Characterization of the Nitrogen Removal Potential of Two Newly Isolated Acinetobacter Strains under Low Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Temperature Characteristics
2.3. Estimation of Nitrogen Removal Capacity
2.4. Gas Detection in Sealed Serum Bottles
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Graphical Work
2.7. Genome Sequence and Analysis
3. Results
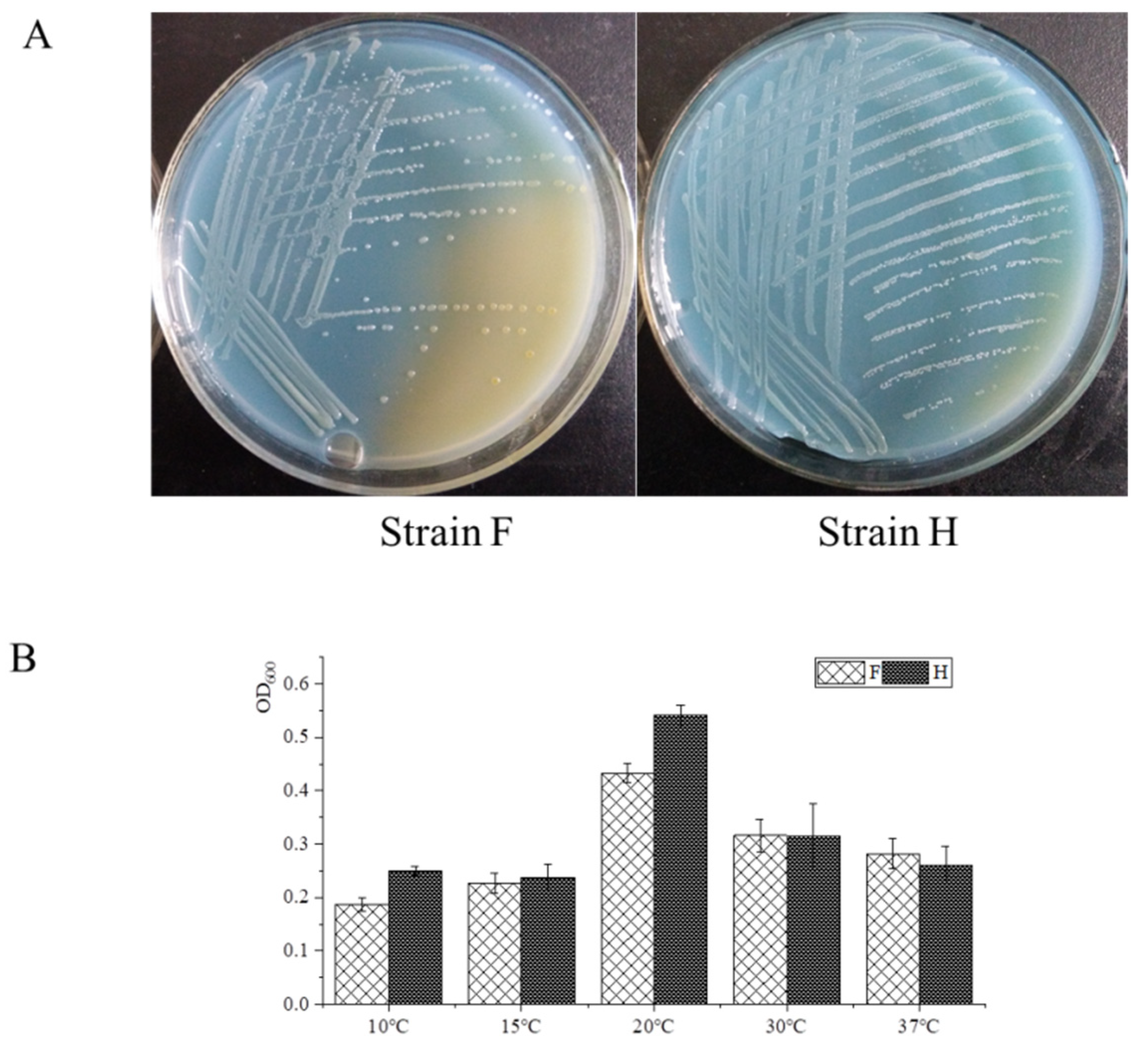
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of Strains F and H
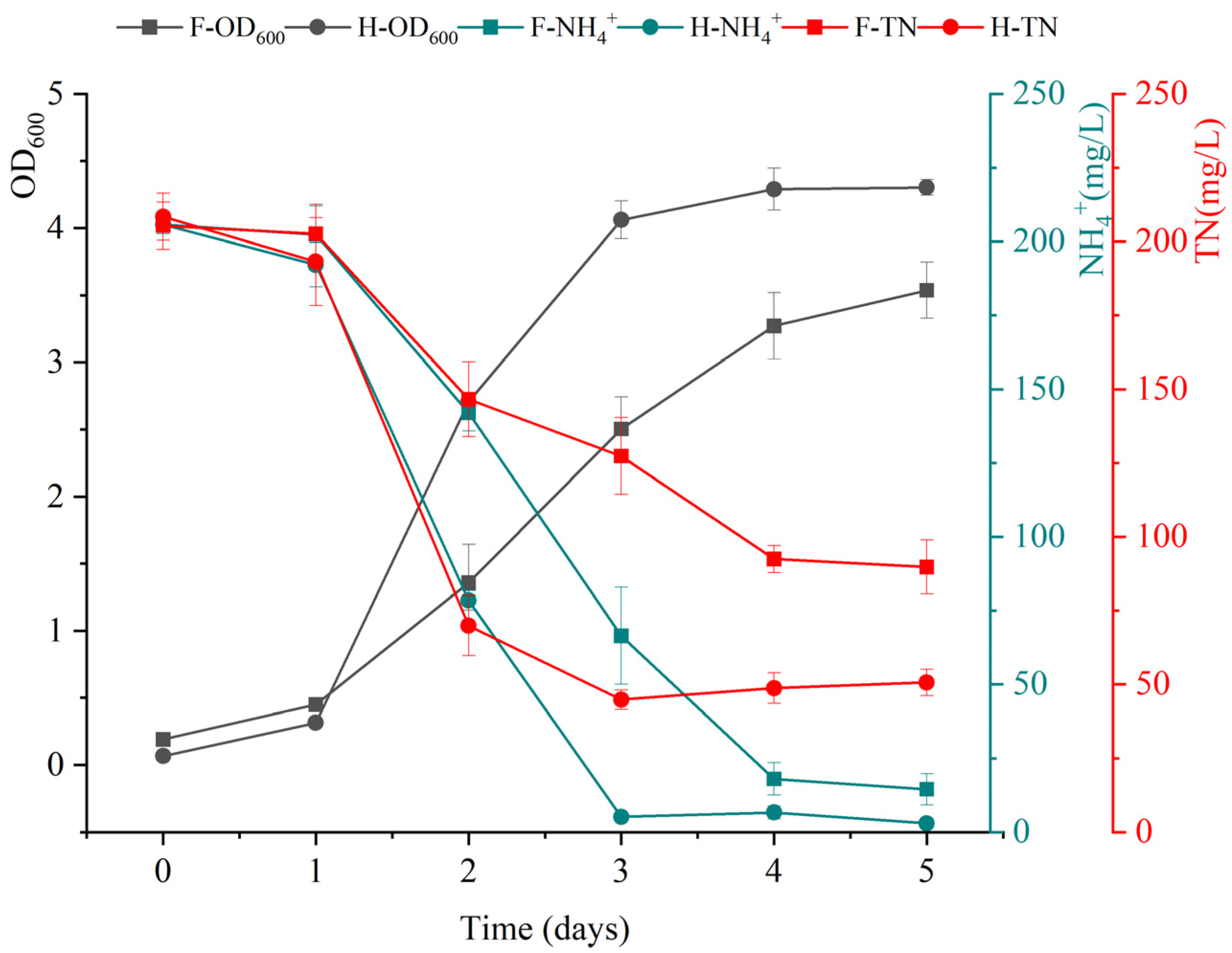
3.2. Evaluation of the Removal Capability of Ammonium
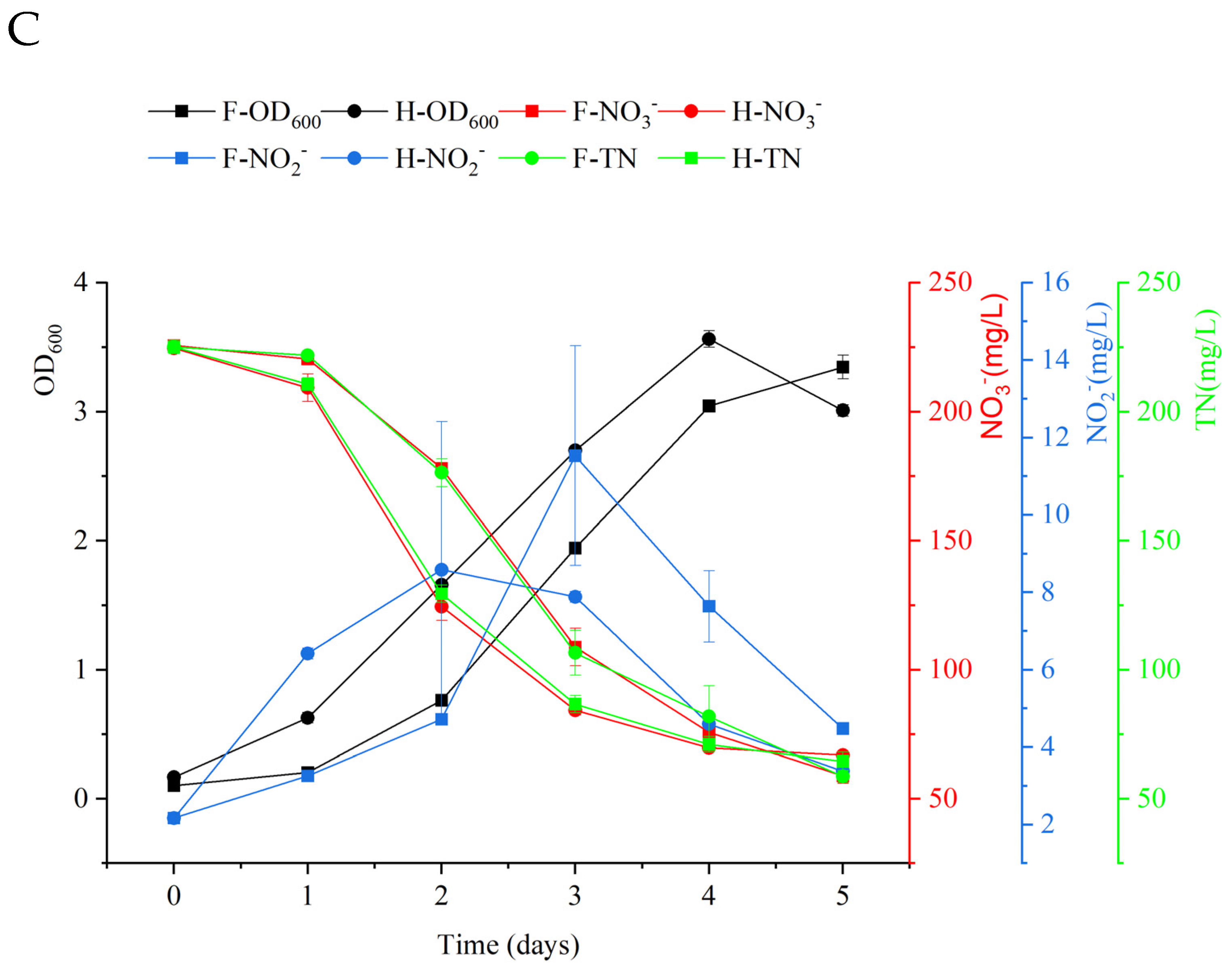
3.3. Evaluation of the Removal Capability of Nitrite and Nitrate
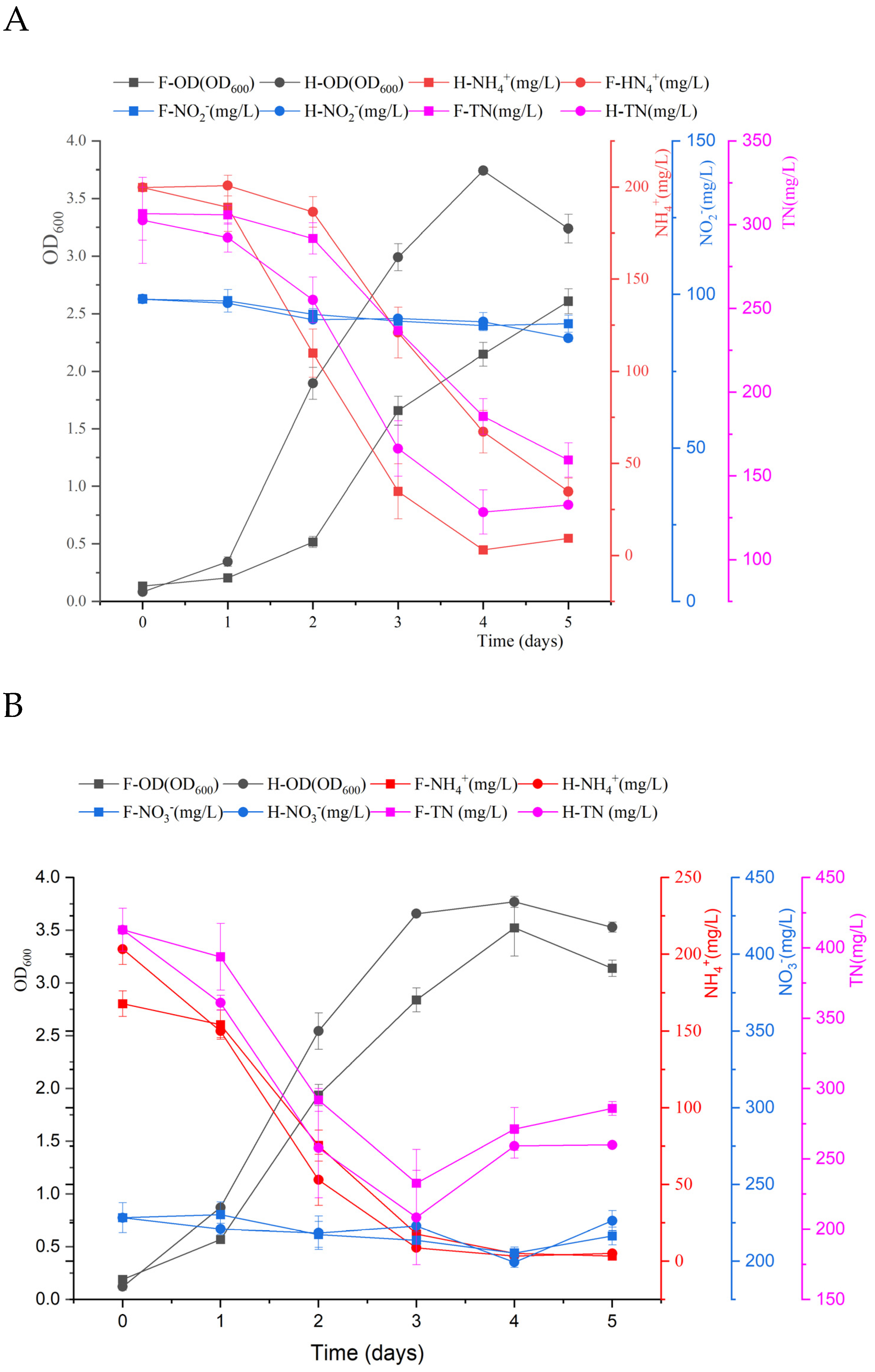
3.4. Characterization of Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium–Nitrite and Ammonium–Nitrate
3.5. Genetic Investigation of the Nitrogen Removal Potential in Strains F and H
3.6. Pathogenic Potential and Antibiotic Resistance Gene Risk Analysis of Both Strains
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romanelli, A.; Soto, D.X.; Matiatos, I.; Martínez, D.E.; Esquius, S. A biological and nitrate isotopic assessment framework to understand eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khardenavis, A.A.; Kapley, A.; Purohit, H.J. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification by diverse Diaphorobacter sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khin, T.; Annachhatre, A.P. Novel microbial nitrogen removal processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2004, 22, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.A.; Van Niel, E.W.; Torremans, R.A.; Kuenen, J.G. Simultaneous Nitrification and denitrification in aerobic chemostat cultures of Thiosphaera pantotropha. