Diagnosis of Groundwater Quality in North Assiut Province, Egypt, for Drinking and Irrigation Uses by Applying Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemical Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
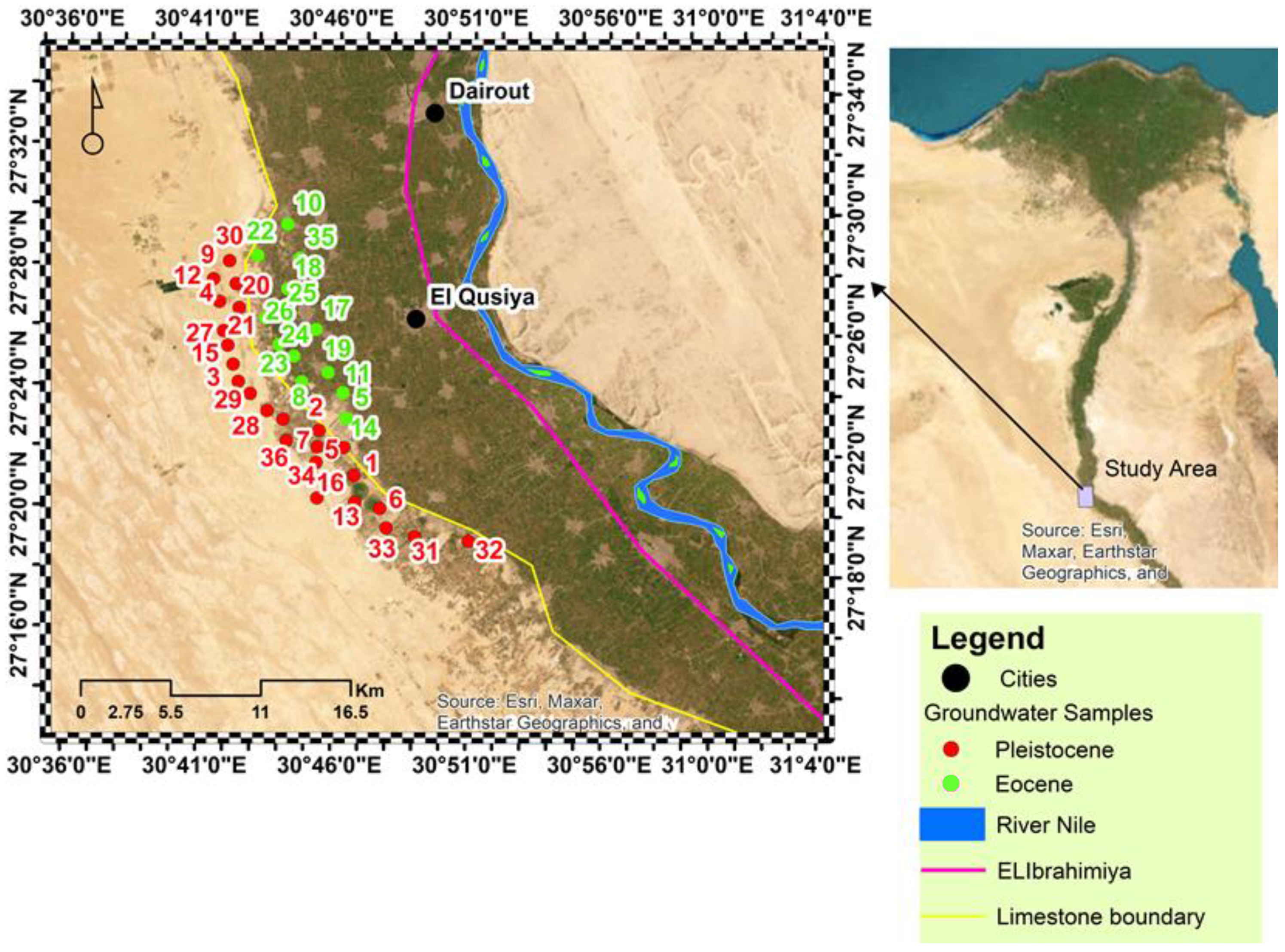
2.1. Geological and Hydrogeological Situation of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Processes
2.3. Statistical Investigation
| Items | Equations | References |
|---|---|---|
| TH | TH = 2.497 Ca2+ + 4.115Mg2+ ions in meg/L | [35] |
| SAR | all ions in meq/L | [36] |
| Na (%) | all ions in meq/L | [37] |
| RSC | all ions in meq/L | [35] |
| MH | all ions in meq/L | [38] |
| SSP | ((Na+ + K+)/(K+ + Na+ + Ca2+ +Mg2+)) ×100 all ions in meq/L | [39] |
| PI | (Na+ + √HCO3−)/(Ca2+ + Mg2+ + Na+) ×100 all ions in meq/L | [40] |
| Kelly’s Ratio | all ions in meq/L | [41] |
3. Results
3.1. Hydrochemical Features
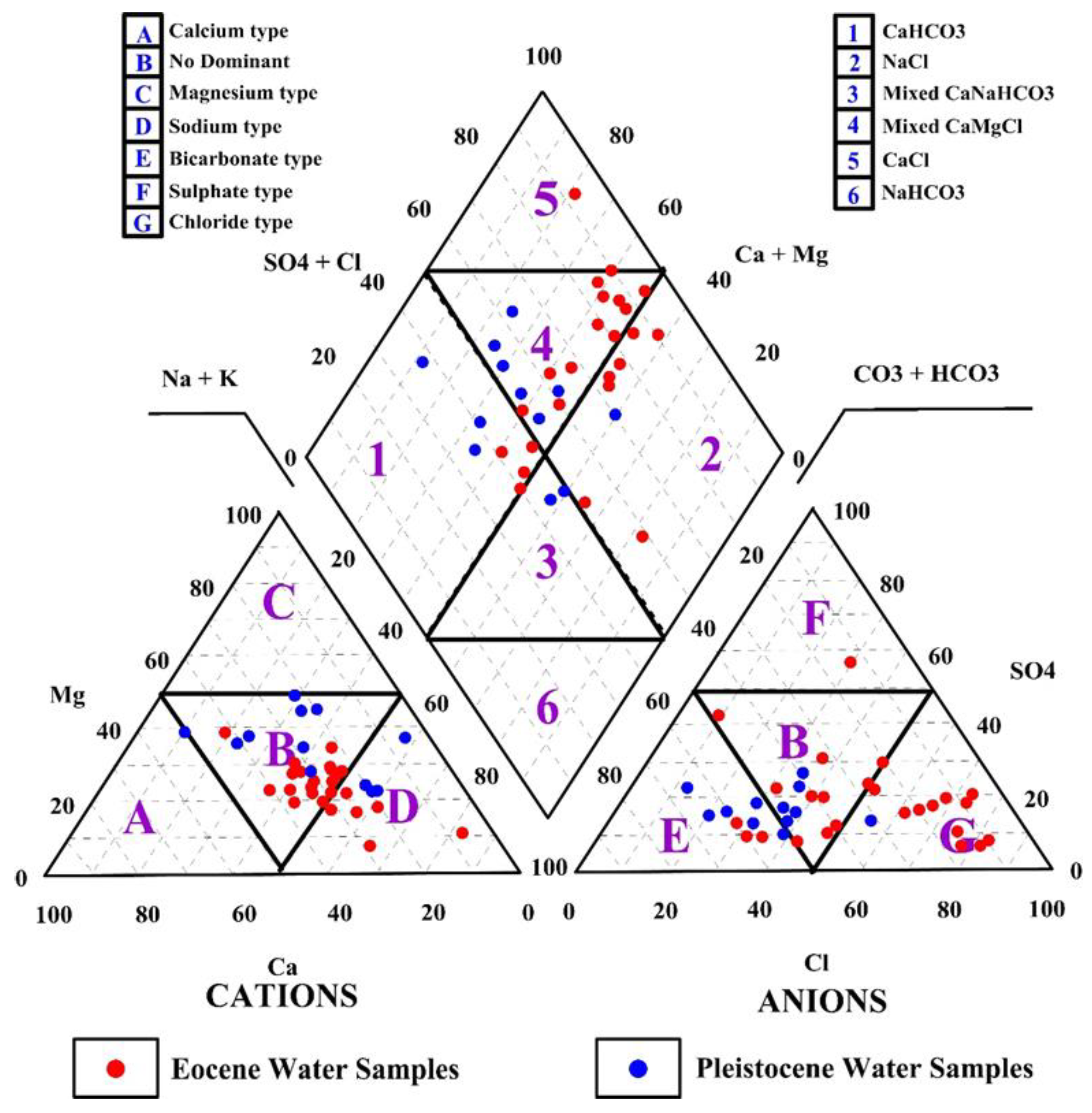
3.2. Groundwater Types
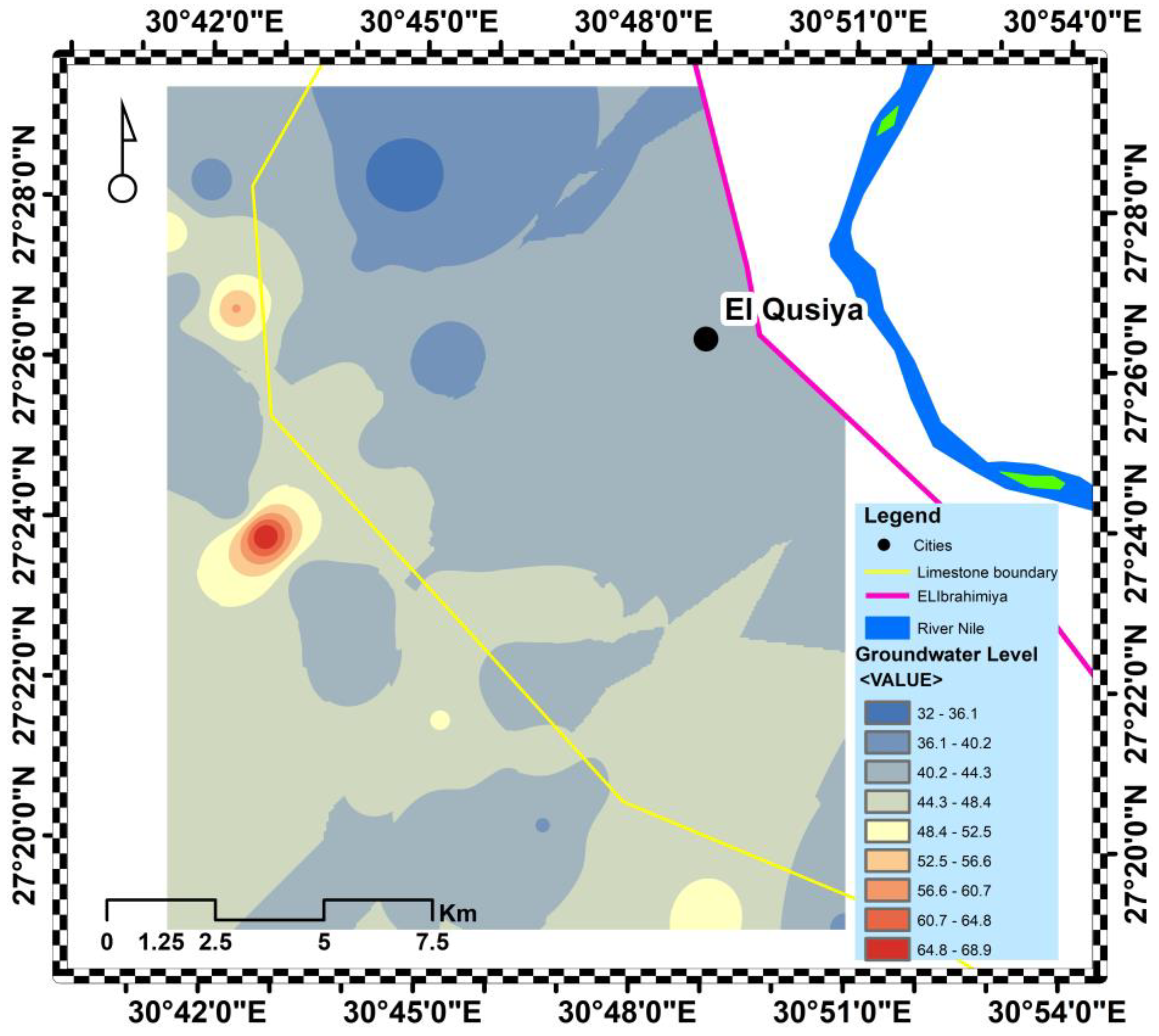
