Groundwater Quality Assessment for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes at Al-Jouf Area in KSA Using Artificial Neural Network, GIS, and Multivariate Statistical Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
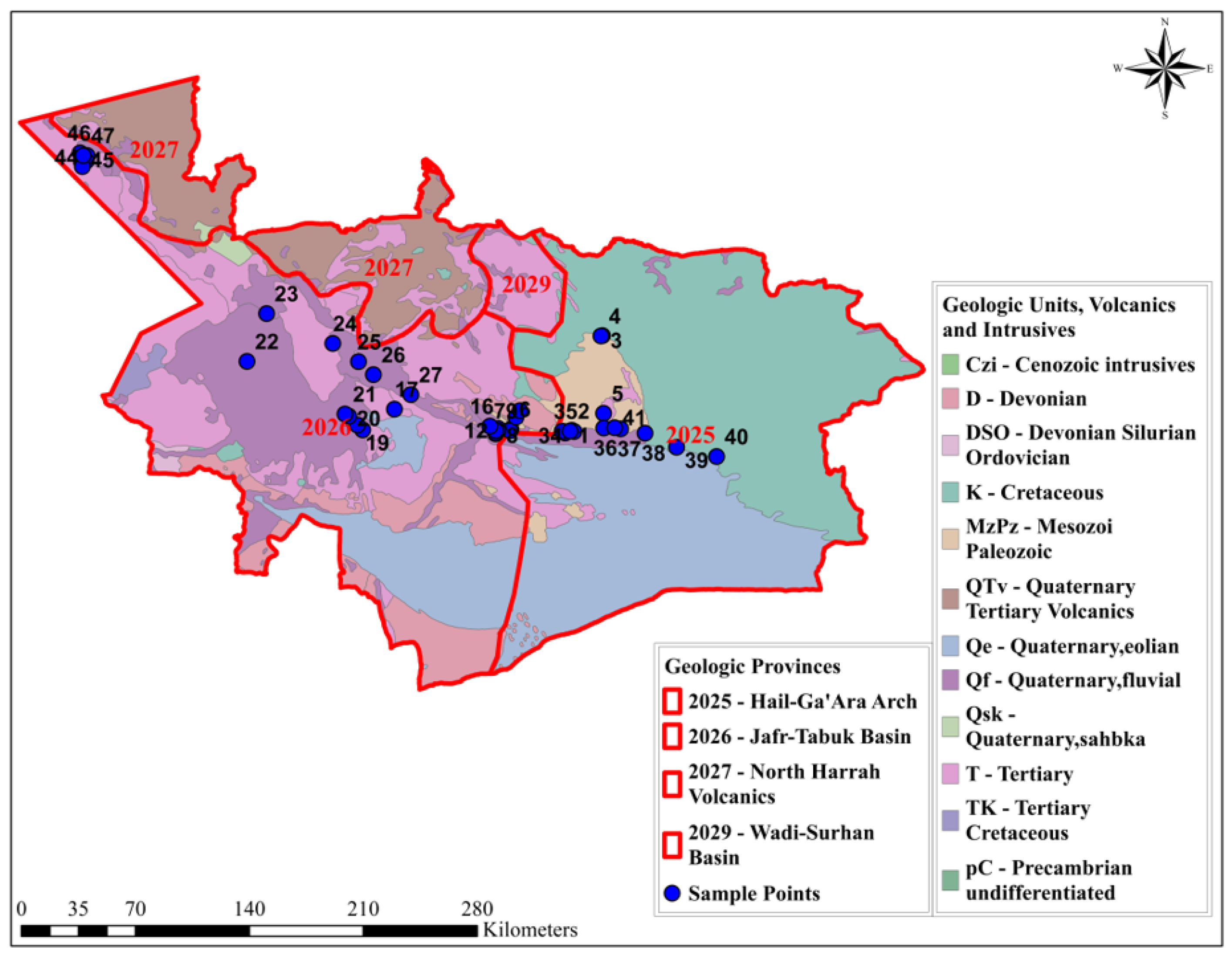
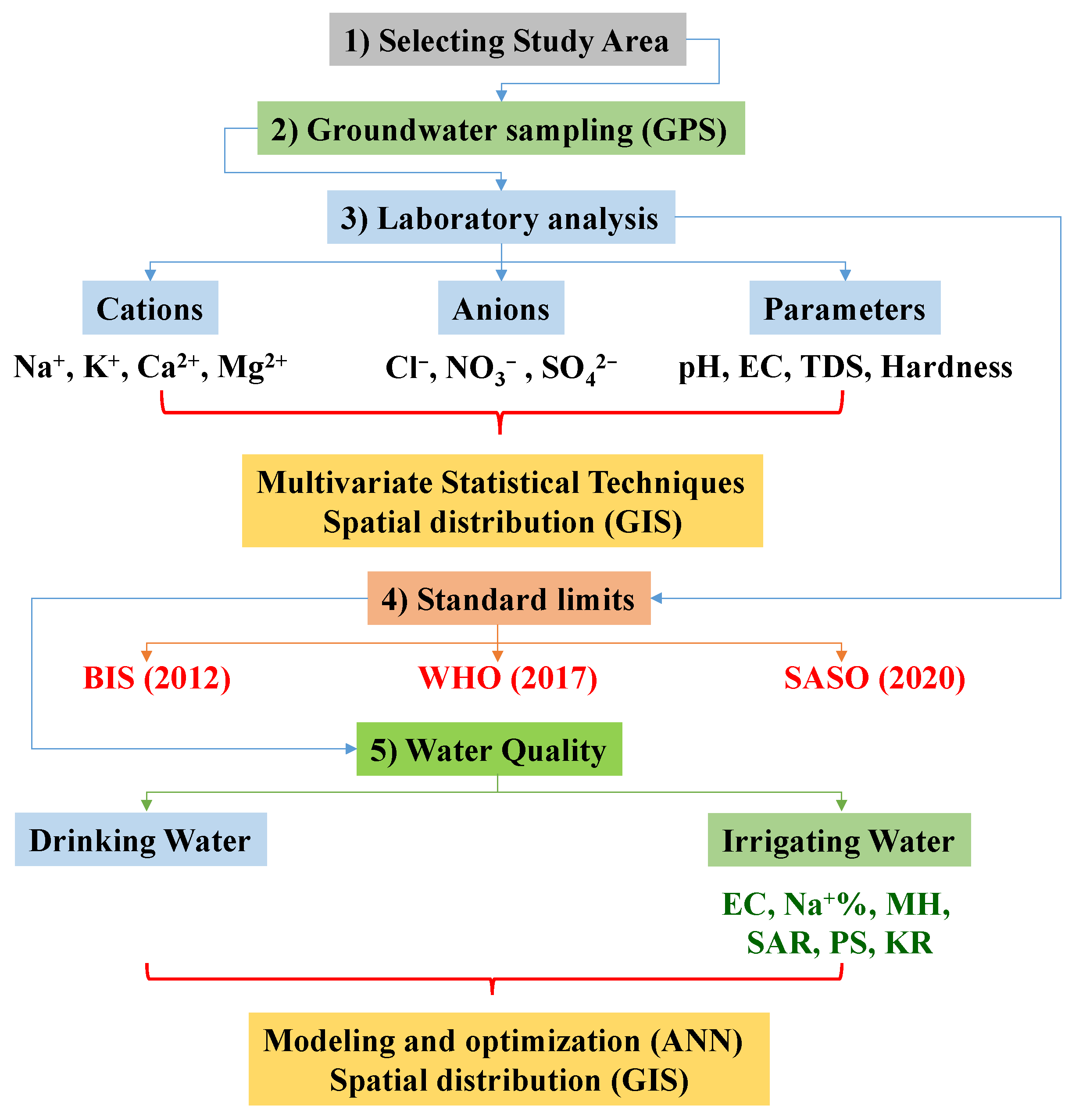
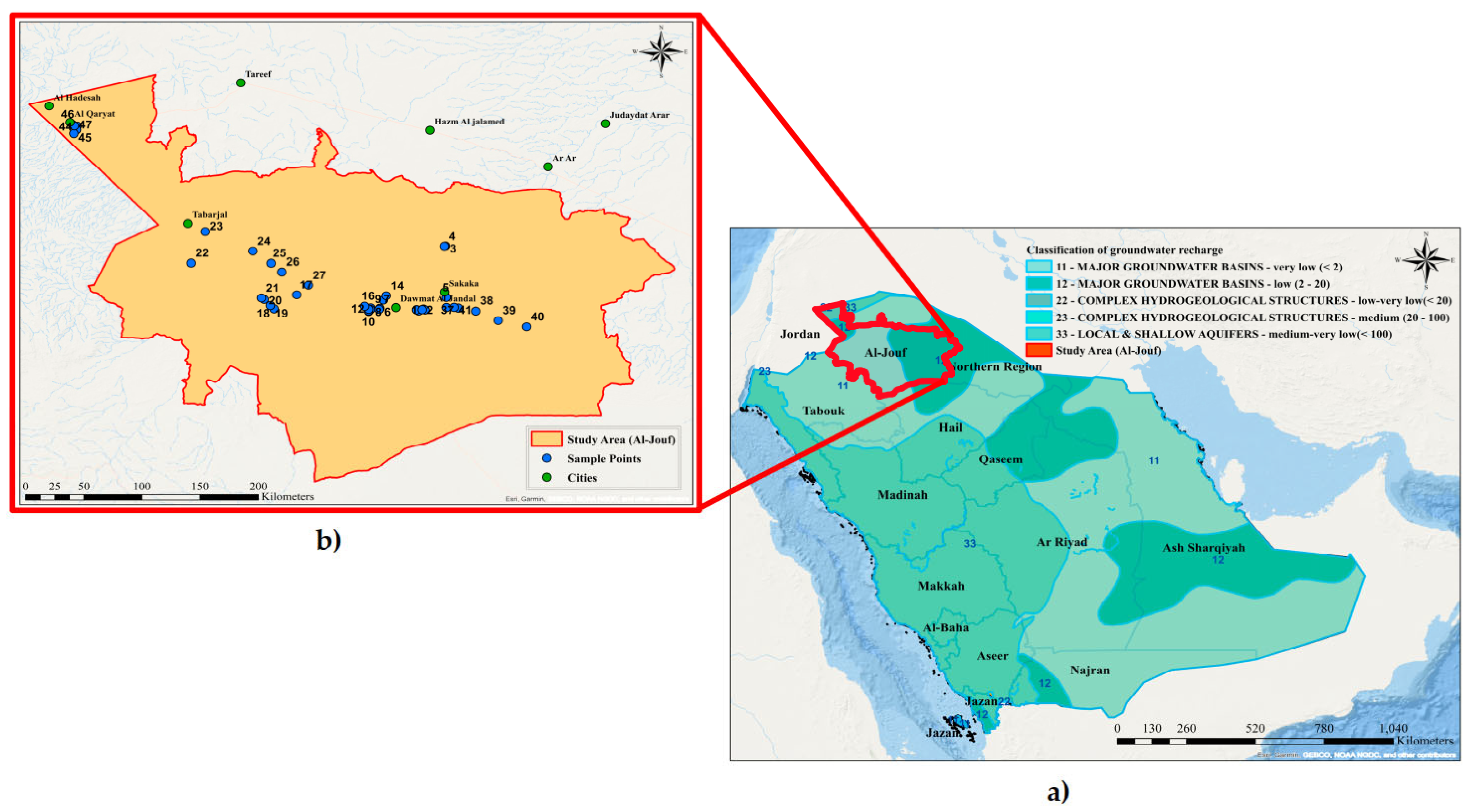
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.2. Water Quality Index
2.2.1. Drinking Purpose
2.2.2. Irrigation Purpose
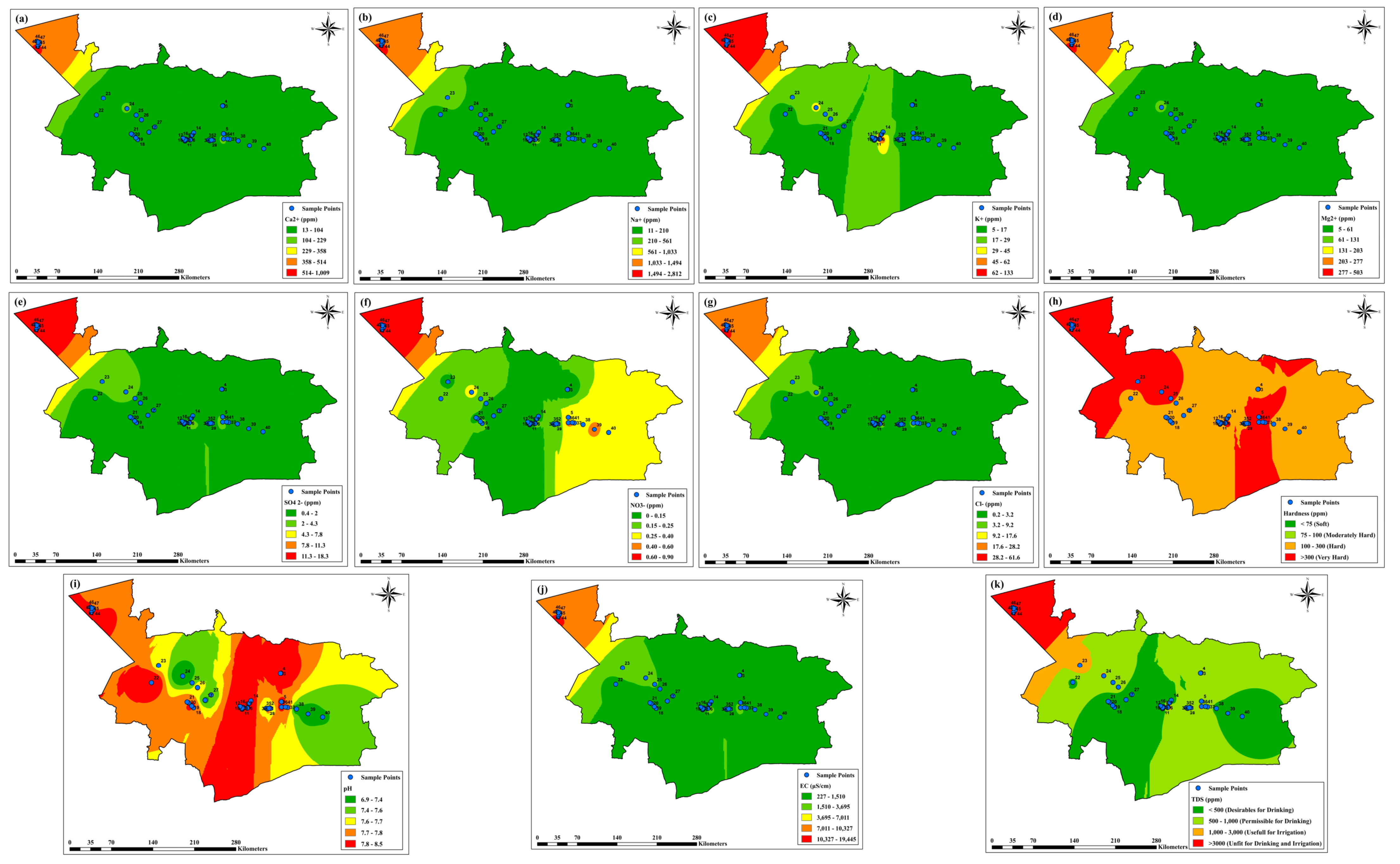
2.3. Data Analysis Utilizing GIS
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Techniques
2.5. Artificial Neural Network
3. Results and Discussion
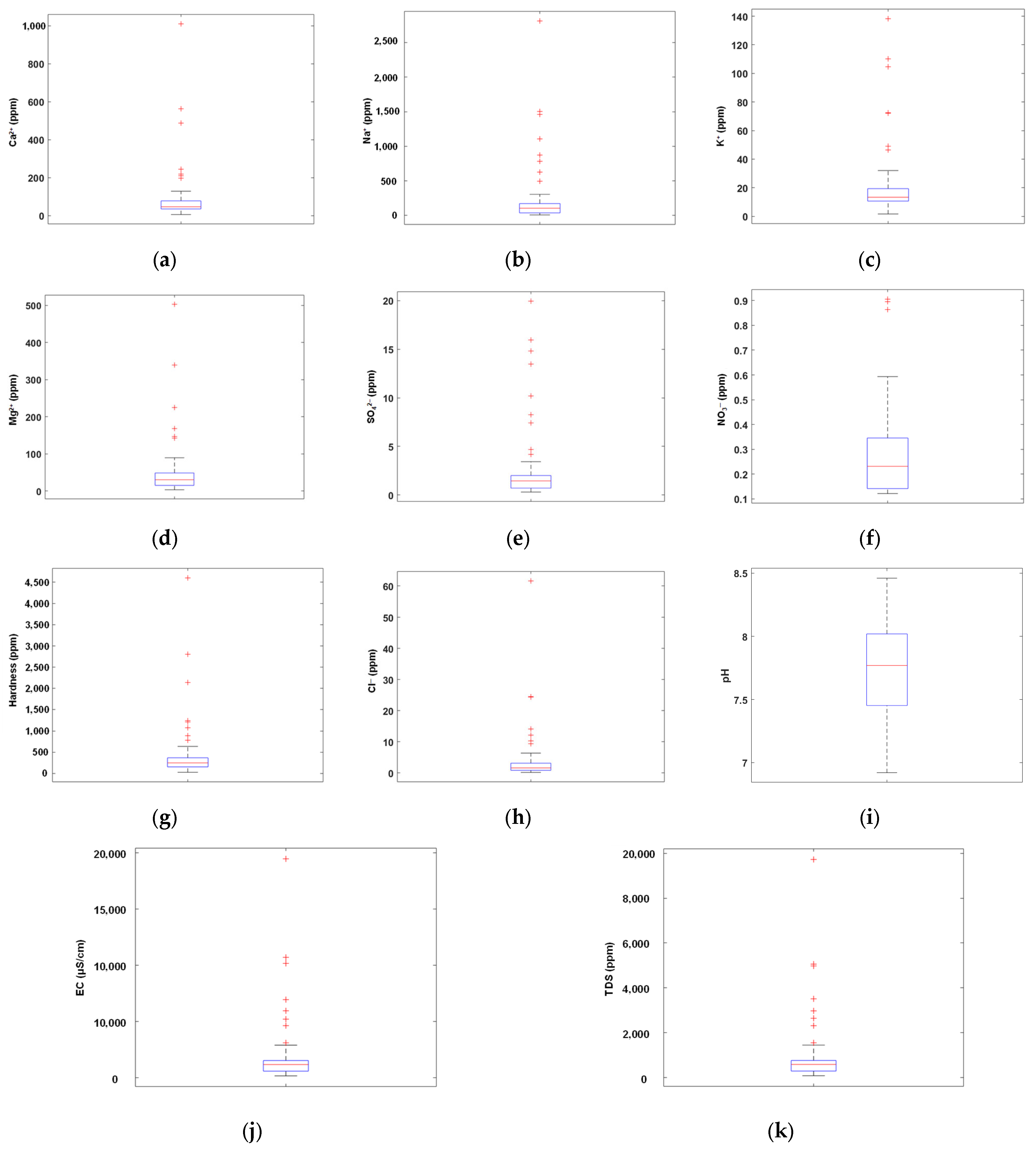
3.1. Groundwater Parameter Analysis
3.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
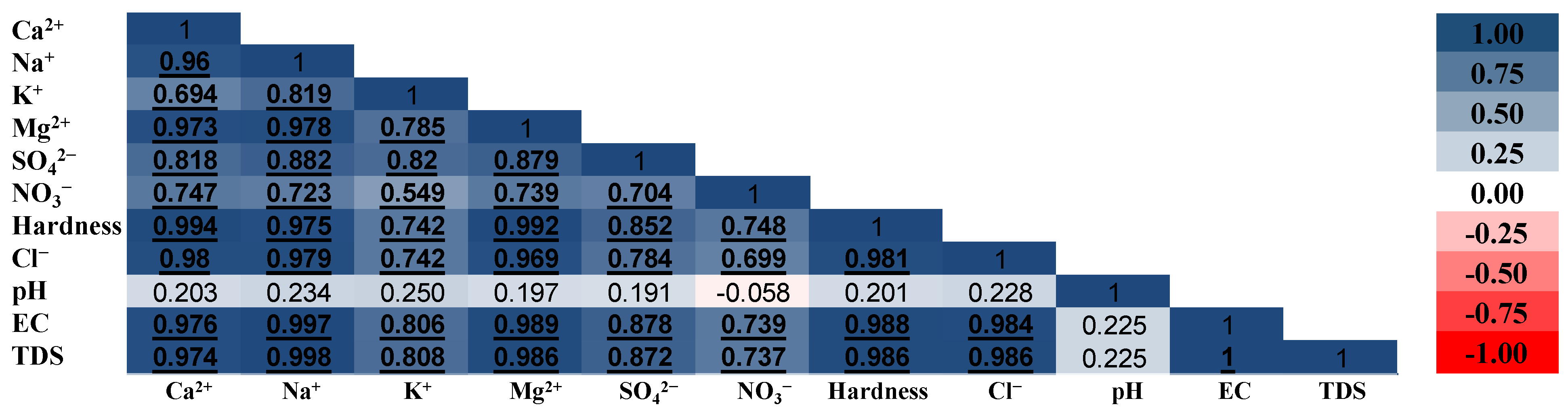
3.2.1. Correlation Analysis
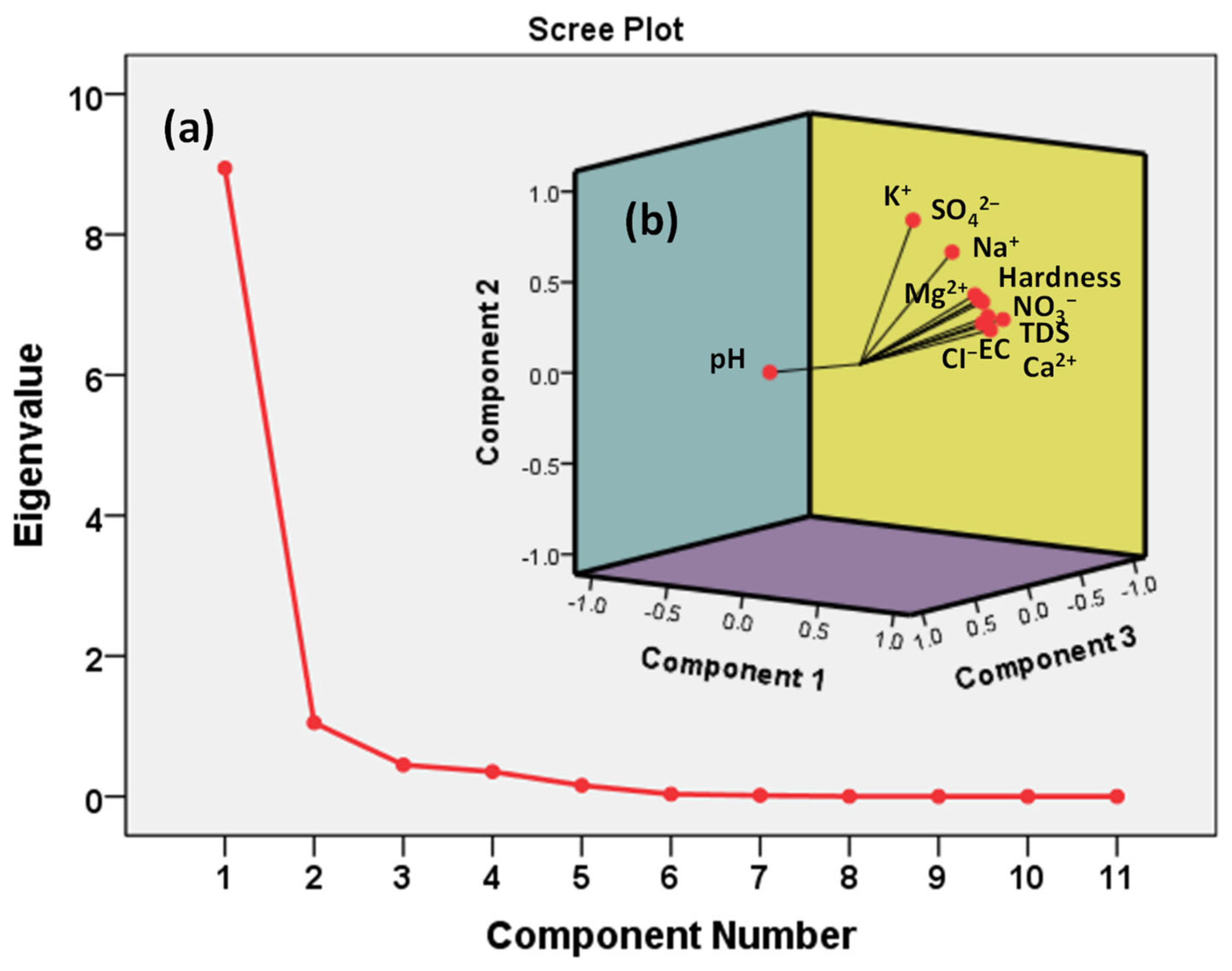
3.2.2. Principal Component Analysis
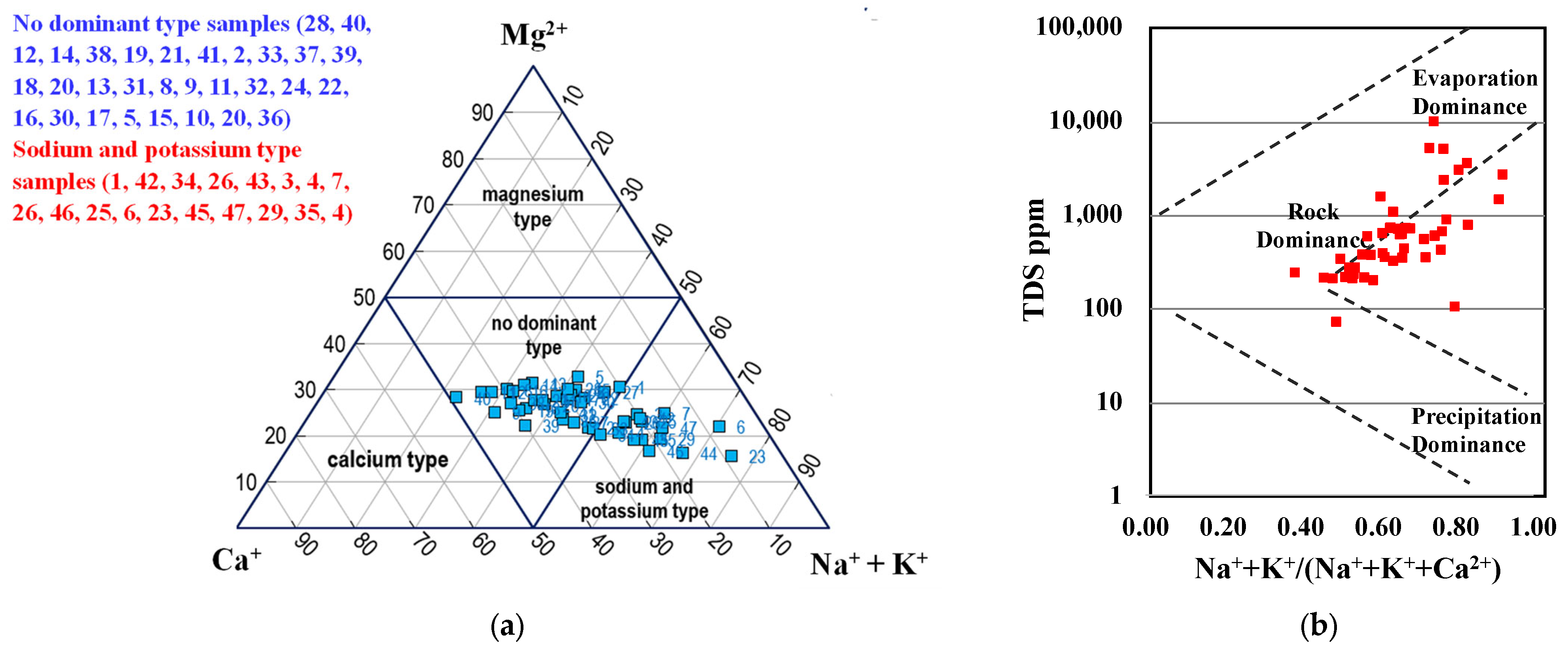
3.2.3. Hydrogeochemical Facies
