Adsorption and Removal of Composite Contaminants in Water Using Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanofiber Membranes with Polydopamine–Polyethyleneimine Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Characterization and Measurement Methods
2.3. Optimization of Synthesis Conditions
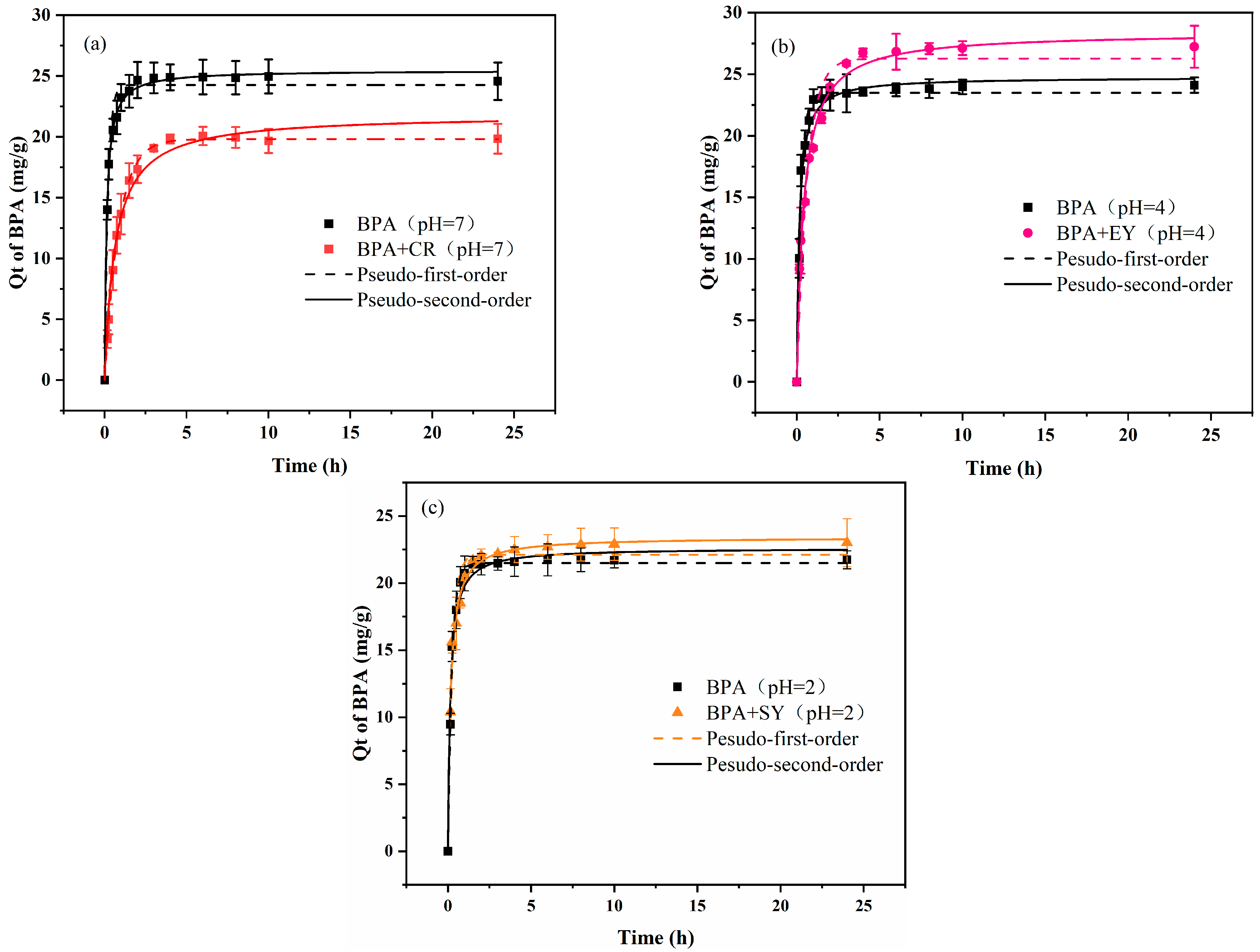
2.4. Kinetic Adsorption
2.5. Equilibrium Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Zeta-Potential Analysis
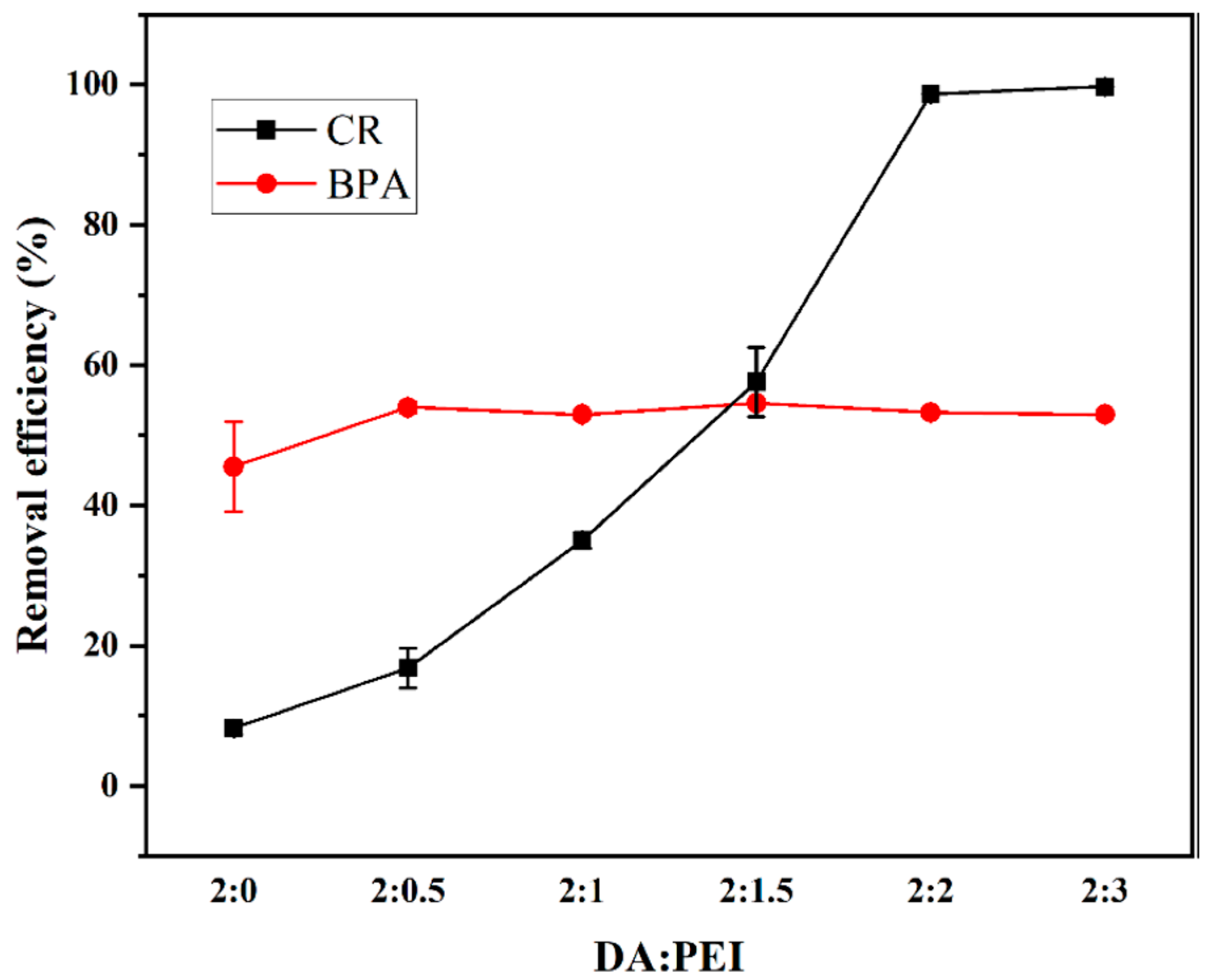
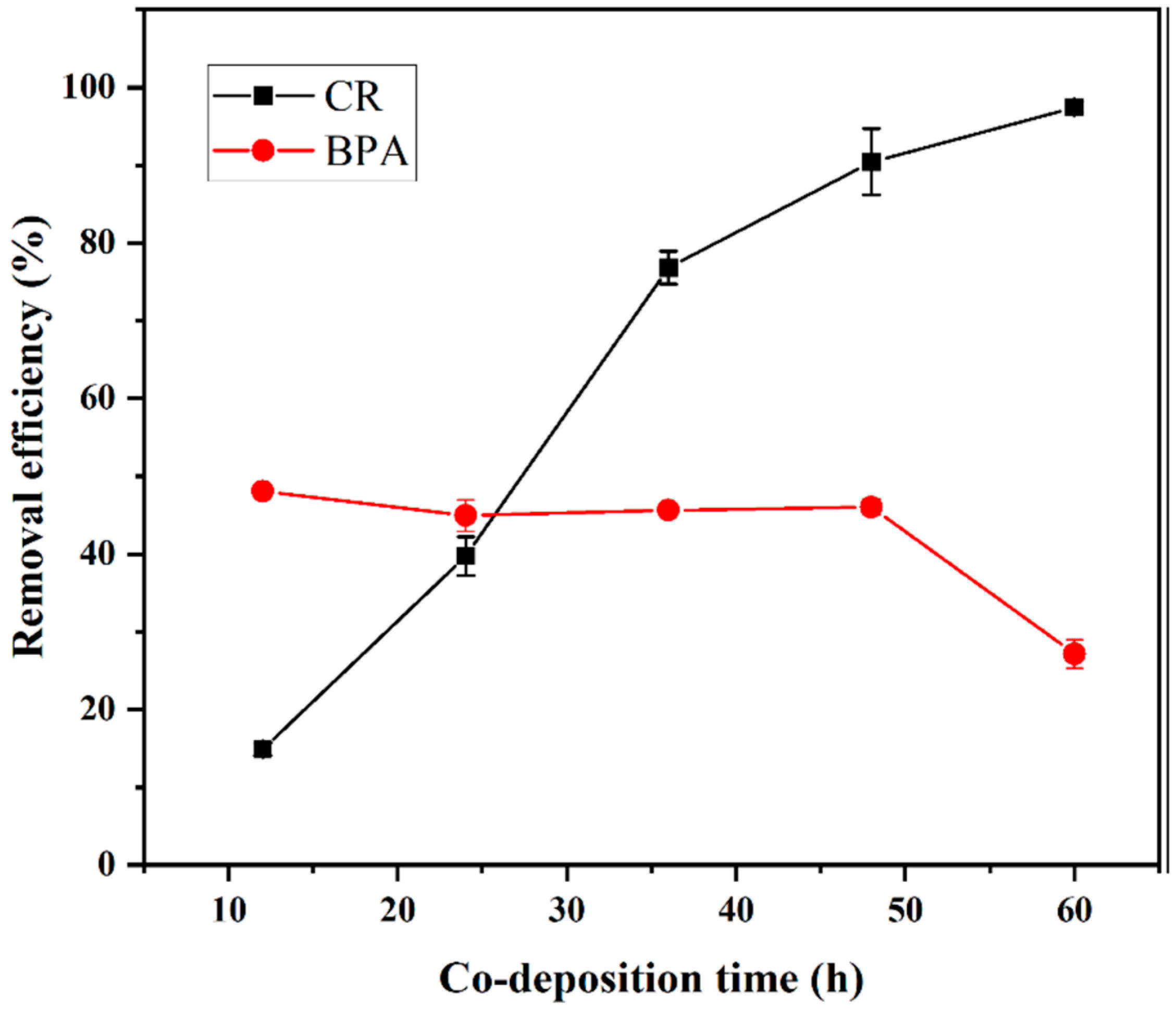
3.2. Optimization of Synthesis Conditions
3.2.1. PEI/DA Monomer Ratio
3.2.2. Effect of Deposition Time
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Thermodynamic Analysis
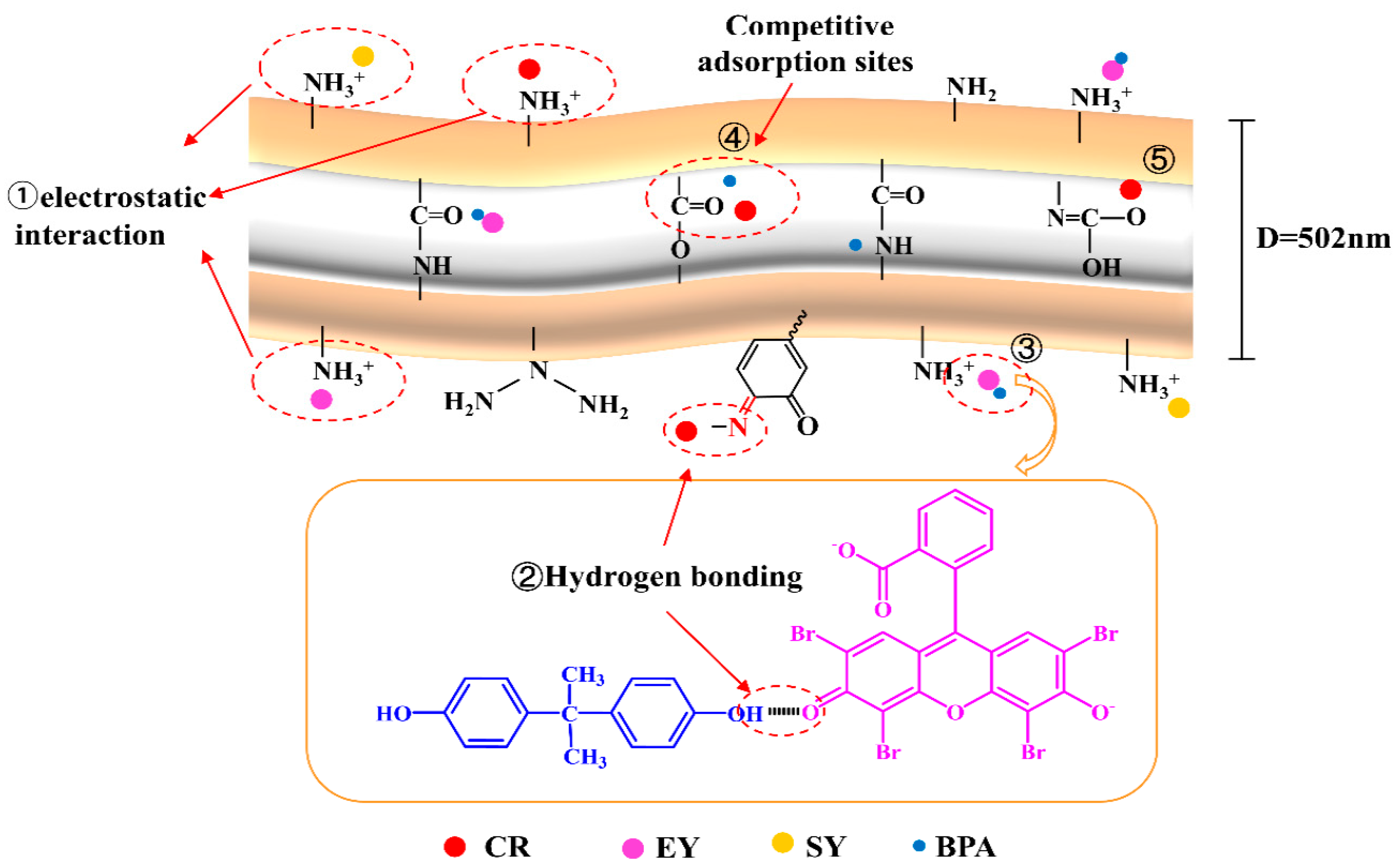
3.5. Mechanistic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Wang, J. Electrospinning Polyvinyl alcohol/silica-based nanofiber as highly efficient adsorbent for simultaneous and sequential removal of Bisphenol A and Cu(II) from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Gómez, R.; Rivera-Ramírez, D.A.; Hernández-Montoya, V.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Durán-Valle, C.J.; Montes-Morán, M.A. Synergic adsorption in the simultaneous removal of acid blue 25 and heavy metals from water using a Ca(PO3)2-modified carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199–200, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fan, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Tang, Z. Magnetic polydopamine decorated with Mg–Al LDH nanoflakes as a novel bio-based adsorbent for simultaneous removal of potentially toxic metals and anionic dyes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Repo, E.; Yin, D.; Meng, Y.; Jafari, S. EDTA-Cross-Linked