Abstract
Moringa is a genus with many applications; some of these applications can be linked to their use in traditional medicine and as a source of nutrients, and traditionally, some species have been used for water purification. Many studies have been conducted to assess the use of different species of Moringa for water purification. One of the species that is extensively studied is M. Oleifera because of its wide geographical distribution. There are limited studies on M. peregrina due to its limited geographical distribution, as it is native to the Arabian Peninsula and some other countries in the Middle East. The aim of this study is to assess the potential use of M. peregrina for water coagulation. This study was conducted using synthetic water samples as well as real, untreated wastewater samples to determine the potential of M. peregrina seeds for water coagulation. The results revealed that M. peregrina seed extract had better turbidity removal at 60 °C compared with the use of the seed extract at room temperature, and increasing the ionic strength of the extracting solution could also improve the efficiency of the seed extract in terms of turbidity removal. Furthermore, the de-oiled seed extract showed efficiency comparable with that of the raw seeds. Application to the real wastewater samples showed that the de-oiled seed extract showed percentage removal of 38%, 81%, and 74% for SCOD, turbidity, and color, respectively. Furthermore, the de-oiled M. peregrina seed extract at a dose of 200 mg/L equivalent to raw seeds was capable of removing 97.4%, 66.5%, 51.8%, 50.3%, and 45.8% of Mo, Cu, Cd, Cr, and Co, respectively.
1. Introduction
Moringa is a genus with many applications; some of these applications can be linked to their use in traditional medicine and as a source of nutrients, and traditionally, some species have been used for water purification []. The Moringa genus of the family Moringaceas has up to 13 species known to date, including M. Oleifera, M. drouhardii, M. hildebrandtii, M. ovalifolia, M. peregrine, M. pygmaea, M. ruspoliana, M. stenopetala, M. longituba, M. rivae, M. arborea, M. borziana, and M. concanensis []. The most famous species is M. Oleifera, which is well known for having many health and medicinal benefits in addition to its water purification ability. Many studies have been conducted on different species of Moringa. The M. Oleifera species has been extensively studied to identify its coagulation efficiency. Historically, various seeds have been used for water coagulation, such as apricot seeds, peach seeds, and mango seeds [,].
The coagulation process is an essential step in water and wastewater purification. It relies on converting suspended particles into larger flocs that can settle or be easily filtrated from water. This process involves the addition of certain chemicals called coagulants. These chemicals have the ability to aid in the flocculation of suspended particles in water []. Moringa is known to have certain proteins that are positively charged in solutions and can bind to negatively charged particles to remove turbidity from water. Previous studies have identified the active ingredient in Moringa as cationic polymers, and the aqueous extract of Moringa oleifera contains dimeric cationic proteins with a molecular weight of about 13,000 daltons and iso-electric points between 10 to 11. These groups of water-extractable polymers give Moringa the potential power to be used as a coagulant [].
Many researchers have studied the use of seed extracts for water coagulation as a potential coagulant instead of iron and aluminum salts. Bashir et al. used different doses of Moringa seed powder, ranging from 50 to 150 mg/L, in water samples collected from the Nile River, and the results showed a significant reduction in turbidity. The removal of turbidity was impacted by the settling time and the dosage of the seed powder. The turbidity dropped from 337 NTU to 13 NTU after treatment with a dose of 150 mg/L of M. Oleifera seed powder []. Farouk and Karwan found that M. Oleifera is more efficient in removing turbidity from high-turbidity water with a turbidity of 300 NTU; however, its seed extract was less efficient in low-turbidity water []. M. Oleifera seed extract showed a potential treatment efficiency comparable to conventional aluminum salts, especially at higher turbidites. It was found that the average turbidity removal efficiency was 83.2% for M. Oleifera seed extract compared to 92.4% for poly-aluminum chloride [,]. Coagulation by using inorganic metal salts may be easier and more efficient; however, the use of naturally occurring coagulants has the advantages of offering a good option to explore environmentally friendly products and avoiding the disposal of chemically produced sludge [,]. Natural coagulants such as Moringa seed extract have minimal impact on water pH compared to the use of conventional inorganic salts. It has been reported that the use of aluminum sulfate as a coagulant has many negative consequences, such as lowering the pH of water from 7.2 to 3.6 due to the lack of natural alkalinity to counterbalance the impact of the addition of inorganic aluminum salts. However, the use of M. Oleifera seed extract shows no significant impact on water pH [].
