The Hydraulic and Boundary Characteristics of a Dike Breach Based on Cluster Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Object and Analysis Methods
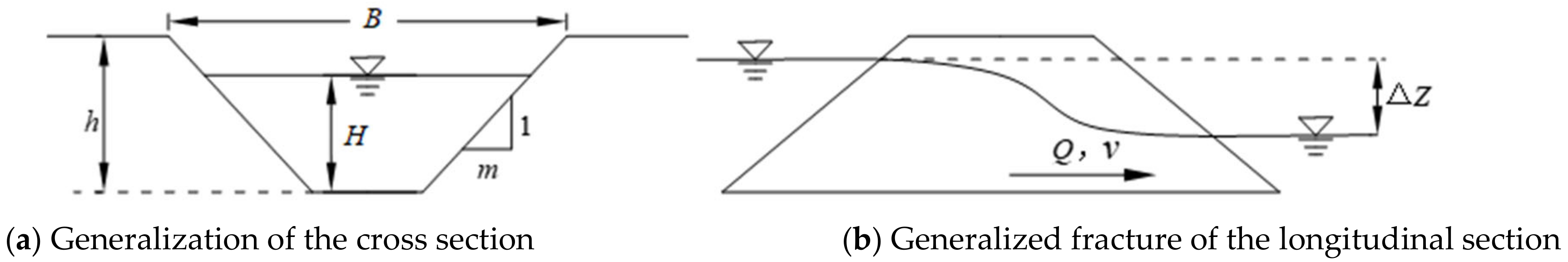
2.1. Research Object
- (1)
- Embankment breach and developing characteristics
- (2)
- Dike collapse characteristic value
2.2. Analytical Research Methods
2.2.1. Research Ideas
2.2.2. Specific Analysis Methods
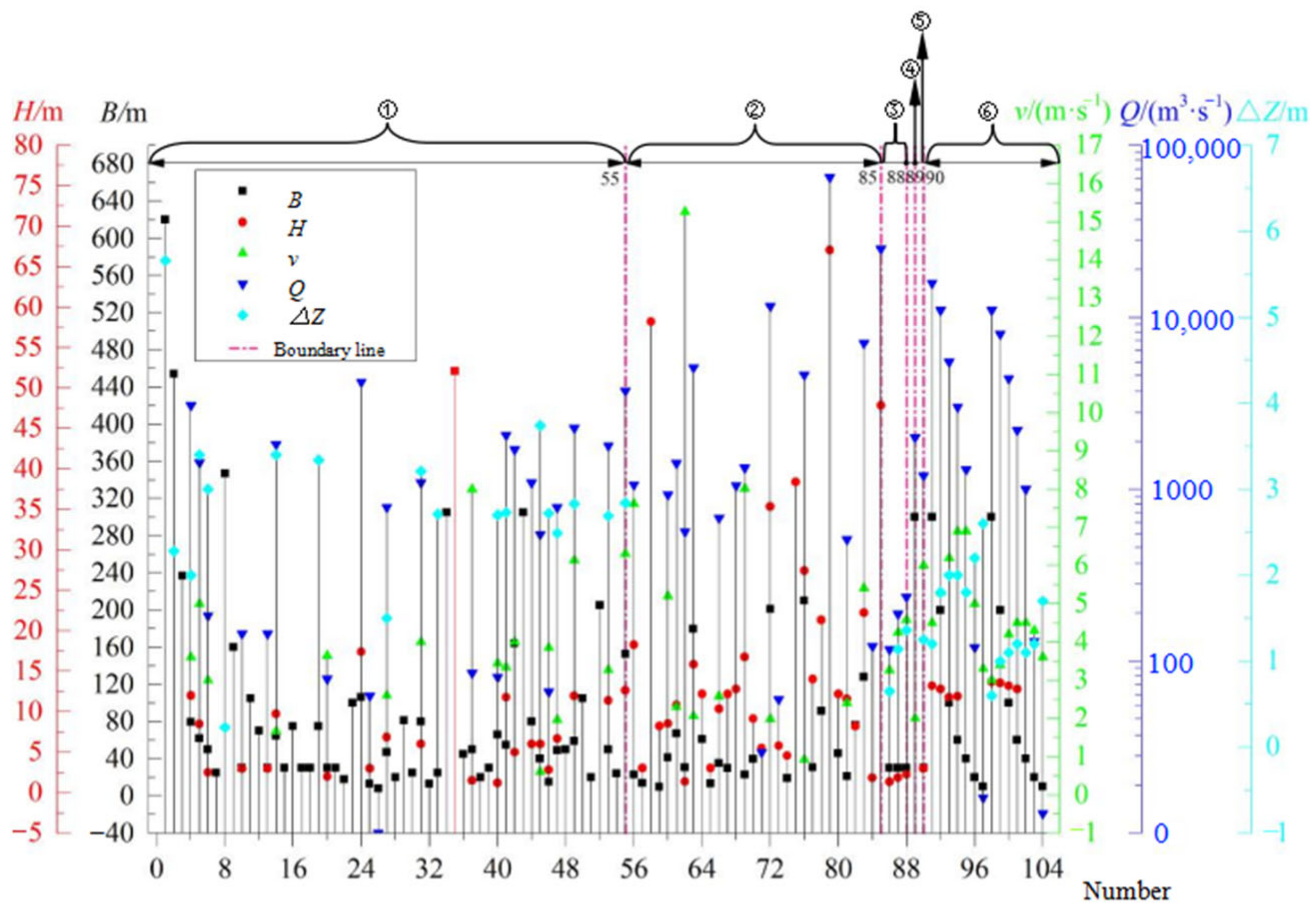
3. Results and Discussion (Analysis of Eigenvalues of Generalized Hydraulic Boundary)
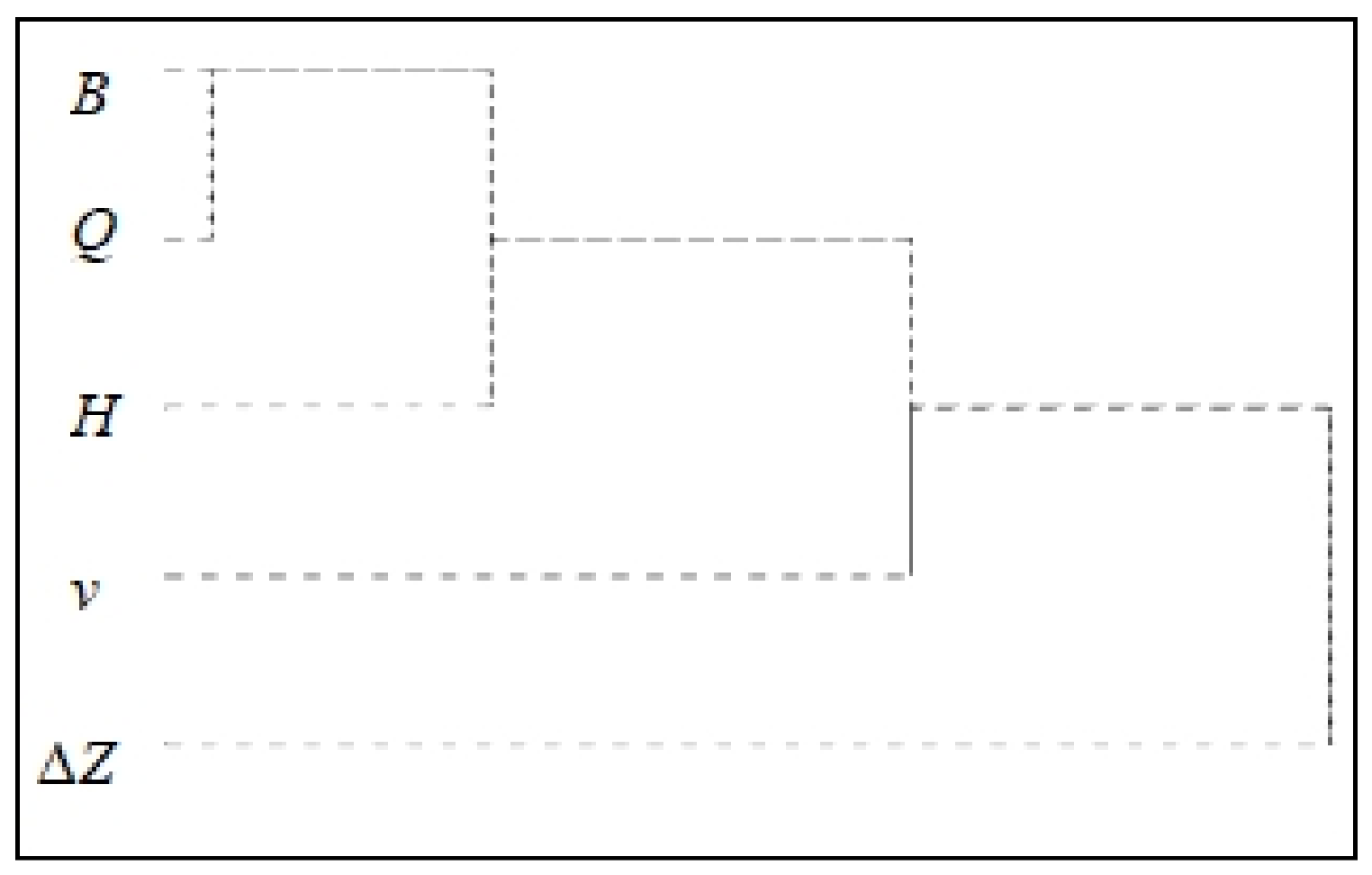
3.1. Cluster Analysis Results for the Eigenvalues of the Breaches
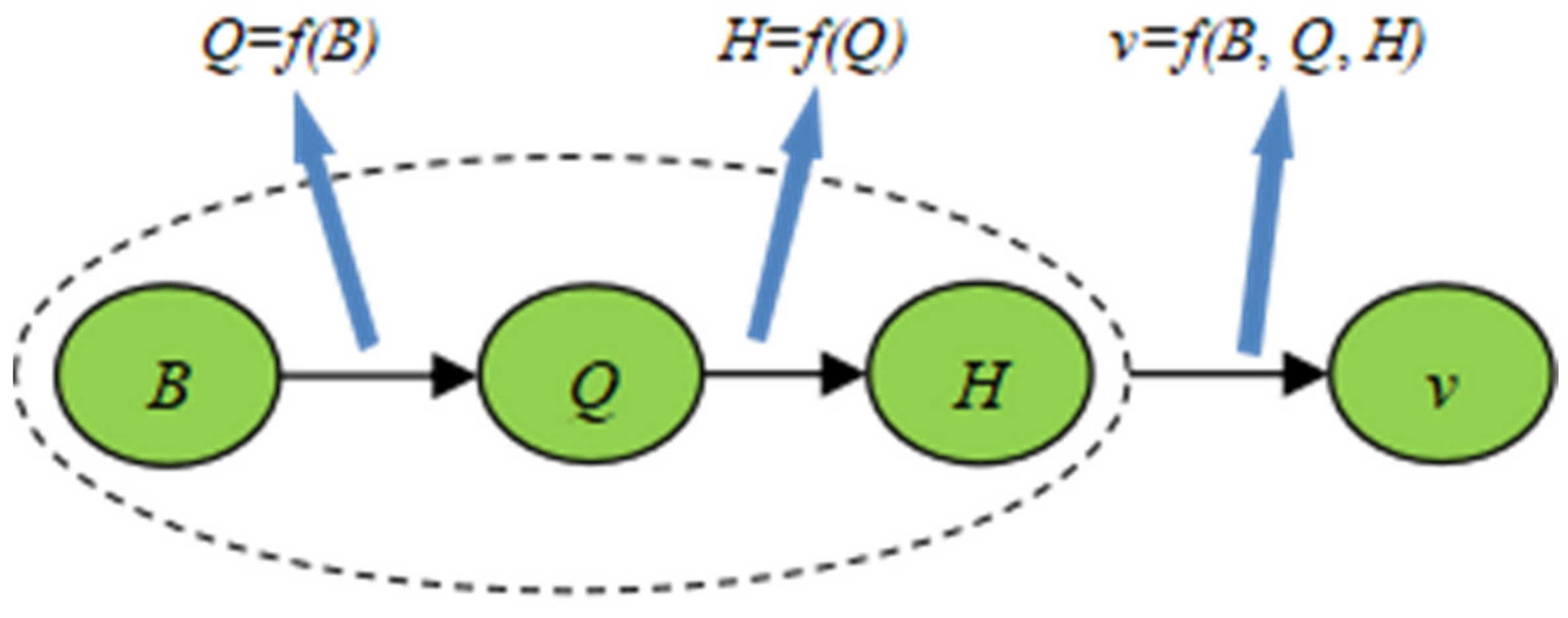
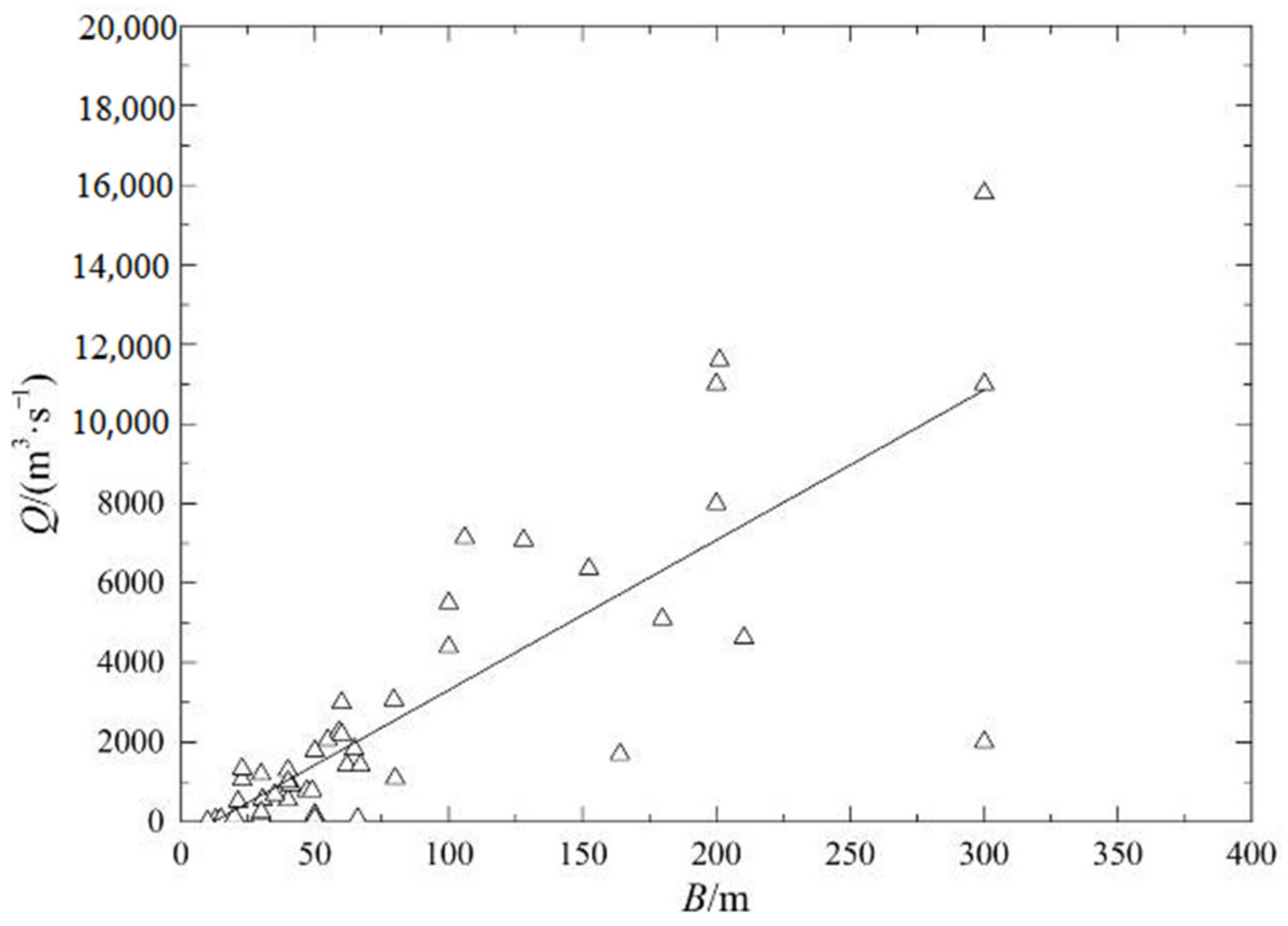
3.2. Results of Fitting Regression Analysis
- (1)
- Fitting relationship between Q and B
- (2)
- Fitting relationship between H and Q
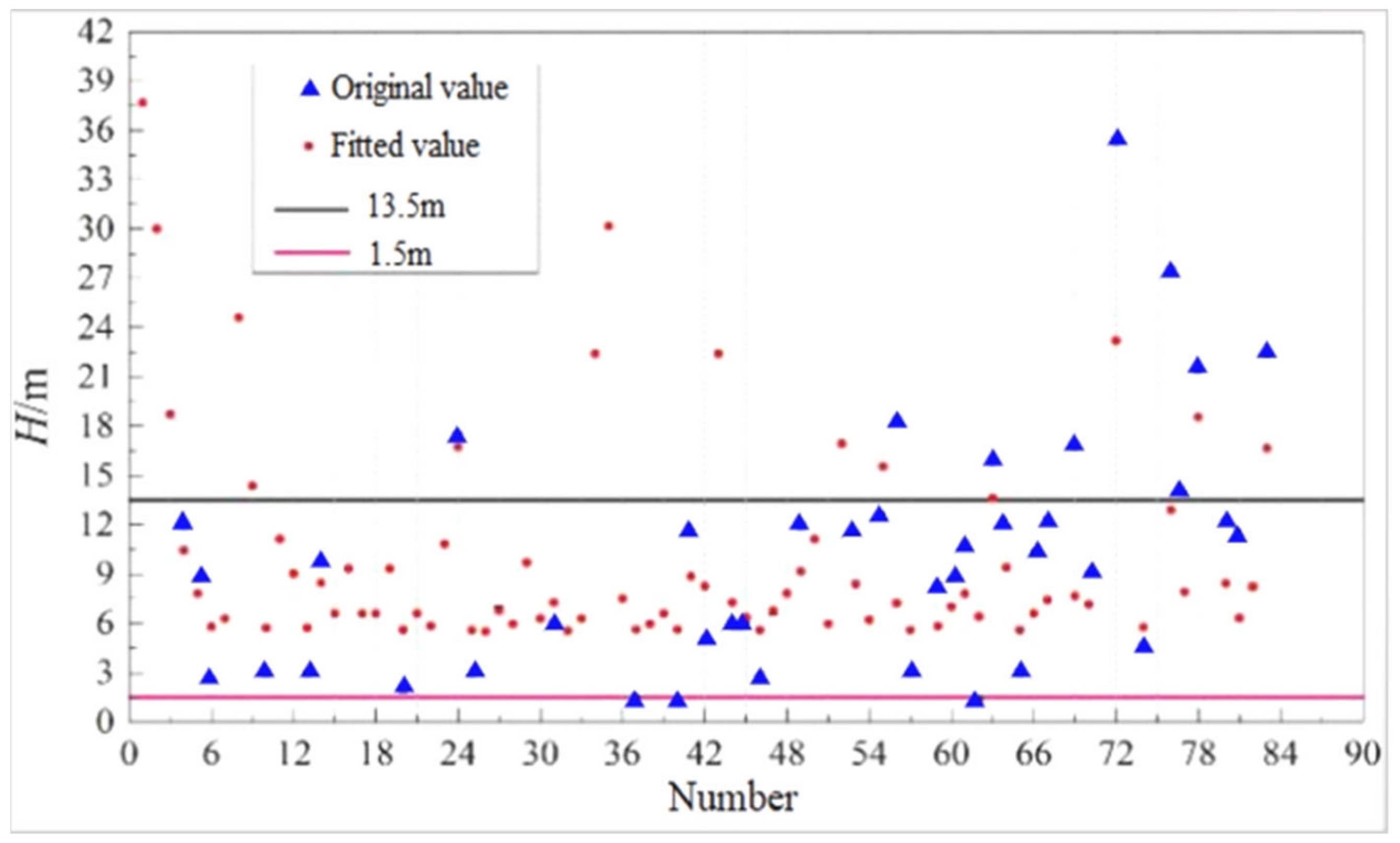
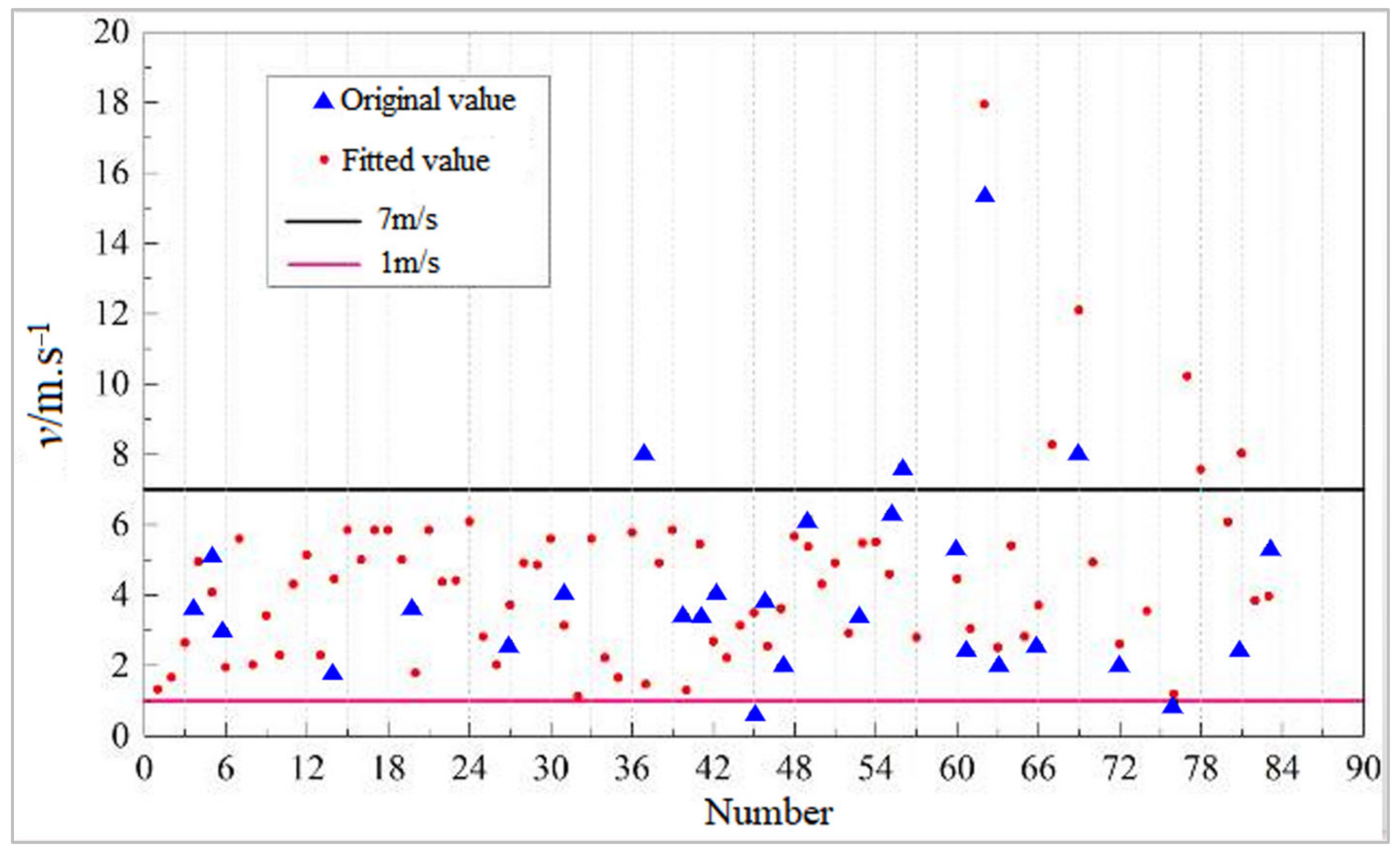
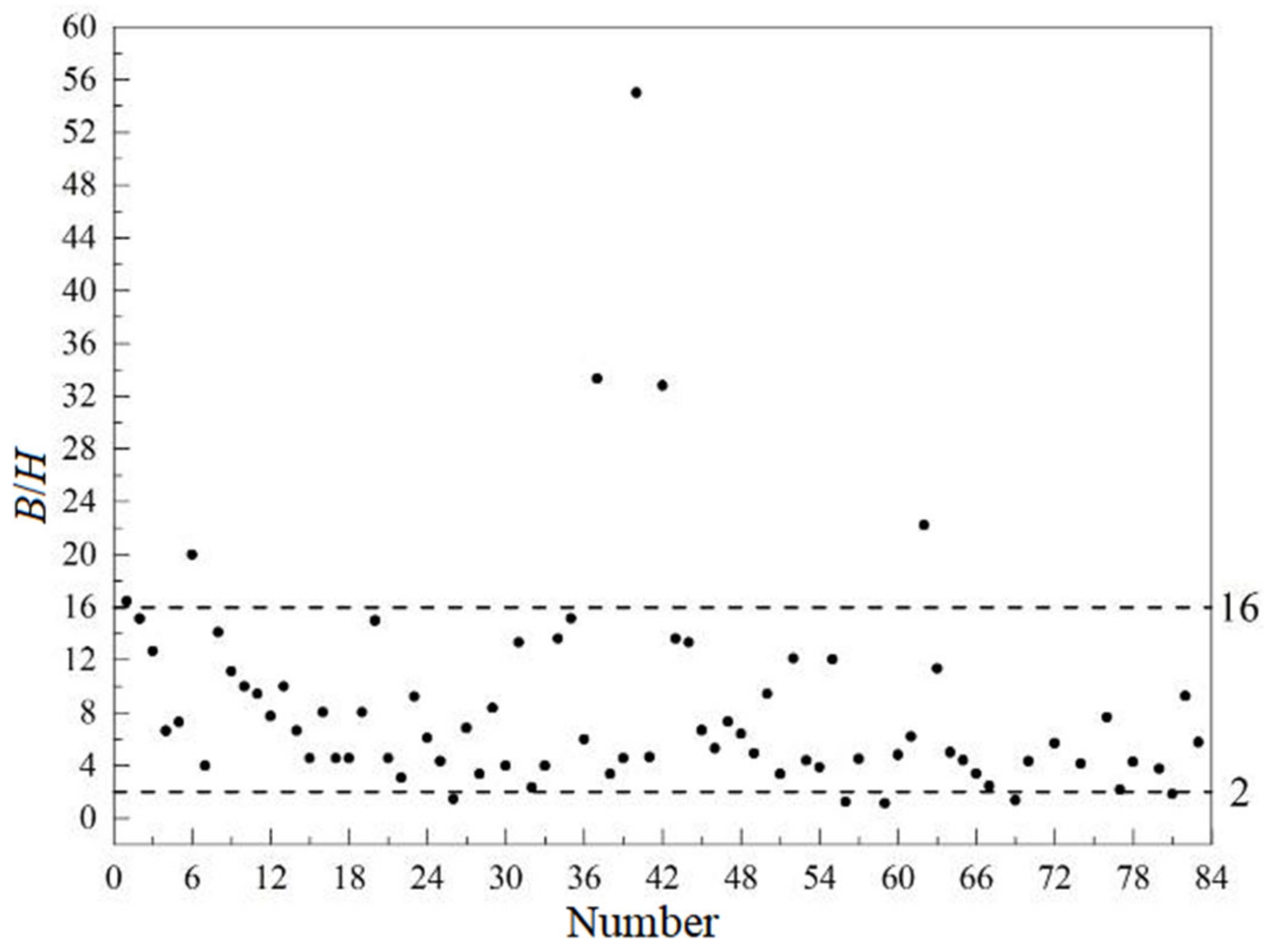
3.3. Fitting Complement and Dimensionless Parameter Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Z.Q.; Su, H.Z.; Han, Z.; Wen, Z.P. Multiple failure modes-based practical calculation model on comprehensive risk for levee structure. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, W.; Li, W.; Song, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, T.; Jiao, Y. Impact evaluation of geomorphic changes caused by extreme floods on inundation area considering geomorphic variations and land use types. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.E. Floods from dam failures. US Geol. Surv. 1985, 85, 560. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, M.; Fell, R.; Spannagle, M. The statistics of embankment dam failures and accidents. Can. Geotech. J. 2000, 37, 1000–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resio, D.T.; Boc, S.J.; Ward, D.; Kleinman, A.; Fowler, J.; Welsh, B.; Matalik, M.; Phil, G. US Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Rapid Repair of Levee Breaches; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.Z.; Liang, Y.P.; Xie, J.X.; Zhao, J.L. Model test studies on hydraulic and eroding and depositing characteristics in the gate areas of embankment breach. Yellow River 2003, 25, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.K.; Zeng, Z.C.; Deng, B.M. Hydraulic characteristics of levee breach closure. Hydro Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X. Experimental and numerical model studies of dike-break induced flood processes over a typical floodplain domain. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 1843–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Frazão, S.; Le Grelle, N.; Spinewine, B.; Zech, Y. Dam-break Dam-break induced morphological changes in a channel with uniform sedi-ments: Measurements by a laser-sheet imaging technique. J. Hydraul. Res. 2007, 45, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellos, C.V.; Soulis, V.; Sakkas, J.G. Experimental investigation of two-dimensional dam-break induced flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 1992, 30, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, K.A.; Nouman, A.; Yao, J.T.; Alanazi, E. A three-way clustering approach for handling missing data using GTRS. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2018, 98, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.F.; Li, M.L.; Lin, W.C. A class center based approach for missing value imputation. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 151, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaser, B.; Marce, M. Multivariate linear regression with missing values. Anal. Chem. Acta 2013, 796, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, G.; Ivo, D. Maximum Consistency of Incomplete Data via Non-Invasive Imputation. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2003, 19, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.A.M.; Entesar, A.S.E.-G. Investigating scale effects on breach evolution of overtopped sand embankments. Water Sci. 2016, 30, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yohannis, B.T.; Peter, F. An Integrated Approach to Simulate Flooding due to River Dike Breach; CUNY Academic Works: New York City, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.S.; Cui, T.J.; Liu, J. Research on the clustering analysis and similarity in factor space. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2018, 33, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wan, D.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y. Similarity Analysis of Small- and Medium-Sized Watersheds Based on Clustering Ensemble Model. Water 2020, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, M.F.; Wright, N.G.; Sleigh, A. 2D Process-Based Morphodynamic Model for Flooding by Noncohesive Dyke Breach. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, S. Clustering analysis for elastodynamic homogenization. Comput. Mech. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.F.; Watson, G.A. Numerical Analysis 1993; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sutarto, E.T. Application of large scale particle image velocimetry (L SPIV) to identify flow pattern in a channel. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Visser, P.J.; Ren, Y.; Uijttewaal, W.S.J. Flow hydrodynamics in embankment breach. J. Hydrodyn. 2015, 27, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, P.L. Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics for Engineers; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Chinnarasri, C.Y.; Jirakitlerd, S.B.; Wongwises, S.C. Embankment dam breach and its outflow characteristics. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2004, 21, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsop, W.; Kortenhaus, A.; Morris, M.; Buijs, F.A.; Visser, P.J.; ter Horst, W.L.A.; Hassan, R.; Young, M.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.; Doorn, N.; et al. Failure Mechanisms for Flood Defense Structures; Hydraulic Structures and Flood Risk; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; p. 203. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.Z.; Zhao, J.J.; Yan, J.G.; Chen, P. Hydraulic test studies of dike breach. Yangtze River 2003, 34, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, F.D.; He, C.H. Numerical Simulation of Hydraulic Conditions of Dike Closure Based on Flow-3D. