Hydrodynamic Behaviors and Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater for Irrigation in Yaoba Oasis, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
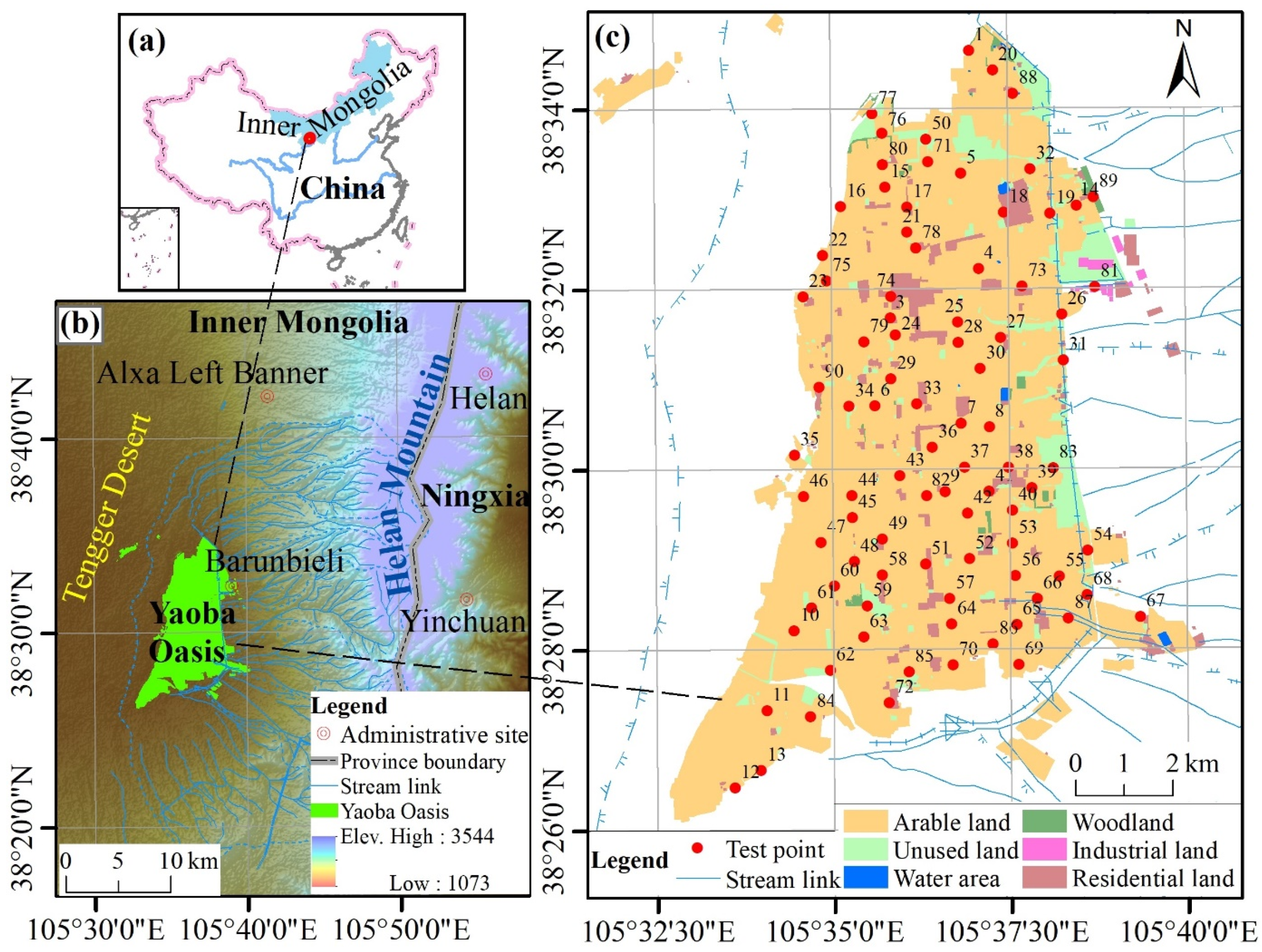
