Effects of Soil Particle Structure on the Distribution and Transport of Soil Water and Salt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Test Design
2.3. Data Acquisition
3. Results and Analysis
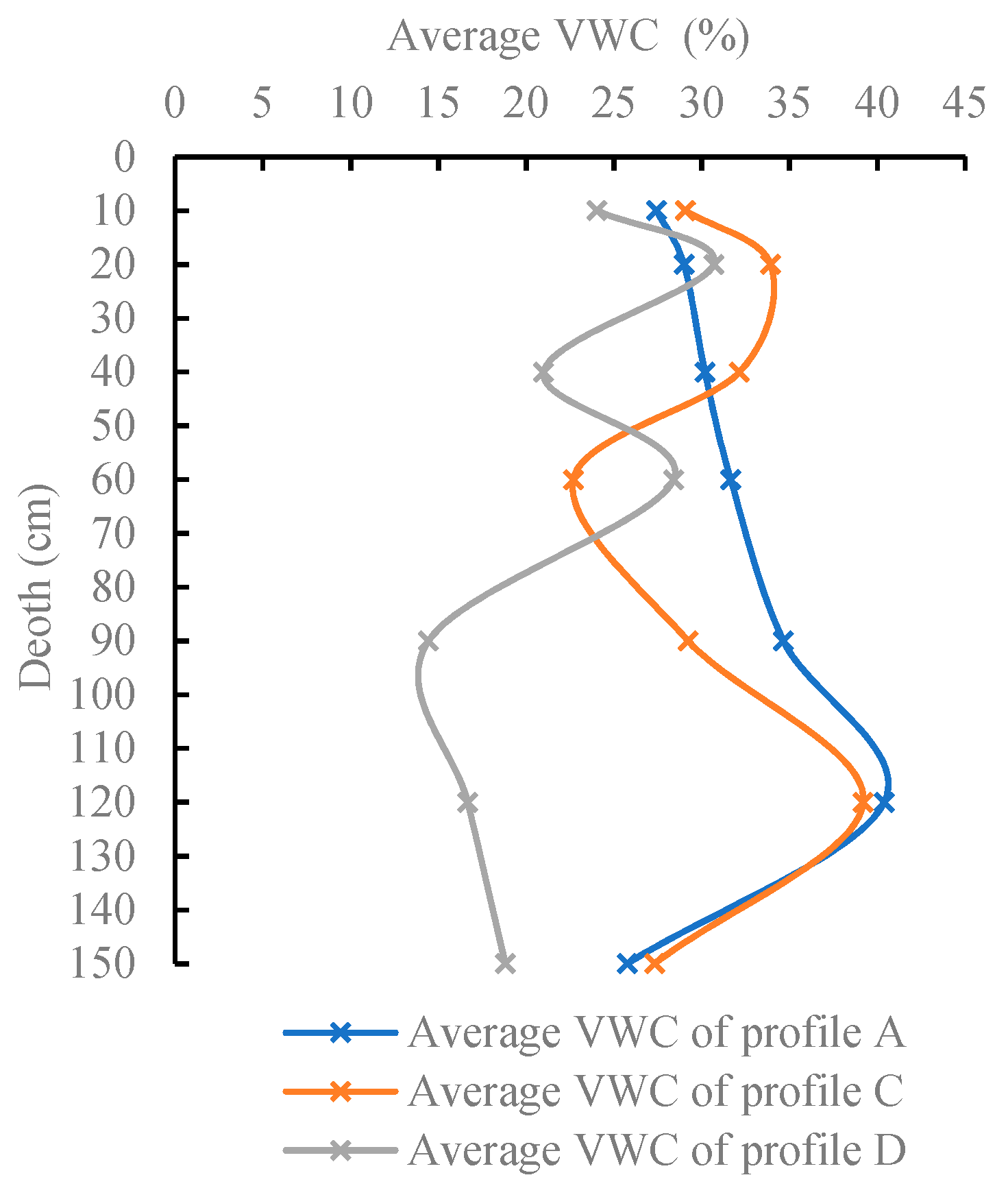
3.1. Distribution of VWC
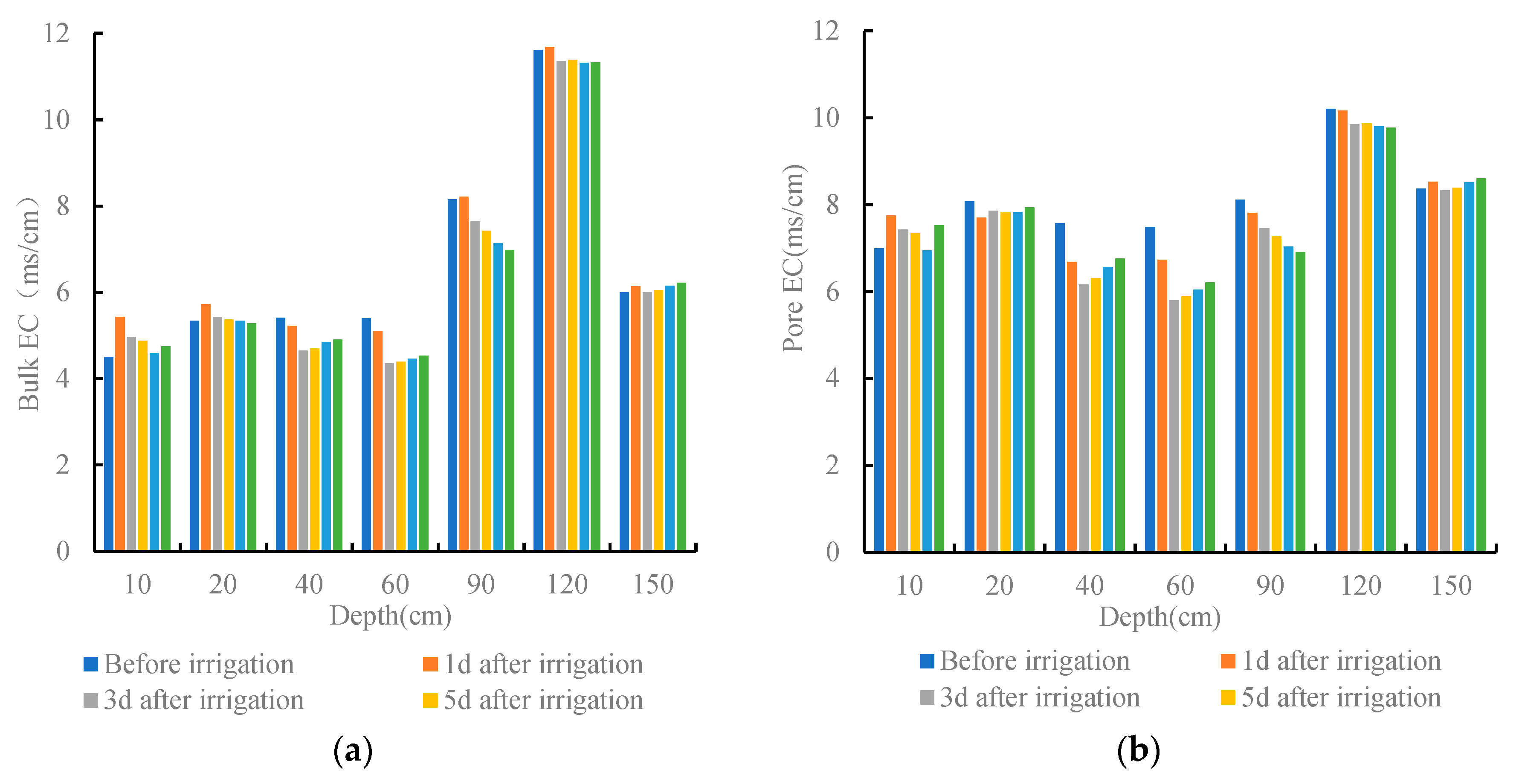
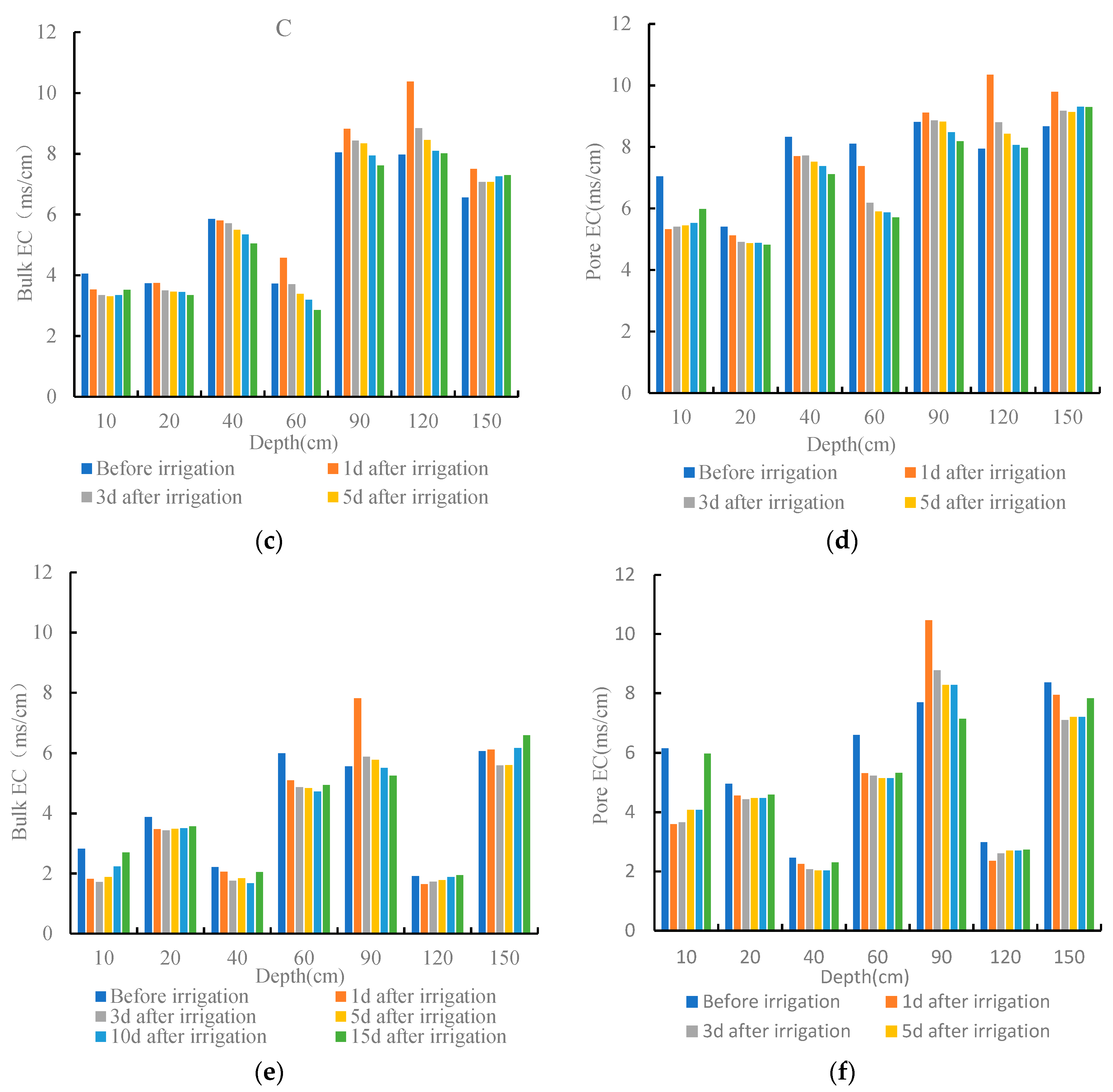
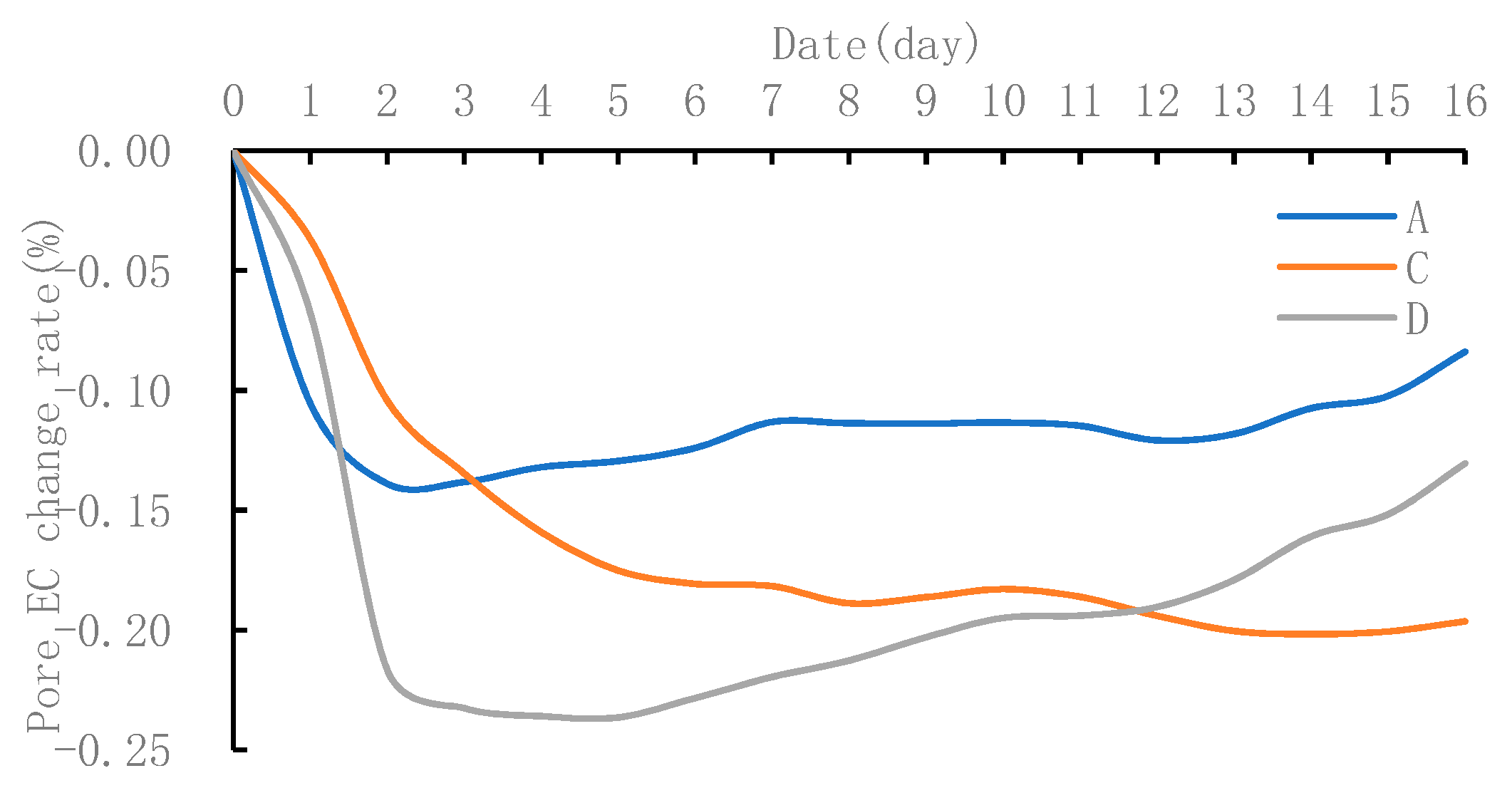
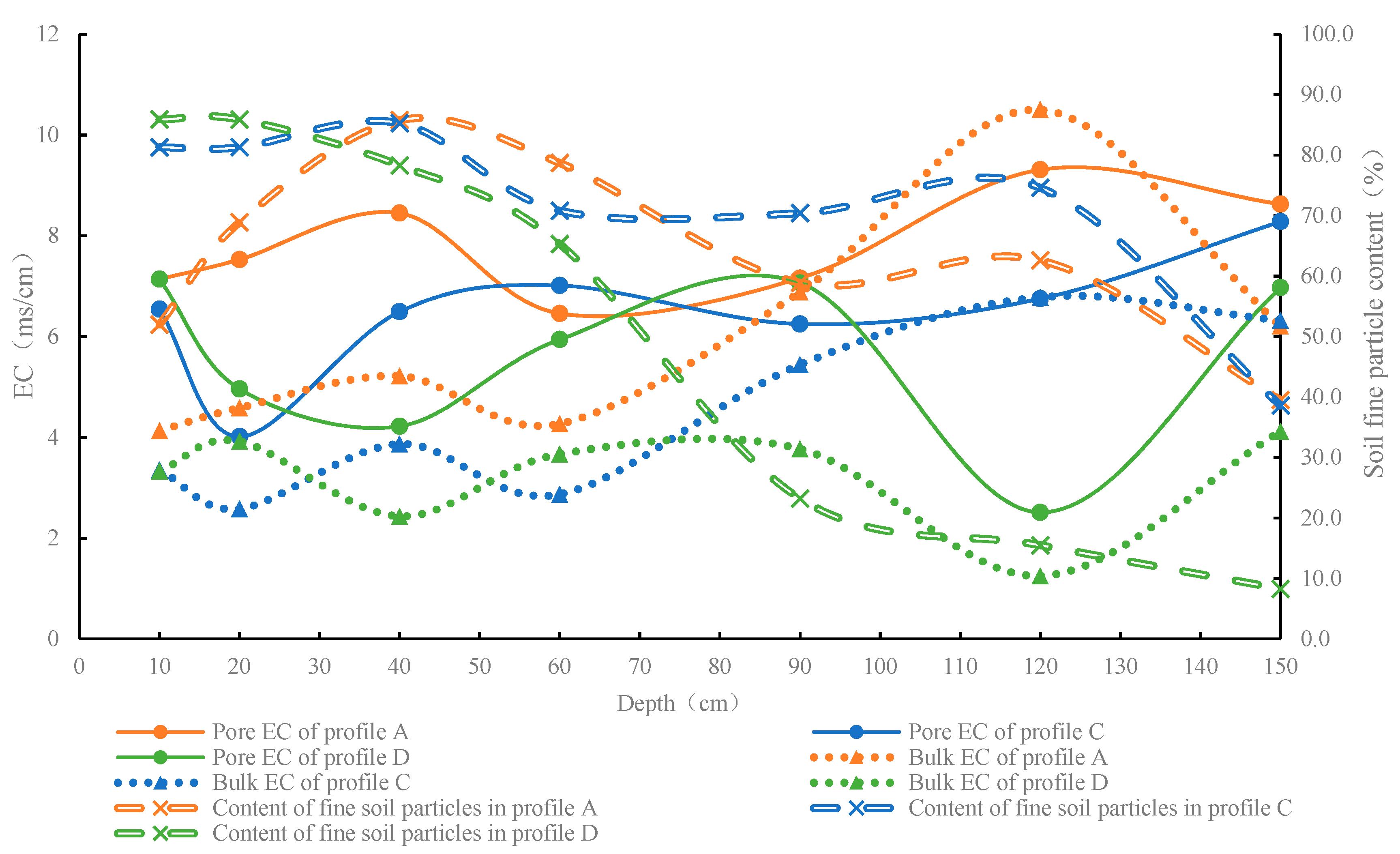
3.2. Distribution of Soil EC
3.3. Relationships between Soil Particle Structure and the Distribution of Soil Water and Salts
3.3.1. Relationship between Soil Particle Structure and the Annual Average Distribution of Soil Water and Salts
3.3.2. Relationship between Soil Particle Structure and the Migration of Soil Water and Salt during the Irrigation Period
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Yan, M. Study on Index of Groundwater Ecological Function Crisis Classification and Early Warning in Northwest China. Water 2022, 14, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Cui, H.; Liu, P. Construction and application of evaluation index system of groundwater ecological function in northwest arid area. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Deo, R.C.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, R. An interplay of soil salinization and groundwater degradation threatening coexistence of oasis-desert ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 806 Pt 2, 150599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Feng, Q.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, M.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal dynamics and eco-hydrological controls of water and salt migration within and among different land uses in an oasis-desert system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Liu, P.; Nie, Z.; Zhu, P. Law of Soil Water and Salt Transport in Vadose Zone of Transition Zone between Farmland and Desert. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 8640–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.B.; Su, C.L.; Xie, X.J.; Pan, H.; Ji, Q.; Tao, Y. Mechanism of salinization of shallow groundwater in Western Hetao Irrigation Area. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 2267–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X. Environmental groundwater depth for groundwater-dependent terrestrial ecosystems in arid/semiarid regions: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Ochoa, C.G.; Chen, X. Assessing environmental water requirement for groundwater-dependent vegetation in arid inland basins by combining the copula joint distribution function and the dual objective optimization: An application to the Turpan Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Study on Coupling Model of Groundwater Balance and Ecological Succession: A Case Study of Shule River Irrigation Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Q. Influences of lithology and structure of the vadose zone on groundwater ecological function. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2022, 49, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Nie, Z.; Cao, L.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, P. Comprehensive evaluation on the ecological function of groundwater in the Shiyang River watershed. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H. Review of studies on the relationship between soil water movement and energy and their driving forces in the vadose zone of arid regions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H. Advances in moisture migration in vadose zone of dryland and recharge effects on groundwater dynamics. Adv. Earth Sci. 2017, 32, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Ma, Z.; Song, H. Biomass of Artemisia ordosica in sand land and its root system distribution characteristics in the semiarid regions. Arid Land Geogr. 2018, 41, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, B.; Qin, S.; Fa, K. Fine-root distribution, production, decomposition, and effect on soil organic carbon of three revegetation shrub species in northwest China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 359, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Han, B. Effects of farmland plastic mulching on rainfall infiltration using Hydrus-2D model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Fu, X.; Li, Z. Redistribution Mechanism for Irrigation Water and Salinity in Typical Irrigation and Drainage Unit in the Hetao Irrigation District, China. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W. Dynamic and Transformation Relationship between Soil Water and Groundwater in Typical Areas of Hetao Irrigation District. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chai, J.; Zhang, H. Experimental Study on the Rise of Capillary Water in Layered Soil. J. Inn. Mong. Univ. (Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. NeiMongol) 2021, 52, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, R.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y. Root Water Source of Pinus sylvestris L. var. Mongholica and Influencing Factors in the Southeastern Part of Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 1336–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S.; Nie, Z.; Cui, H.; Wang, Q. Effects of Groundwater Level Control on Soil Salinity Change in Farmland around Wetlands in Arid Areas: A Case Study of the Lower Reaches of the Shiyang River Basin, China. Water 2023, 15, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Liu, P.; Nie, Z.; Zhu, P.; Geng, X. Characteristics of Water and Salt Movement in Aeration Zone after Irrigation with Brackish Water under Water Level Regulation. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaye, K.T.; Boulange, J.; Tu, L.H.; Saito, H.; Watanabe, H. Soil water content and soil temperature modeling in a vadose zone of Andosol under temperate monsoon climate. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y.; Ma, X. Effects of different crop covers on vertical groundwater recharge. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2019, 46, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, T.K.; Šimůnek, J.; Pramanik, P.; Sudhishri, S.; Vashisth, A.; Krishnan, P.; Chakraborty, D.; et al. Modelling soil water balance and root water uptake in cotton grown under different soil conservation practices in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y. Study on Movement Mechanism of Water and Salt in Vadose Zone under Saline Water Irrigation. Master’s Thesis, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsilas, I.; Angelaki, A.; Chalkidis, I. Hydrodynamics of the Vadose Zone of a Layered Soil Column. Water 2023, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A. Advances in Water Infiltration and Solute Transport in Layered Soil. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2017, 39, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Xie, X. A Study on the Influence of Different Salinity on the Infiltration Law of Layered Soil. Water Sav. Irrig. 2019, 5, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Effects of textural layering on water regimes in sandy soils in a desert-oasis ecotone, Northwestern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 627500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, S.; Gao, C.; Hao, Z. Retardation Effect of Layered Soil to Salt Transfer under Drip Irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Gong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ghen, L. Influence of lithologic structure of vadose zone on rainfall infiltration capacity. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2019, 50, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Y. Numerically Simulated Water Movement in Reclaimed Multi-Layered Soil Backfilled with Yellow River Sediments. 2021; Preprint (Version 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, J.; Gerrard, J. Fundamentals of Soils; Routledge: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Progress of the Researches on Functions of Soil Particles. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2008, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessitsch, A.; Weilharter, A.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Kirchmann, H.; Kandeler, E. Microbial population structures in soil particle size fractions of a long-term fertilizer field experiment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4215–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G. Monitoring and predicting the soil water content in the deeper soil profile of Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Tian, F.; Hu, H. Soil particle size distribution and its relationship with soil water and salt under mulched drip irrigation in Xinjiang of China. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, G.; Zhao, C.; Shi, F. Characteristics of soil infiltration in the Tarim River floodplain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orradóttir, B.; Archer, S.; Arnalds, O.; Wilding, L.; Thurow, T. Infiltration in Icelandic Andisols: The role of vegetation and soil frost. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2008, 40, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, C. Experimental Investigation of the Infiltration Features of Different Types of Soil in Hilly Area. Shanxi Hydrotech. 2016, 3, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, P.; Feng, H.; Zhao, X.; Huang, J. Effects of soil clay particle content on soil infiltration capacity by simulated experiments. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2009, 27, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S.; Liu, S.; Nie, Z. Threshold value of ecological water table and dual control technology of the water table and its quantity in the salinized farmland around wetland in arid areas. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2022, 49, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.R. Preliminary Analysis of Soil Water Content Change in Typical Karst Rocky Desertification Area—A Case Study of Chenjiazhai Rocky Desertification Base in Puting County. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z. Research on Soil Moisture Monitoring Technology and Movement Law. Ph.D. Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Calibration on Measurement of Soil Salinity and Water Using Time Domain Reflectrometry (TDR). J. Tarim Univ. 2007, 19, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Lv, H.; Fu, X. Spatio-temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilhorst, M.A. A Pore Water Conductivity Sensor. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1922–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Depth (cm) | Particle Composition (%) | d: mm | Lithology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60–2 | 2–0.5 | 0.5–0.25 | 0.25–0.075 | ≤0.075 | ||
| 10 | / | 1.1 | 1.3 | 45.6 | 52.0 | Silty soil |
| 20 | / | 0.55 | 0.7 | 29.85 | 68.9 | Silty soil |
| 40 | / | / | 0.1 | 14.1 | 85.8 | Silty soil |
| 60 | / | 0.1 | 0.1 | 21.1 | 78.7 | Silty soil |
