Optimum Multiparameter Analysis of Water Mass Structure off Western Guangdong during Spring Monsoon Transition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Optimum Multiparameter Method
3. Results and Discussion
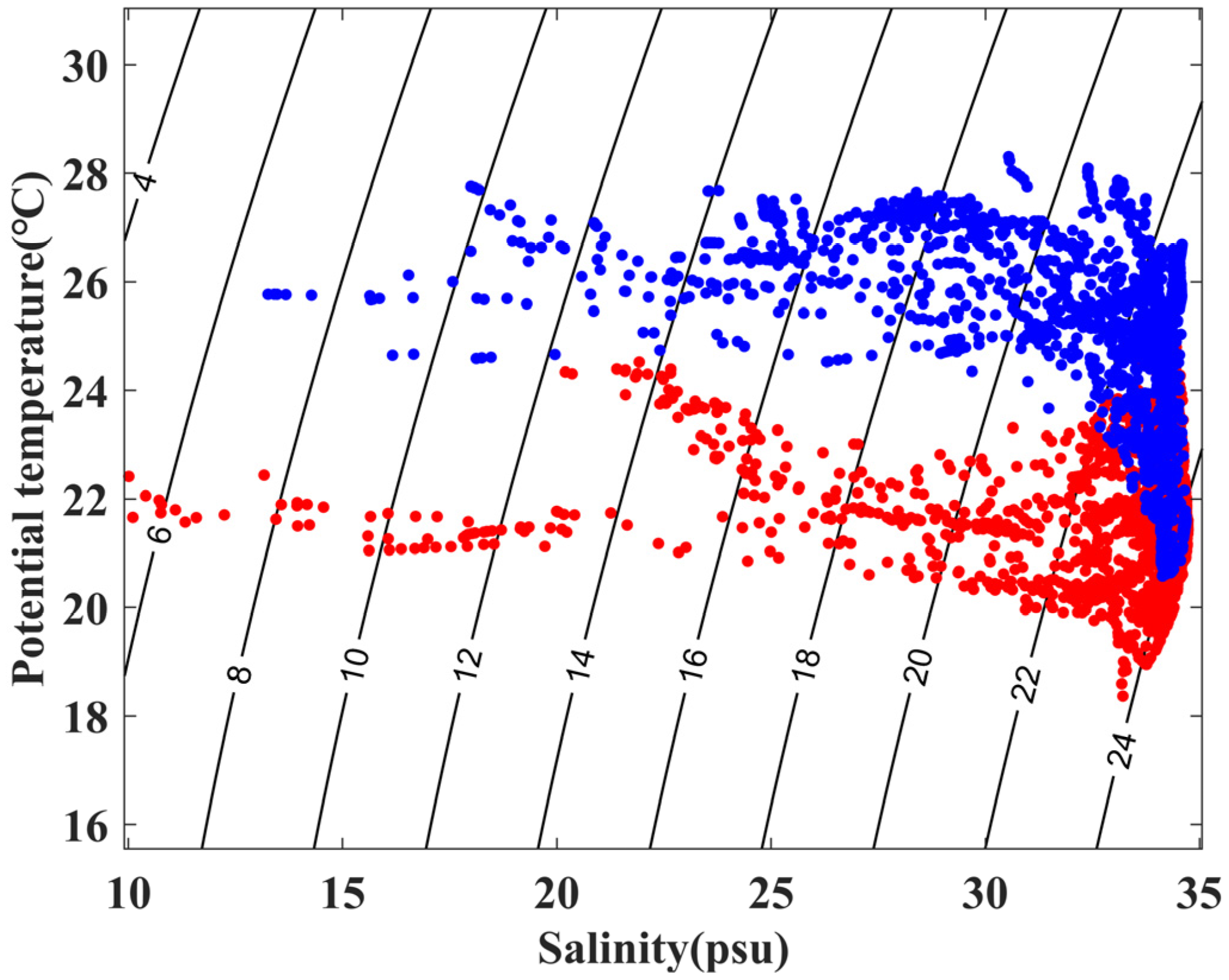
3.1. Definition of Source Water Types
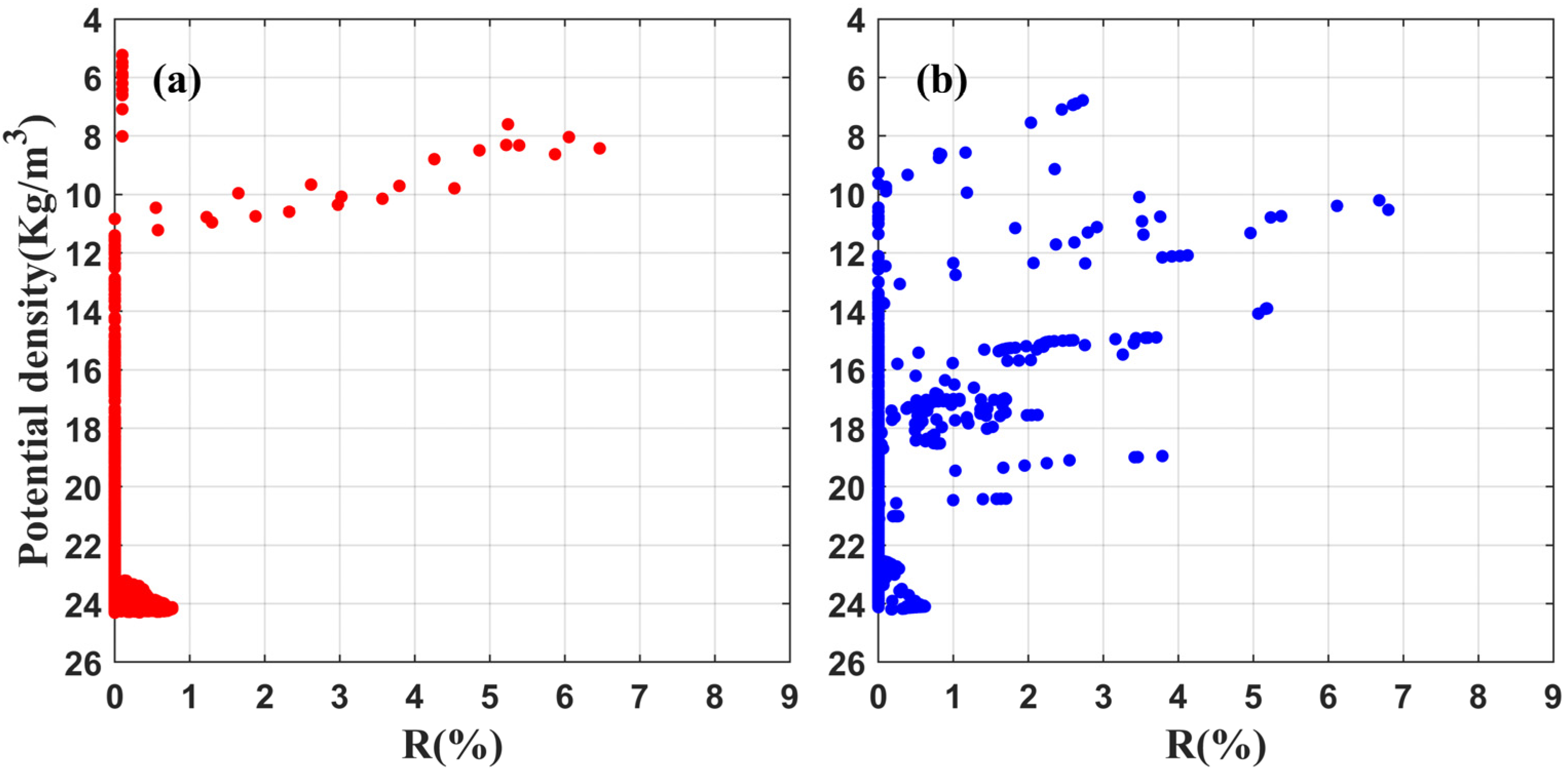
3.2. Uncertainties
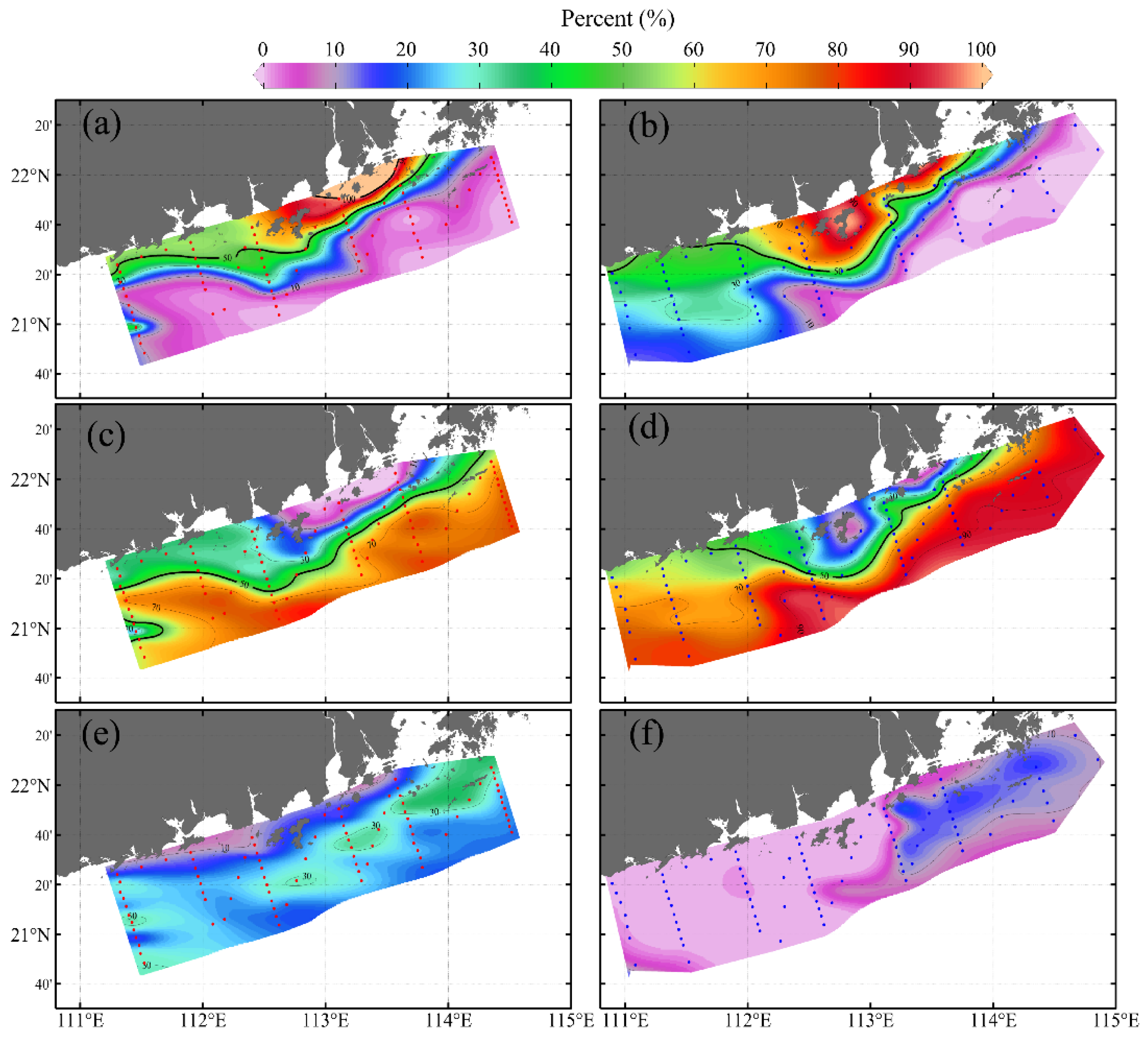
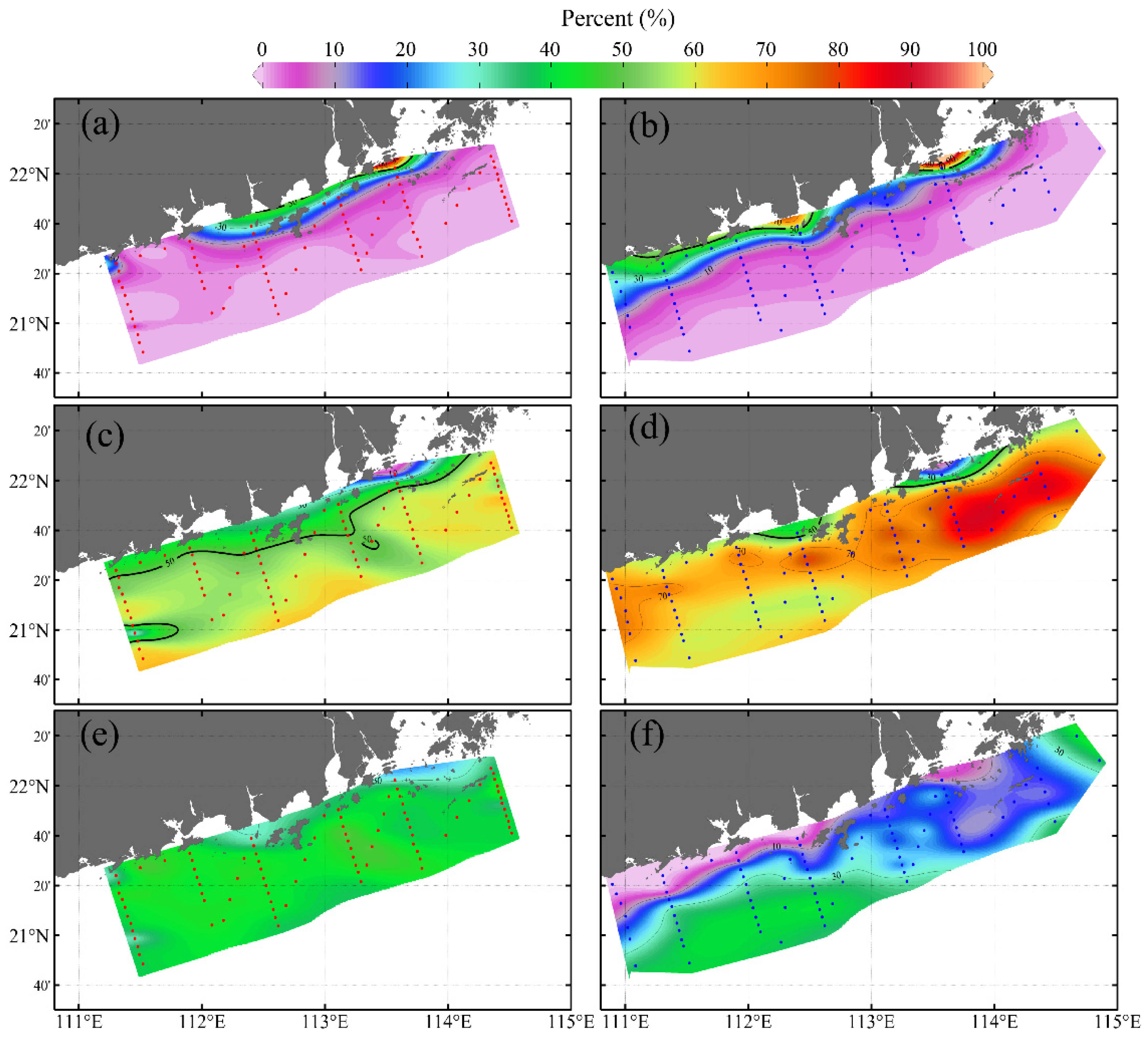
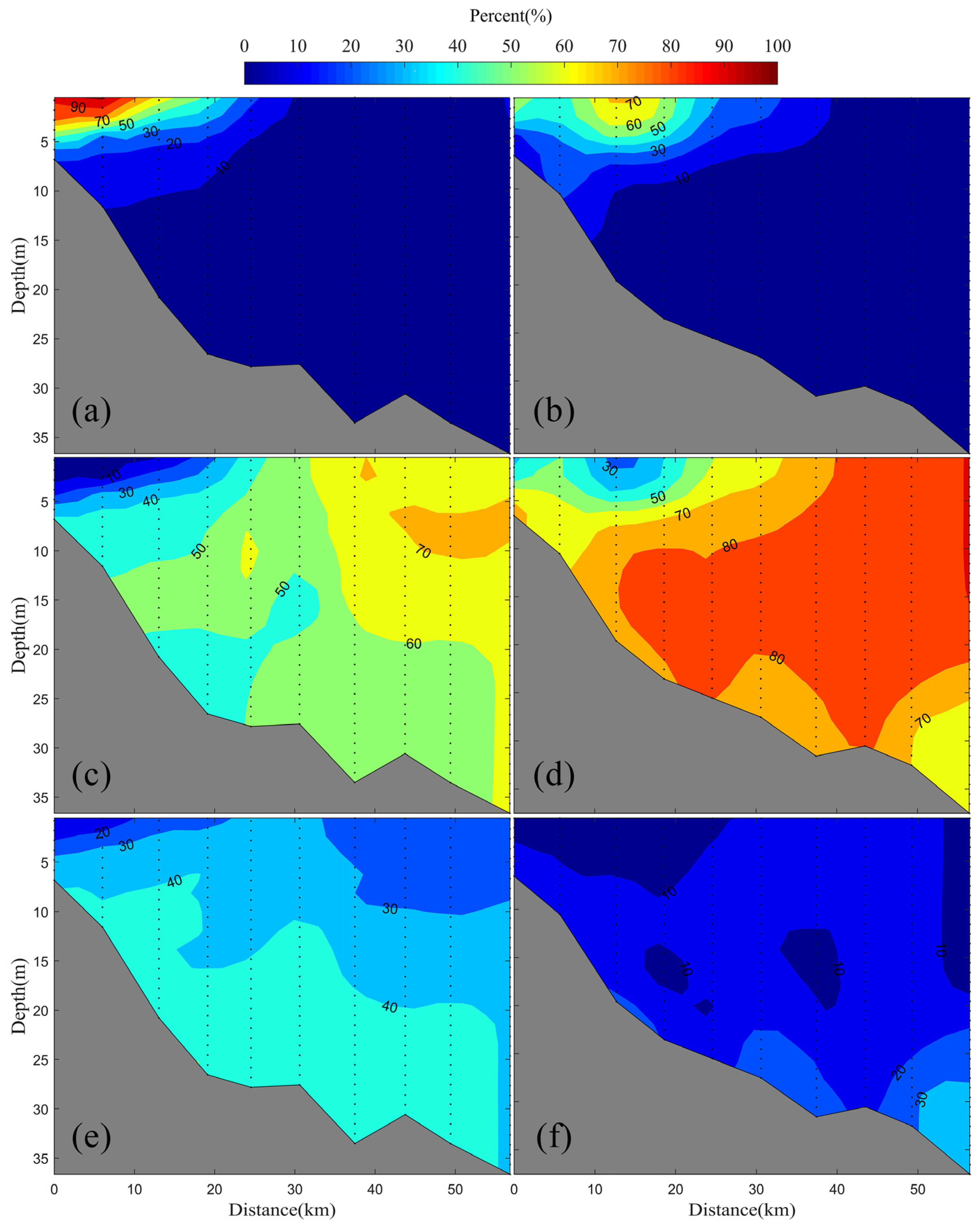
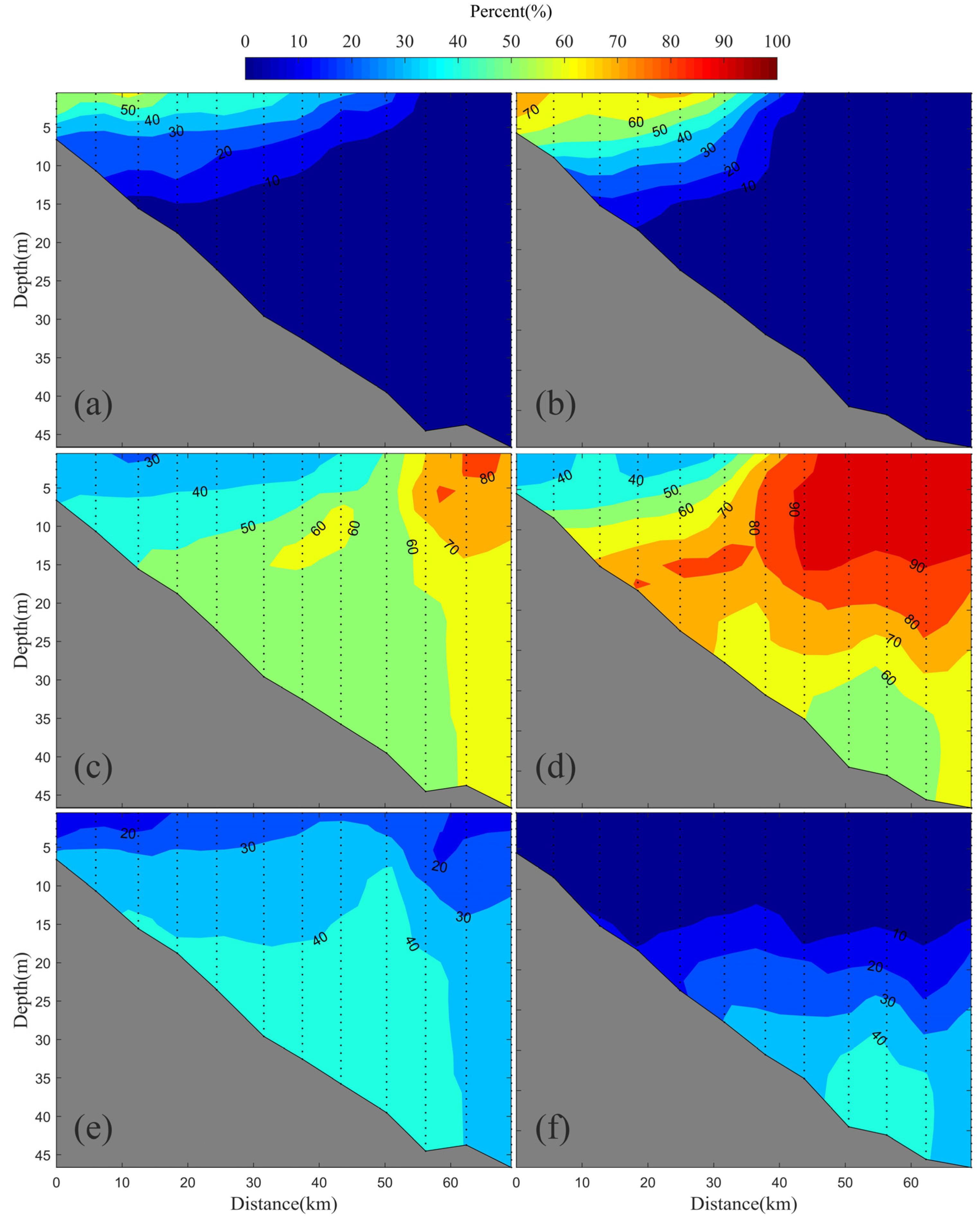
3.3. Water Mass Distributions
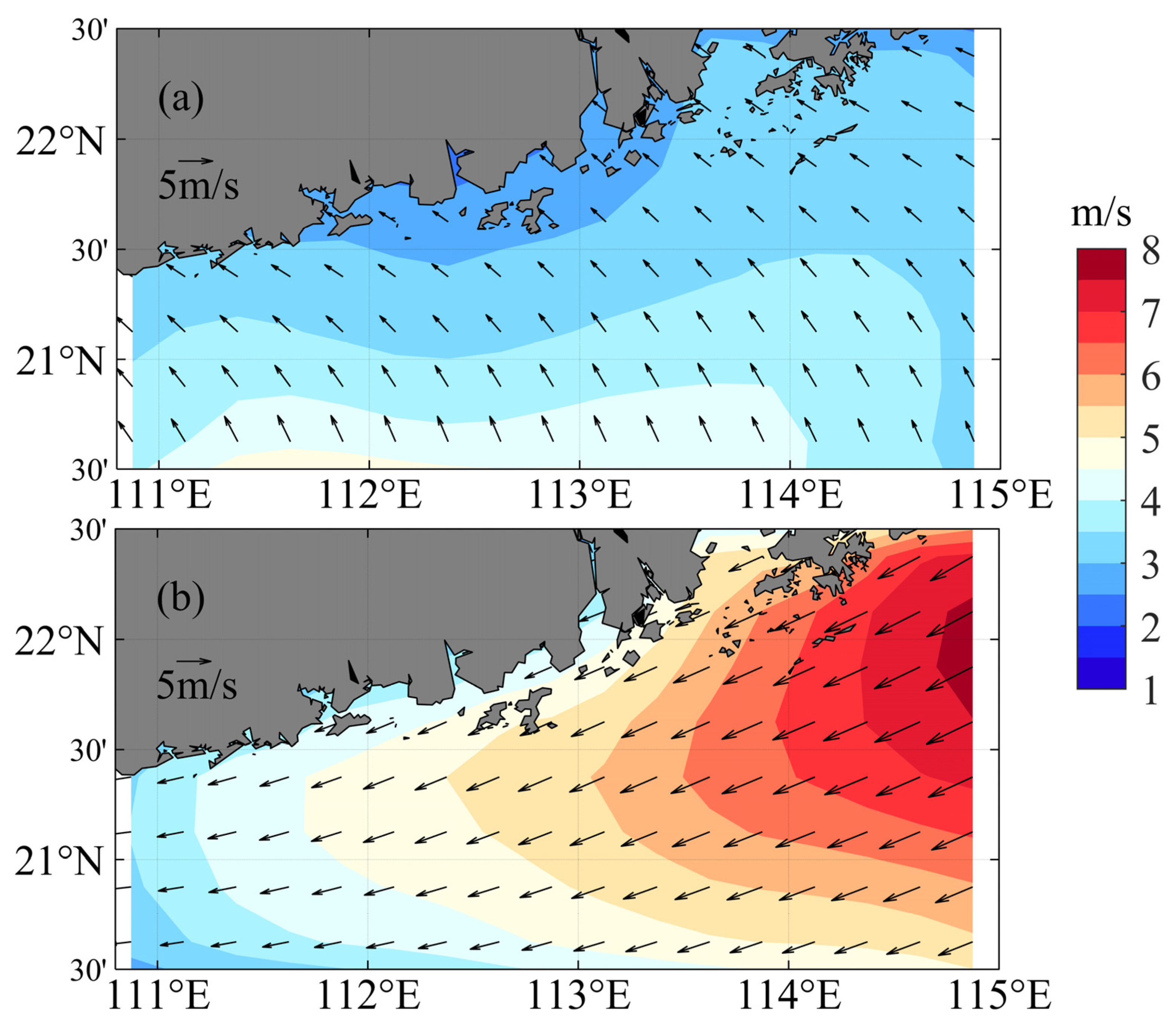
3.4. Factors Influencing Water Mass Variability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helland-Hansen, B. Nogen Hydrografiske Metoder; Scand, Naturforsker Mote, Kristiana: Oslo, Norway, 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, R.B. Water characteristics of Atlantic Ocean and of world ocean. Deep Sea Res. (1953) 1958, 5, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Q.; Su, Y.S.; Wang, F.Q.; Yu, Z.X. Discussion of some concepts of the water mass by the theory of fuzzy sets. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1986, 17, 102–110, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tomczak, M. Some historical, theoretical and applied aspects of quantitative water mass analysis. J. Mar. Res. 1999, 57, 275–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haine, T.W.N.; Hall, T.M. A generalized transport theory: Water-mass composition and age. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 1932–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M.; Godfrey, J.S. Regional Oceanography: An Introduction; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, A.K.; Frolicher, T.L.; Sarmiento, J.L. Upwelling in the Southern Ocean. Phys. Today 2015, 68, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk, N.; Llovel, W.; Portela, E. Interannual Variability of Upper Ocean Water Masses as Inferred from Argo Array. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 6067–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Y.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, Z.J.; Ge, Z.M.; Ma, M.Z.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, Q. Distribution of Pearl diluted water and its ecological characteristics during spring monsoon transitional period in 2016. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2021, 40, 63–71, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Jiang, X.; Xie, S.P.; Liu, W.T. A gap in the Indo-Pacific warm pool over the South China Sea in boreal winter: Seasonal development and interannual variability. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109, C07012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrtki, K. Physical Oceanography of the Southeast Asian Waters; University of California, Scripps Institution of Oceanography: La Jolla, CA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Shang-Ping, X.; Qiang, X.; Dongxiao, W.; Liu, W.T. Summer upwelling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Li, J.X.; Wang, C.Z.; Yan, Y.W. Interactions among the winter monsoon, ocean eddy and ocean thermal front in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, C08002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Ma, R.; Gao, G.; Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.C. Impact of multichannel river network on the plume dynamics in the Pearl River estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 5766–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Ma, R.; Huang, M.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Xie, C.; Beardsley, R.C. Downwelling wind, tides, and estuarine plume dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 4245–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.; Zu, T.T. Progress on shelf and slope circulation in the northern South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Q.; Su, Y.S.; Fan, L.Q. Discrimination analysis of water masses in the north area of the South China Sea. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 1987, 3, 15–20, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Q.; Su, Y.S.; Fan, L.Q. Application of fuzzy mathematics method in water mass analysis in the northern South China Sea. Haiyang Xuebao 1987, 669–680, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.Q.; Su, Y.S.; Li, F.Q. Analysis of water masses in the northern South China Sea. Haiyang Xuebao 1988, 2, 136–145, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.Y. Water mass analysis in Luzon Strait and northern South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 