Using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Combined with Multivariate Change-Point Analysis to Identify Brine Layers Based on the Geochemistry of the Core Sediment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geological Settings and LZ908 Core
2.2. Material
2.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.4. Multivariate Data Change-Point Analysis
3. Results
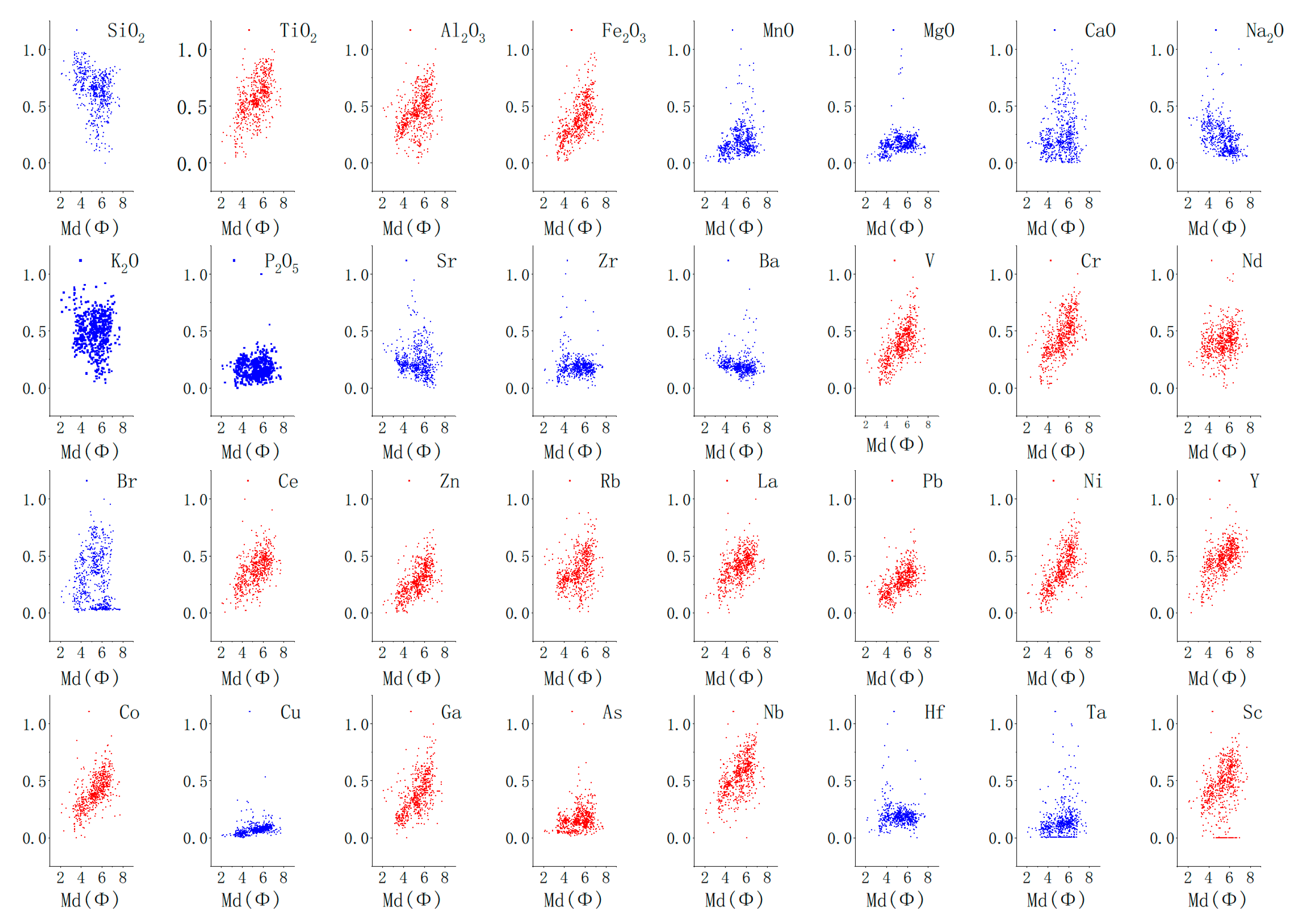
3.1. General Characteristics of Chemical Elements
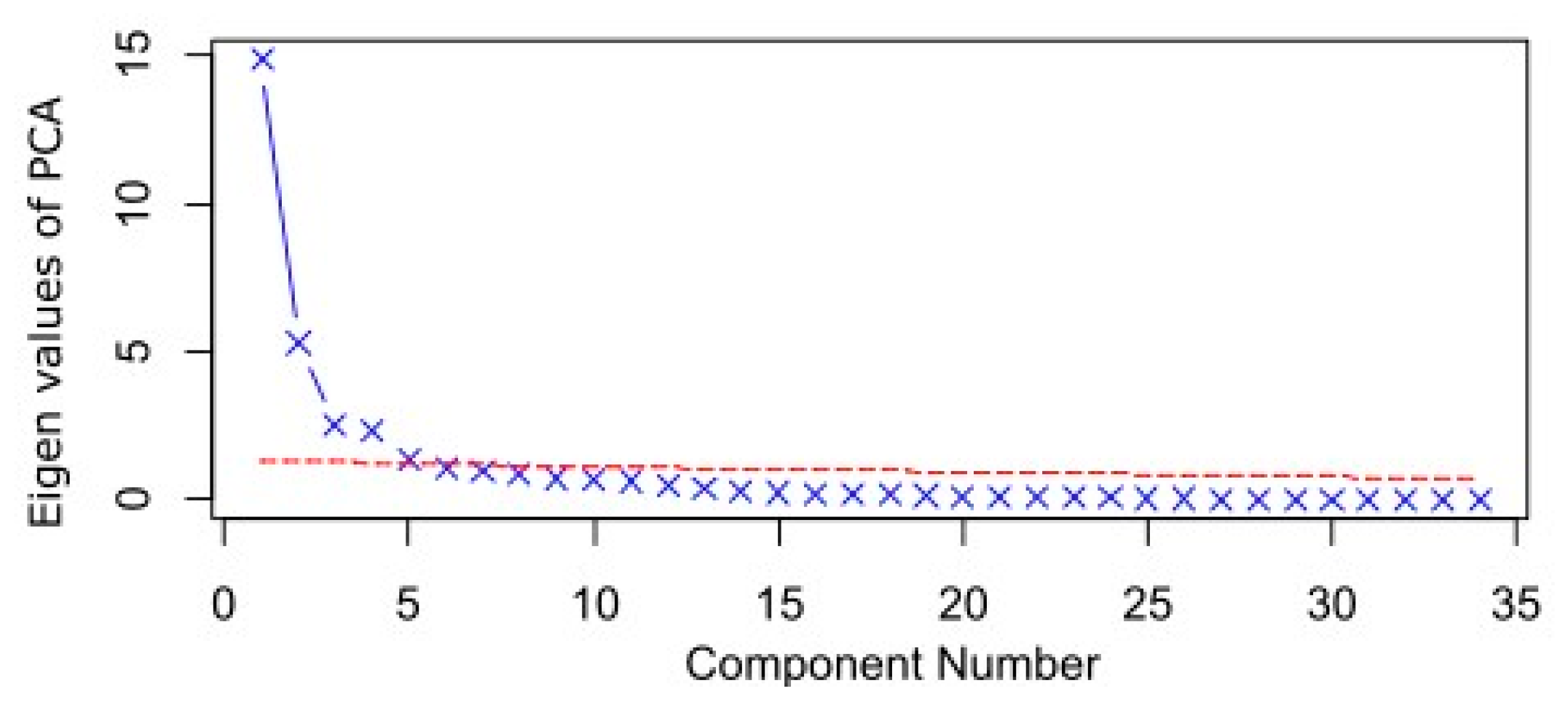
3.2. PCA of Geochemistry
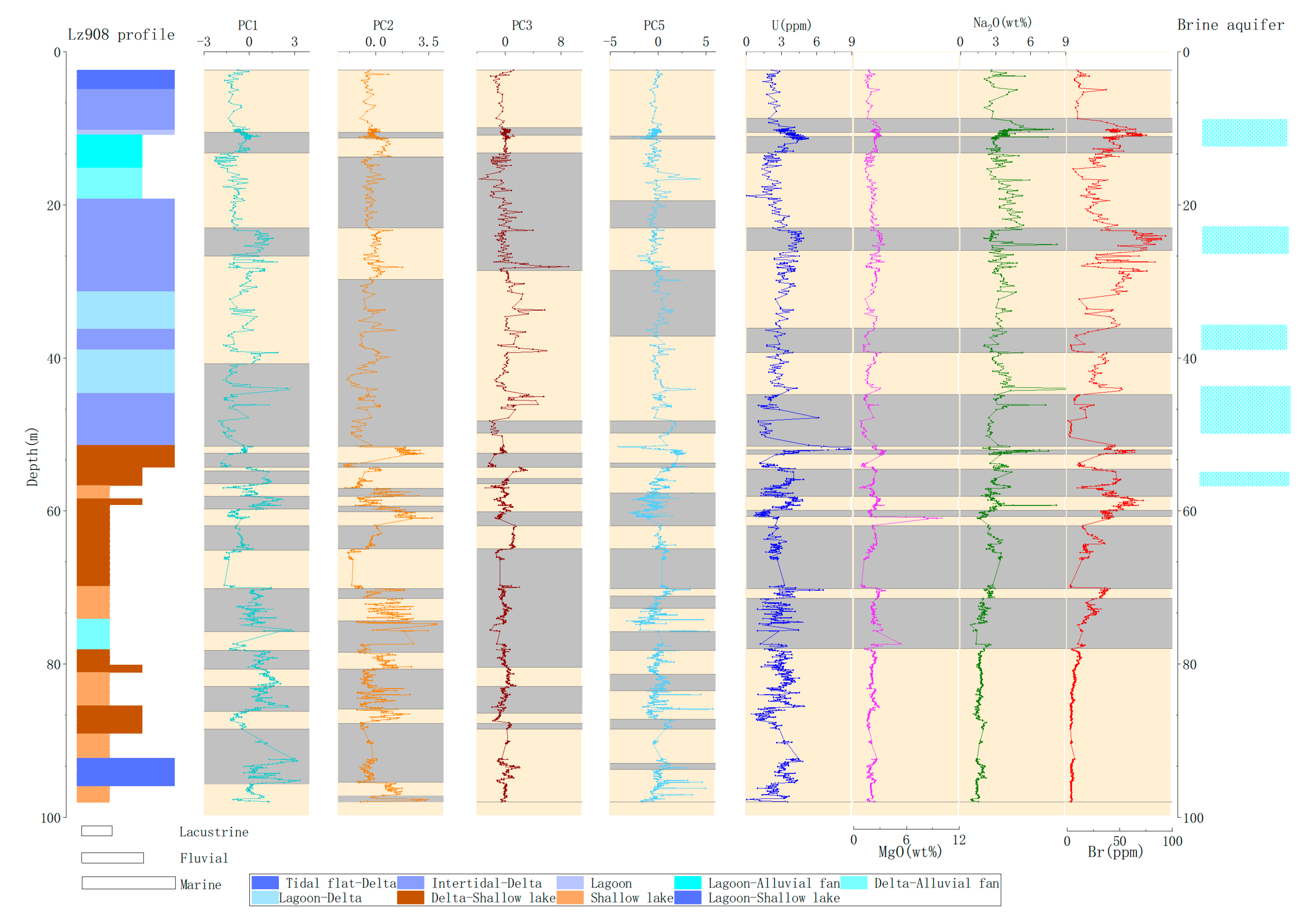
3.3. Multivariate Change-Point Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, C.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Chang, W. Paleoclimatic interpretation in southern Laizhou Bay since the late Pleistocene: Evidence from groundwater and sedimentary strata. Cont. Shelf Res. 2022, 237, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stal, L.J. Coastal Sediments: Transition from Land to Sea. In The Marine Microbiome; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 283–304. ISBN 3319329987; 9783319329987. [Google Scholar]
- Ene, G.E.; Okogbue, C.O.; Chigoziri, O.J. Extraction constraints and environmental significance of brine discharges in the Asu River watershed, Southeastern Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.; Hou, G. Evolutionary process of saline-water intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 607–608, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.; Xiao, C.; Liu, C. Chlorine isotopic constraint on contrastive genesis of representative coastal and inland shallow brine in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 170, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Qiu, J.; Saito, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, G.; Du, X.; Chen, Q. Sedimentary evolution during the last ~1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 451, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, C.; Vaikm, E.R.; Aeschbach, W.; Babre, A.; Jiang, W.; Leuenberger, M.; Lu, Z.-T.; Mokrik, R.; Müller, P.; Raidla, V.; et al. Using 81Kr and Noble Gases to Characterize and Date Groundwater and Brines in the Baltic Artesian Basin on the One-Million-Year Timescale. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 205, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.P.; Akhil, P.S.; Sujatha, C.H. Geochemistry of Core Sediment from Antarctic Region. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2013, 17, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, P.D.; Nagar, Y.C.; Juyal, N.; Smykatz-Kloss, W.; Singhvi, A. Geochemical signatures of Late Holocene paleo-hydrological changes from Phulera and Pokharan saline playas near the eastern and western margins of the Thar Desert, India. