Synthesis of Poly(aniline-co-benzene)-Based Hypercrosslinked Polymer for Hg(II) Ions Removal from Polluted Water: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
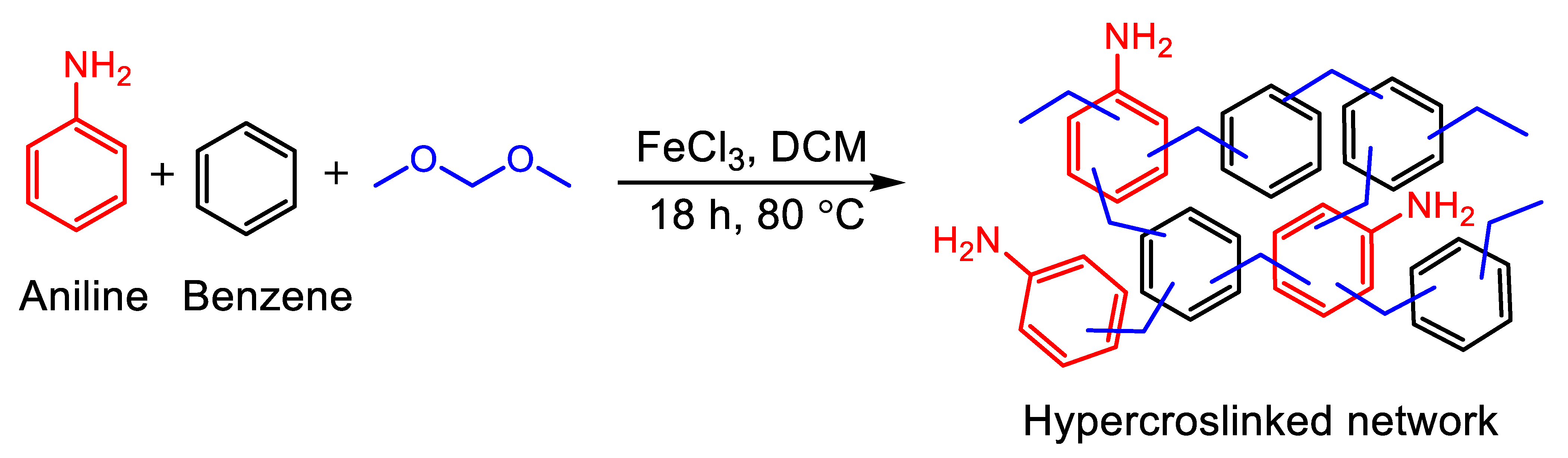
2.2. Synthesis of PAB Adsorbent
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. pH Drift
2.4.2. Effect of Adsorption pH
2.4.3. Adsorption Kinetic
2.4.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.5. Theoretical Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Structure and Properties
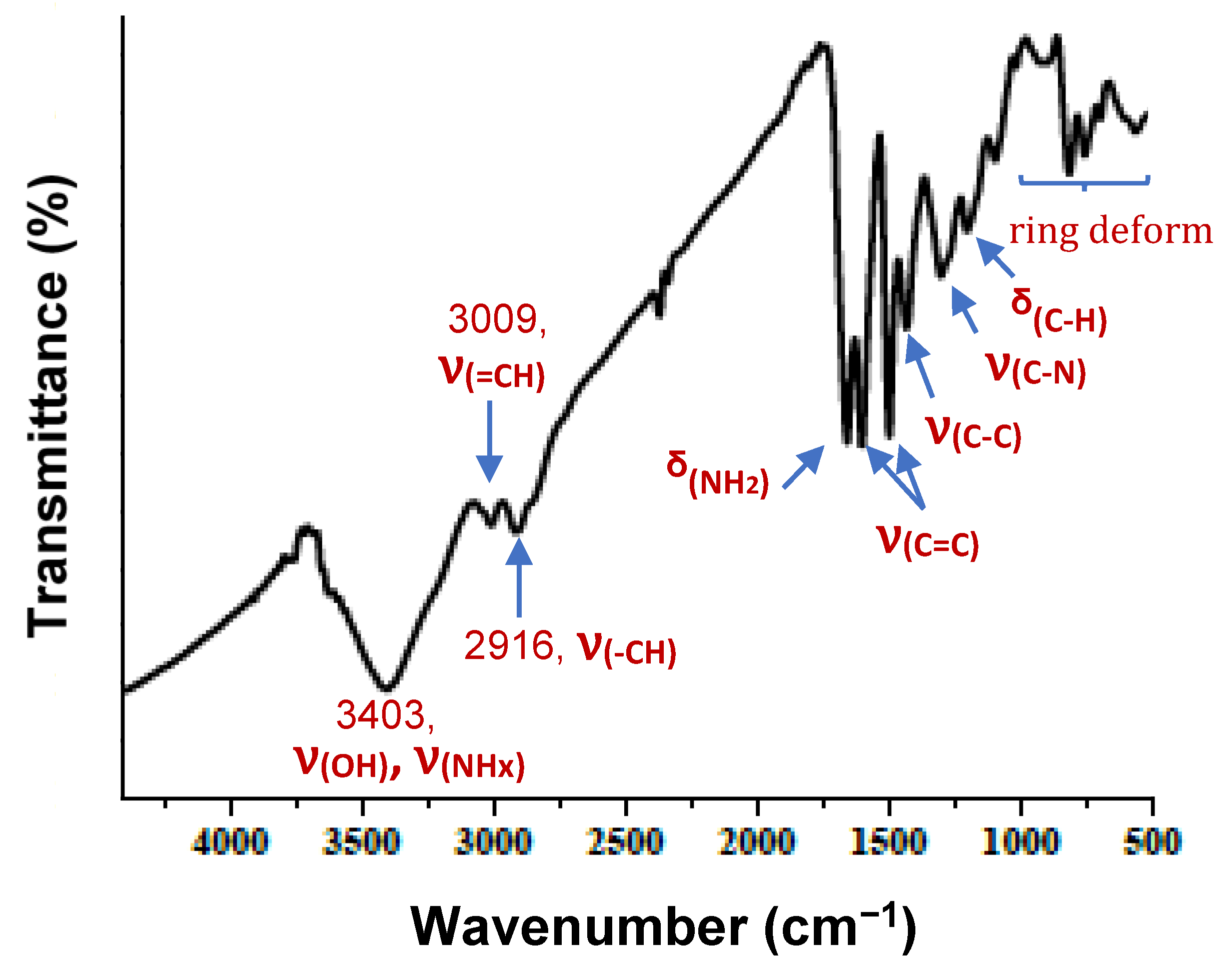
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
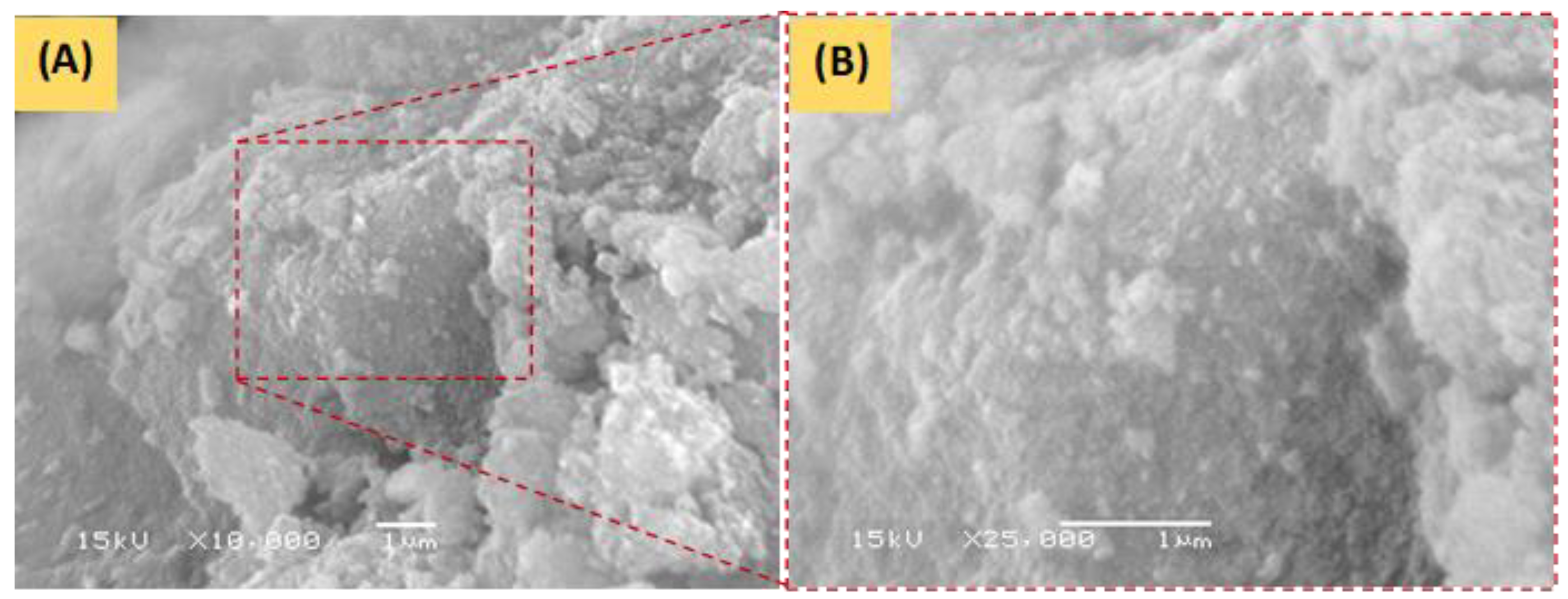
