Synergistic Removal of β-Hexachlorocyclohexane from Water via Microorganism–Plant Technology and Analysis of Bacterial Community Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Preparation of β-HCH-Degrading Bacteria
2.3. Water Remediation
2.3.1. Microbial Remediation
2.3.2. Phytoremediation
2.3.3. Microbe–Plant Remediation
2.4. Experimental Method
2.4.1. Sample Collection Method
2.4.2. Sample Pretreatment Method
2.4.3. Microbial Sequencing Method
2.5. Chromatographic Conditions
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
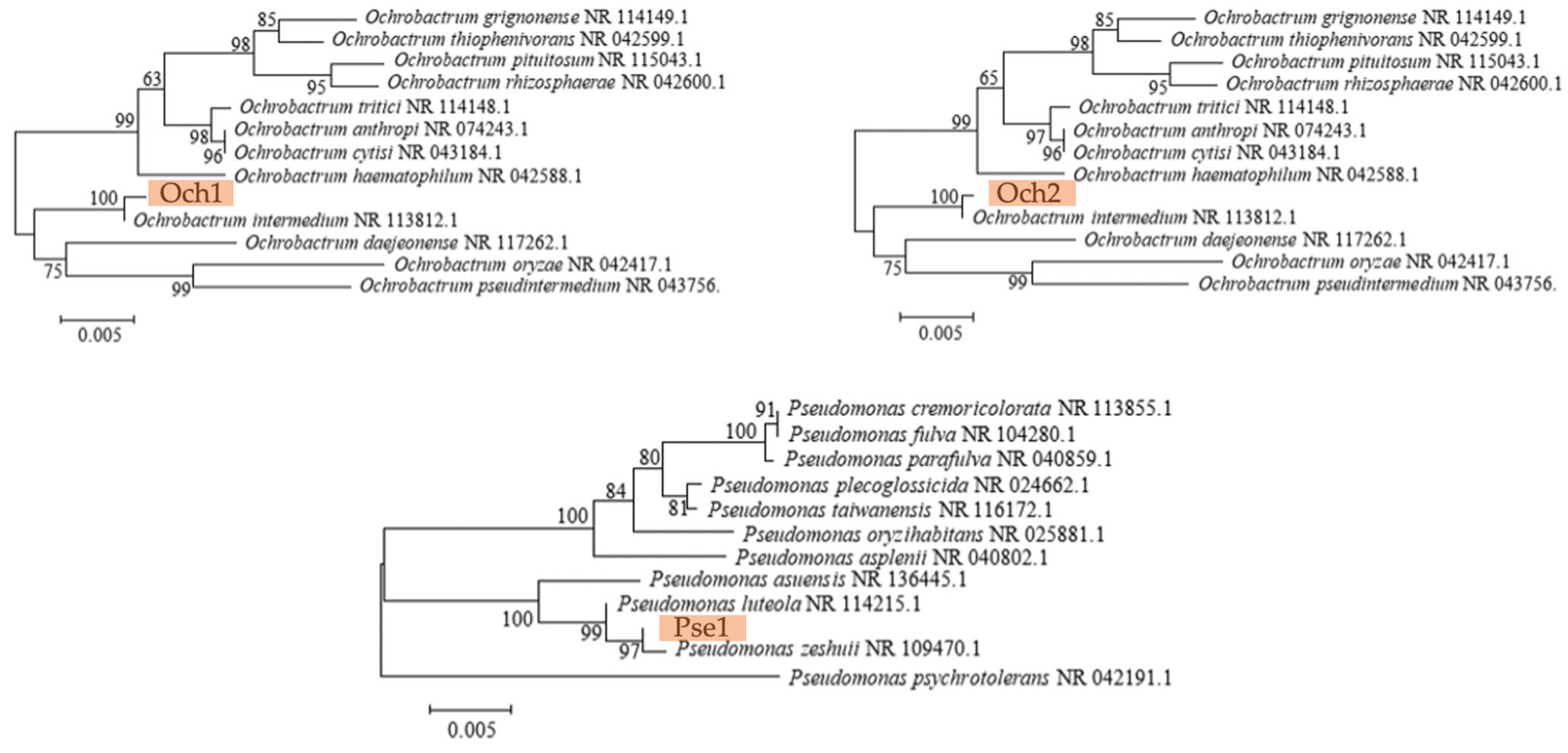
3.1. Identification of Strains
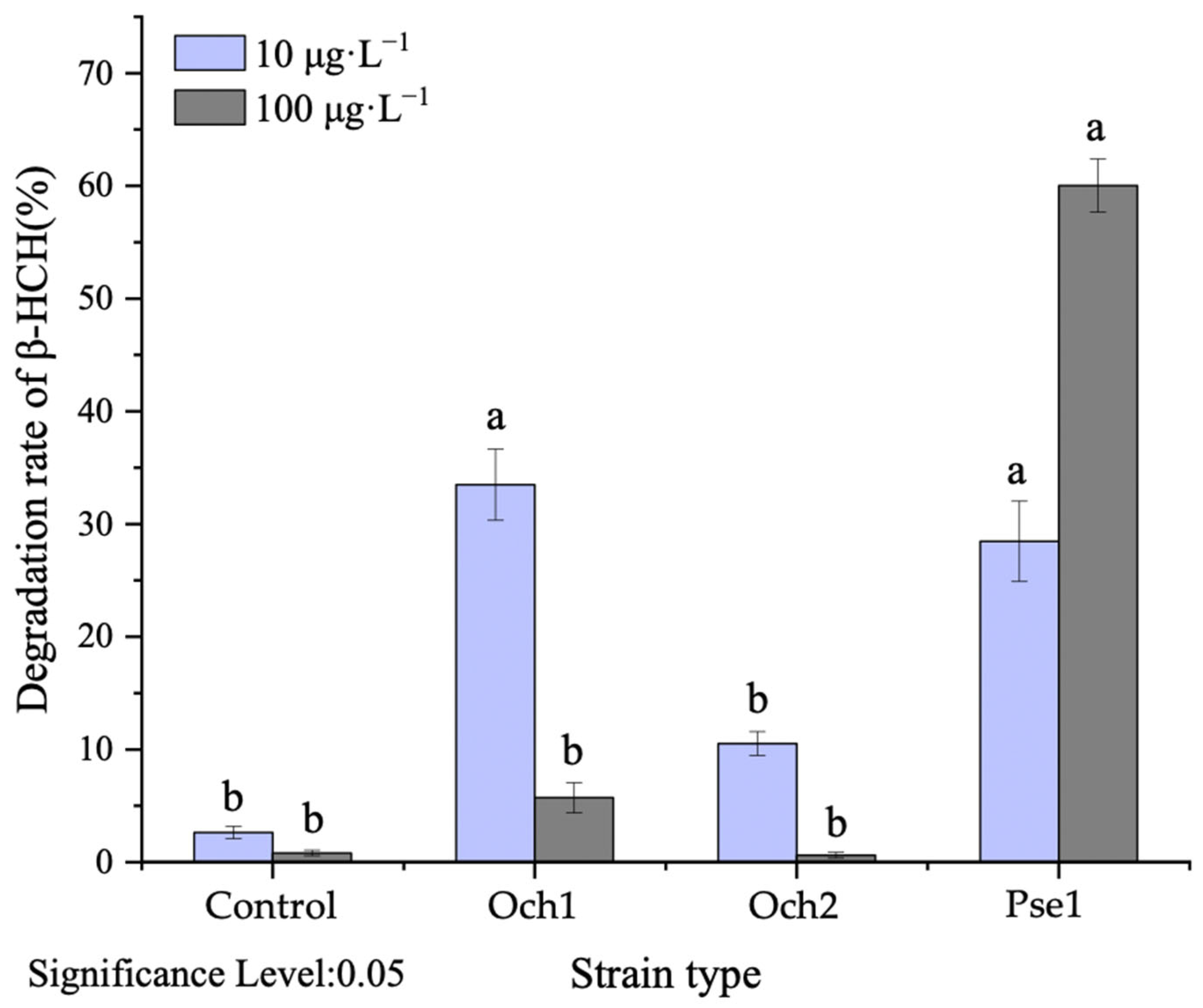
3.2. The Effectiveness of Microbial Remediation for Removal of β-HCH from Water
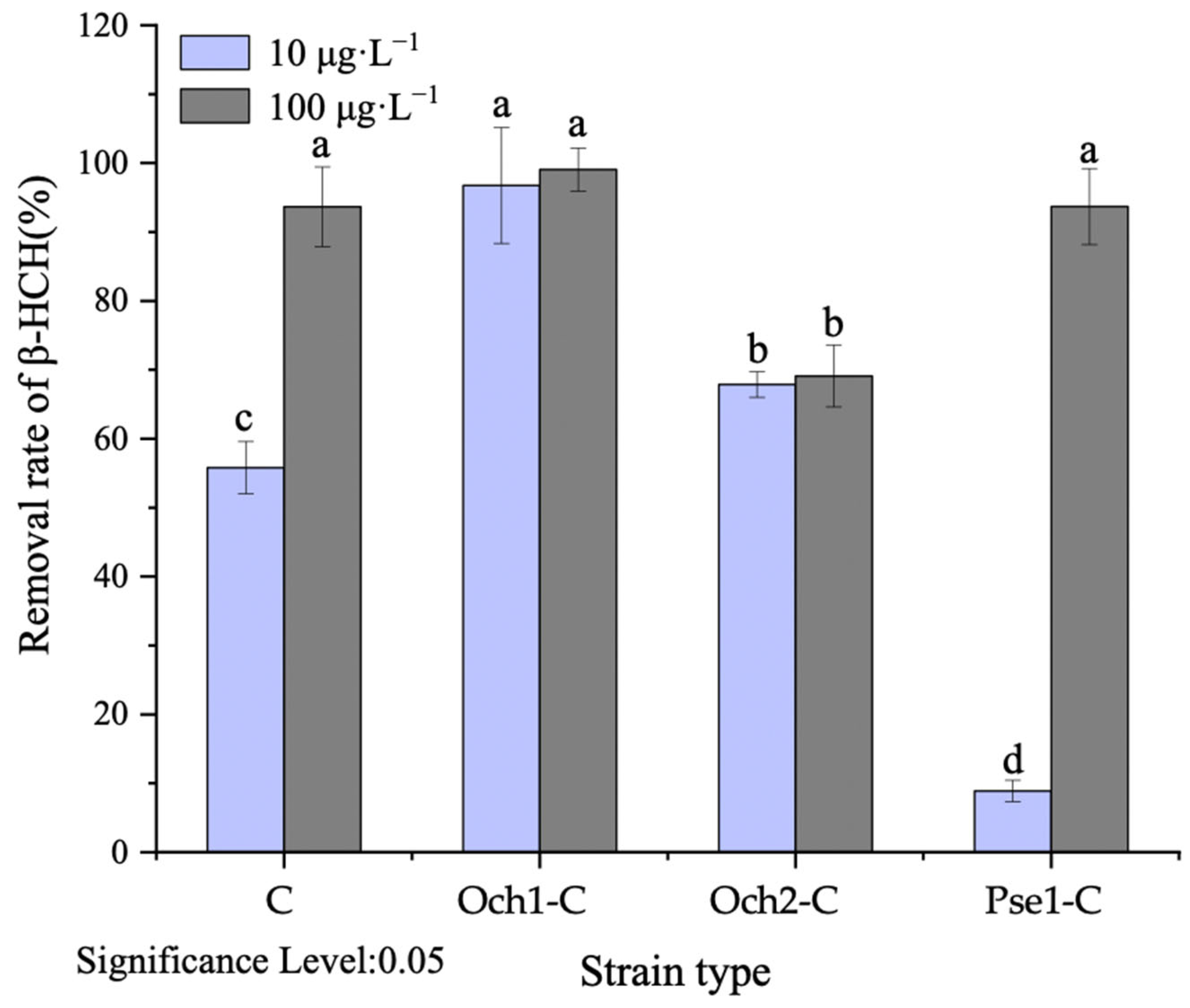
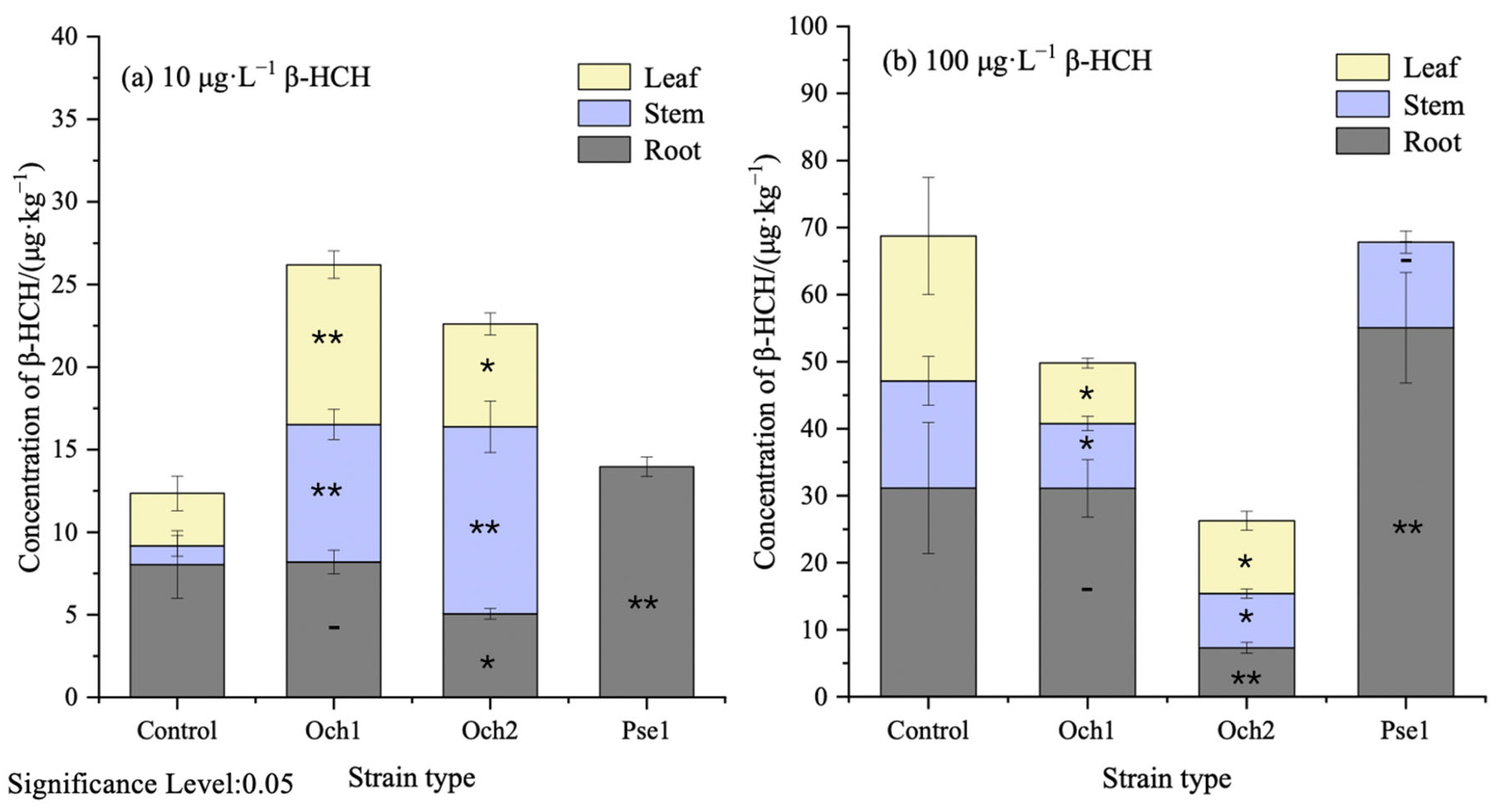
3.3. The Effectiveness of Microbe–Plant Remediation for Removal of β-HCH from Water
3.4. The Effectiveness of Microbe–Plant Remediation for Removal of β-HCH from Water
3.5. Analysis of Bacterial Community Characteristics
3.5.1. Alpha Analysis
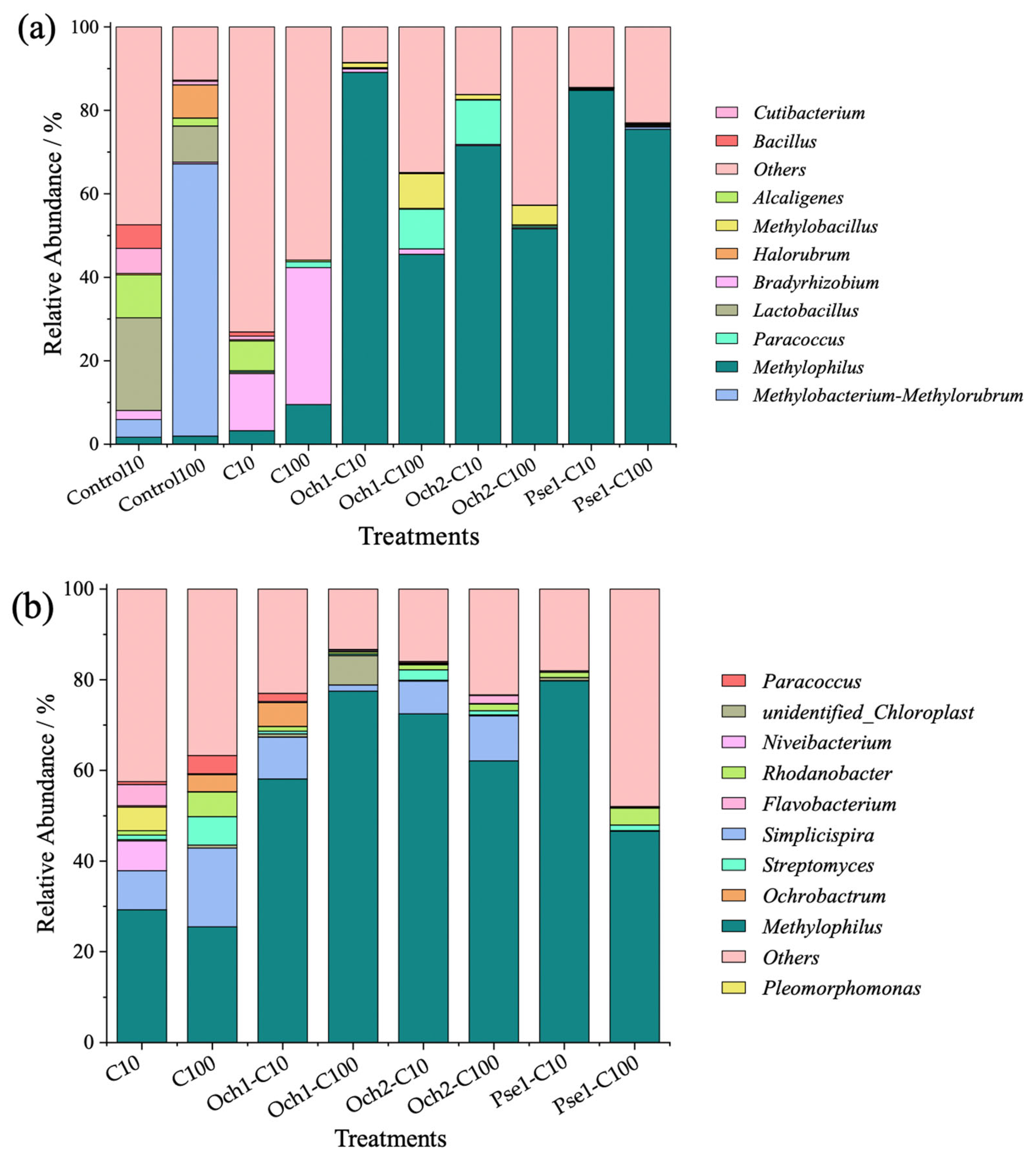
3.5.2. Analysis of Species Composition of Bacterial Community at Genus Level
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Yun, X.T.; Ruan, Z.Y.; Lu, C.J.; Shi, Y.; Qin, Q.; Men, Z.M.; Zou, D.Z.; Du, X.M.; Xing, B.S.; et al. Review of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) contamination in Chinese soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 749, 141212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijgen, J.; de Borst, B.; Weber, R.; Stobiecki, T.; Forter, M. HCH and lindane contaminated sites: European and global need for a permanent solution for a long-time neglected issue. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, V.; Srivastava, T.; Kumar, M.S. Fate of the persistent organic pollutant (POP) Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and remediation challenges. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 140, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozowicka, B.; Jankowska, M.; Hrynko, I.; Kaczynski, P. Removal of 16 pesticide residues from strawberries by washing with tap and ozone water, ultrasonic cleaning and boiling. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacławek, S.; Silvestri, D.; Hrabák, P.; Padil, V.V.; Torres-Mendieta, R.; Wacławek, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemical oxidation and reduction of hexachlorocyclohexanes: A review. Water Res. 2019, 162, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghden, H.; Barhoumi, B.; Jlaiel, L.; Guigue, C.; Chouba, L.; Touil, S.; Sayadi, S.; Tedetti, M. Occurrence, origin and potential ecological risk of dissolved polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorines in surface waters of the gulf of gabès (Tunisia, southern mediterranean sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, H.; Huo, S. Organochlorine pesticides in aquatic hydrophyte tissues and surrounding sediments in Baiyangdian wetland, China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, N.D.; Chierichetti, M.A.; Acuña, F.H.; Miglioranza, K.S. Organochlorine pesticides and chlorpyrifos in the sea anemone Bunodosoma zamponii (Actiniaria: Actiniidae) from Argentina’s southeastern coast. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 806, 150824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Zouari, N.