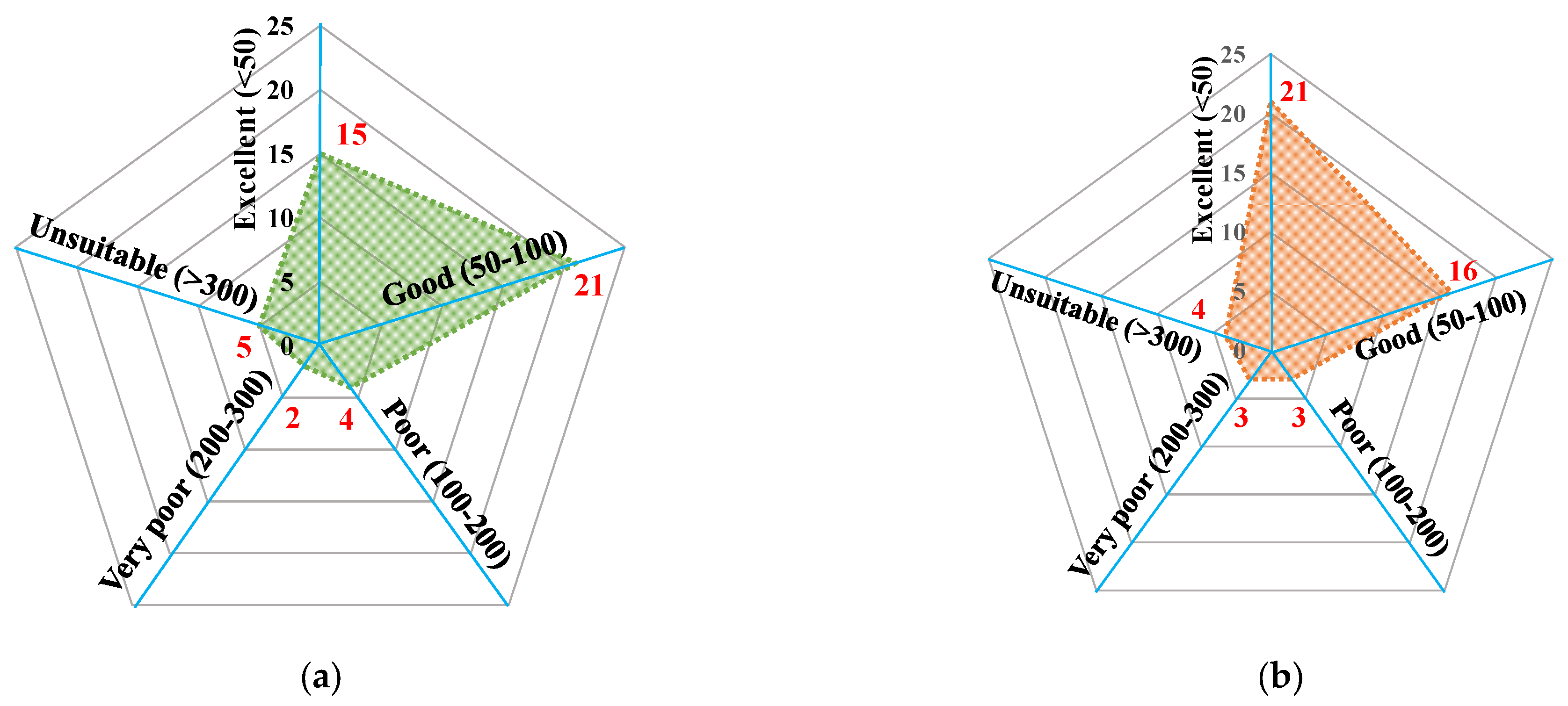
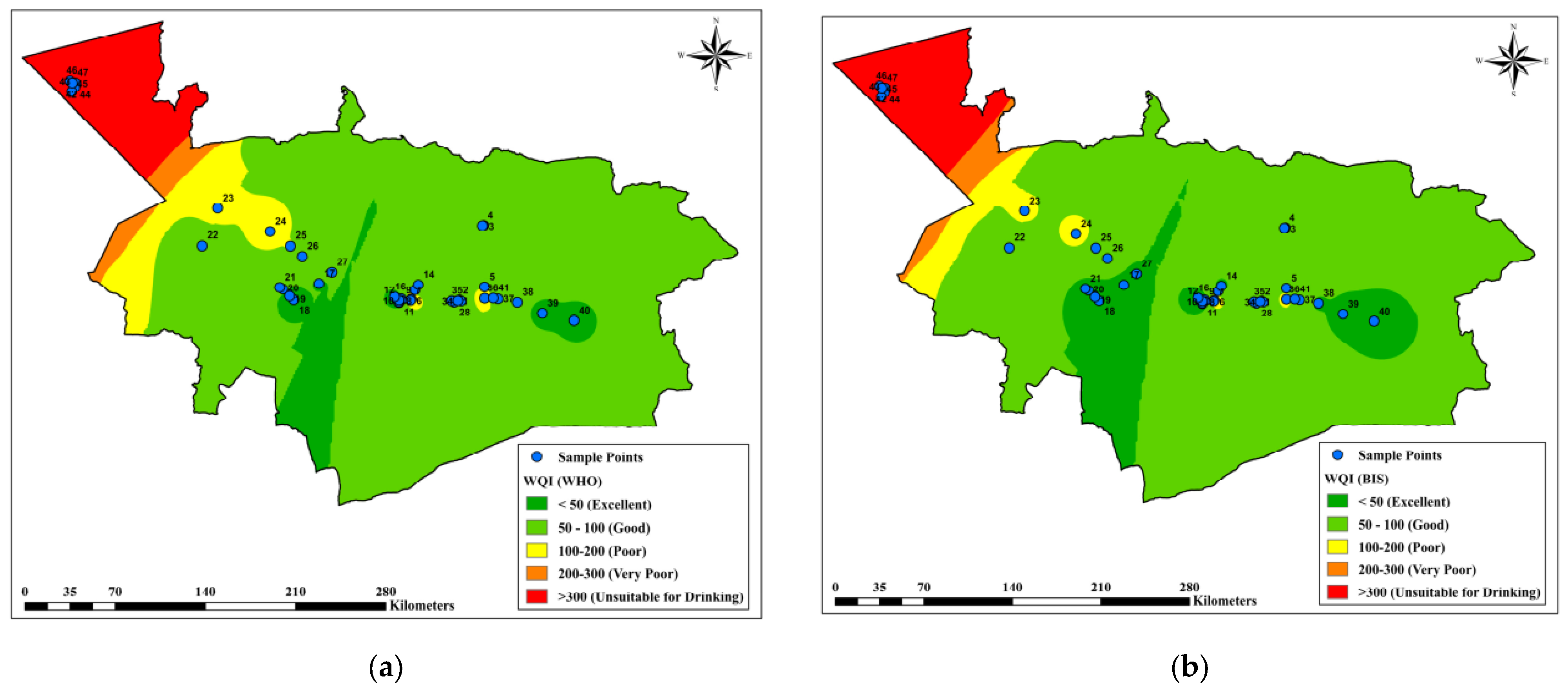
3.3. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Drinking
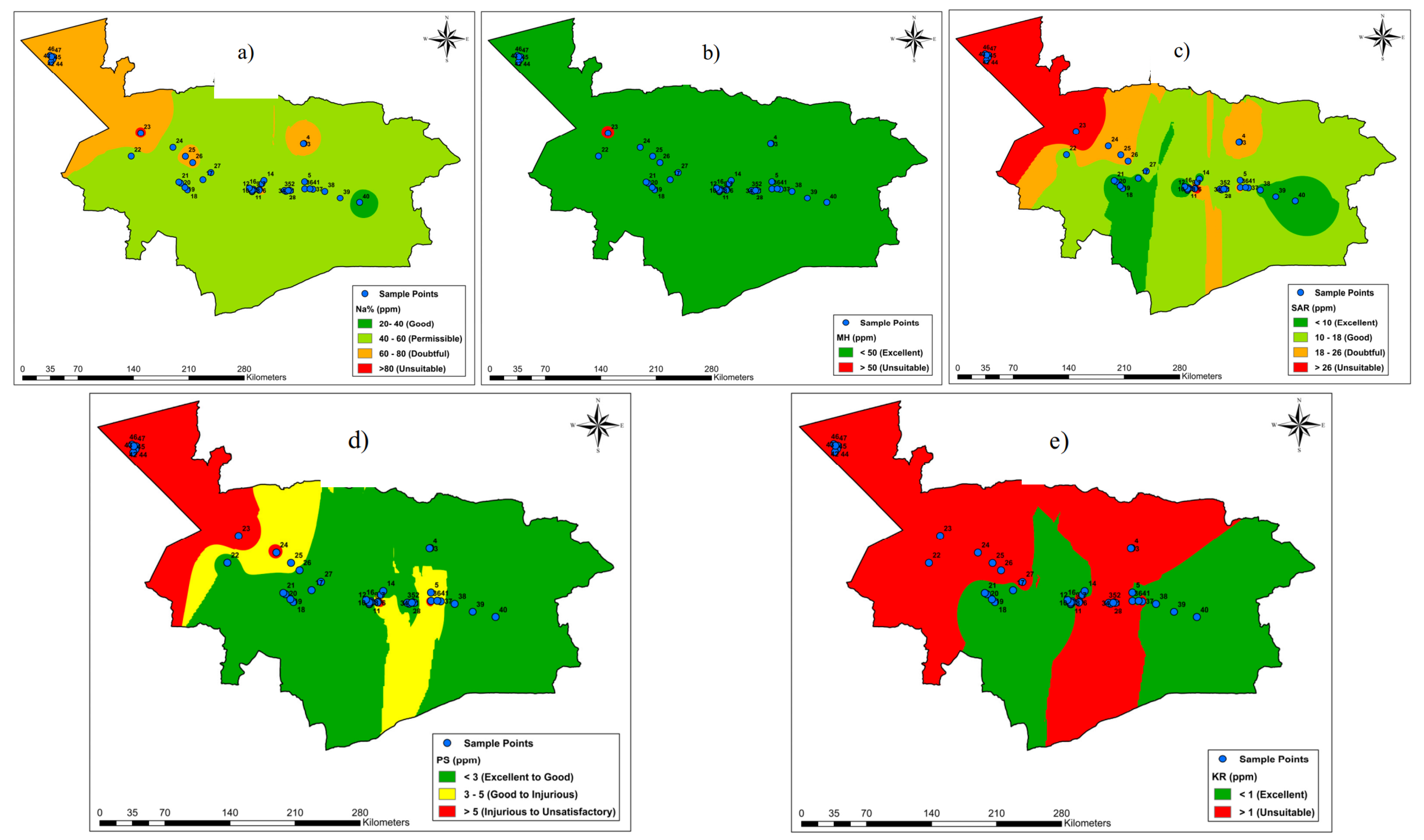
3.4. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation
3.5. Artificial Neural Network
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.Y.A.; El Kashouty, M.; Gusti, W.; Kumar, A.; Subyani, A.M.; Alshehri, A. Geo-temporal signatures of physicochemical and heavy metals pollution in Groundwater of Khulais region—Makkah Province, Saudi Arabia. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Singh, C.K.; AlMesfer, M.K.; Singh, V.P.; Alsubih, M. Groundwater quality studies in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Prevalent research and management dimensions. Water 2021, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Abu Abdullah, M.M.; Pradhan, B.; Gaber, A.F.D. Agriculture sprawl assessment using multi-temporal remote sensing images and its environmental impact; Al-Jouf, KSA. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaggar, A.K.A. Investigation of some physical, chemical, and bacteriological parameters of water quality in some dams in Albaha region, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4605–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, M.; El Osta, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Ezzeldin, H. Application of Environmental Isotopes and Hydrochemistry to Identify the Groundwater Recharge in Wadi Qanunah Basin, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najah, A.; Teo, F.Y.; Chow, M.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Latif, S.D.; Abdullah, S.; Ismail, M.; El-Shafie, A. Surface water quality status and prediction during movement control operation order under COVID-19 pandemic: Case studies in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunanidhi, D.; Subramani, T.; Roy, P.D.; Li, H. Impact of groundwater contamination on human health. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar, R.; Asghari Moghaddam, A.; Adamowski, J.; Nazemi, A.H. Assessing the potential origins and human health risks of trace elements in groundwater: A case study in the Khoy plain, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 981–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollaro, C.; Fuoco, I.; Gennaro, E.; Giuliani, L.; Iezzi, G.; Marini, L.; Radica, F.; Di Luccio, F.; Ventura, G.; Vespasiano, G. Advanced argillic alteration at Cave di Caolino, Lipari, Aeolian Islands (Italy): Implications for the mitigation of volcanic risks and the exploitation of geothermal resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 889, 164333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, I.; Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Brozzo, G.; De Rosa, R.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Geochemical modeling of chromium release in natural waters and treatment by RO/NF membrane processes. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Biswas, B.; Verghese, S. Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purpose using geospatial and statistical techniques in a semi-arid region of Rajasthan, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2021, 97, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, N.S.; Krishnakumar, S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Soundranayagam, J.P. Groundwater quality assessment using WQI and GIS techniques, Dindigul district, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4179–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N. Groundwater quality from a part of Prakasam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, P.; Qian, H. Assessment of groundwater quality and human health risk (HHR) evaluation of nitrate in the Central-Western Guanzhong Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.K.; Liu, D.; Song, K.; Mohamed, M.A.A.; Aldaw, E.; Elubid, B.A. Hydrochemical analysis and fuzzy logic method for evaluation of groundwater quality in the North Chengdu Plain, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IS 10500; BIS Drinking Water-Specification. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 2012.
