Responses of a Submerged Macrophyte Potamogeton crispus and Epiphytic Biofilm to Humic-Substance Enrichment Coupled with Brownification in Freshwater Habitats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Indoor Mesocosms
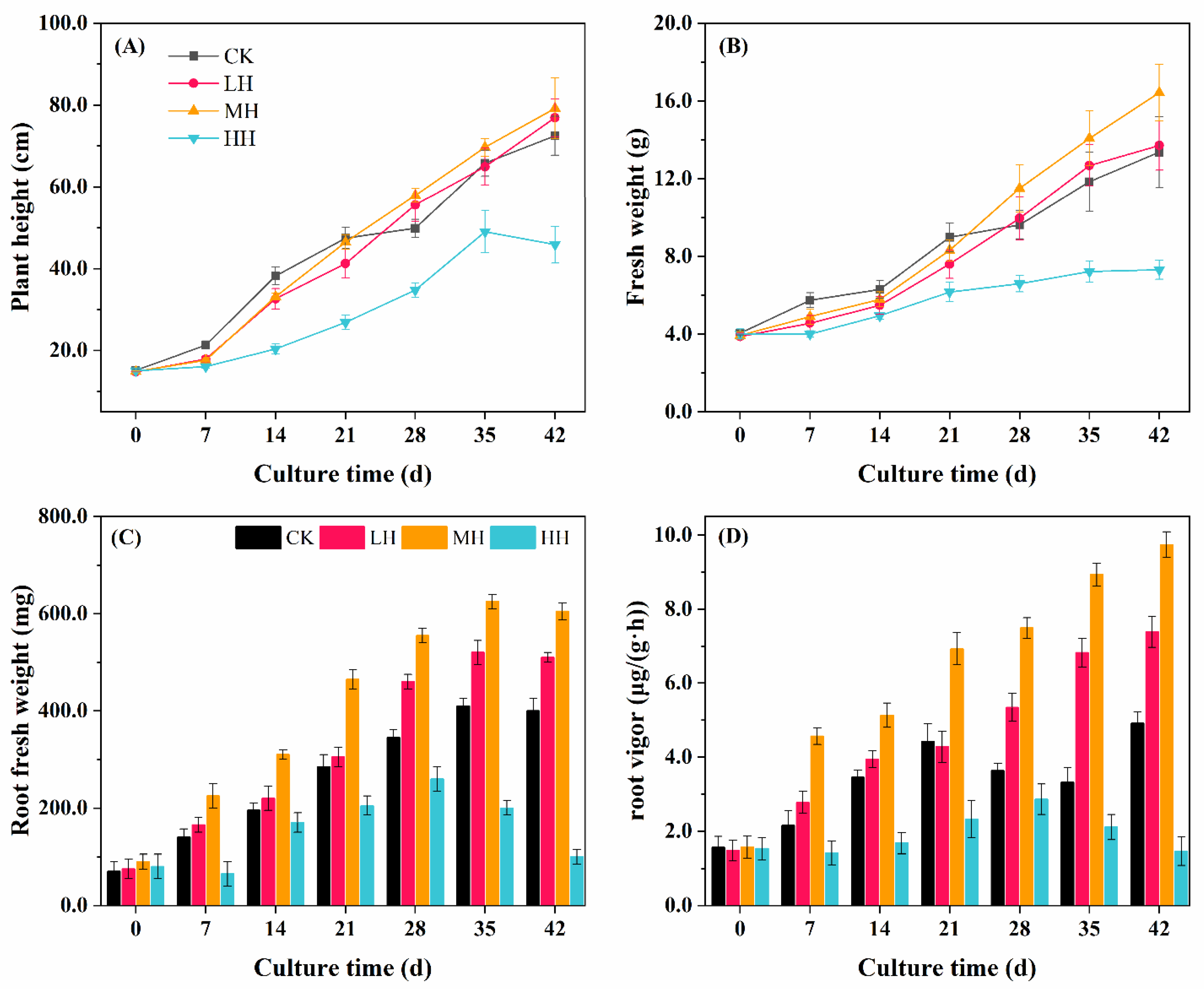
2.3. Determination of Plant Growth and Root Vigor
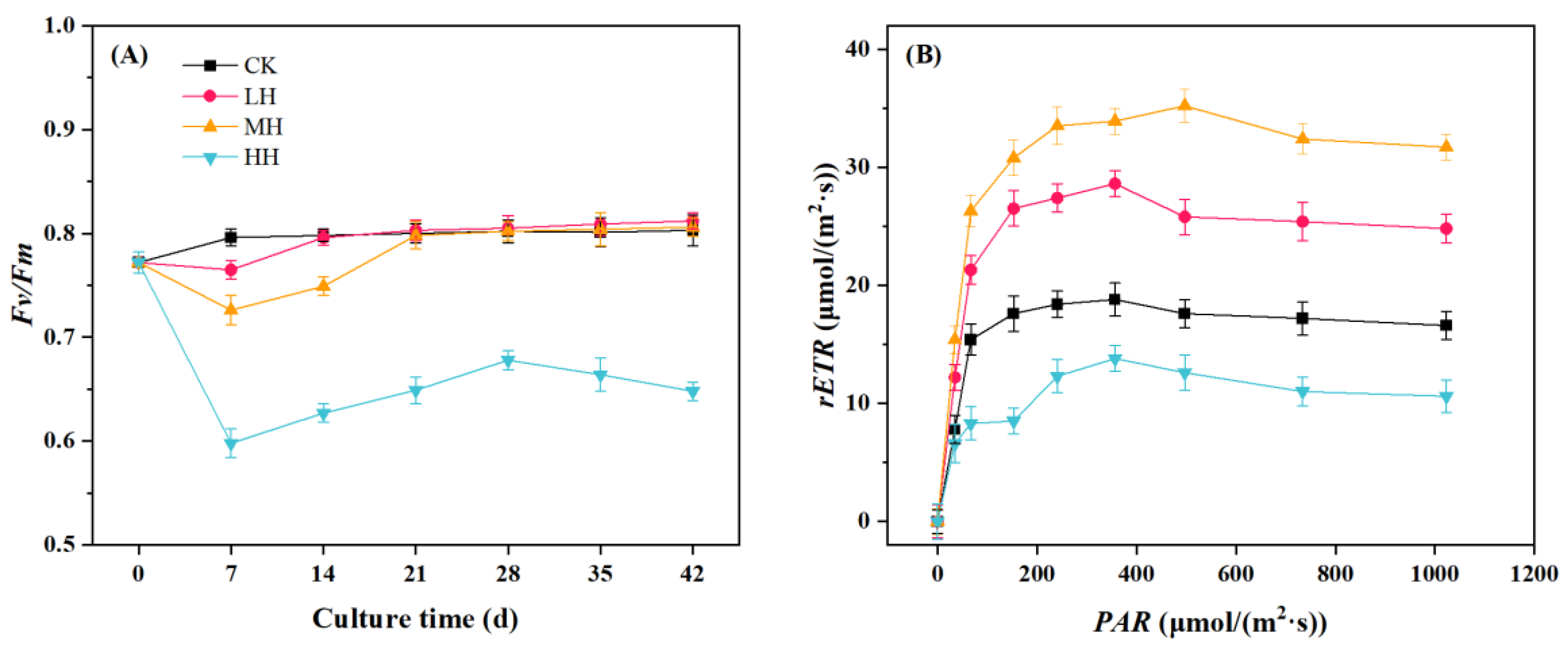
2.4. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters
2.5. Determination of Water Quality Parameters and Color
2.6. Analysis of Biochemical Indicators
2.7. Epiphytic Biofilm Microbial Community
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Quality and Color
3.2. P. crispus Growth Response to Humic Substance Addition
3.3. P. crispus Chlorophyll Fluorescence Response to Humic Substance Addition
3.4. Antioxidant System Response to Humic Substance Addition
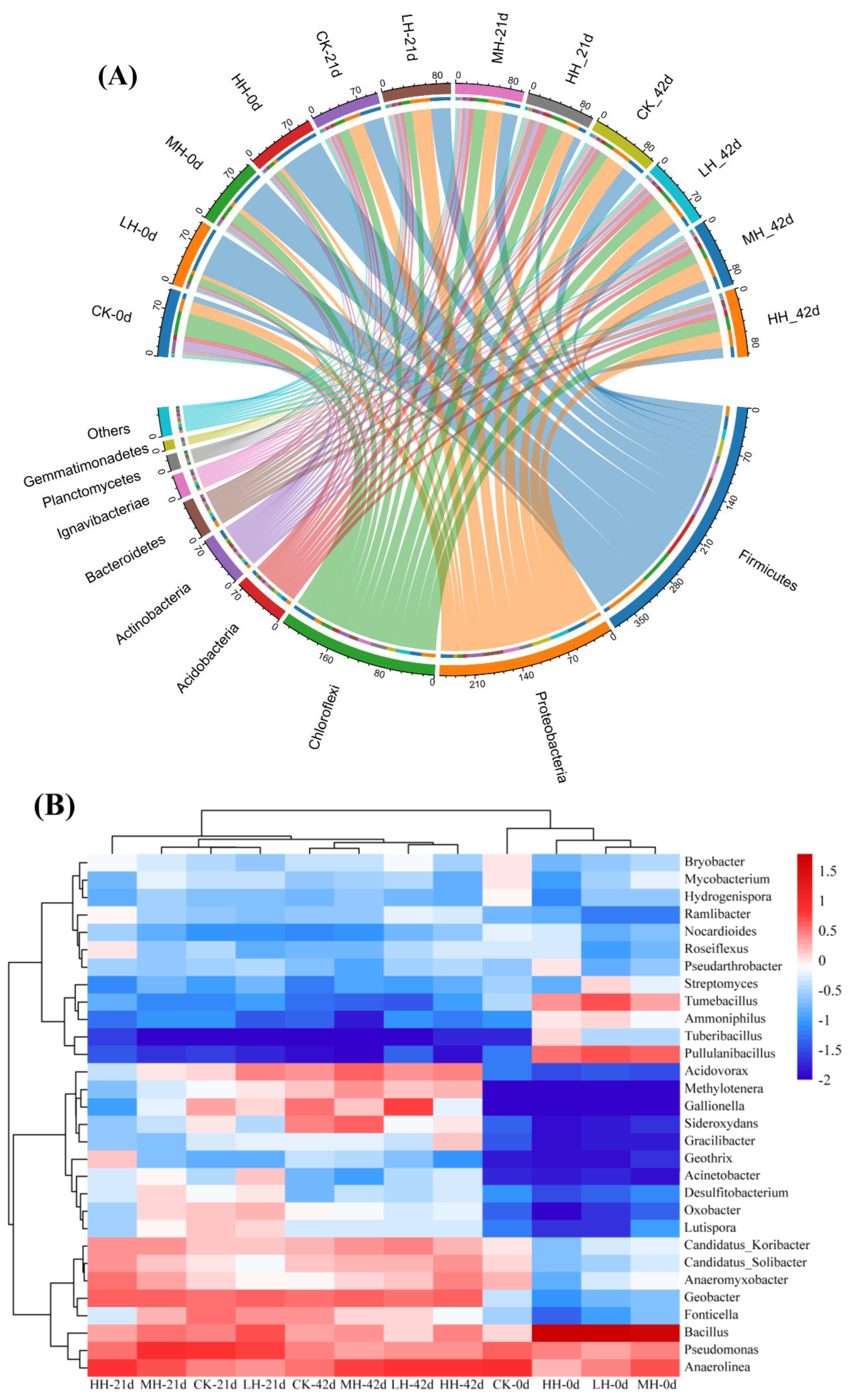
3.5. Microbial Community Diversity and Composition in Epiphytic Biofilm
3.5.1. Analysis of Microbial Diversity
3.5.2. Taxonomic Distribution of Bacteria at the Phylum and Genus Levels
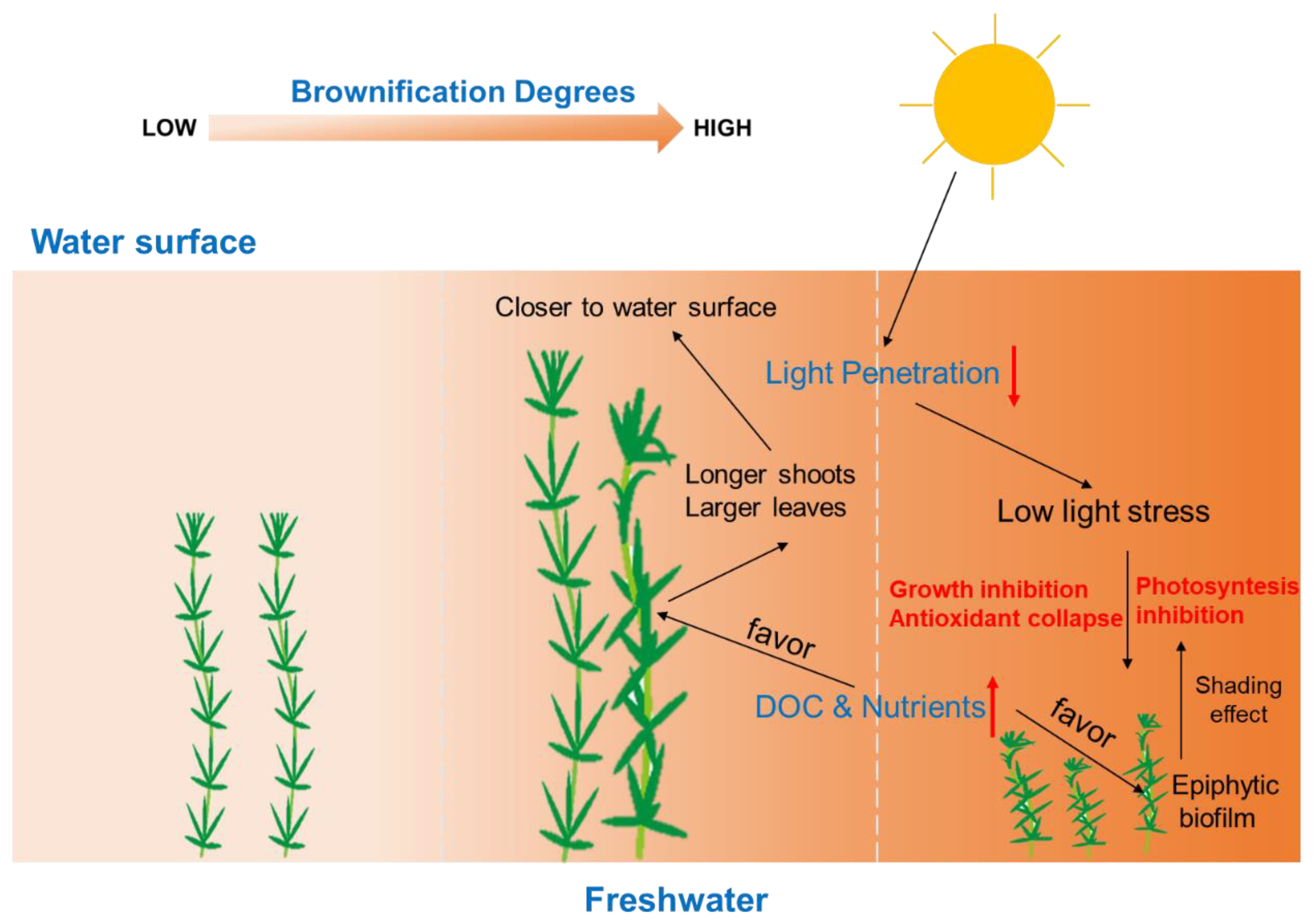
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Christoffersen, K. The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hare, M.T.; Aguiar, F.C.; Asaeda, T.; Bakker, E.S.; Chambers, P.A.; Clayton, J.S.; Elger, A.; Ferreira, T.M.; Gross, E.M.; Gunn, I.D.M.; et al. Plants in aquatic ecosystems: Current trends and future directions. Hydrobiologia 2018, 812, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Chu, Q.; Tang, N.; Shu, B.; Liu, G.; Xing, W. How many submerged macrophyte species are needed to improve water clarity and quality in Yangtze floodplain lakes? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Donk, E.; van de Bund, W.J. Impact of submerged macrophytes including charophytes on phyto- and zooplankton communities: Allelopathy versus other mechanisms. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 72, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahuhta, J.; Kanninen, A.; Hellsten, S.; Vuori, K.