2.1. An Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Methods of Water Level Monitoring, Water Sample Collection, and Analysis
2.3. Data Processing
3. Result and Analysis
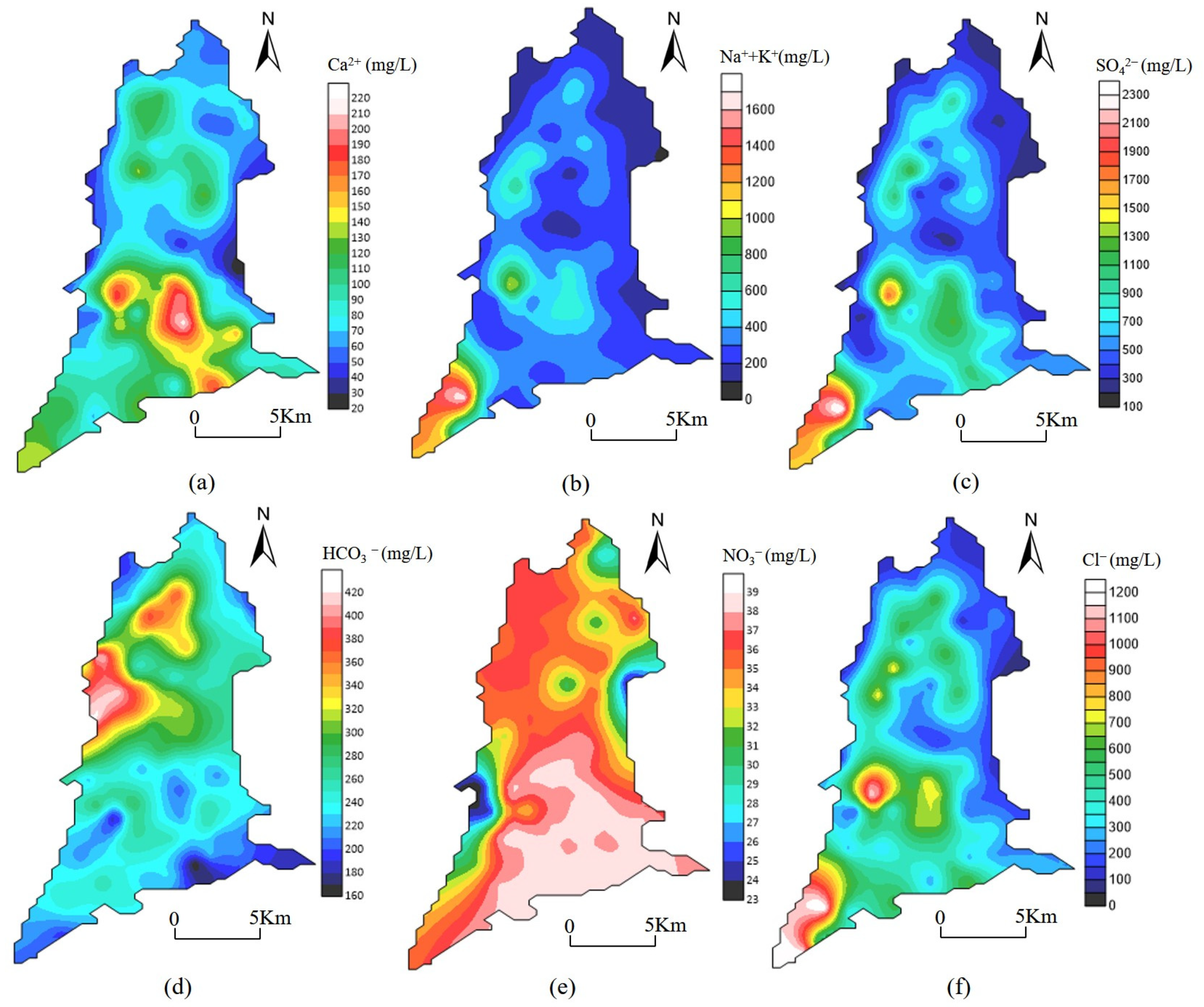
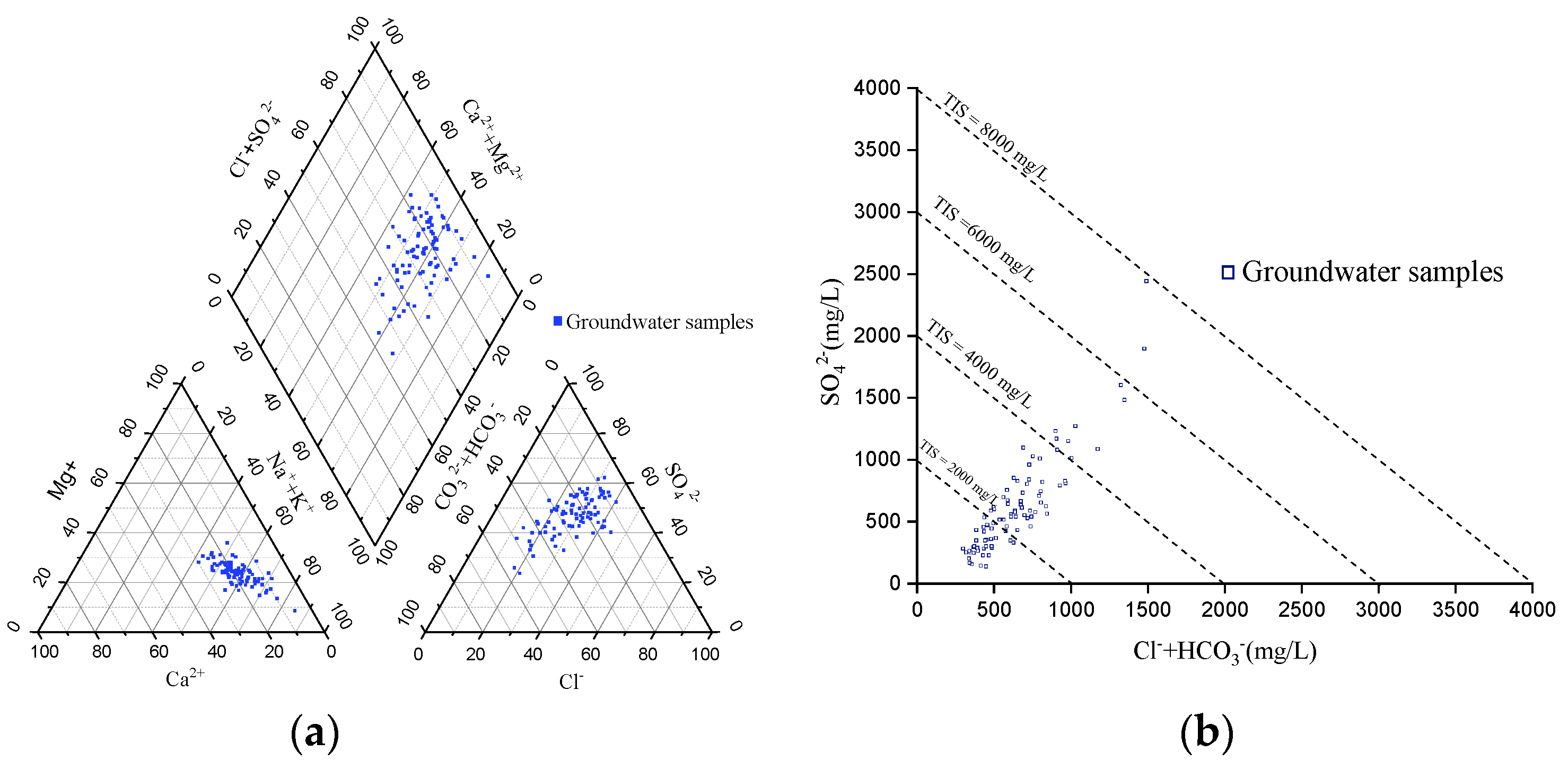
