Evaluation of Original and Enzyme-Modified Fique Fibers as an Azo Dye Biosorbent Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioadsorbent and Dye Solution
2.2. Biosorption Tests in Laboratory Packed Column
2.3. Effect of Fiber Activation on Dye Adsorption
2.4. Effect of Solution pH on Adsorption
2.5. Fiber Enzymatic Modification
2.6. Point of Zero Charge Determination
2.7. Effect of Enzymatic Modification on Dye Removal
3. Results and Discussion
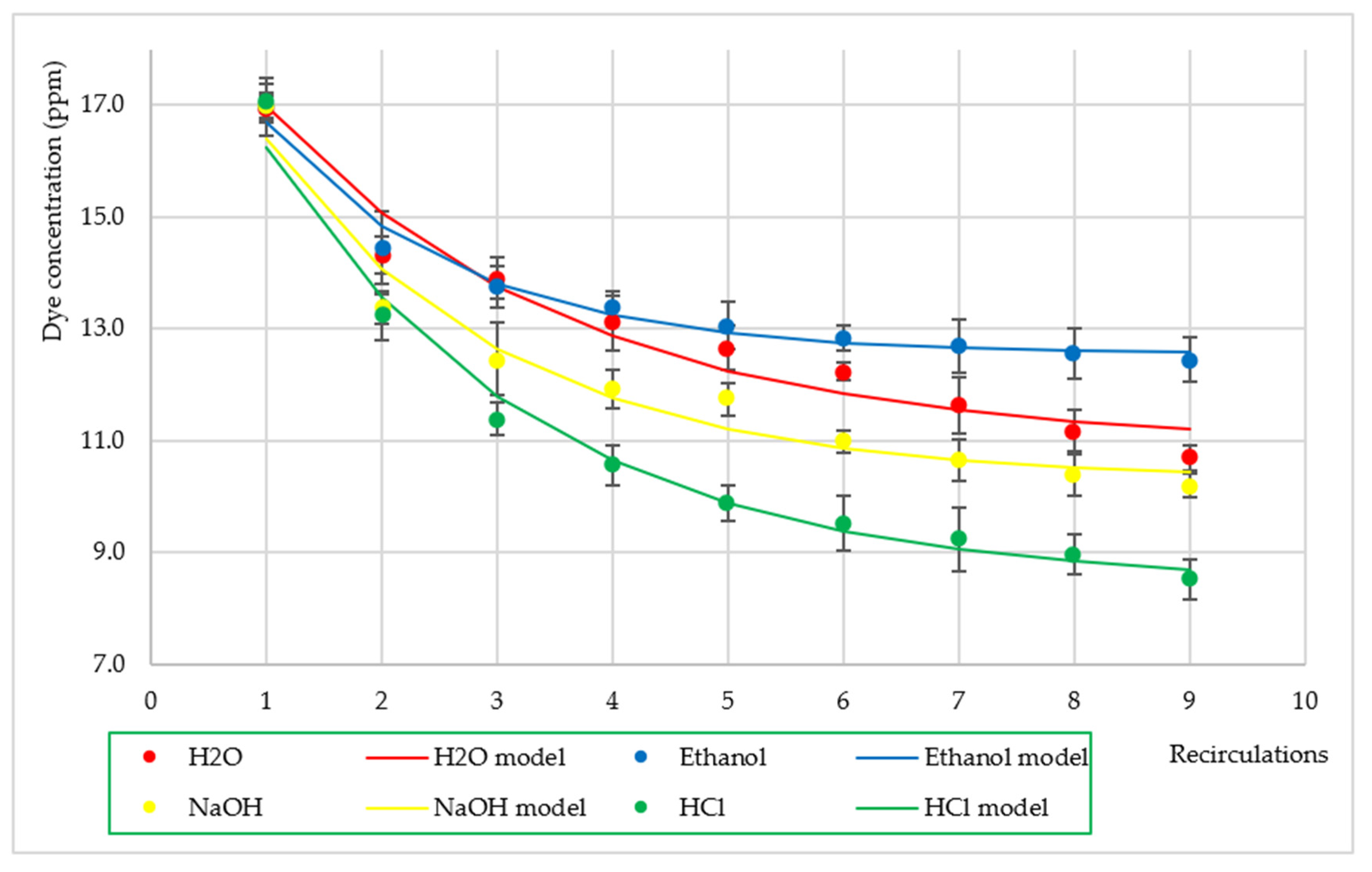
3.1. Effect of Fiber Activation on Dye Removal
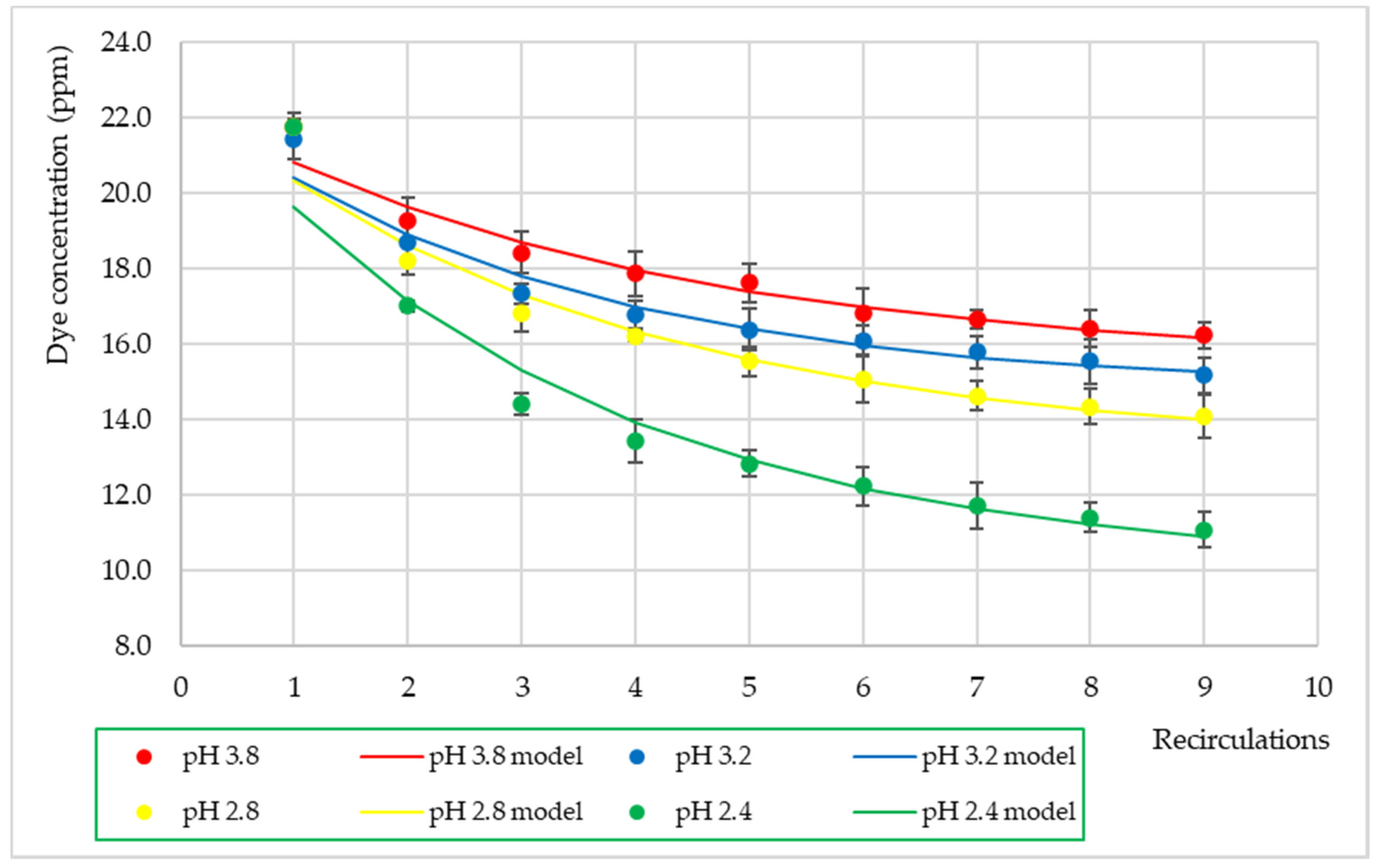
3.2. Effect of Dye Solution pH
3.3. Fiber Enzymatic Modification
3.4. Point of Zero Charge Measurement
3.5. Effect of Enzymatic Modification on Dye Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ihsanullah, I.; Jamal, A.; Ilyas, M.; Zubair, M.; Khan, G.; Atieh, M.A. Bioremediation of dyes: Current status and prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudechiche, N.; Mokaddem, H.; Sadaoui, Z.; Trari, M. Biosorption of cationic dye from aqueous solutions onto lignocellulosic biomass (Luffa cylindrica): Characterization, equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2016, 7, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allied Market Research Textile Dyes Market Outlook. 2026. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/textile-dyes-market#:~:text=TextileDyesMarketOutlook-2026,acertainlooktotextiles (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Benkhaya, S.; M’rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. Classifications, properties, recent synthesis and applications of azo dyes. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hynes, N.R.J.; Kumar, J.S.; Kamyab, H.; Sujana, J.A.J.; Al-Khashman, O.A.; Kuslu, Y.; Ene, A.; Suresh Kumar, B. Modern enabling techniques and adsorbents based dye removal with sustainability concerns in textile industrial sector—A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.Y.; Gan, S.; Yin Tan, M.S.; Lim, S.S.; Lee, X.J.; Lam, Y.F. Effective removal of Acid Blue 113 dye using overripe Cucumis sativus peel as an eco-friendly biosorbent from agricultural residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mbarek, W.; Pineda, E.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.J.; Khitouni, M. High efficiency decolorization of azo dye Reactive Black 5 by Ca-Al particles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6107–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, S.; Kaushik, A.; Kaushik, C.P. Biosorption of reactive dye by waste biomass of Nostoc linckia. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Lata, S.; Balasubramanian, P. Biosorption characteristics of methylene blue and malachite green from simulated wastewater onto Carica papaya wood biosorbent. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 10, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Bharadvaja, N. Phycoremediation of effluents containing dyes and its prospects for value-added products: A review of opportunities. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Syed, Z.; Brighu, U.; Gupta, A.B.; Ram, C. Adsorption of textile wastewater on alkali-activated sand. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tka, N.; Jabli, M.; Saleh, T.A.; Salman, G.A. Amines modified fibers obtained from natural Populus tremula and their rapid biosorption of Acid Blue 25. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 250, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshariani, F.; Roosta, A. Experimental study and mathematical modeling of biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution in a packed bed of microalgae Scenedesmus. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgariu, L.; Escudero, L.B.; Bello, O.S.; Iqbal, M.; Nisar, J.; Adegoke, K.A.; Alakhras, F.; Kornaros, M.; Anastopoulos, I. The utilization of leaf-based adsorbents for dyes removal: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 728–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dallel, R.; Kesraoui, A.; Seffen, M. Biosorption of cationic dye onto “Phragmites australis” fibers: Characterization and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7247–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sa Costa, H.P.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Biosorption of aluminum ions from aqueous solutions using non-conventional low-cost materials: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosanu, I.; Teodosiu, C.; Fighir, D.; Paduraru, C. Simultaneous biosorption of micropollutants from aqueous effluents by rapeseed waste. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 132, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Castillo, N.A.; Hernández-Ramírez, M.G.; Salazar-Rábago, J.J.; Labrada-Delgado, G.J.; Aragón-Piña, A. Bioadsorción de plomo (II) presente en soluciónacuosa sobre residuos de fibras naturales procedentes de la industria ixtlera (Agave lechuguilla Torr. y Yucca carnerosana (Trel.) McKelvey). Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2017, 33, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagojev, N.; Vasić, V.; Kukić, D.; Šćiban, M.; Prodanović, J.; Bera, O. Modelling and efficiency evaluation of the continuous biosorption of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) from water by agricultural waste materials. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, S.T.; Özcan, A.; Akar, T.; Özcan, A.; Kaynak, Z. Biosorption of a reactive textile dye from aqueous solutions utilizing an agro-waste. Desalination 2009, 249, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Lange, L.C.; Santos, L.V.S. Simultaneous biosorption of Cd(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) onto a brown macroalgae Fucus vesiculosus: Mono- and multi-component isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, A.; Bayol, E.; Abdullah, M.I. Characterization of the biosorption of fast black azo dye K salt by the bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris 51ATA strain. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 46, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbout, R.; Taha, S. Biodecolorization of Textile Dye Effluent by Biosorption on Fungal Biomass Materials. Phys. Procedia 2014, 55, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gül, Ü.D.; Taştan, B.E.; Bayazıt, G. Assessment of algal biomasses having different cell structures for biosorption properties of acid red P-2BX dye. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 127, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.E.; Murguía, M.C. Biosorption of an anionic dye by peanut shell modified with gemini surfactants: A study on the stability of the modification and the removal efficiency. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 317, 114262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukaram Bai, M.; Shaik, O.; Kavitha, J.; Hemanth Varma, M.S.; Chittibabu, N. Biosorption of eosin yellow dye from aqueous solution using sugarcane bagasse: Equillibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müssig, J. Industrial Applications of Natural Fibres; Müssig, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010; ISBN 9780470660324. [Google Scholar]