Moringa peregrina, also known as Forssk, is another species that can grow in deserts. Its seeds are rich in oil, and the oil extracted is known as ben oil, which can be used as a lubricant for delicate machinery such as watches. Ben oil has been used for thousands of years as a perfume base []. Moringa peregrina is a tropical plant native to arid and semi-arid regions. It can grow in various regions such as the Arabian Peninsula, India, Iran, parts of Africa, and as far north as the Dead Sea []. Morinaga peregrina can be grown in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and it can be a good economic crop that can be grown for the purpose of oil production in the UAE. A M. peregrina kernel contains 1.8% of moisture, 54.3% of oil, 22.1% of protein, 3.6% of fiber, 15.3% of carbohydrate, and 2.5% of ash []. The oil contents of its seeds may vary from area to area; for example, M. peregrina seeds from Egypt were found to contain 42% of oil, whereas seeds from Saudi Arabia had a yield of 45% []. Moringa peregrina seeds contain more than 20% of crude protein, and Moringa protein content is rich in arginine, leucine, glycine, and proline. A comparison of Moringa peregrina with Moringa oleifera showed that the former is richer in protein contents; this can give a better opportunity for M. peregrina to be used as a bio-coagulant [].
The process of oil production can generate a considerable amount of filter cake waste, which may have additional economic value in the treatment of water and wastewater. Al-Harthi et al. investigated the use of oil-extracted M. peregrina seed cake as a feed ingredient in poultry []. Their study showed that seed cake contains a valuable level of nutrients, such as proteins, essential amino acids, and minerals, in addition to fatty acids, which makes it a potential ingredient for poultry diets. There are limited publications on the use of Moringa peregrina seed extract for water purification. Shirin et al. evaluated the proteins extracted from M. peregrina seeds versus the proteins extracted from M. Oleifera seeds and concluded that M. peregrina seed proteins could provide an effective flocculent for colloidal particles and act in a similar manner to M. Oleifera seed proteins []. The aim of this study is to evaluate the coagulation efficiency of M. peregrina seeds collected from the UAE. This study also aims to investigate the possibility of using Moringa peregrina filter cake extracted from oil production as a biodegradable wastewater coagulant.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Moringa Coagulant
Dry Moringa peregrina seeds were collected locally from the Sharjah Desert Park. The collected dry seeds were deshelled and crushed into powder using a pestle and mortar (Figure S1). The resulting powder was further used either as it was or extracted via liquid extraction. In the second part of the experiment, the crushed seeds were de-oiled prior to their use, where the amount of de-oiled seeds used in each dose was adjusted to be equivalent to the amount of raw seeds used.
The Moringa peregrina seed extract was prepared by stirring 1 g of Moringa peregrina seed powder in 100 °C mL of water for 1 h. The extraction process was performed at three different temperatures (20 °C, 40 °C, and 60 °C), and then the seed extract was filtered. Each mL of this solution was equivalent to 10 mg of dry Moringa seeds. Previous studies have shown that Moringa seed extract can be enhanced using salts at different concentrations [,]. Based on these earlier findings on M. Oleifera extraction, the Moringa seed powder was extracted with 100 mL of 0.1, 0.5, and 1 M NaCl solutions to determine the optimum extraction conditions in terms of temperature and salt concentration. Once the optimum extraction conditions had been determined, the coagulation experiment was performed to determine the optimum dose.
Previous studies have shown that Moringa peregrina seeds contain up to 53% of oil [,]. The oil fraction in the seeds was removed via extraction of the crushed seeds with petroleum ether by adding 5 g of the crushed seeds in petroleum ether and stirring for about 2 h to remove oil from the crushed seeds. After oil removal, the crushed seeds were filtered and left overnight to dry at room temperature [,]. The dried seeds were then extracted with 500 mL of the extracting solution (1 g of raw seeds/100 mL of extracting solution) under the predetermined optimum conditions (temperature of 60 °C and with a salt concentration of 0.5 M NaCl) for 1 h, where each mL of this solution was equivalent to 10 mg of dry Moringa seeds. The resulting raw crushed seeds (MPRw), aqueous seed extract (MPEx), and seed extract after oil removal (MPDOEx) were used as coagulants in the coagulation experiment.
2.2. Coagulation Experiment
The coagulation experiment was conducted using synthetic water samples with different initial turbidities and real wastewater samples. The coagulation experiment was performed in triplicate for each water sample to confirm the results and check the reproducibility of the findings.
