Soil Water Use Strategies of Dominant Tree Species Based on Stable Isotopes in Subtropical Regions, Central China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Observation of Meteorological Factor
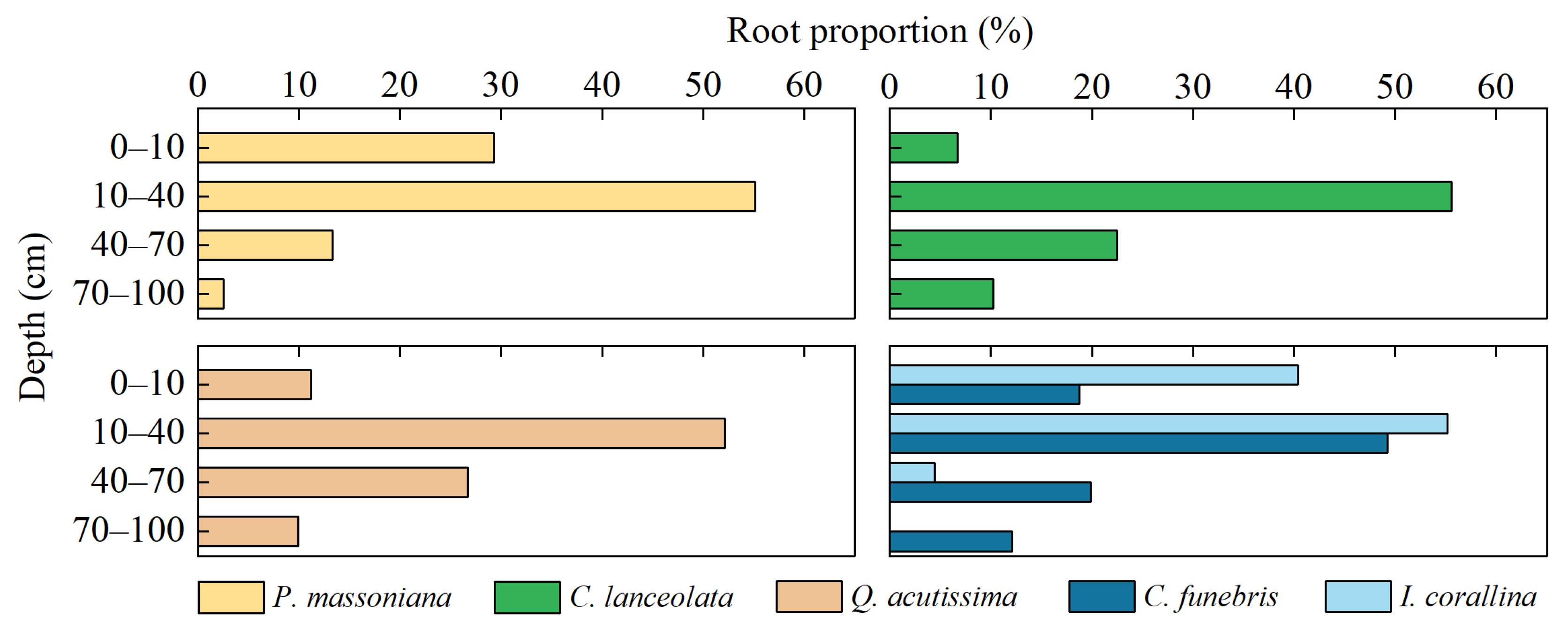
2.3. Litter Collection and Root Characteristics Investigation
2.4. Stable Isotope Sample Collection and Determination
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
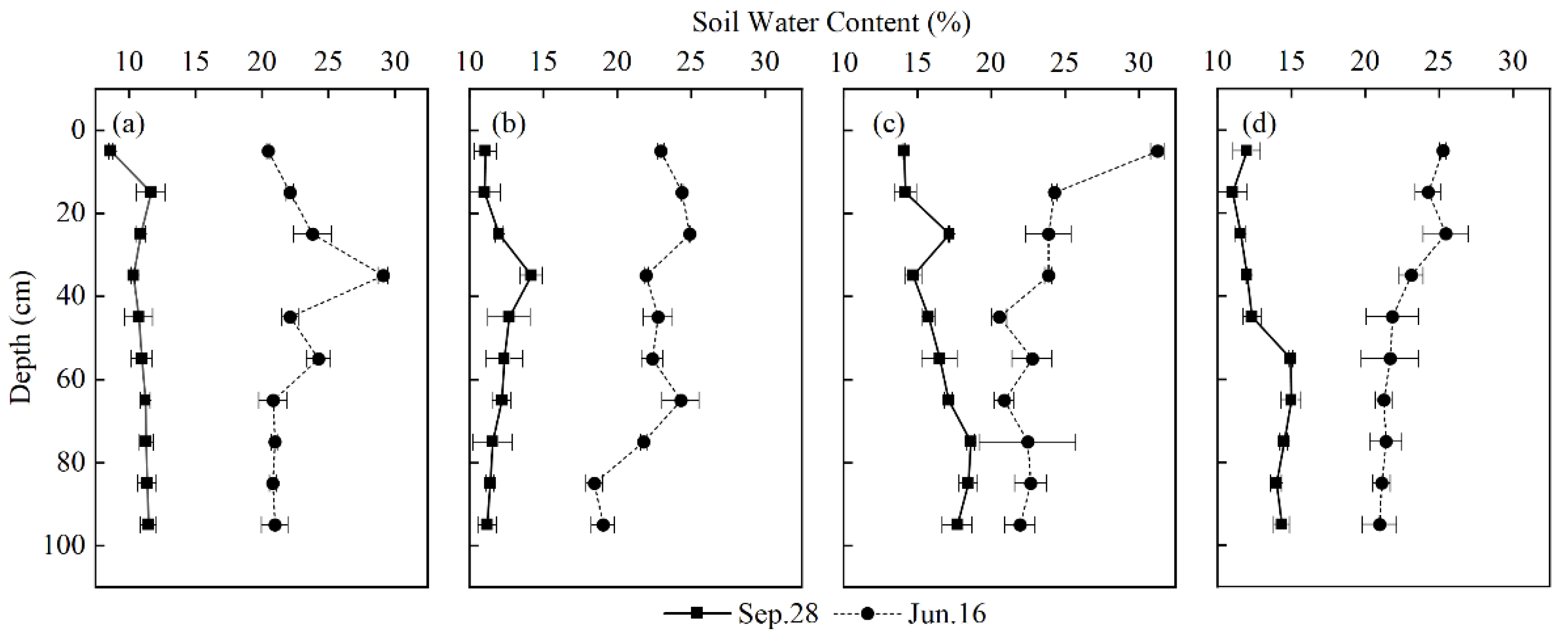
3.1. Characteristics of Litter and Soil Water Content in Different Stand Types
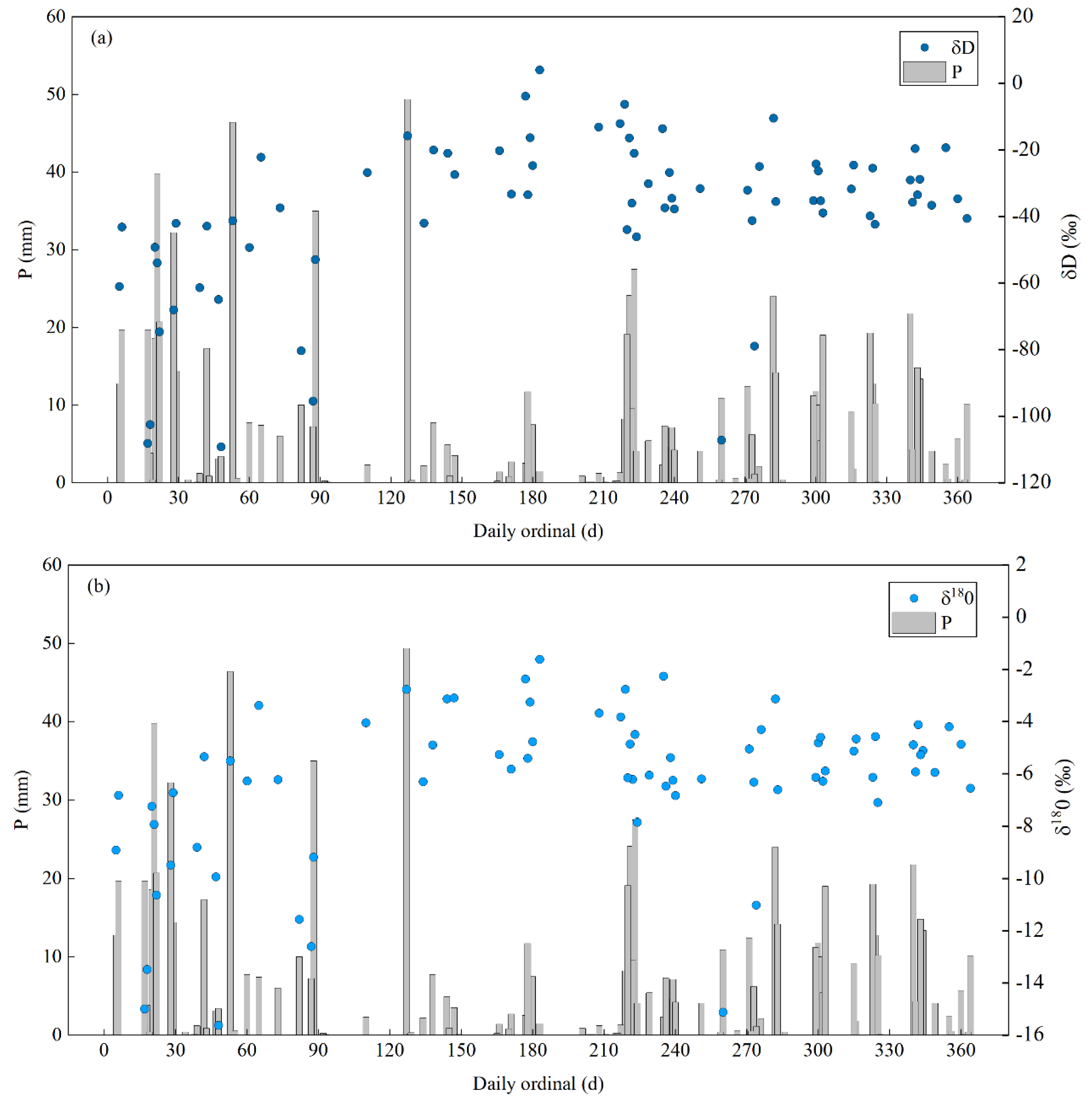
3.2. Precipitation Distribution and Isotopic Composition
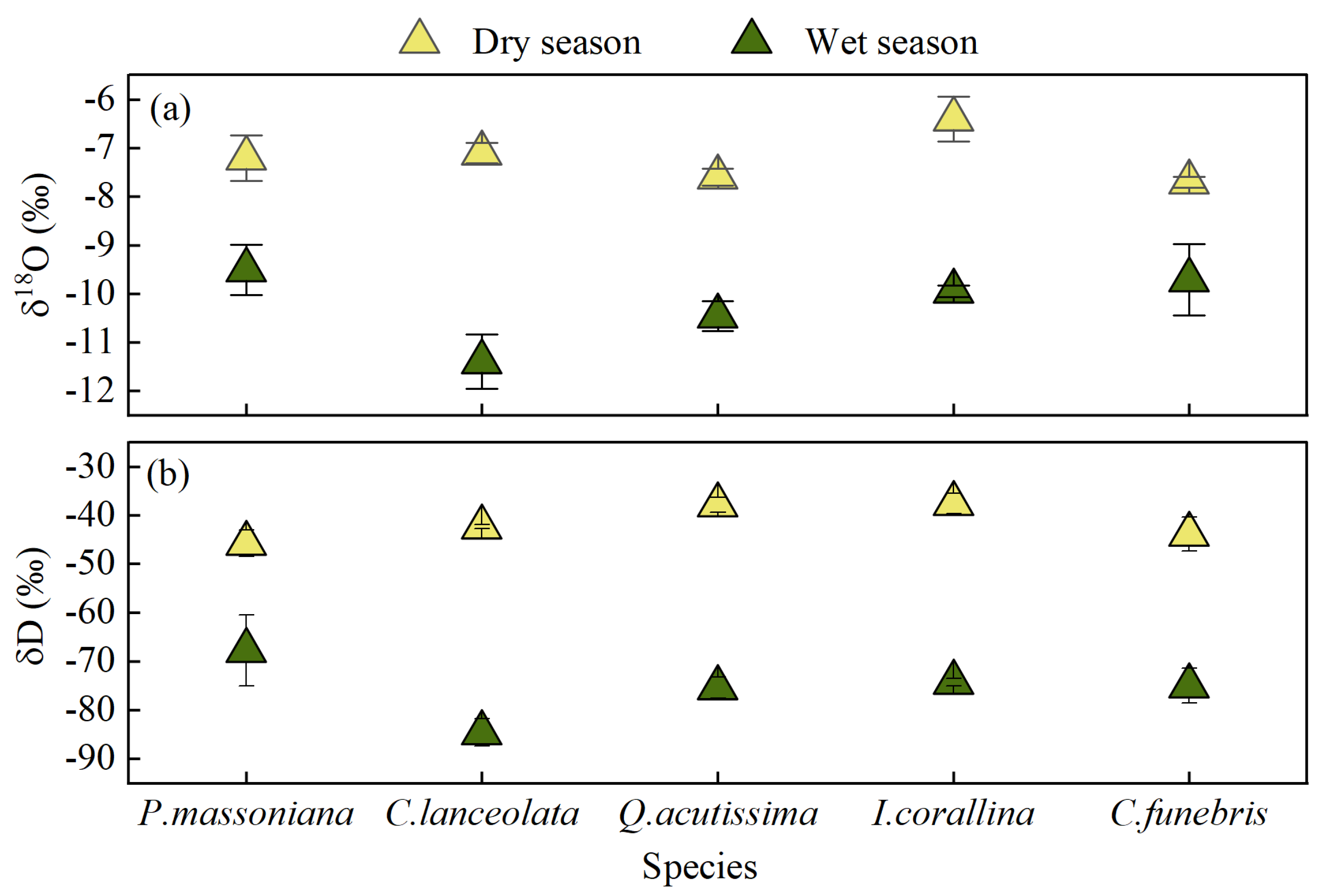
3.3. Isotopic Composition and Variation in Xylem Water
3.4. Seasonal Variations in the Proportion of Plant Water Uptake
4. Discussion
4.1. The Linear Regression Relationship of δD and δ18O in Rainfall, Soil Water, Xylem Water
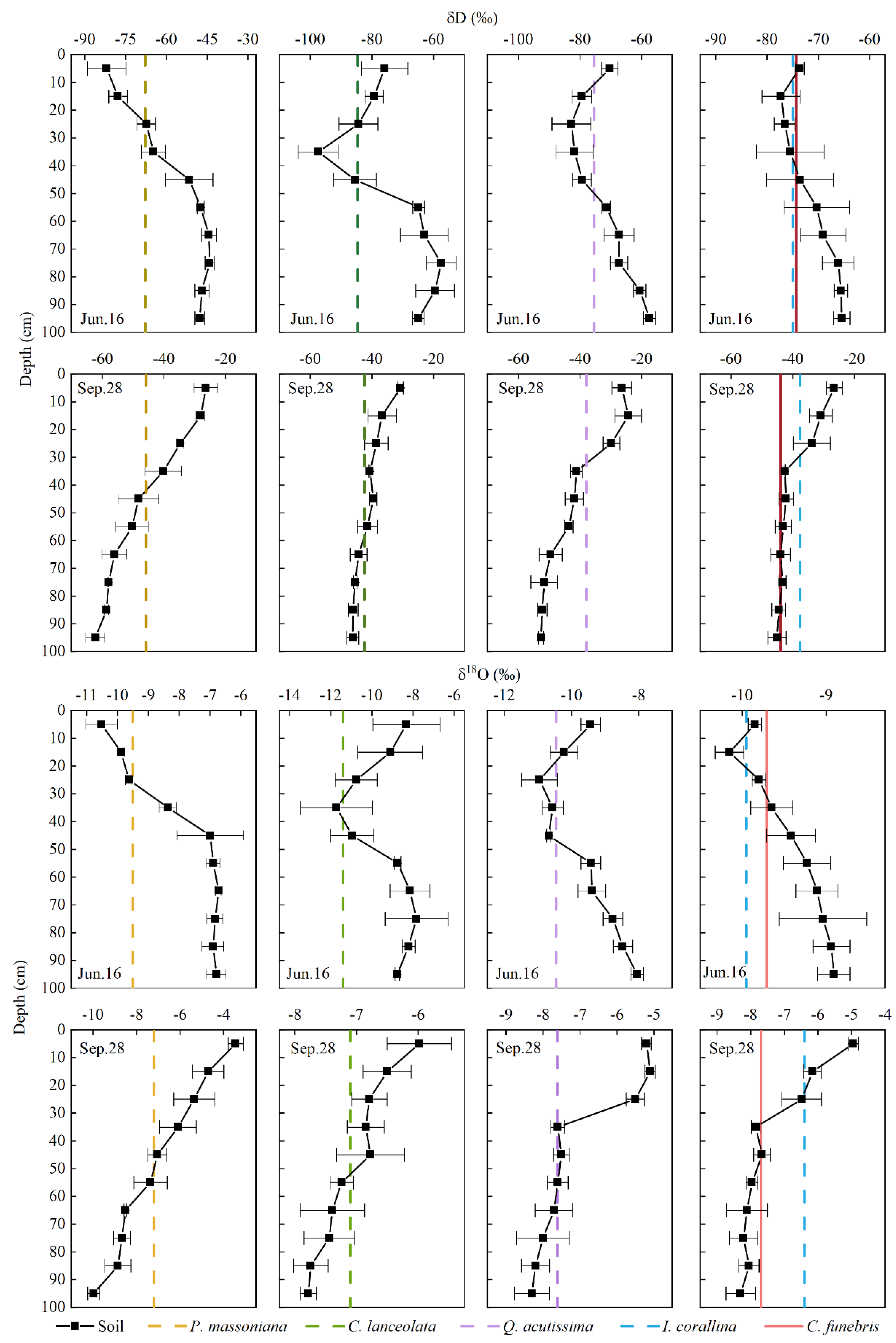
4.2. Vertical Gradient of Isotopic Composition in Soil Water
4.3. Differences in Seasonal Water Uptake Patterns among Species
4.4. Limitation and Constraints
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, C.R.; Kulmatiski, A. Improving Inferences from Hydrological Isotope Techniques. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger, M.; Leistert, H.; Gimbel, K.; Weiler, M. Illuminating hydrological processes at the soil-vegetation-atmosphere interface with water stable isotopes. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 674–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Lu, N.; Zhang, L. Seasonal variation in water uptake patterns of three plant species based on stable isotopes in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, M.B.