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Removal of pesticides from water and wastewater: Chemical, physical and biological treatment approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.P.; Jaiswal, D.K.; Sagar, R. Pesticide relevance and their microbial degradation: A-state-of-art. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio./Technol. 2014, 13, 429–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, S.D.; Broadbelt, L.J.; Hatzimanikatis, V. In silico feasibility of novel biodegradation pathways for 1, 2, 4-trichlorobenzene. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xing, Y.; Fu, X.; Ji, L.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Biochemical mechanisms of rhizospheric Bacillus subtilis-facilitated phytoextraction by alfalfa under cadmium stress–Microbial diversity and metabolomics analyses. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 112016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurasvili, M.V.; Adamia, G.S.; Amiranashvili, L.L.; Ananiasvili, T.I.; Khatisashvili, G.A. Targeting of detoxification potential of microorganisms and plants for cleaning environment polluted by organochlorine pesticides. Ann. Agr. Sci. 2016, 14, 222–226. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.; Roman, D.; Kintz, T.; delas Alas, M.; Yap, R.; Doty, S. Degradation, phytoprotection and phytoremediation of phenanthrene by endophyte Pseudomonas putida, PD1. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12221–12228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergani, L.; Mapelli, F.; Zanardini, E.; Terzaghi, E.; Di Guardo, A.; Morosini, C.; Borin, S. Phyto-rhizoremediation of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminated soils: An outlook on plant-microbe beneficial interactions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, F.; Tahseen, R.; Arslan, M.; Iqbal, S.; Afzal, M. Removal of hexadecane by hydroponic root mats in partnership with alkane-degrading bacteria: Bacterial augmentation enhances system’s performance. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 4611–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Toyama, T.; Sei, K. Surfactants degrading activities in the rhizosphere of giant duckweed (Spirodela polyrrhiza). Jpn. J. Water Treat. Biol. 2005, 41, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, C.C.; Headley, T.R. Components of floating emergent macrophyte treatment wetlands influencing removal of stormwater pollutants. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.S.; Lu, Y.Q.; Zeng, H.H.; Qin, L.T. Purification Effect of β-HCH by Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands with Different Plant. Technol. Water Treat. 2020, 46, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Liang, Y.P.; Zeng, H.H.; Qin, L.T. Screening and identification of bacteria β-HCH rhizosphere degradation in constructed wetland plants. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2021, 42, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, A.; Fu, W.; Peng, D.; Wang, G.; Ji, J.; Guan, C. Tobacco-associated with Methylophilus sp. FP-6 enhances phytoremediation of benzophenone-3 through regulating soil microbial community, increasing photosynthetic capacity and maintaining redox homeostasis of plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.H.; Zhang, G.L.; Li, H.H.; Ma, L.L.; Yang, N. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of Stenotrophomonas sp. MNB17 revealed mechanisms of manganese tolerance at different concentrations and the role of histidine biosynthesis in manganese removal. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Imran, A.; Khan, Q.M.; Afzal, M. Plant–bacteria partnerships for the remediation of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4322–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Cui, N.; Dai, Y.; Kong, L.; Wu, J.; Cheng, S. Enhancing the water purification efficiency of a floating treatment wetland using a biofilm carrier. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7437–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.J.; Arslan, M.; Siddique, M.; Ali, S.; Tahseen, R.; Afzal, M. Potentialities of floating wetlands for the treatment of polluted water of river Ravi, Pakistan. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 133, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorén, A.-K. Urea transformation of wetland microbial communities. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Zhang, S.; Lv, X.; Han, B.; Liu, K.; Qiu, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Toland, H.; He, Z. Characterization of bacterial community in biofilm and sediments of wetlands dominated by aquatic macrophytes. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.J.; Al-Surhanee, A.A.; Kouadri, F.; Ali, S.; Nawaz, N.; Afzal, M. Role of microorganisms in the remediation of wastewater in floating treatment wetlands: A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Kazmi, A.A.; Ahmed, N. Study on effects of temperature, moisture and pH in degradation and degradation kinetics of aldrin, endosulfan, lindane pesticides during full-scale continuous rotary drum composting. Chemosphere 2014, 102, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardoim, P.R.; van Overbeek, L.S.; Berg, G.; Pirttilä, A.M.; Compant, S.; Campisano, A.; Sessitsch, A. The