The synthetic water samples were prepared by mixing 20 g of dried Kaolin powder with 200 mL of distilled water (Figure S2). The resulting suspension was left at room temperature overnight. After being left over night, the suspension was completely mixed for 30 min using an electrical blender, and then the mixture was left to settle for 4 h to remove settleable particles [,]. The resulting supernatant was used as a synthetic stock solution with turbidity for the coagulation experiment. To prepare the synthetic water samples, a specified volume was taken from the stock solution and added to 10 L of tap water. After adding the stock solution with turbidity, the synthetic water samples were mixed thoroughly and used in the coagulation experiment. Table 1 shows the preparation of solutions with different initial turbidities.

Table 1.
Preparation of stock solutions with different initial turbidities.
The coagulation experiment was carried out using a Jar tester. The Jar tests were conducted according to the ASTM D 2035 [] by adding different doses of the bio-coagulant. The added bio-coagulant was mixed for 1 min with each water sample at a relatively high speed of 200 rpm, followed by flocculation at a speed of 35 rpm for 30 min. After flocculation, the samples were allowed to settle for 1 h to simulate a real coagulation process []. The efficiency of the bio-coagulant and the optimum dose were assessed by measuring turbidity in the supernatant of each sample after the completion of the coagulation process. In the Results and Discussion section, the doses are presented as equivalent to the raw seed doses.
The coagulation experiment was performed using wastewater samples collected from a wastewater treatment plant in the neighborhood to assess the efficiency of M. peregrina de-oiled seed extract (MPDOEx) for the removal of turbidity, color, and soluble COD. Similarly, the wastewater samples were treated with different doses of Moringa peregrina de-oiled seed extract to explore the efficiency of the extract in removing metals from wastewater. The supernatants of the samples treated with different doses of Moringa peregrina seeds extract were tested for metals using inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy. All sample preparations were performed according to the standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater []. Turbidity was measured according to method 2130B via Nephelometry, color was measured according to experiment number 2120F, and soluble chemical oxygen demand was determined according to the standard method 5220D. Metal determination was conducted according to the standard method number 3120B for plasma emission spectroscopy using ICP/AES.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Optimum Extraction Temperature
To determine the optimum extraction temperature for M. peregrina seeds, the crushed seeds were extracted with deionized water at three different temperatures: 60 °C, 40 °C, and room temperature. The coagulation efficiency and turbidity removal rate were higher when the M. peregrina seeds were extracted at the elevated temperature of 60 °C. Figure 1 compares the efficiency of turbidity removal at three different temperatures; the lowest turbidity removal efficiency was observed when the seed powder was extracted at room temperature. In most previous studies, the optimum extraction temperature was not investigated extensively. In a similar study conducted on M. Oleifera, it was found that bio-coagulant could be extracted at temperatures ranging from 30 to 100, but the results revealed that protein extractability decreased at a temperature higher than 70 °C []. The findings of the current study are in accordance with this previous study conducted on M. Oleifera. Nouhi et al. found that proteins extracted from both M. Oleifera and M. peregrina could offer unique adsorption and flocculation properties; however, the efficiency of M. peregrina is less exploited because its growth is limited by its geographical locations [].
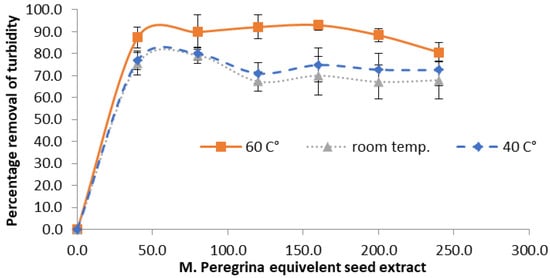
Figure 1.
The efficiency of turbidity removal of M. peregrina seeds extracted at different temperatures with an initial turbidity of 15 NTU.
