Numerical Evaluation of Large-Scale Groundwater Extraction in Groundwater System at Wellfields in the Namwon Area of Jeju Island, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
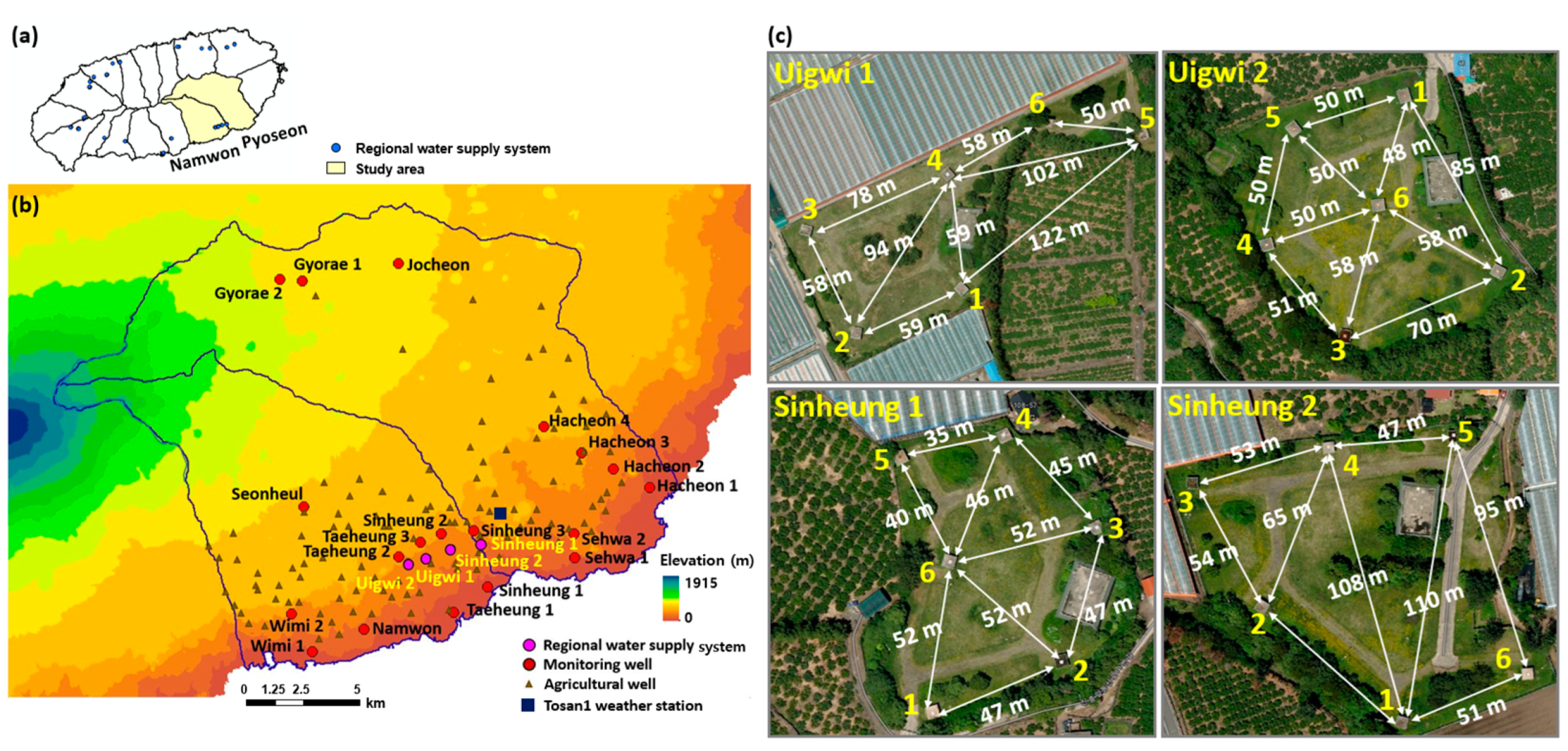
2.1. Study Area Description
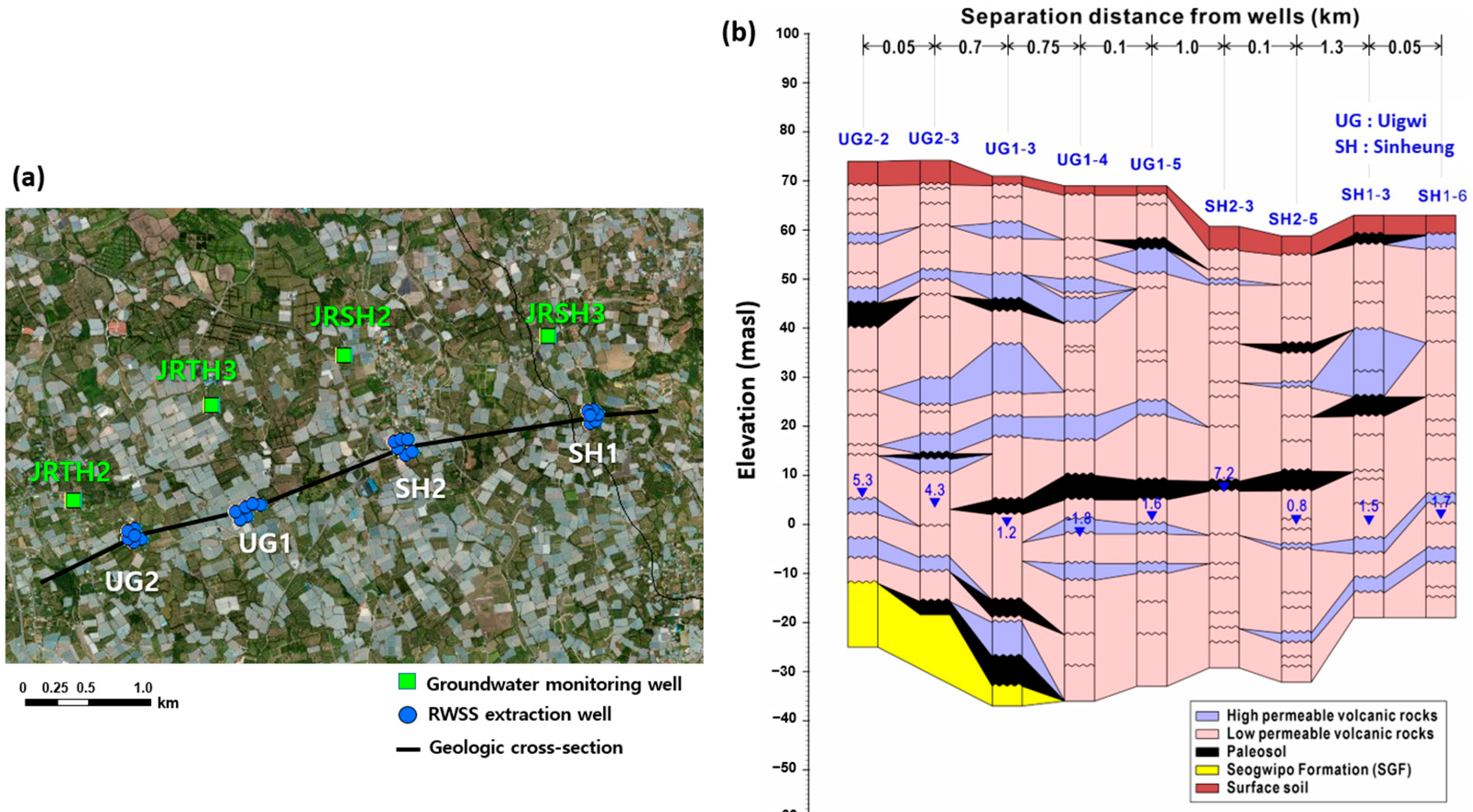
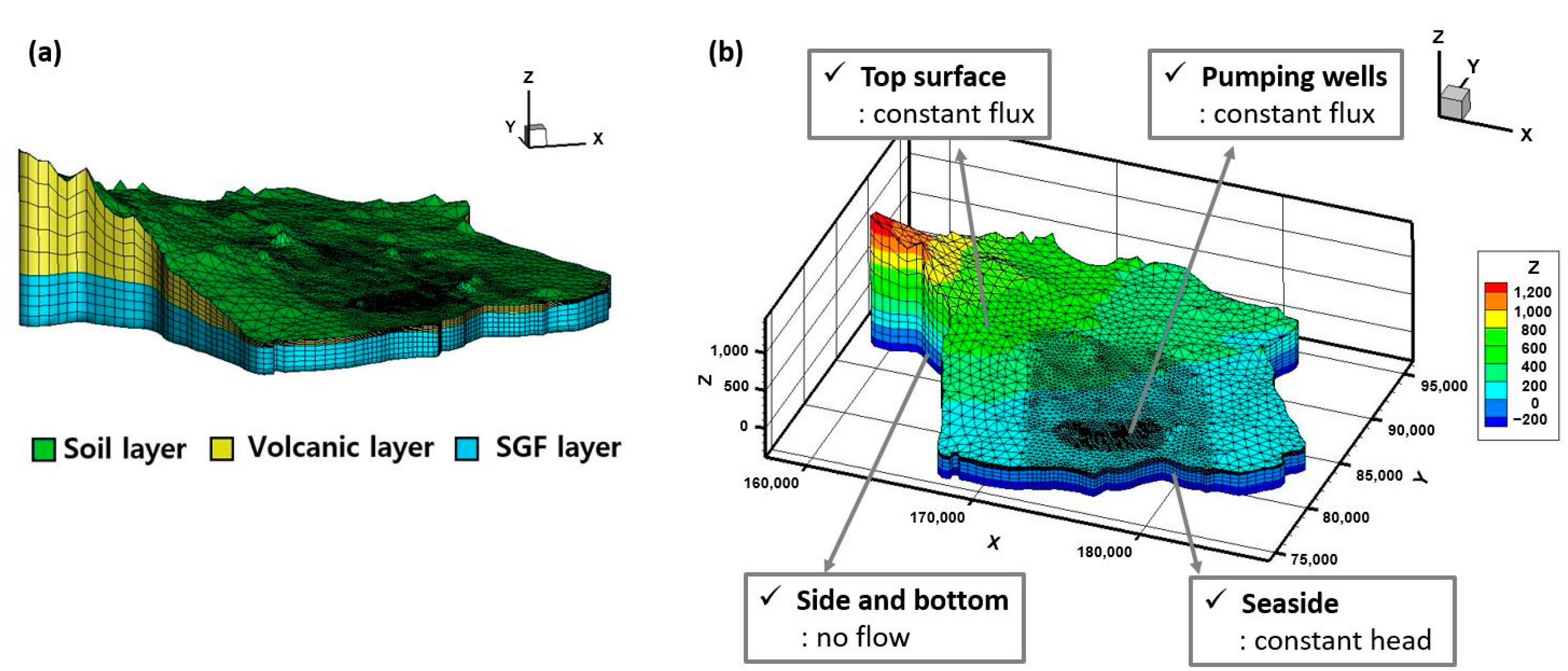
2.2. Numerical Model Construction
2.3. Model Scenarios
2.3.1. Groundwater Extraction at the RWSS
2.3.2. Drought Conditions
2.3.3. Adjustment of Well Separation Distances
3. Results
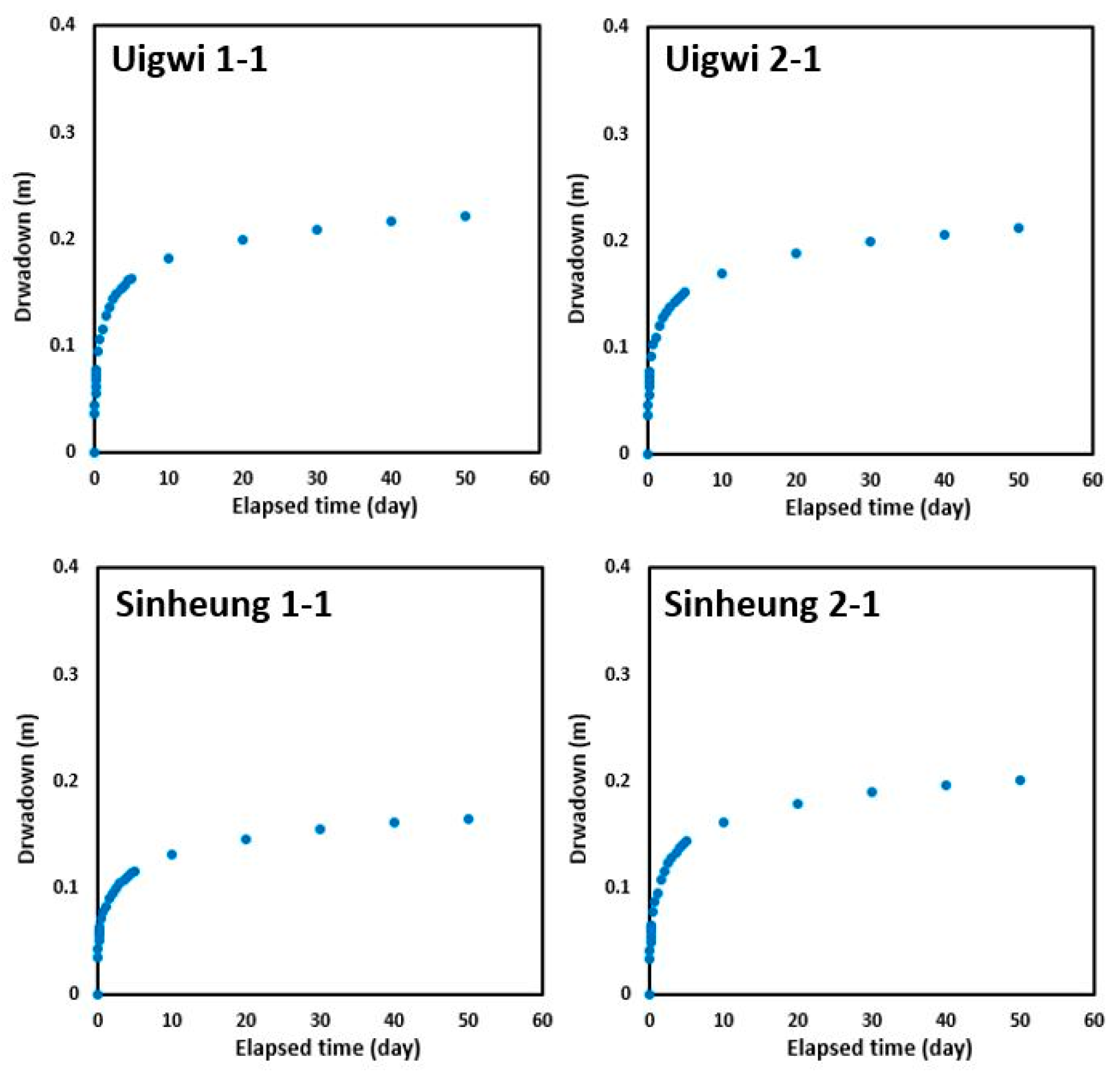
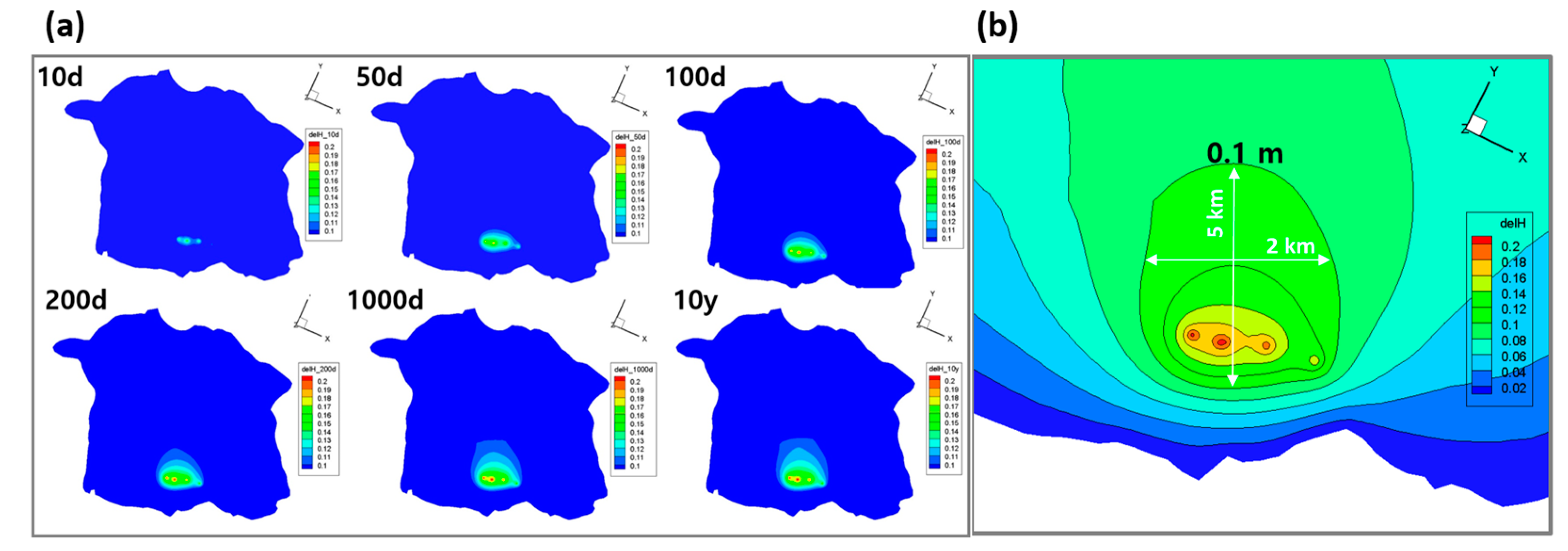
3.1. Groundwater Flow Model Results
3.2. Model Scenario Results
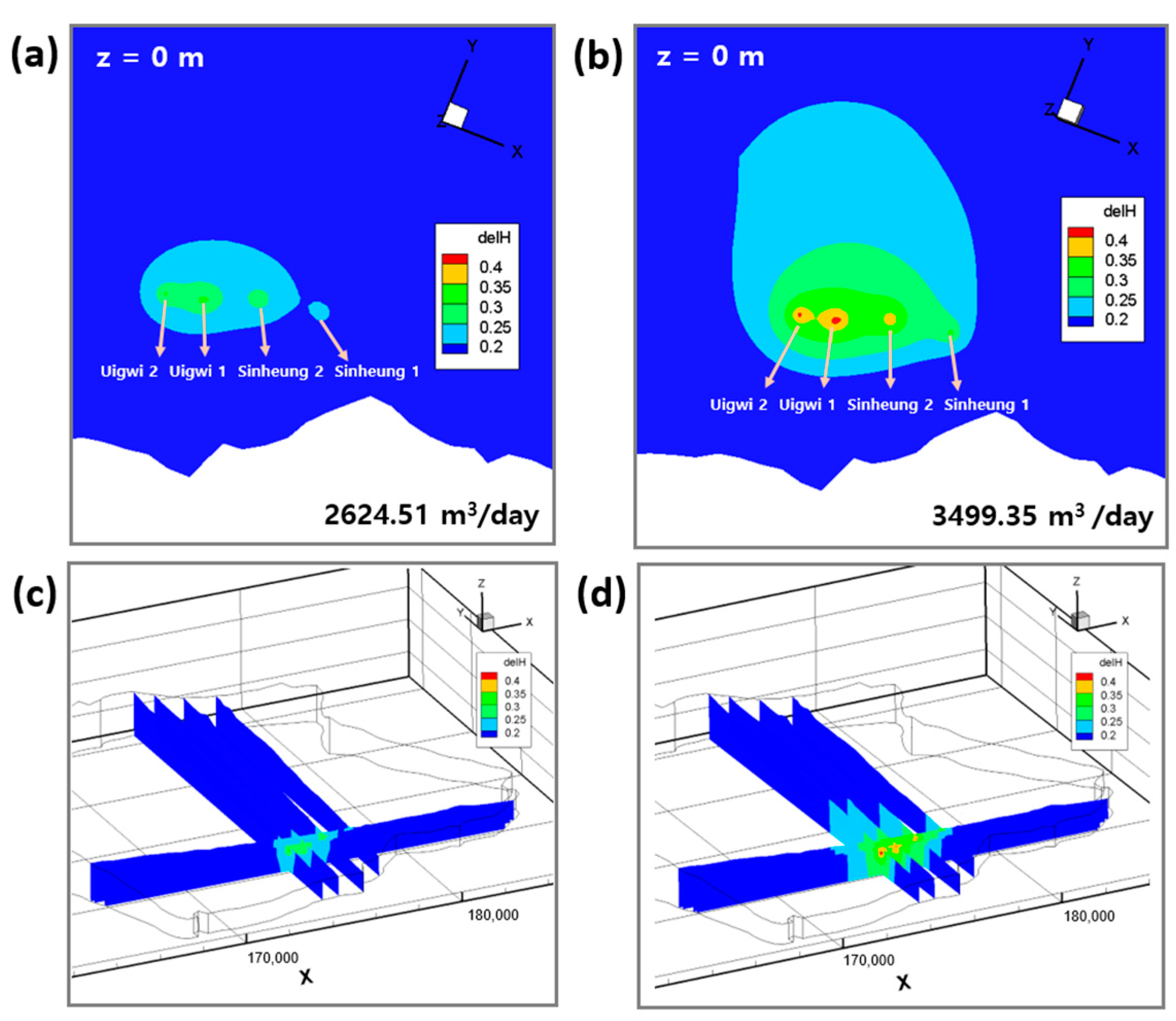
3.2.1. Operation of the RWSS
3.2.2. Drought Condition
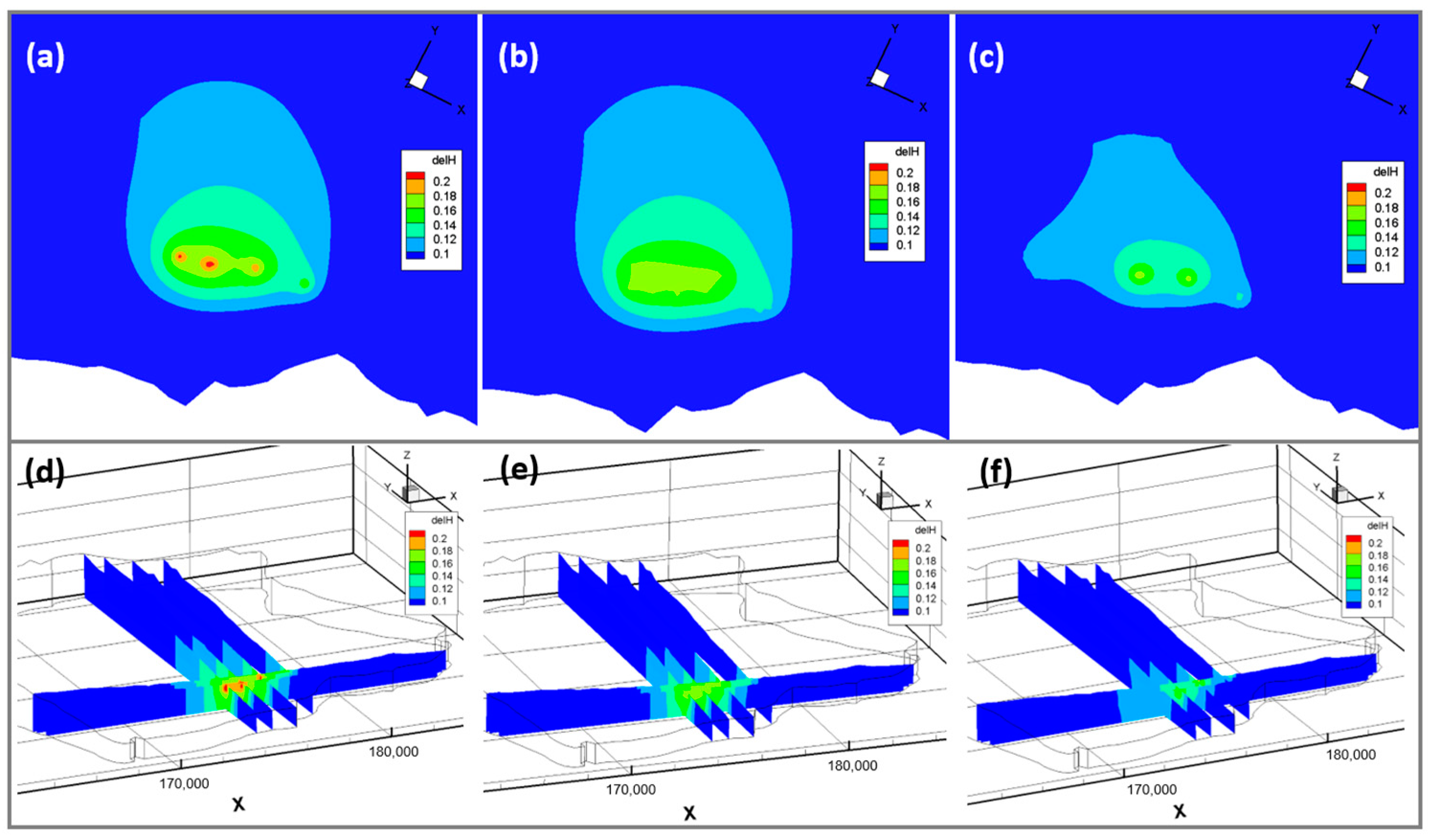
3.2.3. The Adjustment of the Separation Distances
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Margat, J.; Van der Gun, J. Groundwater around the World: A Geographic Synopsis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolino, J.R. Ground-water depletion across the nation. In Open File Report USGS Fact Sheet-103-03; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jasechko, S.; Perrone, D. Global groundwater wells at risk of running dry. Science 2021, 372, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.; Luo, J. Groundwater depletion and contamination: Spatial distribution of groundwater resources sustainability in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korus, J.T.; Burbach, M.E. Analysis of aquifer depletion criteria with implications for groundwater management. Great Plains Res. 2009, 19, 187–200. [Google Scholar]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Faunt, C.C.; Longuevergne, L.; Reedy, R.C.; Alley, W.M.; McGuire, V.L.; McMahon, P.B. Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Van Beek, L.P.; Van Kempen, C.M.; Reckman, J.W.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F. Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophy. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebraheem, A.M.; Riad, S.; Wycisk, P.; Seif El Nasr, A.M. Simulation of present and future groundwater extraction from the non-replenished Nubian Sandstone Aquifer, SW Egypt. Environ. Geol. 2002, 43, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhan, H.; Dong, H.; Ma, L. Numerical simulation and evaluation of groundwater resources in a fractured chalk aquifer: A case study in Zinder well field, Niger. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3053–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldenhuys, I. Making the invisible visible. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2022, 122, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Lee, J.Y. Parametric and Non-parametric Trend Analyses for Water Levels of Groundwater Monitoring Wells in Jeju Island. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2009, 14, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jeju Groundwater Research Center. A Study on Causes of Declines of the Groundwater Level and Response Plans; Jeju Research Institute: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jeju Special Self-Governing Province. Basic Plan for Integrated Water Management in Jeju Special Self-Governing Province (2023–2032); Jeju Special Self-Governing Province: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.B.; Kang, B.R.; Kim, J.M. Improvement of Water Management System for Sustainable Groundwater Resources in the Age of Climate Crisis; Issue Brief, 365; Jeju Research Institute: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Baut, V. Aquifer Hydraulics: A Comprehensive Guide to Hydrogeologic Data Analysis; A Wiley-Interscience Publication; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Alfarrah, N.; Walraevens, K. Groundwater overexploitation and seawater intrusion in coastal areas of arid and semi-arid regions. Water 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater extraction, land subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 84010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janža, M. Optimization of well field management to mitigate groundwater contamination using a simulation model and evolutionary algorithm. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebraheem, A.M.; Garamoon, H.K.; Riad, S.; Wycisk, P.; Seif El Nasr, A.M. Numerical modeling of groundwater resource management options in the East Oweinat area, SW Egypt. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, J.W.; Beljin, M.S.; Maynard, J.B.J. Groundwater models and wellfield management: A case study. Environ. Eng. Policy 1998, 1, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.F.; Fernández, B.; Escauriaza, C. Evaluation of groundwater availability and sustainable extraction rate for the Upper Santiago Valley Aquifer, Chile. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastev, M.; Rivera, A.; Lefebvre, R.; Martel, R.; Savard, M. Numerical simulation of groundwater flow in regional rock aquifers, southwestern Quebec, Canada. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétré, M.A.; Rivera, A.; Lefebvre, R. Numerical modeling of a regional groundwater flow system to assess groundwater storage loss, capture and sustainable exploitation of the transboundary Milk River Aquifer (Canada–USA). J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousquer, Y.; Pryet, A.; Delbart, C.; Valois, R.; Dupuy, A. Adaptive optimization of a vulnerable well field. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Xu, C.Y.; Guo, S.; Chen, X. Toward Monitoring Short-Term Droughts Using a Novel Daily Scale, Standardized Antecedent Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X. Global drought trends under 1.5 and 2 °C warming. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.D.; Petrone, K.C.; Silberstein, R.P. Drought, groundwater storage and stream flow decline in southwestern Australia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L03408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.B.; Kang, B.R.; Koh, E.H. Protecting Regional Water Supply System for a Safe and Secure Water Supply; Policy Research 2021; Jeju Research Institute: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, G.W. Characteristics of the Groundwater and Hydrogeologic Implication of the Seoquipo Formation in Cheju Island. Ph.D. Thesis, Busan National University, Busan, Republic of Korea, 1997. (In Korean). [Google Scholar]
- Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA). 2021. Available online: https://www.kma.go.kr/ (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Koh, E.H.; Lee, E.; Lee, K.K. Application of geographically weighted regression models to predict spatial characteristics of nitrate contamination: Implications for an effective groundwater management strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jejudo. Report on the Overall Investigation of Hydrogeology and the Groundwater Resource in Jeju Island (III); Jeju Provincial Government: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2003.