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2017, 5, 77–80+86. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.M. Breaching Parameters for Earth and Rockfill Dams. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 1957–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WU, W. Simplified physically based model of earthen embankment breaching. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.M.; Mustafa, A.; Mahmoud, A.-R.; Nathanie, B.; Scott, B.; Cao, Z.X.; Chen, Q.; George, C.; Jennifer, D.; Gee, D.; et al. Earthen Embankment Breaching. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar]




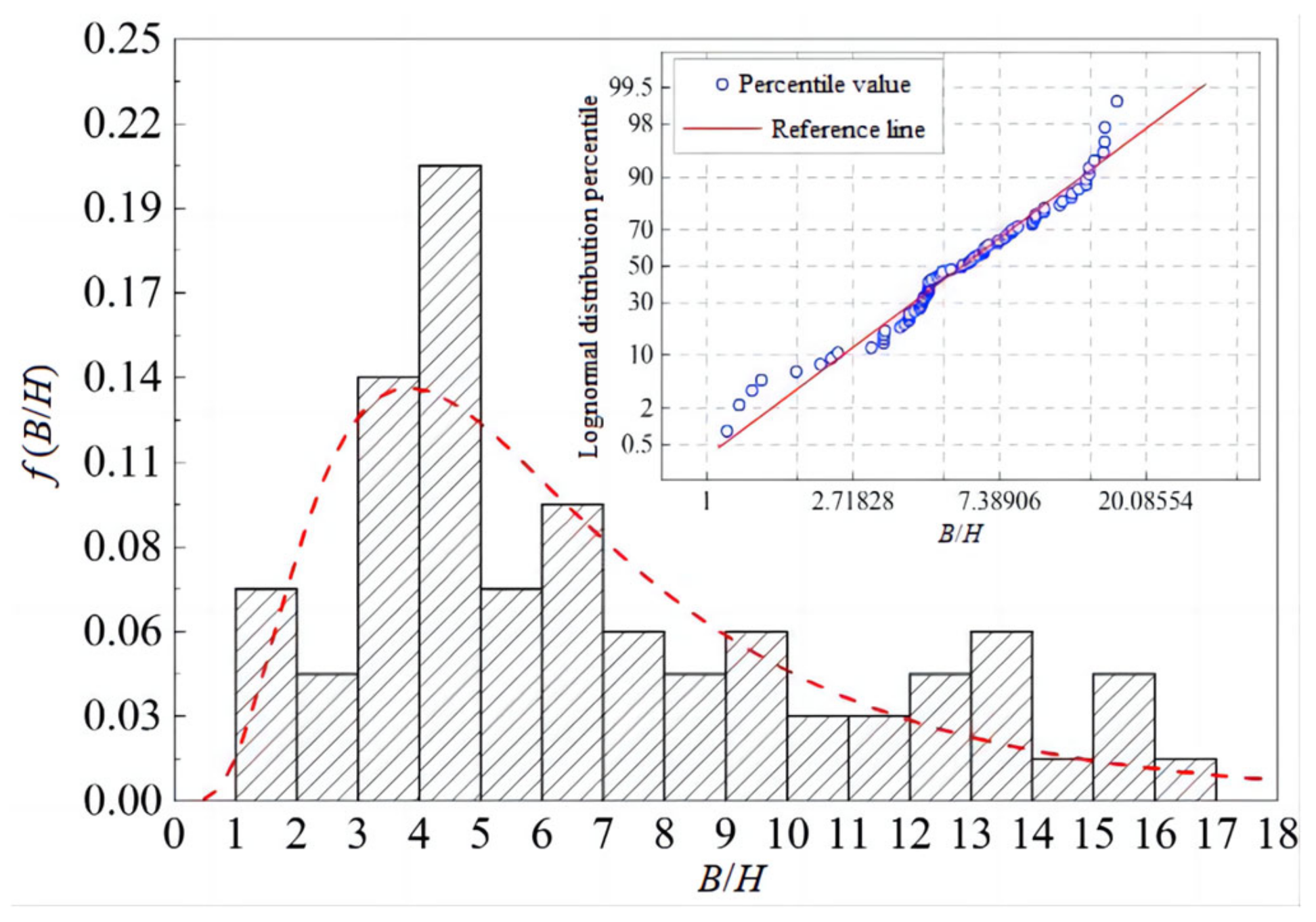
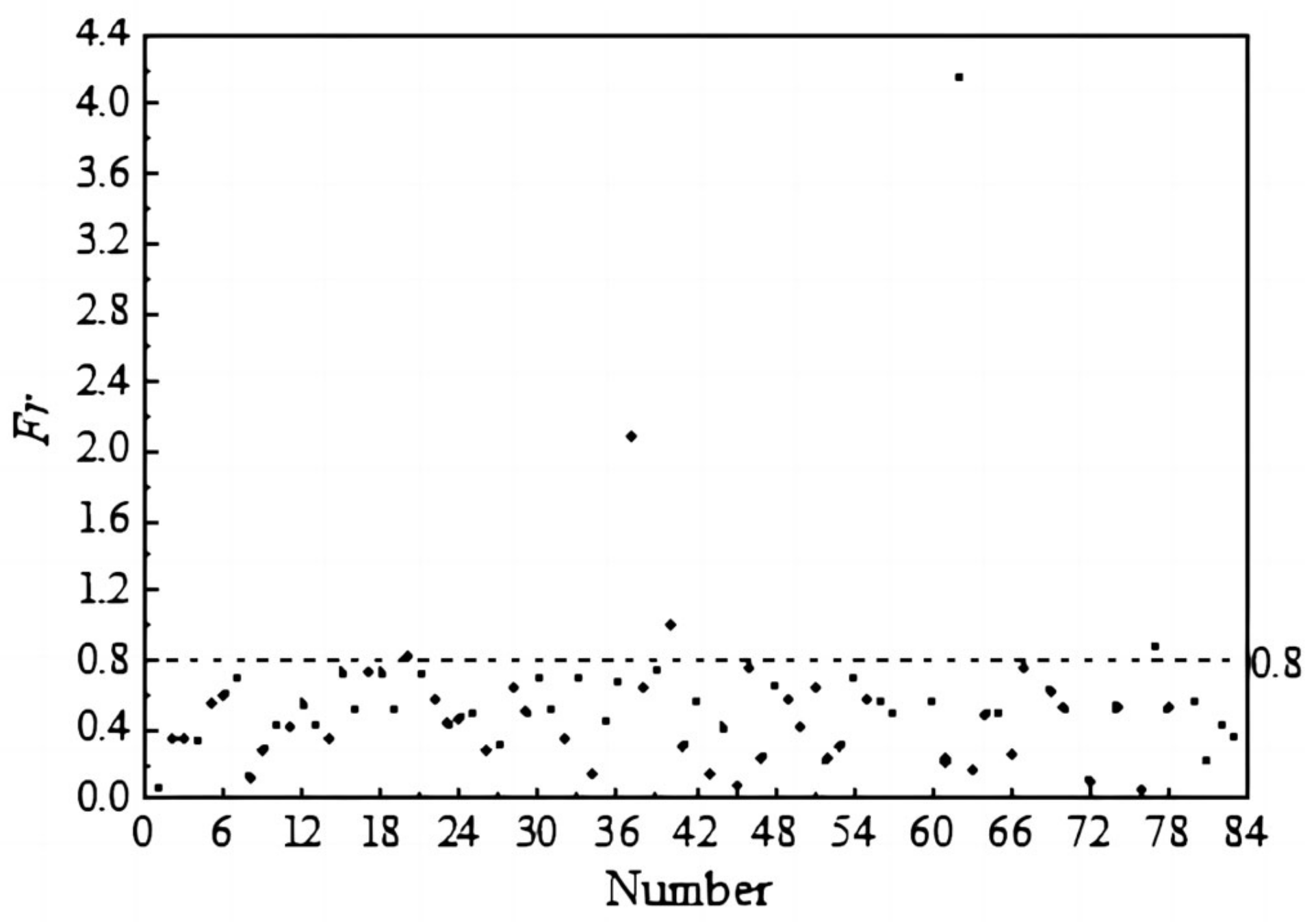
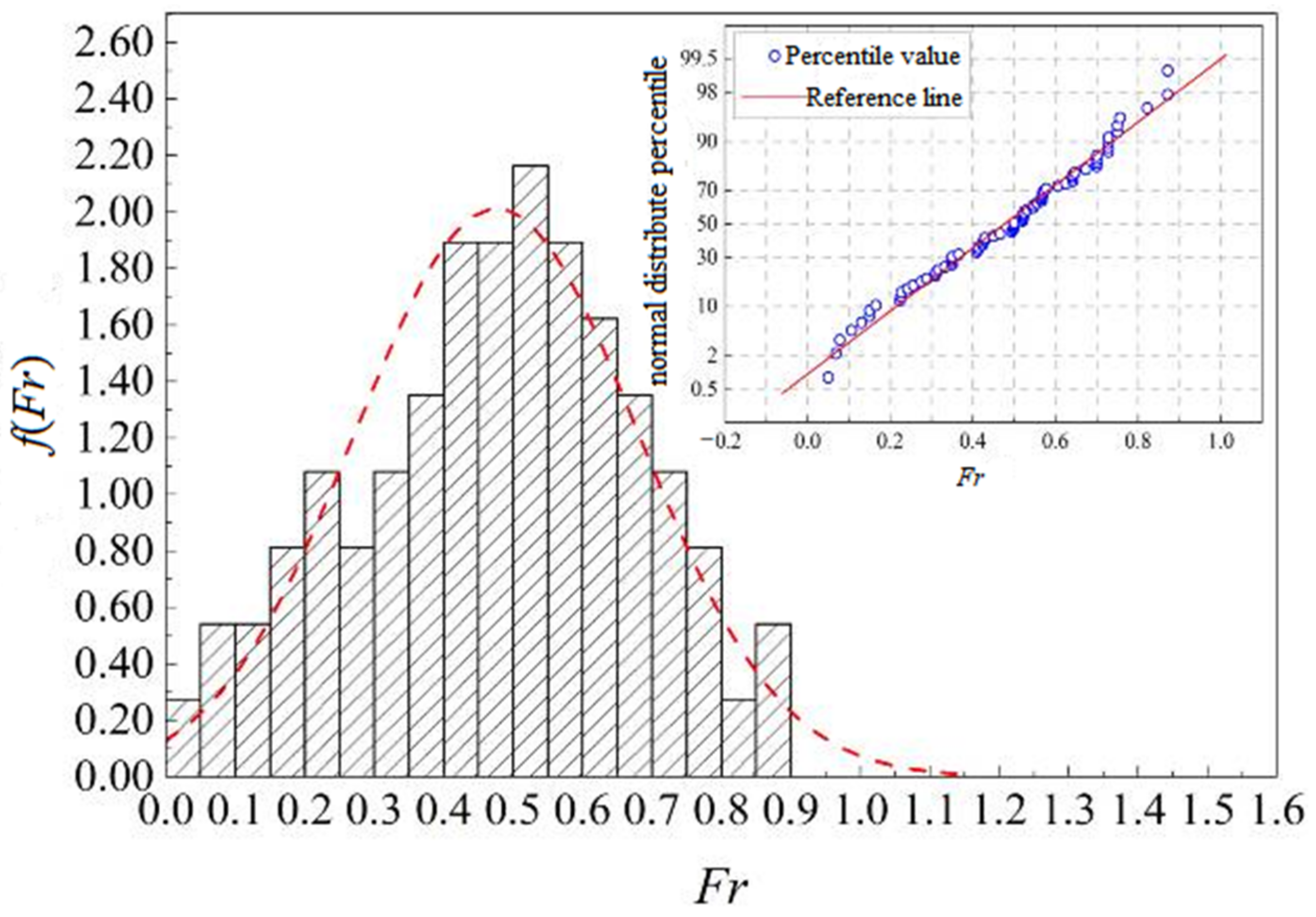
| Eigenvalues | B /m | H /m | v /(m·s−1) | ΔZ /m | Q /(m3·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B/m | 1.000 | 0.535 | −0.232 | 0.275 | 0.811 |
| H/m | 1.000 | −0.191 | −0.093 | 0.865 | |
| v/(m·s−1) | 1.000 | −0.226 | −0.068 | ||
| ΔZ/m | 1.000 | −0.307 | |||
| Q/(m3·s−1) | 1.000 |
| Number | B/H | Fr | Number | B/H | Fr | Number | B/H | Fr | Number | B/H | Fr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.45 | 0.07 | 20 | 15.00 | 0.82 | 39 | 4.55 | 0.73 | 60 | 4.82 | 0.57 |
