Long-Term Monitoring of Water and Air Quality at an Indoor Pool Facility during Modifications of Water Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Pool Description
2.2. Swimming Pool Water Sampling
2.3. Air Sampling
2.4. Water Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
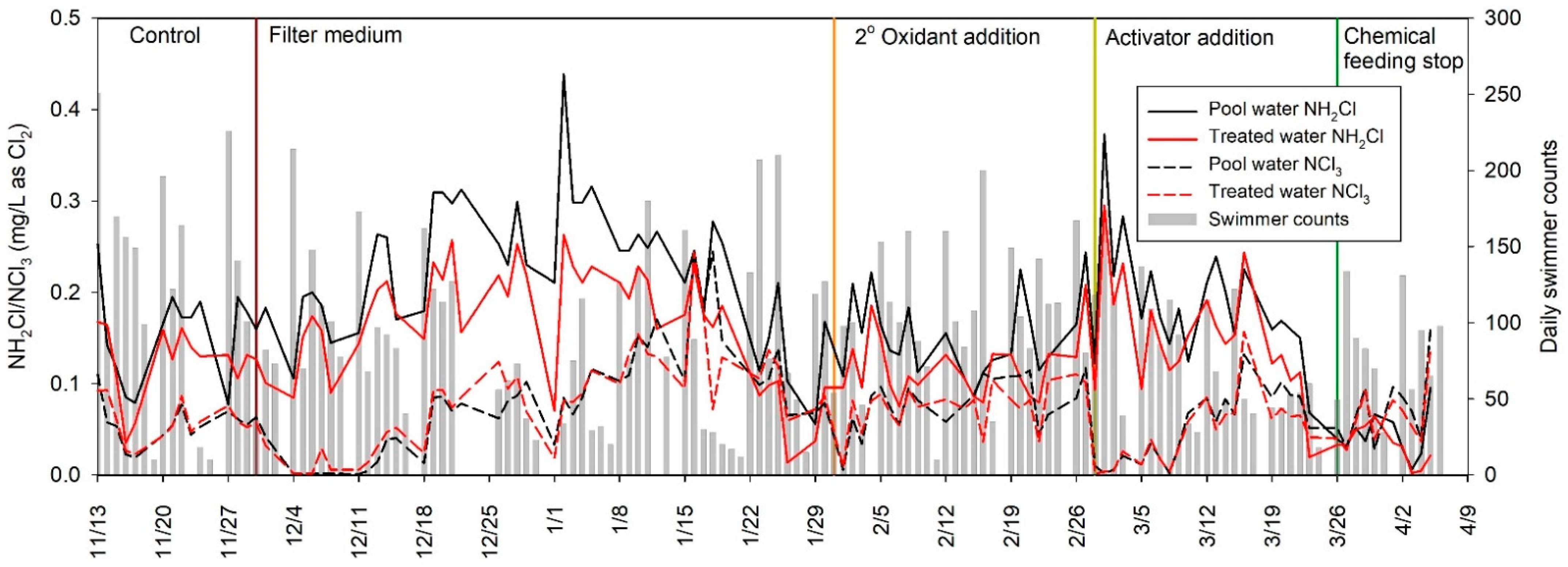
3.1. Liquid-Phase NH2Cl and NCl3
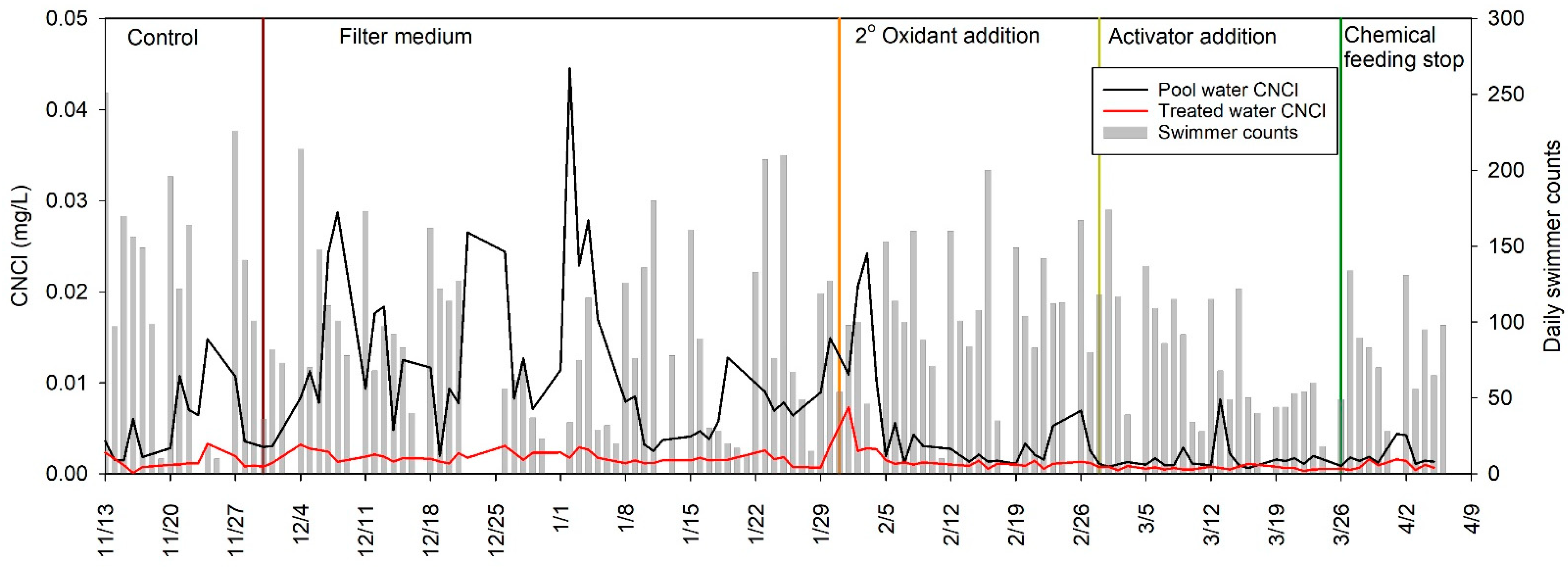
3.2. Liquid-Phase CNCl
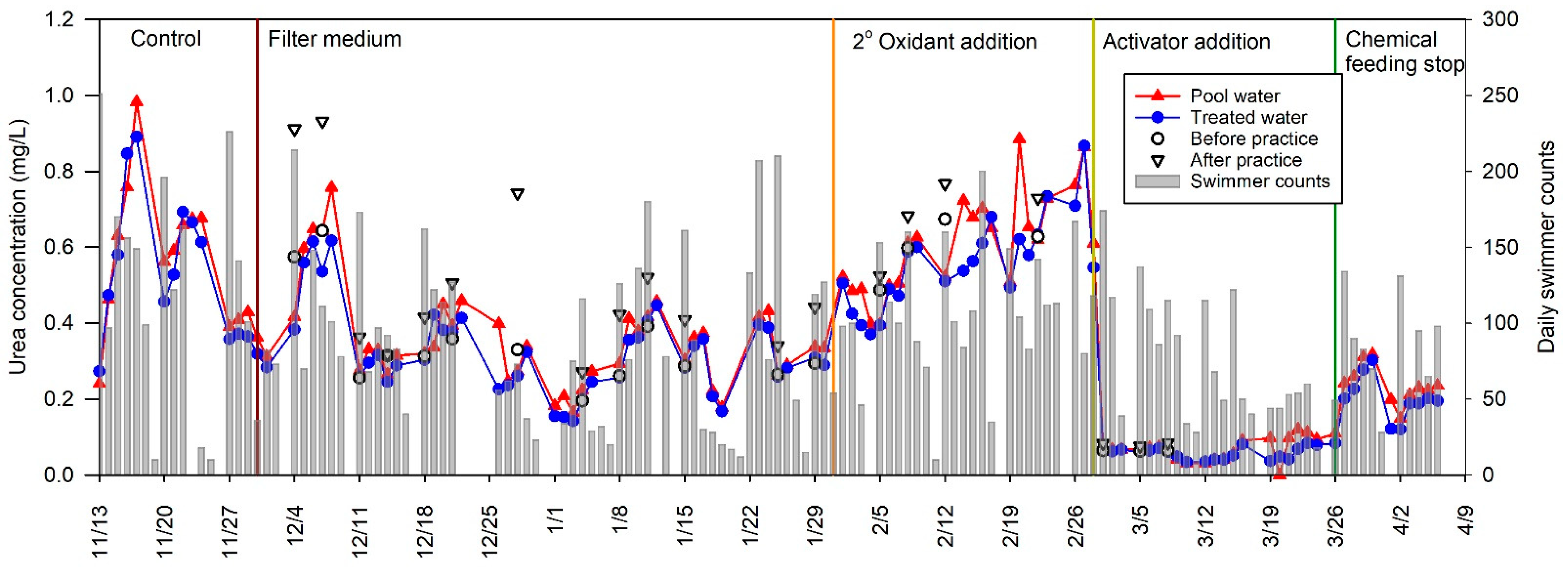
3.3. Urea
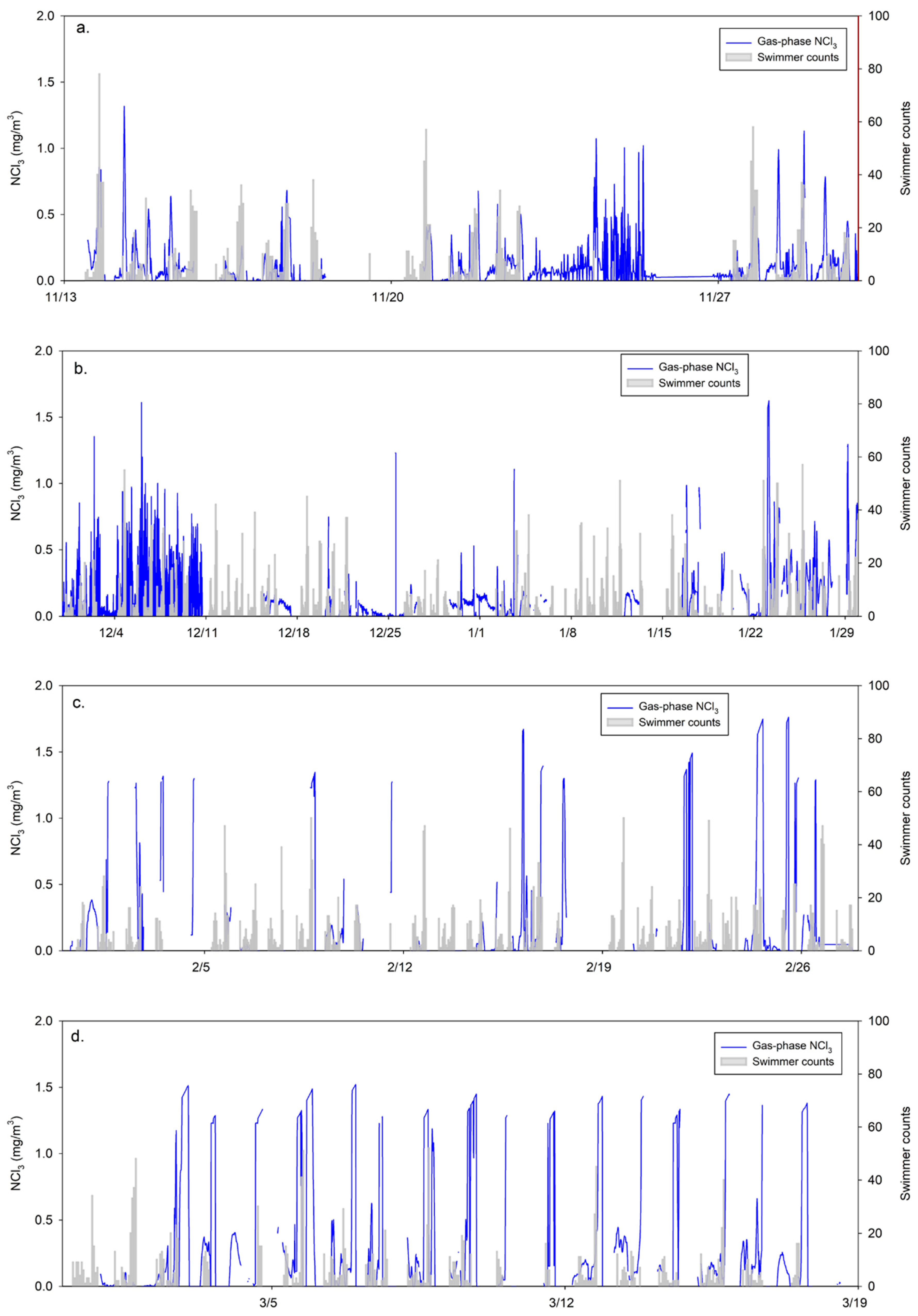
3.4. Gas-Phase NCl3
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bessonneau, V.; Derbez, M.; Clément, M.; Thomas, O. Determinants of Chlorination By-Products in Indoor Swimming Pools. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 215, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florentin, A.; Hautemanière, A.; Hartemann, P. Health Effects of Disinfection By-Products in Chlorinated Swimming Pools. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Blatchley, E.R., III. Volatile Disinfection Byproduct Formation Resulting from Chlorination of Organic−Nitrogen Precursors in Swimming Pools. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6732–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glauner, T.; Waldmann, P.; Frimmel, F.H.; Zwiener, C. Swimming Pool Water—Fractionation and Genotoxicological Characterization of Organic Constituents. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4494–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S.J.; Black, S.H. Disinfection By-Product Formation in Swimming Pool Waters: A Simple Mass Balance. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, W.A.; Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Johnston, J.; Blatchley, M.R.; Blatchley, E.R., III. Volatile Disinfection By-Product Analysis from Chlorinated Indoor Swimming Pools. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3308–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiener, C.; Richardson, S.D.; de Marini, D.M.; Grummt, T.; Glauner, T.; Frimmel, F.H. Drowning in Disinfection Byproducts? Assessing Swimming Pool Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-Ribera, L.; Kogevinas, M.; Zock, J.-P.; Gómez, F.P.; Barreiro, E.