3.2. Determination of Salt Concentration in the Extract
Many studies assessed the impact of salt type and concentrations on the extraction of Moringa as a bio-coagulant. In the current study, Moringa peregrina seed powder was extracted with NaCl at three different concentrations, and deionized water was used as a control. As shown in Figure 2, it was found that extraction of M. peregrina seeds with NaCl in the range from 0.5 to 1 M produces the highest turbidity removal rate; this can be explained on the basis that the extractability of this bio-coagulant can be enhanced by using NaCl during the extraction process. It was found that with an initial turbidity of 56 (SD = 4.5) NTU and at a dose of 40 mg seed equivalent per liter, the average removal efficiency of turbidity was 81% (SD = 1), 85% (SD = 0.72), 65% (SD = 0.34), and 40% (SD = 0.42) for extraction with NaCl solution at 1 M, 0.5 M, and 0.1 M, and water, respectively. Similar findings were reported by Okuda et al. [], who studied the impact of the ionic strength of extracting solutions on the extraction efficiency of active bio-coagulants in the case of M. Oleifera seeds. The results of their study showed that Moringa extracts produced via extraction with 1 M NaCl showed 7.4 times as high efficiency as the bio-coagulants produced via extraction using distilled water only. In the current study, the use of salt extraction showed some improvements, where Moringa extracts produced via extraction with 1 M, 0.5 M, and 0.1 M NaCl showed 1.6, 2.1, and 1.99 times as high efficiency as the bio-coagulant produced via extraction using plain distilled water. Adding sodium chloride or any other salt like potassium chloride to the extraction solution resulted in an improvement in the turbidity removal efficiency for the same dose of Moringa. This finding has been explained as the addition of salt will increase the ionic strength of the extraction solution, which in turn can loosen up the protein associations, leading to more soluble and coagulation-active species in the solution. One of the possible drawbacks of the use of salt extraction is the increase in electrical conductivity of the treated water []; accordingly, using lower salt concentrations for extraction, such as 0.1 M or 0.5 M NaCl, may be better in practical applications over the use of high salt concentrations for extraction.
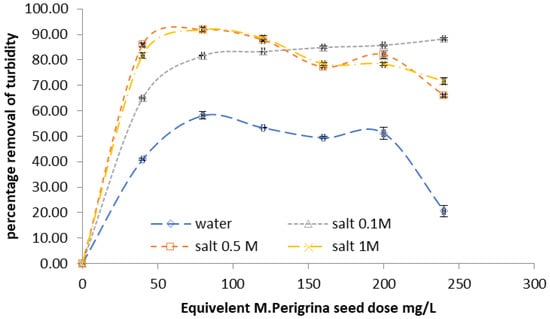
Figure 2.
Effect of salt concentration on the percentage removal of turbidity of synthetic water sample with an initial turbidity of 56 NTU.
3.3. Comparison between Different Forms of M. peregrina Coagulant
After the assessment of the optimum condition for extraction, the Moringa peregrina seed powder was de-oiled using petroleum ether. The de-oiled seed extract (MPDOEx) was compared with the raw seed extract (MPOEx), and the raw seed powder (MPRw) was used as a control. The experiment was conducted using water samples with three different initial turbidities, with an average of 7 NTU (SD = 0.88), 12 NTU (SD = 1.6), and 35.5 NTU (SD = 2.27). The optimum dose of Moringa peregrina raw seeds or equivalent seed extract was found to be 100 to 200 mg/L. It was found that the turbidity removal efficiency was higher for the solutions with higher initial turbidity (water samples with an average initial turbidity of 35.5 NTU); however, at low initial turbidity of 7 NTU, the removal efficiency was lower compared to the samples with a higher initial turbidity. These results were in agreement with an earlier study conducted on Moringa oleifera, which found that turbidity removal efficiency was 83.2% for samples with an initial turbidity of 50 NTU, compared to the relatively higher removal efficiency of 99.8% for samples with an initial turbidity of 450 NTU []. As shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, raw seeds showed better performance compared to the raw seed extract and the de-oiled seed extract. Despite the better efficiency of the raw seeds, the use of the de-oiled seed extract as a bio-coagulant is more feasible because seeds can be used for oil production, and the residues remaining after oil extraction can be used as an environmentally friendly water treatment solution. In this study, the authors used raw seed powder as a control only. As shown in Table 2, the order of efficiency is as follows: raw seeds > de-oiled seed extract ≥ raw seed extract. Apparently, the process of oil removal slightly decreases the coagulation efficiency of raw seeds; however, this decrease in coagulation efficiency is very negligible compared to the benefits gained from the extracted oil as it can be used for many purposes, such as perfumery and fuel production. Also, the efficiency of the de-oiled seed extract was almost comparable with the efficiency of the raw seed extract. The use of de-oiled seed extracts has additional advantages over the use of raw seeds, as reported by Chales et al., who found that the use of raw seeds could increase the DOC of the solution due to the high contents of oils in the raw seeds []. The mechanism of turbidity removal by Moringa seed extracts can be described on the basis of the bridge formation model. The cationic protein of high molecular weight from Moringa extracts binds to the surface of negatively charged particles, where this can lead to the neutralization of part of the surface containing turbidity-causing particles. The neutralization of the negative surface charge leads to a reduction of the electrostatic repletion and agglomeration of particles []. Measurements of the Zeta potential of different proteins extracted from Moringa showed that the different proteins have a positive zeta potential of +20 ± 5 mV, which can support the suggested mechanism for turbidity removal [].
