Pumping Induced Hydraulic Gradient Driven Tracer Migration through Defects: Implications for Rapid Detection of Leakage in Vertical Flexible Barrier
Abstract
:1. Introduction
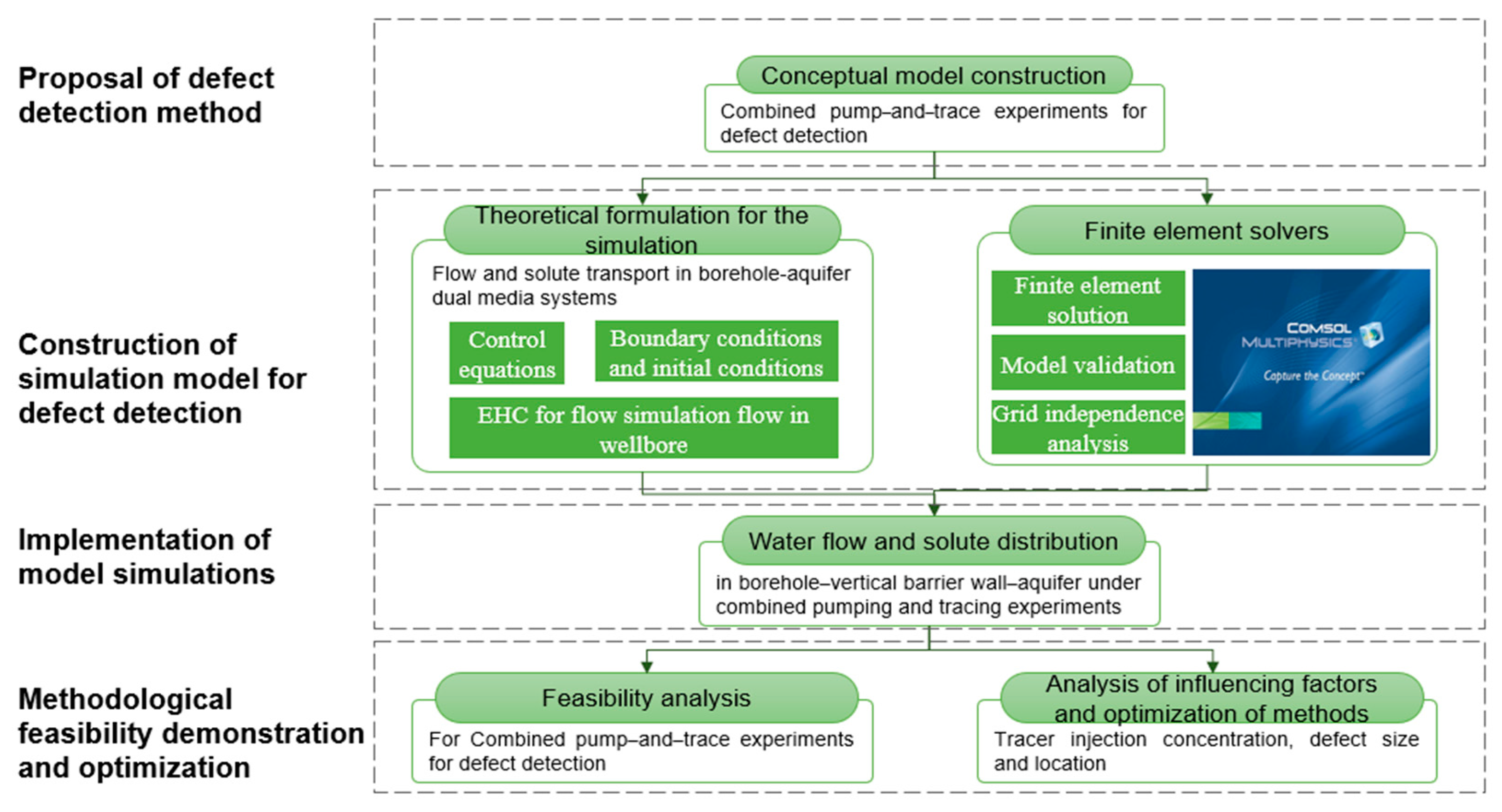
2. Model and Method
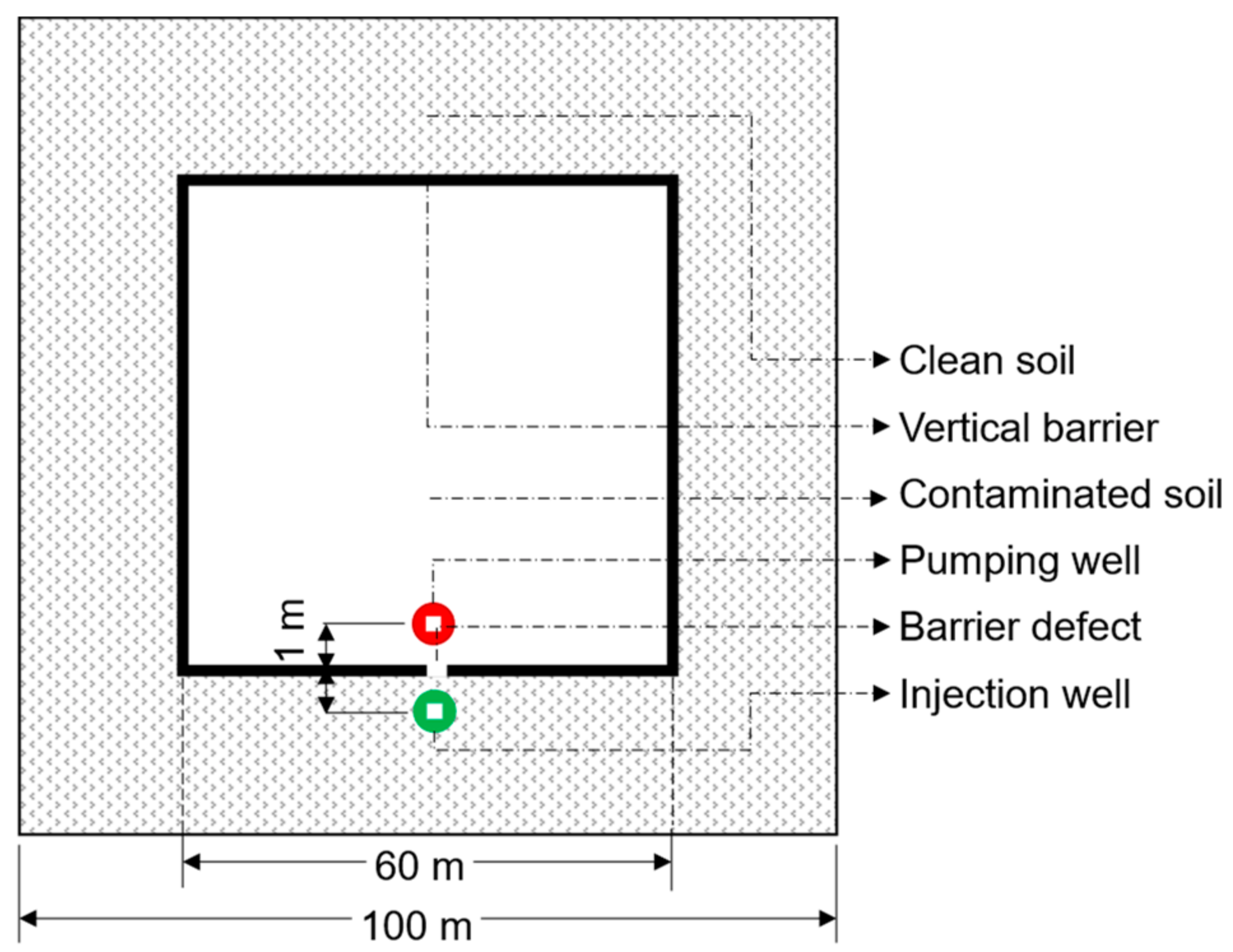
2.1. Typical Scenario Construction
2.2. Simulation of Pumping and Tracer Penetration Process
2.2.1. Expression of Equivalent Conductivity Coefficient in Well Pipe
2.2.2. Water Flow Control Equation in Wellbore Pore Media System
2.2.3. Solute Field
2.2.4. Boundary Conditions and Initial Conditions
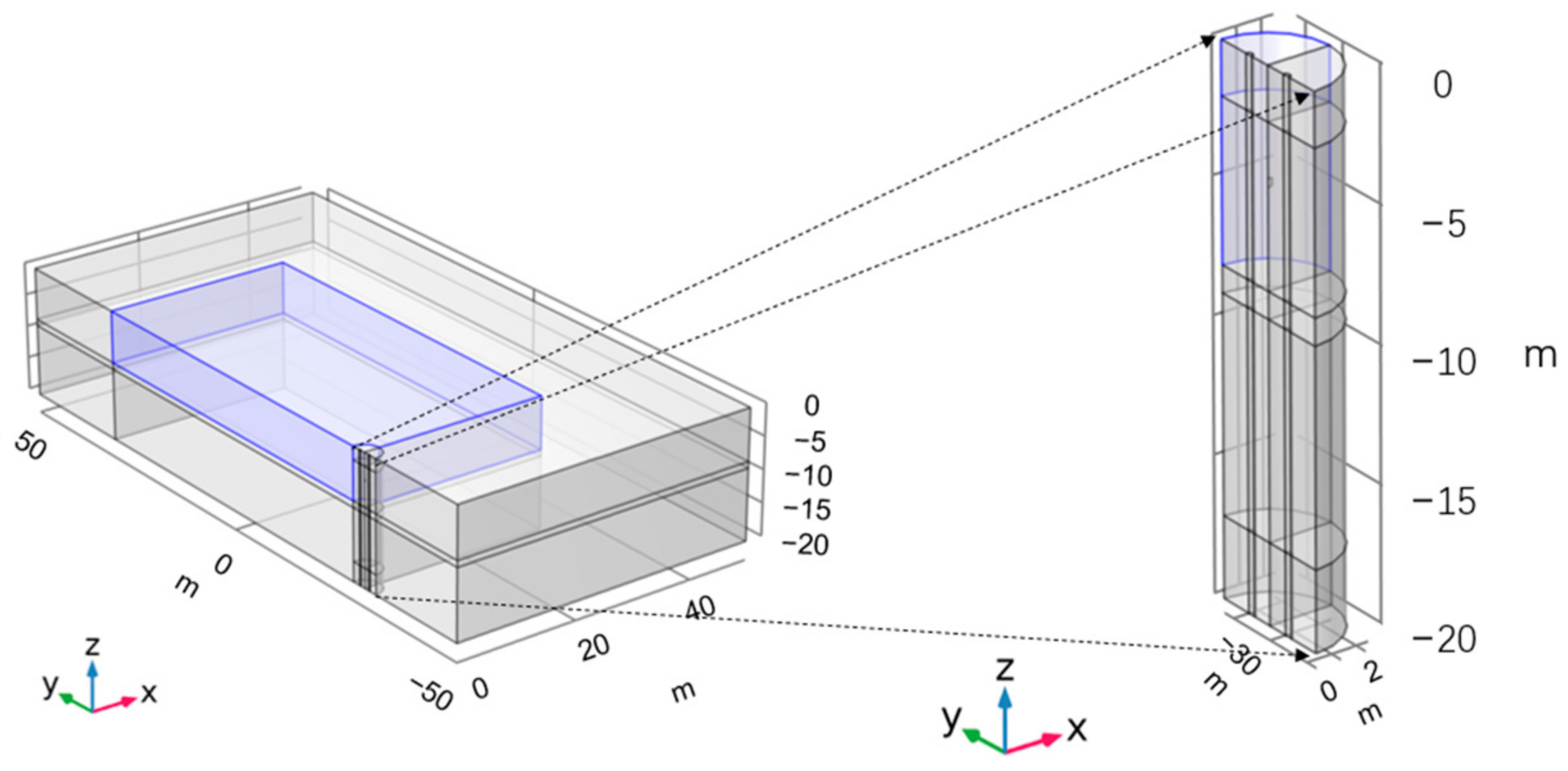
2.3. Geometric Model and Mesh Generation
3. Results and Discussion
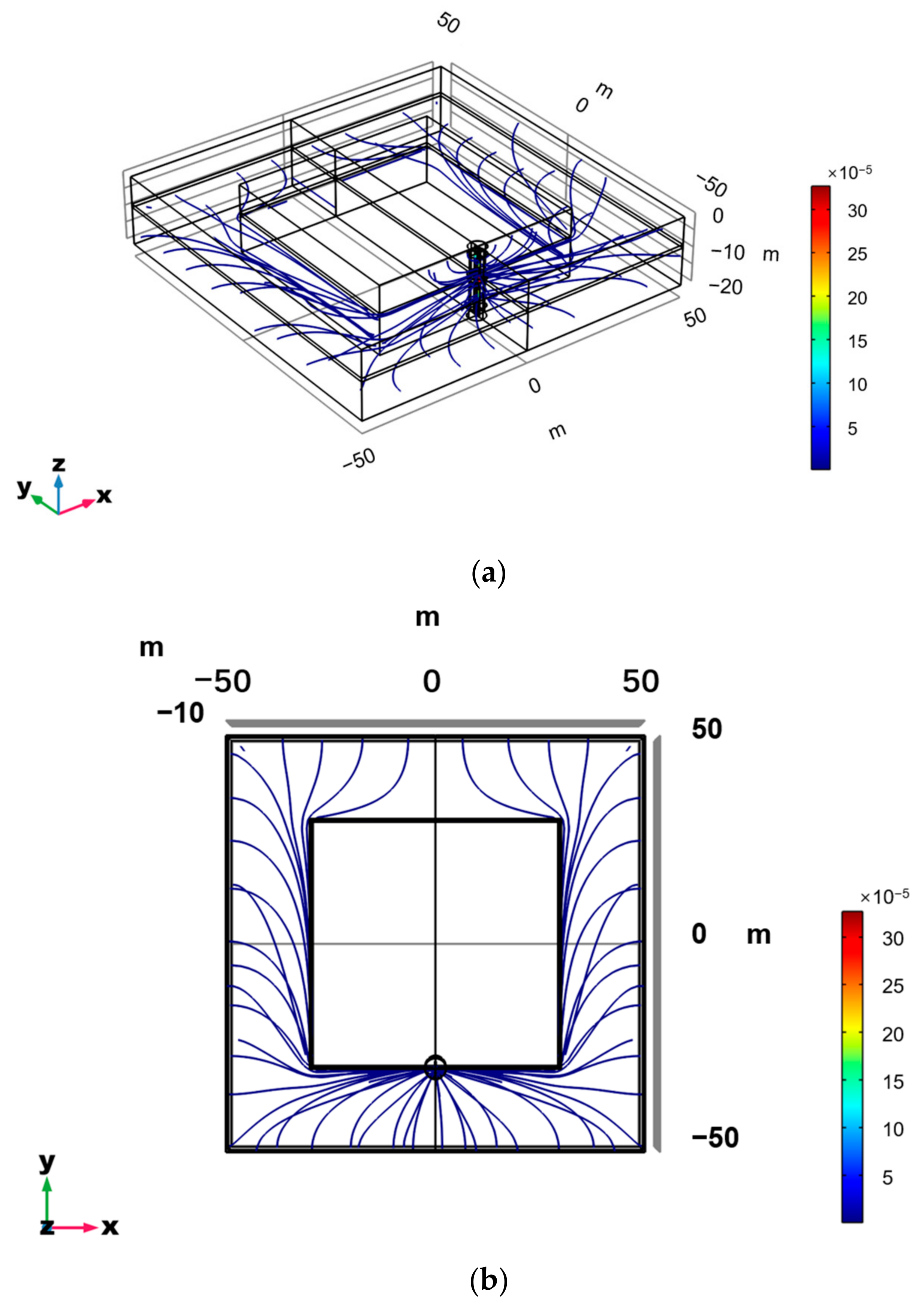
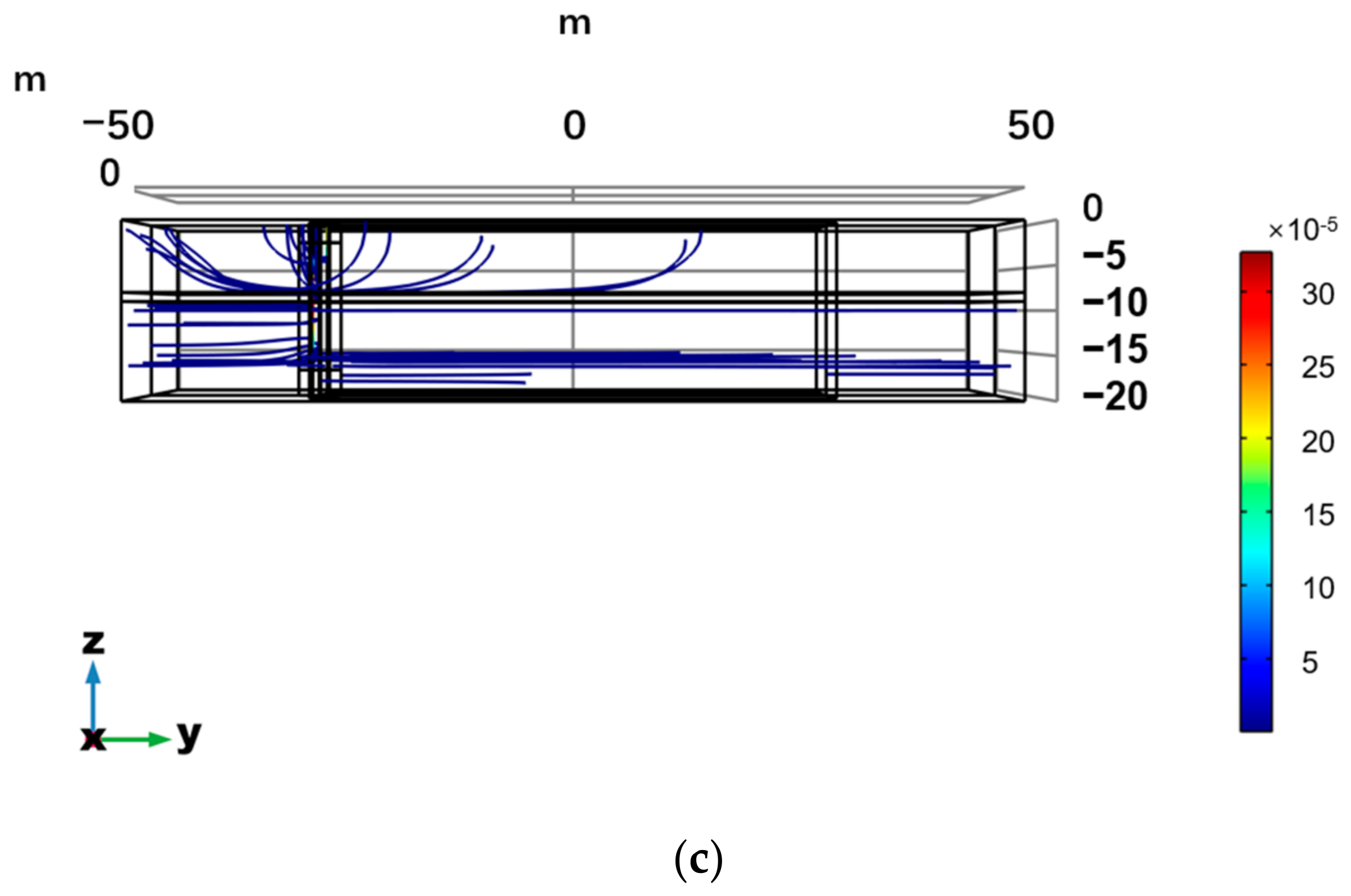
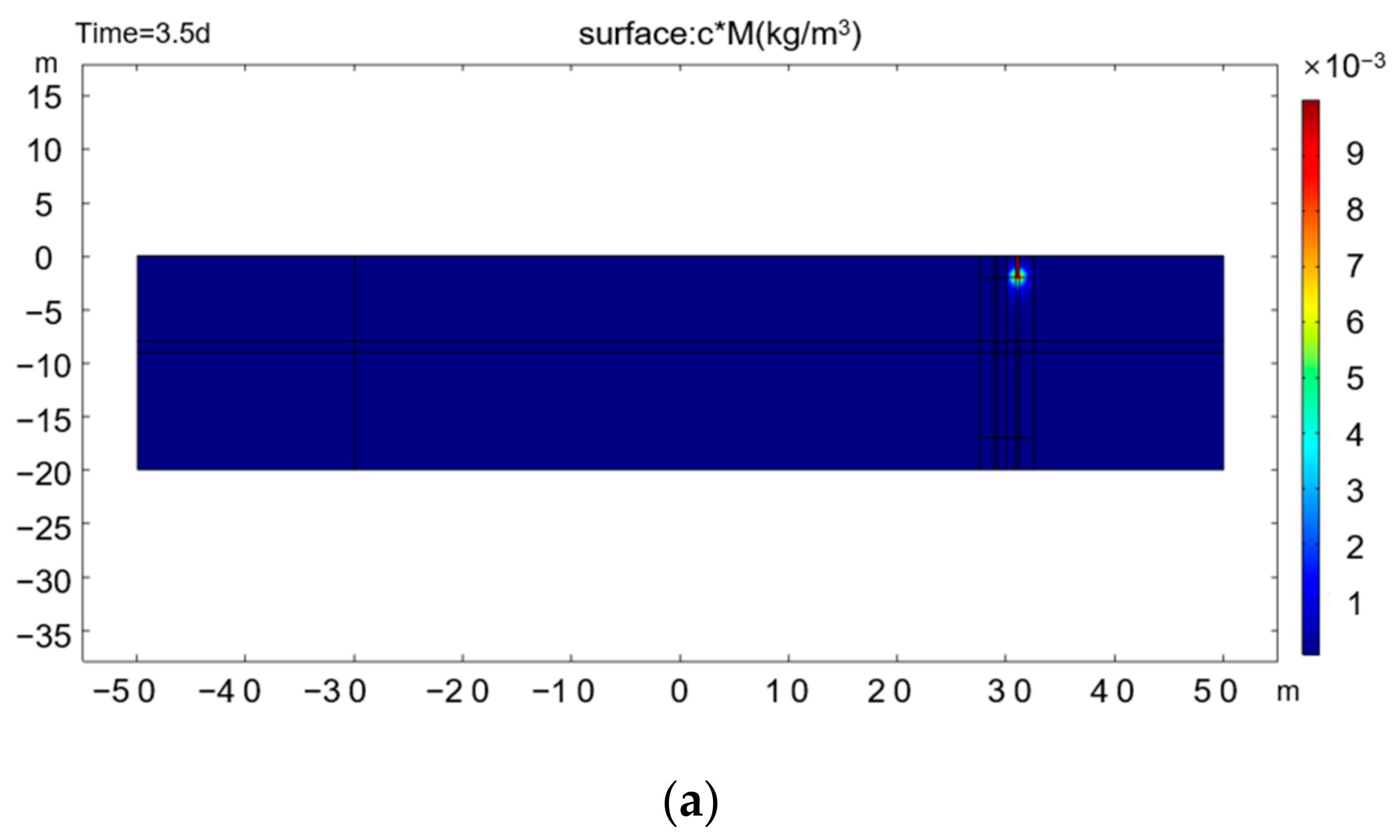
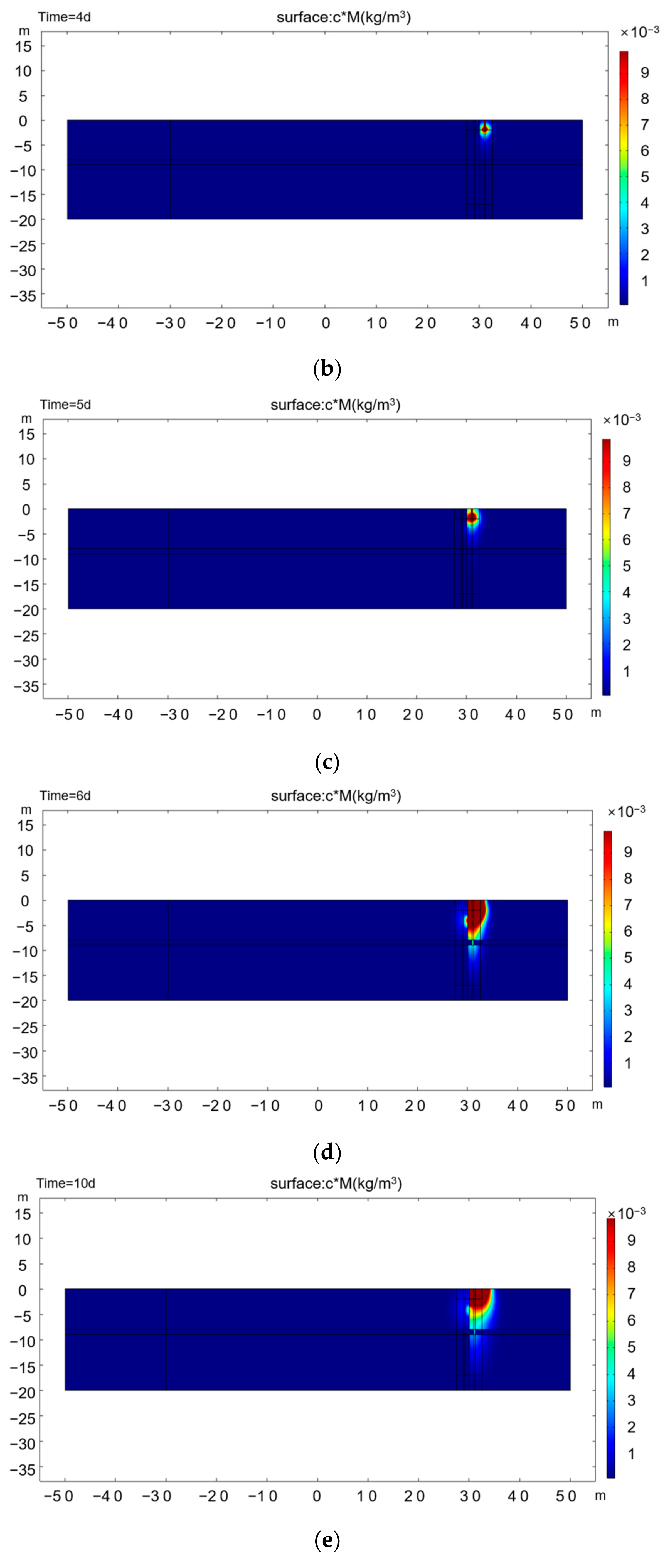
3.1. Simulation Results in Typical Scenes
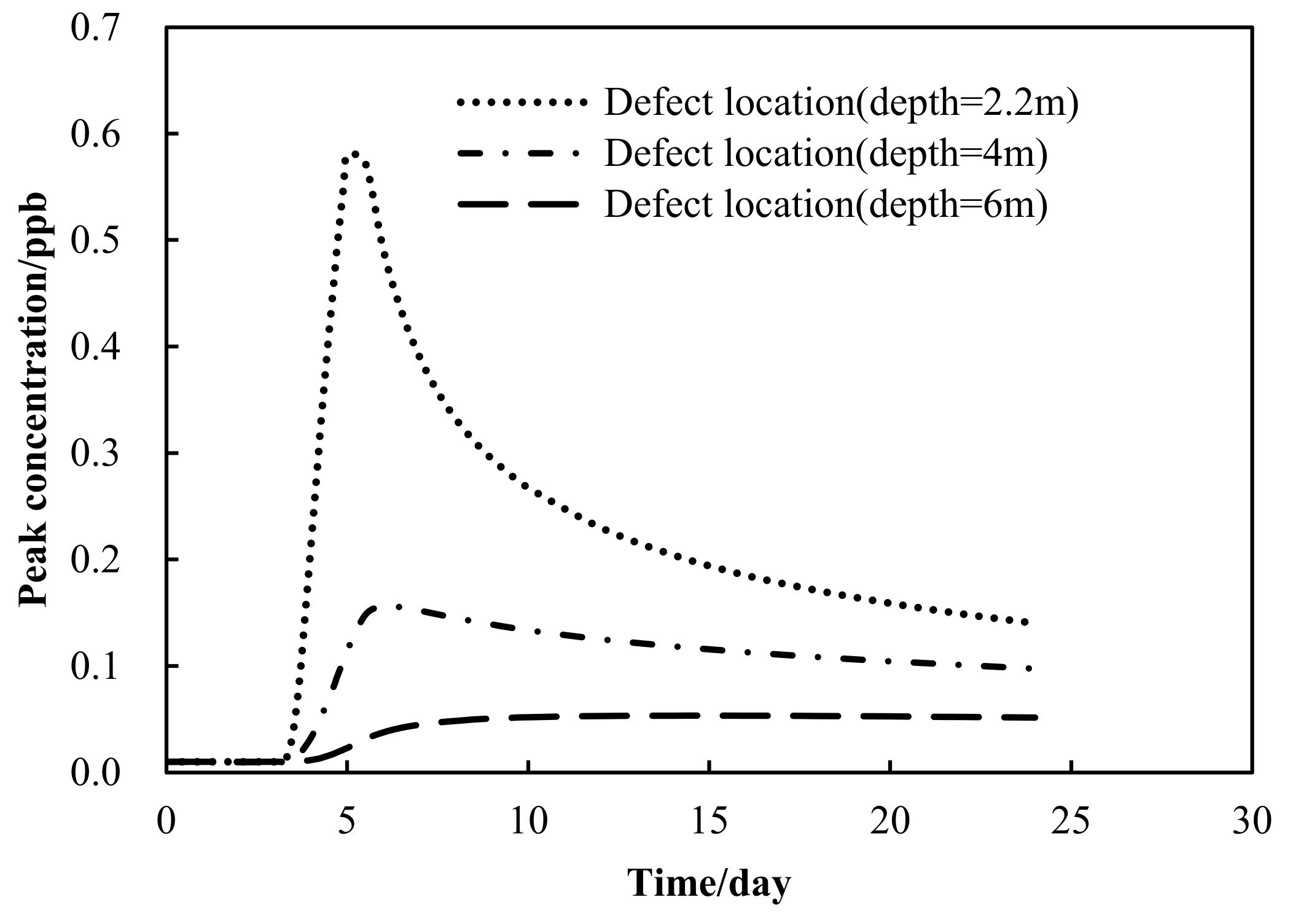
3.2. Influence of Defect Location on Detection Performance
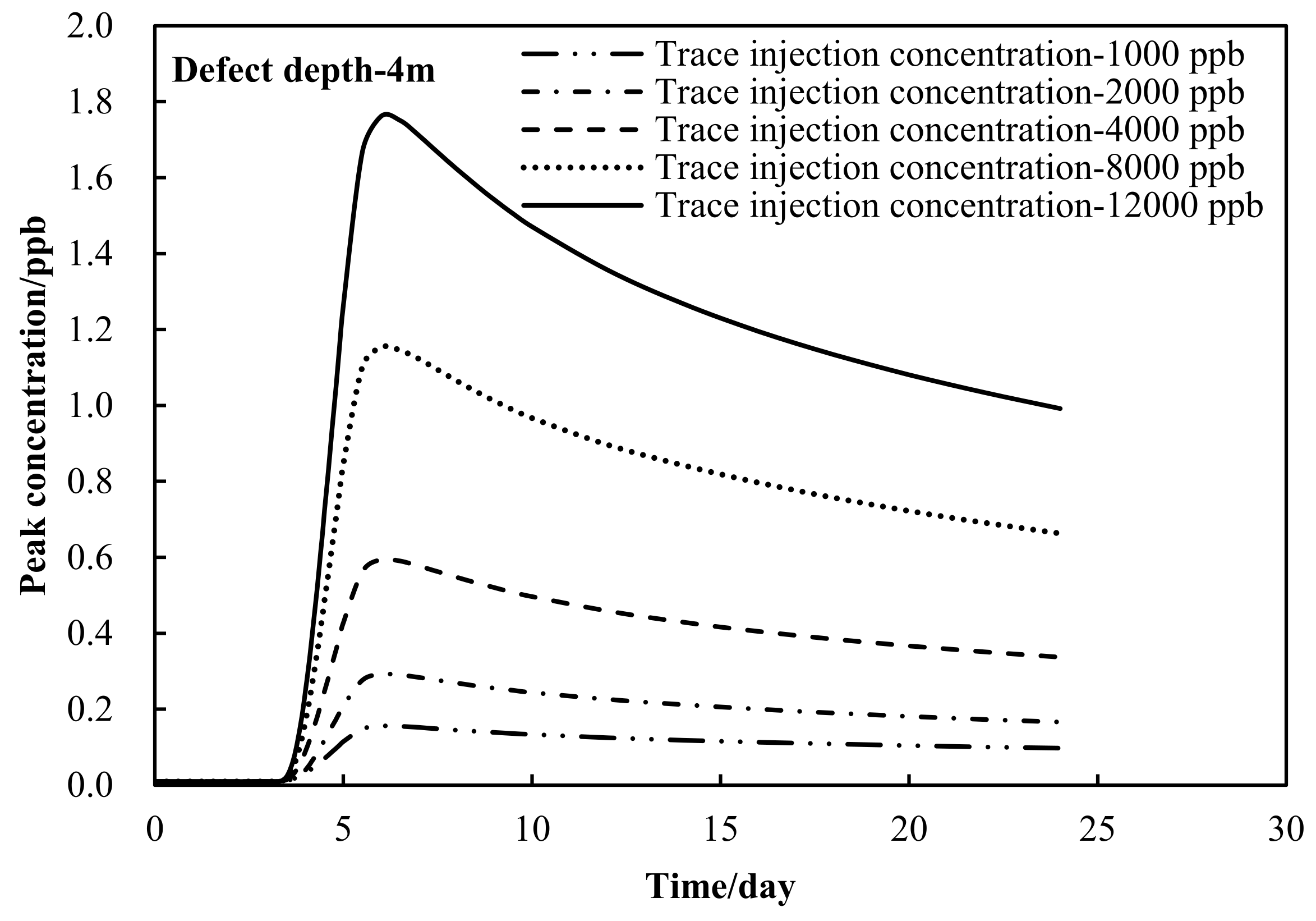
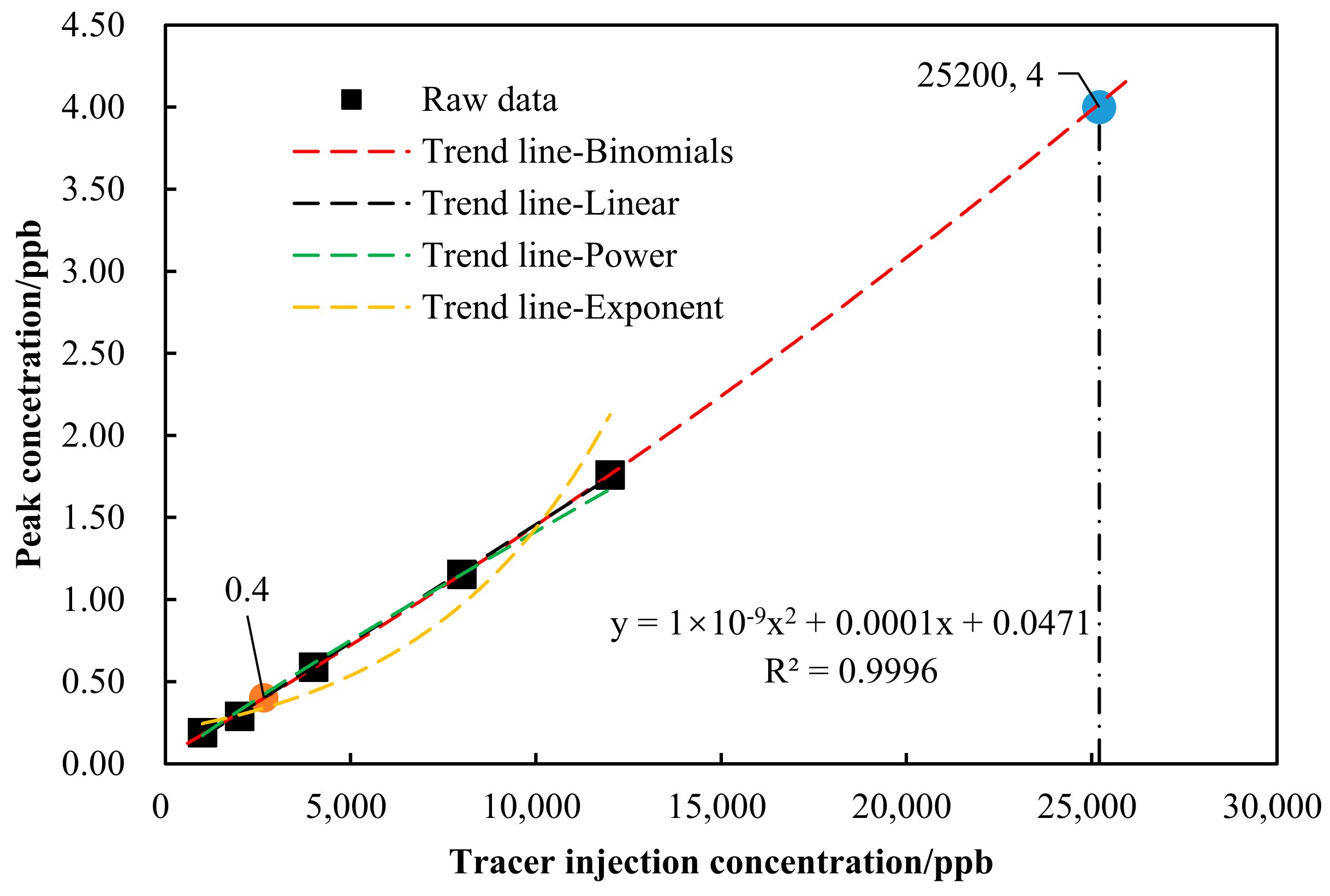
3.3. Effect of Injection Concentration on Detection Performance