hidden world within plants: Ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 2015, 79, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, F.; Breschigliaro, S.; Borin, M. Screening of 18 species for digestate phytodepuration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2015, 22, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoyo, G.; Guzmán-Guzmán, P.; Parra-Cota, F.I.; Santos-Villalobos, S.D.L.; Orozco-Mosqueda, M.D.C.; Glick, B.R. Plant growth stimulation by microbial consortia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, V.J.; Perez-Jaramillo, J.; Cordovez, V.; Tracanna, V.; de Hollander, M.; Ruiz-Buck, D.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Pathogen-induced activation of disease-suppressive functions in the endophytic root microbiome. Science 2019, 366, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Ren, L.; Wu, Q. Epiphytic bacterial communities on two common submerged macrophytes in Taihu Lake: Diversity and host-specificity. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haichar, F.Z.; Marol, C.; Berge, O.; Rangel-Castro, J.I.; Prosser, J.I.; Balesdent, J.; Heulin, T.; Achouak, W. Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure. ISME J. 2008, 2, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, H.J.; Liang, Y.; Qin, L.T.; Zeng, H.H.; Song, X.H. Degradation Characteristics and Remediation Ability of Contaminated Soils by Using β-HCH Degrading Bacteria. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbe, C.C.; Oyetibo, G.O.; Ilori, M.O. Ecological impact of organochlorine pesticides consortium on autochthonous microbial community in agricultural soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, Y.S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, J. Tomato microbiome under long-term organic and conventional farming. iMeta 2022, 1, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Torelli, S.; Le Paslier, D.; Barbance, A.