Evaluation of the Effects of Different Phosphorus Sources on Microcystis aeruginosa Growth and Microcystin Production via Transcriptomic Surveys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microcystis aeruginosa and Cultures
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Physiological Measurements
2.3.1. Measurement of Cell Density and Growth Rate
2.3.2. Extraction and Analysis of Chlorophyll a
0.10 × (OD630 − OD750)]·V1V−1 δ−1
2.3.3. Analysis of Photosynthetic Activity
2.3.4. Measurement of Total Phosphorus and PO4-P
2.3.5. Extraction and Measurement of Microcystins
2.3.6. Extraction and Analysis of Alkaline Phosphatase
2.4. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
3. Results and Discussion
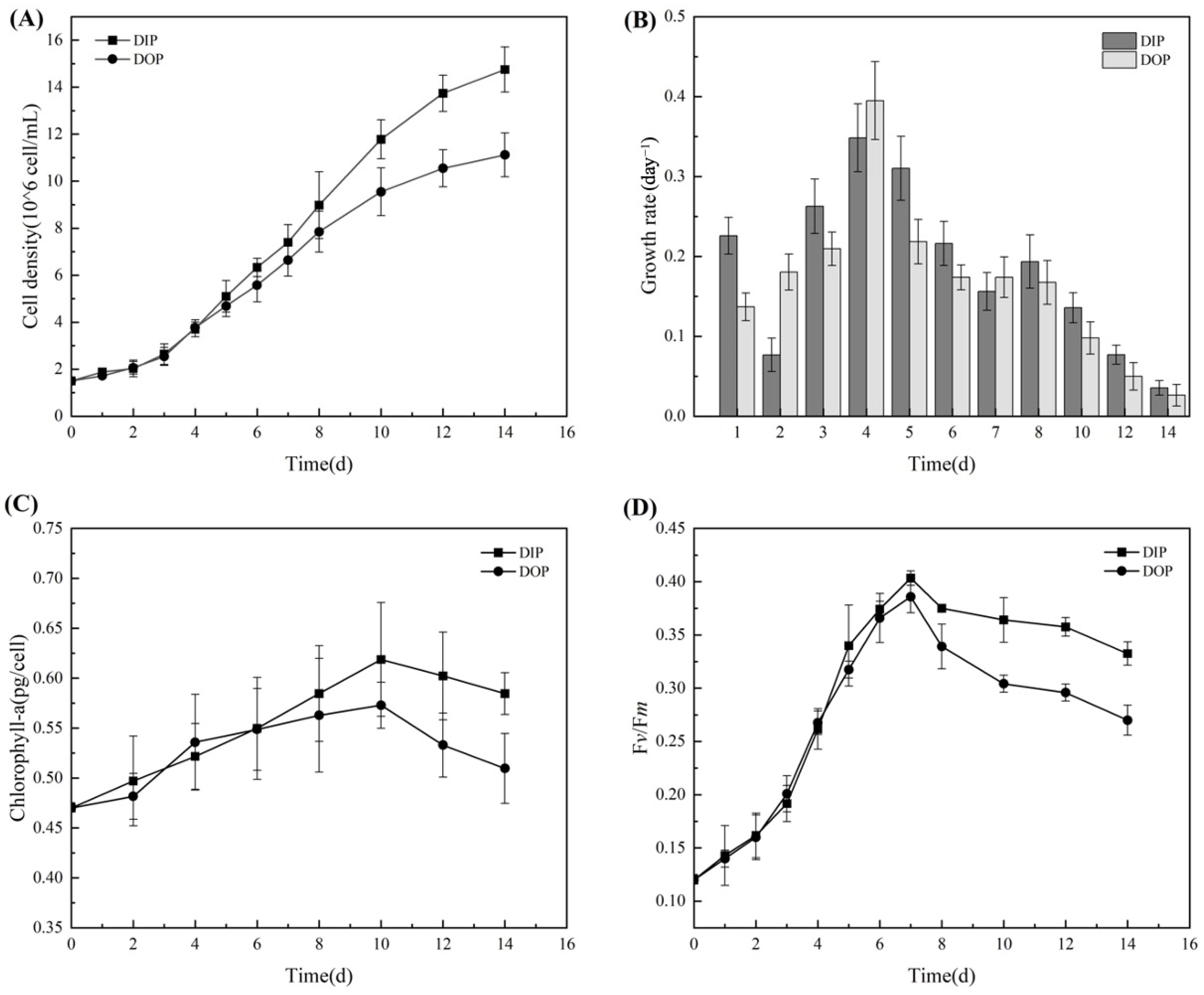
3.1. Growth and Photosynthetic Activity of Microcystis aeruginosa
3.1.1. Physiological Changes in Growth and Photosynthesis
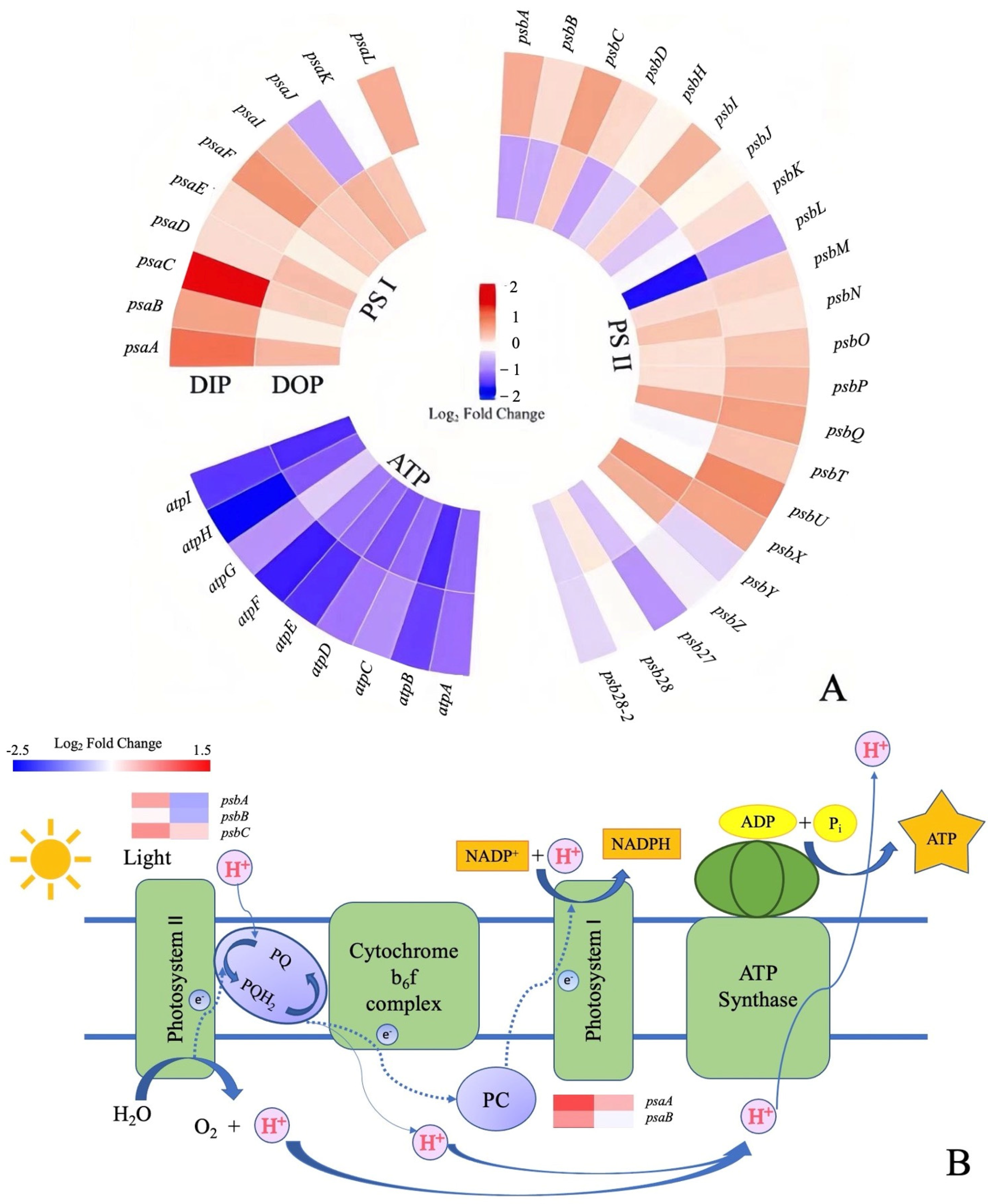
3.1.2. Changes in Photosynthetic Genes’ Response to Different Phosphorus Sources
3.2. Variations in Related Genes’ Responses to Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus and Dissolved Organic Phosphorus
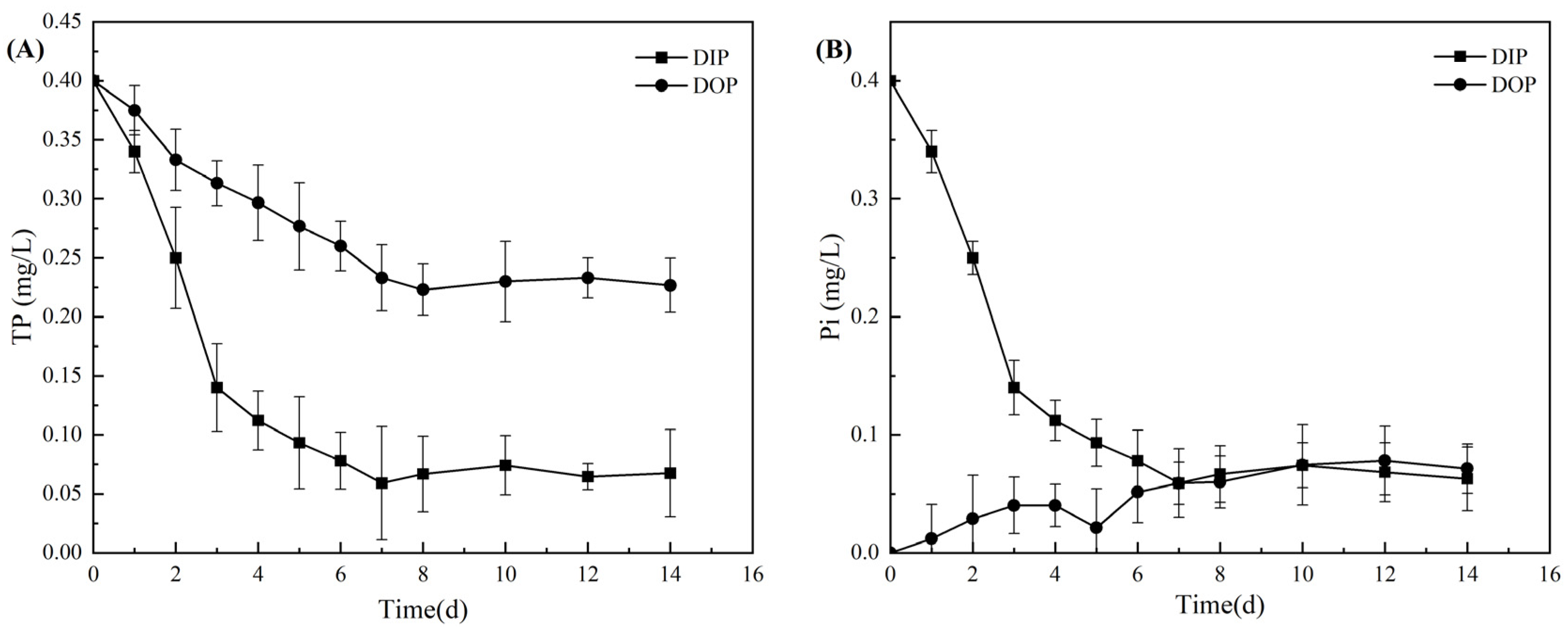
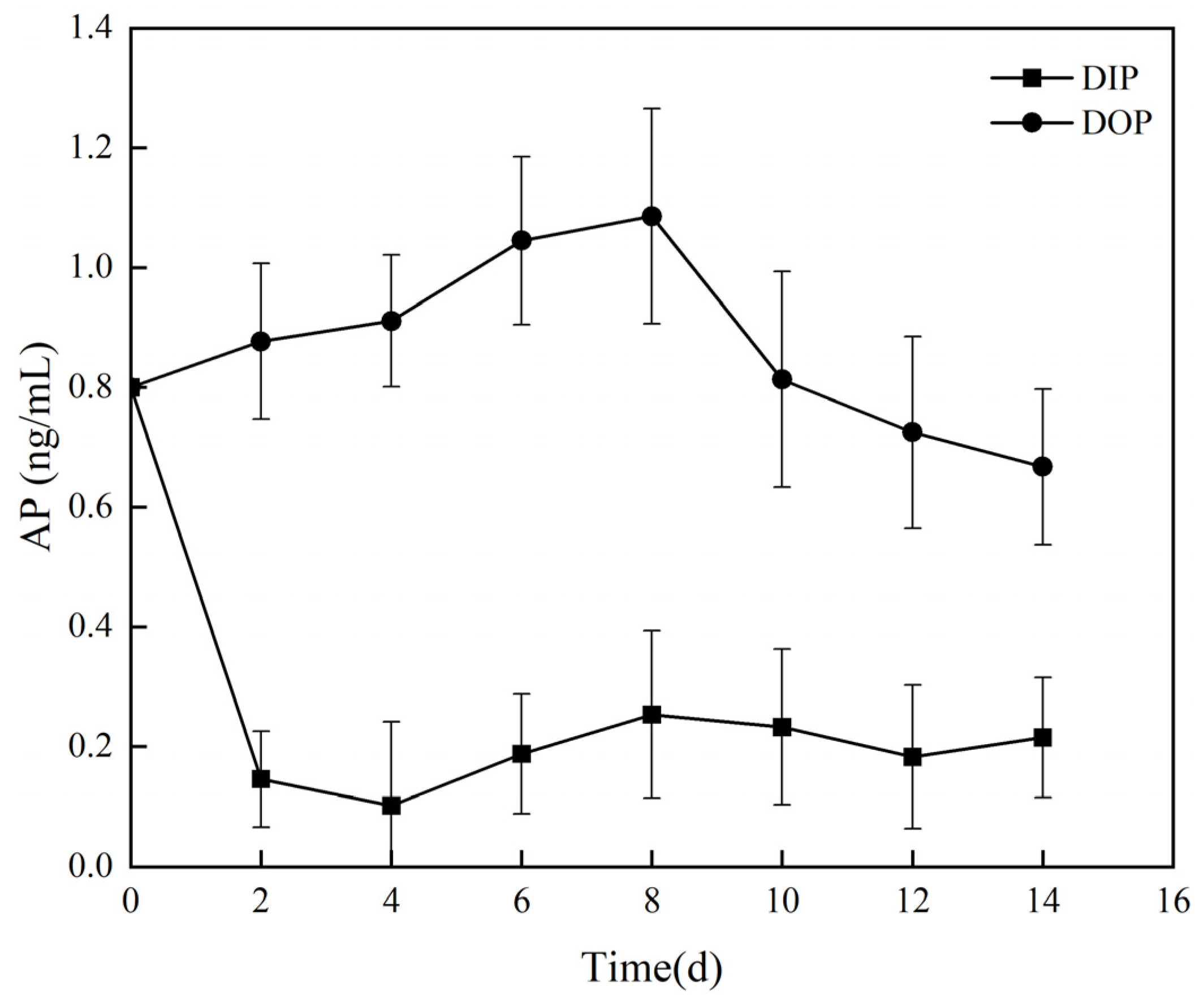
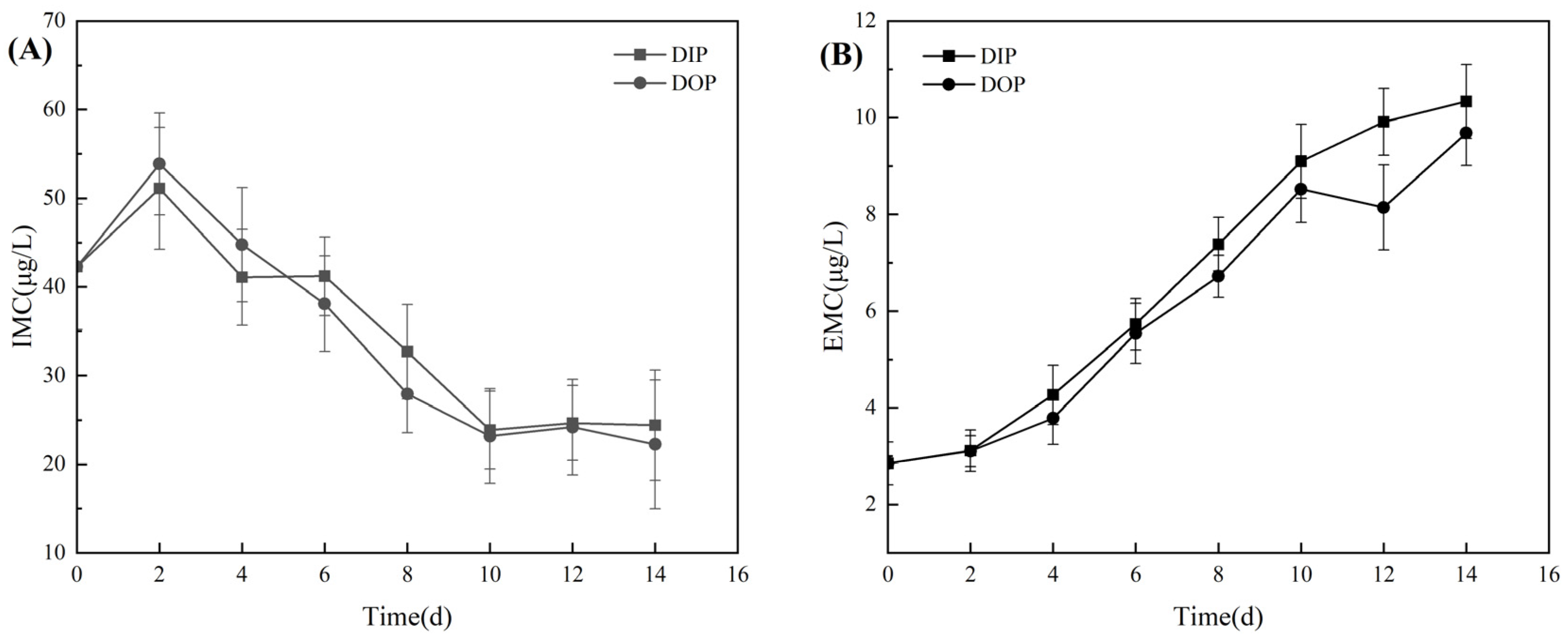
3.2.1. Utilization of Different Phosphorus Sources and Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
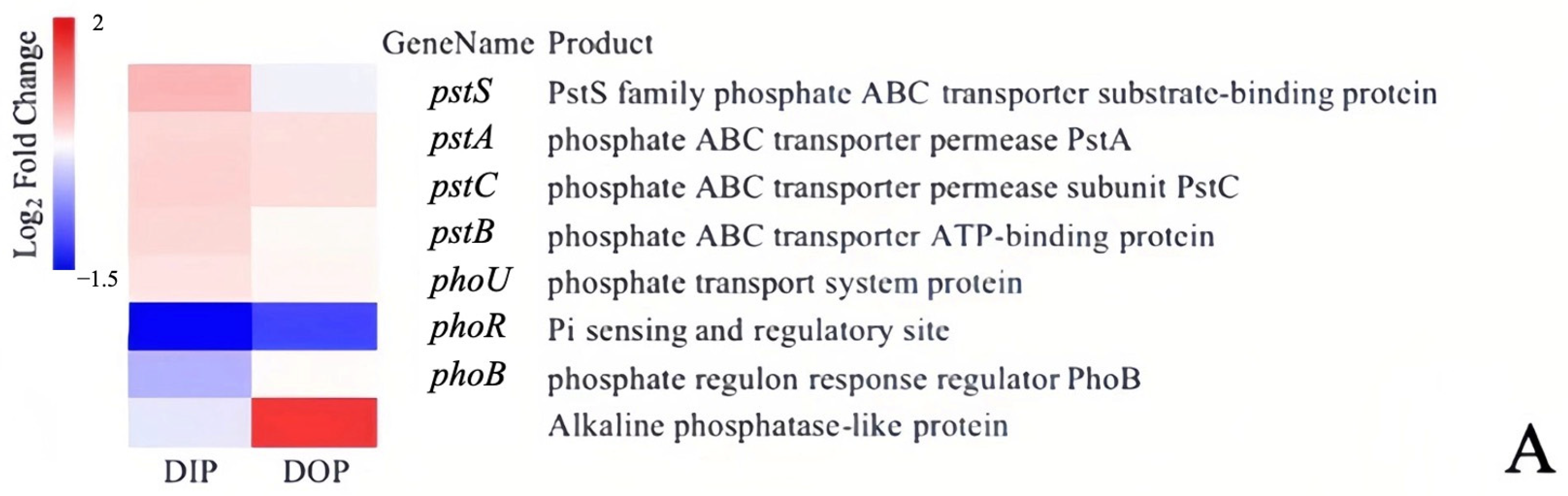
3.2.2. Variations in Related Genes Encoding Phosphorus Metabolism under Different Phosphorus Sources
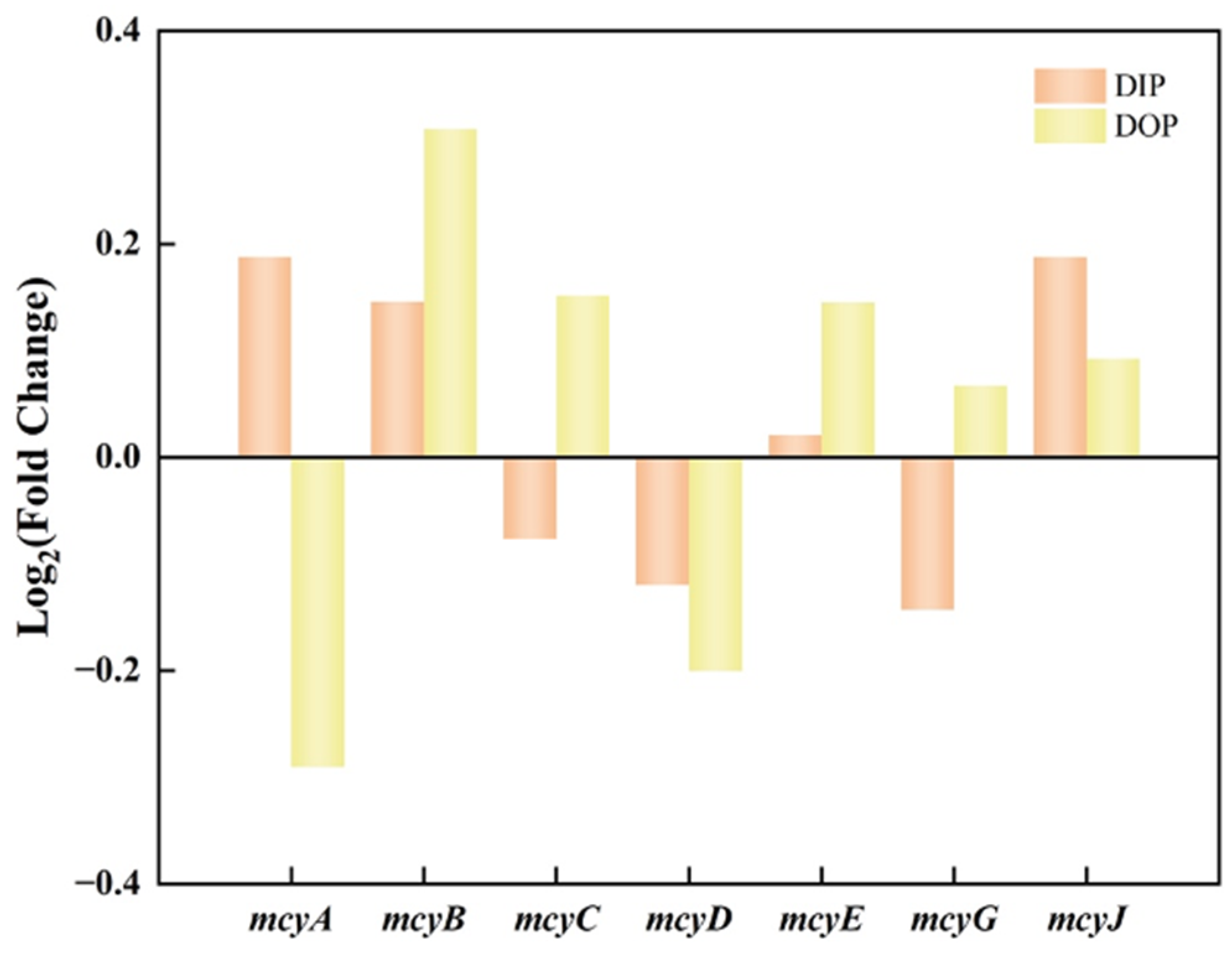
3.3. Effects of Different Phosphorus Sources on Microcystins Production
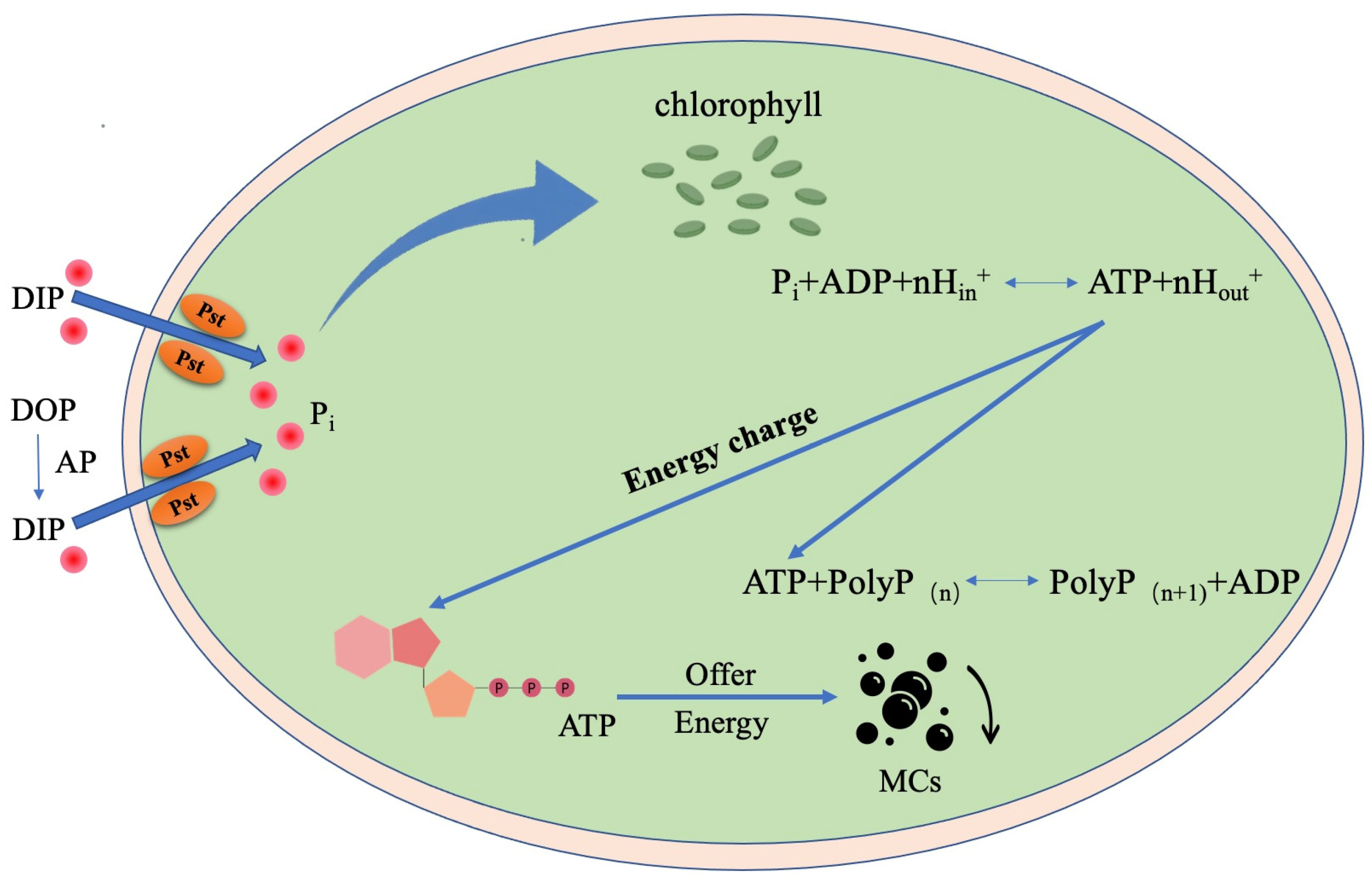
3.4. Relation between Microcystins Biosynthesis and Phosphorus
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 2007, 317, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.; Davis, T.W.; Baker, D.B.; Boyer, G.L.; D’Anglada, L.V.; Doucette, G.J.; Ho, J.C.; Irwin, E.G.; Kling, C.L. Global solutions to regional problems: Collecting global expertise to address the problem of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. A Lake Erie case study. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.; Mou, X. A brief review of the structure, cytotoxicity, synthesis, and biodegradation of microcystins. Water 2021, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, E.; Wiegand, C. Cyanobacterial toxins–occurrence, biosynthesis and impact on human affairs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Jia, P.; Dai, R. Evaluation of changes in Microcystis aeruginosa growth and microcystin production by urea via transcriptomic surveys. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xia, Q.; Dai, R. Transcriptomic survey on the microcystins production and growth of Microcystis aeruginosa under nitrogen starvation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Bi, Y.; Ma, X.; Dong, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Transcriptomic analysis dissects the regulatory strategy of toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa under differential nitrogen forms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, Z. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on Microcystis aeruginosa growth and microcystin production. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Science 1983, 221, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.E.; Peters, R.H. The relationship between chemically analyzed phosphorus fractions and bioavailable phosphorus 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1987, 32, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bi, Y.; Hu, Z. Phytoplankton communities determine the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of alkaline phosphatase activity: Evidence from a tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Chen, X.; Deng, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X. Phosphorus strategy in bloom-forming cyanobacteria (Dolichospermum and Microcystis) and its role in their succession. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Ren, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Hou, J.; Qian, J. Algal growth and utilization of phosphorus studied by combined mono-culture and co-culture experiments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Smith, S.; Sedlak, D.L.; Gu, A.Z. Bioavailability and characterization of dissolved organic nitrogen and dissolved organic phosphorus in wastewater effluents. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, D. Molecular responses to inorganic and organic phosphorus sources in the growth and toxin formation of Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, B.; Lin, H.; Miller, T.R.; Newton, R.J.; Guo, L. Causal relationship between alkaline phosphatase activities and phosphorus dynamics in a eutrophic coastal lagoon in Lake Michigan. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likens, G.; Bartsch, A.; Lauff, G.; Hobbie, J. Nutrients and eutrophication. Science 1971, 172, 873–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecky, R.; Kilham, P. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: A review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 796–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z. Effect of orthophosphate and bioavailability of dissolved organic phosphorous compounds to typically harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lin, L.; Li, W.; Fang, D.; Lv, Z.; Li, M.; Ma, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; He, L. Long-Term Study of Monitoring History and Change Trends in Surface Water Quality in China. Water 2022, 14, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Hou, Y. Effects of amino acids on microcystin production of the Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, C.J. Determination of Chlorophyll and pheopigments: Spectrophotometric equations. Limnol. Ocean. 1967, 12, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, D.; Kestel, S.; Lee, G. The coagulation–ultrafiltration process from pilot testing to full-scale design for the achievement of ultra-low phosphorus limit. Water Pract. Technol. 