3.4. Impact of Defect Size on Detection Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sankoh, A.A.; Amara, J.; Komba, T.; Laar, C.; Sesay, A.; Derkyi, N.S.; Frazer-williams, R. Seasonal assessment of heavy metal contamination of groundwater in two major dumpsites in Sierra Leone. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2185955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong-Anane, A.B.; Quiñones, K.Y.D.; Harris, W.; Townsend, T.; Bonzongo, J.C.J. Iron reductive dissolution in vadose zone soils: Implication for groundwater pollution in landfill impacted sites. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 94, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, D.; Birindelli, F.; Rinaldi, M.; Vettraino, E.; Bezzi, A. Fluorescent tracer tests for detection of dam leakages: The case of the Bumbuna dam—Sierra Leone. Eng. Geol. 2016, 205, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidichimo, F.; De Biase, M.D.; Straface, S. Groundwater pollution assessment in landfill areas: Is it only about the leachate. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darilek, G.T.; Laine, D.L. Costs and benefits of geomembrane liner installation CQA. In Proceedings of the Geosynthetics 2001 Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 12–14 February 2001; pp. 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Soupios, P.M.; Loupasakis, C.; Vallianatos, F. Reconstructing former urban environments by combining geophysical electrical methods and geotechnical investigations—An example from Chania, Greece. J. Geophys. Eng. 2008, 5, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luück, E.; Ruehlmann, J.; Kirchmann, H. Properties of soils from the Swedish long-term fertility experiments: VI. Map-ping soil electrical conductivity with different geophysical methods. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant. Sci. 2011, 61, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Ding, Z.; Shi, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, Z. Groundwater pollution risk assessment based on groundwater vulnerability and pollution load on an isolated island. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Wilson, A.M.; Rostron, B.J. Groundwater age, brine migration, and large-scale solute transport in the Alberta Basin, Canada. Geofluids 2015, 15, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaiji, Z.; Wenfeng, D.; Zhengwen, L.; Xiaoyu, G. Migration