Drag Coefficient Parameterization under Hurricane Wind Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
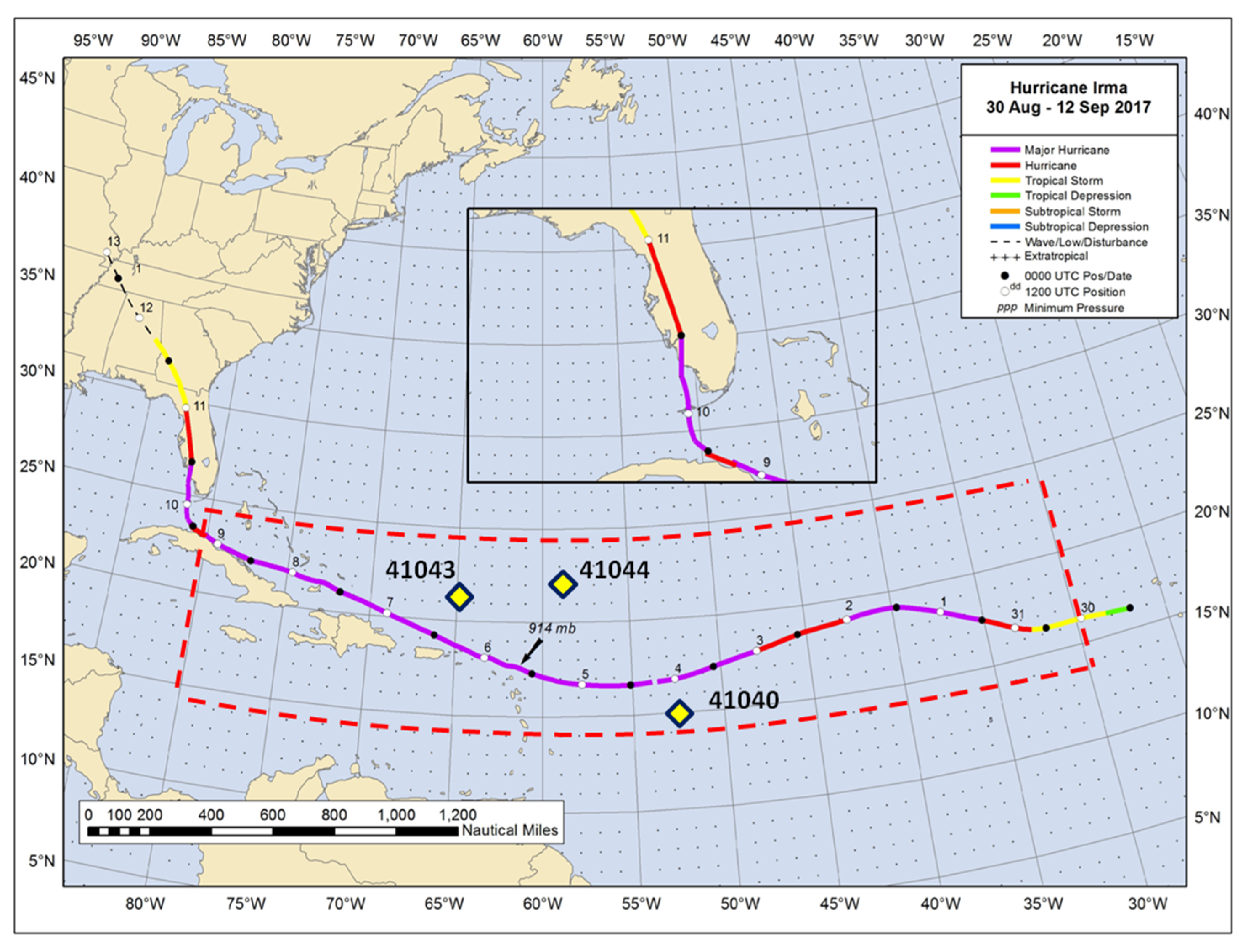
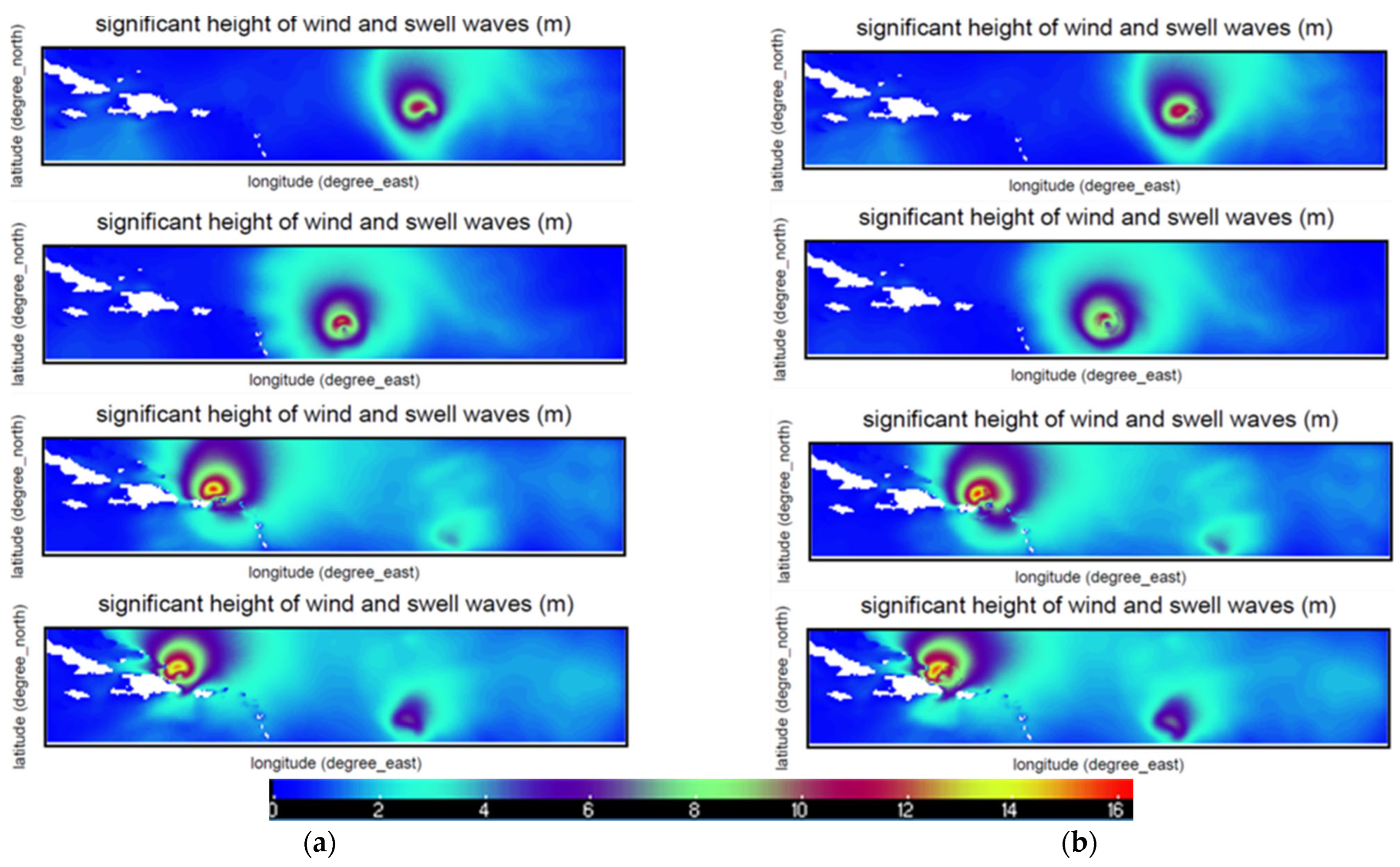
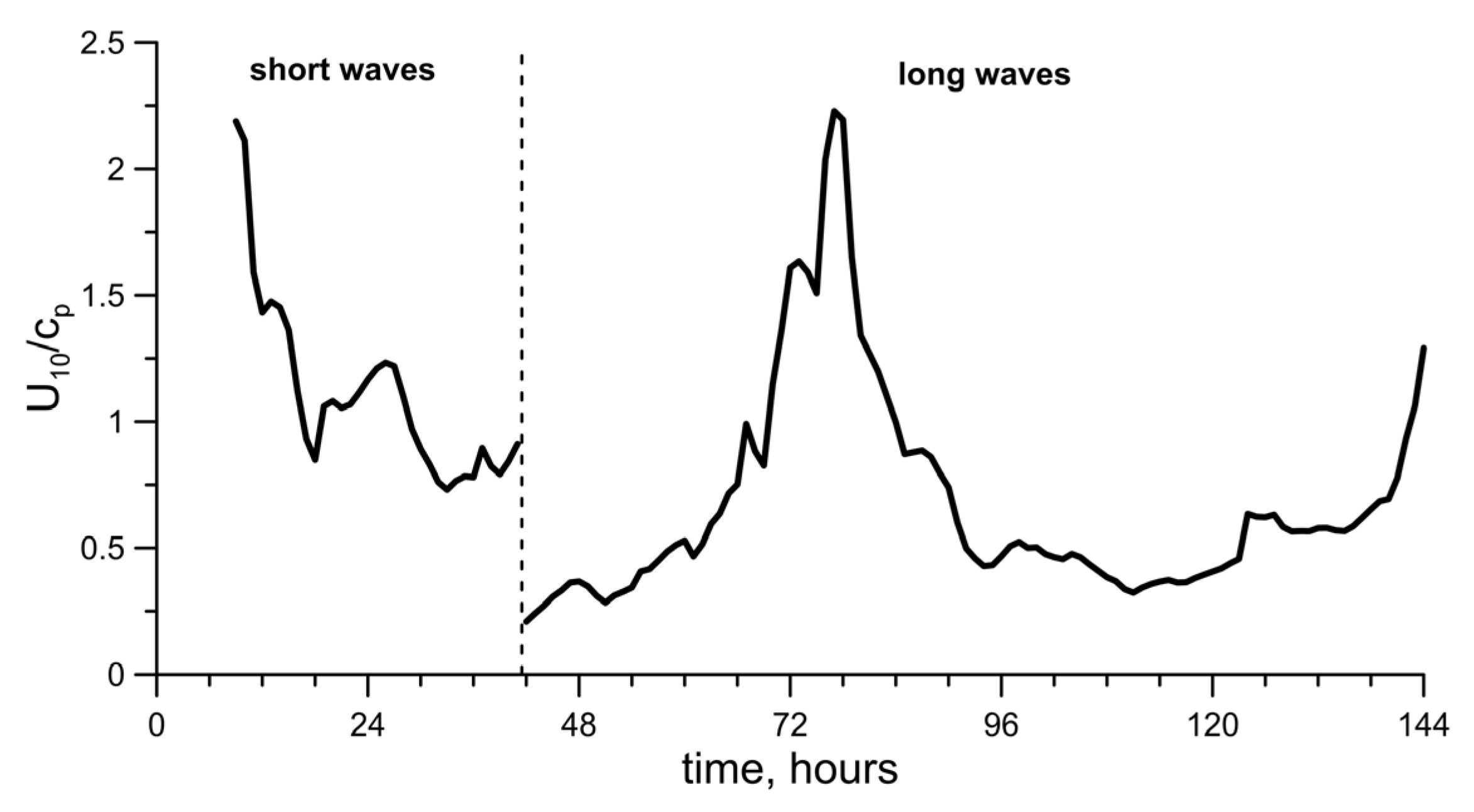
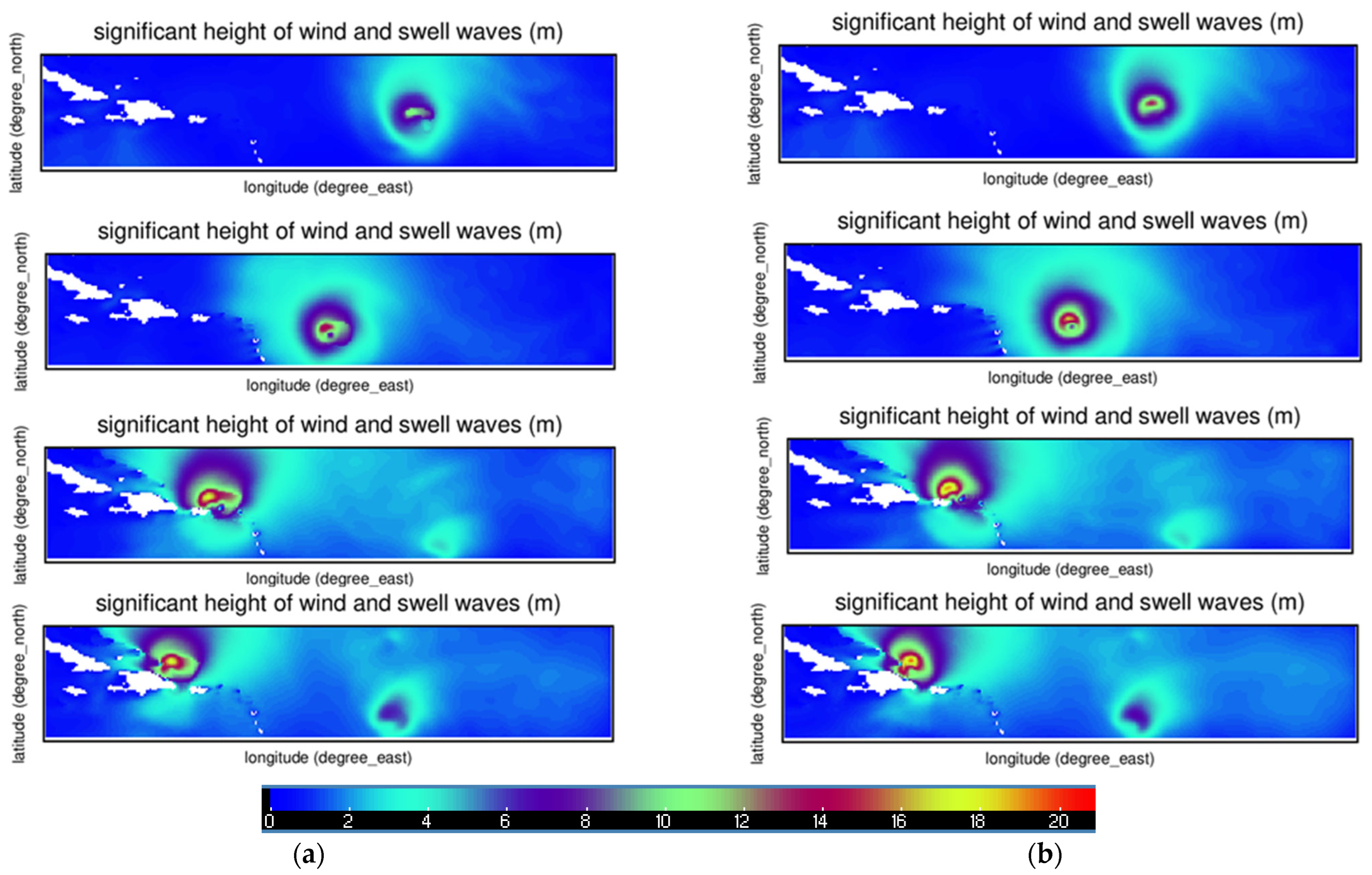
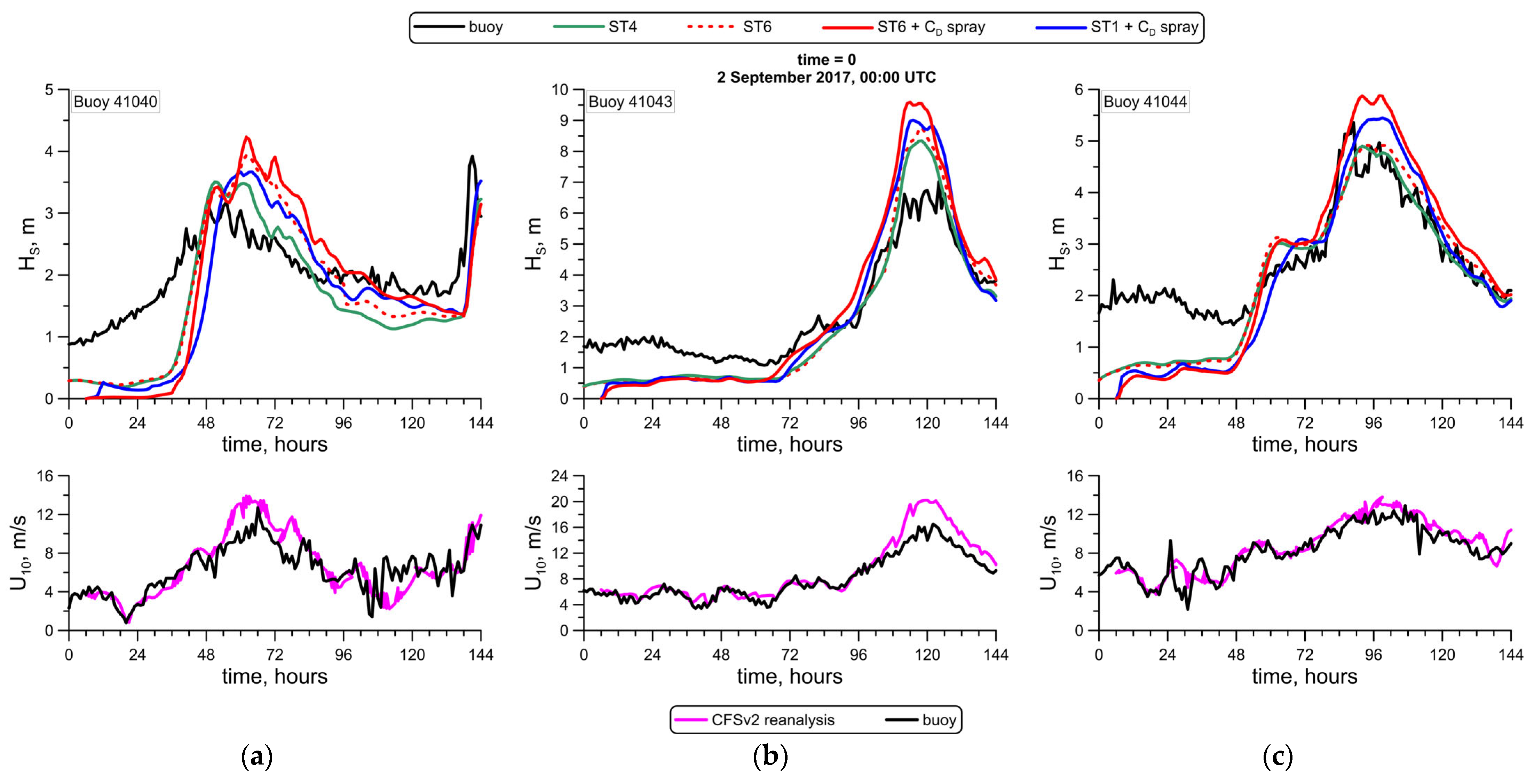
3.1. Simulation
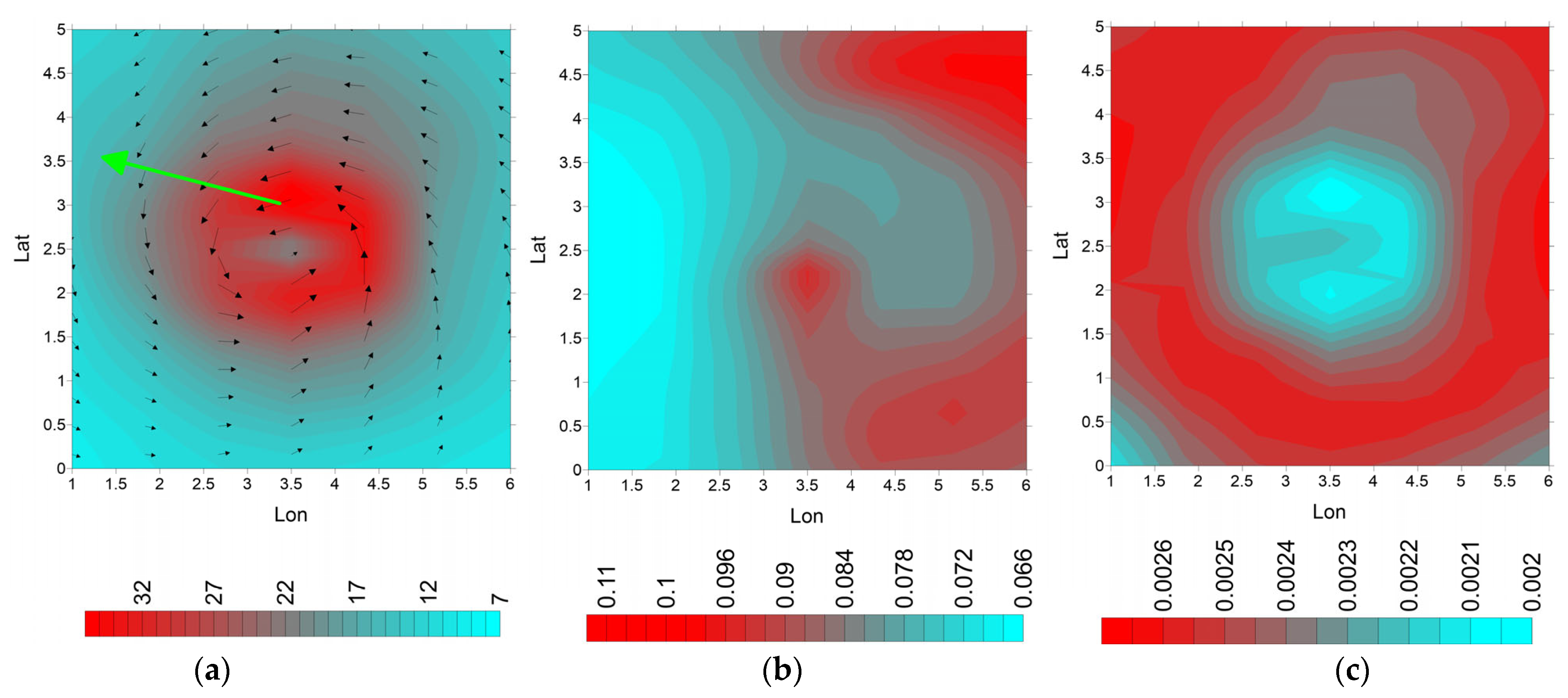
3.2. Estimation of the Air-Sea Exchange Processes Parameters
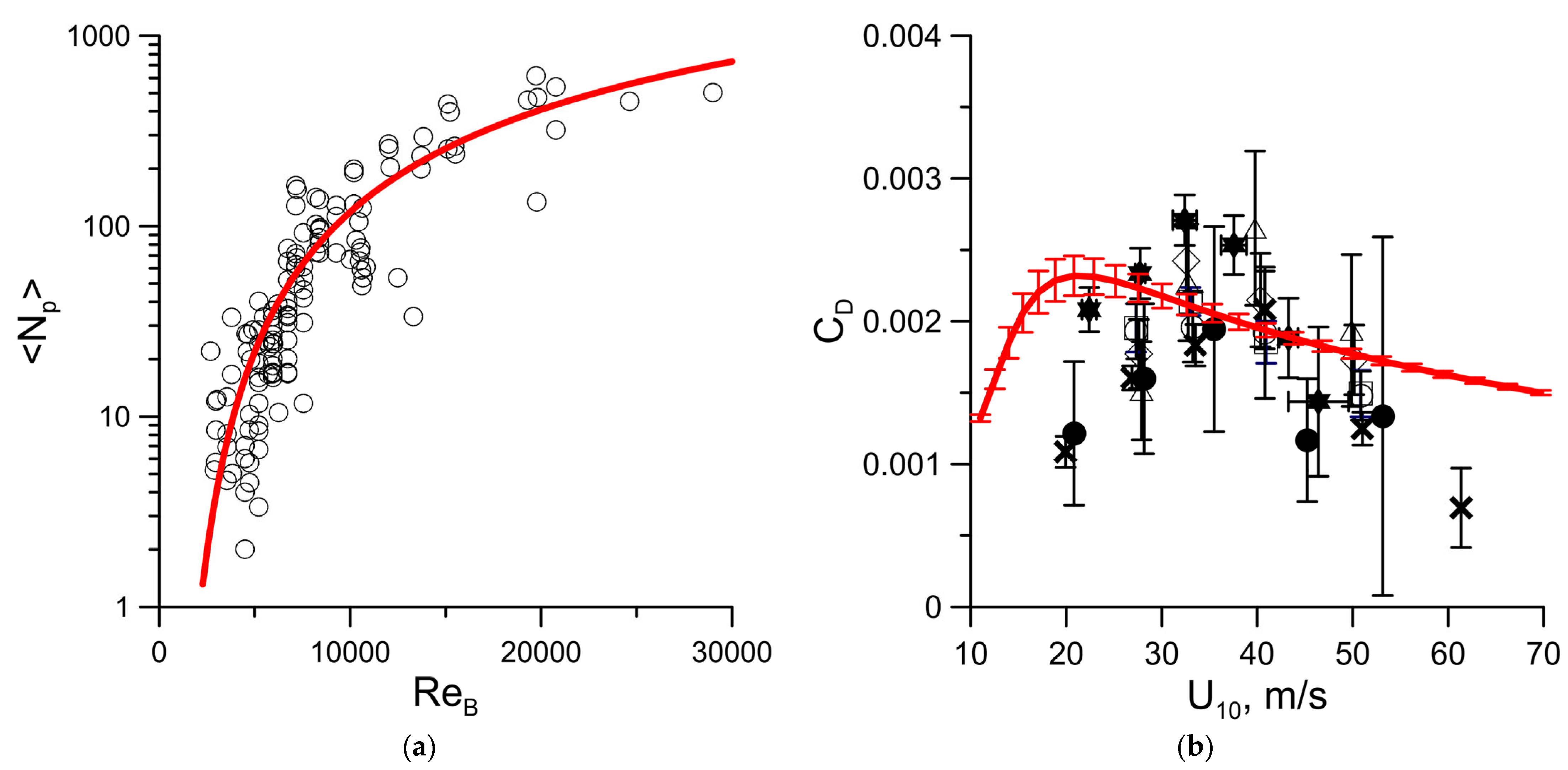
3.3. Implementation of New Drag Coefficient Parameterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WAVEWATCH III R© Development Group. User Manual and System Documentation of WAVEWATCH III (R) Version 5.16; Technical note, NOAA/NWS/NCEP/MMAB; WAVEWATCH III R© Development Group: College Park, MD, USA, 2016; 326p. [Google Scholar]
- Swan Team. SWAN User Manual Version 40.51; Environmental Fluid Mechanics Section, Department of Civil Engineering; University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2006; 129p. [Google Scholar]
- Günter, H.; Hasselmann, S.; Janssen, P.A.E.M. The Wam Model. Cycle 4; Technical Report No. 4; DKRZ: Hamburg, Germany, 1992; 101p. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, A.; Ardhuin, F. On the developments of spectral wave models: Numerics and parameterizations for the coastal ocean. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, E.M.; Emanuel, K.A.; Lengaigne, M.; Vialard, J.; Madec, G. Influence of upper ocean stratification interannual variability on tropical cyclones. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2014, 6, 680–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, P.J.; DWadhera Twisdale, L.A.; Lavelle, F.M. U.S. hurricane wind speed risk and uncertainty. J. Struct. Eng. 2009, 135, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, P.J.; Wadhera, D.; Galsworthy, J.; Peterka, J.A.; Irwin, P.A.; Griffis, L.A. Ultimate wind load design gust wind speeds in the United States for use in ASCE-7. J. Struct. Eng. 2010, 136, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.S.; Pang, W.; Zhao, L.; Xu, K.; Cao, S.Y.; Ge, Y.J. Tropical-Cyclone-Wind-Induced Flutter Failure Analysis of Long-Span Bridges. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 132, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Hong, H.P. Typhoon wind hazard estimation for China using an empirical track model. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 1009–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.P.; Li, S.H.; Duan, Z.D. Typhoon wind hazard estimation and mapping for coastal region in mainland China. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2016, 17, 04016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.S.; Pang, W.; Zhao, L.; Rawal, P.; Cao, S.Y.; Ge, Y.J. Toward a refined estimation of typhoon wind hazards: Parametric modeling and upstream terrain effects. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2021, 209, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.R.; Schwartz, S.E. Sea salt aerosol production: Mechanisms, methods, measurements and models—A Critical Review. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2004, 152, 413. [Google Scholar]
- De Leeuw, G.; Andreas, E.L.; Anguelova, M.D.; Fairall, C.W.; Lewis, E.R.; O’Dowd, C.; Schulz, M.; Schwartz, S.E. Production flux of sea spray aerosol. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Spray stress revisited. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, Y.I.; Ermakova, O.; Kandaurov, A.; Kozlov, D.; Sergeev, D.; Zilitinkevich, S. Fragmentation of the “bag-breakup” type as a mechanism of the generation of sea spray at strong and hurricane winds. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2017, 477, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, Y.I.; Kandaurov, A.; Ermakova, O.; Kozlov, D.; Sergeev, D.; Zilitinkevich, S. Bag-breakup fragmentation as the dominant mechanism of sea-spray production in high winds. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, Y.; Druzhinin, O.; Kozlov, D.; Zilitinkevich, S. The “Bag Breakup” Spume Droplet Generation Mechanism at High Winds. Part II: Contribution to Momentum and Enthalpy Transfer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2018, 48, 2189–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, J.W. On the generation of surface waves by shear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1957, 3, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, G. Micrometeorology. Sci. Am. 1964, 211, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, F.W.D.R.L.; Elliott, J.A.; Long, R.B. Array measurement of atmospheric pressure fluctuations above surface gravity waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1981, 102, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Wind-stress coefficients over sea surface from breeze to hurricane. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1982, 87, 9704–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.E.; Babanin, A.V.; Wang, D.W. Observation-consistent input and whitecapping dissipation in a model for wind-generated surface waves: Description and simple calculations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 1329–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieger, S.; Babanin, A.V.; Rogers, W.E.; Young, I.R. Observation-based source terms in the third-generation wave model WAVEWATCH. Ocean Model. 2015, 96, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komen, G.J.; Hasselmann, S.; Hasselmann, K. On the existence of a fully developed wind-sea spectrum. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1984, 14, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A. A note on the ocean surface roughness spectrum. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelan, M.A. Wind-induced growth and attenuation of laboratory waves. Inst. Math. Its Appl. Conf. Ser. 1999, 69, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Ardhuin, F.; Rogers, E.; Babanin, A.V.; Filipot, J.