- Ridzuan, M.B.; Daud, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; Md Nordin, N.A.; Zakariah, Z. Development of Natural Fiber as a Filter Media in Removing Organic Pollutants from Greywater. Defect Diffus. Forum 2018, 382, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sfiligoj, M.; Hribernik, S.; Stana, K.; Kree, T. Plant Fibres for Textile and Technical Applications. In Advances in Agrophysical Research; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.R.; Pai, R.S.; Shendarkar, A.D. Adsorption of Ni(II), Zn(II) and Fe(II) on modified coir fibres. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 47, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinchia-Figueroa, A.; Ramírez-Carmona, M.; Tafurt-García, G. Biosorption of Chlorothalonil on Fique’s Bagasse (Furcraea sp.): Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas, G.K.G.; Sierra, C.A.; Ramirez, H.R.Z. Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of Orange II using iron nanoparticles supported on natural and functionalized fique fiber. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4178–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Navarro, Y.M.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Dataset for effect of pH on caffeine and diclofenac adsorption from aqueous solution onto fique bagasse biochars. Data Br. 2019, 25, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz, P.; Ovalle, S.; Blanco, C.; Combariza, M. Síntesis in situ de nanopartículas de óxidos de hierro soportadas en fibras de fique y su uso en la degradación de colorantes. Rev. Colomb. Mater. 2014, 5, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Agudelo-Valencia, R.; Husserl, J. Evaluación de la Remoción de Sales por Medio del uso de Fibras de Furcraea Bedinghausii (fique) y Fibras de Fique Modificadas Químicamente; Universidad de Los Andes: Bogotá, Colombia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas, K. Wastewater Treatment Using an Iron Nanocatalyst Supported on Fique Fibers; Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, H.M.; Wee, S.Y.; Aris, A.Z.; Abdullah, L.C.; Ismail, I. Processing of natural fibre and method improvement for removal of endocrine-disrupting compounds. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yi, C.; Xu, M.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, D.; Shin, C.-H.; Ryu, M.-H.; Zhao, Y. Adsorption of As(III) and As(V) by using the Fenton reaction modified kapok fiber. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscusi, G.; Lamberti, E.; Gorrasi, G. Hemp fibers modified with graphite oxide as green and efficient solution for water remediation: Application to methylene blue. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs-Páez, E.D.; García-Pérez, A.J.; Nieto-Delgado, C.; Chazaro-Ruiz, L.F.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Enhanced CO2 capture kinetics by using macroporous carbonized natural fibers impregnated with an ionic liquid. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 350, 118602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Chen, L.; Dong, M.; Fu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, H. Cleaner production of lignocellulosic nanofibrils: Potential of mixed enzymatic treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Biotechnology of Lignocellulose; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-94-007-6897-0. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Wang, L.; Long, J.-J. Biodegumming of ramie fiber with pectinases enhanced by oxygen plasma. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 101, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, B.M.; Ibrahim, N.A. Recent developments in sustainable finishing of cellulosic textiles employing biotechnology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konczewicz, W.; Kozłowski, R.M. Enzymatic treatment of natural fibres. In Handbook of Natural Fibres; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 168–184. [Google Scholar]
- Michelin, M.; Polizeli, M.L.T.M.; Ruzene, D.; Silva, D.; Teixeira, J. Application of Lignocelulosic Residues in the Production of Cellulase and Hemicellulases from Fungi. In Fungal Enzymes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, K.; Kalia, S.; Pathania, D.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, N.; Schauer, C.L. Surface functionalization of lignin constituent of coconut fibers via laccase-catalyzed biografting for development of antibacterial and hydrophobic properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Hughes, S. Fractional extraction and physico-chemical characterization of hemicelluloses and cellulose from sugar beet pulp. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 36, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Ahring, B.K. Lignin degradation under anaerobic digestion: Influence of lignin modifications—A review. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 128, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmipathy, R.; Sarada, N.C. Adsorptive removal of basic cationic dyes from aqueous solution by chemically protonated watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) rind biomass. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 6175–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, Q.; Huo, J.; Yang, B. Adsorption of methyl orange onto protonated cross-linked chitosan. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosique Hueso, M. Bioadsorción de Cadmio Por Biomasa de Opuntia; Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena: Cartagena, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.M.F.; Oliveira, M.M.; Avelino, M.C.; Fonseca, M.G.; Almeida, R.K.S.; Silva Filho, E.C. Adsorption of an industrial anionic dye by modified-KSF-montmorillonite: Evaluation of the kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium data. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litefti, K.; Freire, M.S.; Stitou, M.; González-Álvarez, J. Adsorption of an anionic dye (Congo red) from aqueous solutions by pine bark. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saha, T.K.; Bhoumik, N.C.; Karmaker, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Ichikawa, H.; Fukumori, Y. Adsorption Characteristics of Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Solution onto Chitosan. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2011, 39, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, M.; Zolghadrnasab, H.; Godini, K.; Poormohammadi, A.; Ahmadian, M.; Shanesaz, S. Kinetic and adsorption studies of reactive black 5 removal using multi-walled carbon nanotubes from aqueous solution. Der Pharma Chem. 2015, 7, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, H.A.; Mondal, A.K.; Muslim, T. Adsorptive Removal of Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Solution using Chitin Prepared from Shrimp Shells. Bangladesh Pharm. J. 2012, 15, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaheed, M.A.; Hussein, F.H. Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 on Synthesized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Equilibrium Isotherm and Kinetic Studies. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beni, A.A.; Esmaeili, A. Biosorption, an efficient method for removing heavy metals from industrial effluents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Han, D.; Lu, Y.; Rong, Y.; Fang, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, R. Characterization of pine-sawdust pyrolytic char activated by phosphoric acid through microwave irradiation and adsorption property toward CDNB in batch mode. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.; Adeli, M.; Kakanejadifard, A.; Movahedi, S.; Bani, F. Enzymatic functionalization of nanomaterials: A strategy for engineering their surfaces. Polymer 2013, 54, 4802–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minten, I.J.; Abello, N.; Schooneveld-Bergmans, M.E.F.; van den Berg, M.A. Post-production modification of industrial enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6215–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaringo Villa, F.A. Determinación del punto de carga cero y punto isoeléctrico de dos residuos agrícolas y su aplicación en la remoción de colorantes. Rev. Investig. Agrar. Y Ambient. 2013, 4, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Flynn, S.L.; Alessi, D.S.; Konhauser, K.O. Change of the point of zero net proton charge (pHPZNPC) of clay minerals with ionic strength. Chem. Geol. 2018, 493, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarrete, L.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno, J. Influencia de la química superficial en la entalpía de inmersión de carbones activados en soluciones acuosas de fenol y 4-nitro fenol. Rev. Colomb. Química 2006, 35, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wieckowski, A. Interfacial Electrochemistry: Theory: Experiment, and Applications; Marcel Deker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiruddin Khan, M.; Sarwar, A. Determination of points of Zero Charge of natural and treated adsorbents. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2007, 14, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Lara, M. Caracterización y Aplicación de Biomasa Residual a la Eliminación de Metales Pesados; Universidad de Granada: Granada, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, S.; Stephenson, T. Process Science and Engineering for Water and Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, P.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno, J. Influencia del pH sobre la adsorción en carbón activado de Cd(II) y Ni(II) desde soluciones acuosas. Rev. Colomb. Química 2010, 39, 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Suib, S. New and Future Developments in Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 9780444538802. [Google Scholar]
