Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalgal Species
2.2. Experimental Setup
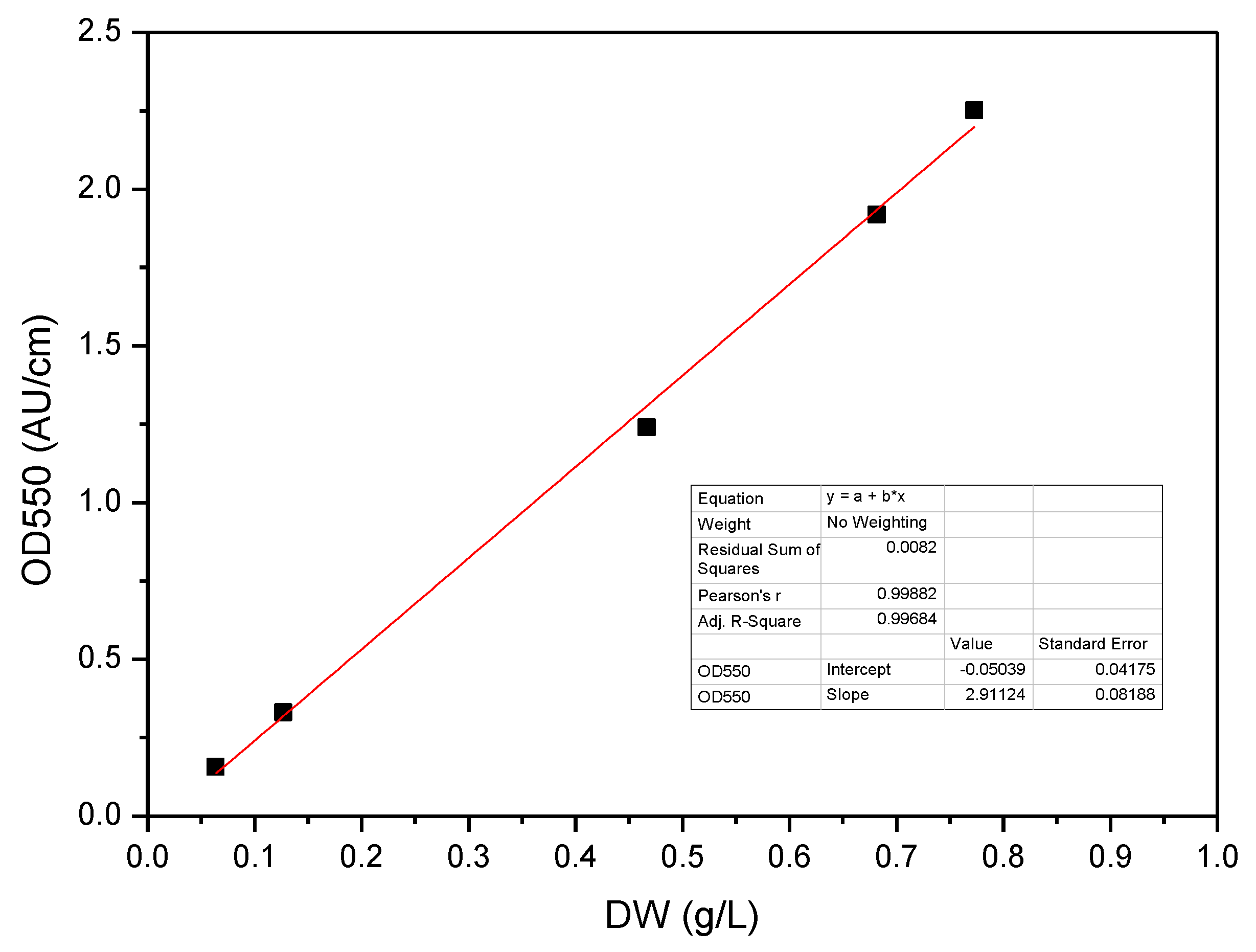
2.3. Analytical Techniques
2.4. Model Development
2.5. Numerical Methods
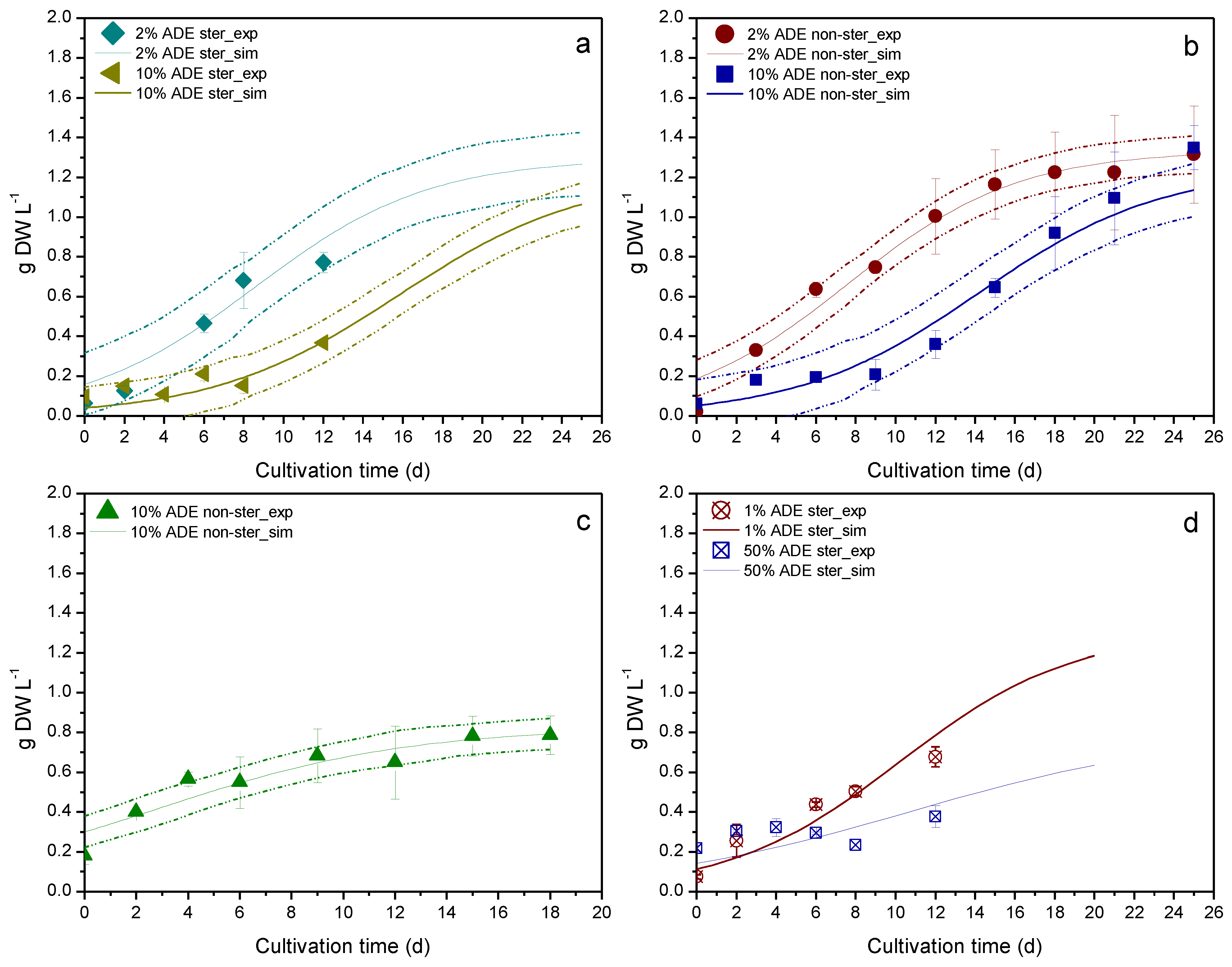
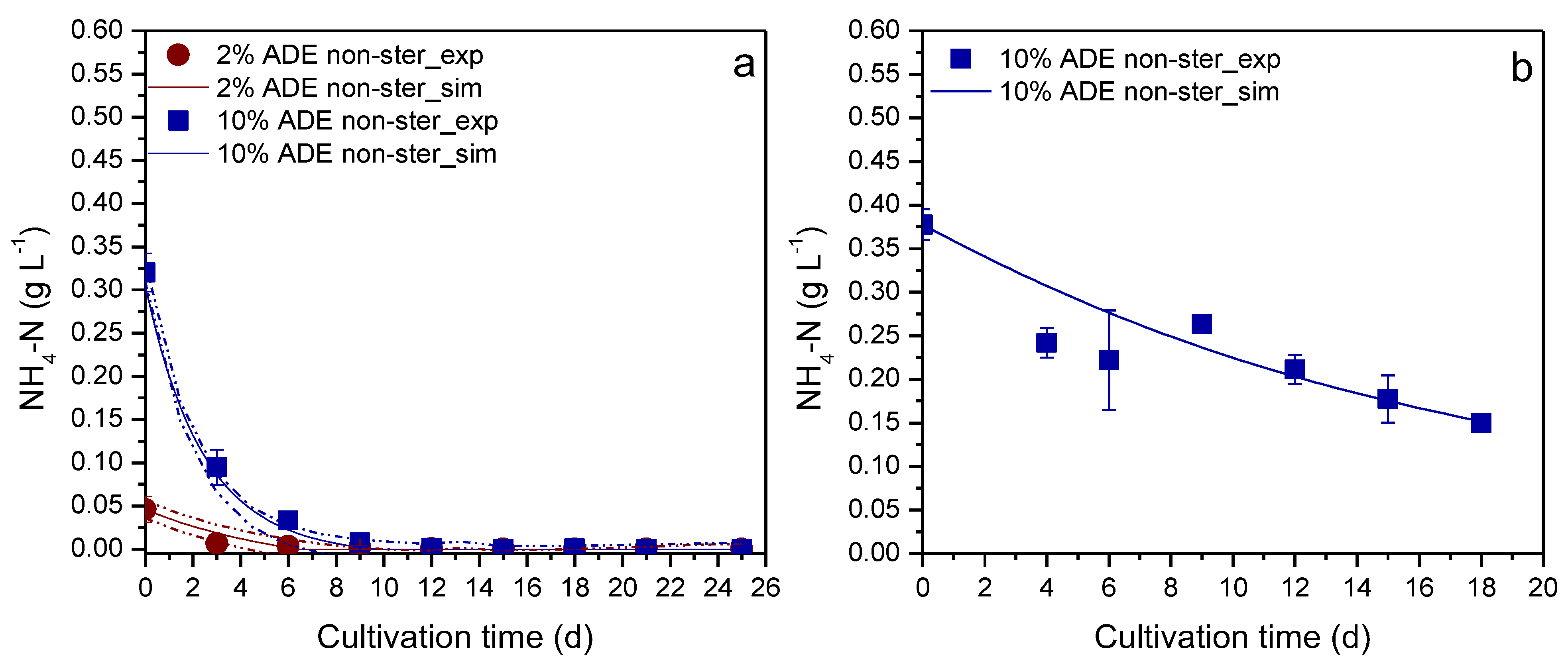
3. Results & Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Slorach, P.C.; Jeswani, H.K.; Cuéllar-Franca, R.; Azapagic, A. Environmental Sustainability of Anaerobic Digestion of Household Food Waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 798–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamri, M.F.M.A.; Hasmady, S.; Akhiar, A.; Ideris, F.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Mofijur, M.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Mahlia, T.M.I. A Comprehensive Review on Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styles, D.; Adams, P.; Thelin, G.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Chadwick, D.; Withers, P.J.A. Life Cycle Assessment of Biofertilizer Production and Use Compared with Conventional Liquid Digestate Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7468–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Nutrient Removal and Microalgal Biomass Production from Different Anaerobic Digestion Effluents with Chlorella Species. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Golkowska, K.; Lebuf, V.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Michels, E.; Meers, E.; Benetto, E.; Koster, D. Environmental Assessment of Digestate Treatment Technologies Using LCA Methodology. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Environmental Sustainability Assessment of Pig Manure Mono-and Co-Digestion and Dynamic Land Application of the Digestate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Qiu, X.; Feng, H.; Yin, J.; Shen, D. Solid Digestate Disposal Strategies to Reduce the Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption of Food Waste-Based Biogas Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri-Rumbau, M.S.; Briceño, K.; Søtoft, L.F.; Christensen, K.V.; Roda-Serrat, M.C.; Errico, M.; Norddahl, B. Treatment of Manure and Digestate Liquid Fractions Using Membranes: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limoli, A.; Langone, M.; Andreottola, G. Ammonia Removal from Raw Manure Digestate by Means of a Turbulent Mixing Stripping Process. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, D.; Corona, F.; Martín-Marroquín, J.M.; del Álamo, J.; Aguado, A. Resource Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate: Struvite Crystallisation versus Ammonia Stripping. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2626–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Miao, Y.; Dong, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, C. Enhanced Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Analysis in Partially Saturated Constructed Wetland for Treating Anaerobically Digested Swine Wastewater. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutra, E.; Economou, C.N.; Tsafrakidou, P.; Kornaros, M. Bio-Based Products from Microalgae Cultivated in Digestates. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh Banu, J.; Preethi; Kavitha, S.; Gunasekaran, M.; Kumar, G. Microalgae Based Biorefinery Promoting Circular Bioeconomy-Techno Economic and Life-Cycle Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuka-ogwude, D.; Ogbonna, J.; Borowitzka, M.A.; Moheimani, N.R. Screening, Acclimation and Ammonia Tolerance of Microalgae Grown in Food Waste Digestate. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 3775–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.P.; van Keulen, M.; Wong, S.K.S.; Hamley, E.; Nwoba, E.; Moheimani, N.R. Light Spectral Effect on a Consortium of Filamentous Green Algae Grown on Anaerobic Digestate Piggery Effluent (ADPE). Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigkou, K.; Zagklis, D.; Tsafrakidou, P.; Zafiri, C.; Kornaros, M. Composting of Anaerobic Sludge from the Co-Digestion of Used Disposable Nappies and Expired Food Products. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K.; Jeon, J.Y.; Oh, S.J. Potential for Heavy Metal (Copper and Zinc) Removal from Contaminated Marine Sediments Using Microalgae and Light Emitting Diodes. Ocean Sci. J. 2017, 52, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narala, R.R.; Garg, S.; Sharma, K.K.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Deme, M.; Li, Y.; Schenk, P.M. Comparison of Microalgae Cultivation in Photobioreactor, Open Raceway Pond, and a Two-Stage Hybrid System. Front. Energy Res. 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuccaro, G.; Yousuf, A.; Pollio, A.; Steyer, J.-P. Microalgae Cultivation Systems. In Microalgae Cultivation for Biofuels Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cicci, A.; Bravi, M. Production of the Freshwater Microalgae Scenedesmus Dimorphus and Arthrospira Platensis by Using Cattle Digestate. Chem. Eng. 2014, 38, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Mastropetros, S.G.; Koutra, E.; Amouri, M.; Aziza, M.; Ali, S.S.; Kornaros, M. Comparative Assessment of Nitrogen Concentration Effect on Microalgal Growth and Biochemical Characteristics of Two Chlorella Strains Cultivated in Digestate. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaghat, M.R.; Mokhtari, S.; Saadat, M. Modeling and Optimization of Biodiesel Production from Microalgae in a Batch Reactor. Fuel 2020, 280, 118578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Malea, M.C.; Acién, F.G.; Fernández, J.M.; Cerón, M.C.; Molina, E. Continuous Production of Green Cells of Haematococcus Pluvialis: Modeling of the Irradiance Effect. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Zhang, Q. Integrated Co-Limitation Kinetic Model for Microalgae Growth in Anaerobically Digested Municipal Sludge Centrate. Algal Res. 2016, 18, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Cai, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Guo, Z. Analysis and Model Delineation of Marine Microalgae Growth and Lipid Accumulation in Flat-Plate Photobioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 111, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ho, S.-H. Optimizing Real Swine Wastewater Treatment with Maximum Carbohydrate Production by a Newly Isolated Indigenous Microalga Parachlorella Kessleri QWY28. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, R.; Gaffney, M.; Murphy, R. The Effects of Parachlorella Kessleri Cultivation on Brewery Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viriato, C.; da Silveira, C.B.; de Souza, M.P.; de Souza Schneider, R.C.; Skoronski, E.; Neves, F.F. Cultivation of the Microalgae Parachlorella Kessleri Using Wastewater from a Fishmeal & Oil Industry and Its Application for Nitrogen Removal. Rev Latinoam Hiperte 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Beigbeder, J.-B.; Sanglier, M.; de Medeiros Dantas, J.M.; Lavoie, J.-M. CO2 Capture and Inorganic Carbon Assimilation of Gaseous Fermentation Effluents Using Parachlorella Kessleri Microalgae. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 50, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Franson, M.A.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Li, A.; Li, H.; Shen, Z.; Ma, T.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, Q.; Sun, Y. Effect of Membrane Blocking on Attached Cultivation of Microalgae. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambriz-Pérez, D.L.; Orozco-Guillen, E.E.; Galán-Hernández, N.D.; Luna-Avelar, K.D.; Valdez-Ortiz, A.; Santos-Ballardo, D.U. Accurate Method for Rapid Biomass Quantification Based on Specific Absorbance of Microalgae Species with Biofuel Importance. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 73, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellezuome, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R. Mitigation of Ammonia Inhibition in Anaerobic Digestion of Nitrogen-Rich Substrates for Biogas Production by Ammonia Stripping: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafrakidou, P.; Manthos, G.; Zagklis, D.; Mema, J.; Kornaros, M. Assessment of Substrate Load and Process PH for Bioethanol Production–Development of a Kinetic Model. Fuel 2022, 313, 123007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthos, G.; Zagklis, D.; Kornaros, M. Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of PH on 4-Ethylphenol Formation during Two-Phase Olive Pomace Storage. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 186, 108552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmuson, A.; Andersson, B.; Olsson, L.; Andersson, R. Mathematical Modeling in Chemical Engineering; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satthong, S.; Saego, K.; Kitrungloadjanaporn, P.; Nuttavut, N.; Amornsamankul, S.; Triampo, W. Modeling the Effects of Light Sources on the Growth of Algae. Adv. Differ. Equations 2019, 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-X.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Zhu, X. Kinetic Characteristics and Modeling of Microalgae Chlorella Vulgaris Growth and CO2 Biofixation Considering the Coupled Effects of Light Intensity and Dissolved Inorganic Carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aketo, T.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Nojima, D.; Yabu, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Takano, H.; Tanaka, T. Selection and Characterization of Microalgae with Potential for Nutrient Removal from Municipal Wastewater and Simultaneous Lipid Production. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decostere, B.; De Craene, J.; Van Hoey, S.; Vervaeren, H.; Nopens, I.; Van Hulle, S.W.H. Validation of a Microalgal Growth Model Accounting with Inorganic Carbon and Nutrient Kinetics for Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Arbib, Z.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.D.; Garrido-Pérez, C.; Barragán, J.; Perales, J.A. Photobiotreatment Model (PhBT): A Kinetic Model for Microalgae Biomass Growth and Nutrient Removal in Wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, Q.; Nan, F.; Jiao, X.; Xie, S. Comparison of Growth Characteristics and Nitrogen Removal Capacity of Five Species of Green Algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viruela, A.; Aparicio, S.; Robles, Á.; Falomir, L.B.; Serralta, J.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. Kinetic Modeling of Autotrophic Microalgae Mainline Processes for Sewage Treatment in Phosphorus-Replete and-Deplete Culture Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Experiment | Sterilized Medium | Apparatus | Digestate Loading (v/v) | Available Data | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | Biomass | T |