2016, 11, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.; Bell, S.; Codd, G. Production of novel polyclonal antibodies against the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR and their application for the detection and quantification of microcystins and nodularin. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2761–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yan, F.; An, L.; Shen, W.; Tang, T.; Li, Z.; Dai, R. Transcriptome analysis of changes in M. aeruginosa growth and microcystin production under low concentrations of ethinyl estradiol. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Formation mechanism of the Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in the water with low dissolved phosphorus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 148, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lu, X.; Yu, R.; Qin, M.; Wei, C.; Hong, S. Response of extracellular and intracellular alkaline phosphatase in Microcystis aeruginosa to organic phosphorus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 42304–42312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchie, E.H.; Lawson, T. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: A guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3983–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrogojski, J.; Adamiec, M.; Luciński, R. The chloroplast genome: A review. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hong, J.; Wei, Z.; Yang, J.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Bai, F.; Liu, L. Research Progress of Photosynthetic Proteins in Photosynthesis. Hans J. Comput. Biol. 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, G.; You, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, W.; Kuang, T.; Han, G.; Sui, S.-F.; Shen, J.-R. Structural insights into cyanobacterial photosystem II intermediates associated with Psb28 and Tsl0063. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Zhang, S.; Rockwell, N.C.; Martin, S.S.; Lagarias, J.C.; Bryant, D.A. Extensive remodeling of a cyanobacterial photosynthetic apparatus in far-red light. Science 2014, 345, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debus, R.; Sevrinck, J.; Saetaert, P.; McIntosh, L. Nucleotide sequence of a second psbA gene from the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 3991. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Jia, Y.; Bai, F.; Yang, S.; Mi, W.; He, S.; Wu, Z. Unveiling the impact of glycerol phosphate (DOP) in the dinoflagellate Peridinium bipes by physiological and transcriptomic analysis. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, J.H. Oxygenic photosynthesis: Electron transfer in photosystem I and photosystem II. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamori, W.; Shikanai, T. Physiological functions of cyclic electron transport around photosystem I in sustaining photosynthesis and plant growth. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Fu, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z. Physiological and transcriptomic analyses to determine the responses to phosphorus utilization in Nostocs. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, C.; Lu, C.; Zhao, M. Effects of glufosinate on the growth of and microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa at environmentally relevant concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, S.; Martiny, A.C. Prevalence of a calcium-based alkaline phosphatase associated with the marine cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus and other ocean bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Ren, L.; Wang, X.; Paerl, H.W. Using alkaline phosphatase activity as a supplemental index to optimize predicting algal blooms in phosphorus-deficient lakes: A case study of Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Su, Y.; Deng, S.; Kontopyrgou, M.; Zhang, D. Significant influence of phosphorus resources on the growth and alkaline phosphatase activities of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarche, M.G.; Wanner, B.L.; Crépin, S.; Harel, J. The phosphate regulon and bacterial virulence: A regulatory network connecting phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-Q.; Ou-Yang, T.; Yang, S.