and pollution control of chlorinated hydrocarbons in groundwater system of eastern Jinan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Ravindra, K.; Dahiya, R.P.; Chandra, A. Leachate Characterization and Assessment of Groundwater Pollution Near Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Site. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 118, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey LM, S.; Shukla, S.K.; Habibi, D. Resistivity profiles of Perth soil in Australia in leak-detection test. Geotech. Res. 2017, 4, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvar, K.; Yurii, O. Phreatic seepage around a rectilinear cutoff wall: The Zhu-kovsky-Vedernikov-Polubarinova-Kochina dispute revisited. Adv. Water Resour. 2023, 173, 104367. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.X.; Wan, J.W.; Zhan, H.B. Theoretical and experimental studies of coupled seepage-pipe flow to a horizontal well. J. Hydrol. 2003, 281, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.T.; Chen, C.X.; Chen, X.H. Simulation of groundwater flow within observation boreholes for confined aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2011, 398, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilip, K.J.; Naveen, K.; Raja, R.Y. Analytical solution for transport of pollutant from time-dependent locations along groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127826. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Y.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Illman, W.A.; Mok, C.M.W.; Tso, C.H.M.; Carrera, B.A.; Wang, Y.L. Exploitation of pump-and-treat remediation systems for characterization of hydraulic heterogeneity. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwede, R.L.; Li, W.; Leven, C.; Cirpka, O.A. Three-dimensional geostatistical inversion of synthetic tomographic pumping and heat-tracer tests in a nested-cell setup. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 63, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, D.L.; Cook, P.G.; Simmons, C.T.; McCallum, J.M.; Noorduijn, S.L.; Dogramaci, S. A constant rate salt tracer injection method to quantify pumped flows in long-screened or open borehole wells. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Lin, P.; Xu, Z.H. Laboratory and temporal moment analysis of tracer-based solute transport in karst conduits. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 306–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiperski, F.; Oertwich, M.; Scheytt, T.; Licha, T. Solubility of Tinopal CBS-X fluorescent dye at different EDTA concentrations and pH values: Implications regarding its applicability in field tracer tests. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiperski, F.; Gabrovsek, F. Spreading of tracer plumes through confined telogenetic karst aquifers: A model. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Isokangas, E.; Ronkanen, A.K.; Rossi, P.M.; Marttila, H.; Kløve, B. A tracer-based method for classifying groundwater dependence in boreal headwater streams. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. National Oil and Hazardous Substance Pollution Contingency Plan [EB/OL]; Final Rule, 50 Federal Register 47912; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1985.
- Gao, H.; Tatomir, A.B.; Karadimitriou, N.K.; Steeb, H.; Sauter, M. Reservoir characterization by push-pull tests employing kinetic interface sensitive tracers—A pore-scale study for understanding large-scale processes. Adv. Water Resour. 2023, 174, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, N.M.; Clark, J.F.; Fisher, A.T.; Wheat, C.G.; Haymon, R.M.; Becker, K. Cross-hole tracer experiment reveals rapid fluid flow and low effective porosity in the upper oceanic crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 450, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Inner Aquifer | Outer Aquifer | Fluid Density (kg/m3) | Dynamic Viscosity Coefficient (Pa∙s) | Permeability Coefficient of Impervious Membrane Defect (cm/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Permeability Coefficient (cm/s) | Porosity | Permeability Coefficient (cm/s) | ||||
| First layer | 0.5 | 2 × 10−3 | 0.5 | 10−3 | 1000 | 0.001 | (Outside + inside)/2 |
| Second layer | 0.5 | 10−8 | 0.5 | 10−8 | |||
| Third layer | 0.5 | 2 × 10−4 | 0.5 | 10−4 | |||
| Defect Depth, m | Response Concentration | Peak Concentration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration, ppb | Response Time, t | Concentration, ppb | Reach Time | |
| 2.2 | 0.4 | 4.4–4.5 | 0.58 | 5 |
| 4 | / | 0.16 | 6 | |
| 6 | / | 0.054 | 14 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Qiu, P.; Dong, L. Pumping Induced Hydraulic Gradient Driven Tracer Migration through Defects: Implications for Rapid Detection of Leakage in Vertical Flexible Barrier. Water 2023, 15, 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101882
Li X, Chen Z, Xu Y, Liu Y, Zhao M, Qiu P, Dong L. Pumping Induced Hydraulic Gradient Driven Tracer Migration through Defects: Implications for Rapid Detection of Leakage in Vertical Flexible Barrier. Water. 2023; 15(10):1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101882
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xingrong, Zengsiche Chen, Ya Xu, Yuqiang Liu, Manying Zhao, Panpan Qiu, and Lu Dong. 2023. "Pumping Induced Hydraulic Gradient Driven Tracer Migration through Defects: Implications for Rapid Detection of Leakage in Vertical Flexible Barrier" Water 15, no. 10: 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101882
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, Z., Xu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, M., Qiu, P., & Dong, L. (2023). Pumping Induced Hydraulic Gradient Driven Tracer Migration through Defects: Implications for Rapid Detection of Leakage in Vertical Flexible Barrier. Water, 15(10), 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101882