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Hydrochemistry
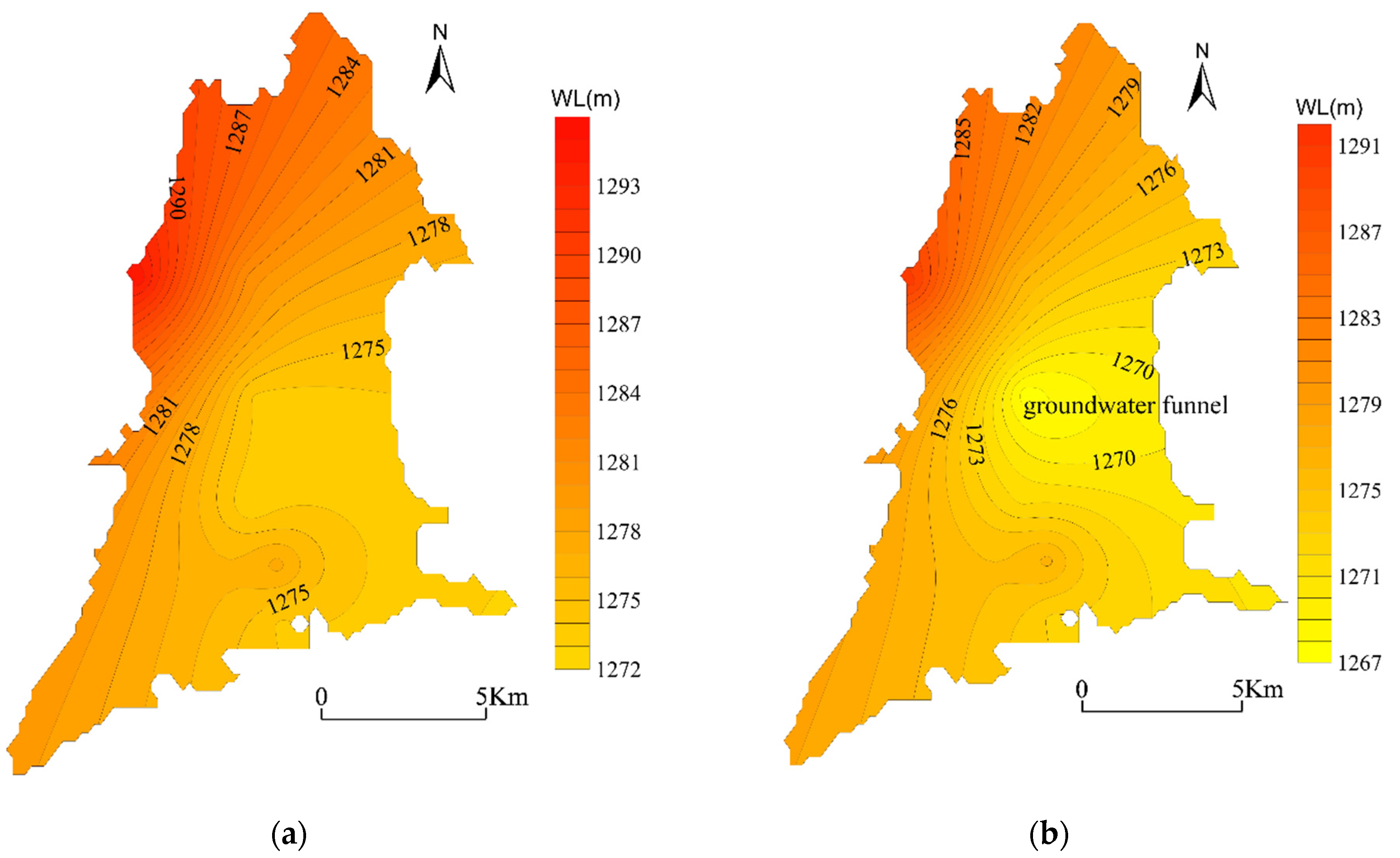
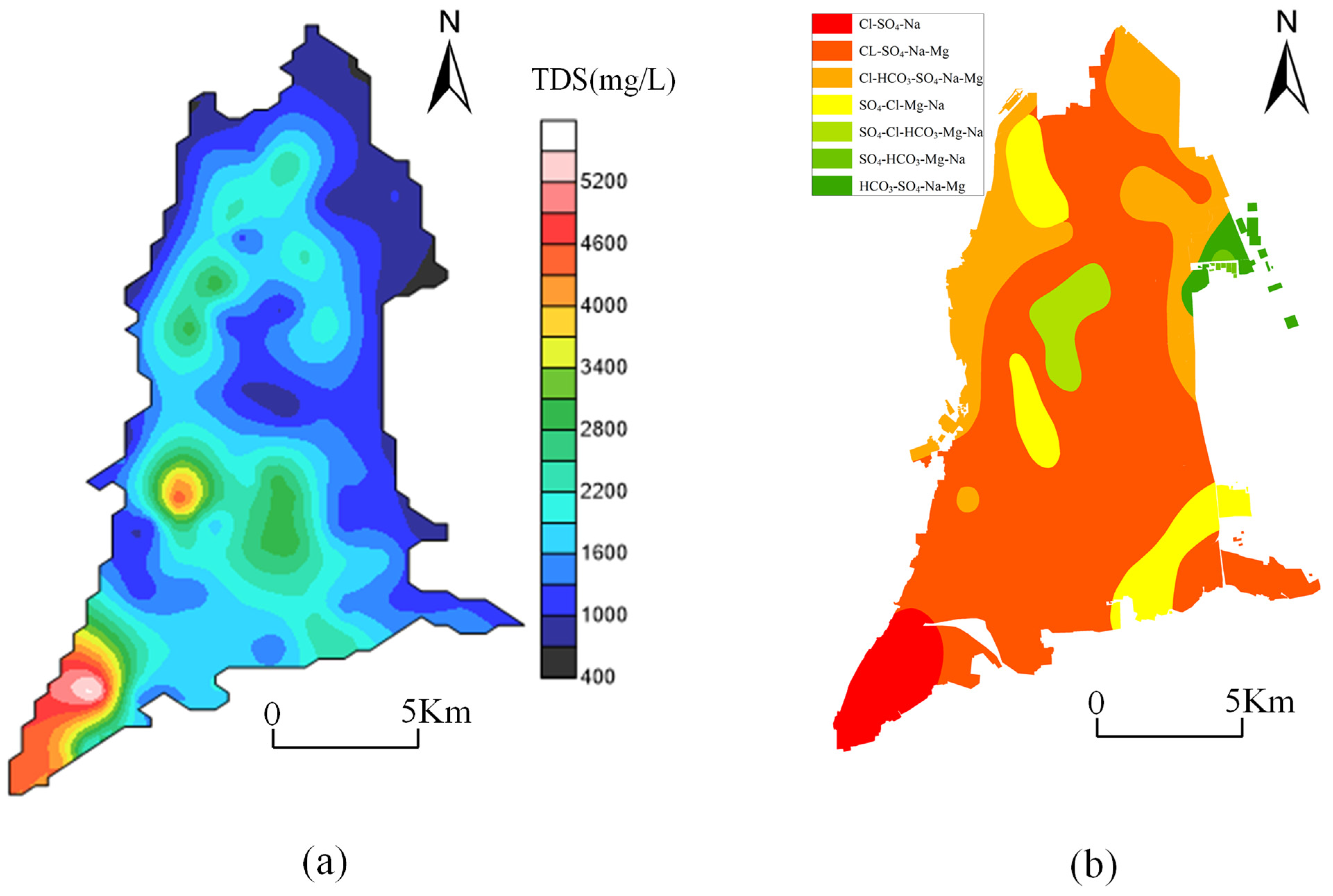
3.2. Spatial Evolution Law of Groundwater Hydrochemistry
3.3. Hydrochemical Formation Mechanism of Groundwater
