Characteristics of Ions Composition and Chemical Weathering of Tributary in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region: The Perspective of Stratified Water Sample from Xiaojiang River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
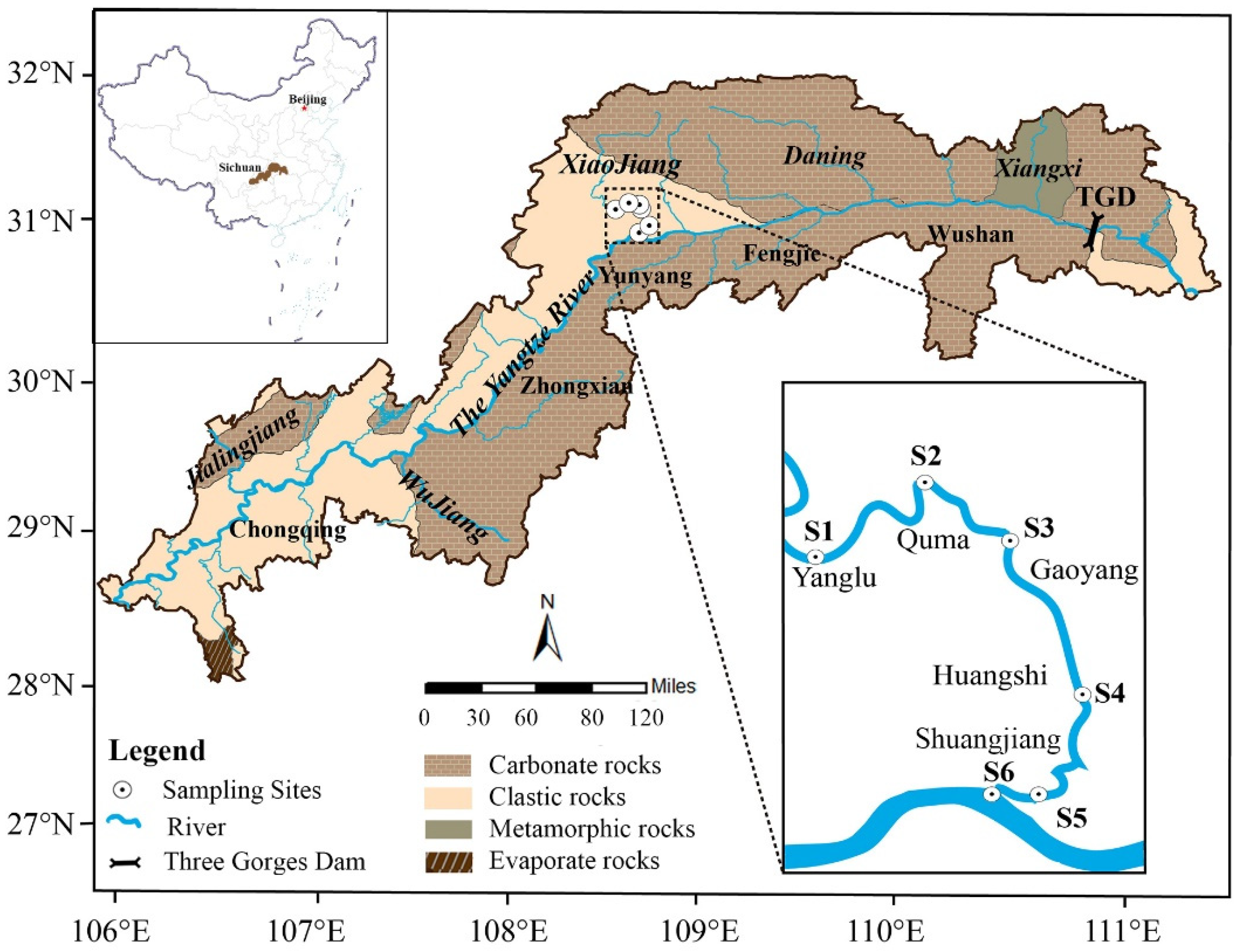
2.1. Location of Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Treatment