3.1.2. SEM and EDS Analysis
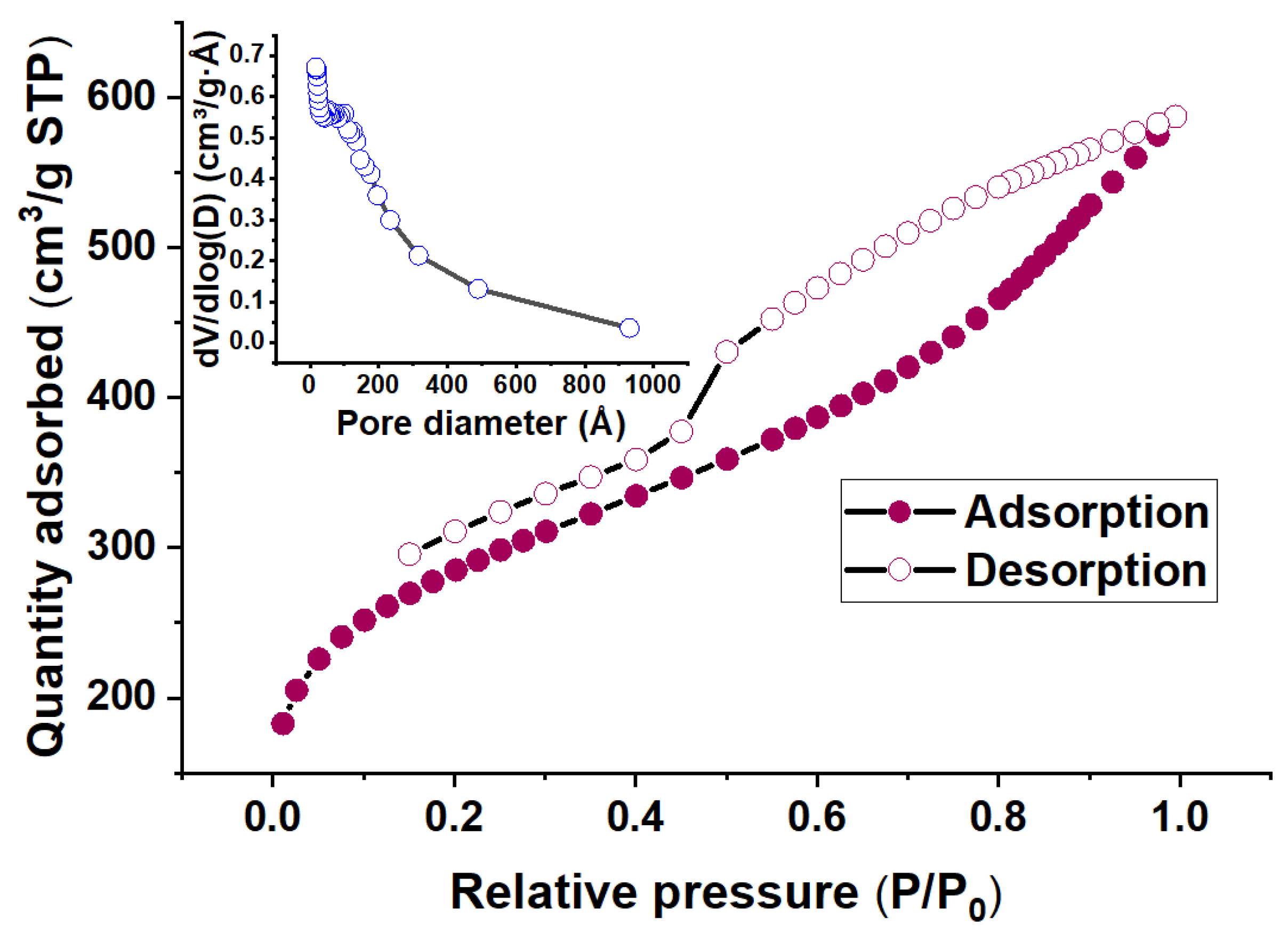
3.1.3. BET Analysis
3.1.4. Thermal Analysis
3.1.5. Point of Zero Charge
3.2. Effect of Solution pH
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics—Effect of Contact Time
3.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
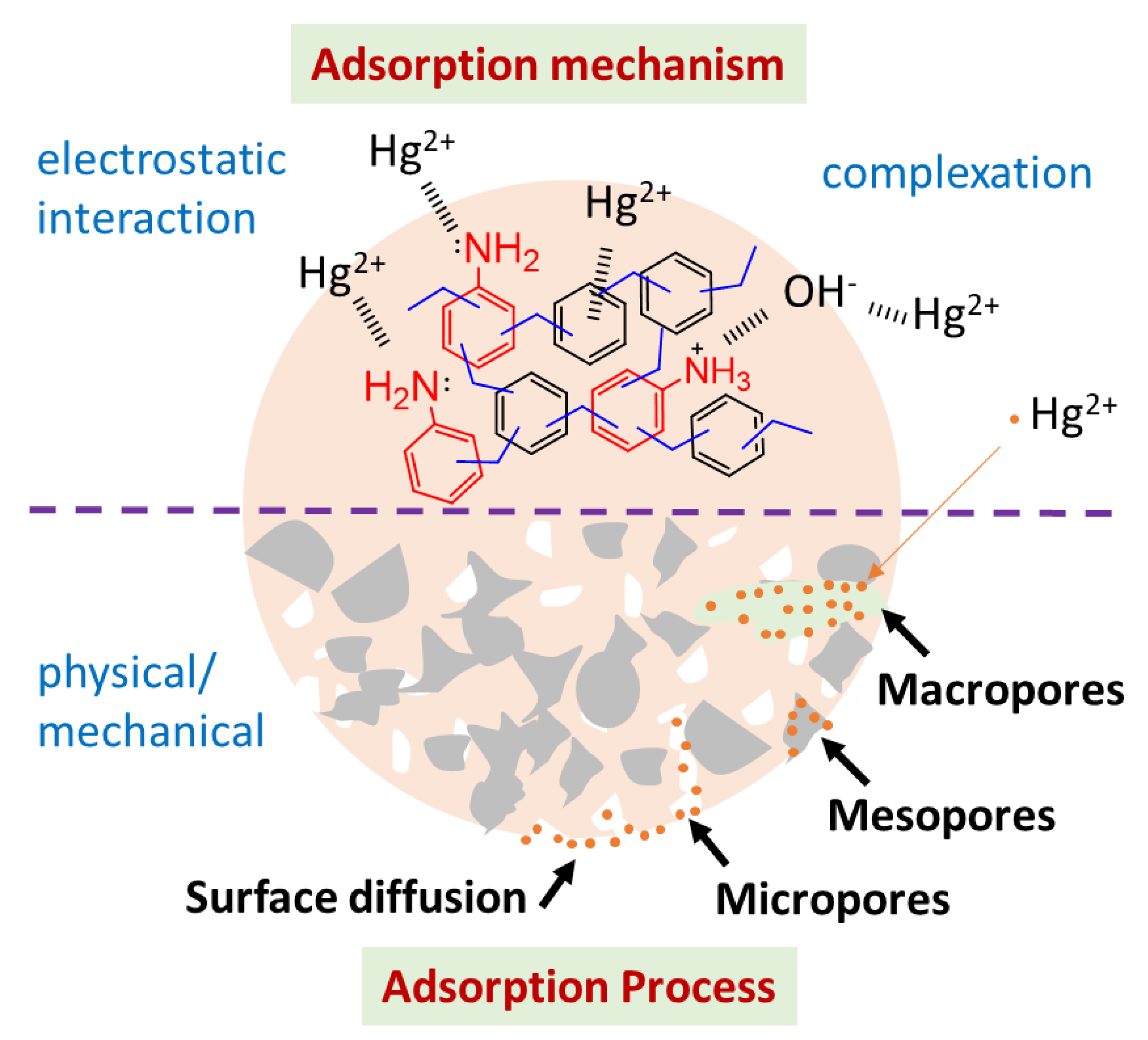
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
3.6. Relative Performance of PAB
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Algarni, T.S.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Abduh, N.A. Activated Carbon/ZnFe2O4 Nanocomposite Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Crystal Violet Cationic Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahadat, M.; Nabi, S.; Bushra, R.; Raeissi, A.; Umar, K.; Ansari, M.O. Synthesis, characterization, photolytic degradation, electrical conductivity and applications of a nanocomposite adsorbent for the treatment of pollutants. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7207–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ma, C.; Liao, Y.; Min, C.; Du, P.; Jiang, Y. Removal of mercury (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on poly (1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone) nanofibrils: Equilibrium, kinetics, and mechanism studies. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 7245829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlish, J.H.; Holmes, M.J.; Benson, S.A.; Crocker, C.R.; Galbreath, K.C. Application of sorbents for mercury control for utilities burning lignite coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2004, 85, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J. Removal of aqueous Hg (II) by polyaniline: Sorption characteristics and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5223–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1.