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Welker, J.M. Differential water resource use by herbaceous and woody plant life-forms in a shortgrass steppe community. Oecologia 1998, 117, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, T.E.; Mambelli, S.; Plamboeck, A.H.; Templer, P.H.; Tu, K.P. Stable Isotopes in Plant Ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 507–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, J.; McDonnell, J.J. Prevalence and magnitude of groundwater use by vegetation: A global stable isotope meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evaristo, J.; McDonnell, J.J.; Scholl, M.A.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Chun, K.P. Insights into plant water uptake from xylem-water isotope measurements in two tropical catchments with contrasting moisture conditions. Hydrol. Process 2016, 30, 3210–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxy, M.K.; Ghosh, S.; Pathak, A.; Athulya, R.; Mujumdar, M.; Murtugudde, R.; Terray, P.; Rajeevan, M. A threefold rise in widespread extreme rain events over central India. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Oki, T.; Kanae, S.; Hu, H. Hydrological Cycles Change in the Yellow River Basin during the Last Half of the Twentieth Century. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1790–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Q.; Wang, H.; Rutishauser, T.; Dai, J. Phenological response to climate change in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, T.; Wei, L.; Shu, Y. The spatial distribution of forest carbon sinks and sources in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, W.; Tian, H.; Tao, B.; Chappelka, A.; Sun, G.; Lu, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, G.; Xu, X. Impacts of