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 2812–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Wong, M.H.; Hu, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Li, S. A study on the nitrogen removal efficacy of bacterium Acinetobacter tandoii MZ-5 from a contaminated river of Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbaendert, I.; De Vos, P.; Boon, N.; Heylen, K. Denitrification in Gram-positive bacteria: An underexplored trait. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.L.; Zhou, S.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhou, N.; Guo, L.; Di, S.Y.; Zhou, Z.Z. Nitrogen removal from micro-polluted reservoir water by indigenous aerobic denitrifiers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8008–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yang, J.; Ma, F.; Pi, S.; Xing, L.; Li, A. Characterisation of Pseudomonas stutzeri T13 for aerobic denitrification: Stoichiometry and reaction kinetics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 135181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Lyu, Y.K. Ammonium removal characteristics of an acid-resistant bacterium Acinetobacter sp. JR1 from pharmaceutical wastewater capable of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, M.; Ishikawa, Y. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification of high-strength ammonium in anaerobically digested sludge by Alcaligenes faecalis strain No. 4. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cui, Y.W.; Huang, J.L. A novel halophilic Exiguobacterium mexicanum strain removes nitrogen from saline wastewater via heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; He, Y.L.; Hughes, J.; Zhang, X.F. Heterotrophic nitrogen removal by a newly isolated Acinetobacter calcoaceticus HNR. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5194–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Yao, S.; Ni, J. High-efficient nitrogen removal by coupling enriched autotrophic-nitrification and aerobic-denitrification consortiums at cold temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Camargo, J.A. Effects of pulse duration and post-exposure period on the nitrite toxicity to a freshwater amphipod. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 2005–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, T.; Shi, Y.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, Z.; Shi, G. The nitrogen removal characterization of a cold-adapted bacterium: Bacillus simplex H-b. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Ai, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by a novel Acinetobacter sp. TAC-1 at low temperature and high ammonia nitrogen. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, G.M.; Wu, M.R.; Li, S.S.; Miao, L.L.; Liu, Z.P. Photobacterium sp. NNA4, an efficient hydroxylamine-transforming heterotrophic nitrifier/aerobic denitrifier. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Li, Z.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ye, Q. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by Pseudomonas tolaasii Y-11 without nitrite accumulation during nitrogen conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Environmental Bureau. Methods for the Analysis of Water and Wastewater; Chinese Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, P.R.; Bhunia, P.; Dash, R.R. Simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorous from domestic wastewater using Bacillus cereus GS-5 strain exhibiting heterotrophic nitrification, aerobic denitrification and denitrifying phosphorous removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Liu, C.; Tang, S.Q.; Guo, T.T.; Pan, L.; Xue, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.G. Characterization of Acinetobacter indicus ZJB20129 for heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification isolated from an urban sewage treatment plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ren, Y.X.; Liang, X.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wang, J.P.; Xia, Z.H. Nitrogen removal characteristics of a heterotrophic nitrifier Acinetobacter junii YB and its potential application for the treatment of high-strength nitrogenous wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Qin, W. Ammonium removal by a novel oligotrophic Acinetobacter sp. Y16 capable of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bru, D.; Sarr, A.; Philippot, L. Relative abundances of proteobacterial membrane-bound and periplasmic nitrate reductases in selected environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5971–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Kang, P.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J.; Jia, J.; Yan, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. Paracoccus versutus KS293 adaptation to aerobic and anaerobic denitrification: Insights from nitrogen removal, functional gene abundance, and proteomic profiling analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.L.; Chen, H.; Lv, Y.K. Nitrate removal performances of a new aerobic denitrifier, Acinetobacter haemolyticus