β-Cyclodextrin: An environmentally friendly bifunctional adsorbent for simultaneous adsorption of metals and cationic dyes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10570–10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wu, Y.; Cha, L. Shaddock peels-based activated carbon as cost-saving adsorbents for efficient removal of Cr (VI) and methyl orange. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19828–19842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Tian, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, B.; Akindolie, M.S.; Hu, Q.; Feng, C.; Feng, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y. Multi-component adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) onto microwave-functionalized cellulose: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, mechanisms and application for electroplating wastewater purification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Liu, W.; Kannan, K. Bisphenols, Benzophenones, and bisphenol A diglycidyl ethers in textiles and infant clothing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5279–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, W.; Cheng, G.; Cui, C.; Lu, J. A novel amphoteric β-cyclodextrin-based adsorbent for simultaneous removal of cationic/anionic dyes and bisphenol A. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Standard of China Full Text Disclosure System Home Page. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/index (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Chlanda, A.; Kijeńska, E.; Rinoldi, C.; Tarnowski, M.; Wierzchoń, T.; Swieszkowski, W. Structure and physico-mechanical properties of low temperature plasma treated electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds examined with atomic force microscopy. Micron 2018, 107, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yin, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, H. Polyethyleneimine cross-linked graphene oxide for removing hazardous hexavalent chromium: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, Z.M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X. Synthesis and application of polyethyleneimine (PEI)-based composite/nanocomposite material for heavy metals removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. A 2022, 8, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, F.; Selvaraj, M.; Zain, J.; Banat, F.; AbuHaija, M. Polyethylenimine modified graphene oxide hydrogel composite as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G. Adsorption mechanism of polyethyleneimine modified magnetic core–shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for anionic dye removal. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32462–32471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Du, P.; Bi, W.; Yao, G.; Li, S.; Liu, H. Graphene oxide aerogels co-functionalized with polydopamine and polyethylenimine for the adsorption of anionic dyes and organic solvents. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 154, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.; Zheng, H.; Fan, J.; Hu, Y. Adsorption behaviors of typical endocrine disrupting chemicals by TPU nanofiber membrane. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 5680–5687. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Fan, J. Different adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of anionic azo dyes on polydopamine–polyethyleneimine modified thermoplastic polyurethane nanofiber membranes. Water 2022, 14, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantripragada, S.; Deng, D.; Zhang, L. Remediation of GenX from water by amidoxime surface-functionalized electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous adsorbent. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Jin, P.; Xu, D.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, R.; Depuydt, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Bruggen, B.V. A PEI/TMC membrane modified with an ionic liquid with enhanced permeability and antibacterial properties for the removal of heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, G.; Ding, J. Styrene-maleic anhydride/polyethersulfone blending membranes modified by PEI functionalized TiO2 to enhance separation and antifouling properties: Dye purification. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusuz, Y.D. Exploring the structure of RNA-incorporated PEG/PEI modified silica network. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 279, 125779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wei, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, N.; Zhou, B. Adsorption of bisphenol A based on synergy between hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13861–13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeid, A. Kinetic models of sorption: A theoretical analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zuliani, A.; Chelazzi, D.; Mastrangelo, R.; Giorgi, R.; Baglioni, P. Adsorption kinetics of acetic acid into ZnO/castor oil-derived polyurethanes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 632, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimelazhagan, V.; Yashwath, P.; Arukkani Pushparajan, D.; Carpenter, J. Rapid Removal of Toxic Remazol Brilliant Blue-R Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Juglans nigra Shell Biomass Activated Carbon as Potential Adsorbent: Optimization, Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Investigation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimelazhagan, V.; Natarajan, K.; Shanbhag, S.; Madivada, S.; Kumar, H.S. Effective Adsorptive Removal of Coomassie Violet Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Green Synthesized Zinc Hydroxide Nanoparticles Prepared from Calotropis gigantea Leaf Extract. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimelazhagan, V.; Rampal, N.; Jeppu, G. Adsorption of toxic Congo red dye from aqueous solution using untreated coffee husks: Kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and desorption study. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 2789–2808. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, D.; Chander, S. Single, binary, and multicomponent sorption of iron and manganese on lignite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.A.; Khan, A.Y. Selective adsorption of anionic dye from wastewater using polyethyleneimine based macroporous sponge: Batch and continuous studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Choi, T.R.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, Y.K.; Lee, H.J.; Ham, S.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Adsorptive removal of synthetic plastic components bisphenol-A and solvent black-3 dye from single and binary solutions using pristine pinecone biochar. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.P.; Luo, J.J.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhen, B.; Dong, C.