1998, 2, 207–213, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T.; Wei, H. Analysis of Water Masses in the Northern South China Sea and Bashi Channel. Period. Ocean. Univ. Qingdao 2005, 1, 9–12, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.S.; Sun, J.D.; Zu, T.T.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.X. Analysis of water masses in the northern South China Sea in summer 2011. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2014, 33, 10–16, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zheng, Q.A.; Hu, J.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Chen, D.W.; Chen, Z.Z.; Sun, Z.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Kong, H. Classification and 3-D distribution of upper layer water masses in the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, R.X.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Y.X.; Hu, J.Y. Using the Sigma-Pi Diagram to Analyze Water Masses in the Northern South China Sea in Spring. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zhong, Y.S.; Zhu, Y.W.; Yang, C.H.; Xu, M.Q.; Xu, D.F.; Hu, Z.Y. Intrusions of Kuroshio and Shelf Waters on Northern Slope of South China Sea in Summer 2015. J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M., Jr. A multi-parameter extension of temperature/salinity diagram techniques for the analysis of non-isopycnal mixing. Prog. Oceanogr. 1981, 10, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M.; Large, D.G.B. Optimum multiparameter analysis of mixing in the thermocline of the Eastern Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16141–16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budillon, G.; Pacciaroni, M.; Cozzi, S.; Rivaro, P.; Catalano, G.; Ianni, C.; Cantoni, C. An optimum multiparameter mixing analysis of the shelf waters in the Ross Sea. Antarct. Sci. 2003, 15, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffanue, H.; Tomczak, M. Using OMP analysis to observe temporal variability in water mass distribution. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 48, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, P.C.; Perez, F.F.; Velo, A.; Gilcoto, M. Water masses distribution in the Southern Ocean: Improvement of an extended OMP (eOMP) analysis. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 103, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frants, M.; Gille, S.T.; Hewes, C.D.; Holm-Hansen, O.; Kahru, M.; Lombrozo, A.; Measures, C.I.; Mitchell, B.G.; Wang, H.L.; Zhou, M. Optimal multiparameter analysis of source water distributions in the Southern Drake Passage. Deep-Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2013, 90, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparin, F.; Maes, C.; Sudre, J.; Garcon, V.; Ganachaud, A. Water mass analysis of the Coral Sea through an Optimum Multiparameter method. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 7229–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, C.; Berx, B.; Austin, W.E.N. The decomposition of the Faroe-Shetland Channel water masses using Parametric Optimum Multi-Parameter analysis. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 107, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Song, X.X.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Cao, X.H.; Wang, W.T.; Chi, L.B.; Yu, Z.M. Water Mass Analysis of the East China Sea and Interannual Variation of Kuroshio Subsurface Water Intrusion Through an Optimum Multiparameter Method. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 3723–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstensen, J.; Tomczak, M. Age determination of mixed water masses using CFC and oxygen data. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 18599–18609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiao, N.; Xu, D. Water mass shapes the distribution patterns of planktonic ciliates (Alveolata, Ciliophora) in the subtropical Pearl River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bograd, S.J.; Schroeder, I.D.; Jacox, M.G. A water mass history of the Southern California current system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6690–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.X. Dynamics of the buoyant plume off the Pearl River Estuary in summer. Environ. Fluid. Mech. 2009, 9, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.A.; Chen, J.C.; Xue, H.; Dong, L.X.; Guan, W.B.; Su, J.L. A model study of the circulation in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE) and its adjacent coastal waters: 2. Sensitivity experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.M.; Sheng, J.Y.; Tang, L.Q.; Liu, D.B.; Yang, X.L. Process Study of Dry-Season Circulation in the Pearl River Estuary and Adjacent Coastal Waters using a Triple-Nested Coastal Circulation Model. Atmosphere-Ocean 2011, 49, 138–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.M.; Sheng, J.Y.; Tang, L.Q.; Liu, D.B.; Yang, X.L. Process study of circulation in the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent coastal waters in the wet season using a triply-nested circulation model. Ocean Model. 2011, 38, 138–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, T.T.; Wang, D.X.; Gan, J.P.; Guan, W.B. On the role of wind and tide in generating variability of Pearl River plume during summer in a coupled wide estuary and shelf system. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 136, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, D. Responses of the river plume to the external forcing in Pearl River Estuary. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, P.L.; Barth, J.A.; Shearman, R.K.; Erofeev, A. Buoyancy-driven coastal currents off Oregon during fall and winter. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 2854–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, C.; Lentz, S. On the response of a buoyant plume to downwelling-favorable wind stress. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, S.E.; Largier, J.L.; Lentz, S.J. Observations of a pulsed buoyancy current downstream of Chesapeake Bay. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 18227–18240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-J.; Wilkin, J.L. The Effect of Wind on the Dispersal of the Hudson River Plume. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2007, 37, 1878–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.P.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z. Phytoplankton response to a plume front in the northern South China Sea. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2551–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Xie, G.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Z.; Cui, X.; Zhang, H. Optimum Multiparameter Analysis of Water Mass Structure off Western Guangdong during Spring Monsoon Transition. Water 2022, 14, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030375
Li H, Xie G, Zhao J, Hu Z, Cui X, Zhang H. Optimum Multiparameter Analysis of Water Mass Structure off Western Guangdong during Spring Monsoon Transition. Water. 2022; 14(3):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030375
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huadong, Guanghao Xie, Jun Zhao, Zifeng Hu, Xiaoyang Cui, and Hui Zhang. 2022. "Optimum Multiparameter Analysis of Water Mass Structure off Western Guangdong during Spring Monsoon Transition" Water 14, no. 3: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030375
APA StyleLi, H., Xie, G., Zhao, J., Hu, Z., Cui, X., & Zhang, H. (2022). Optimum Multiparameter Analysis of Water Mass Structure off Western Guangdong during Spring Monsoon Transition. Water, 14(3), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030375