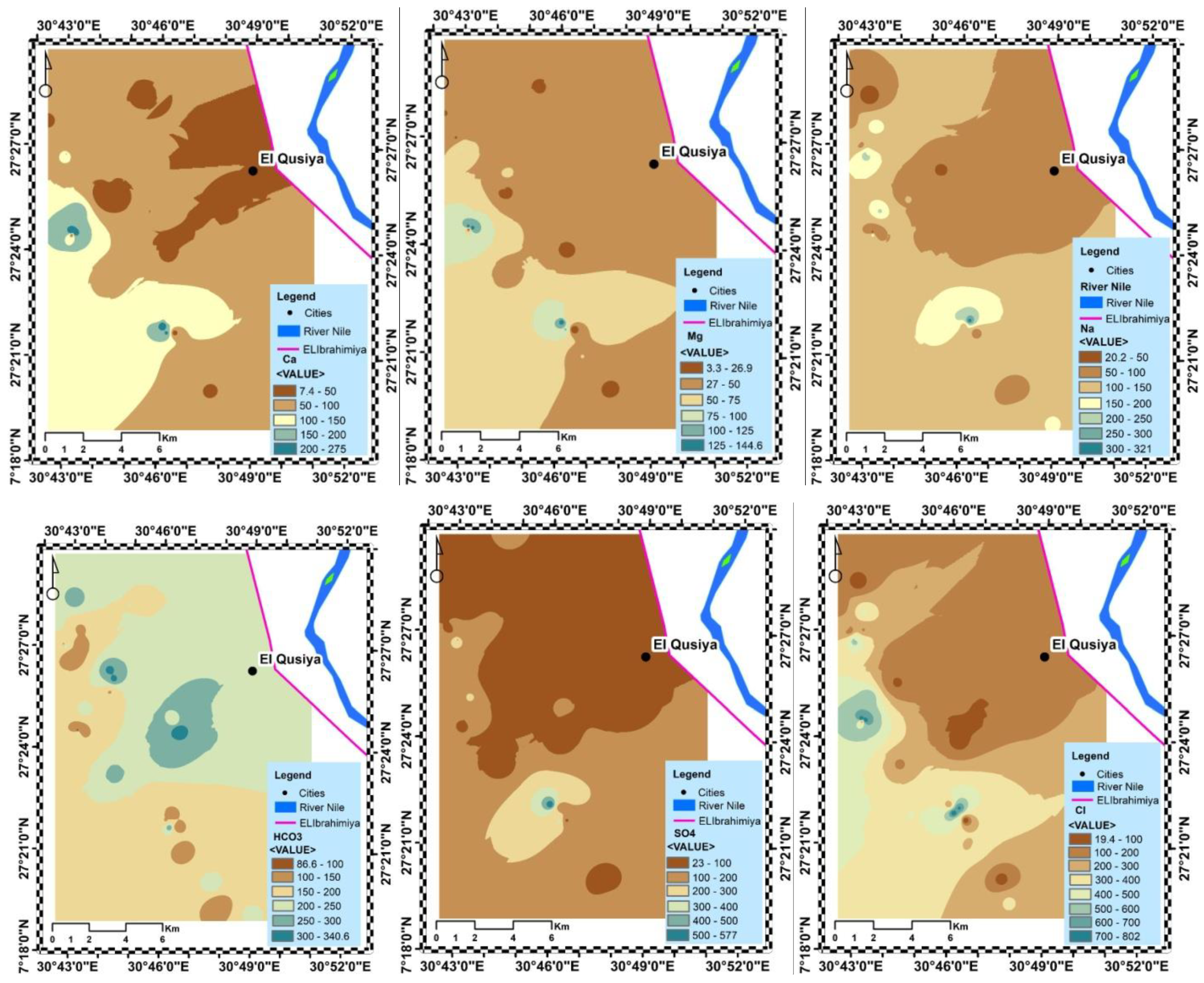
3.3. Groundwater Constituents Origins and Regulatory Factors
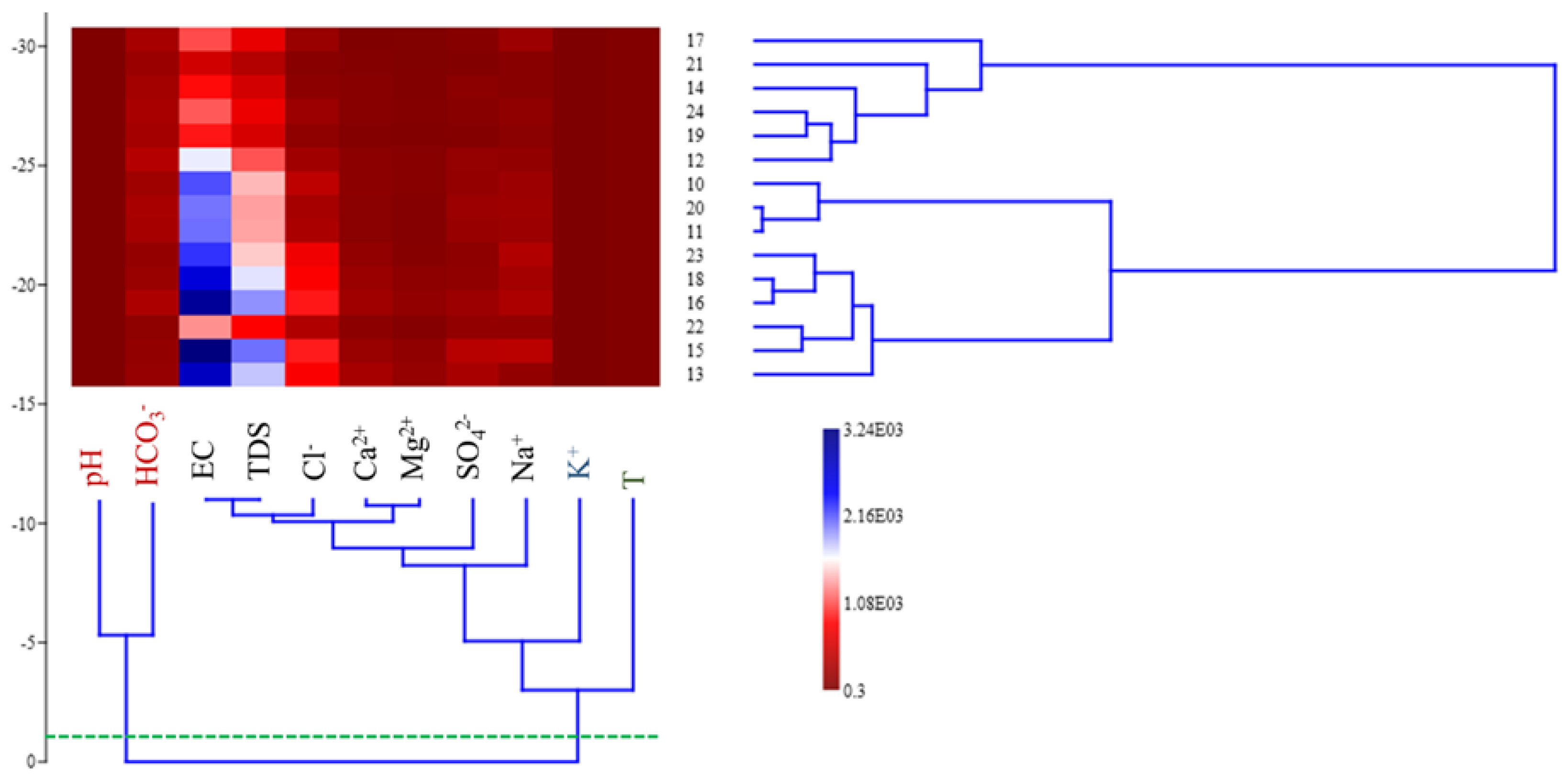
3.4. Pleistocene Aquifer Quality Controlling Factors
3.5. Eocene Water Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
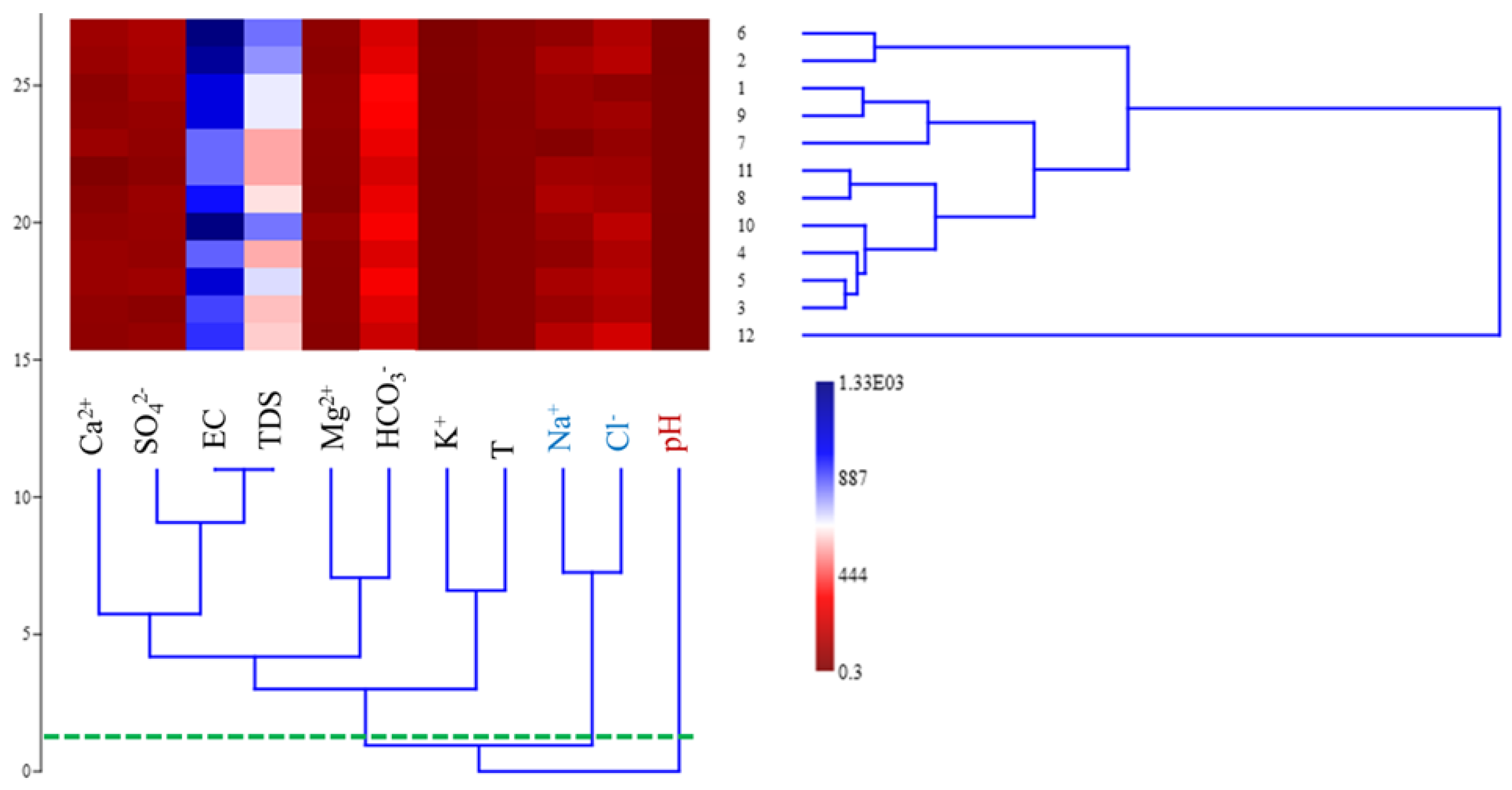
3.6. Pleistocene Water Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
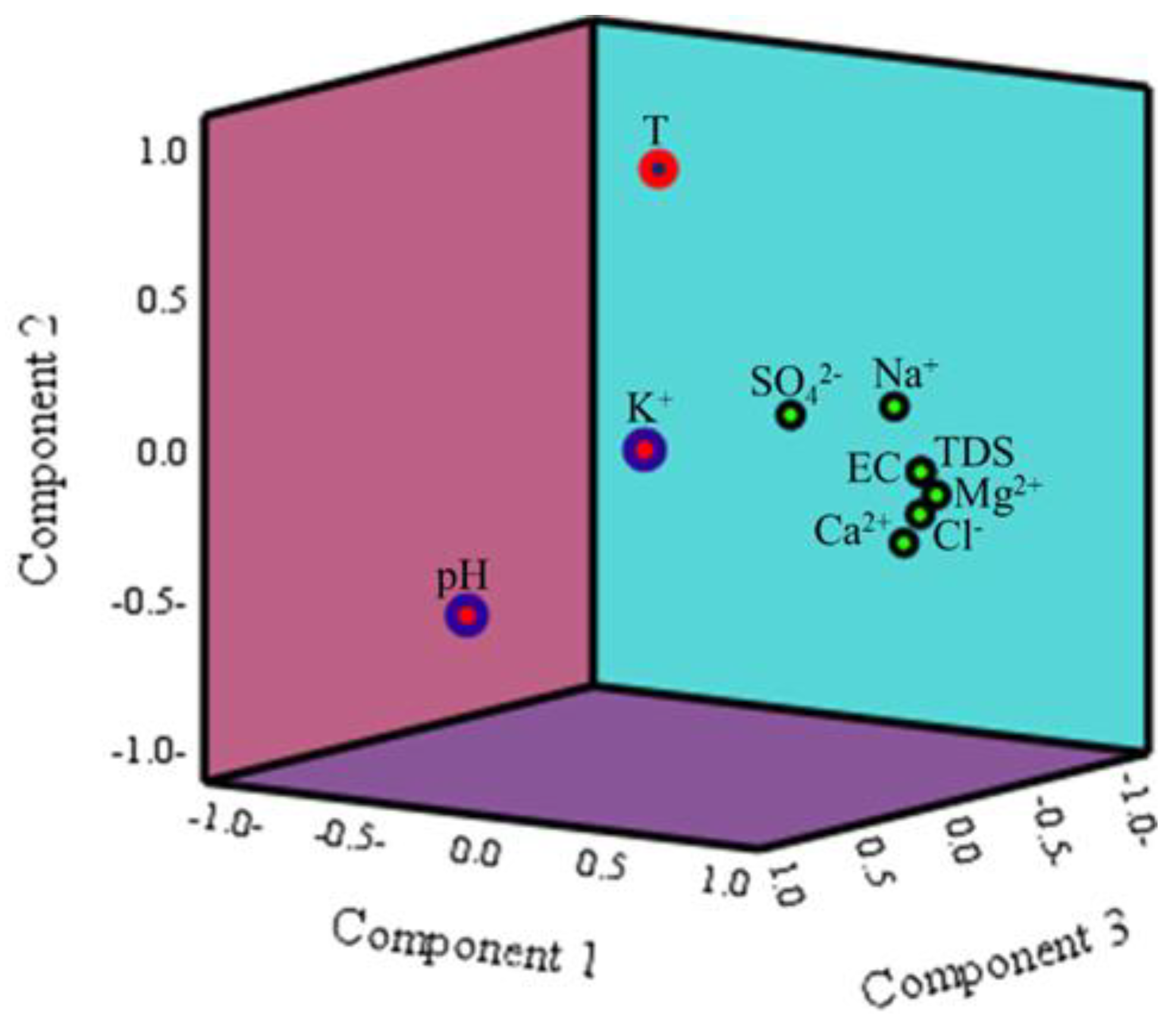
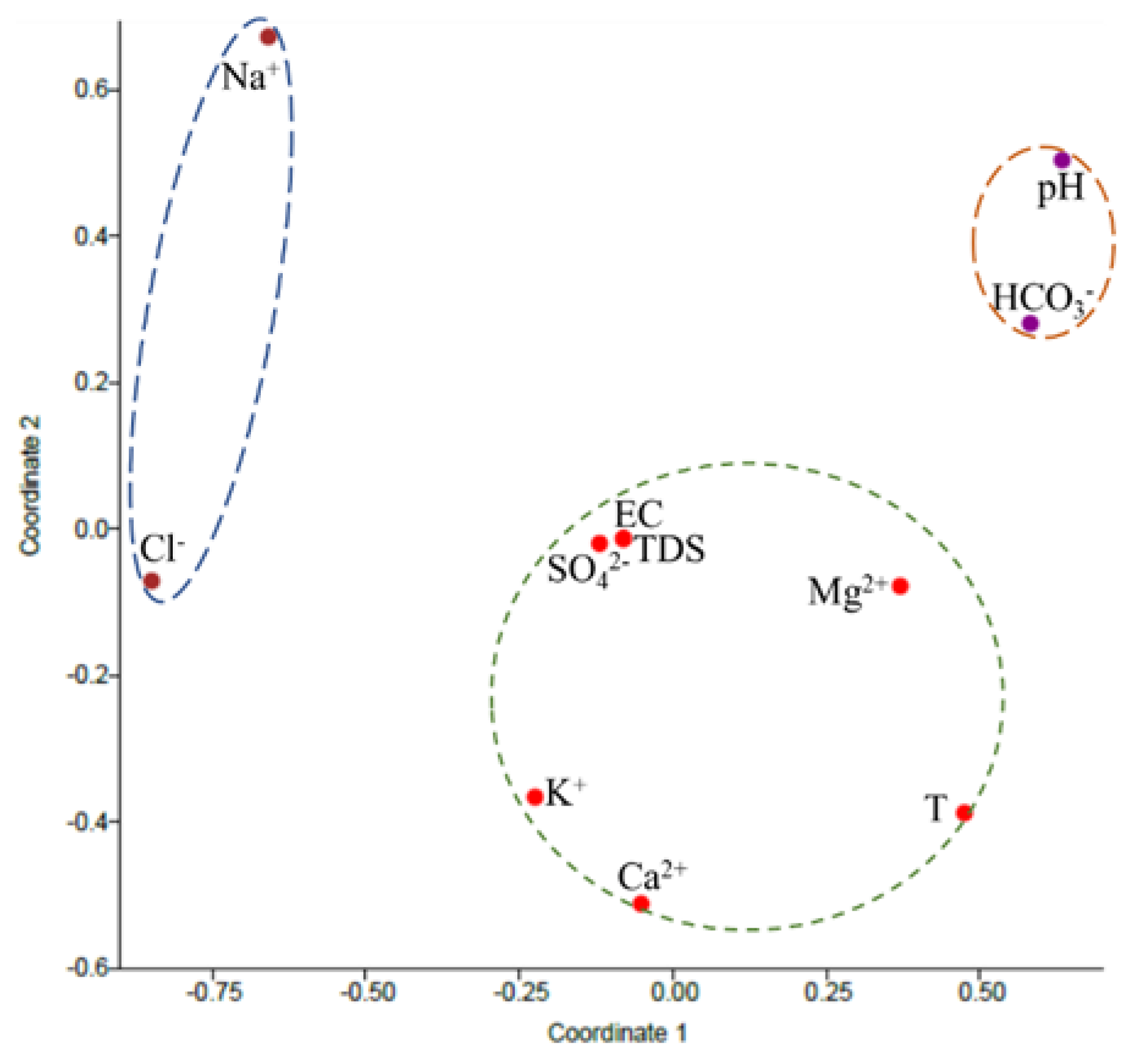
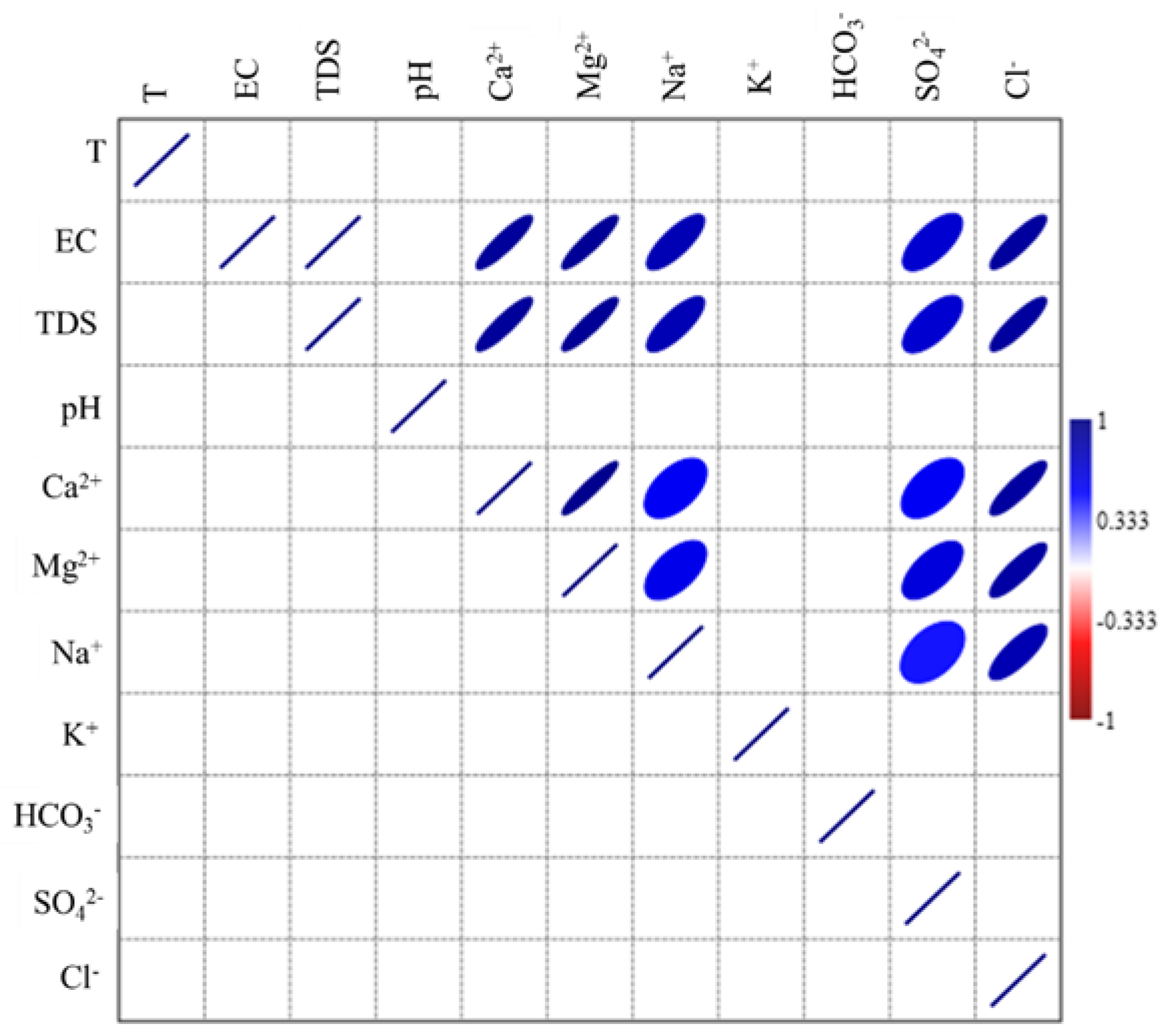
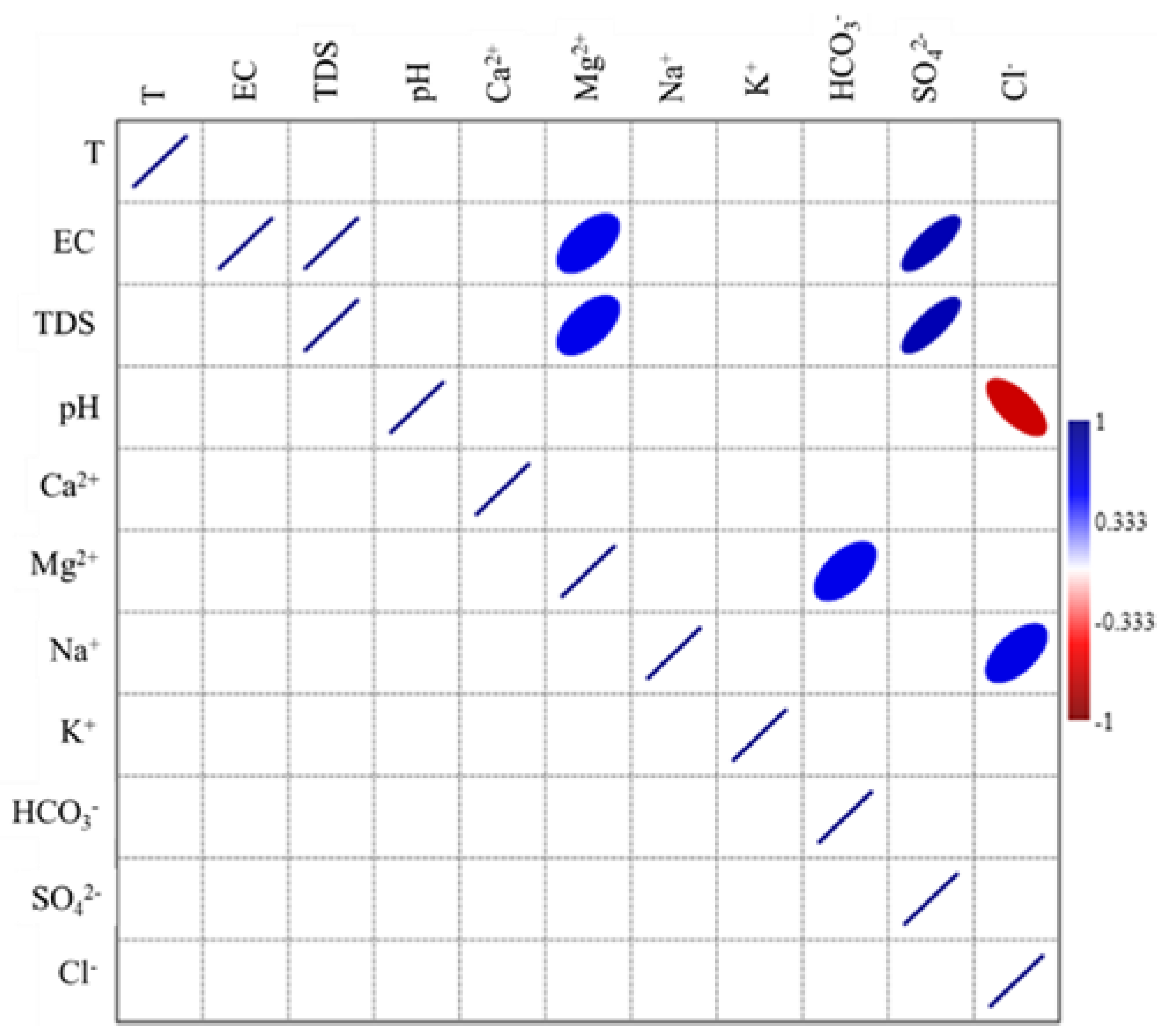
3.7. Correlation Analysis
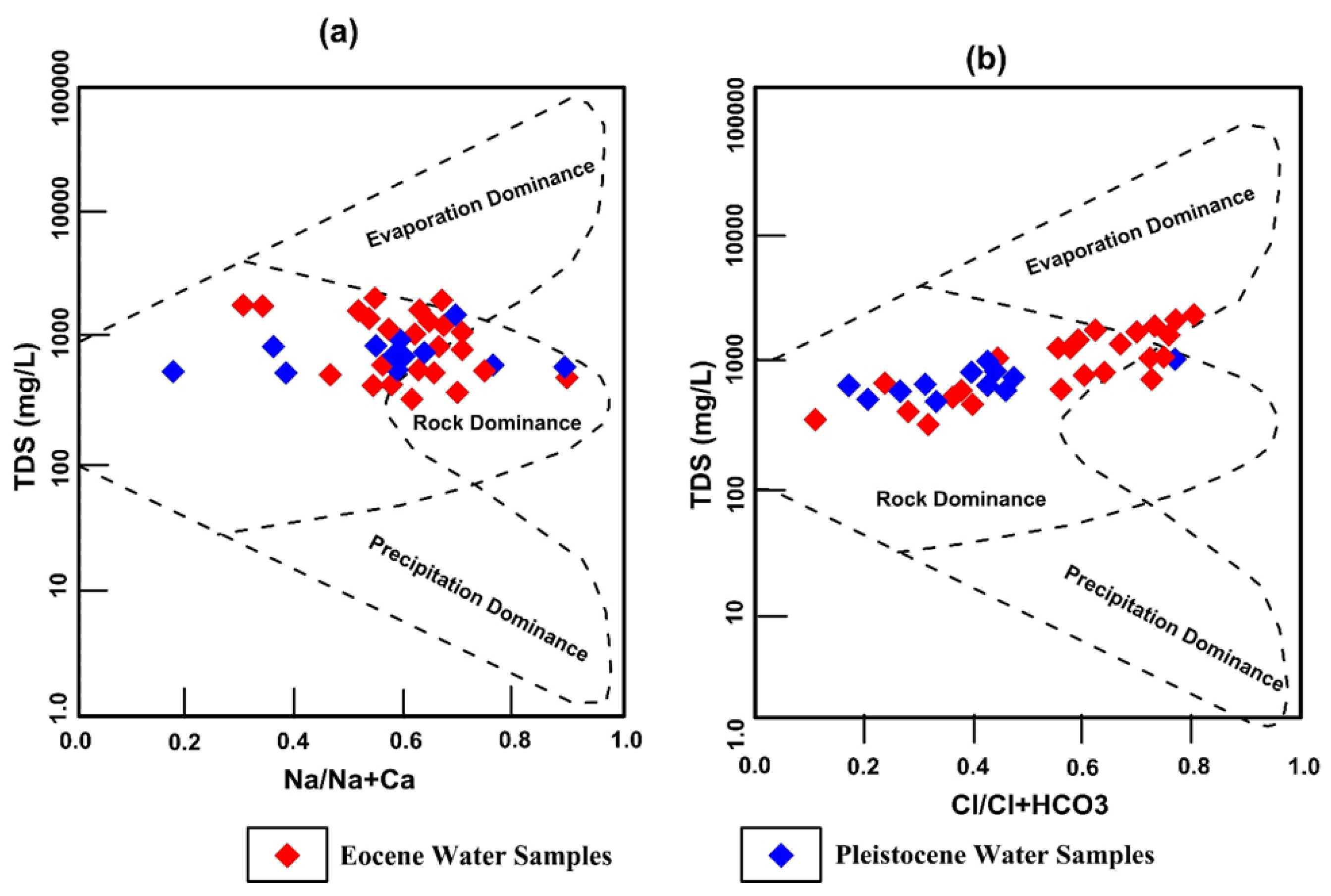
3.8. Groundwater Chemistry Evolution Mechanisms
3.9. Physicochemical Analysis for Drinking Water
3.10. Groundwater Quality for Irrigation
3.10.1. Electrical Conductivity (EC)
3.10.2. Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR)
3.10.3. Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC)
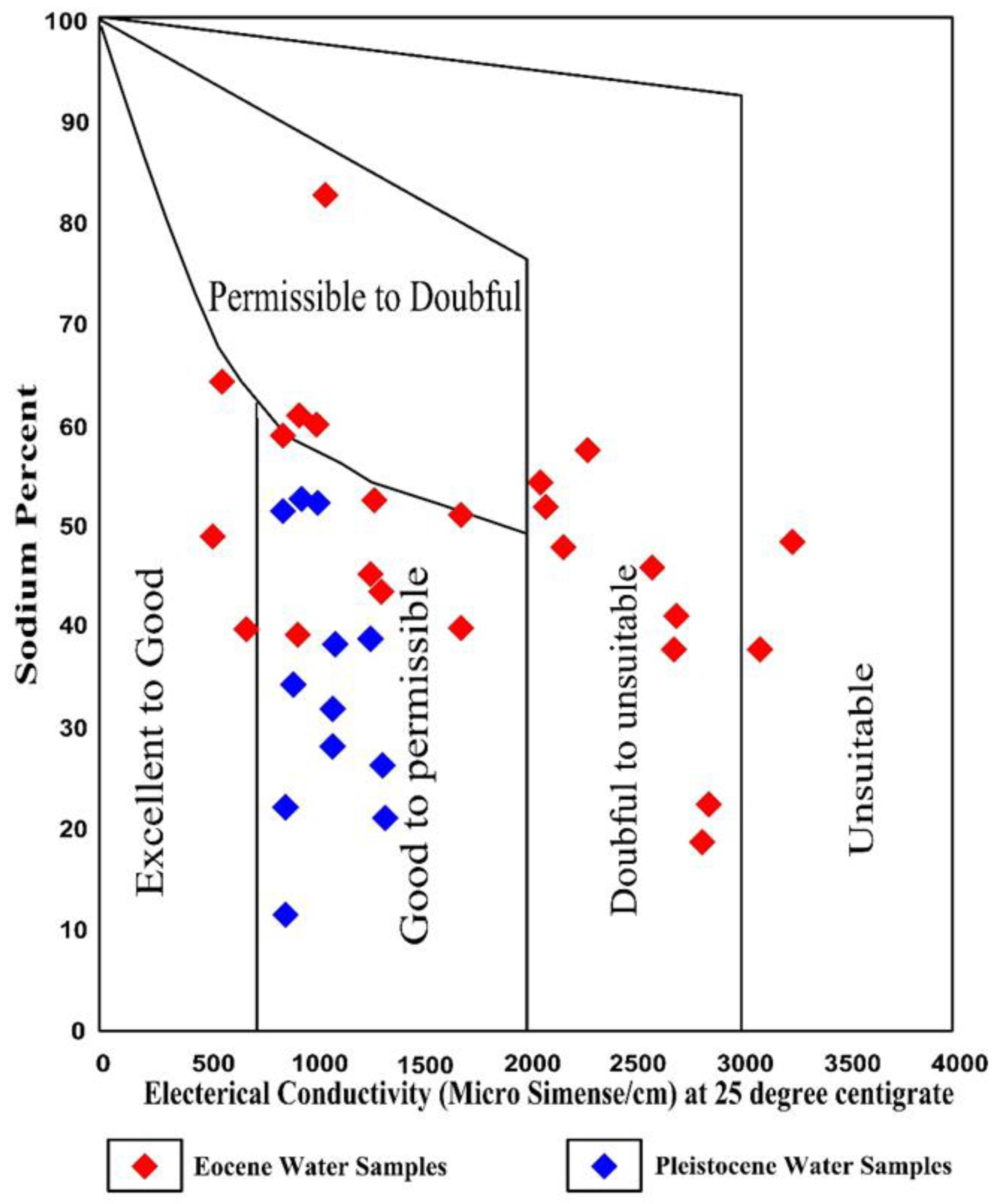
3.10.4. Sodium Percent (% Na)
3.10.5. Kelly Ratio (KR)
3.10.6. Magnesium Hazard (MH)
