Bamboo-Activated Carbon Synthesized by One-Pot Pyrolysis and FeCl2 Activation for the Removal of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Activated Carbon
2.3. Characterization
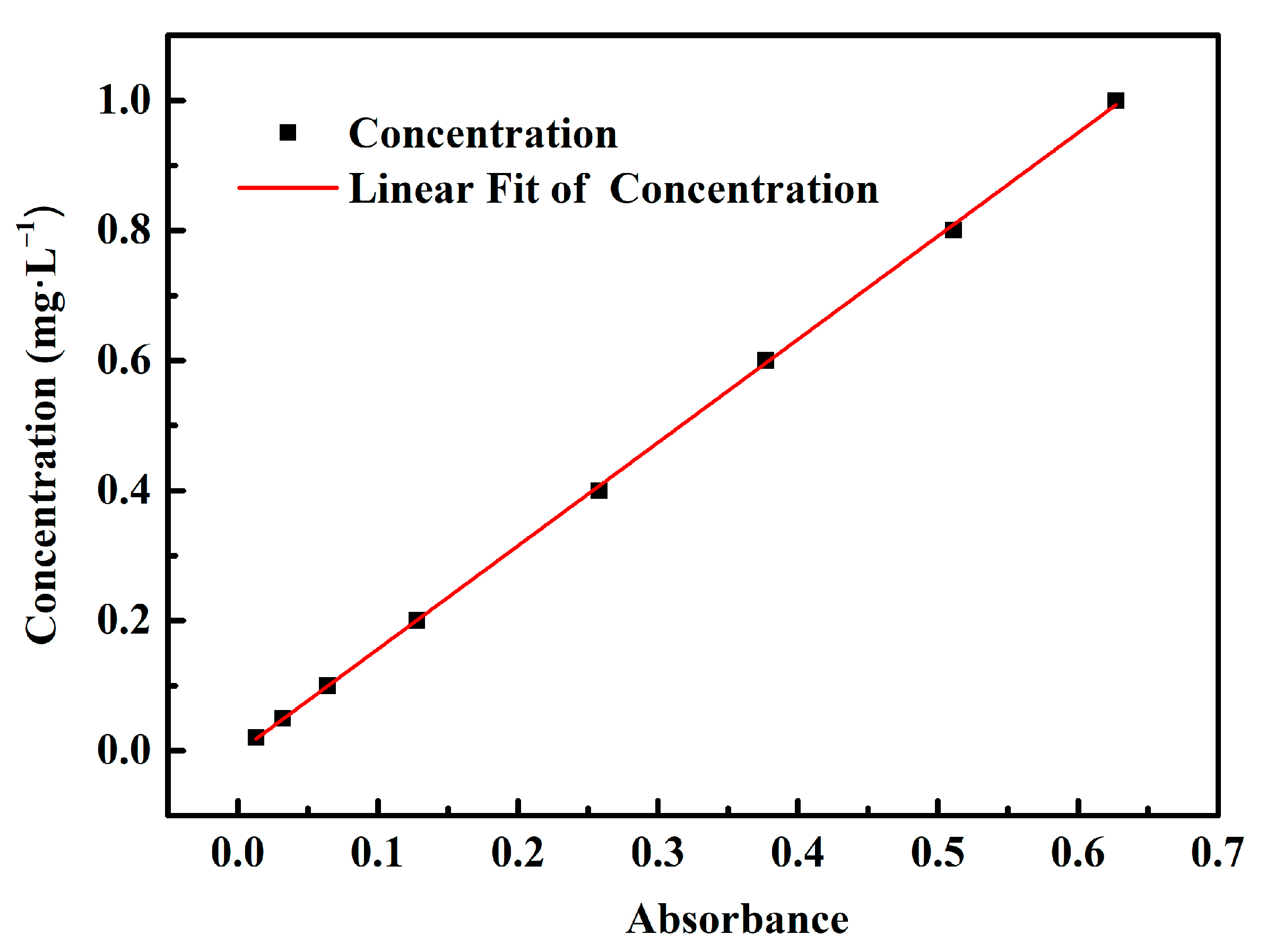
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
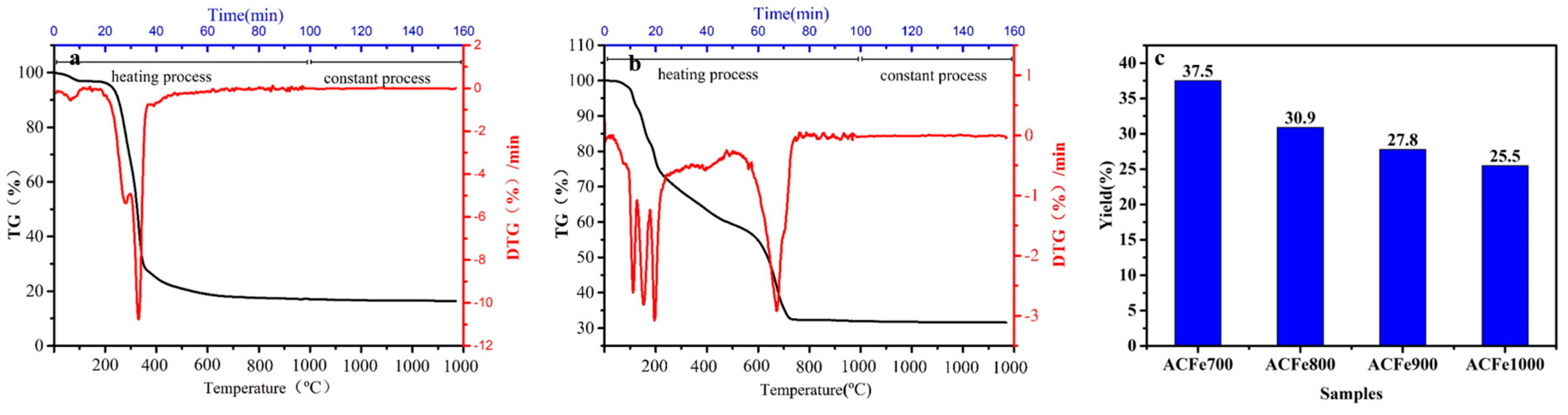
3.1. Thermal Analysis
3.2. Morphology Analysis
3.3. Pore Structural Analysis
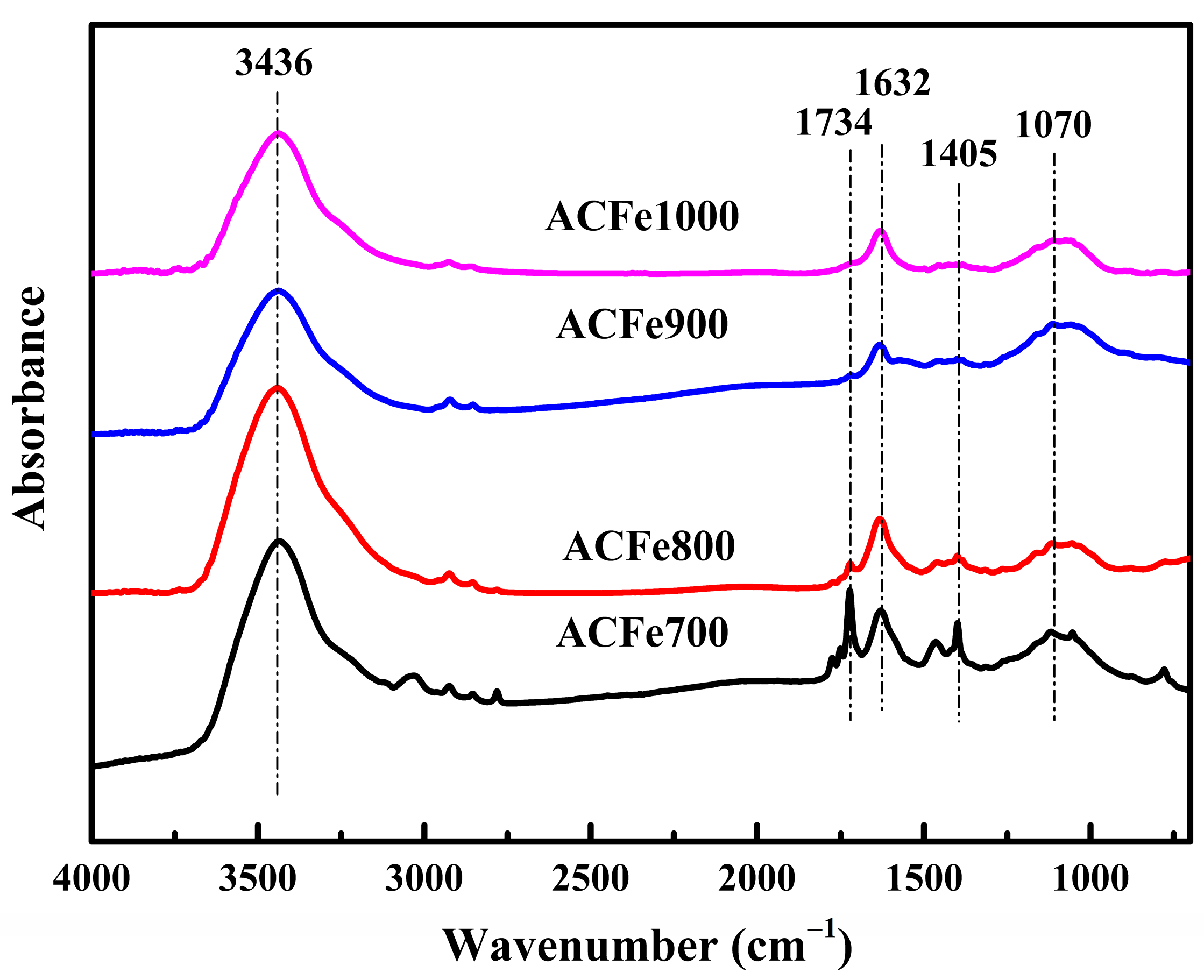
3.4. FTIR Analysis
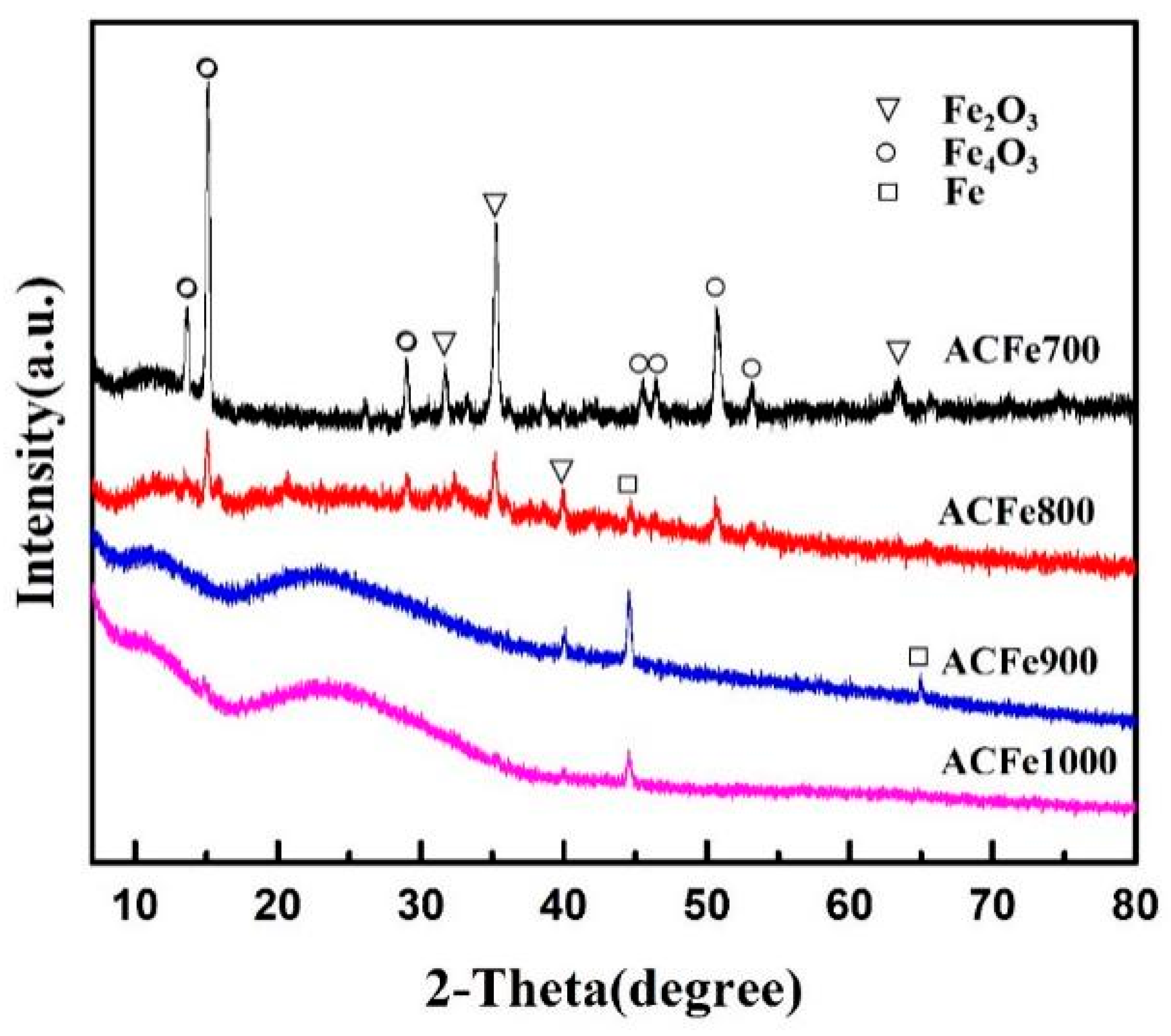
3.5. XRD Analysis
3.6. Sorption Studies
3.6.1. Sorption Capacity
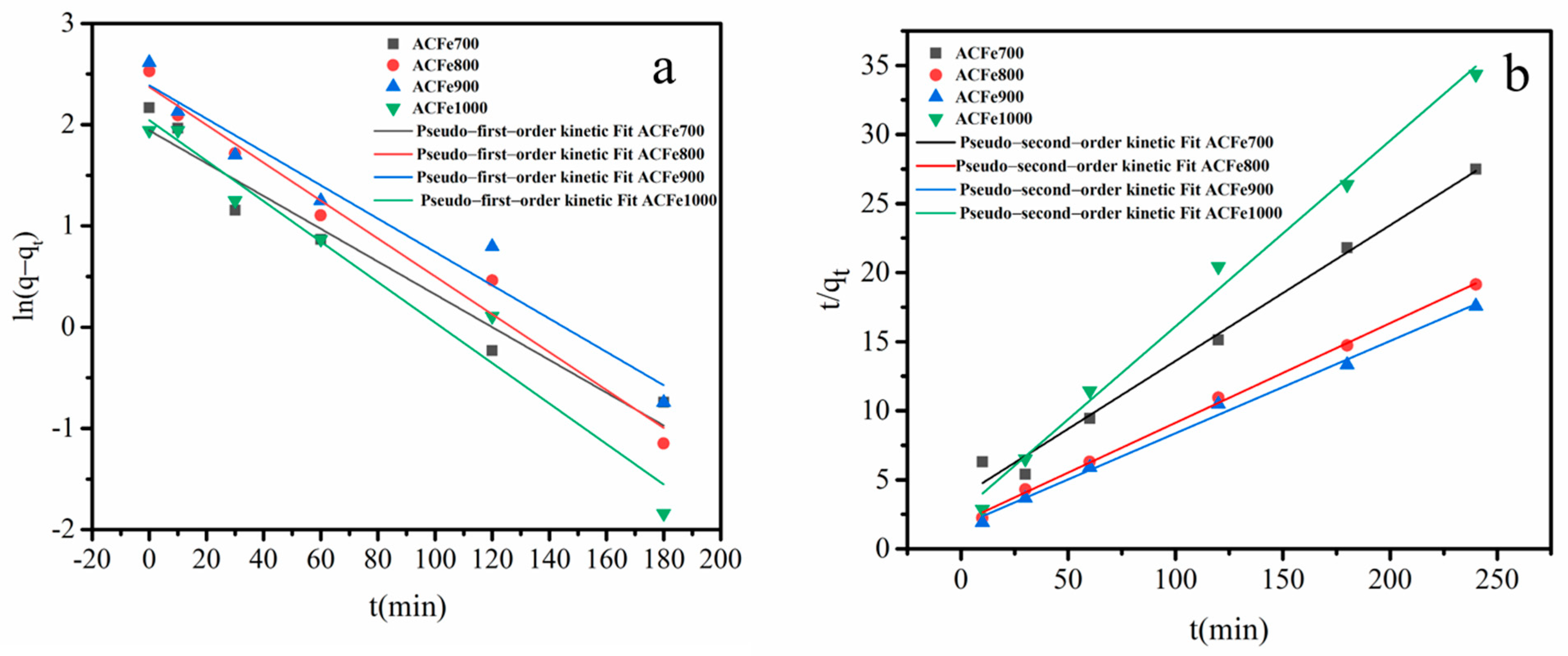
3.6.2. Adsorption Kinetics
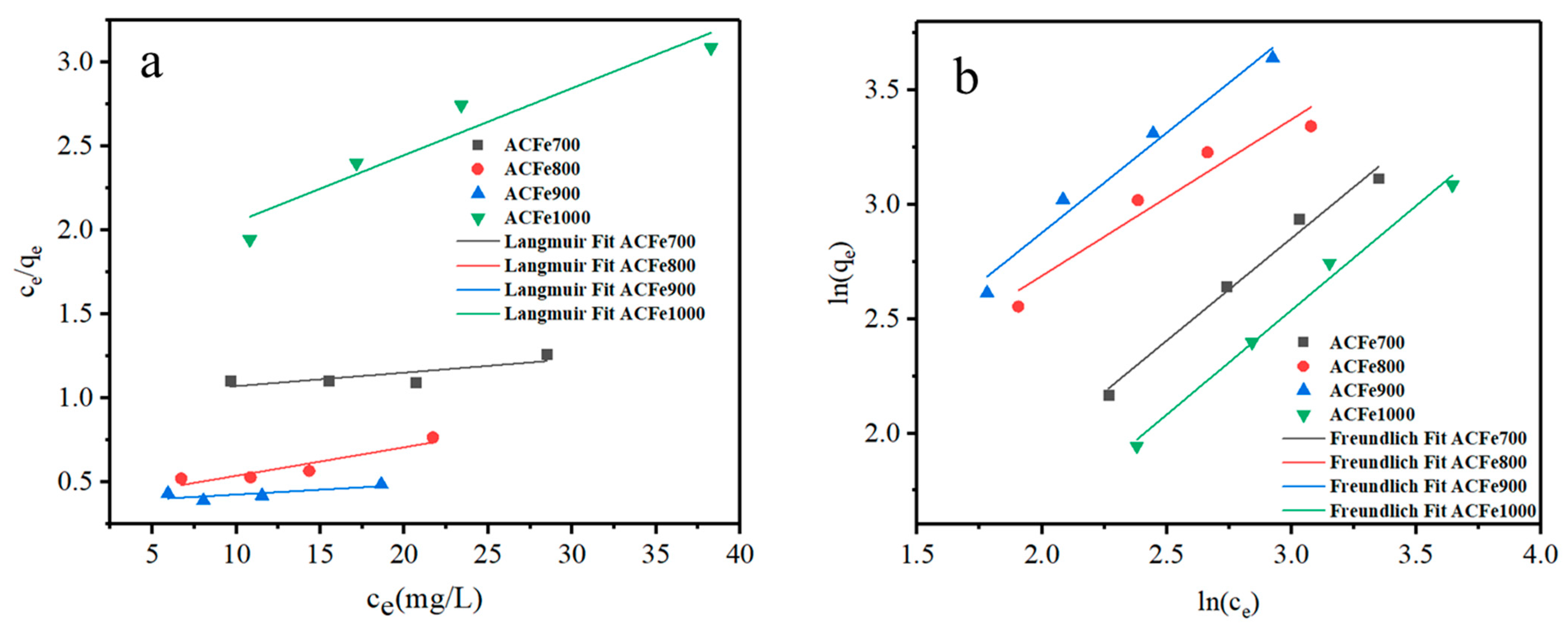
3.6.3. Isothermal Adsorption Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, D.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Qiao, J.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y. A 3D porous structured cellulose nanofibrils-based hydrogel with carbon dots-enhanced synergetic effects of adsorption and photocatalysis for effective Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; An, W.; Hu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, W. Removal of chromium (VI) by a self-regenerating and metal free g-C3N4/graphene hydrogel system via the synergy of adsorption and photo-catalysis under visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 219, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pađan, J.; Marcinek, S.; Cindrić, A.M.; Layglon, N.; Lenoble, V.; Salaün, P.; Garnier, C.; Omanović, D. Improved voltammetric methodology for chromium redox speciation in estuarine waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1089, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahador, F.; Foroutan, R.; Esmaeili, H.; Ramavandi, B. Enhancement