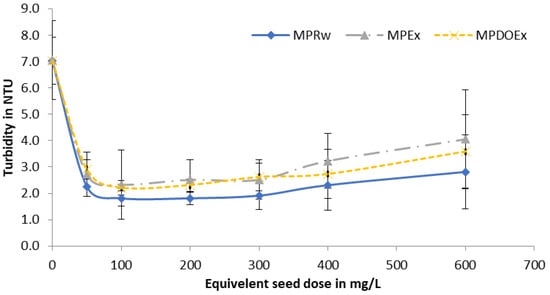
Figure 3.
Impact of Moringa dose on the removal of turbidity from synthetic water samples with relatively low turbidity (7 NTU).
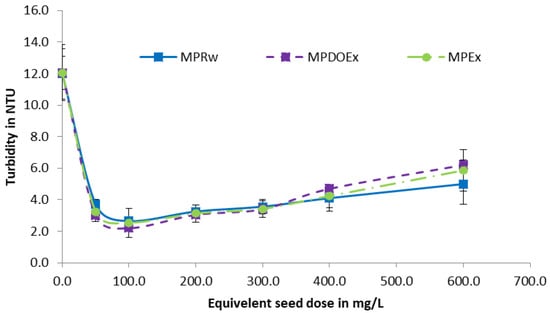
Figure 4.
Impact of Moringa dose on the removal of turbidity from synthetic water samples with moderate turbidity (12 NTU).
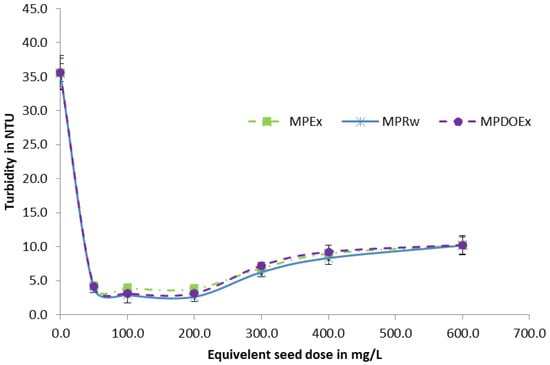
Figure 5.
Impact of Moringa dose on the removal of turbidity from synthetic water samples with relatively high turbidity (35 NTU).

Table 2.
The average percentage removal of Moringa seeds (MPRw), raw seed extract (MPEx), and de-oiled seed extract (MPDOEx) with different initial turbidities.
In this study, it was found that the efficiency of turbidity removal showed slight improvement at higher pH values. As shown in Figure 6, different forms of Peregrina were tested with different initial solution pHs ranging from 5 to 9 and with an initial solution turbidity of 25 NTU. It was found that the turbidity removal efficiency of the de-oiled Moringa seed extract with a dose equivalent to 100 mg/L of raw seeds was 88% for an initial pH of 5 and 93% for an initial pH of 9. In a previous study conducted using Moringa oleifera to treat wastewater, it was found that the efficiencies of turbidity removal and color removal were better with higher pH values []. The results obtained in this study show a similar tendency toward improvement in the removal efficiency at higher pH values, which suggests that the removal efficiency of M. peregrina follows the same mechanism as that in M. Oleifera. One of the advantages of using bio-coagulants such as M. peregrina and M. Oleifera is that these types of coagulants can work effectively at a wide range of pH values and has less effect on overall water pH []. In contrast, the use of conventional aluminum and iron salts for coagulation is affected by the buffering capacity of water and can affect the overall water pH, especially at higher doses, which may impact other downstream treatment processes that may need pH adjustment. pH value is one of the most important control parameters in water purification, especially in coagulation applications. As mentioned above, the neutralization of charges is the main mechanism of coagulation. Earlier studies showed that the use of Moringa hardly affects the pH and conductivity of water, and the efficiency of coagulation is relatively stable over a wide range of pH values. Therefore, the application of Moringa seed extract in water and wastewater purification can reduce the cost of chemicals used for pH adjustment needed for water purification using conventional metal salt coagulation applications [,].