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Bru, D.; Jouanneau, Y. Betaproteobacteria dominance and diversity shifts in the bacterial community of a PAH-contaminated soil exposed to phenanthrene. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Geng, Z.; Pang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Ji, J.; Guan, C. Isolation and characterization of a novel benzophenone-3-degrading bacterium Methylophilus sp. strain FP-6. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, J.G.; Hang, B.J.; Cai, S.; He, J.; Zhou, S.G.; Li, S.P. Cloning of a novel arylamidase gene from Paracoccus sp. strain FLN-7 that hydrolyzes amide pesticides. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2012, 78, 4848–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Maitra, S.S. Biodegradation of endocrine disruptor dibutyl phthalate (DBP) by a newly isolated Methylobacillus sp. V29b and the DBP degradation pathway. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment | 10 μg·L−1 β-HCH | 100 μg·L−1 β-HCH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTU | Shannon | Chao1 | Ace | OTU | Shannon | Chao1 | Ace | |
| Control | 204 | 3.96 | 233 | 257 | 263 | 2.91 | 288 | 294 |
| C | 321 | 3.83 | 355 | 363 | 186 | 2.56 | 210 | 222 |
| Och1 | 316 | 3.08 | 360 | 385 | 315 | 2.60 | 349 | 362 |
| Och2 | 142 | 2.18 | 152 | 160 | 96 | 2.30 | 107 | 105 |
| Pse1 | 297 | 2.83 | 325 | 346 | 273 | 3.68 | 294 | 310 |
| Och1-C | 280 | 1.16 | 327 | 357 | 405 | 3.61 | 457 | 468 |
| Och2-C | 248 | 1.99 | 304 | 315 | 301 | 2.38 | 345 | 358 |