| 2 | 15.13 | 0.10 | 21 | 4.55 | 0.73 | 40 | 55.00 | 1.00 | 61 | 6.20 | 0.22 |
| 3 | 12.67 | 0.20 | 22 | 3.08 | 0.58 | 41 | 4.65 | 0.31 | 62 | 22.22 | 4.16 |
| 4 | 6.63 | 0.33 | 23 | 9.23 | 0.43 | 42 | 32.80 | 0.57 | 63 | 11.35 | 0.17 |
| 5 | 7.29 | 0.55 | 24 | 6.09 | 0.47 | 43 | 13.62 | 0.15 | 64 | 5.00 | 0.49 |
| 6 | 20.00 | 0.61 | 25 | 4.33 | 0.52 | 44 | 13.33 | 0.41 | 65 | 4.40 | 0.52 |
| 7 | 3.98 | 0.71 | 26 | 1.45 | 0.27 | 45 | 6.67 | 0.08 | 66 | 3.38 | 0.26 |
| 8 | 14.10 | 0.13 | 27 | 6.84 | 0.32 | 46 | 5.30 | 0.73 | 67 | 2.45 | 0.76 |
| 9 | 11.15 | 0.29 | 28 | 3.35 | 0.64 | 47 | 7.34 | 0.24 | 69 | 1.36 | 0.62 |
| 10 | 10.00 | 0.42 | 29 | 8.36 | 0.50 | 48 | 6.40 | 0.65 | 70 | 4.33 | 0.52 |
| 11 | 9.44 | 0.41 | 30 | 3.98 | 0.71 | 49 | 4.93 | 0.57 | 72 | 5.69 | 0.11 |
| 12 | 7.75 | 0.55 | 31 | 13.33 | 0.52 | 50 | 9.44 | 0.41 | 74 | 4.13 | 0.53 |
| 13 | 10.00 | 0.42 | 32 | 2.35 | 0.15 | 51 | 3.35 | 0.64 | 76 | 7.67 | 0.06 |
| 14 | 6.65 | 0.17 | 33 | 3.98 | 0.71 | 52 | 12.12 | 0.23 | 77 | 2.17 | 0.87 |
| 15 | 4.55 | 0.73 | 34 | 13.62 | 0.15 | 53 | 4.39 | 0.31 | 78 | 4.29 | 0.52 |
| 16 | 8.04 | 0.52 | 35 | 15.16 | 0.10 | 54 | 3.86 | 0.71 | 80 | 3.75 | 0.56 |