- Hofrichter, M. Review: Lignin conversion by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C. Lignocellulosic residues: Biodegradation and bioconversion by fungi. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paës, G.; Berrin, J.-G.; Beaugrand, J. GH11 xylanases: Structure/function/properties relationships and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 564–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayani, R.S.; Saxena, S.; Gupta, R. Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2931–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; Zaror, C.A. Influencia de la composición química superficial del carbón activado en la adsorción de benzotiazoles. Ingeniare. Rev. Chil. De Ing. 2010, 18, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, V.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno, J.C. Adsorción de compuestos fenólicos sobre carbones activados modificados químicamente: Efecto del sustituyente en el anillo aromático en las interacciones carbón activado-adsorbato. Afinidad 2017, 74, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, M.; Otero-Calvis, A.; Falcón-Hernández, J.; Yperman, Y. Características fisicoquímicas del carbón activado de conchas de coco modificado con HNO3. Rev. Cuba. Química 2017, 29, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pejic, B.; Vukcevic, M.; Kostic, M.; Skundric, P. Biosorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by short hemp fibers: Effect of chemical composition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakarinen, A.; Zhang, J.; Brock, T.; Maijala, P.; Viikari, L. Enzymatic accessibility of fiber hemp is enhanced by enzymatic or chemical removal of pectin. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | H2O | Ethanol | NaOH | HCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 8.8671 | 7.5169 | 9.7960 | 11.8700 |
| d | 10.923 | 12.540 | 10.316 | 8.425 |
| R2 | 0.957 | 0.983 | 0.965 | 0.985 |
| Parameters | pH 3.80 | pH 3.20 | pH 2.80 | pH 2.40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 6.9197 | 7.6630 | 9.3656 | 12.9879 |
| d | 15.473 | 14.784 | 13.248 | 10.024 |
| R2 | 0.960 | 0.962 | 0.958 | 0.954 |
| Treatment | Cellulose (%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Lignin (%) | Pectin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMF | 55.78 ± 1.45 | 18.58 ± 1.03 | 14.23 ± 0.42 | 6.15 ± 1.71 |
| Pec | 59.45 ± 1.56 | 19.73 ± 1.14 | 15.11 ± 0.64 | 1.19 ± 0.62 |
| Xil | 63.29 ± 2.13 | 9.04 ± 1.47 | 16.14 ± 1.28 | 6.66 ± 1.12 |
| Lig | 61.78 ± 3.25 | 21.58 ± 2.61 | 6.14 ± 1.96 | 5.74 ± 0.98 |
| Parameters | Nmf | Xil | Lig | Pec |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 11.2922 | 11.8036 | 11.8778 | 16.3732 |
| d | 11.162 | 10.622 | 10.586 | 6.456 |
| R2 | 0.958 | 0.968 | 0.958 | 0.949 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Blandón, O.; Ramírez-Carmona, M.; Cuartas-Uribe, B.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Evaluation of Original and Enzyme-Modified Fique Fibers as an Azo Dye Biosorbent Material. Water 2022, 14, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071035
Muñoz-Blandón O, Ramírez-Carmona M, Cuartas-Uribe B, Mendoza-Roca JA. Evaluation of Original and Enzyme-Modified Fique Fibers as an Azo Dye Biosorbent Material. Water. 2022; 14(7):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071035
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Blandón, Oscar, Margarita Ramírez-Carmona, Beatriz Cuartas-Uribe, and José Antonio Mendoza-Roca. 2022. "Evaluation of Original and Enzyme-Modified Fique Fibers as an Azo Dye Biosorbent Material" Water 14, no. 7: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071035
APA StyleMuñoz-Blandón, O., Ramírez-Carmona, M., Cuartas-Uribe, B., & Mendoza-Roca, J. A. (2022). Evaluation of Original and Enzyme-Modified Fique Fibers as an Azo Dye Biosorbent Material. Water, 14(7), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071035








