Summer Chlorophyll-a Increase Induced by Upwelling off the Northeastern Coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
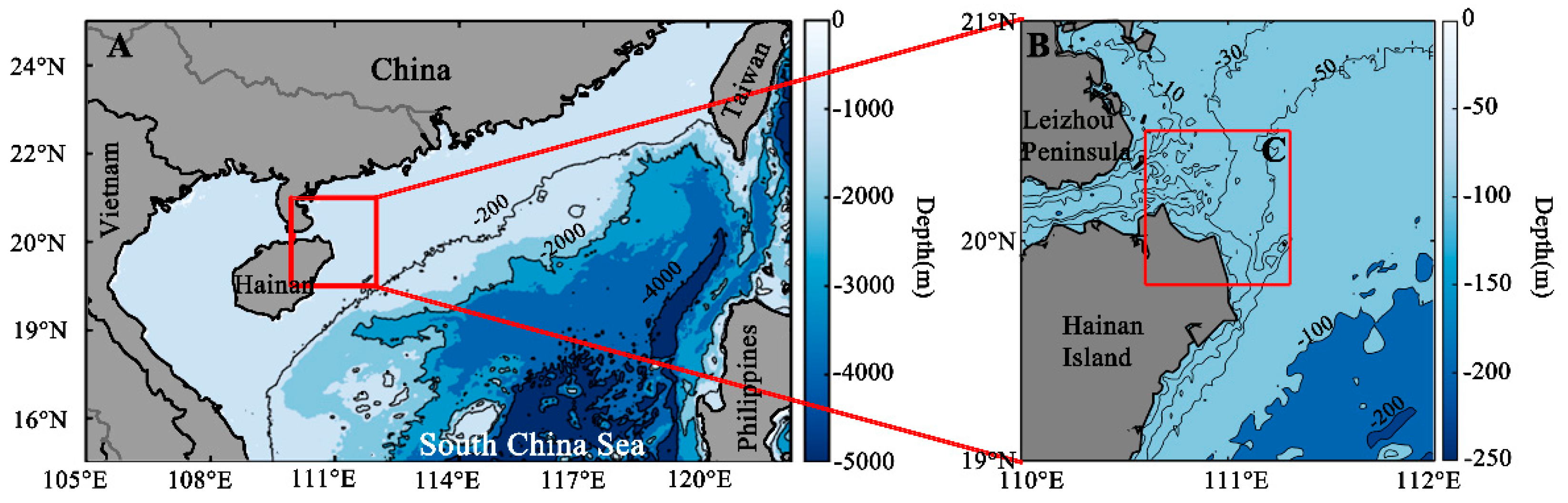
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Ekman Pumping Velocity and Ekman Transport
2.3.2. Temperature Anomalies in the Upwelling Region
2.3.3. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
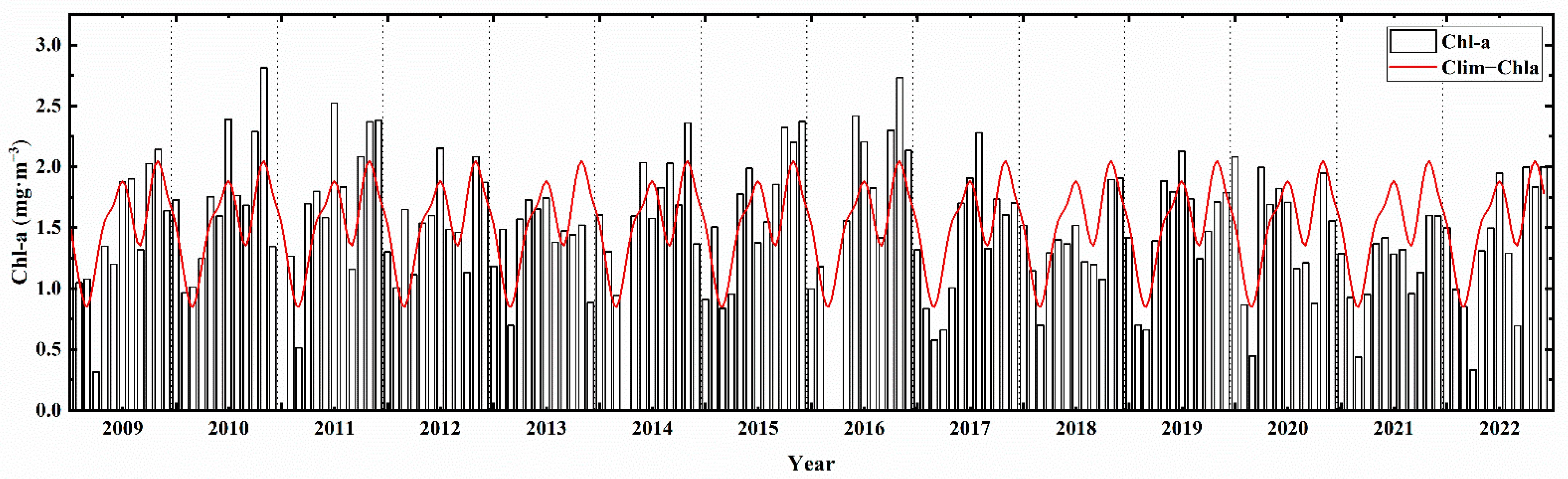
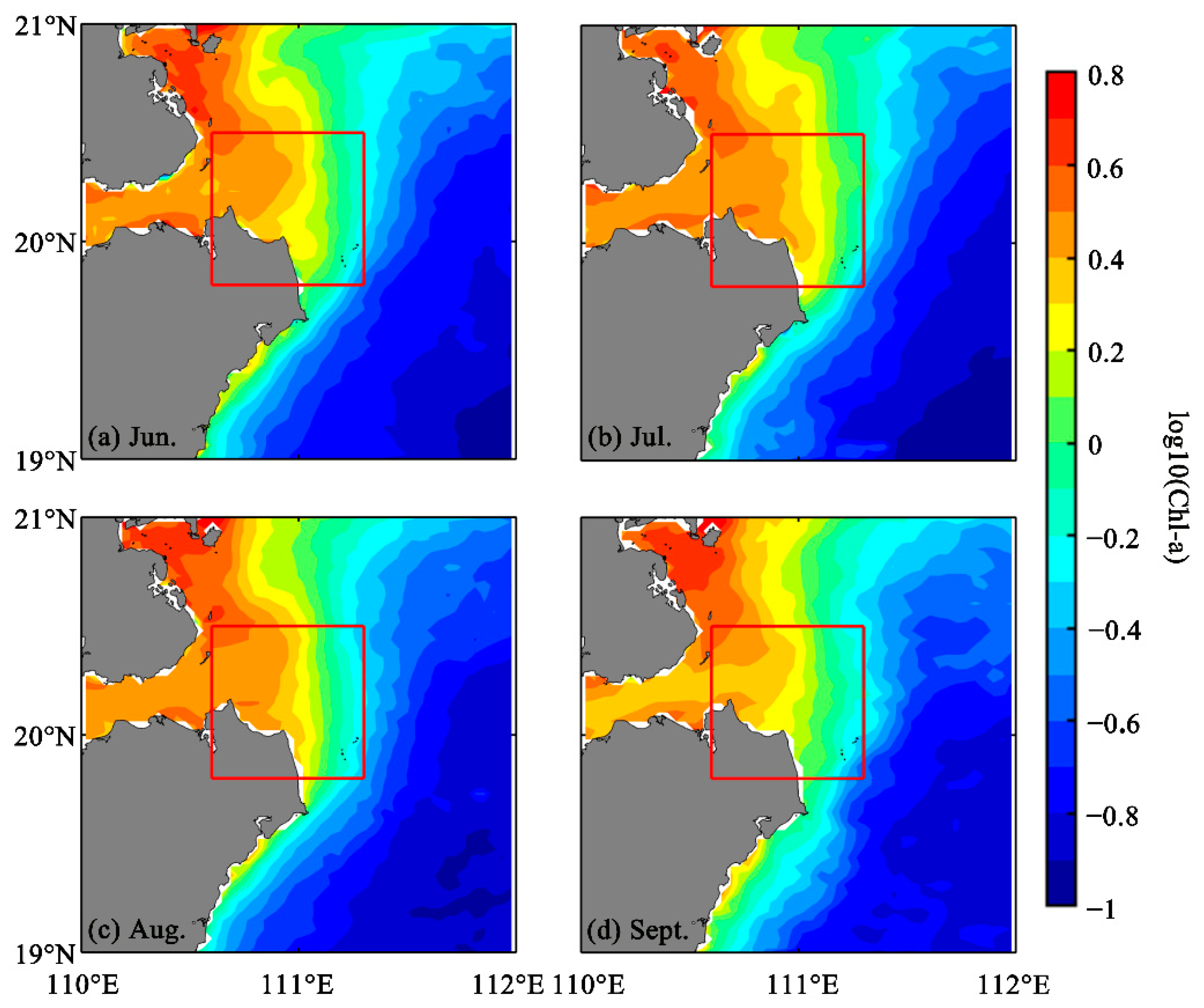
3.1. Distribution of Chl-a Northwest of Hainan Island
3.2. Satellite Observation of Environmental Variables
3.2.1. Sea Surface Temperature
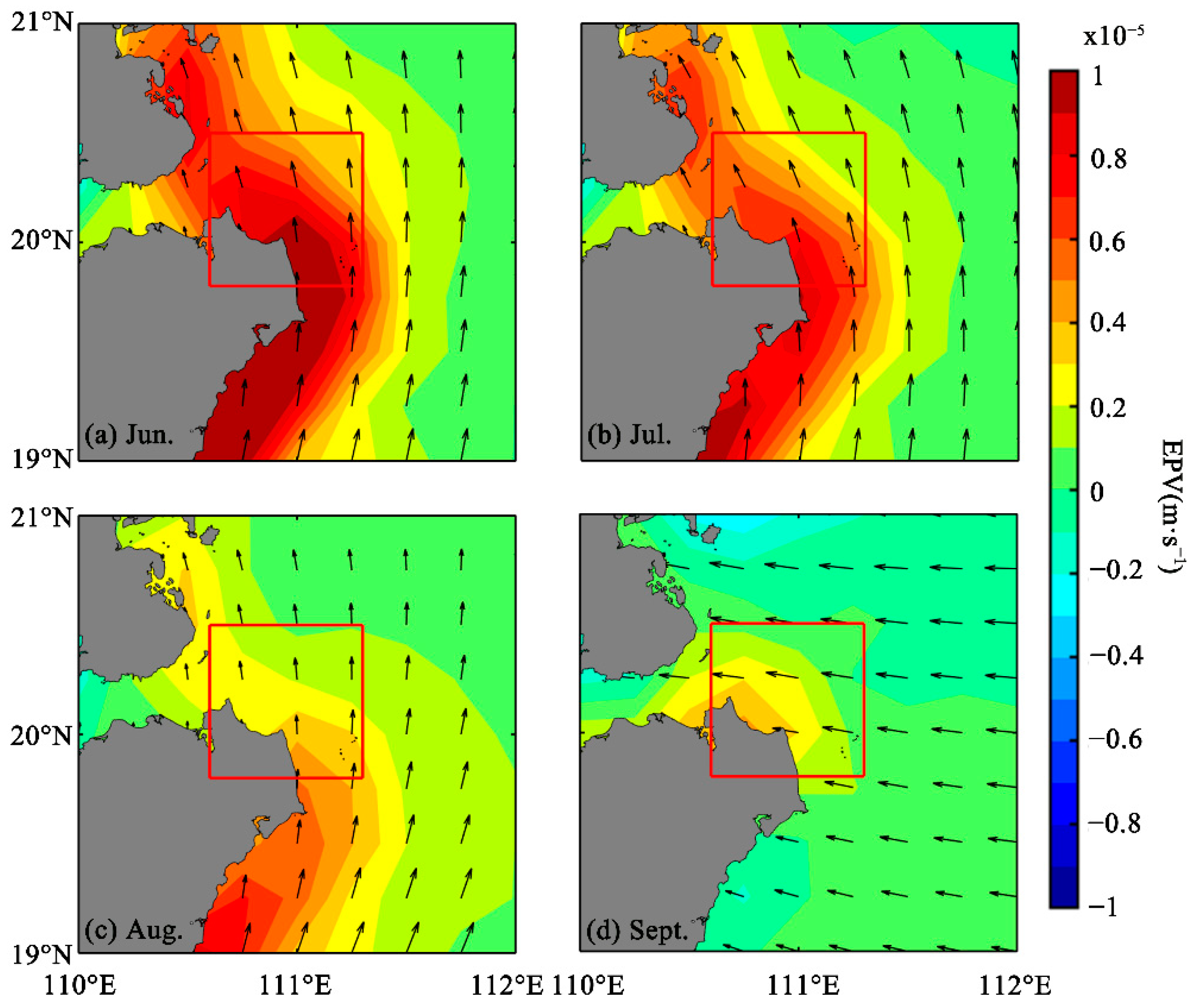
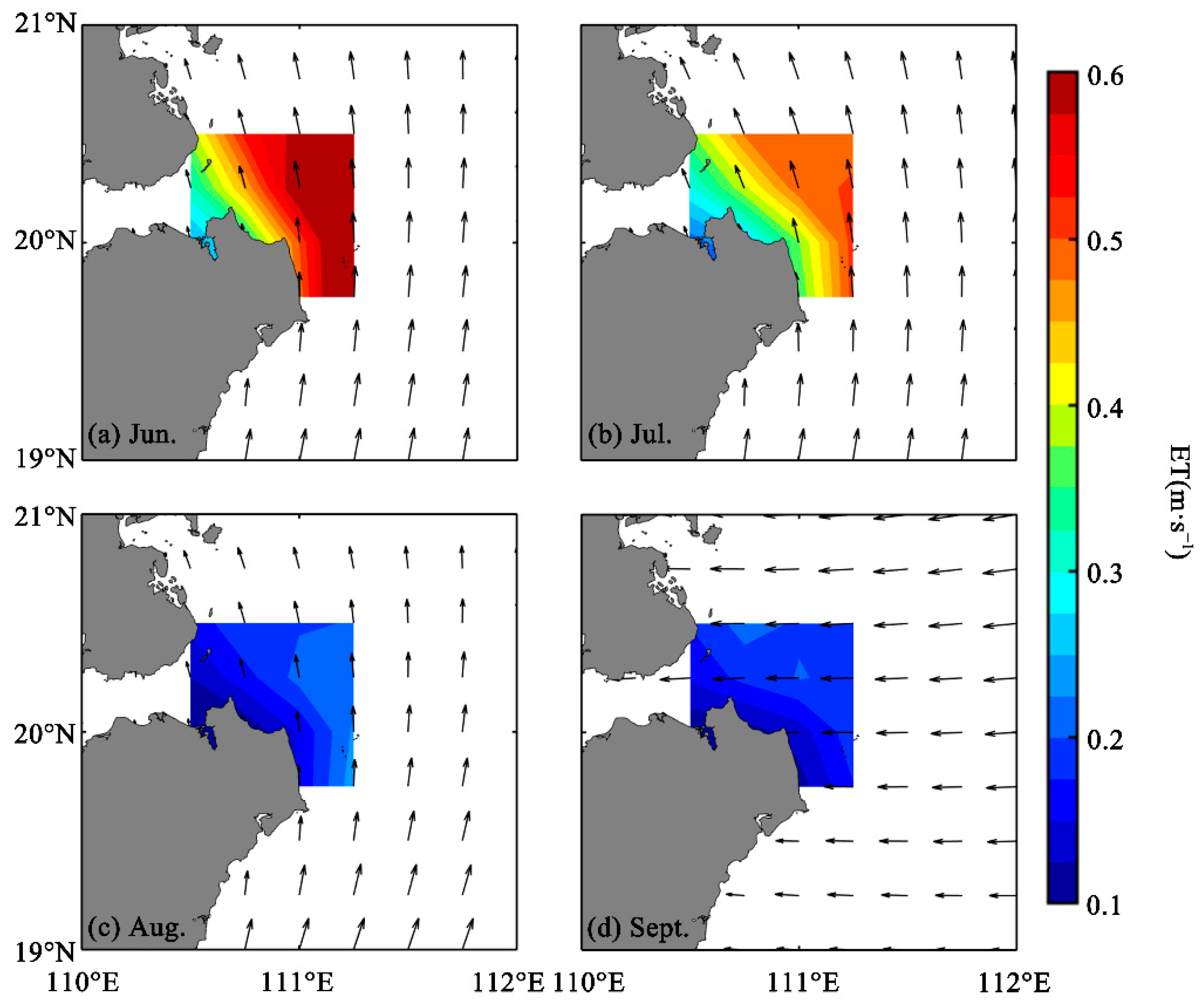
3.2.2. EPV and ET Caused by Wind Stress
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Chl-a and Other Conditions
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Upwelling on Summer Chl-a Increase
4.2. Key Environmental Factors Inducing Summer Chl-a Increase
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, M. The relationship between major upwelling and the upwelling fishing grounds in the South China Sea. Mar. Sci. 2015, 39, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V. Primary production required to sustain global fisheries. Nature 1995, 374, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Liu, G.; Wu, X. Role of Ekman transport versus Ekman pumping in driving summer upwelling in the South China Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2013, 12, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, D. Offshore Ekman transport and Ekman pumping off Peru during the 1997–1998 El Niño. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 19–1–19-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R. Summarization of study on upwelling system in the South China Sea. J Ocean. Taiwan Strait 2003, 22, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Ling, Z.; Chen, C. Winter coastal upwelling off northwest Borneo in the South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hong, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wan, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liang, H. Variable temperature, salinity and water mass structures in the southwestern Taiwan Strait in summer. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S13–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Ren, G.; Cao, D.; Yang, Y. Characteristics of the ecological environment in upwelling area adjacent to the Changjiang River estuary. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2001, 32, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshid, D.; Fredolin, T.; Liew, J. Simulation of southwest monsoon current circulation and temperature in the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Sains Malays. 