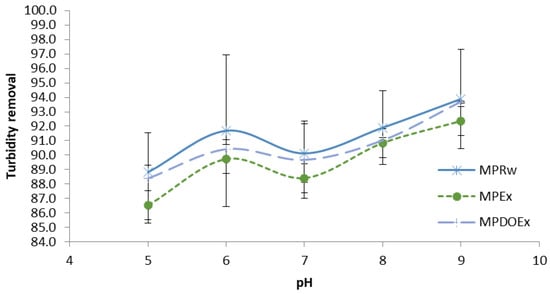
Figure 6.
Effect of pH on coagulation efficiency of various forms of M. peregrina coagulants with a coagulant dose equivalent to 100 mg/L and an initial turbidity of 25 NTU.
3.4. Testing M. peregrina on Real Wastewater Samples
The real wastewater samples were collected from a nearby wastewater treatment plant. The samples were treated with the de-oiled Moringa seed extract produced via extraction using 0.5 M NaCl at 60 °C. Table 3 shows the characteristics of the real wastewater samples, and Figure 7 shows the impact of the de-oiled seed extract of M. peregrina on the removal of SCOD, turbidity, and color. It was found that at an optimum equivalent seed dose of 400 mg/L, the percentage removal of SCOD, turbidity, and color was 38%, 81%, and 74%, respectively. These findings suggest that M. peregrina can be used to enhance the primary treatment of wastewater treatment plants.

Table 3.
Real wastewater characteristics used for the coagulation experiment.
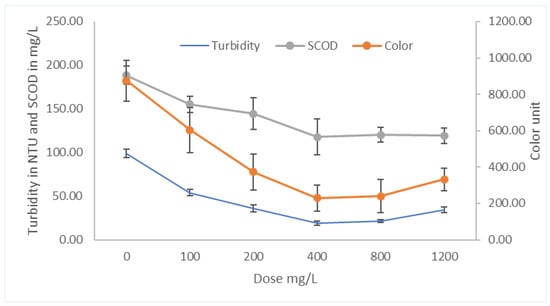
Figure 7.
Effect of M Peregrina de-oiled seed extract’s equivalent dose on SCOD, turbidity, and color removal.
The de-oiled M. peregrina seed extract showed a tendency to remove some metals in the tested wastewater samples. The seed extract was added in doses ranging from 40 to 200 mg/L, equivalent to raw seeds. Table 4 shows the initial metal concentration and the percentage removal efficiency at different doses for cadmium, cobalt, chromium, copper, manganese, molybdenum, and nickel. Manganese and nickel showed negligible removal efficiency of less than 15 percent. However, other metals tested showed moderate to high removal efficiency. It was found that the de-oiled Moringa peregrina seed extract at a dose of 200 mg/L equivalent to raw seeds could remove 97.4, 66.5, 51.8, 50.3, and 45.8 percent of Mo, Cu, Cd, Cr, and Co, respectively.

Table 4.
Percentage removal of Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Mo, and Ni at different doses of de-oiled M. peregrina extract.
There are very limited studies on the use of Moringa peregrina for metal removal, with most of the publications having tested the efficiency of Moringa oleifera seeds or seed extract to remove heavy metals from water. In one study conducted using Moringa oleifera seeds in Fiji to investigate metal removal efficiency, it was found that the use of Moringa seeds could remove 80% of lead, 60% of cadmium, and 50% of zinc and chromium []. Similarly, Shan et al. reported that 1% of Moringa oleifera seed cake may be enough to remove metals such as iron, copper, and cadmium from water []. There are many factors that may impact the efficiency of metal removal, such as the initial concentration, the pH of the solution used, the forms of metals in the water being treated, and the presence of competing metals in water. Some studies used seed powder for metal removal. The form of Moringa used can govern the mechanism by which metals are removed, and using seed powder can create a basis for the adsorption mechanism []. The use of seed extract can involve the removal of non-dissolvable metals. The results obtained in the current study using M. peregrina suggest that its seed extract shows good efficiency in metal removal, which needs to be investigated further in future research.