tropospheric ozone and climate change on net primary productivity and net carbon exchange of China’s forest ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, K.; Nie, Y.; Wang, K. Analysis of soil water movement inside a footslope and a depression in a karst catchment, Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Lu, N.; Fu, B. Inter-comparison of stable isotope mixing models for determining plant water source partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delzon, S.; Loustau, D. Age-related decline in stand water use: Sap flow and transpiration in a pine forest chronosequence. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 129, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y. Water-use strategy of three central Asian desert shrubs and their responses to rain pulse events. Plant Soil 2006, 285, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggemeyer, K.D.; Awada, T.; Harvey, F.E.; Wedin, D.A.; Zhou, X.; Zanner, C.W. Seasonal changes in depth of water uptake for encroaching trees Juniperus virginiana and Pinus ponderosa and two dominant C4 grasses in a semiarid grassland. Tree Physiol. 2009, 29, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, R.; Barnard, H.R.; Mao, D.; Revil, A.; Singha, K. Examining diel patterns of soil and xylem moisture using electrical resistivity imaging. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, S.; Lesparre, N.; Flores-Orozco, A.; Wagner, F.; Kemna, A.; Javaux, M. Imaging plant responses to water deficit using electrical resistivity tomography. Plant Soil 2020, 454, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, F.C.; Clearwater, M.J.; Goldstein, G. Water transport in trees: Current perspectives, new insights and some controversies. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2001, 45, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geris, J.; Tetzlaff, D.; McDonnell, J.J.; Soulsby, C. Spatial and temporal patterns of soil water storage and vegetation water use in humid northern catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.C.; Meinzer, F.C.; Mercedes, B.; Guillermo, G.; Augusto, F.; Rundel, P.W.; Linda, C.; Erica, I.; Fabio, C. Partitioning of soil water among tree species in a Brazilian Cerrado ecosystem. Tree Physiol. 1999, 19, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prechsl, U.E.; Burri, S.; Gilgen, A.K.; Kahmen, A.; Buchmann, N. No shift to a deeper water uptake depth in response to summer drought of two lowland and sub-alpine C(3)-grasslands in Switzerland. Oecologia 2015, 177, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, X. Using stable isotopes to determine seasonal variations in water uptake of summer maize under different fertilization treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardanto, A.; Röll, A.; Hendrayanto, J.; Hölscher, D. Tree soil water uptake and transpiration in mono-cultural and jungle rubber stands of Sumatra. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 397, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Guan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Dai, J.; Hua, M. Examination of the ecohydrological separation hypothesis in a humid subtropical area: Comparison of three methods. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothfuss, Y.; Javaux, M. Reviews and syntheses: Isotopic approaches to quantify root water uptake: A review and comparison of methods. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2199–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellsworth, P.Z.; Williams, D.G. Hydrogen isotope fractionation during water uptake by woody xerophytes. Plant Soil 2007, 291, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Streamside trees that do not use stream water. Nature 1991, 350, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Si, B.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Feng, H. Stable isotopes of deep soil water retain long-term evaporation loss on China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, D.; Geris, J.; Hopp, L.; Scandellari, F. Water sources for root water uptake: Using stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen as a research tool in agricultural and agroforestry systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 291, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, G.; Jahren, A.H. Isotopic evidence for the role of plant development on transpiration in deciduous forests of southern United States. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, K.A.; Williams, D.G. Water sources used by riparian trees varies among stream types on the San Pedro River, Arizona. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Gregg, J.W. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Saltos, H.; Sternberg, L.; Moreira, M.Z.; Nepstad, D. Rainfall exclusion in an eastern Amazonian forest alters soil water movement and depth of water uptake. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.W.; Semmens, B.X. Incorporating uncertainty and prior information into stable isotope mixing models. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, B.C.; Semmens, B.X. MixSIAR GUI User Manual, Version 3.1. 2013. Available online: http://conserver.iugocafe.org/user/brice.semmens/MixSIAR (accessed on 10 March 2016).