- Qasem, N.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushra, R.; Shahadat, M.; Ahmad, A.; Nabi, S.; Umar, K.; Oves, M.; Raeissi, A.; Muneer, M. Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activity and applications of polyanilineTi (IV) arsenophosphate adsorbent for the analysis of organic and inorganic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidu, R.; Matei, E.; Predescu, A.M.; Alhalaili, B.; Pantilimon, C.; Tarcea, C.; Predescu, C. Removal of heavy metals from wastewaters: A challenge from current treatment methods to nanotechnology applications. Toxics 2020, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, M.; Liu, A.; Jiang, M.; Niu, X.; Liu, X. Adsorption mechanisms and characteristics of Hg2+ removal by different fractions of biochar. Water 2020, 12, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwin Mabes Raj, A.; Bauman, M.; Lakić, M.; Dimitrušev, N.; Lobnik, A.; Košak, A. Removal of Pb2+, CrT, and Hg2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Amino-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using carbon-based adsorbents: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, D.; Bakhshpour, M.; Akgönüllü, S.; Aşır, S.; Denizli, A. Heavy metal ions removal from wastewater using cryogels: A review. Front. Sustain. 2022, 3, 765592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, N.A.; Khan, A.; Umar, K.; Muneer, M. Photocatalytic study of a xanthene dye derivative, phloxine B in aqueous suspension of TiO2: Adsorption isotherm and decolourization kinetics. Energy Environ. Focus 2013, 2, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, H.; Huq, A.; Yahya, R. Polymer-based adsorbent for heavy metals removal from aqueous solution. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 206, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Saeed, W.S.; Al-Kahtani, A.; Alharthi, F.A.; Aouak, T. Efficient adsorption of lead (II) from aqueous phase solutions using polypyrrole-based activated carbon. Materials 2019, 12, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.E.; Rangel-Méndez, J.R.; Gimeno, M.; Tecante, A.; Lapidus, G.T.; Shirai, K. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater with Poly-ε-Caprolactone-Reinforced Chitosan Composite. Polymers 2022, 14, 5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.T.; Huong, N.T.; Dan, L.L.; Tung, N.D.; Trung, V.B.; Minh, T.D. Removal of heavy metal ion using polymer-functionalized activated carbon: Aspects of environmental economic and chemistry education. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8887488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Zhao, H.; Chen, G.; Yang, Q.; Cao, X.; Xiong, S.; Xiao, A.; Li, G.; Liu, B.; Liu, Q. Synthesis of novel magnetic pitch-based hypercrosslinked polymers as adsorbents for effective recovery of Ag+ with high selectivity. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoumi, H.; Ghaemi, A.; Gilani, H.G. Exploiting the performance of hyper-cross-linked polystyrene for removal of multi-component heavy metal ions from wastewaters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Che, W.; Liu, S.-Y.; Liao, G. Hypercrosslinked microporous polystyrene: From synthesis to properties to applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 29, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, G. Multifunctional porous aromatic frameworks: State of the art and opportunities. EnergyChem 2020, 2, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Mao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Liao, Z.; Deng, R.; Liu, D.; Beiyuan, J.; Lv, D. Two Facile Aniline-Based Hypercrosslinked Polymer Adsorbents for Highly Efficient Iodine Capture and Removal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Abdullahi, S.S.a.; Habibu, S.; Jagaba, A.H.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Parveen, T.; Umar, K. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue cationic dye in aqueous solution using polypyrrole-polyethylenimine nano-adsorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Jia, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Q. Hypercrosslinked polymers: Controlled preparation and effective adsorption of aniline. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8579–8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Shu, Z.; Huang, J. Hydroquinone-modified hyper-crosslinked polymer and its adsorption of aniline. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Sun, P.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Jia, Y.; Peng, B.; Nie, C. Hyper-crosslinked polymers with controlled multiscale porosity for effective removal of benzene from cigarette smoke. e-Polymers 2021, 22, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, H.; Ghaemi, A.; Gilani, H.G. Synthesis of polystyrene-based hyper-cross-linked polymers for Cd (II) ions removal from aqueous solutions: Experimental and RSM modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, R.; Ratvijitvech, T.; Corker, M.; Laybourn, A.; Khimyak, Y.Z.; Cooper, A.I.; Adams, D.J. Microporous copolymers for increased gas selectivity. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 2034–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Abduh, N.A.; Alramadhan, S.A.; Aljboar, M.T.; Saeed, W.S. Adsorptive performance of polypyrrole-based KOH-activated carbon for the cationic dye crystal violet: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 5527594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagegren, S.; Svenska, B. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloester stoffe. Vaternskapsakad Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.-S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber Jr, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alwarthan, A. Uptake of propranolol on ionic liquid iron nanocomposite adsorbent: Kinetic, thermodynamics and mechanism of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeboree, A.M.; Alshirifi, A.N.; Alkaim, A.F. Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3381–S3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Saeed, W.S.; Almutairi, M.S.; Alharthi, F.A.; Aouak, T.; Al-Kahtani, A. Adsorption of azo dye methyl orange from aqueous solutions using alkali-activated polypyrrole-based graphene oxide. Molecules 2019, 24, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-Q.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Geng, J.-C.; Sun, L.-B. Molecular template-directed synthesis of microporous polymer networks for highly selective CO2 capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20340–20349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-C.; Li, J.; Wang, X.-H.; Jing, X.-b.; Wang, F.-S. Synthesis and Characterization of Oligoanilines. Polym. Bull. 2001, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, M.R.; Torkashvand, A.; Ramezanipour Penchah, H.; Ghaemi, A. Amine functionalized benzene based hypercrosslinked polymer as an adsorbent for CO2/N2 adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xia, J.; He, J.; Qi, K.; Peng, A.; Liu, Y. Highly Efficient Capture of Heavy Metal Ions on Amine-Functionalized Porous Polymer Gels. Gels 2023, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, G.; Ni, W.; Shen, L. Preparation and anticorrosive property of soluble aniline tetramer. Coatings 2019, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazulla, M.; Rodrigo, M.; Blasco, E.; Orduña, M. Nitrogen determination by SEM-EDS and elemental analysis. X-ray Spectrom. 2013, 42, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gong, R.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Hu, C.; Tan, B. A new strategy to microporous polymers: Knitting rigid aromatic building blocks by external cross-linker. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2410–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdravkov, B.; Čermák, J.; Šefara, M.; Janků, J. Pore classification in the characterization of porous materials: A perspective. Open Chem. 2007, 5, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M. Physical adsorption characterization of nanoporous materials. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2010, 82, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, E.; Hilal, N.; Henderson, J. Porosity in ancient glass from Syria (c. 800 AD) using gas adsorption and atomic force microscopy. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, G.; Li, Q.; Ai, H.; Yao, X.; Ji, H. Removal of various pollutants from wastewaters using an efficient and degradable hypercrosslinked polymer. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Zhong, L.; Cheung, C.S.; Du, C.; Wu, J.; Du, W.; Zheng, H.; Gao, H. Direct synthesis of hypercrosslinked microporous poly (para-methoxystyrene) for removal of iron (III) ion from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 307, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintola, O.S.; Saleh, T.A.; Khaled, M.M.; Al Hamouz, O.C.S. Removal of mercury (II) via a novel series of cross-linked polydithiocarbamates. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 60, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Xi, C.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, F. Adsorption and removal of mercury (II) by a crosslinked hyperbranched polymer modified via sulfhydryl. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12231–12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Adsorbent | Nitrogen Adsorption–Desorption Isotherm | EDS Elemental Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | BET Pore Width (nm) | BJH Pore Diameter (nm) | C | O | N | Cl | |
| PAB | 987 | 0.908 | 3.681 | 4.960 | 86.6 | 8.3 | 4.8 | 0.4 |
| Adsorbent | TGA | d-TGA | DTA | DSC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step | Temp. (°C) | Mass Loss (%) | Temp. (°C) | Temp. (°C) | ||
| PAB | 1 | 25–125 | 2.9 | 74 | 61, endo | 365 °C, exothermic |
| 2 | 126–280 | 4.4 | 195 | 293, exo | ||
| 3 | 281–780 | 28.3 | 420, 526 | 556, exo | ||
| Residue | 1000 | 43 | - | - | ||
| qe, exp. (mg/g) | PFO | PSO | IPD | LFD | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe, calc. (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (min−1) | qe, calc. (mg/g) | h (mg/(g·min) | R2 | kid (mg/g·min0.5) | Cid (mg/g) | R2 | kfd (min−1) | Cfd (mg/g) | R2 | |
| 99.75 | 0.579 | 99.04 | 0.999 | 0.030 | 98.84 | 293 | 0.999 | 6.484 | 46.71 | 0.468 | 0.032 | 3.19 | 0.836 |
| Temp. (K) | ln Kd | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol·K) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 1.85 | −4.41 | 32.39 | 123.48 | 0.977 |
| 308 | 2.09 | −5.64 | |||
| 318 | 2.60 | −6.88 | |||
| 328 | 3.02 | −8.11 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Adsorption Conditions | Kinetic Model | Mechanism | Ref. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCP Adsorbent | SSA | Pore Type | Dose (g/L) | Metal Ion | Conc. (mg/L) | Capacity (qe; mg/g) | Time (min) | pH | Temp. (°C) | |||
| Polystyrene- based HCP | 854 | Meso and micro | - | Cd2+ | 120 | 822 | 90 | 7 | 20 | PFO | physical | [28] |
| Polystyrene- based HCP | 824 | Meso and micro | - | Ni2+ | 51 | 162 | 24 h | 7 | 60 | - | physical | [20] |
| Pb2+ | 80 | 137 | 24 h | 7 | ||||||||
| HTC-HCP | 168 | Meso and micro | 1.0 | Pb2+ | 100 | 178 | 80 | 7 | 25 | - | - | [47] |
| Cd2+ | 70 | 45 | - | |||||||||
| HCPMOS | 813 | micro | 0.5 | Fe3+ | 10 | 13 | 1000 | 7 | 25 | PSO | physical | [48] |
| DTCP | 3.9 | - | 1.5 | Hg2+ | 40 | 30 | 40 | 5 | 50 | PSO | physical | [49] |
| CHAP-SH | 1.9 | - | 1.0 | Hg2+ | 300 | 237 | 100 | 4.5 | 25 | PSO | chemical | [50] |
| PAB HCPs | 987 | Meso and micro | 0.4 | Hg2+ | 50 | 99 | 120 | 5.5 | 25 | PFO | physical | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljboar, M.T.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Al-Zaben, M.I.; Al-Kahtani, A.; Saeed, W.S. Synthesis of Poly(aniline-co-benzene)-Based Hypercrosslinked Polymer for Hg(II) Ions Removal from Polluted Water: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Water 2023, 15, 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163009
Aljboar MT, Alghamdi AA, Al-Odayni A-B, Al-Zaben MI, Al-Kahtani A, Saeed WS. Synthesis of Poly(aniline-co-benzene)-Based Hypercrosslinked Polymer for Hg(II) Ions Removal from Polluted Water: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Water. 2023; 15(16):3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163009
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljboar, Mashael T., Abdulaziz Ali Alghamdi, Abdel-Basit Al-Odayni, Maha I. Al-Zaben, Abdullah Al-Kahtani, and Waseem Sharaf Saeed. 2023. "Synthesis of Poly(aniline-co-benzene)-Based Hypercrosslinked Polymer for Hg(II) Ions Removal from Polluted Water: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies" Water 15, no. 16: 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163009
APA StyleAljboar, M. T., Alghamdi, A. A., Al-Odayni, A.-B., Al-Zaben, M. I., Al-Kahtani, A., & Saeed, W. S. (2023). Synthesis of Poly(aniline-co-benzene)-Based Hypercrosslinked Polymer for Hg(II) Ions Removal from Polluted Water: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Water, 15(16), 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163009