2.3. Measurement of Parameters
2.4. Measurement of Contribution Ratio
2.5. Measurement of Chemical Weathering Rate and CO2 Consumption
2.6. Statistical and Spatial Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
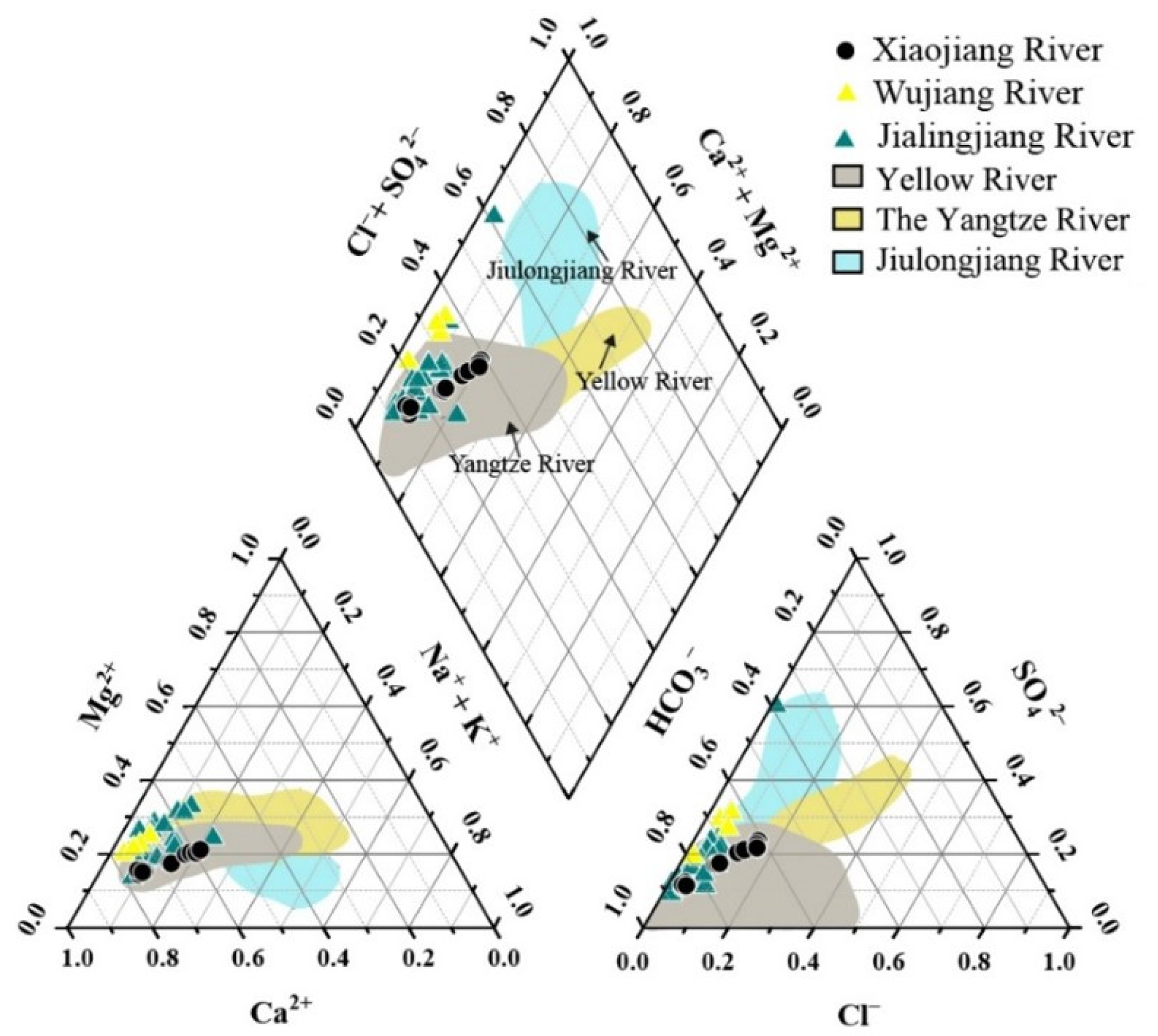
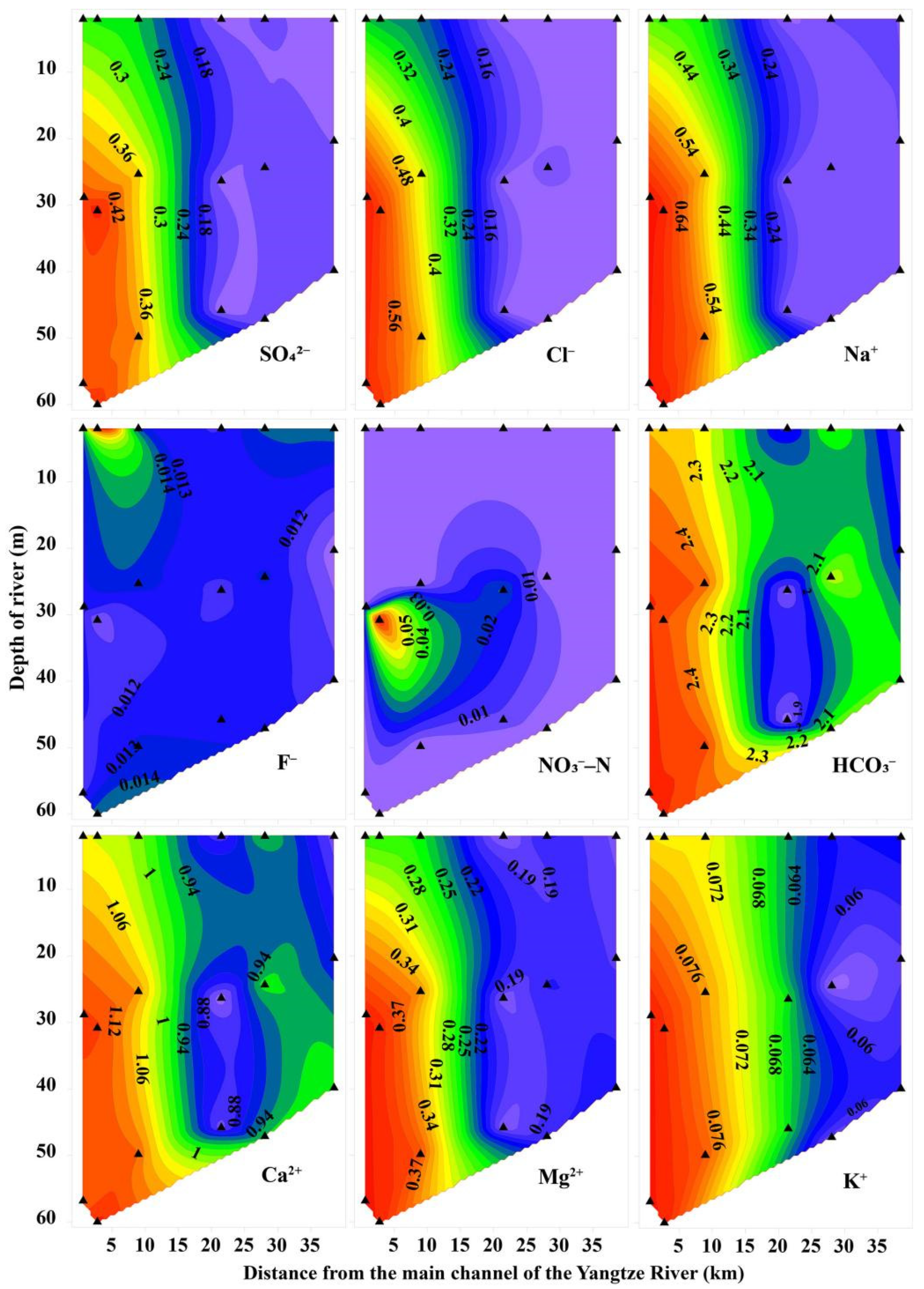