- Therrien, R.; Sudicky, E.A.; McLaren, R. Hydrogeosphere: A Three-Dimensional Numerical Model Describing Fully-Integratedsubsurface and Surface Flow and Solute Transport; Groundwater Simulations Group, University of Waterloo: Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jeju Water Resources Management Office. Data Collection Book of Geological Logs of Jeju Island; Jeju Special Self-Governing Province: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jeju Water Resources Management Office. Data Collection Book of Geological Logs of Jeju Island (II); Jeju Special Self-Governing Province: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990; 824p. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.P.; Woessner, W.W. Applied Groundwater Modeling—Simulation of Flow and Advective Transport; Academic Press, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992; 381p. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.H.; Yoo, S.H.; Bae, S.J. Regional drought assessment considering climate change and relationship with agricultural water in Jeju Island. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2013, 22, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeju Metropolitan Water Resources Management Headquarters. Groundwater Impact Survey for Jeju Island Multi-Regional Water Supply Phase 1 Water Source Period Extension Permit; Jejudo: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jejudo. Report on the Overall Investigation of Hydrogeology and the Groundwater Resource in Jeju Island (I); Jeju Provincial Government: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2001.
- Park, W.B.; Kang, B.R.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, G.P. Analysis on the Influence of Groundwater Level Variation by Large-Scale Groundwater Pumping: The Case of Daejeong-Hangyeong Basin; Policy Research 2020; Jeju Research Institute: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, C.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Thanh, H.V.; Soltanian, M.R. Subsurface sedimentary structure identification using deep learning: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 239, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, H.; Zou, X. An effective method for 3D geological modeling with multi-source data integration. Comput. Geosci. 2005, 31, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, I.; Gibson, H.; Hamzaoui-Azaza, F.; Negro, F.; Rachid, K.; Bouhlila, R. 3D geological modeling of the Kasserine Aquifer System, Central Tunisia: New insights into aquifer-geometry and interconnections for a better assessment of groundwater resources. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, E.; Bertoni, C.; Van Goethem, M.; Blazevic, L.A.; Ruden, F. A 3D geological model of the horn of Africa: New insights for hydrogeological simulations of deep groundwater systems. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Wellfield ID | No. of Well | Elevation | Well Depth | Water Level | Withdrawal Permit Rate | Extraction Rate (2010–2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (masl) | (m) | (masl) | (m3/Month) | (m3/Month) | ||
| Sinheung 1 (SH1) | 1 | 61 | 82 | 1.53 | 60,000 | 47,392 |