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Fernandez, P.; Lourencetti, C.; Pérez-Olabarría, M.; Bustamante, M.; et al. Short-Term Changes in Respiratory Biomarkers after Swimming in a Chlorinated Pool. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loos, R.; Barceló, D. Determination of Haloacetic Acids in Aqueous Environments by Solid-Phase Extraction Followed by Ion-Pair Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometric Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 938, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, C.M.; Cantor, K.P.; Grimalt, J.O.; Malats, N.; Silverman, D.; Tardon, A.; Garcia-Closas, R.; Serra, C.; Carrato, A.; Castano-Vinyals, G.; et al. Bladder Cancer and Exposure to Water Disinfection By-Products through Ingestion, Bathing, Showering, and Swimming in Pools. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, C.P.; Richardson, S.D.; Nemery, B.; Aggazzotti, G.; Baraldi, E.; Blatchley, E.R.; Blount, B.C.; Carlsen, K.-H.; Eggleston, P.A.; Frimmel, F.H.; et al. Childhood Asthma and Environmental Exposures at Swimming Pools: State of the Science and Research Recommendations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Héry, M.; Hecht, G.; Gerber, J.M.; Gendre, J.C.; Hubert, G.; Rebuffaud, J. Exposure to Chloramines in the Atmosphere of Indoor Swimming Pools. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1995, 39, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.H.; Spaan, S.; van Rooy, G.B.G.J.; Meliefste, C.; Zaat, V.A.C.; Rooyackers, J.M.; Heederik, D. Exposure to Trichloramine and Respiratory Symptoms in Indoor Swimming Pool Workers. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thickett, K.M.; McCoach, J.S.; Gerber, J.M.; Sadhra, S.; Burge, P.S. Occupational Asthma Caused by Chloramines in Indoor Swimming-Pool Air. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 19, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massin, N.; Bohadana, A.B.; Wild, P.; Héry, M.; Toamain, J.P.; Hubert, G. Respiratory Symptoms and Bronchial Responsiveness in Lifeguards Exposed to Nitrogen Trichloride in Indoor Swimming Pools. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 55, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parrat, J.; Donzé, G.; Iseli, C.; Perret, D.; Tomicic, C.; Schenk, O. Assessment of Occupational and Public Exposure to Trichloramine in Swiss Indoor Swimming Pools: A Proposal for an Occupational Exposure Limit. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2012, 56, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lévesque, B.; Vézina, L.; Gauvin, D.; Leroux, P. Investigation of Air Quality Problems in an Indoor Swimming Pool: A Case Study. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2015, 59, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zare Afifi, M.; Blatchley, E.R., 3rd. Seasonal Dynamics of Water and Air Chemistry in an Indoor Chlorinated Swimming Pool. Water Res. 2015, 68, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Afifi, M.; Blatchley, E.R. Effects of UV-Based Treatment on Volatile Disinfection Byproducts in a Chlorinated, Indoor Swimming Pool. Water Res. 2016, 105, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiener, C.; Schmalz, C. Ion Mobility Spectrometry to Monitor Trichloramine in Indoor Pool Air. In Recent Advances in Disinfection By-Products; ACS Publications: Tuebingen, Germany, 2015; pp. 431–446. ISBN 0-8412-3076-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Földes, T.; Lee, L.T.; Wagner, D.N.; Jiang, J.; Tasoglou, A.; Boor, B.E.; Blatchley, E.R. Real-Time Measurements of Gas-Phase Trichloramine (NCl3) in an Indoor Aquatic Center. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8097–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethera Labs. Trichloramine Monitor NEMo TC. Available online: http://www.ethera-labs.com/en/trichloramine-monitor (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Nguyen, T.H.; Chevallier, E.; Garcia, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Laurent, A.M.; Beaubestre, C.; Karpe, P.; Tran-Thi, T.H. Innovative Colorimetric Sensors for the Detection of Nitrogen Trichloride at Ppb Level in Swimming Pools. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Weaver, W.A.; Zare Afifi, M.; Blatchley, T.N.; Cramer, J.S.; Chen, J.; Blatchley, E.R. Dynamics of Gas-Phase Trichloramine (NCl3) in Chlorinated, Indoor Swimming Pool Facilities. Indoor Air 2011, 21, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Blatchley, E.R., III. Differentiation