| 90 | 0.2 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 35.5 | 58.9 | Silty soil |
| 120 | 0.2 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 33.6 | 62.6 | Silty soil |
| 150 | / | 1.6 | 0.9 | 58.0 | 39.5 | Silty sand |
| Depth (cm) | Particle Composition (%) | d: mm | Lithology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60–2 | 2–0.5 | 0.5–0.25 | 0.25–0.075 | ≤0.075 | ||
| 10 | / | / | 0.1 | 18.6 | 81.3 | Silty soil |
| 20 | / | / | 0.1 | 18.6 | 81.3 | Silty soil |
| 40 | / | / | / | 14.7 | 85.3 | Silty soil |
| 60 | / | 0.1 | 0.1 | 29.0 | 70.8 | Silty soil |
| 90 | / | 0.7 | 0.1 | 28.8 | 70.4 | Silty soil |
| 120 | / | 0.1 | 0.1 | 25.2 | 74.6 | Silty soil |
| 150 | / | 1.7 | 1.7 | 58.0 | 38.6 | Silty sand |
| Depth (cm) | Particle Composition (%) | d: mm | Lithology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60–2 | 2–0.5 | 0.5–0.25 | 0.25–0.075 | ≤0.075 | ||
| 10 | / | / | 0.1 | 14.0 | 85.9 | Silty soil |
| 20 | / | / | 0.1 | 14.0 | 85.9 | Silty soil |
| 40 | / | / | / | 21.7 | 78.3 | Silty soil |
| 60 | / | 0.3 | 0.3 | 34.1 | 65.3 | Silty soil |
| 90 | / | 1.65 | 2 | 73.15 | 23.2 | Silty sand |
| 120 | / | 2.2 | 2.7 | 79.6 | 15.5 | Silty sand |
| 150 | / | 0.1 | 0.2 | 91.4 | 8.3 | Fine sand |
| Depth (cm) | A | C | D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine Particle Content (%) | VWC Variation Time (h) | Fine Particle Content (%) | VWC Variation Time (h) | Fine Particle Content (%) | VWC Variation Time (h) | |
| 10 | 52 | 0.5 | 81.3 | 0.5 | 85.9 | 0.5 |
| 20 | 68.9 | 0.5 | 81.3 | 0.5 | 85.9 | 0.5 |
| 40 | 85.8 | 0.5 | 85.3 | 1 | 78.3 | 1 |
| 60 | 78.7 | 1 | 70.8 | 1 | 65.3 | 1.5 |
| 90 | 58.9 | 1 | 70.4 | 1.5 | 30.9 | 2 |
| Depth (cm) | A | C | D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VWC Changing Amplitude (%) | Weighted Average (%) | VWC Changing Amplitude (%) | Weighted Average (%) | VWC Changing Amplitude (%) | Weighted Average (%) | |