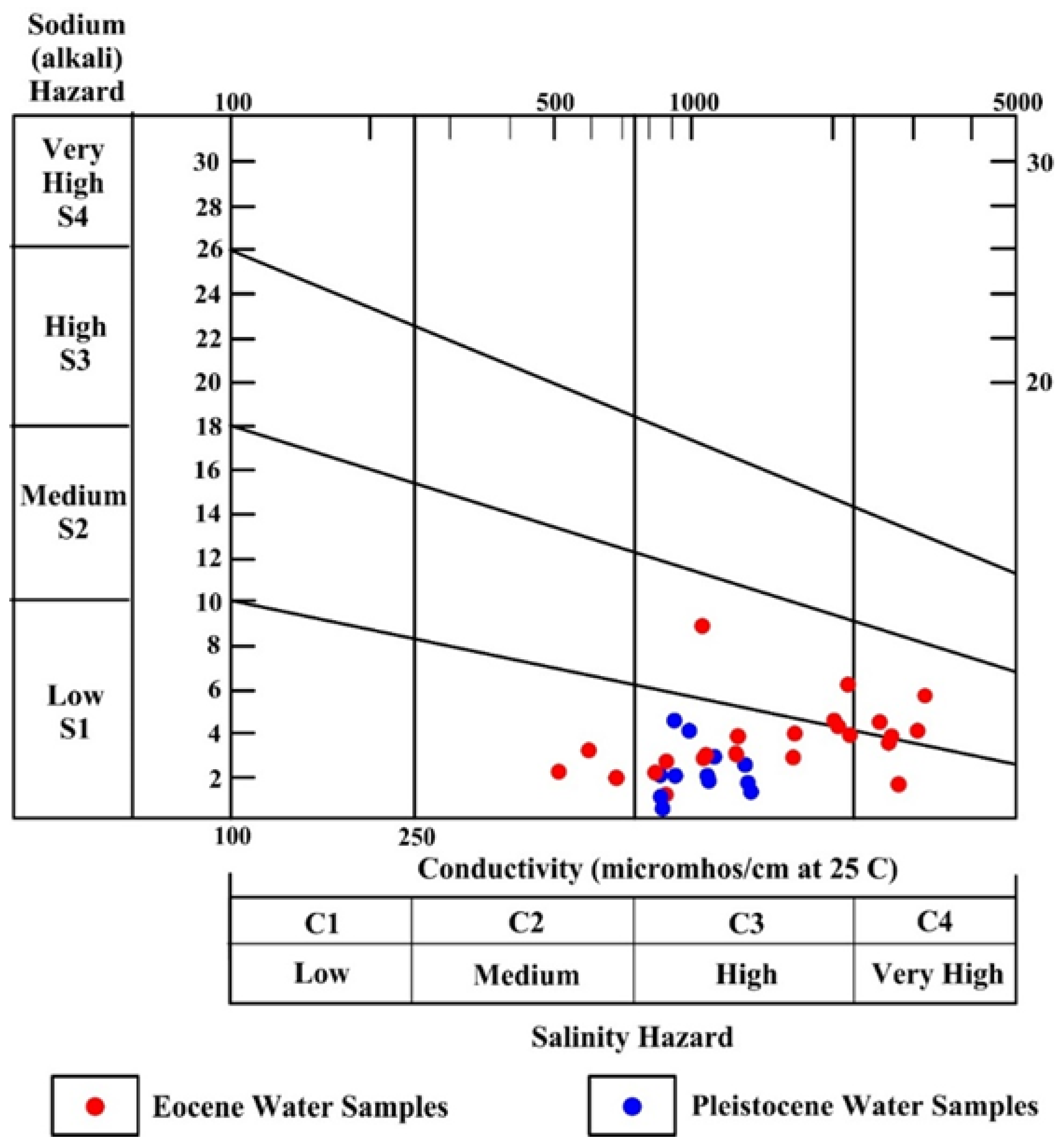
3.10.7. United States Salinity Laboratory (USSL) Diagram
3.10.8. Wilcox Diagram
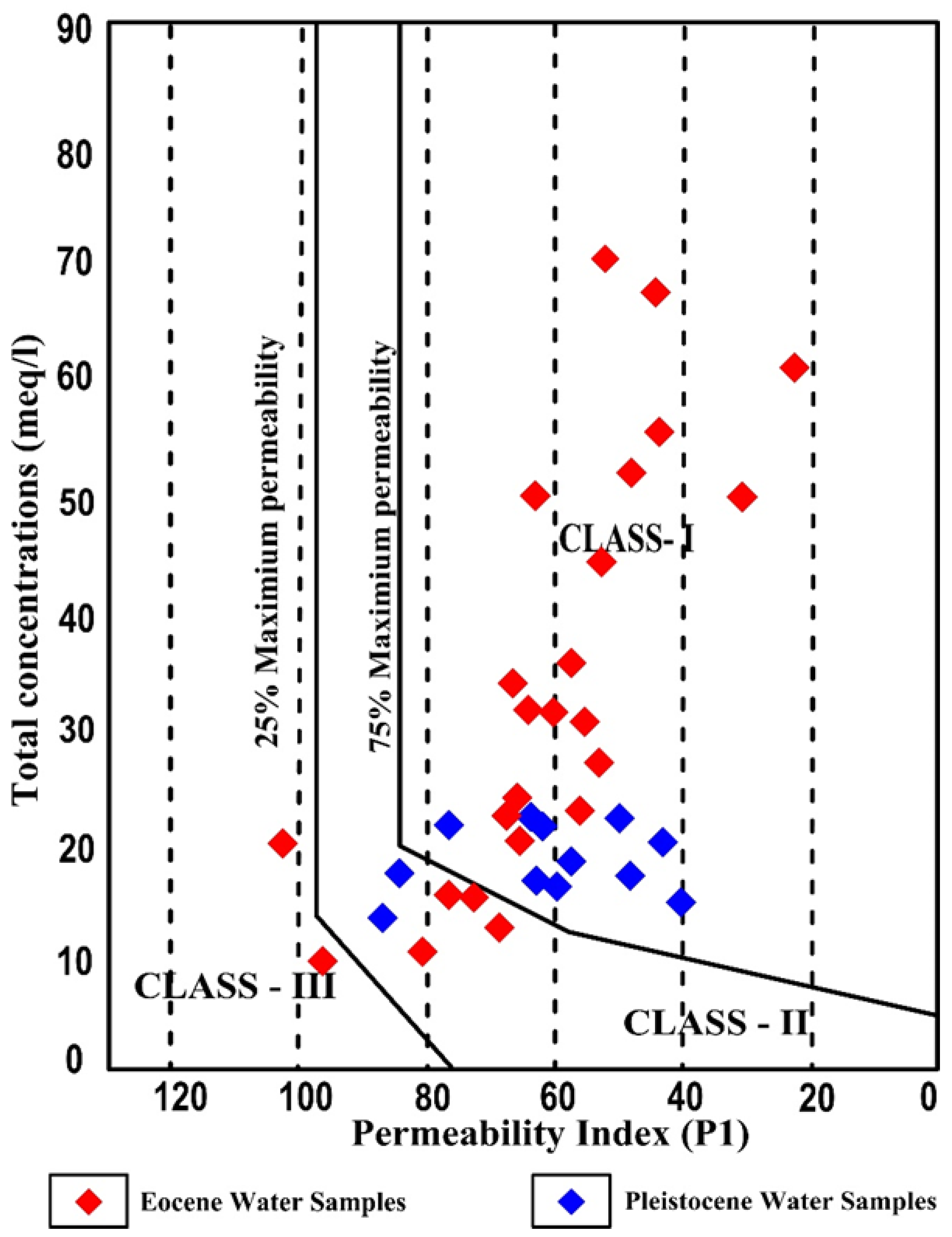
3.10.9. Permeability Index (PI)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North-West China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Venkatayogi, S. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes and Integrated Interpretation with Water Quality Index Studies. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Chizari, M.; Sadighi, H.; Bijani, M. Assessment of agricultural groundwater users in Iran: A cultural environmental bias. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; El-Sayed, E.; Sakr, S.; Youssef, E. Characteristic of groundwater potentialities in West Nile Valley South, Minia Governorate, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; Zaki, I.; Rapantova, N.; Licbinska, M.; Sharawi, H. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the groundwater in the quaternary aquifer of western fringes of El-Minia Governorate, Egypt using an integration of geochemical modeling and geo-statistical techniques. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 189, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; El-Rawy, M. Assessment of groundwater quality in West Sohag, Egypt. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 123, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snousy, M.G.; Ismail, E.; Zaki, R. Trace element occurrence and distribution problems in the irrigation water at El-Minia district, north upper Egypt. Arab J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, A.; Sefelnasr, A.; Ismail, E. Numerical modeling technique for groundwater management in Samalut city, Minia Governorate, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, A.; Sefelnasr, A.; Ismail, E. Response of the interaction between surface water and groundwater to climate change and proposed megastructure. J. Afri. Earth Sci. 2020, 162, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snousy, M.G.; Wu, J.; Su, F.; Abdelhalim, A.; Ismail, E. Groundwater Quality and Its Regulating Geochemical Processes in Assiut Province, Egypt. Expo. Health 2022, 14, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotalib, Z.A.; Essam, H.; Mohammed, B.; Esam, I.; Ahmed, G.; Mohamed, A. Groundwater mounding: A diagnostic feature for mapping aquifer connectivity in hyper-arid deserts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abotalib, A.Z.; Abdelhady, A.A.; Heggy, E.; Salem, S.G.; Ismail, E.; Ali, A.; Khalil, M.M. Irreversible and large-scale heavy metal pollution arising from increased damming and untreated water reuse in the Nile Delta. Earths Future 2023, 11, e2022EF002987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Sudarshan, V. Geochemical characterization and evaluation of groundwater suitability for domestic and agricultural utility in the semi-arid region of Basara, Telangana State, South India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheikh, M.A.; Azad, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Rina, K. An assessment of groundwater salinization in Haryana state in India using hydrochemical tools in association with GIS. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, S.; Vijay Prabhu, M.; Mohammed Rafi, M.; Vallel, L.K. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigational use in Cumbum Valley, Madurai District, Tamil Nadu, India. Nat. Environ. Poll. Tech. 2011, 10, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Tian, R.; Xue, C.; Wu, J. Progress, opportunities, and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13224–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: The Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. [Google Scholar]
- Egypt Drinking Water Standards. EHCW (Egyptian Higher Committee of Water), Egyptian Standards for Drinking and Domestic Water According to the Act 27/1978 in Regulation of the Public Water Supplies; Egyptian Governmental Press: Cairo, Egypt, 2007.