| 2 | 60 | 82 | 1.21 | 60,000 | 40,963 | |
| 3 | 60 | 82 | 1.22 | 60,000 | 44,692 | |
| 4 | 61 | 82 | 1.22 | 60,000 | 48,138 | |
| 5 | 62 | 82 | 1.34 | 60,000 | 46,324 | |
| 6 | 61 | 82 | 1.81 | 60,000 | 45,872 | |
| Sinheung 2 (SH2) | 1 | 65 | 90 | 0.99 | 60,000 | 48,545 |
| 2 | 65 | 90 | 1.46 | 60,000 | 46,837 | |
| 3 | 65 | 90 | 1.47 | 60,000 | 50,274 | |
| 4 | 61 | 90 | 1.51 | 60,000 | 49,907 | |
| 5 | 63 | 90 | 1.29 | 60,000 | 47,083 | |
| 6 | 65 | 90 | 0.80 | 60,000 | 45,062 | |
| Uigwi 1 (UG1) | 1 | 68 | 101 | 1.10 | 60,000 | 45,190 |
| 2 | 68 | 103 | 1.66 | 60,000 | 48,494 | |
| 3 | 71 | 105 | 1.35 | 60,000 | 43,781 | |
| 4 | 69 | 105 | 1.48 | 60,000 | 51,209 | |
| 5 | 69 | 104 | 1.19 | 60,000 | 42,703 | |
| 6 | 67 | 102 | 1.45 | 60,000 | 42,291 | |
| Uigwi 2 (UG2) | 1 | 75 | 90 | 5.88 | 60,000 | 45,598 |
| 2 | 73 | 95 | 5.67 | 60,000 | 46,789 | |
| 3 | 73 | 95 | 5.38 | 60,000 | 48,121 | |
| 4 | 76 | 99 | 5.29 | 60,000 | 48,528 | |
| 5 | 75 | 93 | 5.40 | 60,000 | 49,219 | |
| 6 | 74 | 90 | 5.84 | 60,000 | 45,678 |
| Geologic Layers | Porosity * | Hydraulic Conductivity † (m/s) | Specific Storage * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kx | Ky | Kz | (1/m) | ||
| Top soil | 0.2 | 2.0 × 10−5 | 2.0 × 10−5 | 4.0 × 10−6 | 5.0 × 10−4 |
| Volcanic rocks | 0.3 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 1.8 × 10−5 | 5.0 × 10−4 |
| SGF | 0.1 | 9.0 × 10−6 | 9.0 × 10−6 | 1.8 × 10−6 | 3.5 × 10−6 |
| Wellfield ID | No. of Well | Drawdown of Groundwater Level in the Survey (2005) | Drawdown of Groundwater Level in the Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (m) | ||
| Sinheung 1 (SH1) | 1 | 0.20 | 0.21 |
| 2 | - | 0.21 | |
| 3 | 0.20 | 0.21 | |
| 4 | 0.40 | 0.21 | |
