Meteoric Water Incursion, Crude Oil Degradation and Calcite Cementation of an Upper Cretaceous Reservoir in the Zagros Foreland Basin (Kurdistan Region of Iraq)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
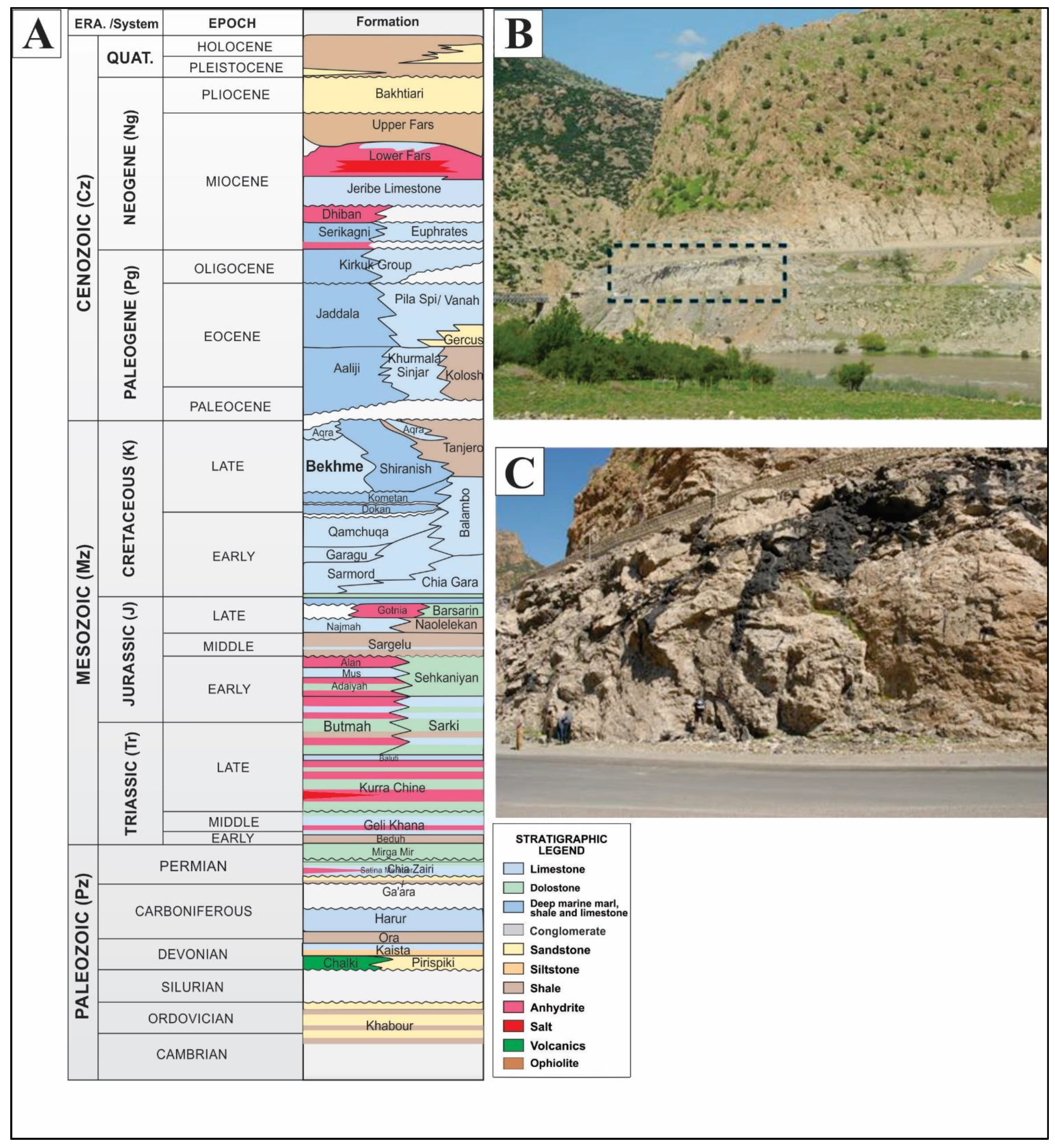
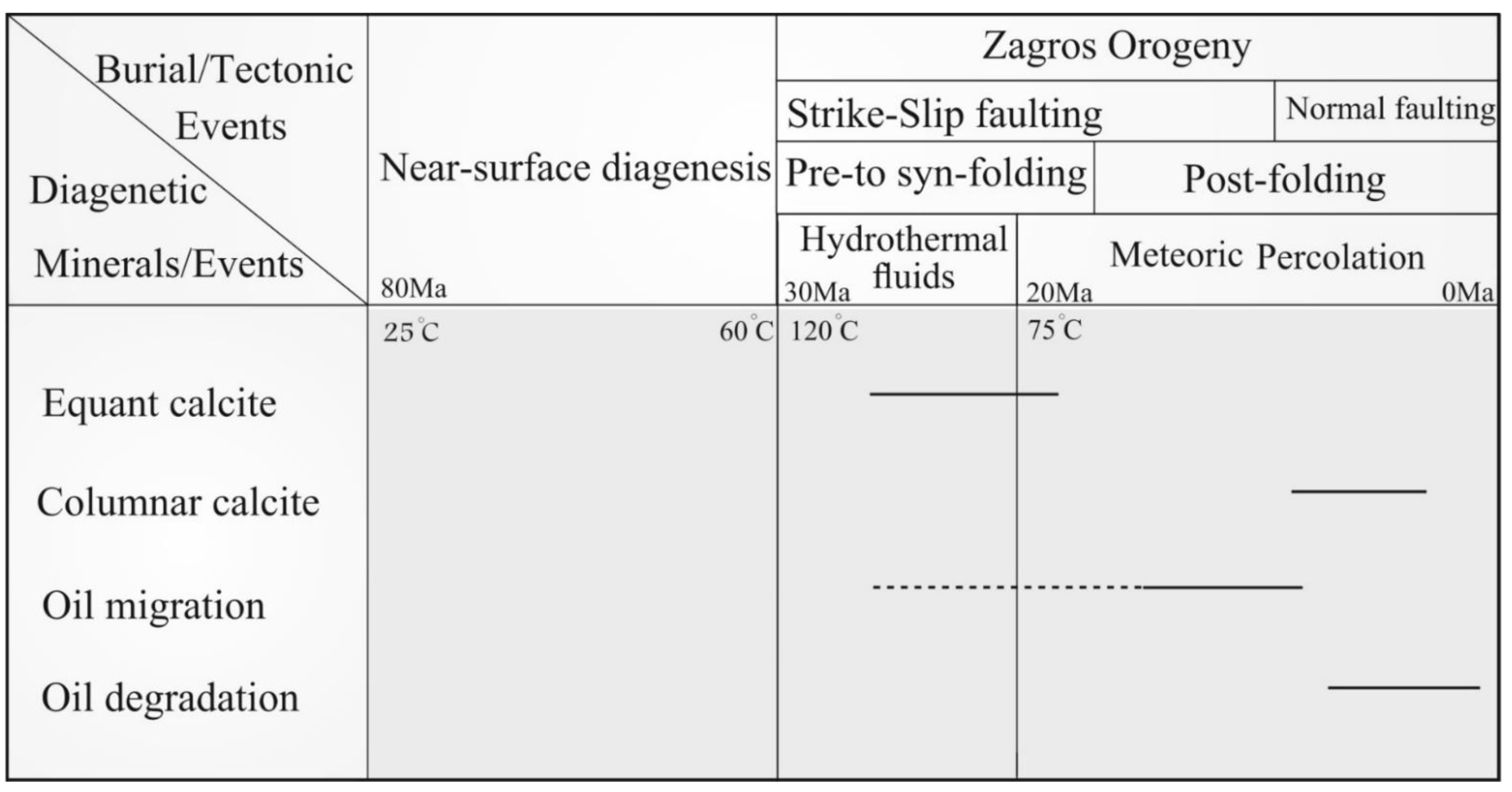
2. Geological Setting