-Q.; Zhao, L.; Ji, L.-L.; Wu, Z.-X. Transcriptomic responses to phosphorus in an invasive cyanobacterium, Raphidiopsis raciborskii: Implications for nutrient management. Harmful Algae 2022, 111, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harke, M.J.; Berry, D.L.; Ammerman, J.W.; Gobler, C.J. Molecular response of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to phosphorus limitation. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, B. Gene regulation by phosphate in enteric bacteria. J. Cell. Biochem. 1993, 51, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torriani, A. From cell membrane to nucleotides: The phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli. Bioessays 1990, 12, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, E.A.; Henry, J.T.; Fiebig, A.; Crosson, S.; Laub, M.T. Identification of the PhoB regulon and role of PhoU in the phosphate starvation response of Caulobacter crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyhrman, S.T.; Jenkins, B.D.; Rynearson, T.A.; Saito, M.A.; Mercier, M.L.; Alexander, H.; Whitney, L.P.; Drzewianowski, A.; Bulygin, V.V.; Bertrand, E.M. The transcriptome and proteome of the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana reveal a diverse phosphorus stress response. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietsch, J.; Bornmann, K.; Schmidt, W. Relevance of intra-and extracellular cyanotoxins for drinking water treatment. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2002, 30, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, S.; Kifle, D.; Zewde, T.W.; Johansen, J.A.; Demissie, T.B.; Hansen, J.H. Temporal dynamics of intra-and extra-cellular microcystins concentrations in Koka reservoir (Ethiopia): Implications for public health risk. Toxicon 2019, 168, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, N.; Song, L.; Gan, N. Quantitative proteomic and microcystin production response of Microcystis aeruginosa to phosphorus depletion. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Lin, S.