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Xiaojiang River
3.2. Source Apportionment of Riverine Ions
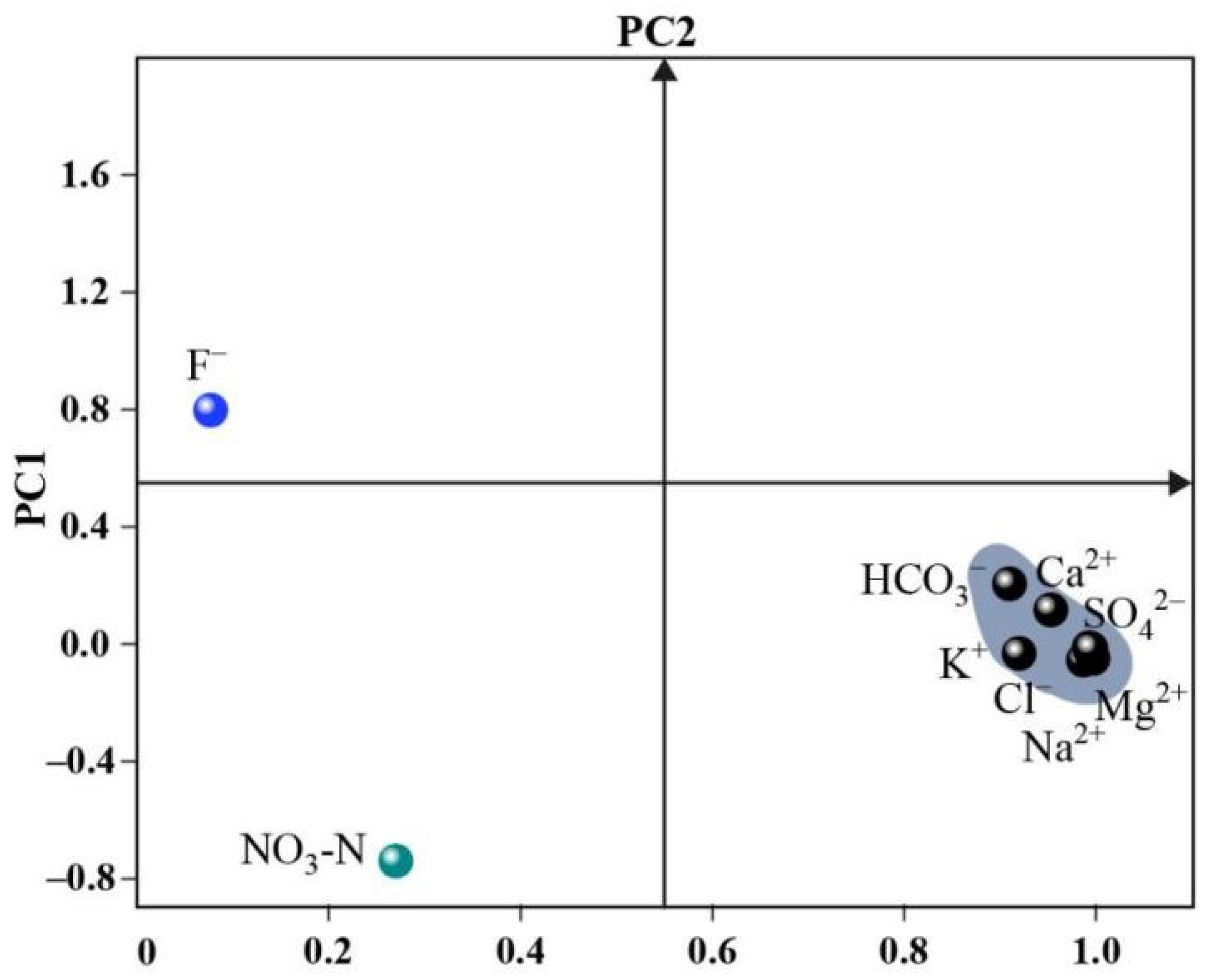
3.2.1. PCA Analysis
3.2.2. Stoichiometry of Weathering Processes
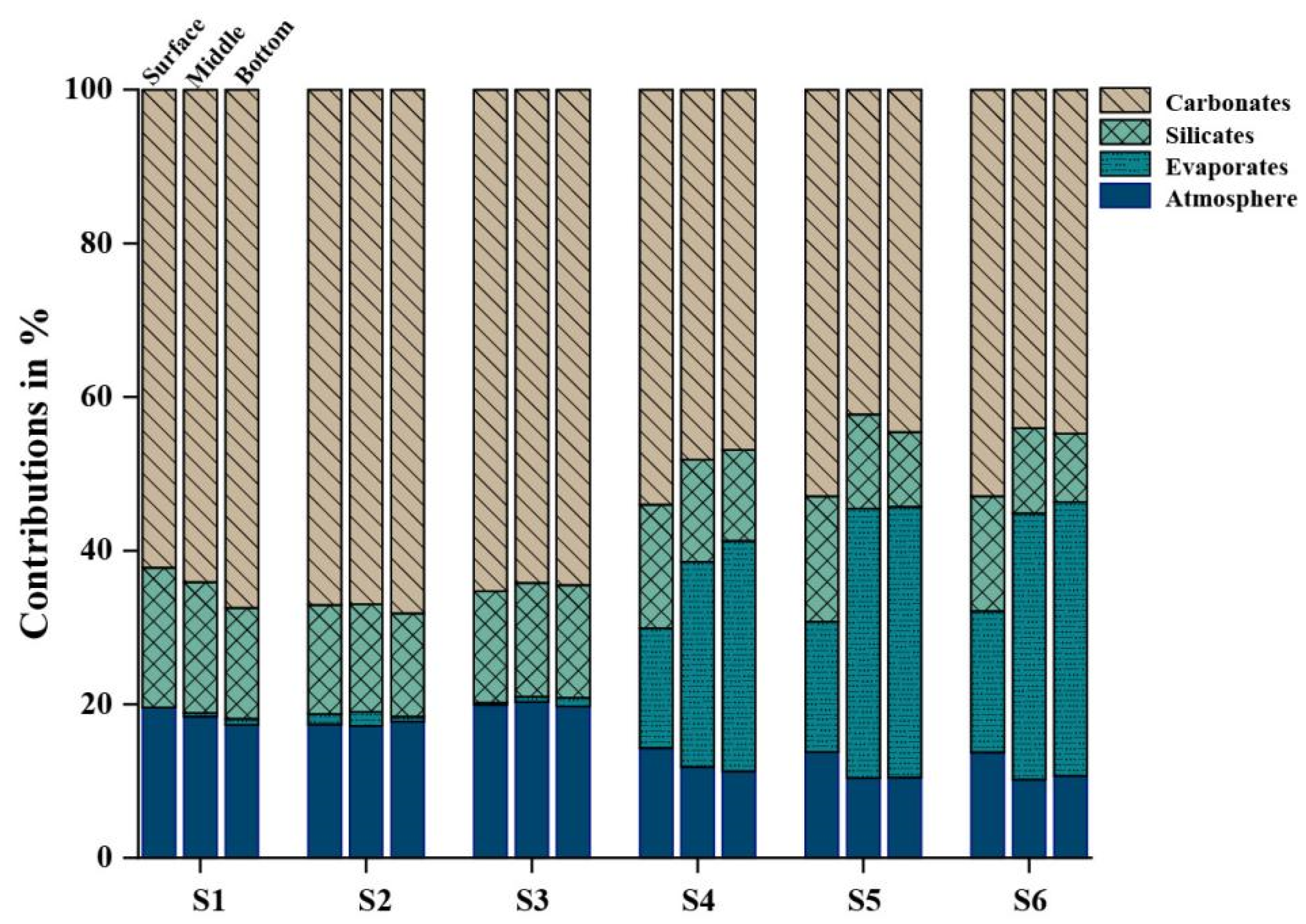
3.2.3. Contribution Proportion of Weathering Sources
3.3. Protons of Chemical Weathering Agent and CO2 Consumption
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The hydrochemical type of Xiaojiang River at different depths was consistent (Ca2+−HCO3− type), and the concentrations of Ca2+ and HCO3− dominated the total cations and anions of stratified water, respectively. This ionic characteristic was similar to that of other rivers in the TGR during wet season.