2014, 43, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Wang, D.; Feng, M.; Geng, B.; Chen, J.; Yao, J.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Q.Y. The contribution of local wind and ocean circulation to the interannual variability in coastal upwelling intensity in the Northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 6766–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, D.; Sui, Y. Winter phytoplankton bloom induced by subsurface upwelling and mixed layer entrainment southwest of Luzon Strait. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 83, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Yan, X.H.; Jiang, Y. Winter bloom and associated upwelling northwest of the Luzon Island: A coupled physical-biological modeling approach. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roughan, M.; Middleton, J.H. A comparison of observed upwelling mechanisms off the east coast of Australia. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 2551–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.D.; Matano, R.P. Disentangling the upwelling mechanisms of the South Brazil Bight. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Kawamura, H.; Tang, D. Tidal front around the Hainan Island, northwest of the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2003, 108, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Qiao, F.; Wang, G.; Xia, C.; Yuan, Y. Upwelling off the west coast of Hainan Island in summer: Its detection and mechanisms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Yang, Y.; Lü, X.; Xia, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Yuan, Y. Coastal upwelling in the East China Sea in winter. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, C11S06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Qiao, F.; Xia, C.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y. Tidally induced upwelling off Yangtze River estuary and in Zhejiang coastal waters in summer. Sci. China. Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.J.; Li, L.; Guo, X.G.; Xu, J.D. A preliminary study of the internal tide in the summertime upwelling regime off the Guangdong shelf edge in 2002 and its local feedback. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2012, 31, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D. Two phytoplankton blooms near Luzon Strait generated by lingering Typhoon Parma. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2013, 118, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, H. Impact of Typhoon on Coastal Upwelling Off The Eastern Hainan Island: A Case Study of Typhoon Rammasun (2014). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Huang, H.; Zheng, N.; Pan, A.; Wang, S.; Huo, C.; Zhou, K.; Lin, H.; Ji, W. Acidification mediated by a river plume and coastal upwelling on a fringing reef at the east coast of Hainan Island, Northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7521–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Guo, X. Interaction of a river plume with coastal upwelling in the northeastern South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean-Padman, J.; Padman, L. Summer upwelling on the Sydney inner continental shelf: The relative roles of local wind forcing and mesoscale eddy encroachment. Cont. Shelf Res. 1991, 11, 321–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannigan, L. Intense submesoscale upwelling in anticyclonic eddies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X. Progress on upwelling studies in the China seas. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Huang, Z.; Hu, J. Using TPI to Map Spatial and Temporal Variations of Significant Coastal Upwelling in the Northern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H. Overview of studies on Qiongdong upwelling. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2012, 31, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Qi, Y.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, H. Numerical study on the summer upwelling system in the northern continental shelf of the South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, D. Numerical simulation of the structure and variation of upwelling off the east coast of Hainan Island using QuikSCAT winds. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, J. Observation of summertime upwelling off the eastern and northeastern coasts of Hainan Island, China. Ocean Dyn. 2016, 66, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Guo, X.; Cao, Z.; Su, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Carbonate dynamics in a tropical coastal system in the South China Sea featuring upwelling, river plumes and submarine groundwater discharge. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 2267–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Gu, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, K. Modelling the upwelling offthe east Hainan Island coast in summer 2010. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 1358–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Pohlmann, T. Wind and topography influence on an upwelling system at the eastern Hainan coast. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2009, 114, C06017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shu, Y.; Xue, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, W.; Zu, T.; Xu, J. Relative contributions of local wind and topography to the coastal upwelling intensity in the northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 2550–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, W.; Zhou, F. Phytoplankton bloom triggered by eddy-wind interaction in the upwelling region east of Hainan Island. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 214, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; He, C.; Li, M.; Tian, J.; Jing, Z. Response of sea surface temperature to typhoon passages over the upwelling zone east of Hainan Island. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2017, 35, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Li, J. Volume and Nutrient Transports Disturbed by the Typhoon Chebi (2013) in the Upwelling Zone East of Hainan Island, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Curchitser, E.N.; Wang, J.; Peng, S. Tidal Effects on the Surface Water Cooling Northeast of Hainan Island, South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC016016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xie, L. Multiple mechanisms for chlorophyll-a concentration variations in coastal upwelling regions: A case study east of Hainan Island in the South China Sea. EGUsphere 2023, 19, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.; Chao, S.Y.; Shaw, P.T.; Gong, G.C.; Chen, C.C.; Tang, T.Y. Monsoon-forced chlorophyll distribution and primary production in the South China Sea: Observations and a numerical study. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 1387–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Lai, Z.; Ji, R.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Yin, J.; Wang, Y.; Lian, S.; Zhu, X. Summertime primary production in northwest South China Sea: Interaction of coastal eddy, upwelling and biological processes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 48, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, A. Eddy effects on biogeochemistry. Nature 2014, 506, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-W.; Najjar, R.G.; Lee, K. Influence of precipitation events on phytoplankton biomass in coastal waters of the eastern United States. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xie, L. A modeling study of the effects of river runoff, tides, and surface wind-wave mixing on the Eastern and Western Hainan upwelling systems of the South China Sea, China. Ocean Dyn. 2015, 65, 1143–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhao, H. Effects of typhoon and upwelling on Chlorophyll-a distribution in the northeastern coast of Hainan during Summer. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhong, H.; Wang, M.; Yun, F. On relation between upwelling off Qionghai and fishery. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 1995, 14, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Kester, D.R.; Ni, I.-H.; Kawamura, H.; Hong, H. Upwelling in the Taiwan Strait during the summer monsoon detected by satellite and shipboard measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Qi, Y.; Du, Y. Upwelling in the continental shelf of northern South China Sea associated with 1997–1998 El Niño. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, C02033, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Qi, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, L. Summer upwelling and thermal fronts in the northwestern South China Sea: Observational analysis of two mesoscale mapping surveys. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; You, Q.; Jing, G.; Zhang, W. Characteristics analysis of current and residual current in the northeastern sea area of Hainan island. Guangxi Sci. 2018, 25, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A. Consistent merging of satellite ocean color data sets using a bio-optical model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritorena, S.; d’Andon, O.H.F.; Mangin, A.; Siegel, D.A. Merged satellite ocean color data products using a bio-optical model: Characteristics, benefits and issues. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H. Spatial distribution of the summer subsurface chlorophyll maximum in the North South China Sea. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, D.; Wang, S. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll a concentration in summer in western South China Sea and its response to oceanographic environmental factors. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2005, 24, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Zhao, H.; Han, G.; Dong, C. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Winter Phytoplankton Blooms Northwest of the Luzon Island in the South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhao, H. Summer Phytoplankton Blooms Induced by Upwelling in the Western South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 740130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y. On the importance of the Pearson correlation coefficient in noise reduction. Ieee Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2008, 16, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhao, H.; Chen, F.; Xiao, H. The distribution of aerosols and their impacts on chlorophyll-a distribution in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2020, 125, e2019JG005490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yu, J.; Ho, T.-Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Kong, L.; Liu, H. Dynamics of phytoplankton community structure in the South China Sea in response to the East Asian aerosol input. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1519–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, W. Study on the features of chlorophyll-a derived from SeaWiFS in the South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin 2005, 27, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xiu, P.; Chai, F. Physical and biological controls on the summer chlorophyll bloom to the east of Vietnam. J. Oceanogr. 2014, 70, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zong, X.; Yi, X.; Li, M. The interannual variation and long-term trend of Qiongdong upwelling. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin 2016, 47, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.J.; Ternon, J.-F.; Morris, T. Interaction of dipole eddies with the western continental slope of the Mozambique Channel. Deep-Sea Res. Part Ii-Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 100, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, I.; Vialard, J.; Lengaigne, M.; Izumo, T.; Parvathi, V.; Muraleedharan, P.M. Sea Level Interannual Variability Along the West Coast of India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 12440–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Qi, Y.; Hua, Z. Numerical study on summer upwelling over northern continental shelf of South China Sea. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2008, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y. Phytoplankton Increases Induced by Tropical Cyclones in the South China Sea During 1998–2015. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 2903–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, M.; Chen, W.; Huh, C.-A.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Charette, M.A. How significant is submarine groundwater discharge and its associated dissolved inorganic carbon in a river-dominated shelf system? Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1777–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Tan, E.; Dai, M. Submarine groundwater discharge on the western shelf of the northern South China Sea influenced by the Pearl River plume and upwelling. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, W.; Tang, D. Evaluation of water residence time, submarine groundwater discharge, and maximum new production supported by groundwater borne nutrients in a coastal upwelling shelf system. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 631–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kawamura, H.; Van Dien, T.; Lee, M. Offshore phytoplankton biomass increase and its oceanographic causes in the South China Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 268, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedras, F.R.; Odebrecht, C. The response of surf-zone phytoplankton to nutrient enrichment (Cassino Beach, Brazil). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 432, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kester, D.R.; Ni, I.-H.; Qi, Y.; Kawamura, H. In situ and satellite observations of a harmful algal bloom and water condition at the Pearl River estuary in late autumn 1998. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Huang, L.; Devlin, A.T.; Lin, H. Quantification of Typhoon-Induced Phytoplankton Blooms Using Satellite Multi-Sensor Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Chai, F.; Tang, D.; Wang, D. Marine phytoplankton biomass responses to typhoon events in the South China Sea based on physical-biogeochemical model. Ecol. Model. 2017, 356, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ΔSST | SSW | ET | EPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | −0.521 | 0.026 | 0.316 | 0.322 |
| p | <0.01 | >0.10 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Shen, C. Summer Chlorophyll-a Increase Induced by Upwelling off the Northeastern Coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea. Water 2023, 15, 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152770
Chen Y, Zhao H, Shen C. Summer Chlorophyll-a Increase Induced by Upwelling off the Northeastern Coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea. Water. 2023; 15(15):2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152770
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yingjun, Hui Zhao, and Chunyan Shen. 2023. "Summer Chlorophyll-a Increase Induced by Upwelling off the Northeastern Coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea" Water 15, no. 15: 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152770
APA StyleChen, Y., Zhao, H., & Shen, C. (2023). Summer Chlorophyll-a Increase Induced by Upwelling off the Northeastern Coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea. Water, 15(15), 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152770