| 10 | −4.78 | −2.13 | −2.52 | −4.38 | −7.70 | −5.61 |
| 20 | −3.20 | −1.51 | −4.24 | |||
| 40 | −2.55 | −2.07 | −8.94 | |||
| 60 | −1.98 | −12.59 | −4.99 | |||
| 90 | −0.89 | −2.74 | −2.63 | |||
| 120 | 0.60 | 0.14 | −0.75 | |||
| 150 | 0.27 | 1.72 | −1.38 | |||
| Depth (cm) | A | C | D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk EC Changing Amplitude (%) | Weighted Average | Bulk EC Changing Amplitude (%) | Weighted Average | Bulk EC Changing Amplitude (%) | Weighted Average | |
| 10 | 5.57 | −10.88 | −13.15 | −10.91 | −4.49 | −9.55 |
| 20 | −1.18 | −10.19 | −8.04 | |||
| 40 | −9.27 | −13.82 | −7.42 | |||
| 60 | −16.17 | −23.30 | −17.64 | |||
| 90 | −14.41 | −5.41 | −5.50 | |||
| 120 | −2.40 | 0.42 | 1.35 | |||
| 150 | 3.58 | 11.24 | 8.76 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, S.; Zhu, P.; Liu, P.; Geng, X. Effects of Soil Particle Structure on the Distribution and Transport of Soil Water and Salt. Water 2023, 15, 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152842
Cui S, Zhu P, Liu P, Geng X. Effects of Soil Particle Structure on the Distribution and Transport of Soil Water and Salt. Water. 2023; 15(15):2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152842
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Shangjin, Pucheng Zhu, Pengfei Liu, and Xinxin Geng. 2023. "Effects of Soil Particle Structure on the Distribution and Transport of Soil Water and Salt" Water 15, no. 15: 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152842
APA StyleCui, S., Zhu, P., Liu, P., & Geng, X. (2023). Effects of Soil Particle Structure on the Distribution and Transport of Soil Water and Salt. Water, 15(15), 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152842