of the chromium removal behavior of Moringa oleifera activated carbon by chitosan and iron oxide nanoparticles from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Sun, R.; Song, B.; Sun, Q.; Peng, P.; She, D. Preparation of nitrogen-doped porous carbon material by a hydrothermal-activation two-step method and its high-efficiency adsorption of Cr(VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cai, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, R.; Chen, X. Constructing Cd0.5Zn0.5S/Bi2WO6 S-scheme heterojunction for boosted photocatalytic antibiotic oxidation and Cr(VI) reduction. Adv. Powder Mater. 2023, 2, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P. CuBi2O4/calcined ZnAlBi-LDHs heterojunction: Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and tetracycline through effective adsorption and photocatalytic redox. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; An, B.; Chen, H.; Chu, J.; Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z. Botryoidal nanolignin channel stabilized ultrasmall PdNP incorporating with filter membrane for enhanced removal of Cr(VI) via synergetic filtration and catalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, X. Advances in sorptive removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] in aqueous solutions using polymeric materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Parakh, S.K.; Tong, Y.W. Health hazards of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] and its microbial reduction. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4923–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakade, V.E.; Tavengwa, N.T.; Madikizela, L.M. Recent advances in hexa-valent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by adsorptive methods. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26142–26164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of methylene blue in water onto activated carbon by surfactant modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Biomass-derived microporous carbon with large micropore size for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2020, 448, 227396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifetew, M.; Alemayehu, E.; Fito, J.; Worku, Z.; Prabhu, S.V.; Lennartz, B. Adsorptive removal of reactive yellow 145 dye from textile industry effluent using teff straw activated carbon: Optimization using central composite design. Water 2023, 15, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Liu, X.; Shang, L.; Tian, G.; Yang, S.; Ma, J. Research advance of adjustment for pore size distribution of plant-based activated carbon. Biomass Chem. Eng. 2022, 56, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. A study on the mechanism research on cellulose pyrolysis under catalysis of metallic salts. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Hamid, S.B.; Teh, S.J.; Lim, Y.S. Catalytic Hydrothermal upgrading of α-cellulose using iron salts as a lewis acid. Bioresources 2015, 10, 5974–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Gu, S.; Chen, W. Understanding reactions and pore-forming mechanisms between waste cotton woven and FeCl3 during the synthesis of magnetic activated carbon. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.C.; Pereira, E.; Guimaraes, I.R.; Vallone, A.; Pereira, M.; Mesquita, J.P.; Sapag, K. Preparation of activated carbons from coffee husks utilizing FeCl3 and ZnCl2 as activating agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmukai, Y.; Hasegawa, I.; Fujisawa, H.; Okuma, O.; Mae, K. Production of an iron-loaded carbonaceous material through pyrolyzing biomass impregnated with FeCl2. Fuel 2008, 87, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ba, Y.; Wang, X.; Niu, M.; Fang, K. Evolved gas analysis and slow pyrolysis mechanism of bamboo by thermogravimetric analysis, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.A.; Mostafa, M.E. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetic parameters determination of biomass fuel powders by differential thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA/DTG). Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; Lin, L.D. Adsorption capacity and removal efficiency of heavy metal ions by Moso and Ma bamboo activated carbons. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Xing, Z.J.; Duan, Z.K.; Li, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of steam activation on the pore structure and surface chemistry of activated carbon derived from bamboo waste. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 315, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.G.; Pliego-Cuervo, Y.B. Physicochemical and microtextural characterization of activated carbons produced from water steam activation of three bamboo species. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 99, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.P.S.; Jawaid, M.; Firoozian, P.; Rashid, U.; Islam, A.; Akil, H.M. Activated carbon from various agricultural wastes by chemical activation with KOH: Preparation and characterization. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2013, 7, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, M.; Chang, J. Study on fabrication of bamboo based high specific surface area activated carbon. Chem. Ind. For. Prod. 2001, 21, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J. Preparation of Bamboo Based Activated Carbon and Its Application in Chromium Waste Water Treatment. Master’s Thesis, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huan, B.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Biomass-based pyrolytic polygeneration system for bamboo industry waste: Evolution of the char structure and the pyrolysis mechanism. Energy Fuel 2016, 30, 6430–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Xu, L.; Dong, H.; Hu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y. Advanced nanonetwork-structured carbon materials for high-performance formaldehyde capture. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2019, 537, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaikwad, M.S.; Balomajumder, C. Removal of Cr(VI) and fluoride by membrane capacitive deionization with nanoporous and microporous Limonia acidissima (wood apple) shell activated carbon electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tian, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Deng, H. Highly porous activated carbon synthesized by pyrolysis of polyester fabric wastes with different iron salts: Pore development and adsorption behavior. Colloid. Surface A 2019, 565, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, M.; Xing, J.; Bi, W.; Wang, K.; Ma, J. Effects of biomass pre-pyrolysis and pyrolysis temperature on magnetic biochar properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 127, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Pang, L.; He, Z.; Sun, S. Research on performance of FeCl3 and FeCl2 solution systems. J. Shandong Jiaotong