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the Frst Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- SASO. Technical Regulation for Water Rationalization Tools Version (1)—Amendment (1); Official Gazette (06-04-16-156), Saudi Standards; Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO): Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chidiac, S.; El Najjar, P.; Ouaini, N.; El Rayess, Y.; El Azzi, D. A comprehensive review of water quality indices (WQIs): History, models, attempts and perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2023, 22, 349–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouser, B.; Bala, A.; Verma, O.; Prashanth, M.; Khosla, A.; Pir, R.A. Hydrochemistry for the assessment of groundwater quality in the Kathua region, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, R.; Ayyavoo, R.; Rajangam, L.; Madasamy, N.; Murugaiyan, B.; Shanmugam, S. Comparative Analysis of Groundwater Quality Index for Bhavani River Basin Using Remote Sensing and Statistical Analysis. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 17, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maghraby, M.; Bamousa, A.O. Evaluation of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using physicochemical parameters at Salilah area, Madinah Munawarah District, Saudi Arabia. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2021, 15, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhababy, A.M.; Al-Rajab, A.J. Groundwater quality assessment in Jazan region, Saudi Arabia. Curr. World Environ. J. 2015, 10, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Daiem, M.M.; Hatata, A.; Galal, O.H.; Said, N.; Ahmed, D. Prediction of biogas production from anaerobic Co-digestion of Waste Activated sludge and wheat straw using two-dimensional mathematical models and an artificial neural network. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Daiem, M.M.; Hatata, A.; El-Gohary, E.H.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Said, N. Application of an artificial neural network for the improvement of agricultural drainage water quality using a submerged biofilter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5854–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Daiem, M.M.; Hatata, A.; Said, N. Modeling and optimization of semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of activated sludge and wheat straw using Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous neural network and seagull algorithm. Energy 2022, 241, 122939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrowais, R.; Said, N.; Alotaibi, A.; Hatata, A.; Essa, M.A.; Abdel Daiem, M.M. Comparing the effect of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion for sustainable biogas production: An experimental and recurrent neural network model study. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 392, 136248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.D.; Azmi, M.; Ahmed, A.N.; Fai, C.M.; El-Shafie, A. Application of artificial neural network for forecasting nitrate concentration as a water quality parameter: A case study of Feitsui Reservoir, Taiwan. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodyn. 2020, 15, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, E.-S.A.; Tawfik, R.T.; Alomran, M.S. An Assessment of Irrigation Water Quality with Respect to the Reuse of Treated Wastewater in Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, C.A.; Dini, S.M.; Al-Farasani, A.A. Geological Map of the Wadi as Sirhan Quadrangle, Sheet 30C, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia with Explanatory Notes: Saudi Geological Survey, Geoscience Map, 2000, GM-127C, Scale 1: 250,000. Available online: https://sgs.gov.sa/en/products/geologic-map-of-wadi-as-sirhan-quadrangle-sheet-30ckingdom-of-saudi-arabia-with-explanatory-notes (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Coleman, R.G.; Gregory, R.T.; Brown, G.F. Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks of Saudi Arabia; US Department of the Interior, Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1983; Volume 83.
- Geological Survey (US); Meissner, C.R. Preliminary Geologic Map of the Wadi as Sirhan Quadrangle, Sheet 30C, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1990.