4. Conclusions
Moringa is a genus with numerous applications, including in traditional medicine, as a source of nutrients, and in water purification. The most famous species is M. oleifera, which is well known for its health and medicinal benefits in addition to its water purification ability. Moringa is known to have certain proteins that are positively charged in solutions and can bind to negatively charged particles to remove turbidity from water. Moringa peregrina is another species that can grow in deserts. The use of Moringa peregrina seed extract has the potential to offer an environmentally friendly bio-coagulant and avoid the need for disposal of chemically produced sludges resulting from the use of aluminum salts used as traditional coagulants. This study focused on the use of M. peregrina seed extract under different temperatures and salt concentrations, with the use of raw seed powder as a control. The results show that M. peregrina can be used as a potential coagulant for turbidity removal either in water purification or as an enhanced primary treatment coagulant. The results obtained from this study show that M. peregrina can be an effective bio-coagulant, but further studies need to be conducted to investigate economical methods to recover beneficial bio-proteins that can be used in different water purification practices. This study showed that the coagulation efficiency and turbidity removal were higher when M. peregrina seeds were extracted at an elevated temperature of 60 °C. The use of NaCl at a concentration of 0.5 M could improve the extraction process. With respect to de-oiled seeds, it was found that de-oiled Moringa seed extract is still an efficient bio-coagulant. These findings suggest that the use of de-oiled seed extract can maximize the use of residual press cake after oil extraction from seeds, where such a press cake can be used for the production of environmentally friendly bio-coagulants. The use of M. peregrina seed extracts in real wastewater samples resulted in the removal of some metals from the samples, including Mo, Cu, Cd, Cr, and Co.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w15152804/s1. Figure S1. Stages of Moringa peregrina preparations; Figure S2. Stock solution with turbidity used for the coagulation experiment.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available from the corresponding author upon request made via email.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rani, N.Z.A.; Husain, K.; Kumolosasi, E. Moringa Genus: A Review of Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, K.T.; Mugal, T.; Haq, I.U. Moringa oleifera: A Natural Gift—A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2010, 2, 775–781. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, G.H.; Hegazy, B.E.; Fouad, H.A.; Rehab, M. Comparative Study on Natural Products Used for Pollutants Removal from Water. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2008, 5, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Elmolla, E.S.; Hamdy, W.; Mansour, S.; Boktor, M. Natural Products for Surface Water Coagulation: An Alternative Sustainable Solution for Rural Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2020, 14, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Sanghi, R. Advances in Water Treatment and Pollution Prevention; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9400742045. [Google Scholar]
- ElGeed, B.A.A.; Abdalsalam, M.H. Evaluation the efficacy of Moringa oleifera seed powder on physico-chemical parameters of white nile river water. Int. J. Sci. Acad. Res. 2023, 4, 5341–5346. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, F.A.; Alkaradaghi, K.; Al-Ansari, N. The Potential of Moringa oleifera Seed in Water Coagulation-Flocculation Technique to Reduce Water Turbidity. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarahmadi, M.; Hossieni, M.; Bina, B.; Mahmoudian, M.H.; Naimabadie, A.; Shahsavani, A. Application of Moringa oleifera Seed Extract and Poly Aluminium Chloride in Water Treatment. World Appl. Sci. J. 2009, 7, 962–967. [Google Scholar]
- Muyibi, S.; Alfugara, A. Treatment of Surface Water with Moringa oleifera Seed Extract and Alum—A Comparative Study Using a Pilot Scale Water Treatment Plant. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 60, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Gao, B.; Ren, J.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Coagulation/Flocculation in Dewatering of Sludge: A Review. Water Res. 2018, 143, 608–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfina, S.; Nikhil, N.A.; Akhilesh, V.S.; Anandhu, S.; Anu, N. Production of Natural Coagulant from Plant Materials and to Evaluate the Efficiency for Water Treatment Along with Its Validation by ANN. In Advanced Engineering Optimization through Intelligent Techniques; Venkata Rao, R., Taler, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Delelegn, A.; Sahile, S.; Husen, A. Water Purification and Antibacterial Efficacy of Moringa oleifera Lam. Agric. Food Secur. 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, A.K.; Hammouda, O.; Lovett-Doust, J.; Gomaa, N.H. Population Dynamics of Moringa peregrina along Altitudinal Gradient in the Northwestern Sector of the Red Sea. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadamouny, M.A.; Unterseher, M.; König, P.; Schnittler, M. Population Performance of Moringa peregrina (Forssk.) Fiori (Moringaceae) at Sinai Peninsula, Egypt in the Last Decades: Consequences for Its Conservation. J. Nat. Conserv. 