-M.; Kuoppala, M.; Hämäläinen, H. Variable response of functional macrophyte groups to lake characteristics, land use, and space: Implications for bioassessment. Hydrobiologia 2013, 737, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G. Rapid adaptive responses of rosette-type macrophyte Vallisneria natans juveniles to varying water depths: The role of leaf trait plasticity. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 14268–14281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ga, Z.; Yan, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zuo, L.; Wang, G. Vertical patterns of leaf physiology and biofilm characteristics for Hydrilla verticillata in both single and mixed communities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 59802–59812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shi, X.; Nan, J.; Huang, Q.; Shen, X.; Li, J. Morphological responses of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans along an underwater light gradient: A mesocosm experiment reveals the importance of the Secchi depth to water depth ratio. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Shi, K.; Qin, B. Response of community composition and biomass of submerged macrophytes to variation in underwater light, wind and trophic status in a large eutrophic shallow lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, X.; Cui, Z.; Tao, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Huang, Q. Driving forces and recovery potential of the macrophyte decline in East Taihu Lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Thomaz, S.M.; Deng, J. Global loss of aquatic vegetation in lakes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C.; Li, H.C.; Shiau, L.J. Impacts of anthropogenic disturbances on diatom diversity in a shallow spring-fed pool. Diversity 2022, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.J.; Zeng, G.M.; Sang, L.H.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Z.J.; Dai, J.; Yin, D.C.; Lang, J.; et al. Effects of dam construction on biodiversity: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaland, S.; Hongve, D.; Laudon, H.; Riise, G.; Vogt, R.D. Quantifying the drivers of increasing coloured organic matter in boreal surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jane, S.F.; Winslow, L.A.; Remucal, C.K.; Rose, K.C. Long-term trends and synchrony in dissolved organic matte characteristics in Wisconsin, USA, lakes: Quality, not quantity, is highly sensitive to climate. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeo. 2017, 122, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luimstra, V.M.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Xu, T.; Schuurmans, J.M.; Huisman, J. Changes in water color shift competition between phytoplankton species with contrasting light-harvesting strategies. Ecology 2020, 101, e02951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Muller, R.A.; Norman, M.; Tranvik, L.J. Sensitivity of freshwaters to browning in response to future climate change. Clim. Chang. 2016, 134, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulie, T.; Stibor, H.; Mas, S.; Braun, B.; Knechtel, J.; Nejstgaard, J.C.; Sommer, U.; Vidussi, F.; Mostajir, B. Brownification reduces oxygen gross primary production and community respiration and changes the phytoplankton community composition: An in situ mesocosm experiment with high-frequency sensor measurements in a North Atlantic bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsema, R.E.; Meire, P.; Schoelynck, J. The future of freshwater macrophytes in a changing world: Dissolved organic carbon quantity and quality and its interactions with macrophytes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ask, J.; Karlsson, J.; Persson, L.; Ask, P.; Bystrom, P.; Jansson, M. Terrestrial organic matter and light penetration: Effects on bacterial and primary production in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horppila, J.; Pippingsköld, E.; Estlander, S. Effects of water colour on the pigment content of a floating-leaved macrophyte—Implications of lake brownification. Aquat. Bot. 2022, 181, 103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebret, K.; Langenheder, S.; Colinas, N.; Östman, Ö.; Lindström, E.S. Increased water colour affects freshwater plankton communities in a mesocosm study. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 81, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spilling, K.; Asmala, E.; Haavisto, N.; Haraguchi, L.; Kraft, K.; Lehto, A.M.; Lewandowska, A.M.; Norkko, J.; Piiparinen, J.; Seppala, J.; et al. Brownification affects phytoplankton community composition but not primary productivity in eutrophic coastal waters: A mesocosm experiment in the Baltic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchet, C.C.; Arzel, C.; Davranche, A.; Kahilainen, K.K.; Secondi, J.; Taipale, S.; Lindberg, H.; Loehr, J.; Manninen-Johansen, S.; Sundell, J.; et al. Ecology and extent of freshwater browning—What we know and what should be studied next in the context of global change. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, M.I.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Zhang, H.; Ekvall, M.K.; Medeiros, L.R.; Hansson, L.A. Charophytes collapse beyond a critical warming and brownification threshold in shallow lake systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reitsema, R.E.; Wolters, J.W.; Preiner, S.; Meire, P.; Hein, T.; De Boeck, G.; Blust, R.; Schoelynck, J. Response of submerged macrophyte growth, morphology, chlorophyll content and nutrient stoichiometry to increased flow velocity and elevated CO2 and dissolved organic carbon concentrations. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 8, 527801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewardene, L.; Wu, N.; Fohrer, N.; Riis, T. Epiphytic biofilms in freshwater and interactions with macrophytes: Current understanding and future directions. Aquat. Bot. 2022, 176, 103467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, M.; Wen, C.; Liu, D. Nitrogen release and its influence on anammox bacteria during the decay of Potamogeton crispus with different values of initial debris biomass. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, T.; García Molinos, J.; Li, C.; Hu, B.; Pan, M.; Zhang, M. Effects of warming, climate extremes and phosphorus enrichment on the growth, sexual reproduction and propagule carbon and nitrogen stoichiometry of Potamogeton crispus L. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Xu, H.; Zou, W.