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Qian, H. Evaluation of groundwater contamination for fluoride and nitrate in the semi-arid region of Nirmal Province, South India: A special emphasis on human health risk assessment (HHRA). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess 2018, 25, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsimha, A.; Sudarshan, V. Hydrogeochemistry of groundwater in Basara area, Adilabad district, Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 15, 224–237. [Google Scholar]
- Narsimha, A.; Sudarshan, V. Contamination of fluoride in groundwater and its effect on human health: A case study in hard rock aquifers of Siddipet, Telangana State, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality assessment based on rough sets attribute reduction and TOPSIS method in a semi-arid area, China. Environ. Monit Assess. 2012, 184, 4841–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qian, H. Water resources research to support a sustainable China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P. Occurrence, health risks, and geochemical mechanisms of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of the rock dominant semi-arid region, Telangana State, India. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 25, 14803–14853. [Google Scholar]
- Alexakis, D.E. Applying Factor Analysis and the CCME Water Quality Index for Assessing Groundwater Quality of an Aegean Island (Rhodes, Greece). Geosciences 2022, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.; Kiskira, K.; Gamvroula, D.; Emmanouil, C.; Psomopoulos, C. Evaluating toxic element contamination sources in groundwater bodies of two Mediterranean sites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34400–34409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, N.J. Hydrogeochemical parameters for assessment of groundwater quality in the upper Gunjanaeru River basin, Cuddapah District, Andhra Pradesh, South India. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R. The Geology of Egypt; Balkema Publisher: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; 734p. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Monaim, A.E. Geoelectrical and Hydrogeologic Studies on the Quaternary Aquifer in the Nile Valley in Assiut and Sohag Governorates, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Dept. of Geophysics, Faculty of Science, Ain shams University: Cairo, Egypt, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- El Tahlawi, M.R.; Farrag, A.A.; Ahmed, S.S. Groundwater of Egypt: “An environmental overview”. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 639–652. [Google Scholar]
- APHA American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Greenberg, A.E., Eds.; APHA, AWWA, WPCF: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Snousy, M.G.; Morsi, M.S.; Elewa, A.M.; Ahmed, S.A.E.-F.; El-Sayed, E. Groundwater vulnerability and trace element dispersion in the Quaternary aquifers along middle Upper Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snousy, M.G.; Li, P.; Ismail, E. Trace elements speciation and sources characterization in the main watercourses, middle-upper Egypt. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2021, 27, 1764–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkaline Soils; US Department of Agricultural Handbook, No. 60; US Govt. Print Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1947; Volume 160, p. 1954.
- Wilcox, L.V. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters. US Department of Agriculture, Circular 969: Washington, DC, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, K.V. Irrigation with Saline Water; Monogram No. 2(new series); IARI: New Delhi, India, 1972; p. 198. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, D.M.; Kumar, A.; Agarwal, N. Assessment of the irrigation water quality of River Ganga in Haridwar District India. J. Chem. 2009, 2, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 410–420. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, W.P. Use of Saline Irrigation Water. Soil Sci. 1963, 95, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.R.; Shah, M.H.; Shaheen, N.; Jaffar, M.; Khalique, A. Statistical source identification of metals in groundwater exposed to industrial contamination. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 138, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma-Ruiz, R.; Pastén-Zapata, E.; Parra, R.; Harter, T.; Mahlknecht, J. Investigation of the geochemical evolution of groundwater under agricultural land: A case study in northeastern Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, H.D. The Chemistry of the Atmosphere and Oceans; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Mollema, P.N.; Antonellini, M. Water and (bio)chemical cycling in gravel pit lakes: A review and outlook. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 159, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation and Analysis of Water Samples; United States Geological Survey; Water Supply Paper; 1953; p. 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-W.; Lin, K.-H.; Kuo, Y.-M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.G.; Jamil, N.R.B.; Adam, M.B.; Zulkeflee, Z. Spatial and seasonal changes in monitoring water quality of Savanna River system. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, B.P.; Masachessi, G.; Ferreyra, L.J.; Biganzoli, P.; Grumelli, Y.; Panero, M.D.; Wassaf, M.M.; Pisano, M.B.; Welter, A.; Mangeaud, A.; et al. Searching variables to assess recreational water quality: The presence of infectious human enterovirus and its correlation with the main variables of water pollution by multivariate statistical approach in Córdoba, Argentina. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6586–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Tepe, Y. Water quality and sediment contamination assessment of Pazarsuyu Stream, Turkey using multivariate statistical methods and pollution indicators. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Luo, K. Elements in surface and well water from the central North China Plain: Enrichment patterns, origins, and health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistel, M.; Hurwitz, S.; Evans, W.C.; Barbieri, M. The chemistry and isotopic composition of waters in the low-enthalpy geothermal system of Cimino-Vico Volcanic District, Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 328, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Ramanathan, A.L. Geochemical assessment of groundwater quality in vicinity of Bhalswa landfill, Delhi, India, using graphical and multivariate statistical methods. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetelat, B.; Gaillardet, J. Boron Isotopes in the Seine River, France: A Probe of Anthropogenic Contamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2486–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Whalen, M.; Gagnon, G.A. Adsorption of dissolved organic matter (DOM) onto the synthetic iron pipe corrosion scales (goethite and magnetite): Effect of pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, A.; Sappa, G.; Barbieri, M. Application of boron and tritium isotopes for tracing landfill contamination in groundwater. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 172, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doza, B.; Islam, A.T.; Ahmed, F.; Das, S.; Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S. Characterization of groundwater quality using water evaluation indices, multivariate statistics and geostatistics in central Bangladesh. Water Sci. 2016, 30, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Baquero, J.C.; Laraque, A.; Alfonso, J.A.; Pisapia, D.; Balza, L. Dynamics of dissolved major (Na, K, Ca, Mg, and Si) and trace (Al, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, and Cr) elements along the lower Orinoco River. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; He, X.; Guo, W. Spatial groundwater quality and potential health risks due to nitrate ingestion through drinking water: A case study in Yan’an City on the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.P.; Gami, B.; Patel, A.; Patel, P.; Patel, B. Climatic and anthropogenic impact on groundwater quality of agriculture dominated areas of southern and central Gujarat, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminiyan, M.M.; Aitkenhead-Peterson, J.; Aminiyan, F.M. Evaluation of multiple water quality indices for drinking and irrigation purposes for the Karoon river, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2707–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.; Nielsen, D.; Vigil, M. Quantifying effects of soil conditions on plant growth and crop production. Geoderma 2003, 116, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arveti, N.; Sarma, M.R.S.; Aitkenhead-Peterson, J.A.; Sunil, K. Fluoride incidence in groundwater: A case study from Talupula, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess 2011, 172, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USSL (US Salinity Laboratory). Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkaline Soils; Agriculture Handbook No. 60 USDA; 1954; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.A. Hydrochemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in Naini industrial area, Allahabad District, Uttar Pradesh. J. Geol. Soc. India 2000, 55, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraju, A.; Suresh, S.; Killham, K.; Hudson-Edwards, K. Hydro-geochemistry of waters of Mangampeta Barite Mining Area, Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, India. Turk. J. Eng. Env. Sci. 2006, 30, 203–219. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T °C | 24.9 | 30.6 | 27.93 | 1.37 |
| EC | 860 | 1330 | 1049.75 | 176.51 |
| TDS | 550 | 851 | 671.67 | 112.97 |
| pH | 7.2 | 8.6 | 8.02 | 0.42 |
| Ca2+ | 8 | 82.8 | 52.23 | 21.24 |
| Mg2+ | 22 | 63 | 36.35 | 11.21 |
| Na+ | 18 | 144 | 80.58 | 34.68 |
| K+ | 0.3 | 3.6 | 1.83 | 0.98 |
| HCO3− | 196 | 338 | 270.84 | 45.93 |
| SO42− | 33 | 116 | 67.92 | 26.03 |
| Cl− | 42.6 | 216 | 116.71 | 47.79 |
| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T °C | 26.8 | 30.5 | 28.48 | 1.10 |
| EC | 520 | 3240 | 1767.58 | 859.78 |
| TDS | 333 | 2074 | 1131.29 | 550.25 |
| pH | 7.1 | 8.6 | 7.81 | 0.38 |
| Ca2+ | 12 | 254 | 100.33 | 68.88 |
| Mg2+ | 4.43 | 143 | 54.19 | 37.77 |
| Na+ | 56 | 385 | 163.75 | 86.64 |
| K+ | 0.3 | 4.2 | 2.31 | 1.15 |
| HCO3− | 104 | 348 | 210.51 | 65.91 |
| SO42− | 24 | 620 | 153.29 | 133.72 |
| Cl− | 14.2 | 896.4 | 353.29 | 281.01 |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 5.907 | 59.070 | 59.070 |
| 2 | 1.355 | 13.546 | 72.616 |
| 3 | 1.150 | 11.503 | 84.118 |
| Parameter | PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| T °C | 0.068 | 0.922 | 0.199 |
| EC | 0.985 | −0.023 | 0.009 |
| TDS | 0.985 | −0.023 | 0.009 |
| pH | −0.412 | −0.557 | 0.608 |
| Ca2+ | 0.908 | −0.270 | −0.004 |
| Mg2+ | 0.930 | −0.181 | −0.064 |
| Na+ | 0.798 | 0.159 | −0.106 |
| K+ | 0.411 | 0.102 | 0.770 |
| SO42− | 0.679 | 0.180 | 0.317 |
| Cl− | 0.914 | −0.135 | −0.180 |
| Coordinate | Initial Eigenvalues | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 2.337 | 36.852 | 36.852 |
| 2 | 1.344 | 21.184 | 58.036 |
| 3 | 1.128 | 17.782 | 75.818 |
| T °C | EC | TDS | pH | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | HCO3− | SO42− | Cl− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T °C | 1 | 0.062 | 0.063 | −0.339 | −0.134 | −0.084 | 0.129 | 0.212 | −0.245 | 0.212 | −0.070 |
| EC | 1 | 1.000 ** | −0.353 | 0.893 ** | 0.907 ** | 0.788** | 0.368 | 0.019 | 0.677 ** | 0.877 ** | |
| TDS | 1 | −0.353 | 0.894 ** | 0.907 ** | 0.788** | 0.369 | 0.019 | 0.677 ** | 0.877 ** | ||
| pH | 1 | −0.249 | −0.339 | −0.397 | 0.111 | 0.227 | −0.182 | −0.403 | |||
| Ca2+ | 1 | 0.935 ** | 0.538 ** | 0.344 | 0.007 | 0.538 ** | 0.870 ** | ||||
| Mg2+ | 1 | 0.582 ** | 0.280 | −0.024 | 0.635 ** | 0.857 ** | |||||
| Na+ | 1 | 0.290 | −0.175 | 0.459 * | 0.798 ** | ||||||
| K+ | 1 | −0.282 | 0.337 | 0.319 | |||||||
| HCO3− | 1 | −0.062 | −0.209 | ||||||||
| SO42− | 1 | 0.357 | |||||||||
| Cl− | 1 | ||||||||||
| T °C | EC | TDS | pH | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | HCO3− | SO42− | Cl− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T °C | 1 | 0.163 | 0.162 | −0.054 | 0.205 | 0.404 | −0.503 | 0.530 | 0.336 | 0.168 | −0.371 |
| EC | 1 | 1.000 ** | −0.187 | 0.397 | 0.577 * | 0.061 | 0.056 | 0.313 | 0.794 ** | 0.284 | |
| TDS | 1 | −0.188 | 0.397 | 0.578 * | 0.061 | 0.056 | 0.313 | 0.794 ** | 0.285 | ||
| pH | 1 | −0.268 | −0.044 | −0.303 | −0.174 | 0.218 | −0.034 | −0.694 * | |||
| Ca2+ | 1 | 0.131 | −0.406 | 0.443 | 0.010 | 0.522 | 0.217 | ||||
| Mg2+ | 1 | −0.411 | −0.215 | 0.580 * | 0.136 | −0.054 | |||||
| Na+ | 1 | −0.086 | −0.230 | 0.116 | 0.600 * | ||||||
| K+ | 1 | −0.333 | 0.321 | 0.181 | |||||||
| HCO3− | 1 | 0.124 | −0.464 | ||||||||
| SO42− | 1 | 0.171 | |||||||||
| Cl− | 1 | ||||||||||
| Physicochemical Parameter | Pleistocene Samples Range | Eocene Samples Range | Egyptian Permissible Limit (mg/L) | World Health Organization Guidelines (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.2–8.6 | 7.1–8.6 | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–9.2 |
| EC | 820–1270 | 500–3095 | 2000 | 500–1500 |
| TDS | 550–851 | 333–2074 | 1200 | 1000 |
| Hardness (TH) | 139–389 | 85–1046 | 500 | -- |
| Calcium | 8–82 | 12–254 | 200 | -- |
| Magnesium | 22–63 | 4–143 | 150 | -- |
| Sodium | 18–144 | 56–385 | -- | 200 |
| Sulfates | 33–116 | 24–358 | 250–400 | 400 |
| Chloride | 42–216 | 14–896 | 500 | 250 |
| Classification Pattern | Categories | Ranges | Pleistocene Aquifer (%) | Eocene Aquifer (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (m.mohs/cm) at 25° | Low | <250 | -- | -- |
| Medium | 251–750 | -- | 12.5 | |
| High | 751–2250 | 100 | 54 | |
| Very high | >2250 | -- | 33.5 | |
| Sodium absorption ratio (SAR) | Excellent | 0–10 | 100 | 100 |
| Good | 10–18 | -- | - | |
| Fair | 18–26 | -- | - | |
| Poor | >26 | - | - | |
| Percent sodium (% Na) | Excellent | <20 | 8 | 4 |
| Good | 20–40 | 50 | 25.5 | |
| Permissible | 40–60 | 42 | 62.5 | |
| Doubtful | 60–80 | -- | 4 | |
| Unsuitable | >80 | -- | 4 | |
| Residual sodium carbonate (RSC) | Good quality used for all soils | <1.25 | 58 | 21 |
| Water of medium quality is used in case of good drainage | 1.25–2.5 | 25 | 12.5 | |
| Unsuitable water | >2.5 | 17 | 66.5 | |
| Kelley’s ratio | Good quality water | <1 | 75 | 71 |
| Unsuitable water | >1 | 25 | 29 | |
| Magnesium hazard (MH) | Suitable water | <50 | 42 | 67 |
| Unsuitable water | >50 | 58 | 33 | |
| Permeability index (PI) | Good water quality for irrigation | >75 | 25 | 17 |
| 25–75 | 75 | 79 | ||
| Unsuitable | <25 | -- | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, E.; Snousy, M.G.; Alexakis, D.E.; Abdelhalim, A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Elsayed, E. Diagnosis of Groundwater Quality in North Assiut Province, Egypt, for Drinking and Irrigation Uses by Applying Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemical Methods. Water 2023, 15, 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152812
Ismail E, Snousy MG, Alexakis DE, Abdelhalim A, Ahmed MS, Elsayed E. Diagnosis of Groundwater Quality in North Assiut Province, Egypt, for Drinking and Irrigation Uses by Applying Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemical Methods. Water. 2023; 15(15):2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152812
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Esam, Moustafa Gamal Snousy, Dimitrios E. Alexakis, Ahmed Abdelhalim, Mohamed S. Ahmed, and Esam Elsayed. 2023. "Diagnosis of Groundwater Quality in North Assiut Province, Egypt, for Drinking and Irrigation Uses by Applying Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemical Methods" Water 15, no. 15: 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152812
APA StyleIsmail, E., Snousy, M. G., Alexakis, D. E., Abdelhalim, A., Ahmed, M. S., & Elsayed, E. (2023). Diagnosis of Groundwater Quality in North Assiut Province, Egypt, for Drinking and Irrigation Uses by Applying Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemical Methods. Water, 15(15), 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152812