- Pollastro, R.M.; Karshbaum, A.S.; Viger, R.J. Open-File Report 97-470B; US Geological Survey Open File Report 97, 470B; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1997.
- BGR; UNESCO. Groundwater Resources of the World 1: 25 000 000; BGR: Hannover, Germany; UNESCO: Paris, French, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Esri; Garmin; GEBCO; NOAA NGDC; Other Contributors. Oceans Base Map. 2023. Available online: https://services.arcgisonline.com/ArcGIS/rest/services/Ocean/World_Ocean_Base/MapServer (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Szabolcs, I.; Darab, C. The Influence of Irrigation Water of High Sodium Carbonate Content of Soils. In Proceedings of 8th International Congress Soil Science Sodics Soils; Szabolics, I., Ed.; Research Institute for Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, ISSS Trans II: Tsukuba, Japan, 1964; pp. 802–812. [Google Scholar]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Qian, H. Evaluation of groundwater contamination for fluoride and nitrate in semi-arid region of Nirmal Province, South India: A special emphasis on human health risk assessment (HHRA). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 25, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Mahmudy-Gharaie, M.H.; Ghassemzadeh, F.; Karimi Karouyeh, A. Assessment of groundwater suitability for irrigation in a gold mine surrounding area, NE Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, D.W. Alkali Soils: Their Formation, Properties and Reclamation. WP Kelley. New York: Reinhold, 1951. 176 pp. $5.00. Science 1951, 114, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, F.; Abdelrahman, K. Integrated approach for the investigation of groundwater quality using hydrochemical and geostatistical analyses in Wadi Fatimah, western Saudi Arabia. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1166153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, G.; Elango, L. Hydrogeochemical processes and impact of tanning industries on groundwater quality in Ambur, Vellore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24364–24383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adimalla, N.; Dhakate, R.; Kasarla, A.; Taloor, A.K. Appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes in Central Telangana, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.K. Principal component analysis and hydrochemical facies characterization to evaluate groundwater quality in Varahi river basin, Karnataka state, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N. PIG: A numerical index for dissemination of groundwater contamination zones. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3344–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoye, S.; Fontaine, C.; Gaye, C.B.; Razack, M. Groundwater quality and suitability for different uses in the Saloum area of Senegal. Water 2018, 10, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, S.; Dharmendira, K.M. Investigation of hydrochemical dynamics of groundwater in coastal blocks of Tiruvallur district, Tamilnadu, India. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2021, 66, 5352–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, S.; Gupta, G.; Singh, R.; Tahama, K.; Erram, V.C. Hydrogeochemical processes regulating the groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and irrigation purpose in parts of coastal Sindhudurg District, Maharashtra. J. Geol. Soc. India 2021, 97, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snousy, M.G.; Wu, J.; Su, F.; Abdelhalim, A.; Ismail, E. Groundwater quality and its regulating geochemical processes in Assiut Province, Egypt. Expo. Health 2022, 14, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, M.H.; Hagan, M.T.; Demuth, H.B. Neural network toolbox. In User’s Guide MathWorks; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar]


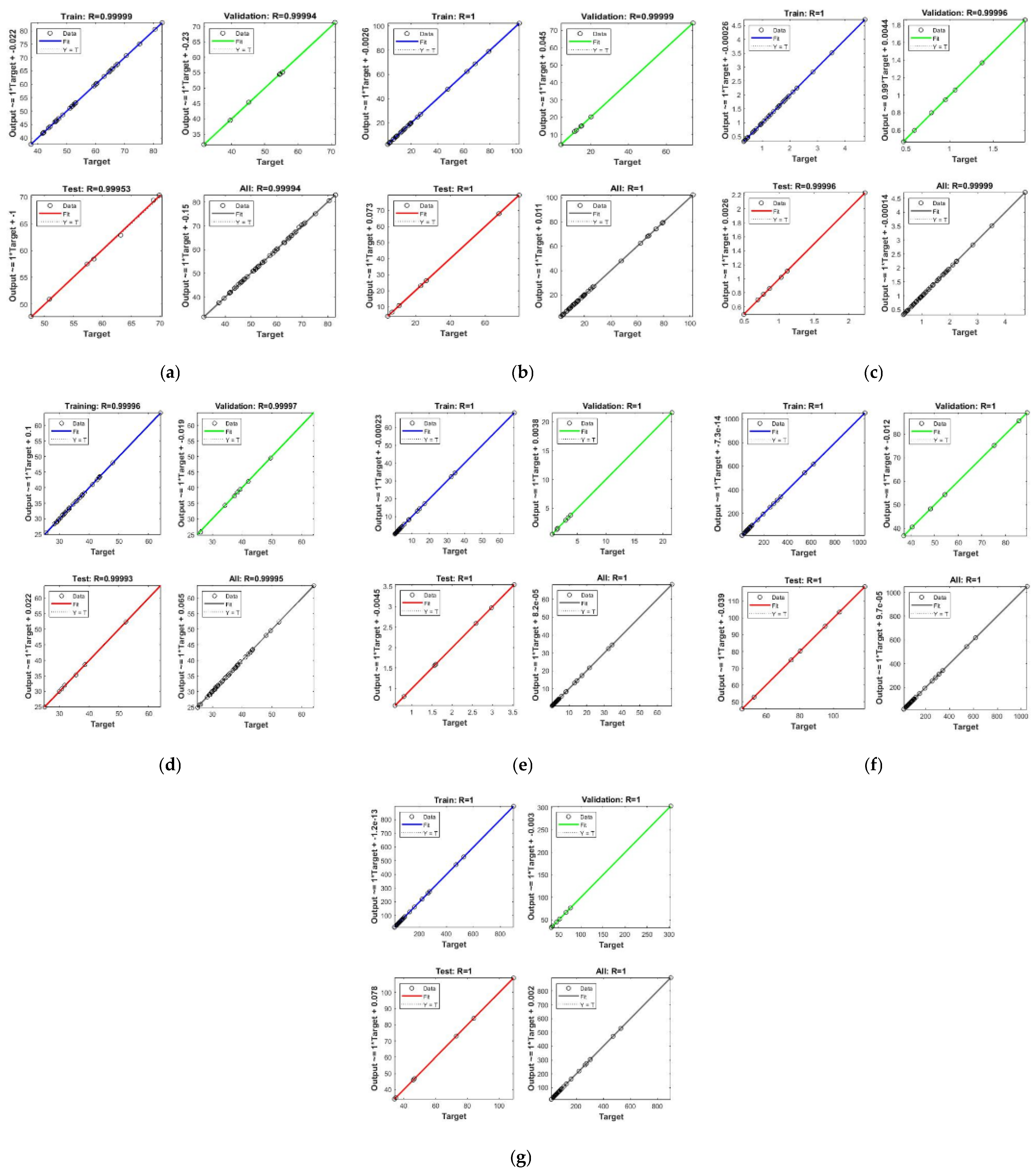
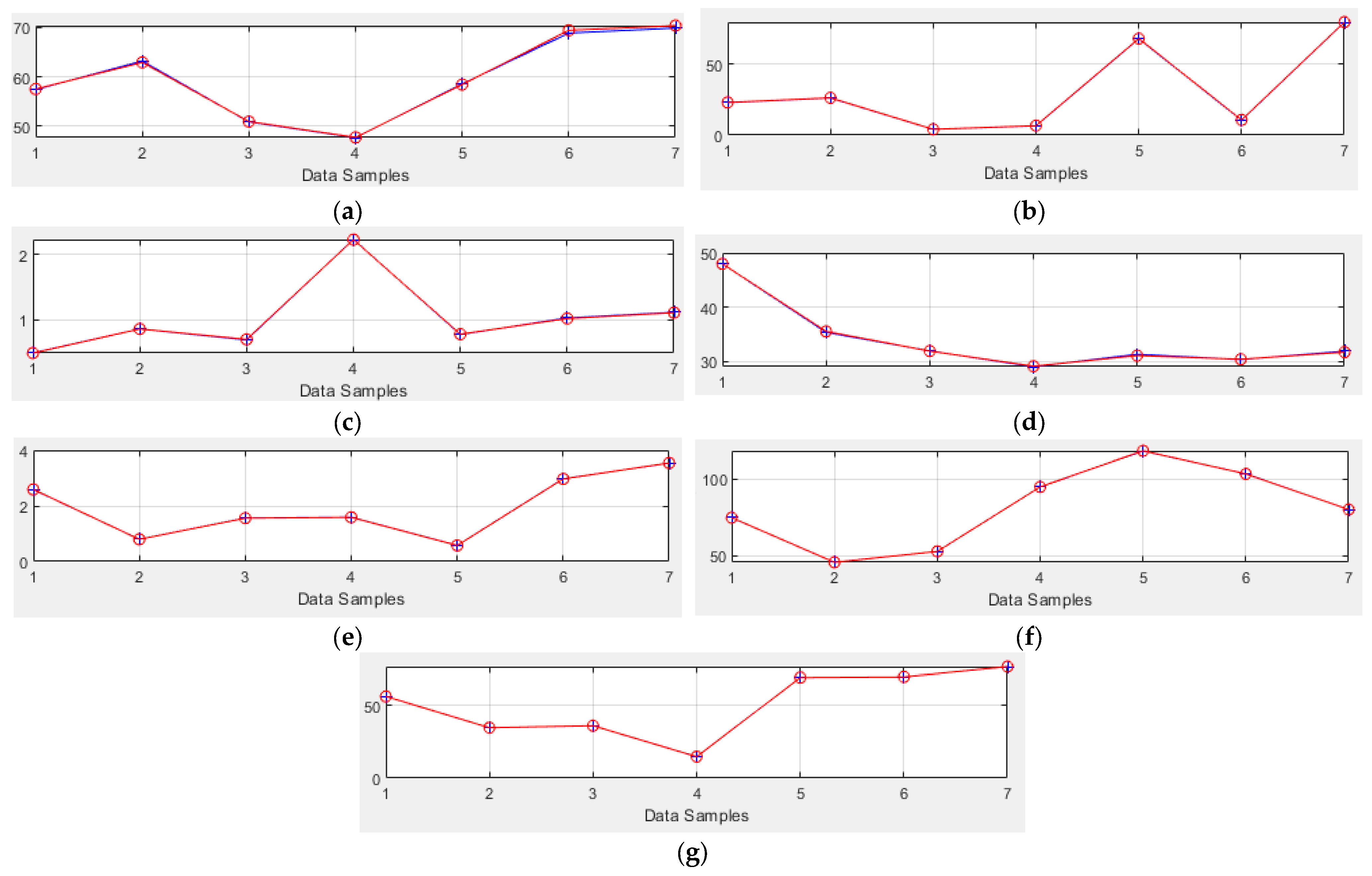
 and predicted values
and predicted values  ).
).
 and predicted values
and predicted values  ).
).
 and predicted values
and predicted values  ).
).
 and predicted values
and predicted values  ).