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Ji, P.; Chen, J. Influence of Potamogeton crispus on lake water environment and phytoplankton community structure. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4053–4061. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rasilo, T.; Ojala, A.; Huotari, J.; Starr, M.; Pumpanen, J. Concentrations and quality of DOC along the terrestrial-aquatic continuum in a boreal forested catchment. Freshw. Sci. 2015, 34, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dai, H.; Skuza, L.; Chen, Y.; Wei, S. Difference in Cd2+ flux around the root tips of different soybean (Glycine max L.) cultivars and physiological response under mild cadmium stress. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, S.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Huang, W. Morphological, photosynthetic, and CAM physiological responses of the submerged macrophyte Ottelia alismoides to light quality. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 202, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, T.; Gallegos, C.L.; Harrison, W.G. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J. Mar. Res. 1980, 38, 687–701. [Google Scholar]
- Ralph, P.J.; Gademann, R. Rapid light curves: A powerful tool to assess photosynthetic activity. Aquat. Bot. 2005, 82, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, D.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J. Responses of submerged plant Vallisneria natans growth and leaf biofilms to water contaminated with microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Lv, X.; Guo, S.; Ma, Y.; Han, B.; Hu, X. Interactions between suspended sediments and submerged macrophytes-epiphytic biofilms under water flow in shallow lakes. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Xing, Y.; Ding, A.; Sun, S.; Cheng, H.; Bian, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhu, G. Brownification of freshwater promotes nitrogen-cycling microorganism growth following terrestrial material increase and ultraviolet radiation reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormul, R.P.; Ahlgren, J.; Ekvall, M.K.; Hansson, L.A.; Brönmark, C. Water brownification may increase the invasibility of a submerged non-native macrophyte. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhina, O.; Virolainen, E.; Fagerstedt, K.V. Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: A review. Ann. Bot. Lond. 2003, 91, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemalatha, D.; Rangasamy, B.; Nataraj, B.; Maharajan, K.; Narayanasamy, A.; Ramesh, M. Transcriptional, biochemical and histological alterations in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to benzotriazole ultraviolet stabilizer-328. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Caparrós, P.; De Filippis, L.; Gul, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Ozturk, M.; Altay, V.; Lao, M.T. Oxidative stress and antioxidant metabolism under adverse environmental conditions: A Review. Bot. Rev. 2020, 87, 421–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, D.M.; Pollard, A.I.; Labou, S.G.; Hampton, S.E. Fewer blue lakes and more murky lakes across the continental U.S.: Implications for planktonic food webs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 2661–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Köhler, J.; Hachol, J.; Hilt, S. Regulation of submersed macrophyte biomass in a temperate lowland river: Interactions between shading by bank vegetation, epiphyton and water turbidity. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 92, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kogure, K.; Zhang, X.H. Diversity of culturable heterotrophic bacteria from the Mariana Trench and their ability to degrade macromolecules. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Parameters | CK | LH | MH | HH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT (° C) | 22.6 ± 1.7 a | 22.6 ± 1.6 a | 22.5 ± 1.6 a | 22.4 ± 1.2 a |
| pH | 8.20 ± 0.07 a | 8.22 ± 0.08 a | 8.35 ± 0.13 a | 8.49 ± 0.19 a |
| DTN (mg/L) | 2.05 ± 0.16 b | 2.62 ± 0.26 ab | 2.99 ± 0.38 a | 3.42 ± 0.64 a |
| DTP (mg/L) | 0.19 ± 0.04 a | 0.18 ± 0.03 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.22 ± 0.04 a |