| 17 | 4.55 | 0.73 | 36 | 5.99 | 0.67 | 55 | 12.06 | 0.57 | 81 | 1.84 | 0.23 |
| 18 | 4.55 | 0.73 | 37 | 33.33 | 2.09 | 56 | 1.25 | 0.57 | 82 | 9.26 | 0.43 |
| 19 | 8.04 | 0.52 | 38 | 3.35 | 0.64 | 57 | 4.50 | 0.51 | 83 | 5.75 | 0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Luo, Y.; Qiao, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Sun, D. The Hydraulic and Boundary Characteristics of a Dike Breach Based on Cluster Analysis. Water 2023, 15, 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162908
Liu M, Luo Y, Qiao C, Wang Z, Ma H, Sun D. The Hydraulic and Boundary Characteristics of a Dike Breach Based on Cluster Analysis. Water. 2023; 15(16):2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162908
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Mingxiao, Yaru Luo, Chi Qiao, Zezhong Wang, Hongfu Ma, and Dongpo Sun. 2023. "The Hydraulic and Boundary Characteristics of a Dike Breach Based on Cluster Analysis" Water 15, no. 16: 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162908
APA StyleLiu, M., Luo, Y., Qiao, C., Wang, Z., Ma, H., & Sun, D. (2023). The Hydraulic and Boundary Characteristics of a Dike Breach Based on Cluster Analysis. Water, 15(16), 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162908