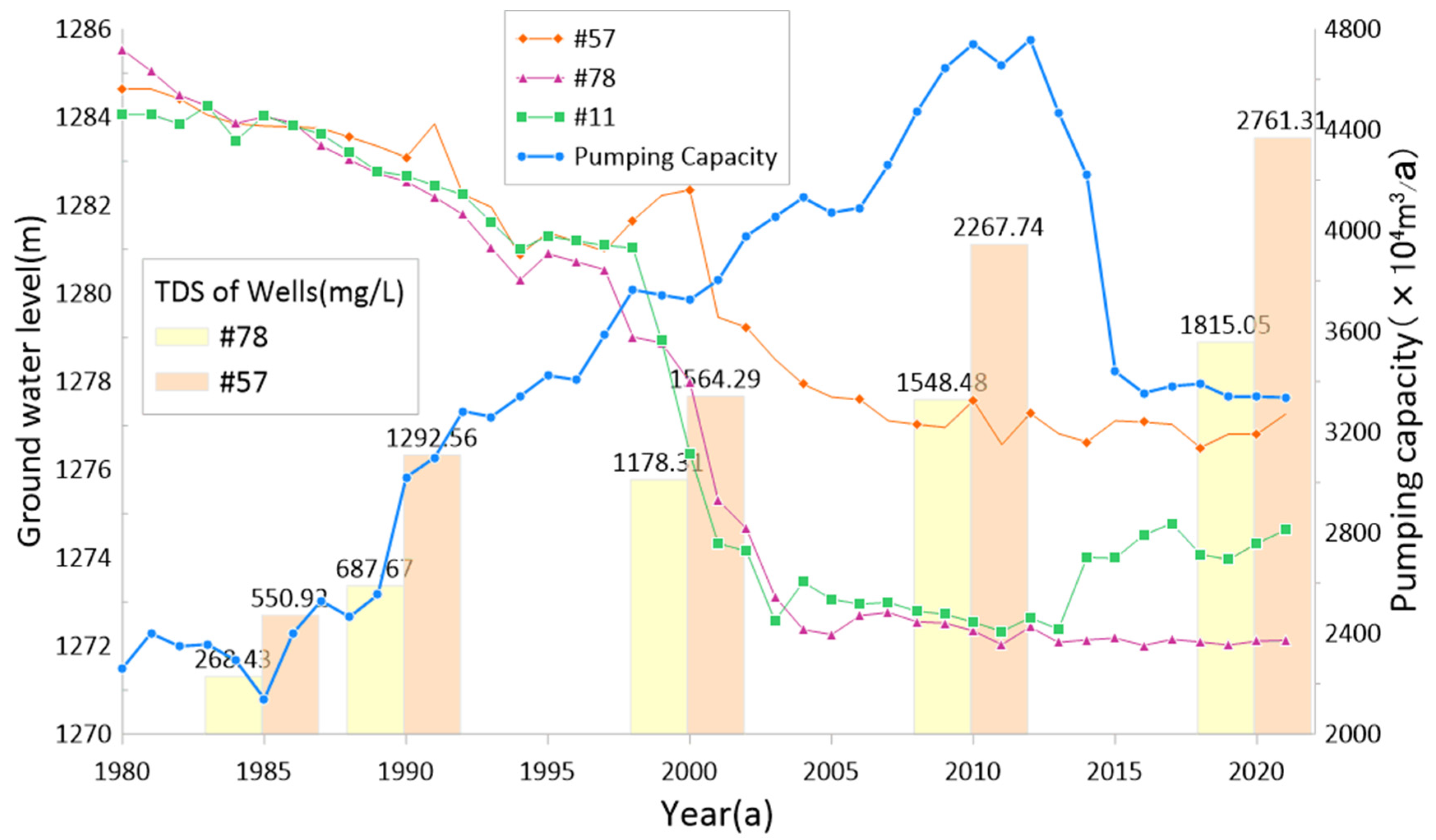
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Water salinity in Yaoba Oasis increased in the direction of groundwater runoff. In addition, Ca2+ and HCO3− concentrations in groundwater decreased, while those of Na+, Mg2+, Cl−, and SO42− increased over time. Moreover, the levels of TDS in groundwater augmented, and according to hydrochemical data, the type of water changed from HCO3·SO4-Na·Mg to Cl·SO4-Mg·Na and later to Cl·SO4-Na.