| DOC (mg/L) | 3.61 ± 0.12 d | 6.82 ± 0.25 c | 9.65 ± 0.52 b | 14.52 ± 0.76 a |
| A420 (cm−1) | 0.011 ± 0.001 d | 0.043 ± 0.004 c | 0.079 ± 0.009 b | 0.121 ± 0.016 a |
| Time | CK | LH | MH | HH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~14 d | 31.4 ± 6.7 a | 21.5 ± 7.6 ab | 25.4 ± 6.4 ab | 14.3 ± 1.0 b |
| 15~28 d | 30.3 ± 1.3 a | 32.9 ± 8.5 a | 42.9 ± 12.8 a | 3.3 ± 9.5 b |
| 29~42 d | 23.6 ± 4.2 a | 25.4 ± 7.8 a | 38.3 ± 6.2 a | −19.4 ± 7.1 b |
| Total | 28.4 ± 1.4 b | 29.0 ± 1.2 b | 33.3 ± 1.6 a | 14.1 ± 0.2 c |
| Groups | rETRm μmol/(m2·s) | α | Ek μmol/(m2·s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 15.22 ± 1.35 b | 0.22 ± 0.02 b | 70.24 ± 2.61 b |
| LH | 21.03 ± 1.74 a | 0.26 ± 0.03 b | 86.23 ± 2.01 a |
| MH | 24.82 ± 2.21 a | 0.33 ± 0.02 a | 90.18 ± 1.94 a |
| HH | 6.58 ± 0.88 c | 0.08 ± 0.01 c | 48.29 ± 1.01 c |
| Samples | Chao | Shannon |
|---|---|---|
| CK-0d | 1730.6 | 6.22 |
| LH-0d | 1600.7 | 3.17 |
| MH-0d | 1696.3 | 4.03 |
| HH-0d | 1498.0 | 2.95 |
| CK-21d | 1874.5 | 5.67 |
| LH-21d | 1710.5 | 5.58 |
| MH-21d | 1765.6 | 5.67 |
| HH-21d | 1696.7 | 5.94 |
| CK-42d | 1763.5 | 5.60 |
| LH-42d | 1931.2 | 5.86 |
| MH-42d | 1727.8 | 5.71 |
| HH-42d | 1765.1 | 5.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, F.; Zhu, Y. Responses of a Submerged Macrophyte Potamogeton crispus and Epiphytic Biofilm to Humic-Substance Enrichment Coupled with Brownification in Freshwater Habitats. Water 2023, 15, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162860
Wan X, Wang G, Yang F, Zhu Y. Responses of a Submerged Macrophyte Potamogeton crispus and Epiphytic Biofilm to Humic-Substance Enrichment Coupled with Brownification in Freshwater Habitats. Water. 2023; 15(16):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162860
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Xiang, Guoxiang Wang, Fei Yang, and Yueming Zhu. 2023. "Responses of a Submerged Macrophyte Potamogeton crispus and Epiphytic Biofilm to Humic-Substance Enrichment Coupled with Brownification in Freshwater Habitats" Water 15, no. 16: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162860