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Shen, J.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chen, H.P. A novel electrospun β-CD/CS/PVA nanofiber membrane for simultaneous and rapid removal of organic micropollutants and heavy metal ions from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.N.; Leckie, J.O. Effect of membrane chemistry and coating layer on physiochemical properties of thin film composite polyamide RO and NF membranes: I. FTIR and XPS characterization of polyamide and coating layer chemistry. Desalination 2009, 242, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Liao, K.J.; Huang, H.; Wu, Q.Y.; Wan, L.Y.; Xu, Z.K. Mussel-inspired modification of a polymer membrane for ultra-high water permeability and oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10225–10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chen, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhu, L. Regenerable adsorptive membranes prepared by mussel-inspired co-deposition for aqueous dye removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Jalali, M.L.; Fard, G.C.; Maleknia, L. Surfactant grafted PDA-PAN nanofiber: Optimization of synthesis, characterization and oil absorption property. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavukkandy, M.O.; Ibrahim, Y.; Almarzooqi, F.; Naddeo, V.; Karanikolos, G.N.; Alhseinat, E.; Banat, F.; Hasan, S.W. Synthesis of polydopamine coated tungsten oxide@ poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) electrospun nanofibers as multifunctional membranes for water applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Wu, M.-B.; Li, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Wan, L.-S.; Xu, Z.