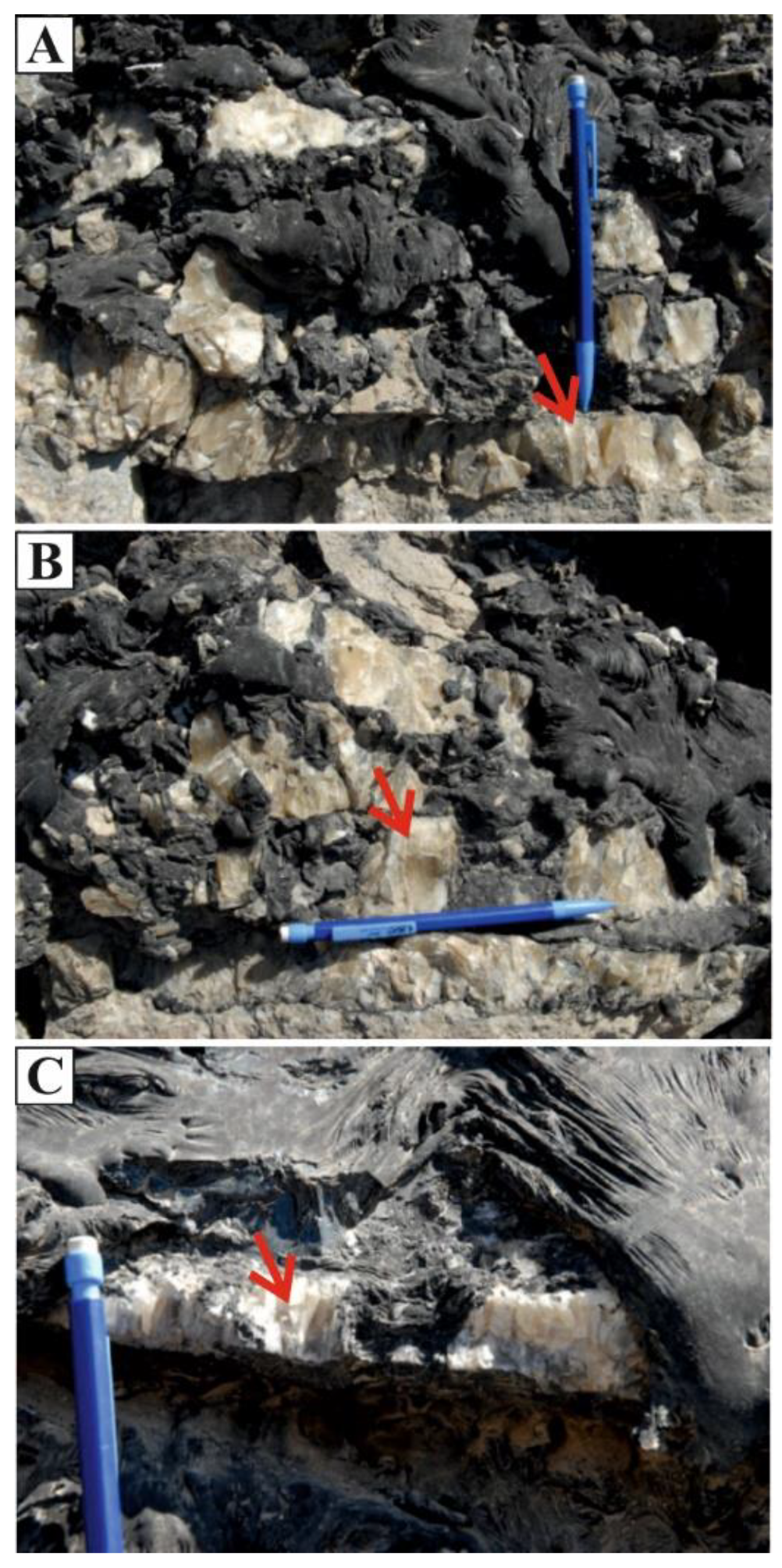
3. Samples and Methods
4. Results
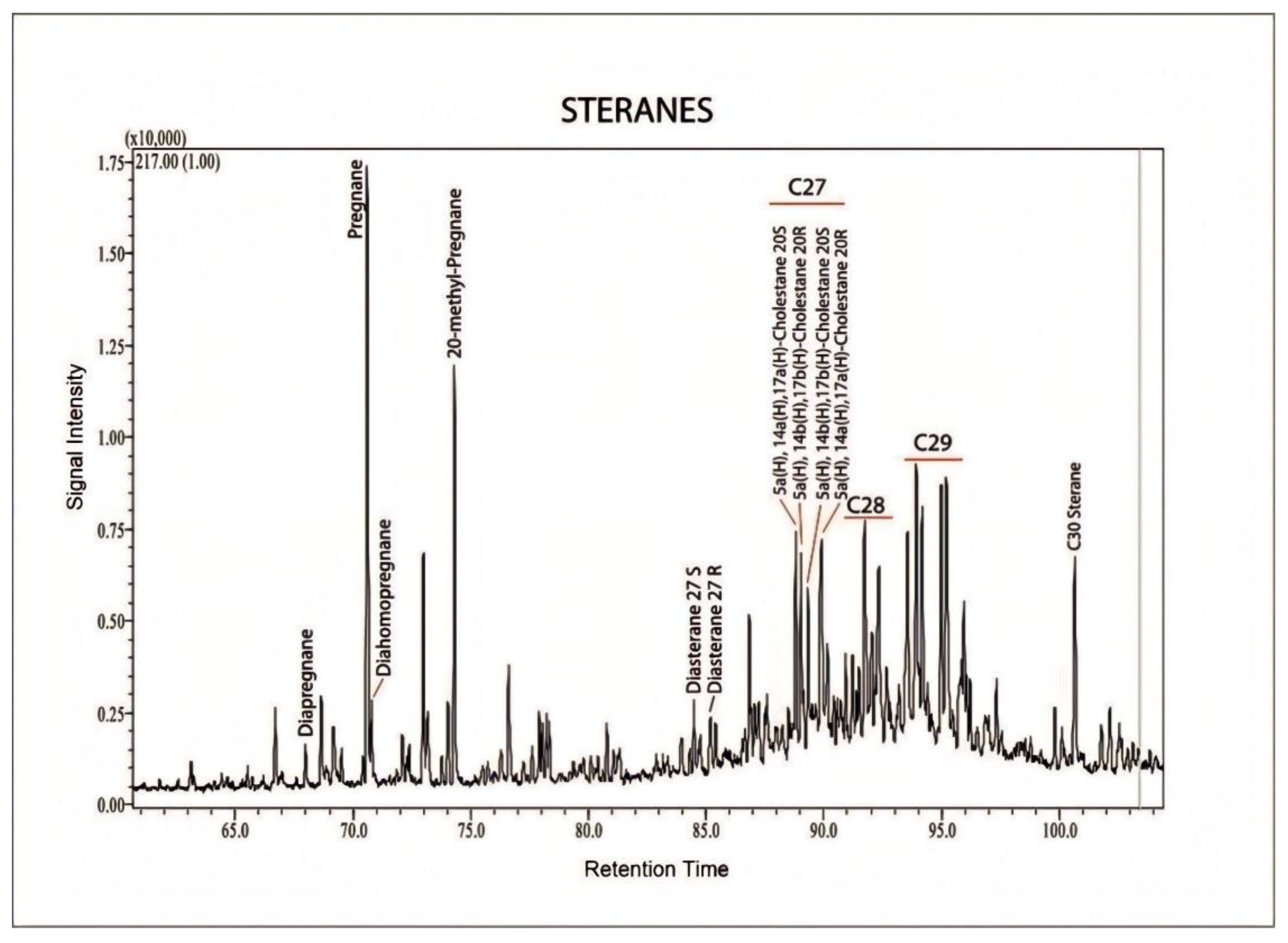
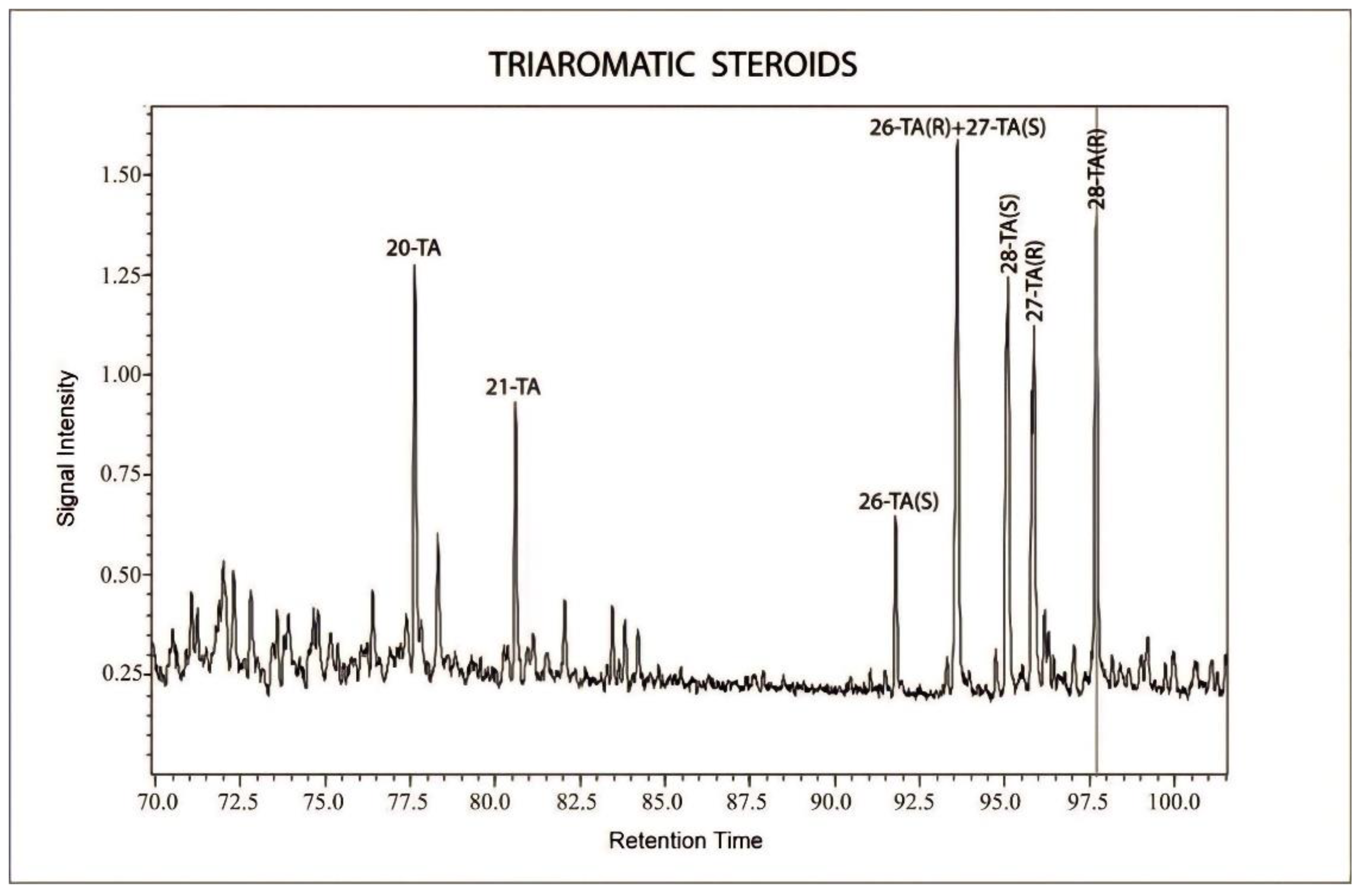
4.1. Composition of Bitumen
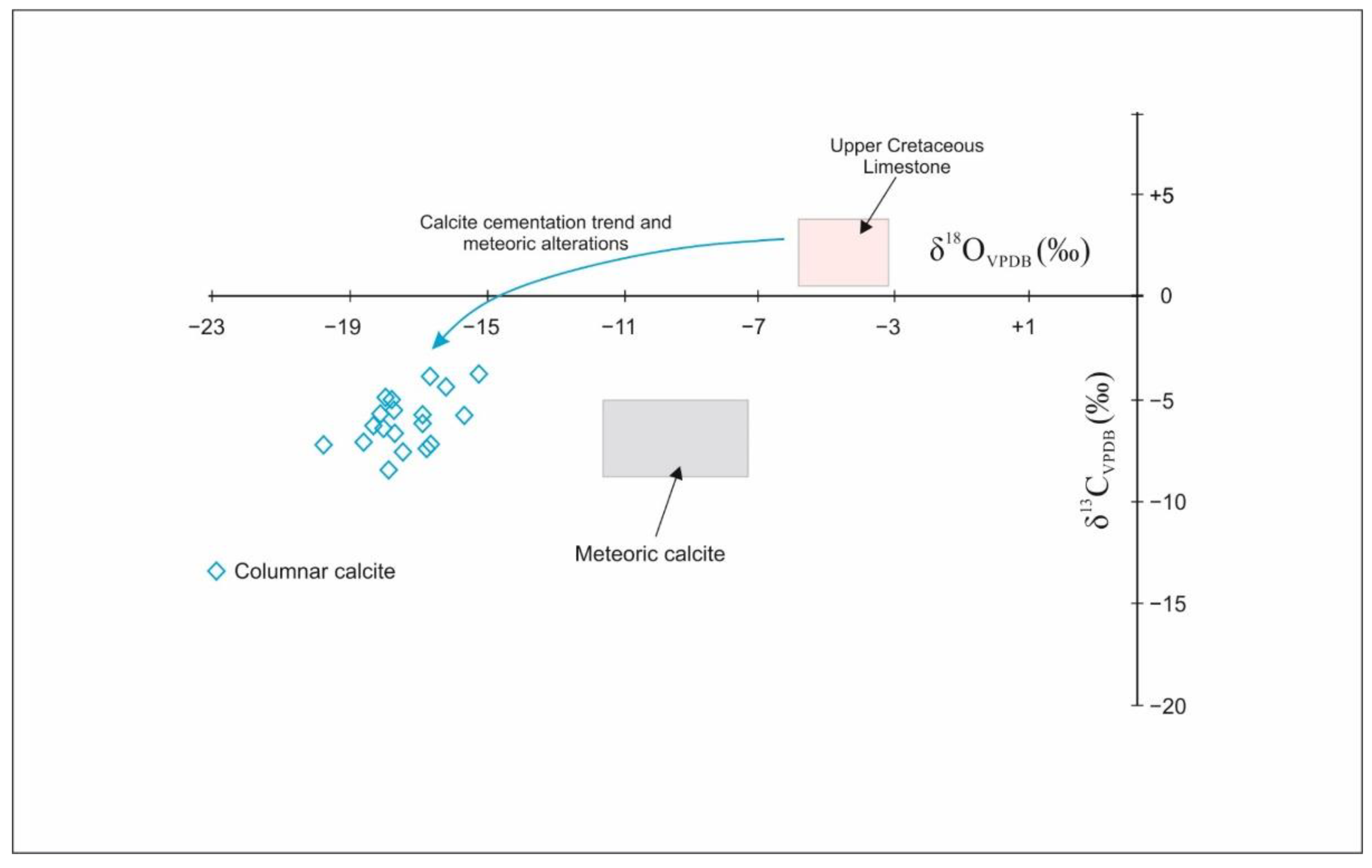
4.2. δ18. O, 87Sr/86Sr Isotopes and Fluid Inclusions of Columnar Calcite
5. Discussion
5.1. Bulk Bitumen Composition: Clues to Its Origin
5.2. Origin of Columnar Calcite
6. Conclusions
- Alteration of hydrocarbons took place via biodegradation and water washing that affected aromatics and steranes. The organic matter precursor was deposited in a restricted carbonatic/evaporitic environment.
- The depletion of n-alkanes and acyclic isoprenoid (pristane and phytane) confirm that biodegradation affected the hydrocarbons. The prominent peaks are mostly terpane and sterane biomarkers, which are more resistant to the biodegradation. The presence of triaromatic steroid (TAS) hydrocarbons in the analyzed sample is evidence of moderate degradation. Moreover, the presence of C26–28 homologues and the C20 and C21 components of TAS are consistent with the interpretation of limited biodegradation of the hydrocarbons.
- High quantities of steranes and diasteranes in the saturated hydrocarbon fraction and a higher proportion of C29 compared with C27 and C28 regular steranes are attributed to terrigenous organic matter contribution.