- Jackson, P.C.; Cavelier, J.; Goldstein, G.; Meinzer, F.C.; Holbrook, N.M. Partitioning of water resources among plants of a lowland tropical forest. Oecologia 1995, 101, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Seasonal variations in depth of water uptake for a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to drought in an East Asian monsoon region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCole, A.A.; Stern, L.A. Seasonal water use patterns of Juniperus ashei on the Edwards Plateau, Texas, based on stable isotopes in water. J. Hydrol. 2007, 342, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbjornsen, H.; Mora, G.; Helmers, M.J. Variation in water uptake dynamics among contrasting agricultural and native plant communities in the Midwestern U.S. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, G. Varying water utilization of Haloxylon ammodendron plantations in a desert-oasis ecotone. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Cook, E.R.; Lawrence, J.R.; Broecker, W.S. The D/H ratios of sap in trees: Implications for water sources and tree ring D/H ratios. Geochim. Cosmochimca Acta 1985, 49, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nippert, J.B.; Knapp, A.K. Soil water partitioning contributes to species coexistence in tallgrass prairie. Oikos 2007, 116, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-G.; Romero-Saltos, H.; Tsujimura, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Sasaki, L.; Davaa, G.; Oyunbaatar, D. Plant water sources in the cold semiarid ecosystem of the upper Kherlen River catchment in Mongolia: A stable isotope approach. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.S. Stable Isotopic Analysis on Water Utilization of Two Xerophytic Shrubs in a Revegetated Desert Area: Tengger Desert, China. Water 2015, 7, 1030–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.J.; Ma, J.J.; Sun, X.H.; Guo, X.H.; Cheng, Q.Y.; Shi, X.K. Estimating the Root Water Uptake of Surface-Irrigated Apples Using Water Stable Isotopes and the Hydrus-1D Model. Water 2018, 10, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qu, D.; Duan, W.; Wang, J.; Su, P.; Guo, R. Water Use Strategies of Dominant Species (Caragana korshinskii and Reaumuria soongorica) in Natural Shrubs Based on Stable Isotopes in the Loess Hill, China. Water 2020, 12, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Si, J.H.; Jia, B.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; He, X.H.; Wang, C.L.; Zhu, X.L. Water Use Characteristics of Two Dominant Species in the Mega-Dunes of the Badain Jaran Desert. Water 2022, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.-F.; Yu, G.-R.; Sun, X.-M.; Li, Q.-K.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhang, L.-M.; Ren, C.-Y.; Fu, Y.-L.; Li, Z.-Q. Soil moisture effect on the temperature dependence of ecosystem respiration in a subtropical Pinus plantation of southeastern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 137, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.F.; Wang, H.M.; Wang, J.L.; Yu, G.R.; Sun, X.M. Ecosystem carbon exchanges of a subtropical evergreen coniferous plantation subjected to seasonal drought, 2003–2007. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Wen, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, H. Interannual variation of the Bowen ratio in a subtropical coniferous plantation in southeast China, 2003–2012. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Wen, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. The limiting effect of deep soilwater on evapotranspiration of a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to seasonal drought. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gutierrez, C.; Dawson, T.E.; Nicolas, E.; Querejeta, J.I. Isotopes reveal contrasting water use strategies among coexisting plant species in a Mediterranean ecosystem. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Niu, J.; Xie, B. Study on hydrological functions of litter layers in North China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, T.E.; Pate, J.S. Seasonal water uptake and movement in root systems of Australian phraeatophytic plants of dimorphic root morphology: A stable isotope investigation. Oecologia 1996, 107, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Kumagai, T.O.; Kume, A.; Otsuki, K.; Ogawa, S. Experimental analysis of moisture dynamics of litter layers? The effects of rainfall conditions and leaf shapes. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussière, F.; Cellier, P. Modification of the soil temperature and water content regimes by a crop residue mulch: Experiment and modelling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1994, 68, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, E.J. Using experimental manipulation to assess the roles of leaf litter in the functioning of forest ecosystems. Biol. Rev. 2010, 81, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, N.; Dunkerley, D. The influence of organic litter on the erosive effects of raindrops and of gravity drops released from desert shrubs. CATENA 1999, 36, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H.J.S. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.J.; Birks, S.J.; Edwards, T.W.D. Global prediction ofδAandδ2H-δ18O evaporation slopes for lakes and soil water accounting for seasonality. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benettin, P.; Volkmann, T.H.M.; von Freyberg, J.; Frentress, J.; Penna, D.; Dawson, T.E.; Kirchner, J.W. Effects of climatic seasonality on the isotopic composition of evaporating soil waters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sprenger, M.; Tetzlaff, D.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; McNamara, J.P.; Laudon, H.; Shatilla, N.J.; Soulsby, C. Storage, mixing, and fluxes of water in the critical zone across northern environments inferred by stable isotopes of soil water. Hydrol. Process 2018, 32, 1720–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, R.K. Seasonal Variations of Oxygen-18 in Soil Moisture and Estimation of Recharge in Esker and Moraine Formations. Hydrol. Res. 1984, 15, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazis, C.; Feng, X. A stable isotope study of soil water: Evidence for mixing and preferential flow paths. Geoderma 2004, 119, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fu, B. Soil water migration in the unsaturated zone of semiarid region in China from isotope evidence. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, T.E.; Simonin, K.A. The Roles of Stable Isotopes in Forest Hydrology and Biogeochemistry. In Forest Hydrology and Biogeochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 137–161. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, X.-J.; Tang, L.-S.; Li, Y. Stable oxygen isotopes reveal distinct water use patterns of two Haloxylon species in the Gurbantonggut Desert. Plant Soil 2014, 389, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, X. Contrasting water use pattern of introduced and native plants in an alpine desert ecosystem, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542 Pt A, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Tan, W.; Deng, P.; Yang, J. Seasonal water use patterns of woody species growing on the continuous dolostone outcrops and nearby thin soils in subtropical China. Plant Soil 2010, 341, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Meng, P.; Zhang, J.S.; Wan, X. Variation in soil water uptake and its effect on plant water status in Juglans regia L. during dry and wet seasons. Tree Physiol. 2011, 31, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Yuan, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Characteristics of δ 18O in precipitation over Eastern Monsoon China and the water vapor sources. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 55, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Duan, W.; Li, H. Dry season water uptake by two dominant canopy tree species in a tropical seasonal rainforest of Xishuangbanna, SW China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Dawson, T.E. Water uptake by plants: Perspectives from stable isotope composition. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.M.; Van Bavel, C.H.M. Resistance of Plant Roots to Water Loss. Agron. J. 1986, 78, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleby, T.M.; Mcelrone, A.J.; Jackson, R.B. Environment, Water uptake and hydraulic redistribution across large woody root systems to 20 m depth. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 2132–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, R.B.; Cardon, Z.G. The magnitude of hydraulic redistribution by plant roots: A review and synthesis of empirical and modeling studies. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iborra, J.F. Coupled Transcription and Translation within Nuclei of Mammalian Cells. Science 2001, 293, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
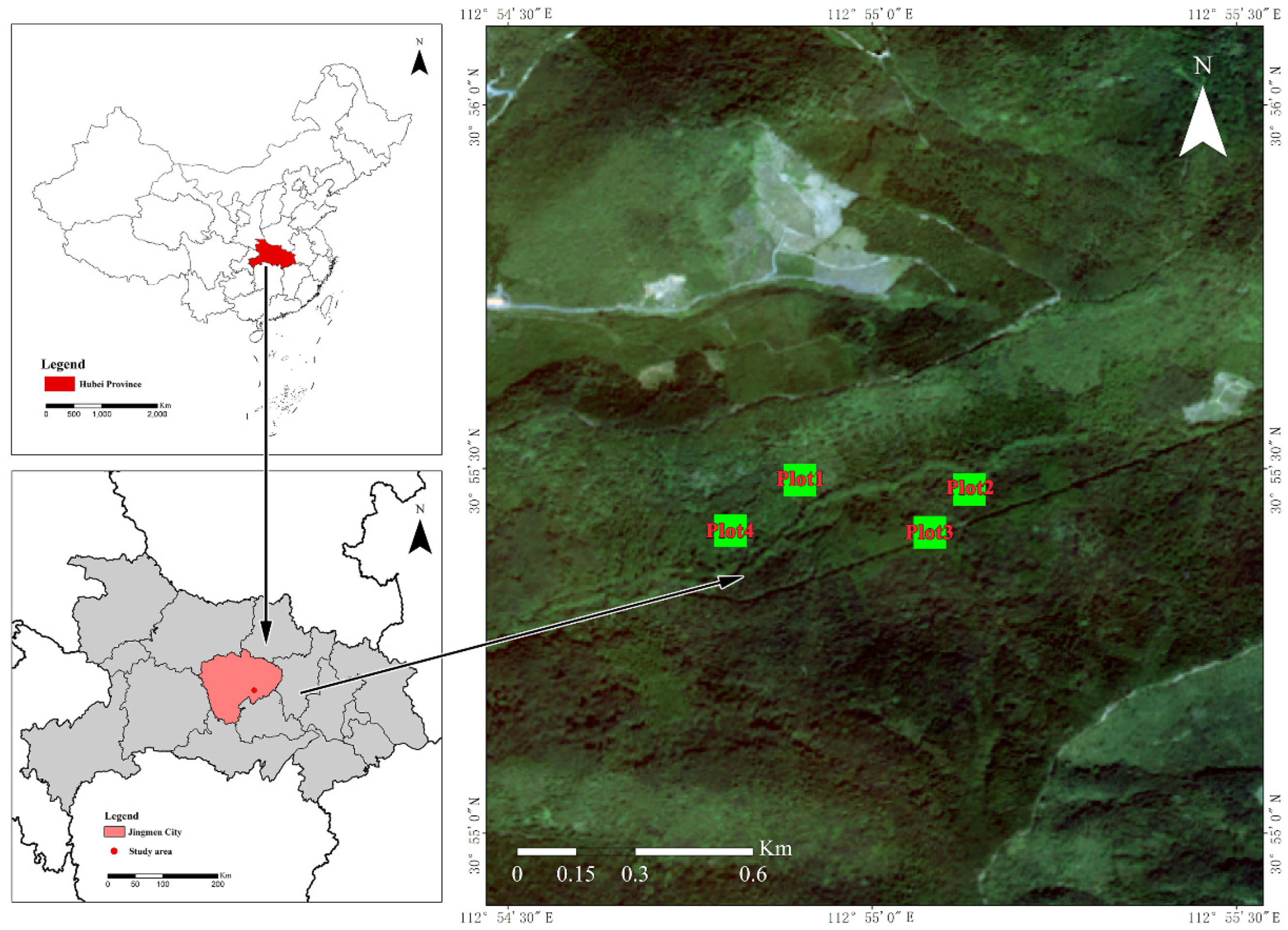




| Plots | Dominant Tree Species | Area (m2) | Slope (°) | Age (a) | Canopy Density (%) | Soil Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Soil Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plot 1 | P. massoniana | 20 × 20 | 15 | 30a | 60 | 1.36 | 40.57 |
| Plot 2 | C. lanceolata | 20 × 20 | 11 | 30a | 64 | 1.45 | 42.58 |
| Plot 3 | Q. acutissima | 20 × 20 | 12 | 35a | 71 | 1.29 | 45.63 |
| Plot 4 | C. funebris and I. corallina | 20 × 20 | 13 | 30a | 69 | 1.31 | 46.1 |
| Plots | Stand Type | Average Depth of Litter (cm) | Litter Storage (t·hm−2) | Maximum Moisture Capacity of Litter (t·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plot 1 | P. massoniana | 1.56 | 7.45 | 11.43 |
| Plot 2 | C. lanceolata | 2.98 | 7.99 | 12.06 |
| Plot 3 | Q. acutissima | 3.66 | 9.6 | 15.49 |
| Plot 4 | C. funebris and I. corallina | 3.35 | 8.25 | 14.79 |
| Average Soil Water Content (%) | P. massoniana | C. lanceolata | Q. acutissima | C. funebris I. corallina | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 June | 28 September | 16 June | 28 September | 16 June | 28 September | 16 June | 28 September | |
| Total | 22.56 ± 2.64 | 10.88 ± 1.07 | 22.29 ± 2.14 | 11.96 ± 1.21 | 23.46 ± 3.11 | 16.44 ± 1.71 | 22.64 ± 1.95 | 13.17 ± 1.55 |
| 0–10 cm | 20.48 ± 0.09 | 8.66 ± 0.19 | 22.96 ± 0.24 | 11.06 ± 0.75 | 31.25 ± 0.44 | 14.1 ± 0.06 | 25.25 ± 0.22 | 12 ± 0.92 |
| 10–40 cm | 25.03 ± 3.26 | 10.98 ± 0.92 | 23.75 ± 1.36 | 12.4 ± 1.56 | 24.02 ± 0.8 | 15.36 ± 1.46 | 24.27 ± 1.4 | 11.53 ± 0.68 |
| 40–70 cm | 22.42 ± 1.69 | 11 ± 0.86 | 23.15 ± 1.24 | 12.41 ± 1.01 | 21.4 ± 1.32 | 16.46 ± 0.88 | 21.6 ± 1.37 | 14.1 ± 1.4 |
| 70–100 cm | 20.93 ± 0.54 | 11.41 ± 0.64 | 19.76 ± 1.62 | 11.39 ± 0.76 | 22.36 ± 1.83 | 18.27 ± 0.74 | 21.17 ± 0.88 | 14.29 ± 0.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J. Soil Water Use Strategies of Dominant Tree Species Based on Stable Isotopes in Subtropical Regions, Central China. Water 2022, 14, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060954
Li Y, Zhu F, Wang Y, Cheng J. Soil Water Use Strategies of Dominant Tree Species Based on Stable Isotopes in Subtropical Regions, Central China. Water. 2022; 14(6):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060954
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuchen, Fangfang Zhu, Yu Wang, and Jinhua Cheng. 2022. "Soil Water Use Strategies of Dominant Tree Species Based on Stable Isotopes in Subtropical Regions, Central China" Water 14, no. 6: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060954
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhu, F., Wang, Y., & Cheng, J. (2022). Soil Water Use Strategies of Dominant Tree Species Based on Stable Isotopes in Subtropical Regions, Central China. Water, 14(6), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060954