-K. Effects of polyethyleneimine molecular weight and proportion on the membrane hydrophilization by codepositing with dopamine. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L. Bisphenol A sorption by organo-montmorillonite: Implications for the removal of organic contaminants from water. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



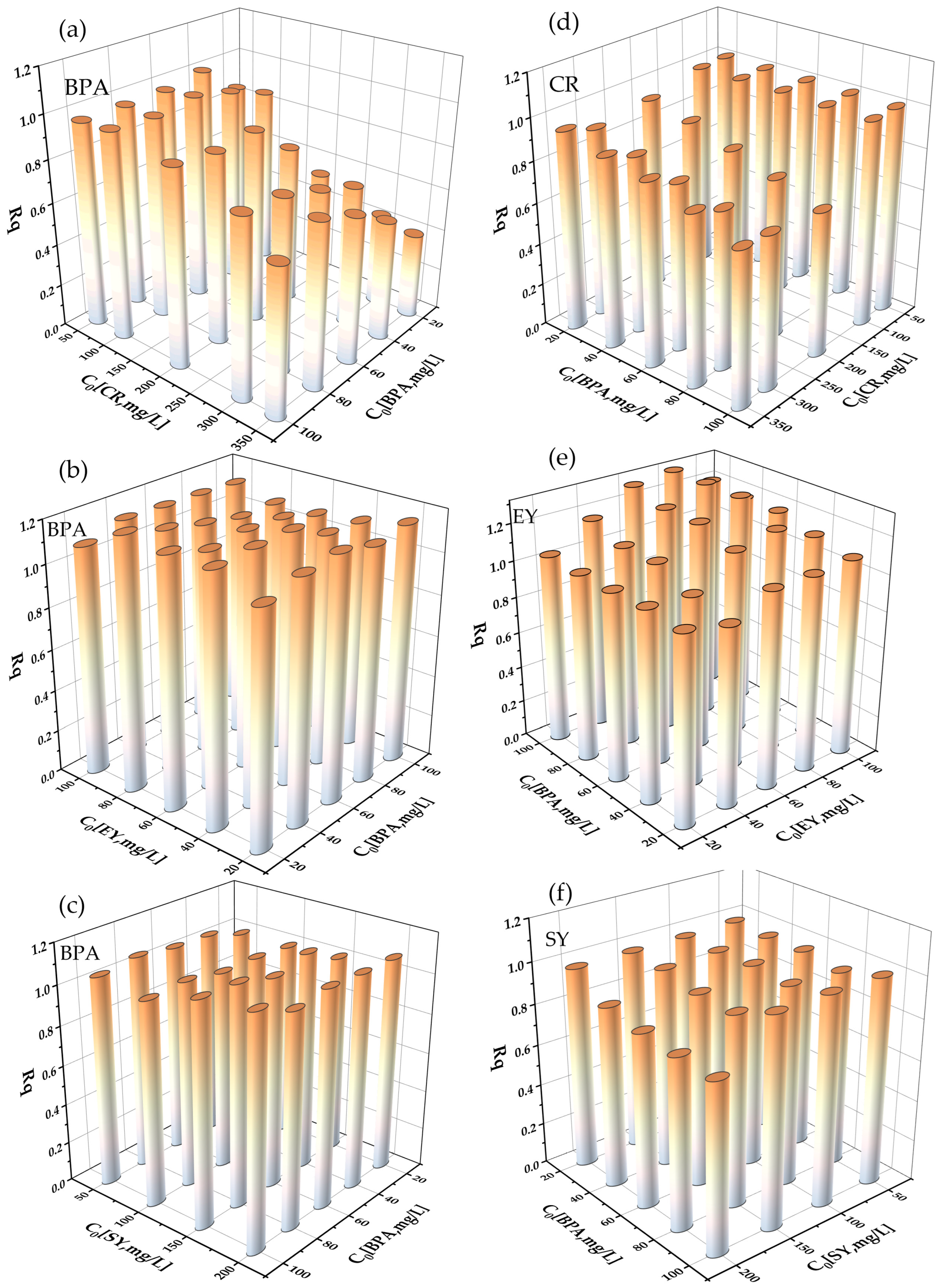
| Levels | Factor B: Concentration of Dyes in Binary Wastewater Systems (mg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | ||
| Concentration of CR | 0 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 350 | |
| Concentration of SY | 0 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 200 | ||
| Concentration of EY | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | |
| Factor A: Concentration of BPA in binary wastewater systems (mg/L) | 0 | Qe[0,C1] | Qe[0,C2] | Qe[0,C3] | Qe[0,C4] | Qe[0,C5] | |
| 20 | Qe[20,C0] | Qe[20,C1] | Qe[20,C2] | Qe[20,C3] | Qe[20,C4] | Qe[20,C5] | |
| 40 | Qe[40,C0] | Qe[40,C1] | Qe[40,C2] | Qe[40,C3] | Qe[40,C4] | Qe[40,C5] | |
| 60 | Qe[60,C0] | Qe[60,C1] | Qe[60,C2] | Qe[60,C3] | Qe[60,C4] | Qe[60,C5] | |
| 80 | Qe[80,C0] | Qe[80,C1] | Qe[80,C2] | Qe[80,C3] | Qe[80,C4] | Qe[80,C5] | |
| 100 | Qe[100,C0] | Qe[100,C1] | Qe[100,C2] | Qe[100,C3] | Qe[100,C4] | Qe[100,C5] | |
| Contaminants | Wastewater System | Qe (exp) mg/g | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg/g) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | k2 (min−1) | R2 | |||
| CR | CR (pH = 7) | 220.67 ± 7.49 | 182.25 | 0.160 | 0.989 | 214.30 | 0.002 | 0.983 |
| CR–BPA (pH = 7) | 192.69 ± 21.17 | 198.75 | 0.307 | 0.939 | 213.31 | 8.37 × 10−4 | 0.998 | |
| SY | SY (pH = 2) | 87.60 ± 0.29 | 80.52 | 1.123 | 0.943 | 86.07 | 0.019 | 0.993 |
