Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalgal Species
2.2. Experimental Setup
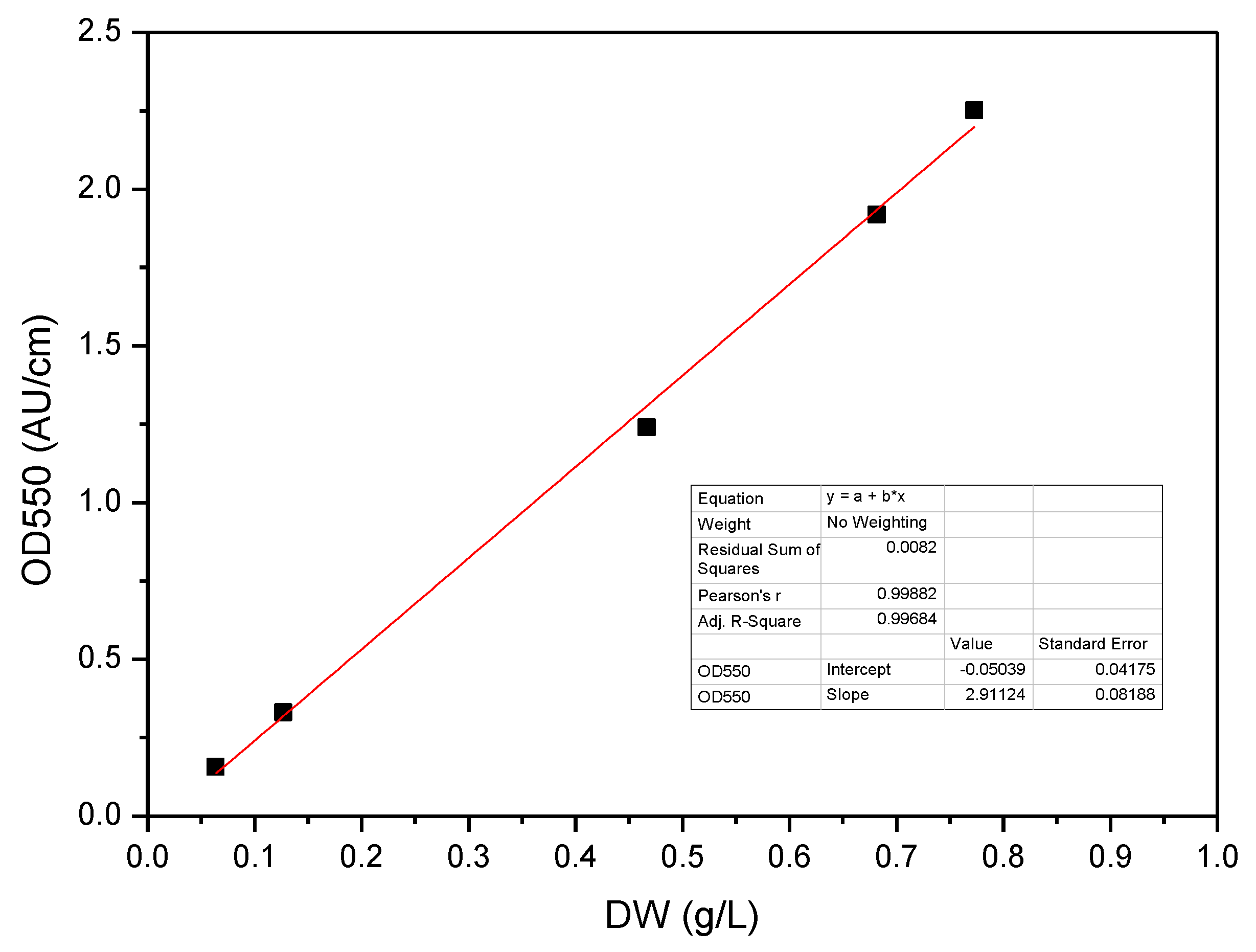
2.3. Analytical Techniques
2.4. Model Development
2.5. Numerical Methods
3. Results & Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Slorach, P.C.; Jeswani, H.K.; Cuéllar-Franca, R.; Azapagic, A. Environmental Sustainability of Anaerobic Digestion of Household Food Waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 798–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamri, M.F.M.A.; Hasmady, S.; Akhiar, A.; Ideris, F.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Mofijur, M.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Mahlia, T.M.I. A Comprehensive Review on Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styles, D.; Adams, P.; Thelin, G.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Chadwick, D.; Withers, P.J.A. Life Cycle Assessment of Biofertilizer Production and Use Compared with Conventional Liquid Digestate Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7468–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Nutrient Removal and Microalgal Biomass Production from Different Anaerobic Digestion Effluents with Chlorella Species. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Golkowska, K.; Lebuf, V.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Michels, E.; Meers, E.; Benetto, E.; Koster, D. Environmental Assessment of Digestate Treatment Technologies Using LCA Methodology. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Environmental Sustainability Assessment of Pig Manure Mono-and Co-Digestion and Dynamic Land Application of the Digestate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Qiu, X.; Feng, H.; Yin, J.; Shen, D. Solid Digestate Disposal Strategies to Reduce the Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption of Food Waste-Based Biogas Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri-Rumbau, M.S.; Briceño, K.; Søtoft, L.F.; Christensen, K.V.; Roda-Serrat, M.C.; Errico, M.; Norddahl, B. Treatment of Manure and Digestate Liquid Fractions Using Membranes: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limoli, A.; Langone, M.; Andreottola, G. Ammonia Removal from Raw Manure Digestate by Means of a Turbulent Mixing Stripping Process. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, D.; Corona, F.; Martín-Marroquín, J.M.; del Álamo, J.; Aguado, A. Resource Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate: Struvite Crystallisation versus Ammonia Stripping. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2626–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Miao, Y.; Dong, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, C. Enhanced Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Analysis in Partially Saturated Constructed Wetland for Treating Anaerobically Digested Swine Wastewater. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutra, E.; Economou, C.N.; Tsafrakidou, P.; Kornaros, M. Bio-Based Products from Microalgae Cultivated in Digestates. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh Banu, J.; Preethi; Kavitha, S.; Gunasekaran, M.; Kumar, G. Microalgae Based Biorefinery Promoting Circular Bioeconomy-Techno Economic and Life-Cycle Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuka-ogwude, D.; Ogbonna, J.; Borowitzka, M.A.; Moheimani, N.R. Screening, Acclimation and Ammonia Tolerance of Microalgae Grown in Food Waste Digestate. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 3775–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.P.; van Keulen, M.; Wong, S.K.S.; Hamley, E.; Nwoba, E.; Moheimani, N.R. Light Spectral Effect on a Consortium of Filamentous Green Algae Grown on Anaerobic Digestate Piggery Effluent (ADPE). Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigkou, K.; Zagklis, D.; Tsafrakidou, P.; Zafiri, C.; Kornaros, M. Composting of Anaerobic Sludge from the Co-Digestion of Used Disposable Nappies and Expired Food Products. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K.; Jeon, J.Y.; Oh, S.J. Potential for Heavy Metal (Copper and Zinc) Removal from Contaminated Marine Sediments Using Microalgae and Light Emitting Diodes. Ocean Sci. J. 2017, 52, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narala, R.R.; Garg, S.; Sharma, K.K.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Deme, M.; Li, Y.; Schenk, P.M. Comparison of Microalgae Cultivation in Photobioreactor, Open Raceway Pond, and a Two-Stage Hybrid System. Front. Energy Res. 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccaro, G.; Yousuf, A.; Pollio, A.; Steyer, J.-P. Microalgae Cultivation Systems. In Microalgae Cultivation for Biofuels Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cicci, A.; Bravi, M. Production of the Freshwater Microalgae Scenedesmus Dimorphus and Arthrospira Platensis by Using Cattle Digestate. Chem. Eng. 2014, 38, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Mastropetros, S.G.; Koutra, E.; Amouri, M.; Aziza, M.; Ali, S.S.; Kornaros, M. Comparative Assessment of Nitrogen Concentration Effect on Microalgal Growth and Biochemical Characteristics of Two Chlorella Strains Cultivated in Digestate. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaghat, M.R.; Mokhtari, S.; Saadat, M. Modeling and Optimization of Biodiesel Production from Microalgae in a Batch Reactor. Fuel 2020, 280, 118578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Malea, M.C.; Acién, F.G.; Fernández, J.M.; Cerón, M.C.; Molina, E. Continuous Production of Green Cells of Haematococcus Pluvialis: Modeling of the Irradiance Effect. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Zhang, Q. Integrated Co-Limitation Kinetic Model for Microalgae Growth in Anaerobically Digested Municipal Sludge Centrate. Algal Res. 2016, 18, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Cai, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Guo, Z. Analysis and Model Delineation of Marine Microalgae Growth and Lipid Accumulation in Flat-Plate Photobioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 111, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ho, S.-H. Optimizing Real Swine Wastewater Treatment with Maximum Carbohydrate Production by a Newly Isolated Indigenous Microalga Parachlorella Kessleri QWY28. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, R.; Gaffney, M.; Murphy, R. The Effects of Parachlorella Kessleri Cultivation on Brewery Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viriato, C.; da Silveira, C.B.; de Souza, M.P.; de Souza Schneider, R.C.; Skoronski, E.; Neves, F.F. Cultivation of the Microalgae Parachlorella Kessleri Using Wastewater from a Fishmeal & Oil Industry and Its Application for Nitrogen Removal. Rev Latinoam Hiperte 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Beigbeder, J.-B.; Sanglier, M.; de Medeiros Dantas, J.M.; Lavoie, J.-M. CO2 Capture and Inorganic Carbon Assimilation of Gaseous Fermentation Effluents Using Parachlorella Kessleri Microalgae. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 50, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Franson, M.A.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Li, A.; Li, H.; Shen, Z.; Ma, T.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, Q.; Sun, Y. Effect of Membrane Blocking on Attached Cultivation of Microalgae. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambriz-Pérez, D.L.; Orozco-Guillen, E.E.; Galán-Hernández, N.D.; Luna-Avelar, K.D.; Valdez-Ortiz, A.; Santos-Ballardo, D.U. Accurate Method for Rapid Biomass Quantification Based on Specific Absorbance of Microalgae Species with Biofuel Importance. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 73, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellezuome, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R. Mitigation of Ammonia Inhibition in Anaerobic Digestion of Nitrogen-Rich Substrates for Biogas Production by Ammonia Stripping: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafrakidou, P.; Manthos, G.; Zagklis, D.; Mema, J.; Kornaros, M. Assessment of Substrate Load and Process PH for Bioethanol Production–Development of a Kinetic Model. Fuel 2022, 313, 123007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthos, G.; Zagklis, D.; Kornaros, M. Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of PH on 4-Ethylphenol Formation during Two-Phase Olive Pomace Storage. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 186, 108552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmuson, A.; Andersson, B.; Olsson, L.; Andersson, R. Mathematical Modeling in Chemical Engineering; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satthong, S.; Saego, K.; Kitrungloadjanaporn, P.; Nuttavut, N.; Amornsamankul, S.; Triampo, W. Modeling the Effects of Light Sources on the Growth of Algae. Adv. Differ. Equations 2019, 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-X.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Zhu, X. Kinetic Characteristics and Modeling of Microalgae Chlorella Vulgaris Growth and CO2 Biofixation Considering the Coupled Effects of Light Intensity and Dissolved Inorganic Carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aketo, T.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Nojima, D.; Yabu, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Takano, H.; Tanaka, T. Selection and Characterization of Microalgae with Potential for Nutrient Removal from Municipal Wastewater and Simultaneous Lipid Production. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decostere, B.; De Craene, J.; Van Hoey, S.; Vervaeren, H.; Nopens, I.; Van Hulle, S.W.H. Validation of a Microalgal Growth Model Accounting with Inorganic Carbon and Nutrient Kinetics for Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Arbib, Z.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.D.; Garrido-Pérez, C.; Barragán, J.; Perales, J.A. Photobiotreatment Model (PhBT): A Kinetic Model for Microalgae Biomass Growth and Nutrient Removal in Wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, Q.; Nan, F.; Jiao, X.; Xie, S. Comparison of Growth Characteristics and Nitrogen Removal Capacity of Five Species of Green Algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viruela, A.; Aparicio, S.; Robles, Á.; Falomir, L.B.; Serralta, J.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. Kinetic Modeling of Autotrophic Microalgae Mainline Processes for Sewage Treatment in Phosphorus-Replete and-Deplete Culture Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

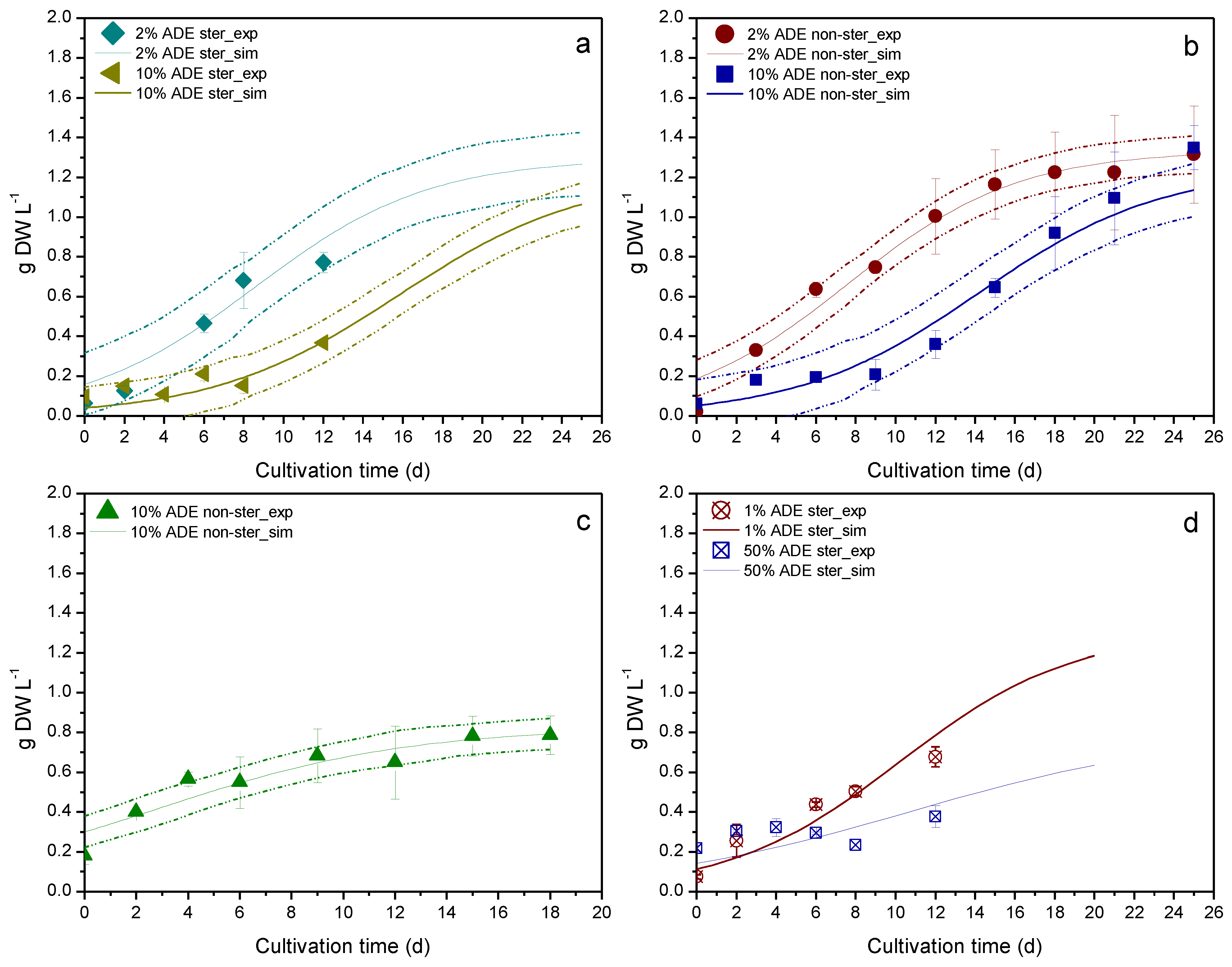

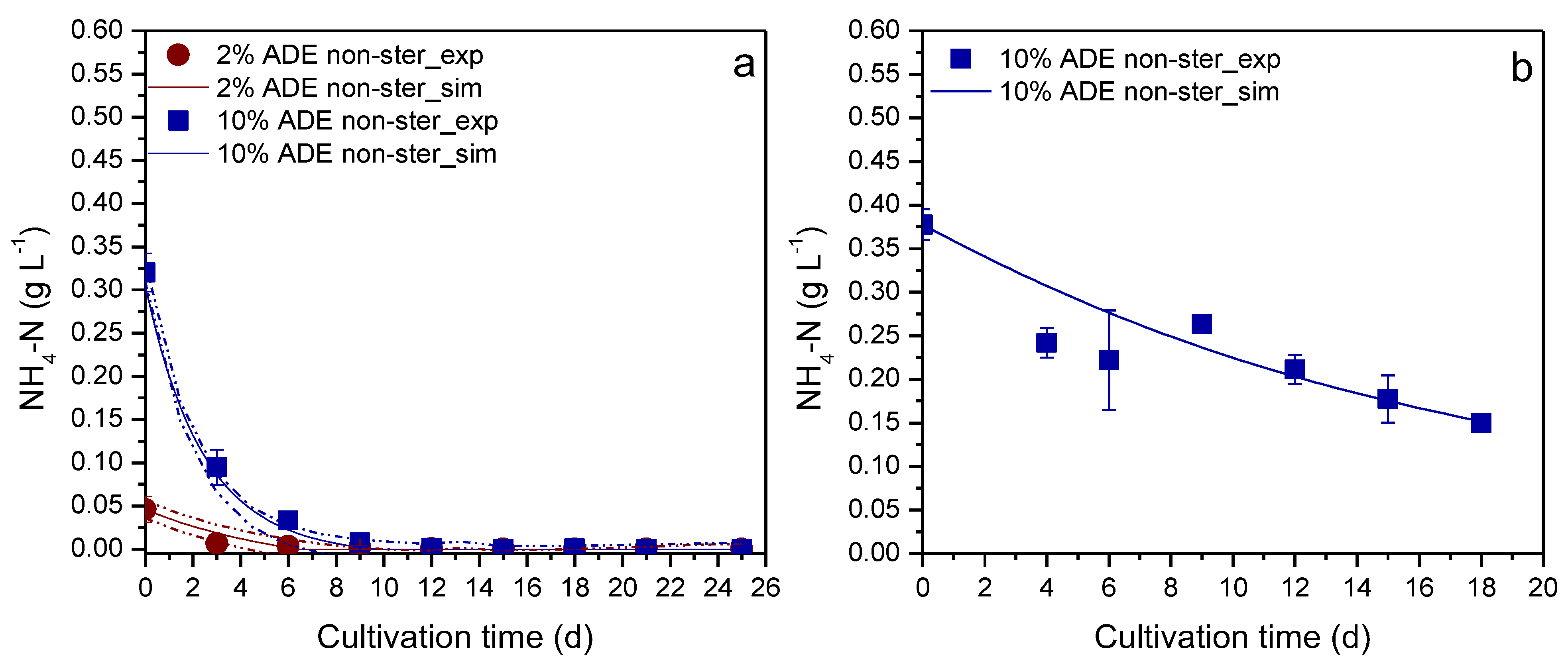