ZYL, isolated from domestic wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Deng, Y. Insights into heterotrophic denitrification diversity in wastewater treatment systems: Progress and future prospects based on different carbon sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Name | Composition (/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NM medium | 7.0 g K2HPO4, 3.0 g KH2PO4, 0.1 g MgSO4·7H2O, 1.0 g (NH4)2SO4, 0.05 g FeSO4·7H2O and 10 g CH3COONa | [18] |
| 2 | DM medium | 7.0 g K2HPO4, 3.0 g KH2PO4, 0.1 g MgSO4·7H2O, 1.8 g KNO3 (DM-1) or 0.986 g NaNO2 (DM-2), 0.05 g FeSO4·7H2O and 10 g CH3COONa | |
| 3 | SND medium | 7.0 g K2HPO4, 3.0 g KH2PO4, 0.1 g MgSO4·7H2O, 1.0 g (NH4)2SO4, 1.8 g KNO3 (SND-1) or 0.986 g NaNO2 (SND-2), 0.05 g FeSO4·7H2O and 10 g CH3COONa |
| Strain/Strains | KCTC23199 | LMG003 | NIPH 3 | IC001 | ACws19 | CIP 64.6 | LXL-C1 | M19 | SH046 | XBB-1 | F | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCTC23199 | 0.000 | 0.022 | 0.163 | 0.523 | 0.518 | 0.520 | 0.520 | 0.514 | 0.510 | 0.514 | 0.504 | 0.132 |
| LMG 1003 | 0.022 | 0.000 | 0.175 | 0.531 | 0.526 | 0.527 | 0.528 | 0.522 | 0.515 | 0.522 | 0.513 | 0.147 |
| NIPH 3 | 0.163 | 0.175 | 0.000 | 0.527 | 0.526 | 0.526 | 0.528 | 0.523 | 0.513 | 0.522 | 0.513 | 0.110 |
| IC001 | 0.523 | 0.531 | 0.527 | 0.000 | 0.190 | 0.207 | 0.198 | 0.204 | 0.199 | 0.185 | 0.188 | 0.529 |
| ACws19 | 0.518 | 0.526 | 0.526 | 0.190 | 0.000 | 0.185 | 0.177 | 0.175 | 0.185 | 0.162 | 0.161 | 0.520 |
| CIP.64.6 | 0.520 | 0.527 | 0.526 | 0.207 | 0.185 | 0.000 | 0.189 | 0.200 | 0.199 | 0.187 | 0.190 | 0.523 |
| LXL-C1 | 0.520 | 0.528 | 0.528 | 0.198 | 0.177 | 0.189 | 0.000 | 0.184 | 0.193 | 0.166 | 0.170 | 0.523 |