- The negative oxygen and carbon stable isotopes, non-radiogenic Sr isotopic ratios, low salinity, and low temperatures in fluid inclusions of the columnar calcite suggest that calcite cementation occurred simultaneously with oil degradation, which acted as the source of 12C in dissolved carbon needed for calcite precipitation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veil, J.; Quinn, J. Water Issues Associated with Heavy Oil Production; Environmental Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory: Lemont, IL, USA, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Pytlak, A.; Leis, A.; Prochaska, W.; Sachsenhofer, R.F.; Gross, D.; Linzer, H.G. Light Hydrocarbon Geochemistry of Oils in the Alpine Foreland Basin: Impact of Geothermal Fluids on the Petroleum System. Geofluids 2017, 2017, 7182959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.C.; Burwood, R.; Mycke, B. The reservoir geochemistry and petroleum charging histories of Palaeogene-reservoired fields in the Outer Witch Ground Graben. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1995, 86, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.; Larter, S.R. Quantitative separation of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons using silver ion-silica solid-phase Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mode, A.W.; Anyiam, O.A.; Amobi, J.O.; Nweke, S.U. Gas chromatographic analysis of whole oil samples: Implications for biodegradation in the Niger Delta. J. Petrol. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2017, 7, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, P.H.; Connan, J. Crude oils in reservoirs: The factors influencing their composition. In Applied Petroleum Geochemistry; Bordenave, M.L., Ed.; Editions Technips: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 151–173. [Google Scholar]
- Shlimon, A.G.; Mansurbeg, H.; Othman, R.S.; Gittel, A.; Aitken, C.M.; Head, I.M.; Finster, K.W.; Kjeldsen, K.U. Microbial community composition in crude oils and asphalts from the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, A.M.; Cook, F.D.; Westlake, D.W.S. Microbial Utilization of Crude Oil. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 23, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlimon, A.; Mansurbeg, H.; Othman, R.; Head, I.; Kjeldsen, K.U.; Finster, K. Identity and hydrocarbon degradation activity of enriched microorganisms from natural oil and asphalt seeps in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq (KRI). Biodegradation 2021, 32, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.E.; Walters, C.C.; Moldowan, J.M. The Biomarker Guide, Vol. 2: Biomarkers and Isotopes in Petroleum Systems and Earth History, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; p. 1132. [Google Scholar]
- English, J.; Davies, L. Regional trends in Jurassic and Triassic thermal maturity in northern Iraq. In Proceedings of the Geological Society of London Conference on Hydrocarbon Exploration in the Zagros Mountains of Iraqi Kurdistan and Iran, London, UK, 23–25 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mackertich, D.S.; Samarrai, A.I. History of hydrocarbon exploration in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. GeoAarabia 2015, 20, 181–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Guindy, M.; Kelly, S.P. September. Logging While Drilling in Kurdistan’s First Horizontal Well Enhances Production Rates. In Second EAGE Workshop on Iraq; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; p. cp-355. [Google Scholar]
- Csontos, L.; Sasvári, Á.; Pocsai, T.; Kósa, L.; Salae, A.T.; Ali, A. Structural evolution of the northwestern Zagros, Kurdistan Region, Iraq: Implications on oil migration. GeoArabia 2012, 17, 81–116. [Google Scholar]
- Mansurbeg, H.; Alsuwaidi, M.; Salih, N.; Shahrokhi, S.; Morad, S. Integration of stable isotopes, radiometric dating and microthermometry of saddle dolomite and host dolostones (Cretaceous carbonates, Kurdistan, Iraq): New insights into hydrothermal dolomitization. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 127, 104989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.O. Sedimentology and Stratigraphy of Bekhme Formation (Upper Cretaceous) in Selected Sections in Kurdistan Region-Iraq. Master’s Thesis, Salahaddin University, Erbil, Iraq, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jassim, S.Z.; Goff, J.C. Geology of Iraq; Dolin, Prague and Moravian Museum: Brno, Czech Republic, 2006; p. 341. [Google Scholar]
- Stöcklin, J. Salt deposits of the Middle East. In Saline Deposits; Mattox, R.B., Ed.; Geological Society of America Special Paper 88; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1968; pp. 157–181. [Google Scholar]
- Stoneley, R. A review of petroleum source rocks in parts of the Middle East. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1987, 26, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Mckenzie, D. Active tectonics of the Alpine-Himalayan Belt between western Turkey and Pakistan. Geophys. J. Int. 1984, 77, 185–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqrawi, A.A.; Goff, J.C.; Horbury, A.D.; Sadooni, F.N. The Petroleum Geology of Iraq; Scientific Press: Beaconsfield, UK, 2010; p. 424. [Google Scholar]