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batayneh, A.; Zumlot, T. Multivariate Statistical Approach to Geochemical Methods in Water Quality Factor Identification; Application to the Shallow Aquifer System of the Yarmouk Basin of North Jordan. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 4, 756–768. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelwahab El-Sayed, S.; Hassan, H.B.; El-Sabagh, M.E.I. Geochemistry and mineralogy of Qaroun Lake and relevant drain sediments, El-Fayoum, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 185, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamori, H.; Yoshida, K.; Nakamura, H.; Kuwatani, T.; Hamada, M.; Haraguchi, S.; Ueki, K. Classification of geochemical data based on multivariate statistical analyses: Complementary roles of cluster, principal component, and independent component analyses. Geochem. Geophys. Geosys. 2017, 18, 994–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Lee, C.; Wakeham, S.G.; Armstrong, R.A. Using principal components analysis (PCA) with cluster analysis to study the organic geochemistry of sinking particles in the ocean. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, C.; Oudre, L.; Vayatis, N. Selective review of offline change point detection methods. Signal. Process. 2020, 167, 107299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.C. Segmenting geochemical records using hierarchical probabilistic models. Chem. Geol. 2021, 559, 119973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.; Shan, H.; Xiao, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Cai, H. Genesis of salinized groundwater in Quaternary aquifer system of coastal plain, Laizhou Bay, China: Geochemical evidences, especially from bromine stable isotope. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 59, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yu, H.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Yi, L.; Su, Q. Deposition characteristics in brine aquifers and brine formation in Laizhou Bay area. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2010, 28, 473–477. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Deng, C.; Xu, X.; Yu, H.; Qiang, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Su, Q.; Chen, G.; Li, P.; et al. Paleo-megalake termination in the Quaternary: Paleomagnetic and water-level evidence from south Bohai Sea, China. Sediment. Geol. 2015, 319, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.J.L.; Da Silva Júnior, J.B.; Abreu, I.M.; Soares, S.A.R.; Araujo, R.G.O.; de Souza, E.S.; Ribeiro, H.J.S.; Hadlich, G.M.; Queiroz, A.F.D.S. Application of PCA and HCA in geochemical parameters to distinguish depositional paleoenvironments from source rocks. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2020, 103, 102734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meglen, R.R. Examining large databases: A chemometric approach using principal component analysis. Mar. Chem. 1992, 39, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyibi, E.A.; Folami, S.L.; Ako, B.D.; Ajayi, T.R.; Adelusi, A.O. Application of the principal component analysis on geochemical data: A case study in the basement complex of Southern Ilesa area, Nigeria. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 4, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, F.N.; Kockar, S.; Yilmaz, H. Efficiency of singularity and PCA mapping of mineralization-related geochemical anomalies: A comparative study using BLEG and <180 μm stream sediment geochemical data. Bull. Miner. Res. Explor. 2022, 168, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, C.; Oudre, L.; Vayatis, N. ruptures: Change point detection in Python. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.00826. [Google Scholar]
- Killick, R.; Eckley, I.A. Changepoint: An R Package for Changepoint Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Longman Scientific & Technical: London, UK, 1993; ISBN 9781315845548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenkov, I.N.; Konyushkova, M.V.; Heidari, A.; Nikolaev, E. Chemical differentiation of recent fine-textured soils on the Caspian Sea coast: A case study in Golestan (Iran) and Dagestan (Russia). Quat. Int. 2021, 590, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Eynatten, H.; Tolosana-Delgado, R.; Karius, V.; Bachmann, K.; Caracciolo, L. Sediment generation in humid Mediterranean setting: Grain-size and source-rock control on sediment geochemistry and mineralogy (Sila Massif, Calabria). Sediment. Geol. 2016, 336, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mei, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Hohl, S.V. Disentangling Combined Effects of Sediment Sorting, Provenance, and Chemical Weathering From a Pliocene-Pleistocene Sedimentary Core (CSDP-1) in the South Yellow Sea. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2021, 22, e2020GC009569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Yu, H.; Ortiz, J.D.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Ge, J.Y.; Hao, Q.Z.; Yao, J.; Shi, X.F.; Peng, S.Z. Late Quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the south Bohai Sea, China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2012, 329–330, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Yu, H.; Ortiz, J.D.; Xu, X.; Qiang, X.; Huang, H.; Shi, X.; Deng, C. A reconstruction of late Pleistocene relative sea level in the south Bohai Sea, China, based on sediment grain-size analysis. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 281, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holser, W.T.; Burns, R.G. Trace elements and isotopes in evaporites. Mineral. Soc. Am. Short. Course Notes 1979, 6, 295–346. [Google Scholar]