| M19 | 0.514 | 0.522 | 0.523 | 0.204 | 0.175 | 0.200 | 0.184 | 0.000 | 0.196 | 0.105 | 0.080 | 0.517 |
| SH046 | 0.510 | 0.515 | 0.513 | 0.199 | 0.185 | 0.199 | 0.193 | 0.196 | 0.000 | 0.181 | 0.178 | 0.515 |
| XBB-1 | 0.514 | 0.522 | 0.522 | 0.185 | 0.162 | 0.187 | 0.166 | 0.105 | 0.181 | 0.000 | 0.083 | 0.516 |
| F | 0.504 | 0.513 | 0.513 | 0.188 | 0.161 | 0.190 | 0.170 | 0.080 | 0.178 | 0.083 | 0.000 | 0.508 |
| H | 0.132 | 0.147 | 0.110 | 0.529 | 0.520 | 0.523 | 0.523 | 0.517 | 0.515 | 0.516 | 0.508 | 0.000 |
| Length (aa) | Hit_Name | Hit_Description | e Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| contig69_3190 | 179 | SEM34325.1 | Hypothetical protein SAMN05216500_1256 [Acinetobacter sp. DSM 11652] | 2.90 × 10−71 |
| contig69_3191 | 305 | SEM34356.1 | Protein involved in the initiation of plasmid replication, partial [Acinetobacter sp. DSM 11652] | 3.80 × 10−156 |
| contig69_3192 | 69 | WP_058952608.1 | Hypothetical protein [Acinetobacter johnsonii] | 1.30 × 10−32 |
| contig69_3193 | 536 | WP_057082130.1 | Hypothetical protein, partial [Acinetobacter pittii] | 1.60 × 10−303 |
| contig69_3194 | 249 | WP_086166669.1 | Hypothetical protein [Acinetobacter sp. ANC 4654] | 1.60 × 10−112 |
| contig69_3195 | 78 | WP_086183153.1 | Hypothetical protein [Acinetobacter sp. ANC 4558] | 3.90 × 10−25 |
| contig69_3196 | 250 | WP_075041359.1 | Hypothetical protein [Acinetobacter radioresistens] | 1.50 × 10−139 |
| contig69_3197 | 68 | WP_075041358.1 | Hypothetical protein [Acinetobacter radioresistens] | 6.00 × 10−30 |
| contig69_3198 | 583 | KQE20847.1 | Hypothetical protein APD38_11590 [Acinetobacter pittii] | 0 |
| contig69_3199 | 79 | ALJ89856.1 | Hypothetical protein AN415_8035 (plasmid) [Acinetobacter baumannii] | 7.00 × 10−38 |