Univ. 2012, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, G.; Qian, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Facile fabrication of magnetic carbon composites from hydrochar via simultaneous activation and magnetization for triclosan adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5840–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Saini, C.; Kumar, E.A.; Singh, S.K. In situ casting of rice husk ash in metal organic frameworks induces enhanced CO2 capture performance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, L.; Jin, X.; Lian, H.; Zheng, J. Preparation of a novel activated carbon from cassava sludge for the high-efficiency adsorption of hexavalent chromium in potable water: Adsorption performance and mechanism insight. Water 2021, 13, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Shahi, G.; Meena, V.; Meena, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Singh, R.; Rai, B.N. Removal of hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) using activated carbon prepared from mango kernel activated with H3PO4. Resour. Technol. 2016, 2, S63–S70. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, D.; Rajput, S.; Singh, V.K.; Steele, P.H.; Pittman, C.U. Modeling and evaluation of chromium remediation from water using low cost biochar, a green adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, Z.; Ali, R.; Naushad, M. Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous medium by activated carbon prepared from peanut shell: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, W. Adsorption behavior comparison of trivalent and hexavalent chromium on biochar derived from municipal sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ren, H.; Kruse, A.; Cui, R. Polyethylene imine modified hydrochar adsorption for chromium (VI) and nickel (II) removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlabji, T.; El-Nemr, M.A.; Nemr, A.E.; Ragab, S.; Alghamdi, M.M.; El-Zahhar, A.A.; Idris, A.A.; Monit Said, T.O. High surface area microporous activated carbon from Pisum sativum peels for hexavalent chromium removal from aquatic environment. Toxin Rev. 2022, 41, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Activated carbon from tomato stem by chemical activation with FeCl2. Colloid. Surface A 2017, 529, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


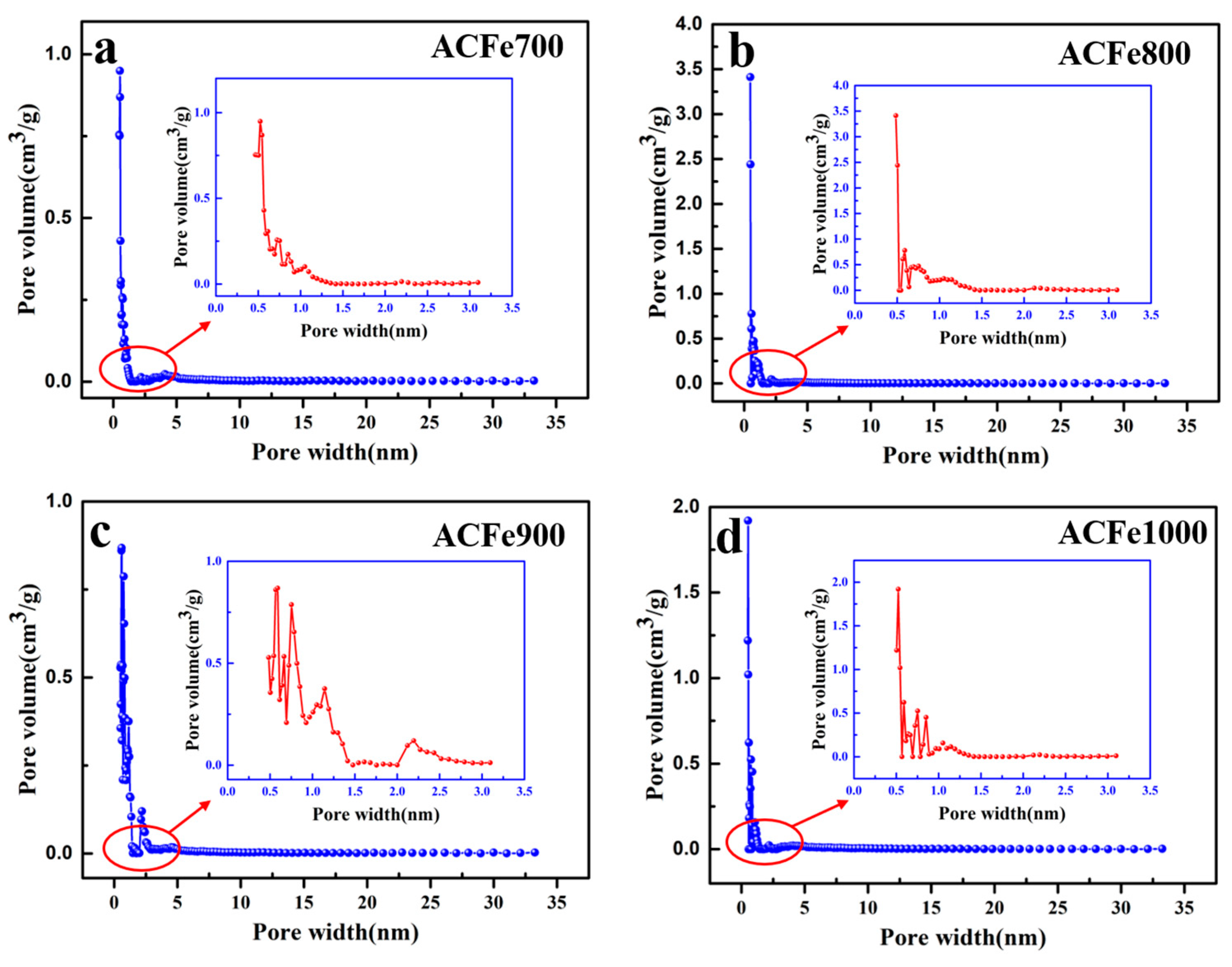

| Samples | SBET (m2/g) | Smic (m2/g) | Smes (m2/g) | Vtot (m3/g) | Vmic (m3/g) | Vmes (m3/g) | Dp (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACFe700 | 670.00 | 581.21 | 54.76 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 2.32 |
| ACFe800 | 1030.36 | 944.18 | 54.95 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 2.09 |
| ACFe900 | 1290.93 | 1192.19 | 69.70 | 0.67 | 0.49 | 0.17 | 2.08 |
| ACFe1000 | 719.09 | 510.92 | 42.93 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 2.27 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| ACFe900 | 13.65 | Present work |
| Cassava sludge | 9.84 | [38] |
| Mango kernel | 6.08 | [39] |
| Oak wood | 5.50 | [40] |
| Peanut shell | 8.31 | [41] |
| Municipal sludge | 7.00 | [42] |
| Adsorbent | Experimental Value | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe.exp (mg/g) | qe.cal (mg/g) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | qe.cal (mg/) | K2 (g/mg·min) | R2 | |
| ACFe700 | 8.73 | 6.98 | 0.0162 | 0.9460 | 9.51 | 0.0035 | 0.9858 |
| ACFe800 | 12.86 | 10.73 | 0.0187 | 0.9719 | 13.87 | 0.0031 | 0.9977 |