- (2)
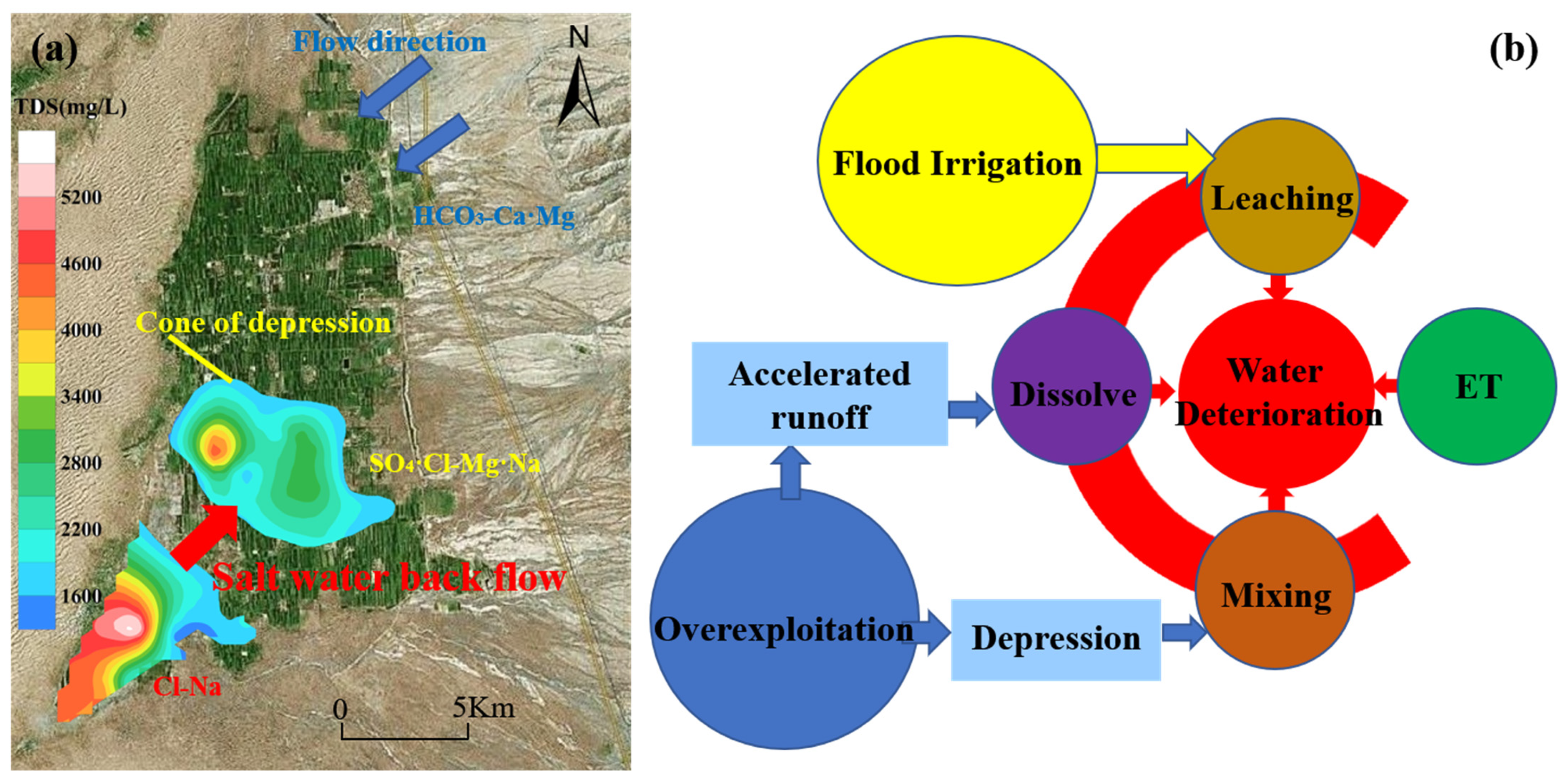
- Because of groundwater exploitation and climate factors, the hydrochemical types displayed island-shaped distribution patterns from the northeast to the southwest. As the hydrochemical type changed, complexity increased. Island-shaped distribution of SO4·Cl-Mg·Na and SO4·Cl·HCO3-Mg·Na type water was observed near the descending funnel in the oasis. As a result of evaporation, the Cl·SO4-Na type water was formed in the discharge area of the desert salty lake in the southwest part of the oasis.
- (3)
- Groundwater quality deterioration in the oasis results from the joint action of the infiltration of irrigation return flow and the intrusion of salty water in the desert lake area. The former only makes a limited contribution to groundwater salinization, while the latter is the main reason for groundwater salinization in the irrigated areas. The high value area of soluble salt ions (Na+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42−) and the island area with abnormal groundwater hydrochemical type in the study area are basically consistent with the groundwater depression funnel area of the oasis.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Lai, X.; Pan, X. Characteristics of Desert Improving Temperature Effect and Distribution of Oasis Agricultural Heat Resource. J. Desert Res. 2004, 24, 751–754. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, K. Evaluation of the stability of the oasis at the regional scale. J. Nat. Resour. 2004, 19, 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, F. Groundwater resources and their characteristics in arid lands of Northwestern China. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 17, 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.-W.; Lu, Y.-Z.; Li, B.-G.; Zhu, J.-R. A Model to Simulate Temporal-spatial Change of Groundwater Mineralization Resulted from Land Use in Oasis. J. Nat. Resour. 2009, 24, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y. Identification and monitoring of desertification lands in China from 2000 to 2015. Arid Land Geogr. 2018, 41, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Theory and Practice of Oasis Ecological Economic Sustainable Development. Chin. Rural Econ. 2003, 18, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M. Rational Development and Utilization of Water Resources Related to Prevention of Desertifi-cation in Arid Area of North-west China. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2005, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, A.D.; Yang, L.; Luo, P.P.; Cheng, Y.X.; Peng, J.B.; Nover, D. Influence of landfill and land use scenario on runoff, evapotranspiration, and sediment yield over the Chinese Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.X.; Huo, A.D.; Zhao, Z.X.; Peng, J.B. Analysis of loess fracture on slope stability based on centrifugal model tests. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 3647–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Nie, Z.; Liu, M.; Lu, H.; Wang, L. Changes in natural vegetation growth and groundwater depth and their relationship in the Minqin oasis in the Shiyang River Basin. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2020, 47, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huo, A.D.; Zhao, Z.X.; Yang, L.Y.; Peng, J.B.; Cheng, Y.X.; Wang, Z.F. Impact of Mountain Reservoir Construction on Groundwater Level in Downstream Loess Areas in Guanzhong Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Guo, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, J. Dynamic characteristics of groundwater level and storage variables in Minqin from 1985 to 2016. Arid Land Geogr. 2021, 44, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shao, J.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q. A study of the determination of indi-cators of dual control of groundwater abstraction amount and water table in northwest China: A case study of the Minqin Basin. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2020, 47, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Z.; Wang, X.S.; Edmundsb, W.M. The characteristics of ground-water resources and their changes under the impacts of humanactivity in the arid northwest China—A case study of the Shiyang River Basin. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 61, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution Mechanism of Groundwater in the Minqin Oasis. Arid Zone Res. 2017, 34, 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, A.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, P.; Zheng, C.; Peng, J.; Abuarab, M.E.-S. Assessment of Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture in the Critical Zone of Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection. Water 2022, 14, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhong, F.; Zheng, C.; Gao, N. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soils at the Northern Foot of the Qinling Mountains, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D. The progress of research on oasis in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1999, 19, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, H. Soil Water Infiltration Characteristics in Oasis on West Side of Helan Mountains. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 37, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.-H.; Lu, Y.-D.; Sai, J.-M.; Li, H.