-F.; Magne, R.; Roland, A.; Westhuysen, A.; Queffeulou, P.; Lefevre, J.-M.; Aouf, L.; et al. Semiempirical dissipation source functions for ocean waves. Part I: Definition, calibration, and validation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1917–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangialosi, J.P.; Latto, A.S.; Berg, R. Hurricane Irma; National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone Report, al112017; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.T.; Chuang, H.Y.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Toba, Y.; Sugioka, K.I.; Komori, S. New sea spray generation function for spume droplets. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111, C02007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, Y.I.; Ermakova, O.; Kandaurov, A.; Kozlov, D.; Sergeev, D.; Zilitinkevich, S. Non-monotonous dependence of the ocean surface drag coefficient on the hurricane wind speed due to the fragmentation of the ocean-atmosphere interface. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2017, 477, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.D.; Vickery, P.J.; Reinhold, T.A. Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature 2003, 422, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuijsen, L.H.; Powell, M.D.; Pietrzak, J.D. Wind and waves in extreme hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C09003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Wang, D.W.; Teague, W.J. Bottom-up determination of air-sea momentum exchange under a major tropical cyclone. Science 2007, 315, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.H.; Bohac, R.; Stern, D.P. An assessment of the flux profile method for determining air–sea momentum and enthalpy fluxes from dropsonde data in tropical cyclones. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 2665–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, Y.; Druzhinin, O.; Gladskikh, D.; Ermakova, O.; Soustova, I. Simulation of inertial droplet dispersion and the spray mediated fluxes in the atmospheric boundary layer above waved water surface: A Lagrangian stochastic model versus direct numerical simulation. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qiao, F.; Zhang, J.A.; Xue, Y.; Ma, H.; Chen, S. Observed Drag Coefficient Asymmetry in a Tropical Cyclone. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127, e2021JC018360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, K.; Lau, J.; Hsu, Y.-H. Theory and application of calibration techniques for an NDBC directional wave measurements buoy. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1985, 10, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuznetsova, A.; Baydakov, G.; Dosaev, A.; Troitskaya, Y. Drag Coefficient Parameterization under Hurricane Wind Conditions. Water 2023, 15, 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101830
Kuznetsova A, Baydakov G, Dosaev A, Troitskaya Y. Drag Coefficient Parameterization under Hurricane Wind Conditions. Water. 2023; 15(10):1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101830
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuznetsova, Alexandra, Georgy Baydakov, Alexander Dosaev, and Yuliya Troitskaya. 2023. "Drag Coefficient Parameterization under Hurricane Wind Conditions" Water 15, no. 10: 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101830
APA StyleKuznetsova, A., Baydakov, G., Dosaev, A., & Troitskaya, Y. (2023). Drag Coefficient Parameterization under Hurricane Wind Conditions. Water, 15(10), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101830