- Sharland, P.R.; Archer, R.; Casey, D.M.; Davies, R.B.; Hall, S.; Heward, A.P.; Horbury, A.D.; Simmons, M.D. Arabian Plate Sequence Stratigraphy; Gulf Petrolink: Manama, Bahrain, 2001; p. 371. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R. Stratigraphy Section on Bekhme Gorge; MPC Report, IR/Rw/4 No. 19; INOC Library: Albany, NY, USA, 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Permanyer, A.; Marfil, R.; Martí-Martín, J.D.; Estupiñan, J.; Márquez, G.; Arroyo, X. Diagenetic evolution of the Upper Cretaceous carbonate and sandstone exhumed reservoirs (Western Basque-Cantabrian Basin, North Spain). J. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, R.P. Biological markers in fossil fuel production. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1985, 4, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohialdeen, I.M.J. Source Rock Appraisal and Oil-Source Correlation for the Chia Gara Formation, Kurdistan-North Iraq Unpublished. Ph.D. Thesis, College of Science, University of Sulaimani, Sulaymaniyah, Iraq, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Aasm, I.S.; Taylor, B.E. South, Stable isotope analysis of multiple carbonate samples using selective aciextraction. Chem. Geol. 1990, 80, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Veizer, J.; Ala, D.; Azmy, K.; Brucksch, P.; Buhl, D.; Bruhn, F.; Carden, G.A.F.; Diener, A.; Ebneth, S.; Godde’ris, Y.; et al. 87Sr/86Sr, d13C and d18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater. Chem. Geol. 1999, 161, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.M.; Donovan, D.T.; Thirlwall, M.F.; Fouke, B.W.; Mattey, D. Strontium isotope profile of the early Toarcian (Jurassic) oceanic anoxic event, the duration of ammonite biozones, and belemnite palaeotemperatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 179, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansurbeg, H.; Morad, D.; Othman, R.; Morad, S.; Ceriani, A.; Al-Aasm, I.; Kolo, K.; Spirov, P.; Proust, N.; Preat, A.; et al. Hydrothermal dolomitization of the Bekhme Formation (Upper Cretaceous), Zagros Basin, Kurdistan Region of Iraq: Record of oil migration. Sediemntary Geol. 2016, 341, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, H.; Reynolds, J. Systematics of Fluid Inclusions in Diagenetic Minerals; Short Course 31; SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mclimans, R.K. The application of fluid inclusions to migration of oil and diagenesis in petroleum reservoirs. Appl. Geochem. 1987, 2, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, B.P.; Welte, D.H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984; p. 538. [Google Scholar]
- Sofer, Z. Stable Carbon Isotope composition of crude oils: Application to source depositional environments and petroleum alteration. AAPG Bull. 1984, 68, 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.M. Petroleum Geochemistry and Geology; W.H. Freeman and Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1996; 743p. [Google Scholar]
- Leila, M.; Moscariello, A. Organic geochemistryof oil and natural gasin the west Dikirnis and El-Tamad Fields, onshore Nile delta, Egypt: Interpretation of potential source rocks. J. Pet. Geol. 2017, 40, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhafaji, M.W.; Connan, J.; Engel, M.H.; Al-Jubouri, S.W. Origin, biodegradation, and water washing of bitumen from the Mishraq Sulfur Mine, northern Iraq. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 124, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, F.H.; Albrecht, P. Correlations between carboxylic acids and hydrocarbons in several crude oils. Alteration by biodegradation. Org. Geochem. 1984, 6, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, T.; Li, M. The Distribution of Triaromatic Steroids and Oil Group Classification of Ordovician Petroleum Systems in the Cratonic Region of the Tarim Basin, NW China. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 1794–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, W.K.; Moldowan, J.M. The effect of biodegradation on steranes and terpanes in crude oils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldowan, J.M.; Seifert, W.K.; Gallegos, E.J. Relationship between petroleum Compositions and depositional environment of Petroleum source rocks. AAPG Bull. 1985, 69, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Waples, D.W.; Machihara, T. Biomarkers for geologists: A practical guide to theI application of steranes and triterpanes in petroleum geology. AAPG Meth. Exp. 1991, 2, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mohialdeen, I.M.J.; Hakimi, M.H. Geochemical characterization of Tithonian- Berriasian Chia Gara organic-rich rocks in northern Iraq with an emphasis on organic matter enrichment and the relationship to the bioproductivity and anoxia conditions. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 116, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsté, J.S.S.; Kenig, F.; Koopmans, M.P.; Köster, J.; Schouten, S.; Hayes, J.M.; de Leeuw, J.W. Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, P.J. The occurence of unusual C27 and C29 sterane predominances in two types of Oman crude oil. Org. Geochem. 1986, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Y.; Meinschein, W.G. Sterols as ecological indicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.E.; Moldowan, J.M. The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments, 1st ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993; p. 363. [Google Scholar]