| Pse1-C | 238 | 1.43 | 275 | 303 | 269 | 2.14 | 299 | 324 |
| Treatment | 10 μg·L−1 β-HCH | 100 μg·L−1 β-HCH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTU | Shannon | Chao1 | Ace | OTU | Shannon | Chao1 | Ace | |
| C | 166 | 0.94 | 201 | 204 | 138 | 0.85 | 181 | 183 |
| Och1-C | 238 | 3.07 | 263 | 269 | 237 | 1.90 | 271 | 269 |
| Och2-C | 248 | 2.27 | 339 | 319 | 248 | 2.91 | 275 | 280 |
| Pse1-C | 187 | 1.79 | 213 | 231 | 237 | 2.82 | 283 | 287 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Luo, S.; Liang, Y.; Qin, L.; Zeng, H.; Song, X. Synergistic Removal of β-Hexachlorocyclohexane from Water via Microorganism–Plant Technology and Analysis of Bacterial Community Characteristics. Water 2023, 15, 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132328
Shi H, Luo S, Liang Y, Qin L, Zeng H, Song X. Synergistic Removal of β-Hexachlorocyclohexane from Water via Microorganism–Plant Technology and Analysis of Bacterial Community Characteristics. Water. 2023; 15(13):2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132328
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Huijun, Shuang Luo, Yanpeng Liang, Litang Qin, Honghu Zeng, and Xiaohong Song. 2023. "Synergistic Removal of β-Hexachlorocyclohexane from Water via Microorganism–Plant Technology and Analysis of Bacterial Community Characteristics" Water 15, no. 13: 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132328
APA StyleShi, H., Luo, S., Liang, Y., Qin, L., Zeng, H., & Song, X. (2023). Synergistic Removal of β-Hexachlorocyclohexane from Water via Microorganism–Plant Technology and Analysis of Bacterial Community Characteristics. Water, 15(13), 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132328