| Experiment | Sterilized Medium | Apparatus | Digestate Loading (v/v) | Available Data | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | Biomass | T |
| 2 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | Biomass | T |
| 3 | No | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | Biomass, N, P | T |
| 4 | No | Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | Biomass, N, P | T |
| 5 | No | PBR | 10% | Biomass, N, P | T, V |
| 6 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 1% | Biomass | V |
| 7 | Yes | Erlenmeyer flask | 50% | Biomass | V |
| Model Parameters | Erlenmeyer Flask | PBR |
|---|---|---|
| μmax [d−1] | 0.24 ± 0.04 | |
| ODmax [AU cm−1] | 4.07 ± 0.30 | 2.79 ± 0.59 |
| Yx/Total-P [g g−1Total-P] | 194.9 ± 13.3 | |
| kLa [d−1] | 3.6 10−4 ± 1.4 10−4 | |
| Culture Parameter | Apparatus | Digestate Loading (v/v) | Sterilized Medium | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | Yes | 0.8955 a |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | Yes | 0.6790 a | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | No | 0.9704 a | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | No | 0.9523 a | |
| PBR | 10% | No | 0.8993 a | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 1% | Yes | 0.8730 b | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 50% | Yes | 0.5417 b | |
| Total P | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | No | 0.8339 a |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | No | 0.9981 a | |
| PBR | 10% | No | 0.9996 b | |
| Nitrogen | Erlenmeyer flask | 2% | No | 0.9394 a |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 10% | No | 0.9901 a | |
| PBR | 10% | No | 0.8335 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manthos, G.; Koutra, E.; Mastropetros, S.G.; Zagklis, D.; Kornaros, M. Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation. Water 2022, 14, 3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938
Manthos G, Koutra E, Mastropetros SG, Zagklis D, Kornaros M. Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation. Water. 2022; 14(23):3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938
Chicago/Turabian StyleManthos, Georgios, Eleni Koutra, Savvas Giannis Mastropetros, Dimitris Zagklis, and Michael Kornaros. 2022. "Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation" Water 14, no. 23: 3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938
APA StyleManthos, G., Koutra, E., Mastropetros, S. G., Zagklis, D., & Kornaros, M. (2022). Mathematical Modeling of Microalgal Growth during Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Bioremediation. Water, 14(23), 3938. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233938