and Quantification of Free Chlorine and Inorganic Chloramines in Aqueous Solution by MIMS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Shang, C. Chlorination Byproduct Formation in the Presence of Humic Acid, Model Nitrogenous Organic Compounds, Ammonia, and Bromide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4995–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, L.M.; Jones, M.E. Modified Methods for the Determination of Carbamyl Aspartate. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 32, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.; Olson, T.M. Stability of Cyanogen Chloride in the Presence of Free Chlorine and Monochloramine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6037–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; E, Y.; Li, J.; Blatchley, E.R., III. Volatile Disinfection Byproducts Resulting from Chlorination of Uric Acid: Implications for Swimming Pools. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3210–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinger, L.; Kirsch, F.; Sonntag, H.G. Potassium as an indicator of anthropogenic contamination of swimming pool water. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Med. 1997, 200, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Gunkel, K.; Jessen, H.-J. Untersuchungen Über Den Harnstoffeintrag in Das Badewasser. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1986, 14, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.M.S.; Willach, S.; Antoniou, M.G.; Mosbæk, H.; Albrechtsen, H.J.; Andersen, H.R. Effect of PH on the Formation of Disinfection Byproducts in Swimming Pool Water—Is Less THM Better? Water Res. 2012, 46, 6399–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmalz, C.; Frimmel, F.H.; Zwiener, C. Trichloramine in Swimming Pools—Formation and Mass Transfer. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laat, J.; Feng, W.; Freyfer, D.A.; Dossier-Berne, F. Concentration Levels of Urea in Swimming Pool Water and Reactivity of Chlorine with Urea. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, S.; Blatchley, E.R., III. Disinfection By-Product Dynamics in a Chlorinated, Indoor Swimming Pool under Conditions of Heavy Use: National Swimming Competition. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5241–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 2.
