |
| 4 | 2018-5-13 | 9 | Moderate rain | 1 | 9.0 | 132 | 27.8 | 0.21 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 16 |
| 5 | 2018-5-20 | 47 | Hard rain | 3 | 15.7 | 20 | 18.4 | 0.33 | 0.87 | 0.03 | 23 |
| 6 | 2018-5-21 | 30 | Hard rain | 5 | 6.0 | 17 | 21.4 | 0.31 | 0.93 | 0.06 | 25 |
| 7 | 2018-5-22 | 9 | Moderate rain | 5 | 1.8 | 3 | 19.9 | 0.39 | 1.23 | 0.01 | 13 |
| 8 | 2018-5-23 | 27 | Heavy rain | 9 | 3.0 | 19 | 27.2 | 0.18 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 26 |
| 9 | 2018-5-26 | 28 | Heavy rain | 2 | 14.0 | 55 | 24.6 | 0.44 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 20 |
| City | Geographical Division | Pollution Index | Green Space (mg/L) | Road (mg/L) | Roof (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taizhou City (This study) | East China | COD | 20.2–110.6 a | 34.0–136.2 | 18.1–122.5 |
| NH4+-N | 0.5–2.0 | 0.1–0.6 | 0.3–0.8 | ||
| TN | 0.7–2.1 | 0.7–2.0 | 0.3–2.8 | ||
| TP | 0.1–1.0 | 0.1–1.6 | 0.05–0.1 | ||
| TSS | 28.2–86.6 | 78.3–226.1 | 48.9–254.4 | ||
| Xiamen City [11] | East China | COD | 37.5–137.5 | / b | / |
| NH4+-N | 6.3–3.75 | / | / | ||
| TSS | 18.5–55.0 | / | / | ||
| Beijing City [18] | North China | NH4+-N | / | 1.9–5.7 | 2.1–7.1 |
| TN | / | / | 5.3–12.7 | ||
| TP | / | / | 0.03–0.2 | ||
| Shenyang City [19] | Northeast China | COD | / | 1.8 -11.0 | 0.2–23.6 |
| TN | / | 0.1–3.8 | 0.6–9.9 | ||
| TP | / | 0.2–1.1 | 0.1–0.2 | ||
| TSS | / | 365.0–1208.1 | 7.0–94.3 | ||
| Xi’an city [20] | Northwest China | COD | / | 102.1–716.1 | 13.4–321.1 |
| NH4+-N | / | 2.0–5.3 | 1.8–15.2 | ||
| TN | / | 1.7–21.1 | 4.0–26.9 | ||
| TP | / | 0.1–1.0 | 0.3–1.2 | ||
| TSS | / | 82.9–640.2 | 17.5–241.1 | ||
| Chongqing City [21] | Southwest China | COD | 38.0 c | 418.0 | 83.0 |
| NH4+-N | 0.5 | 4.3 | 1.7 | ||
| TN | 2.7 | 8.1 | 5.9 | ||
| TP | 0.1 | 1.2 | 0.2 | ||
| TSS | 31.0 | 631.0 | 69.0 | ||
| Guangzhou City [22] | South Central China | TN | 1.9–3.5 | 2.4–10.0 | 2.4–5.0 |
| TP | 0.01–0.1 | 0.04–0.2 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Underlying Surface | Pollutant Index | RF | RD | ARI | EDT | TR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green space | COD | 0.587 | 0.314 | 0.470 | −0.264 | −0.473 |
| NH4+-N | 0.479 | 0.429 | −0.044 | −0.849 ** | 0.404 | |
| TN | 0.757 * | 0.153 | 0.517 | −0.086 | −0.095 | |
| TP | −0.015 | 0.036 | −0.043 | −0.075 | 0.207 | |
| TSS | −0.036 | 0.072 | 0.070 | 0.187 | −0.351 | |
| Food market | COD | 0.200 | 0.120 | −0.171 | −0.610 | 0.725 * |
| NH4+-N | 0.548 | 0.233 | 0.178 | −0.449 | −0.188 | |
| TN | 0.511 | 0.150 | 0.432 | −0.244 | −0.129 | |
| TP | 0.150 | 0.062 | 0.155 | −0.199 | −0.333 | |
| TSS | 0.292 | −0.173 | 0.362 | −0.251 | 0.455 | |
| Road | COD | −0.107 | −0.083 | 0.235 | 0.411 | −0.699 * |
| NH4+-N | 0.254 | −0.120 | 0.340 | 0.087 | 0.194 | |
| TN | 0.350 | 0.242 | 0.382 | 0.400 | −0.769 * | |
| TP | 0.272 | 0.000 | 0.324 | 0.250 | −0.007 | |
| TSS | 0.202 | 0.035 | 0.193 | −0.038 | −0.678 * | |
| Roof | COD | −0.396 | −0.291 | −0.131 | 0.010 | 0.144 |
| NH4+-N | 0.231 | 0.392 | 0.196 | −0.205 | −0.274 | |
| TN | 0.740 * | 0.184 | 0.432 | −0.167 | −0.184 | |
| TP | −0.238 | 0.318 | −0.654 | −0.751 * | 0.752 * | |
| TSS | −0.308 | −0.221 | 0.173 | 0.771 * | −0.417 |
| Rainfall Type | COD (%) | NH4+-N (%) | TN (%) | TP (%) | TSS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate rain | 8.08 | 8.36 | 11.85 | 18.76 | 2.63 |
| Heavy rain | 8.84 | 9.07 | 11.27 | 16.87 | 3.20 |
| Hard rain | 10.41 | 9.20 | 12.09 | 18.05 | 3.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Q.; Ma, J.; Du, W.; Luo, Y.; Ji, D.; He, F. Analysis of the Source Tracing and Pollution Characteristics of Rainfall Runoff in Adjacent New and Old Urban Areas. Water 2023, 15, 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173018
Lai Q, Ma J, Du W, Luo Y, Ji D, He F. Analysis of the Source Tracing and Pollution Characteristics of Rainfall Runoff in Adjacent New and Old Urban Areas. Water. 2023; 15(17):3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173018
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Qiuying, Jie Ma, Wei Du, Yidan Luo, Dawei Ji, and Fei He. 2023. "Analysis of the Source Tracing and Pollution Characteristics of Rainfall Runoff in Adjacent New and Old Urban Areas" Water 15, no. 17: 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173018