- Mckirdy, D.M.; Kantsler, A.J.; Emmett, J.K.; Aldridge, A.K. Hydrocarbon genesis and organic facies in Cambrian carbonates of the Eastern Officer Basin, South Australia. In Petroleum Geochemistry and Source Rock Potential of Carbonate Rocks; Palacas, J.G., Ed.; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1984; pp. 13–31. [Google Scholar]
- Rullkötter, J.; Spiro, B.; Nissenbaum, A. Biological marker characteristics of oils and asphalts from carbonate source rocks in a rapidly subsiding graben, Dead Sea, Israel. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Haven, H.L.; De Leeuw, J.W.; Rullkötter, J.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Schenck, P.A.; Palmer, S.E.; Zumberge, J.E.; Fleet, A.J.; Kelts, K.; Talbot, M.R. Application of biological markers in the recognition of palaeohypersaline environments. Lacustrine Petroleum Source Rocks. Geol. Soc. 1988, 40, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Michael, G.E.; Kovachev, G.; Zhu, H.; Philp, R.P.; Lewis, C.A. Biodegradation of tar-sands bitumens from the Ardmore and Anadarko Basins, Carter Country, Oklahoma. Org. Geochem. 1989, 14, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Shah, K.; Zhang, G.; Landriault, M.; Hollebone, B.; Brown, C.; et al. Aromatic Steroids in Crude Oils and Petroleum Products and Their Applications in Forensic Oil Spill Identification. Environ. Forensics 2013, 14, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Qu, X.L.; Du, L.C.; Jing, X.G.; Cheng, X.Y. Carbonate facies and sedimentary evolution of Upper Devonian Tuqiaozi formation in Ganxi section of Longmen mountain. Lithol. Reserv. 2015, 27, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Volkman, J.K.; Alexander, R.; Kagi, R.I.; Woodhouse, G.W. Demethylated hopanes in crude oils and their applications in petroleum geochemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 47, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, P.K. The geochemistry of carbonate diagenesis: The past, present and future. Sedimentology 2015, 62, 1233–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, I.; O’neil, J.R. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. In Data of Geochemistry; Fleisher, M., Ed.; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 440-KK; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VR, USA, 1977; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; p. 342. [Google Scholar]
- Gluyas, J.; Swarbrick, R. Petroleum Geoscience; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2004; 349p. [Google Scholar]
- Waples, D.W. Geochemistry in Petroleum Exploration; International Human Resources Development Corporation: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; p. 232. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz-Rojahn, J.; Ryan-Grigor, S.; Anderson, A. Structural Controls on Seismic-Scale Carbonate Cementation in Hydrocarbon-Bearing Jurassic Fluvial and Marine Sandstones from Australia: A Comparison. In Carbonate Cementation in Sandstones; Morad, S., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 327–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, J.; Lunn, G.A.; Ferreira, L.; Yacu, G. Geologic evolution of the Iraqi Zagros, and its influence on the distribution of hydrocarbons in the Kurdistan region. AAPG Bull. 2015, 99, 231–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, G. Innovation and Technology Dinarta Block, Kurdistan Region of Iraq. In Proceedings of the Kurdistan-Iraq Oil and Gas Conference, London, UK, 16–18 December 2014; p. 35. [Google Scholar]






| Samples | δ13CVPDB (‰) | Fraction |
|---|---|---|
| SM-1 BIT | −27.8 | Whole bitumen |
| SM-1 ASP | −27.9 | Asphaltenes |
| SM-1 RES | −27.8 | Resins |
| SM-1 ARO | −27.8 | Aromatics |
| SM-1 SAT | −27.9 | Saturates |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansurbeg, H.; Mohialdeen, I.; Al-Juboury, A.; Salih, N.; Alsuwaidi, M.; Shahrokhi, S.; Al-Aasm, I.; Mahmmud, R.; Permanyer, A. Meteoric Water Incursion, Crude Oil Degradation and Calcite Cementation of an Upper Cretaceous Reservoir in the Zagros Foreland Basin (Kurdistan Region of Iraq). Water 2023, 15, 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101953
Mansurbeg H, Mohialdeen I, Al-Juboury A, Salih N, Alsuwaidi M, Shahrokhi S, Al-Aasm I, Mahmmud R, Permanyer A. Meteoric Water Incursion, Crude Oil Degradation and Calcite Cementation of an Upper Cretaceous Reservoir in the Zagros Foreland Basin (Kurdistan Region of Iraq). Water. 2023; 15(10):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101953
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansurbeg, Howri, Ibrahim Mohialdeen, Ali Al-Juboury, Namam Salih, Mohammad Alsuwaidi, Salahadin Shahrokhi, Ihsan Al-Aasm, Rebar Mahmmud, and Albert Permanyer. 2023. "Meteoric Water Incursion, Crude Oil Degradation and Calcite Cementation of an Upper Cretaceous Reservoir in the Zagros Foreland Basin (Kurdistan Region of Iraq)" Water 15, no. 10: 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101953
APA StyleMansurbeg, H., Mohialdeen, I., Al-Juboury, A., Salih, N., Alsuwaidi, M., Shahrokhi, S., Al-Aasm, I., Mahmmud, R., & Permanyer, A. (2023). Meteoric Water Incursion, Crude Oil Degradation and Calcite Cementation of an Upper Cretaceous Reservoir in the Zagros Foreland Basin (Kurdistan Region of Iraq). Water, 15(10), 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101953