- Bernard, A.; Carbonnelle, S.; de Burbure, C.; Michel, O.; Nickmilder, M. Chlorinated Pool Attendance, Atopy, and the Risk of Asthma during Childhood. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seys, S.F.; Feyen, L.; Keirsbilck, S.; Adams, E.; Dupont, L.J.; Nemery, B. An Outbreak of Swimming-Pool Related Respiratory Symptoms: An Elusive Source of Trichloramine in a Municipal Indoor Swimming Pool. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornander, L.; Ghafouri, B.; Lindahl, M.; Graff, P. Airway Irritation among Indoor Swimming Pool Personnel: Trichloramine Exposure, Exhaled NO and Protein Profiling of Nasal Lavage Fluids. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2013, 86, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.F.; Lundstrom, N.-G.; Forsberg, B.; Hagenbjork-Gustafsson, A.; Lagerkvist, B.J.; Nilsson, J.; Svensson, M.; Blomberg, A.; Nilsson, L.; Bernard, A.; et al. Lung Function in Volunteers before and after Exposure to Trichloramine in Indoor Pool Environments and Asthma in a Cohort of Pool Workers. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e000973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, L.T.; Blatchley, E.R., III. Long-Term Monitoring of Water and Air Quality at an Indoor Pool Facility during Modifications of Water Treatment. Water 2022, 14, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030335
Lee LT, Blatchley ER III. Long-Term Monitoring of Water and Air Quality at an Indoor Pool Facility during Modifications of Water Treatment. Water. 2022; 14(3):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030335
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Lester T., and Ernest R. Blatchley, III. 2022. "Long-Term Monitoring of Water and Air Quality at an Indoor Pool Facility during Modifications of Water Treatment" Water 14, no. 3: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030335
APA StyleLee, L. T., & Blatchley, E. R., III. (2022). Long-Term Monitoring of Water and Air Quality at an Indoor Pool Facility during Modifications of Water Treatment. Water, 14(3), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030335