| SY–BPA (pH = 2) | 84.92 ± 14.21 | 80.07 | 0.792 | 0.975 | 85.83 | 0.013 | 0.994 | |
| EY | EY (pH = 4) | 60.91 ± 0.35 | 57.46 | 2.732 | 0.966 | 60.02 | 0.079 | 0.997 |
| EY–BPA (pH = 4) | 85.08 ± 0.04 | 81.62 | 0.747 | 0.989 | 88.15 | 0.012 | 0.997 | |
| BPA | BPA (pH = 2) | 21.73 ± 0.62 | 21.49 | 4.082 | 0.991 | 23.42 | 0.256 | 0.970 |
| SY–BPA (pH = 2) | 23.01 ± 0.09 | 22.11 | 3.715 | 0.893 | 22.61 | 0.305 | 0.978 | |
| BPA (pH = 4) | 24.12 ± 1.05 | 23.49 | 4.012 | 0.982 | 24.77 | 0.269 | 0.977 | |
| EY–BPA (pH = 4) | 27.23 ± 0.51 | 26.27 | 1.606 | 0.961 | 28.40 | 0.086 | 0.991 | |
| BPA (pH = 7) | 24.95 ± 1.59 | 24.27 | 4.852 | 0.980 | 25.47 | 0.331 | 0.996 | |
| CR–BPA (pH = 7) | 19.94 ± 4.40 | 19.81 | 1.177 | 0.999 | 21.84 | 0.072 | 0.984 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, J.; Hu, Y. Adsorption and Removal of Composite Contaminants in Water Using Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanofiber Membranes with Polydopamine–Polyethyleneimine Coatings. Water 2023, 15, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142546
Qin Y, Sun J, Zhou Y, Fan J, Hu Y. Adsorption and Removal of Composite Contaminants in Water Using Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanofiber Membranes with Polydopamine–Polyethyleneimine Coatings. Water. 2023; 15(14):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142546
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Yan, Jiaoxia Sun, Yao Zhou, Jianxin Fan, and Ying Hu. 2023. "Adsorption and Removal of Composite Contaminants in Water Using Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanofiber Membranes with Polydopamine–Polyethyleneimine Coatings" Water 15, no. 14: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142546