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X. Transcriptional and physiological responses to nutrient loading on toxin formation and photosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905. Toxins 2017, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, K. Phosphorus metabolism in plants. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1966, 19, 301–390. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, F.; Shi, J.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Interspecific competition between Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Microcystis aeruginosa on different phosphorus substrates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 42264–42275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Geng, J.; Ren, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Physiological and biochemical responses of Microcystis aeruginosa to glyphosate and its Roundup® formulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Passarini, M.R.Z.; Kumar, A. Cyanobacterial biology in twenty-first century. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1184669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Luque, E.; Bhaya, D.; Grossman, A.R. Polyphosphate: A multifunctional metabolite in cyanobacteria and algae. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Ru, J.; Hou, Y. Relationship of energy charge and toxin content of Microcystis aeruginosa in nitrogen-limited or phosphorous-limited cultures. Toxicon 2008, 51, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillett, D.; Dittmann, E.; Erhard, M.; Von Döhren, H.; Börner, T.; Neilan, B.A. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: An integrated peptide–polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.-R.; Lee, Y.-K.; Srivastava, A.; Park, S.-H.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Oh, H.-M. The selective inhibitory activity of a fusaricidin derivative on a bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anam, G.B.; Guda, D.R.; Ahn, Y.-H. Hormones induce the metabolic growth and cytotoxin production of Microcystis aeruginosa under terpinolene stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, L.; Lin, Y.; Pan, B.; Li, M. Micrometer scale polystyrene plastics of varying concentrations and particle sizes inhibit growth and upregulate microcystin-related gene expression in Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Ko, S.-R.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Oh, H.-M.; Ravi, A.K.; Asthana, R.K. Microcystin biosynthesis and mcyA expression in geographically distinct Microcystis strains under different nitrogen, phosphorus, and boron regimes. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5985987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X. Insights into the conversion of dissolved organic phosphorus favors algal bloom, arsenate biotransformation and microcystins release of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; An, L.; Yan, F.; Shen, W.; Du, W.; Dai, R. Evaluation of the Effects of Different Phosphorus Sources on Microcystis aeruginosa Growth and Microcystin Production via Transcriptomic Surveys. Water 2023, 15, 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101938
Li Z, An L, Yan F, Shen W, Du W, Dai R. Evaluation of the Effects of Different Phosphorus Sources on Microcystis aeruginosa Growth and Microcystin Production via Transcriptomic Surveys. Water. 2023; 15(10):1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101938
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zihao, Lili An, Feng Yan, Wendi Shen, Wenjun Du, and Ruihua Dai. 2023. "Evaluation of the Effects of Different Phosphorus Sources on Microcystis aeruginosa Growth and Microcystin Production via Transcriptomic Surveys" Water 15, no. 10: 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101938
APA StyleLi, Z., An, L., Yan, F., Shen, W., Du, W., & Dai, R. (2023). Evaluation of the Effects of Different Phosphorus Sources on Microcystis aeruginosa Growth and Microcystin Production via Transcriptomic Surveys. Water, 15(10), 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101938