| contig69_3200 | 95 | WP_068553177.1 | Hypothetical protein [Acinetobacter pittii] | 6.80 × 10−48 |
| contig69_3201 | 495 | WP_032002906.1 | Sodium-independent anion transporter [Acinetobacter baumannii] | 3.10 × 10−261 |
| contig69_3202 | 283 | WP_065033555.1 | Universal stress protein [Acinetobacter baumannii] | 1.50 × 10−154 |
| contig69_3203 | 203 | WP_065033561.1 | Resolvase [Acinetobacter baumannii] | 1.30 × 10−101 |
| contig69_3204 | 294 | WP_043974506.1 | Mph(E)/Mph(G) family macrolide 2′-phosphotransferase [Acinetobacter sp. NBRC 110496] | 4.70 × 10−164 |
| contig69_3205 | 491 | WP_031976859.1 | Msr family ABC-F type ribosomal protection protein [Acinetobacter baumannii] EXC89516.1 | 2.80 × 10−270 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Xia, H. Characterization of the Nitrogen Removal Potential of Two Newly Isolated Acinetobacter Strains under Low Temperature. Water 2023, 15, 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162990
Zhong Y, Xia H. Characterization of the Nitrogen Removal Potential of Two Newly Isolated Acinetobacter Strains under Low Temperature. Water. 2023; 15(16):2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162990
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yongjun, and Haiyang Xia. 2023. "Characterization of the Nitrogen Removal Potential of Two Newly Isolated Acinetobacter Strains under Low Temperature" Water 15, no. 16: 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162990
APA StyleZhong, Y., & Xia, H. (2023). Characterization of the Nitrogen Removal Potential of Two Newly Isolated Acinetobacter Strains under Low Temperature. Water, 15(16), 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162990