).
| Parameters | Weightage (wi) [10] | Relative Weigh (Wi) | Desirable Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIS [16] | WHO [17] | |||
| pH | 3 | 0.09 | 8.50 | 8.50 |
| TDS (ppm) | 4 | 0.09 | 500 | 500 |
| Hardness (ppm) | 3 | 0.09 | 200 | 100 |
| Ca2+ (ppm) | 3 | 0.09 | 75 | 75 |
| Na+ (ppm) | 2 | 0.06 | 200 | 200 |
| K+ (ppm) | 2 | 0.13 | 12 | 12 |
| Mg2+ (ppm) | 3 | 0.06 | 30 | 50 |
| Cl− (ppm) | 4 | 0.13 | 250 | 200 |
| SO42− (ppm) | 3 | 0.09 | 200 | 200 |
| NO3− (ppm) | 5 | 0.16 | 45 | 50 |
| ∑ wi = 32 | ∑ Wi = 1 | |||
| Sample | Unit | Min | Max | Mean | SD | BIS [16] | WHO [17] | SASO [18] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | P | D | P | D | P | ||||||
| pH | - | 6.92 | 8.46 | 7.74 | ±0.34 | 6.5 | 8.5 | 6.5 | 8.5 | 6.5 | 8.5 |
| EC | (µS/cm) | 142.00 | 19,470.00 | 2194.47 | ±3483.80 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TDS | (ppm) | 71.00 | 9730.00 | 1090.40 | ±1723.08 | 500 | 2000 | 500 | 1500 | 1000 | - |
| Hardness | (ppm) | 26.82 | 4594.32 | 506.36 | ±803.91 | 200 | 600 | 100 | 500 | - | - |
| Ca2+ | (ppm) | 5.30 | 1010.40 | 103.93 | ±172.86 | 75 | 200 | 75 | 200 | 200 | - |
| Na+ | (ppm) | 5.30 | 2815.10 | 275.74 | ±519.32 | - | 200 | - | 200 | 200 | - |
| K+ | (ppm) | 1.60 | 138.30 | 23.88 | ±29.14 | - | 12 | - | 12 | - | - |
| Mg2+ | (ppm) | 3.10 | 503.00 | 59.94 | ±91.71 | 30 | 100 | 50 | 150 | 150 | - |
| Cl− | (ppm) | 0.17 | 61.65 | 4.77 | ±10.06 | 250 | 1000 | 200 | 600 | 250 | - |
| SO42− | (ppm) | 0.30 | 19.96 | 3.06 | ±4.55 | 200 | 400 | 200 | 400 | 250 | - |
| NO3− | (ppm) | 0.12 | 0.91 | 0.30 | ±0.21 | 45 | - | 50 | - | 50 | - |
| Parameters | F1 | F2 | F3 | Commonalities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 0.972 | −0.033 | −0.202 | 0.986 |
| Na+ | 0.992 | 0.022 | −0.003 | 0.985 |
| K+ | 0.824 | 0.129 | 0.511 | 0.956 |
| Mg2+ | 0.989 | -0.024 | −0.045 | 0.981 |
| SO42− | 0.900 | −0.008 | 0.287 | 0.892 |
| NO3− | 0.772 | −0.365 | −0.072 | 0.734 |
| Hardness | 0.986 | −0.029 | −0.130 | 0.991 |
| Cl− | 0.972 | 0.015 | −0.163 | 0.971 |
| pH | 0.230 | 0.946 | −0.104 | 0.959 |
| EC | 0.997 | 0.005 | −0.034 | 0.994 |
| TDS | 0.996 | 0.007 | −0.035 | 0.992 |
| Eigenvalues | 8.944 | 1.049 | 0.449 | |
| (%) of Variance | 81.312 | 9.534 | 4.078 | |
| Cumulative (%) of Variance | 81.312 | 90.846 | 94.924 |
| Parameter | Range | Classification | Number of Samples | Percentage of Sample (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC μS/cm | <700 | Excellent | 17 | 36.17 |
| 700–3000 | Good | 22 | 46.81 | |
| >3000 | Fair | 8 | 17.02 | |
| Na+ % | <20 | Excellent | 0 | 0.00 |
| 20–40 | Good | 3 | 6.38 | |
| 40–60 | Permissible | 27 | 57.45 | |
| 60–80 | Doubtful | 15 | 31.91 | |
| >80 | Unsuitable | 2 | 4.26 | |
| MH | <50 | Excellent | 45 | 95.74 |
| >50 | Unsuitable | 2 | 4.26 | |
| SAR | <10 | Excellent | 17 | 36.17 |
| 10–18 | Good | 1 | 23.40 | |
| 18–26 | Doubtful | 9 | 19.15 | |
| >26 | Unsuitable | 10 | 21.28 | |
| PS | <3 | Excellent to good | 30 | 36.17 |
| 3–5 | Good to injurious | 7 | 23.40 | |
| >5 | Injurious to Unsuitable | 10 | 21.28 | |
| KR | <1 | Excellent | 23 | 48.94 |
| >1 | Unsuitable | 24 | 51.06 |
| Model | Measure | 10 | 17 | 19 | 21 | 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ % | RMSE | 0.831 | 0.136 | 0.336 | 0.572 | 0.456 |
| R2 | 0.965 | 0.990 | 0.991 | 0.985 | 0.988 | |
| SAR | RMSE | 0.314 | 0.103 | 0.070 | 0.203 | 0.120 |
| R2 | 0.995 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.991 | 0.999 | |
| KR | RMSE | 0.020 | 0.045 | 0.022 | 0.080 | 0.048 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| MH | RMSE | 0.386 | 0.238 | 0.073 | 0.509 | 0.132 |
| R2 | 0.981 | 0.990 | 1.000 | 0.988 | 0.998 | |
| PS | RMSE | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.023 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| WQI (WHO) | RMSE | 0.014 | 0.052 | 0.014 | 0.1114 | 0.073 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.000 | |
| WQI (BIS) | RMSE | 0.327 | 0.042 | 0.011 | 0.246 | 0.087 |
| R2 | 0.987 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.990 | 1.00 |
| Model | Measure | trainlm | trainscg | trainbr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ % | RMSE | 0.136 | 1.493 | 1.349 |
| R2 | 0.998 | 0.886 | 0.984 | |
| SAR | RMSE | 0.070 | 0.676 | 0.796 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.985 | |
| KR | RMSE | 0.022 | 0.120 | 0.281 |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.961 | 0.990 | |
| MH | RMSE | 0.073 | 1.415 | 1.209 |
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.970 | 0.980 | |
| PS | RMSE | 2.45 × 10−3 | 0.142 | 1.63 × 10−2 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.000 | |
| WQI (WHO) | RMSE | 1.45 × 10−2 | 1.110 | 2.12 × 10−2 |
| R2 | 1.00 | 0.998 | 1.000 | |
| WQI (BIS) | RMSE | 1.18 × 10−2 | 1.870 | 4.80 × 10−2 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.000 |
| Model | Measure | Radbas | tribas | tansig |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ % | RMSE | 2.602 | 1.285 | 0.136 |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.970 | 0.998 | |
| SAR | RMSE | 0.081 | 0.304 | 0.070 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 1.000 | |
| KR | RMSE | 0.071 | 0.045 | 0.022 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.996 | |
| MH | RMSE | 0.451 | 0.223 | 0.073 |
| R2 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.992 | |
| PS | RMSE | 3.12 × 10−3 | 2.55 × 10−3 | 2.45 × 10−3 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| WQI (WHO) | RMSE | 1.65 × 10−2 | 2.82 × 10−3 | 1.45 × 10−2 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| WQI (BIS) | RMSE | 3.73 × 10−3 | 2.48 × 10−3 | 1.18 × 10−2 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrowais, R.; Abdel daiem, M.M.; Li, R.; Maklad, M.A.; Helmi, A.M.; Nasef, B.M.; Said, N. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes at Al-Jouf Area in KSA Using Artificial Neural Network, GIS, and Multivariate Statistical Techniques. Water 2023, 15, 2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162982
Alrowais R, Abdel daiem MM, Li R, Maklad MA, Helmi AM, Nasef BM, Said N. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes at Al-Jouf Area in KSA Using Artificial Neural Network, GIS, and Multivariate Statistical Techniques. Water. 2023; 15(16):2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162982
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrowais, Raid, Mahmoud M. Abdel daiem, Renyuan Li, Mohamed Ashraf Maklad, Ahmed M. Helmi, Basheer M. Nasef, and Noha Said. 2023. "Groundwater Quality Assessment for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes at Al-Jouf Area in KSA Using Artificial Neural Network, GIS, and Multivariate Statistical Techniques" Water 15, no. 16: 2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162982
APA StyleAlrowais, R., Abdel daiem, M. M., Li, R., Maklad, M. A., Helmi, A. M., Nasef, B. M., & Said, N. (2023). Groundwater Quality Assessment for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes at Al-Jouf Area in KSA Using Artificial Neural Network, GIS, and Multivariate Statistical Techniques. Water, 15(16), 2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162982