| ACFe900 | 13.65 | 10.91 | 0.0164 | 0.9470 | 14.97 | 0.0032 | 0.9929 |
| ACFe1000 | 6.98 | 5.72 | 0.0199 | 0.9570 | 7.43 | 0.0078 | 0.9914 |
| Adsorbent | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | KL (L/g) | R2 | KF (L/g) | n | R2 | |
| ACFe700 | 123.61 | 0.008 | 0.4557 | 1.22 | 1.12 | 0.9788 |
| ACFe800 | 59.00 | 0.045 | 0.8130 | 3.55 | 1.14 | 0.9346 |
| ACFe900 | 175.13 | 0.015 | 0.7123 | 3.74 | 1.46 | 0.9932 |
| ACFe1000 | 25.09 | 0.024 | 0.8803 | 1.18 | 1.09 | 0.9854 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, M.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Shang, L. Bamboo-Activated Carbon Synthesized by One-Pot Pyrolysis and FeCl2 Activation for the Removal of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solutions. Water 2023, 15, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101891
Zhong M, Liu X, Ma J, Shang L. Bamboo-Activated Carbon Synthesized by One-Pot Pyrolysis and FeCl2 Activation for the Removal of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solutions. Water. 2023; 15(10):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101891
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Meijuan, Xinge Liu, Jianfeng Ma, and Lili Shang. 2023. "Bamboo-Activated Carbon Synthesized by One-Pot Pyrolysis and FeCl2 Activation for the Removal of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solutions" Water 15, no. 10: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101891
APA StyleZhong, M., Liu, X., Ma, J., & Shang, L. (2023). Bamboo-Activated Carbon Synthesized by One-Pot Pyrolysis and FeCl2 Activation for the Removal of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solutions. Water, 15(10), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101891