| 2 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | Biomass | T |
| 3 | No | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | Biomass, N, P | T |
| 4 | No | Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | Biomass, N, P | T |
| 5 | No | PBR | 10% | Biomass, N, P | T, V |
| 6 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 1% | Biomass | V |
| 7 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 50% | Biomass | V |
| Model Parameters | Erlenmeyer Flask | PBR |
|---|---|---|
| μmax [d−1] | 0.24 ± 0.04 | |
| ODmax [AU cm−1] | 4.07 ± 0.30 | 2.79 ± 0.59 |
| Yx/Total-P [g g−1Total-P] | 194.9 ± 13.3 | |
| kLa [d−1] | 3.6 10−4 ± 1.4 10−4 | |
| Culture Parameter | Apparatus | Digestate Loading (v/v) | Sterilized Medium | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | Yes | 0.8955 a |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | Yes | 0.6790 a | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | No | 0.9704 a | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | No | 0.9523 a | |
| PBR | 10% | No | 0.8993 a | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 1% | Yes | 0.8730 b | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 50% | Yes | 0.5417 b | |
| Total P | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | No | 0.8339 a |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | No | 0.9981 a | |
| PBR | 10% | No | 0.9996 b | |
| Nitrogen | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | No | 0.9394 a |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | No | 0.9901 a | |
| PBR | 10% | No | 0.8335 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manthos, G.; Koutra, E.; Mastropetros, S.G.; Zagklis, D.; Kornaros, M. Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation. Water 2022, 14, 3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938
Manthos G, Koutra E, Mastropetros SG, Zagklis D, Kornaros M. Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation. Water. 2022; 14(23):3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938
Chicago/Turabian StyleManthos, Georgios, Eleni Koutra, Savvas Giannis Mastropetros, Dimitris Zagklis, and Michael Kornaros. 2022. "Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation" Water 14, no. 23: 3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938
APA StyleManthos, G., Koutra, E., Mastropetros, S. G., Zagklis, D., & Kornaros, M. (2022). Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation. Water, 14(23), 3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938