- Hongxia, W.; Xianjun, Z.; Xianhong, L.; Zhixun, Z.; Zhenhong, L.; Guangtao, Z. Geochemistry Characteristics of Sediment and Provenance Relations of Sediments in Core NT1 of the South Yellow Sea. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2007, 18, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusi, M.; Booth, J.M.; Marasco, R.; Merlino, G.; Garcias-Bonet, N.; Barozzi, A.; Garuglieri, E.; Mbobo, T.; Diele, K.; Duarte, C.M.; et al. Bioturbation Intensity Modifies the Sediment Microbiome and Biochemistry and Supports Plant Growth in an Arid Mangrove System. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01117-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Peng, X.; Pan, J. Distribution, source and enrichment of some chemical elements in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1857–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, P.J.; Wilson, T.R.; Daniell, E. Potassium enrichments in interstitial waters of recent marine sediments. Science 1969, 165, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhija, B.S.; Varma, V.N.; Nagabhushanam, P.; Reddy, D.V. Differentiation of palaeomarine and modern seawater intruded salinities in coastal groundwaters (of Karaikal and Tanjavur, India) based on inorganic chemistry, organic biomarker fingerprints and radiocarbon dating. J. Hydrol. 1996, 174, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.A.; Bienert, R.W.; Binford, M.W.; Kahl, J.S. Stratigraphy of total metals in PIRLA sediment cores. J. Paleolimnol. 1992, 7, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, S.E.; Pedersen, T.F.; Pasava, J. Sedimentary geochemistry of manganese; implications for the environment of formation of manganiferous black shales. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 1996, 91, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xiang, R.; Cao, L.; He, W.; Liu, S.; Shi, X. Geochemistry of core sediments along the Active Channel, northeastern Indian Ocean over the past 50,000 years: Sources and climatic implications. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 521, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Xu, G.; Xu, F.; Yu, Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, D. Paleoenvironmental evolution and organic matter accumulation in an oxygen-enriched lacustrine basin: A case study from the Laizhou Bay Sag, southern Bohai Sea (China). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 217, 103318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mulligan, C.N. Effect of natural organic matter on arsenic release from soils and sediments into groundwater. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Lai, Z.; Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Su, Q.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, X. Chronologies of sedimentary changes in the south Bohai Sea, China: Constraints from luminescence and radiocarbon dating. Boreas 2013, 42, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainikka, P.; Hupa, M. Review on bromine in solid fuels. Part 1: Natural occurrence. Fuel 2012, 95, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Fatela, F.; Leorri, E.; Moreno, F.; Freitas, M.; Valente, T.; Araújo, M.; Gómez-Navarro, J.; Guise, L.; Blake, W. Bromine soil/sediment enrichment in tidal salt marshes as a potential indicator of climate changes driven by solar activity: New insights from W coast Portuguese estuaries. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 580, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millero, F.J. Chemical Oceanography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chague-Goff, C.; Dawson, S.; Goff, J.R.; Zachariasen, J.; Berryman, K.; Garnett, D.; Waldron, H.; Mildenhall, D. A tsunami (ca. 6300 years BP) and other Holocene environmental changes, northern Hawke’s Bay, New Zealand. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 150, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.; Boulvais, P.; Mercadier, J.; Boiron, M.-C.; Cathelineau, M.; Cuney, M.; France-Lanord, C. From evaporated seawater to uranium-mineralizing brines: Isotopic and trace element study of quartz–dolomite veins in the Athabasca system. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 113, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xu, X.; Liang, J.; Yang, C.; Huang, M.; Su, Q. Machine learning-based seawater concentration pathway prediction. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 94, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herut, B.; Starinsky, A.; Katz, A.; Bein, A. The role of seawater freezing in the formation of subsurface brines. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getenet, M.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Otalora, F.; Emmerling, F.; Al-Sabbagh, D.; Verdugo-Escamilla, C. A Comprehensive Methodology for Monitoring Evaporitic Mineral Precipitation and Hydrochemical Evolution of Saline Lakes: The Case of Lake Magadi Soda Brine (East African Rift Valley, Kenya). Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starinsky, A.; Katz, A. The formation of natural cryogenic brines. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Hu, B.X.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Miao, J.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z. Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion to coastal aquifers and brine water/freshwater interaction in south coast of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Song, X.F.; Currell, M.J.; Yang, J.; Xiao, G. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarathinam, C.; Bhandary, H.; Ali, A. Strategies to characterize the geochemical interrelationship between coastal saline groundwater and seawater. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Dalai, T.K.; Samanta, S.; Rahaman, W.; Singh, S.K.; Horner, T.J. Geochemistry of uranium in the Ganga (Hooghly) River estuary, India: The role of processes in the water column and below the sediment-water interface. Mar. Chem. 2022, 247, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.B.; Calvert, S.E. The contrasting geochemical behaviours of iodine and bromine in recent sediments from the Namibian shelf. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1977, 41, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Q.; Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, B.; Yang, L.; Fu, T.; Liu, W.; Chen, G. Using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Combined with Multivariate Change-Point Analysis to Identify Brine Layers Based on the Geochemistry of the Core Sediment. Water 2023, 15, 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101926
Su Q, Yu H, Xu X, Chen B, Yang L, Fu T, Liu W, Chen G. Using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Combined with Multivariate Change-Point Analysis to Identify Brine Layers Based on the Geochemistry of the Core Sediment. Water. 2023; 15(10):1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101926
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Qiao, Hongjun Yu, Xingyong Xu, Bo Chen, Lin Yang, Tengfei Fu, Wenquan Liu, and Guangquan Chen. 2023. "Using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Combined with Multivariate Change-Point Analysis to Identify Brine Layers Based on the Geochemistry of the Core Sediment" Water 15, no. 10: 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101926
APA StyleSu, Q., Yu, H., Xu, X., Chen, B., Yang, L., Fu, T., Liu, W., & Chen, G. (2023). Using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Combined with Multivariate Change-Point Analysis to Identify Brine Layers Based on the Geochemistry of the Core Sediment. Water, 15(10), 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101926