| 5 | 1.80 | 0.21 | |
| 6 | 2.00 | 0.21 | |
| Sinheung 2 (SH2) | 1 | 0.10 | 0.20 |
| 2 | 0.20 | 0.20 | |
| 3 | 0.10 | 0.20 | |
| 4 | 0.20 | 0.20 | |
| 5 | - | 0.20 | |
| 6 | 0.10 | 0.20 | |
| Uigwi 1 (UG1) | 1 | - | 0.16 |
| 2 | 0.20 | 0.16 | |
| 3 | 0.10 | 0.16 | |
| 4 | - | 0.16 | |
| 5 | 6.90 | 0.16 | |
| 6 | 0.20 | 0.16 | |
| Uigwi 2 (UG2) | 1 | - | 0.19 |
| 2 | 0.20 | 0.19 | |
| 3 | 2.00 | 0.19 | |
| 4 | - | 0.18 | |
| 5 | 3.20 | 0.19 | |
| 6 | 0.20 | 0.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.J.; Koh, E.-H.; Koh, C.-S.; Park, W.-B.; Kim, M.-C. Numerical Evaluation of Large-Scale Groundwater Extraction in Groundwater System at Wellfields in the Namwon Area of Jeju Island, South Korea. Water 2023, 15, 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122151
Kim HJ, Koh E-H, Koh C-S, Park W-B, Kim M-C. Numerical Evaluation of Large-Scale Groundwater Extraction in Groundwater System at Wellfields in the Namwon Area of Jeju Island, South Korea. Water. 2023; 15(12):2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122151
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun Jung, Eun-Hee Koh, Chang-Seong Koh, Won-Bae Park, and Min-Cheol Kim. 2023. "Numerical Evaluation of Large-Scale Groundwater Extraction in Groundwater System at Wellfields in the Namwon Area of Jeju Island, South Korea" Water 15, no. 12: 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122151
APA StyleKim, H. J., Koh, E.-H., Koh, C.-S., Park, W.-B., & Kim, M.-C. (2023). Numerical Evaluation of Large-Scale Groundwater Extraction in Groundwater System at Wellfields in the Namwon Area of Jeju Island, South Korea. Water, 15(12), 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122151