-H. Characteristics of Soil Salinity in Arid Oasis. Arid Zone Res. 2018, 35, 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Sai, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, M. Characteristics of Soil Salinization in Yaoba Oasis of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 37, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.; Peicheng, L.I.; Anyan, H.U.; Zhonghua, X.U. The groundwater chemical characteristics in the Yaoba oasis of Alxa area, Inner Mongolia. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2009, 23, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lu, Y.D.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, R.; Fan, W.; Pan, W.S. Influencing Factors of the Spatial-Temporal Variation of Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures and Infiltration Characteristics under Irrigation in a Desert Oasis by Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods. Water 2019, 11, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of groundwater in Yaoba Oasis of Inner Mongolia. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2021, 40, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Liang, C.; Yin, Z.; Bao, Z.; Qian, L. Hydrogeochemical process of evolution of groundwater in plain area of Yanqi, Xinjiang. Environ. Chem. 2017, 36, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, H. Hydrochemical Characteristic and Reasoning Analysis in Siyi Town, Langzhong City. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 3230–3237. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Chai, C.; Zhang, Y. Spatial Distribution of Brackish Groundwater and Its Formation Causes in the Minqin Oasis in Lower Reaches of the Shiyang River. Arid Zone Res. 2014, 31, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Shanyengana, E.S.; Seely, M.K.; Sanderson, R.D. Major-ion chemistry and ground-water salinization in ephemeral floodplains in some arid regions of Namibia. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 57, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Bi Lali·Yi, M.; Wan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shi, Q. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in Dali yaboyi oasis in the hinterland of the desert. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2021, 35, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Bian, B.; Zhao, G. Correlation analysis among precipitation and soil water and groundwater in oasis-desert transitional belt in Heihe river middle reaches. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2016, 36, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Edmunds, W.M. Groundwater and lake evolution in the Badain Jaran Desert ecosystem, Inner Mongolia. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wu, S. Groundwater System in Arid Area—Groundwater System on the West Side of Helan Mountain; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, X. Analysis of groundwater reservoir system in the piedmont of the west side of Helan Mountain. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2017, 31, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.-C.; Lu, Y.-D.; Wang, J.-K. Study on the Bearing Capacity and Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater Resources in Alashan YaoBa Oasis; Chang’an University: Xi’an, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, X. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of groundwater and their responses to climate change and human activities in arid and desert areas: A case study in Yaoba Oasis, Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Yang, M.; Li, S. Groundwater Level Prediction for the Arid Oasis of Northwest China Based on the Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm and a Back-propagation Neural Network with Double Hidden Layers. Water 2019, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.Q.; Lu, Y.D.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Z.H.; Sai, J.M. Relationship between Soil Salinization and Groundwater Hydration in Yaoba Oasis, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L. Comprehensive treatment plan for groundwater overdraft area in Alxa League. Inn. Mong. Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Fuoco, I.; Marini, L.; De Rosa, R.; Figoli, A.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Use of reaction path modelling to investigate the evolution of water chemistry in shallow to deep crystalline aquifers with a special focus on fluoride. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-H.; Lu, Y.-D.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Zheng, C. Analysis on Groundwater Dynamic Characteristics and Causes in Yao Ba Oasis. Earth Sci. 2015, 4, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trabelsi, F.; Bel Hadj Ali, S. Exploring Machine Learning Models in Predicting Irrigation Groundwater Quality Indices for Effective Decision Making in Medjerda River Basin, Tunisia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Zhu, G.F.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.Z.; Zhang, F.P. Environmental isotopic and hydrochemical study of groundwater in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Merino, L.; Aguilera, H.; Román, A.d.l.L. Are bottled mineral waters and groundwater for human supply different? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, J.; Bachaer, A.; Moez, B.; Emna, B.; Salem, B. Contribution of GIS tools and statistical approaches to optimize the DRASTIC model for groundwater vulnerability assessment in arid and semi-arid regions: The case of Sidi Bouzid shallow aquifer. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, J. Analysis on the Present Situation of Water Resources in Alxa Left Banner and Study on Countermeasures. Inn. Mong. Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.; Ali, M.A. Occurrence of manganese in groundwater of Bangladesh and its im-plications on safe water supply. J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 38, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Fuoco, I.; Rosa, R.D.; Barca, D.; Figoli, A. Arsenic polluted waters: Application of geochemical modelling as a tool to understand the release and fate of the pollutant in crystalline aquifers. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 301, 113796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 14848-93; Quality Standard for Ground Water. Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Apollaro, C.; Curzio, D.D.; Fuoco, I.; Buccianti, A.; Dinelli, E.; Vespasiano, G.; Castrignanò, A.; Rusi, S.; Barca, D.; Figoli, A.; et al. A multivariate non-parametric approach for estimating probability of exceeding the local natural background level of arsenic in the aquifers of Calabria region (Southern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, R.R.; Zhang, F.; Rehman, F.U.; Wang, G.X.; Ye, M.; Zeng, C.; Tang, H.D. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cary, L.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Bertrand, G.; Kloppmann, W.; Aquilina, L.; Martins, V.; Hirata, R.; Montenegro, S.; Pauwels, H.; Chatton, E.; et al. Origins and processes of groundwater salinization in the urban coastal aquifers of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil): A multi-isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530–531, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; CRC Press: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, D.C.; Chin-Fu, T. A summary of subsurface hydrological and hydrochemical models. Rev. Geophys. 1991, 29, 51–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Bian, J.; Martin, J.D. Isotopic and geochemical interpretation of groundwater under the influences of anthropogenic activities. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyfzand, P.J. Patterns in groundwater chemistry resulting from groundwater flow. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbozige, F.J.; Toko, M.A. Piper Trilinear and Gibbs Description of Groundwater Chemistry in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 13, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounslow, A.W. Water Quality Data: Analysis and Interpretation; Lewis Pu1isher: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.R.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, W.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Hou, Y.F.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z.Y. Assessing the Influences of Land Use Change on Groundwater Hydrochemistry in an Oasis-Desert Region of Central Asia. Water 2022, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Han, S.M.; Yang, Y.M.; Ai, Z.P.; Wang, J.S.; Ma, F.Y. Identifying changes in irrigation return flow with gradually intensified water-saving technology using HYDRUS for regional water resources management. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, H.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Liu, G. The Mechanism of Groundwater Salini-zation and Its Control in the Yaoba Oasis, Inner Mongolia. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 74, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, L.N.; Busby, J.F.; Lee, R.W.; Hanshaw, B.B. Geochemical modeling of the Madision Aquifer in parts of Montana, Wyoming, and South Dakota. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 1981–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Item | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K++Na+ | SO42− | Cl− | HCO3− | NO3− | TDS | CO2 | pH | Electrical Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 1 | ||||||||||
| Mg2+ | 0.811 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| K++Na+ | 0.551 ** | 0.667 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| SO42− | 0.770 ** | 0.833 ** | 0.932 ** | 1 | |||||||
| Cl− | 0.763 ** | 0.876 ** | 0.907 ** | 0.932 ** | 1 | ||||||
| HCO3− | −0.310 ** | 0.059 | 0.041 | −0.07 | −0.043 | 1 | |||||
| NO3− | 0.475 ** | 0.398 ** | 0.296 ** | 0.423 ** | 0.348 ** | −0.124 | 1 | ||||
| TDS | 0.751 ** | 0.852 ** | 0.952 ** | 0.987 ** | 0.974 ** | −0.011 | 0.387 ** | 1 | |||
| CO2 | 0.301 ** | 0.398 ** | 0.154 | 0.273 ** | 0.245 * | 0.136 | 0.113 | 0.261 * | 1 | ||
| pH | −0.426 ** | −0.386 ** | −0.09 | −0.262 * | −0.227 * | 0.088 | −0.194 | −0.234 * | −0.636 ** | 1 | |
| Electrical conductivity | 0.857 ** | 0.959 ** | 0.916 ** | 0.960 ** | 0.978 ** | 0.017 | 0.414 ** | 0.985 ** | 0.343 ** | −0.357 ** | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, T.; Huo, A.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, W. Hydrodynamic Behaviors and Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater for Irrigation in Yaoba Oasis, China. Water 2022, 14, 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233924
Lu T, Huo A, Wang J, Lu Y, Zhou W. Hydrodynamic Behaviors and Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater for Irrigation in Yaoba Oasis, China. Water. 2022; 14(23):3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233924
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Ting, Aidi Huo, Jucui Wang, Yudong Lu, and Weibo Zhou. 2022. "Hydrodynamic Behaviors and Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater for Irrigation in Yaoba Oasis, China" Water 14, no. 23: 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233924