- (2)
- The ionic composition of river water was mainly controlled by rock weathering, and carbonate weathering had the highest ionic contribution (about 60%). Evaporites provided about 35% of the ionic contribution to the reach near the mouth. In addition, the ionic contribution of anthropogenic input to stratified water was not obvious.
- (3)
- Compared with other major tributaries of TGR, Xiaojiang River had a high rock weathering rate. The average weathering rate of carbonates in Xiaojiang River was 19.33 ± 0.68 ton/km2/year, which was twice higher than the Jialingjiang River and Wujiang River. However, weathering processes in the Xiaojiang River had a limited ability to consume CO2, which accounted for only about 1% of the CO2 consumption in the TGR basin.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Y. Groundwater in the Earth’s critical zone: Relevance to large-scale patterns and processes. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3052–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ciais, P.; Mackenzie, F.T.; Gruber, N.; Janssens, I.A.; Laruelle, G.G.; Lauerwald, R.; Luyssaert, S.; Andersson, A.J.; et al. Anthropogenic perturbation of the carbon fluxes from land to ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Su, L.; Craig, N.J.; Du, F.; Wu, C.; Shi, H. Comparison of microplastic pollution in different water bodies from urban creeks to coastal waters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Han, G. Tracing riverine particulate black carbon sources in Xijiang River Basin: Insight from stable isotopic composition and bayesian mixing model. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, V.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B.; Eglinton, T. Global carbon export from the terrestrial biosphere controlled by erosion. Nature 2015, 521, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvert, C.; Butman, D.E.; Marx, A.; Ribolzi, O.; Hutley, L.B. CO2 evasion along streams driven by groundwater inputs and geomorphic controls. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffre, P.; Swanson-Hysell, N.L.; Goddéris, Y. Limited carbon cycle response to increased sulfide weathering due to oxygen feedback. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Song, Z. Carbon-nitrogen isotope coupling of soil organic matter in a karst region under land use change, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 107027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luo, J.; Wu, D.; Jun Xu, Y. Carbon and nutrients as indictors of daily fluctuations of pCO2 and CO2 flux in a river draining a rapidly urbanizing area. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Qu, W.; Ren, W.; Qian, H. Impacts of chemical weathering and human perturbations on dissolved loads of the Wei River, the Yellow River catchment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tang, C.; Cao, G.; Wang, X. Hydrochemical zoning: Natural and anthropogenic origins of the major elements in the surface water of Taizi River Basin, Northeast China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, R. Potassium and its isotope behaviour during chemical weathering in a tropical catchment affected by evaporite dissolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 316, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; He, D.; Wang, H. Environmental consequences of damming the mainstream Lancang-Mekong River: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 146, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; McDonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauerwald, R.; Laruelle, G.G.; Hartmann, J.; Ciais, P.; Regnier, P.A.G. Spatial patterns in CO2 evasion from the global river network. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 534–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Q. Effects of agricultural abandonment on soil aggregation, soil organic carbon storage and stabilization: Results from observation in a small karst catchment, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 288, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, F.; Liu, W. Characteristics of streamflow in the main stream of Changjiang River and the impact of the Three Gorges Dam. Catena 2020, 189, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.K.; Wu, S.; Ma, M.; Huang, P. Reservoir CO2 evasion flux and controlling factors of carbon species traced by δ13CDIC at different regulating phases of a hydro-power dam. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, X.X.; He, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Ziegler, A.D. Daily CO2 partial pressure and CO2 outgassing in the upper Yangtze River basin: A case study of the Longchuan River, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 466–467, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Tan, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, C. Comparison of carbon emissions from the southern and northern tributaries of the Three Gorge Reservoir over the Changjiang River Basin, China. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Fang, F.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, J. The biotransformation of soil phosphorus in the water level fluctuation zone could increase eutrophication in reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Chen, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Dan, S.F. Nutrient dynamics in the Changjiang and retention effect in the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G. Tracing zinc sources with Zn isotope of fluvial suspended particulate matter in Zhujiang River, southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, R.R.; Zhang, F.; Rehman, F.U.; Wang, G.; Ye, M.; Zeng, C.; Tang, H. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, H.; Shi, C.; Zhao, T.; Liang, C.; Hu, J.; Xu, Z. Chemical and strontium isotopic characteristics of the rivers around the Badain Jaran Desert, northwest China: Implication of river solute origin and chemical weathering. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wang, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, W. Characterization of mixing processes in the confluence zone between the Three Gorges Reservoir mainstream and the daning river using stable isotope analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9907–9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Chen, H.; Mi, T. Major ion geochemistry and nutrient behaviour in the mixing zone of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River and its tributaries in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Hydrol. Processes 2010, 24, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G. Preliminary copper isotope study on particulate matter in Zhujiang River, southwest China: Application for source identification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetelat, B.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.L. Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin rivers: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4254–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Pace, M.L.; Utz, R.M.; Haq, S.; Gorman, J.; Grese, M. Freshwater salinization syndrome on a continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E574–E583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Liang, B.; Qu, R.; Liu, M.; Liu, J. Potentially toxic elements in cascade dams-influenced river originated from Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Han, G.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, X. Major elements in the upstream of Three Gorges Reservoir: An investigation of chemical weathering and water quality during flood events. Water 2021, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Major element chemistry of the Changjiang (Yangtze River). Chem. Geol. 2002, 187, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, M.; Sun, C.; Wu, W.; Ran, X.; Zang, J. Variability in water chemistry of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, D.; Wei, S.; Yan, J.; Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Gao, J.; et al. Influences of the alternation ofwet-dry periods on the variability of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Tao, Y. Damming effects on dissolved inorganic carbon in different kinds of reservoirs in Jialing River, Southwest China. Acta Geochim. 2017, 36, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liu, C.-Q. Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: A study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province, China. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Li, S.-l.; Tao, F.; Yue, F.; Liu, C.-Q. Sensitivity of chemical weathering and dissolved carbon dynamics to hydrological conditions in a typical karst river. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, C.; Fu, L.; Yu, J.; Taylor, W.D.; Hamilton, P.B.; Cappellen, P.V.; Ji, D.; Liu, D.; et al. Unique surface density layers promote formation of harmful algal blooms in the Pengxi River, Three Gorges Reservoir. Freshw. Sci. 2020, 39, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Engel, B.A.; Peng, H.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, M.; Dai, M. Modelling hydrology and water quality processes in the Pengxi River basin of the Three Gorges Reservoir using the soil and water assessment tool. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 182, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yasarer, L.M.W.; Li, Z.; Sturm, B.S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J.; Shen, Y. Air–water CO2 and CH4 fluxes along a river–reservoir continuum: Case study in the Pengxi River, a tributary of the Yangtze River in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.; Guo, J. Spatio-temporal variations in Phytoplankton communities in sediment and surface water as reservoir drawdown—A case study of Pengxi River in Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water 2021, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, H.W. Using the Köppen classification to quantify climate variation and change: An example for 1901–2010. Environ. Dev. 2013, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, J. Change of water environmental capacity in the Xiaojiang River after impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Res. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wasowski, J.; Juang, C.H. Geohazards in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China–Lessons learned from decades of research. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Wu, L.; Hou, X.-Y.; Zheng, B.-H.; Li, H.; Norra, S. Role of reservoir construction in regional land use change in Pengxi River basin upstream of the Three Gorges Reservoir in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, C.W.; Salisbury, J.E.; Vandemark, D. Contribution of non-carbonate anions to total alkalinity and overestimation of pCO2 in New England and New Brunswick rivers. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 3069–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupreb, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, F.; Tan, Q. Effects of land use on water chemistry in a river draining karst terrain, southwest China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adimalla, N. Groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and potential health risks assessment: A case study from semi-arid region of south India. Expo. Health 2018, 11, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Yang, K. Assessment and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a tropical catchment, northeast Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q. Vertical distribution and contamination of soil mercury in karst catchment, southwest China: Land-use type influence. Clean–Soil Air Water 2021, 49, 2100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Gao, J.; Tian, s.; Shi, G.; Chen, F.; Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Han, D. Chemical and isotopic characteristics of the water and suspended particulate materials in the Yangtze River and their geological and enviromental implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 276–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Yang, K.; Liu, J. Hydro-Geochemistry of the river water in the Jiulongjiang River basin, southeast China: Implications of anthropogenic inputs and chemical weathering. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, T.; Gao, J.; Tian, S.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Han, D. Chemical and isotopic characters of the water and suspended particulate materials in the Yellow River and their geological and environmental implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 285–351. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, C.; Tang, Y.; Han, H. Chemical and strontium isotopic compositions of the Hanjiang Basin Rivers in China: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Aquat. Geochem. 2011, 17, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Han, G. Sulfur isotope and chemical composition of the rainwater at the Three Gorges Reservoir. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, T.K.; Krishnaswami, S.; Sarin, M.M. Major ion chemistry in the headwaters of the Yamuna river system: Chemical weathering, its temperature dependence and CO2 consumption in the Himalaya. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 3397–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Z. Water geochemistry of rivers draining karst-dominated regions, Guangxi province, South China: Implications for chemical weathering and role of sulfuric acid. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 163, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.; Baronas, J.J.; Clark, K.E.; Feakins, S.J.; West, A.J. Mixing as a driver of temporal variations in river hydrochemistry: 1. Insights from conservative tracers in the Andes-Amazon transition. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 3102–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, R.; Hu, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Heat budget contribute rate in the Three Gorges Reservoir tributary bay between mainstream and tributary using stable isotope analysis. Water Supply 2019, 19, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, Q.; Rhoads, B.; Sukhodolov, A.; Constantinescu, G. Advective lateral transport of streamwise momentum governs mixing at Small River confluences. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeya, N.; Kubota, T.; Shimizu, A.; Nobuhiro, T.; Tsuboyama, Y.; Chann, S.; Tith, N. Isotopic investigation of river water mixing around the confluence of the Tonle Sap and Mekong rivers. Hydrol. Processes 2008, 22, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N.; Sunitha, B.; Adimalla, N.; Chaudhary, M. Quality criteria for groundwater use from a rural part of Wanaparthy District, Telangana State, India, through ionic spatial distribution (ISD), entropy water quality index (EWQI) and principal component analysis (PCA). Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Han, G. Distributions and source identification of the major ions in Zhujiang River, southwest China: Examining the relationships between human perturbations, chemical weathering, water quality and health Risk. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Chang, Y.; Du, K.; Chan, A.; Yao, D. Seasonal fluxes and sources apportionment of dissolved inorganic nitrogen wet deposition at different land-use sites in the Three Gorges reservoir area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X. Zn isotope fractionation during the development of low-humic gleysols from the Mun River Basin, northeast Thailand. Catena 2021, 206, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Carbon cycling in global drylands. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2019, 5, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, K.; Chamberlain, C.P. Hydrologic regulation of chemical weathering and the geologic carbon cycle. Science 2014, 343, 1502–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipper, E.T.; Stevenson, E.I.; Alcock, V.; Knight, A.C.G.; Baronas, J.J.; Hilton, R.G.; Bickle, M.J.; Larkin, C.S.; Feng, L.; Relph, K.E.; et al. Global silicate weathering flux overestimated because of sediment–water cation exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2016430118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Huh, Y.; Qin, J.; Pho, N.v. Chemical weathering in the Hong (Red) River basin: Rates of silicate weathering and their controlling factors. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 1411–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.X.; Sun, H.; Han, J.; Higgitt, D.L. Major ion chemistry and dissolved inorganic carbon cycling in a human-disturbed mountainous river (the Luodingjiang River) of the Zhujiang (Pearl River), China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2796–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, B.; Wang, H.; Tian, M.; Cui, J.; Fu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, F. Chemical characteristics of precipitation in a typical urban site of the hinterland in Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 2914313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Yu, S.; Xin, C.; Sun, P.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, T. Impact of the atmospheric deposition of major acid rain components, especially NH4, on carbonate weathering during recharge in typical karst areas of the Lijiang River basin, southwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 114, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Detection Limit | Range | Mean | ±SD | WHO a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [F−] (mmol/L) | 0.03 | 0.01–0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.08 |
| [Cl−] (mmol/L) | 0.04 | 0.08–0.65 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 7.05 |
| [NO3–N] (mmol/L) | 0.06 | 0.00–0.09 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.18 |
| [SO42−] (mmol/L) | 0.10 | 0.12–0.47 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 3.12 |
| [HCO3−] (mmol/L) | - | 1.81–2.51 | 2.21 | 0.25 | - |
| [Na+] (mmol/L) | 0.03 | 0.15–0.72 | 0.37 | 0.23 | - |
| [K+] (mmol/L) | 0.01 | 0.06–0.08 | 0.07 | 0.01 | - |
| [Ca2+] (mmol/L) | 0.04 | 0.82–1.17 | 1.00 | 0.12 | - |
| [Mg2+] (mmol/L) | 0.01 | 0.16–0.41 | 0.27 | 0.09 | - |
| TDS b (mg/L) | 1 | 118–2 02 | 156 | 20 | 1000 |
| EC c (μs/cm) | 1 | 211–360 | 277 | 20 | - |
| pH | 0.1 | 7.50–7.95 | 7.75 | 1.8 | 6.5–8.5 |
| Variable | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| [HCO3−] | 0.91 | 0.205 |
| [Cl−] | 0.987 | −0.055 |
| [NO3–N] | 0.27 | −0.74 |
| [SO42−] | 0.997 | −0.049 |
| [Na+] | 0.993 | −0.012 |
| [K+] | 0.92 | −0.032 |
| [Mg2+] | 0.995 | −0.015 |
| [Ca2+] | 0.953 | 0.117 |
| Eigenvalues | 6.607 | 1.247 |
| Variance (%) | 73.406 | 13.885 |
| Cumulative (%) | 73.406 | 87.261 |
| K+/Cl− | Na+/Cl− | SO42−/Cl− | Ca2+/Cl− | Mg2+/Cl− | Ca2+/Na+ | Mg2+/Na+ | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rain | 0.55 | 0.59 | - | 1.74 | 0.56 | - | - | Wu and Han [57] |
| - | - | 2.06 | - | - | - | - | Zhang et al. [73] | |
| Silicates | - | - | - | - | - | 0.35 | 0.24 | Gaillardet et al. [48] |
| Sample | Silicates | Carbonates | Evaporites | Total Rock Weathering | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φsil (ton/km2/ year) | Catsil a (105 ton/year) | CO2 ssw b (109 mol/year) | CO2 csw c (109 mol/year) | Φcarb (ton/km2/ year) | TDScarb d (105 ton/year) | CO2 scw c (109 mol/year) | CO2 ccw b (109 mol/year) | TDSevap e (105 ton/year) | TDStotal f (105 ton/year) | |
| S1 | 3.43 ± 0.18 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.70 ± 0.05 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | 18.44 ± 1.88 | 2.75 ± 0.24 | 2.46 ± 0.33 | 2.57 ± 0.27 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 2.93 ± 0.25 |
| S2 | 2.95 ± 0.24 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.74 ± 0.05 | 0.74 ± 0.05 | 20.25 ± 0.13 | 3.06 ± 0.03 | 2.83 ± 0.02 | 2.83 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 3.25 ± 0.03 |
| S3 | 2.95 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.68 ± 0.07 | 0.72 ± 0.01 | 16.97 ± 0.37 | 2.55 ± 0.04 | 2.38 ± 0.12 | 2.42 ± 0.06 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 2.72 ± 0.03 |
| S4 | 4.35 ± 0.12 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 1.06 ± 0.04 | 1.06 ± 0.04 | 19.93 ± 0.58 | 3.21 ± 0.13 | 2.92 ± 0.15 | 2.92 ± 0.15 | 1.27 ± 0.51 | 4.71 ± 0.64 |
| S5 | 4.05 ± 0.52 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.98 ± 0.15 | 0.98 ± 0.15 | 20.04 ± 0.59 | 3.25 ± 0.11 | 2.97 ± 0.15 | 2.97 ± 0.15 | 1.68 ± 0.79 | 5.14 ± 0.85 |
| S6 | 3.65 ± 0.58 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.87 ± 0.17 | 0.87 ± 0.17 | 20.32 ± 0.68 | 3.25 ± 0.09 | 3.02 ± 0.18 | 3.02 ± 0.18 | 1.65 ± 0.71 | 5.10 ± 0.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Han, G.; Li, B.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, X. Characteristics of Ions Composition and Chemical Weathering of Tributary in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region: The Perspective of Stratified Water Sample from Xiaojiang River. Water 2022, 14, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030379
Wang D, Han G, Li B, Hu M, Wang Y, Liu J, Zeng J, Li X. Characteristics of Ions Composition and Chemical Weathering of Tributary in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region: The Perspective of Stratified Water Sample from Xiaojiang River. Water. 2022; 14(3):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030379
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Di, Guilin Han, Bogen Li, Mingming Hu, Yuchun Wang, Jinke Liu, Jie Zeng, and Xiaoqiang Li. 2022. "Characteristics of Ions Composition and Chemical Weathering of Tributary in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region: The Perspective of Stratified Water Sample from Xiaojiang River" Water 14, no. 3: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030379
APA StyleWang, D., Han, G., Li, B., Hu, M., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Zeng, J., & Li, X. (2022). Characteristics of Ions Composition and Chemical Weathering of Tributary in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region: The Perspective of Stratified Water Sample from Xiaojiang River. Water, 14(3), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030379