2016, 34, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somali, M.A.; Bajneid, M.A.; Al-Fhaimani, S.S. Chemical Composition and Characteristics of Moringa peregrina Seeds and Seeds Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1984, 61, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Baky, H.H.; El-Baroty, G.S. Characterization of Egyptian Moringa peregrine Seed Oil and Its Bioactivities. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Bus. Res. 2013, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, H.A.M.; Ali, M.; Amar, M.H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.-F. Characterization of Phytochemical and Nutrient Compounds from the Leaves and Seeds of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harthi, M.A.; Attia, Y.A.; Elgandy, M.F.; Bovera, F. Oil Extracted Moringa peregrina Seed Cake as a Feed Ingredient in Poultry: A Chemical Composition and Nutritional Value Study. Animals 2022, 12, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouhi, S.; Kwaambwa, H.M.; Gutfreund, P.; Rennie, A.R. Comparative Study of Flocculation and Adsorption Behaviour of Water Treatment Proteins from Moringa peregrina and Moringa oleifera Seeds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Baes, A.U.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Improvement of Extraction Method of Coagulation Active Components from Moringa oleifera Seed. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3373–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Baes, A.U.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Isolation and Characterization of Coagulant Extracted from Moringa oleifera Seed by Salt Solution. Water Res. 2001, 35, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, E.R.B.; de Menezes, N.N.F.; Silva, F.L.; Garrido, J.W.A.; dos Santos Bezerra Sousa, M.A.; dos Santos, E.S. Effect of Oil Extraction on the Composition, Structure, and Coagulant Effect of Moringa oleifera Seeds. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, B.; Betiku, E. Process Optimization of Solvent Extraction of Seed Oil from Moringa oleifera: An Appraisal of Quantitative and Qualitative Process Variables on Oil Quality Using D-Optimal Design. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 101187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, S.; Karthikeyan, P.; Sirajudheen, P.; Meenakshi, S. Optimization of Sustainable Chitosan/Moringa. Oleifera as Coagulant Aid for the Treatment of Synthetic Turbid Water—A Systemic Study. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2035-19; Standard Practice for Coagulation-Flocculation Jar Test of Water. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- APHA; AWWA. WEF Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 1360. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Subramanian, R.; Manohar, B.; Radha, C. Preparation, Characterization and Functional Properties of Moringa oleifera Seed Protein Isolate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chales, G.G.; Tihameri, B.S.; Milhan, N.V.M.; Koga-Ito, C.Y.; Antunes, M.L.P.; Reis, A.G. dos Impact of Moringa oleifera Seed-Derived Coagulants Processing Steps on Physicochemical, Residual Organic, and Cytotoxicity Properties of Treated Water. Water 2022, 14, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkurunziza, T.; Nduwayezu, J.B.; Banadda, E.N.; Nhapi, I. The Effect of Turbidity Levels and Moringa oleifera Concentration on the Effectiveness of Coagulation in Water Treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.U.; Cusioli, L.F.; Quesada, H.B.; Ferreira, M.E.C.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Vieira, A.M.S.; Gomes, R.G.; Vieira, M.F.; Bergamasco, R. A Review of Moringa oleifera Seeds in Water Treatment: Trends and Future Challenges. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, W.M.; Bote, M.E. Wastewater Treatment Using a Natural Coagulant (Moringa oleifera Seeds): Optimization through Response Surface Methodology. Helyion 2009, 7, E08451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, E.; Kordmostafapour, F.; Faridi, H.; Barikbin, B. Application of Moringa peregrina Seed Extract as a Natural Coagulant for Phenol Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Birjand Univ. Med. Sci. 2012, 19, 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, S.; Othman, Z.; Ahmad, A.L. Coagulation–Flocculation Process for POME Treatment Using Moringa oleifera Seeds Extract: Optimization Studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali Aba Lulesa, T.; Beyene, D.; Ebba, M.; Kenea, G. Water Treatment Using Natural Coagulant and Electrocoagulation Process: A Comparison Study. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 2022, 4640927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nand, V.; Maata, M.; Koshy, K.; Sotheeswaran, S. Water Purification Using Moringa oleifera and Other Locally Available Seeds in Fiji for Heavy Metal Removal. Int. J. Appl. 2012, 2, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.C.; Al Matar, M.; Makky, E.A.; Ali, E.N. The Use of Moringa oleifera Seed as a Natural Coagulant for Wastewater Treatment and Heavy Metals Removal. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatal, M.; Olguin, M.T.; Anastopoulos, I.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Lima, E.C.; Vargas, J.; Aguilar, C. Comparison of Heavy Metals Removal from Aqueous Solution by Moringa oleifera Leaves and Seeds. Coatings 2021, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).