Optimization of a Laboratory Rainfall Simulator to Be Representative of Natural Rainfall
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
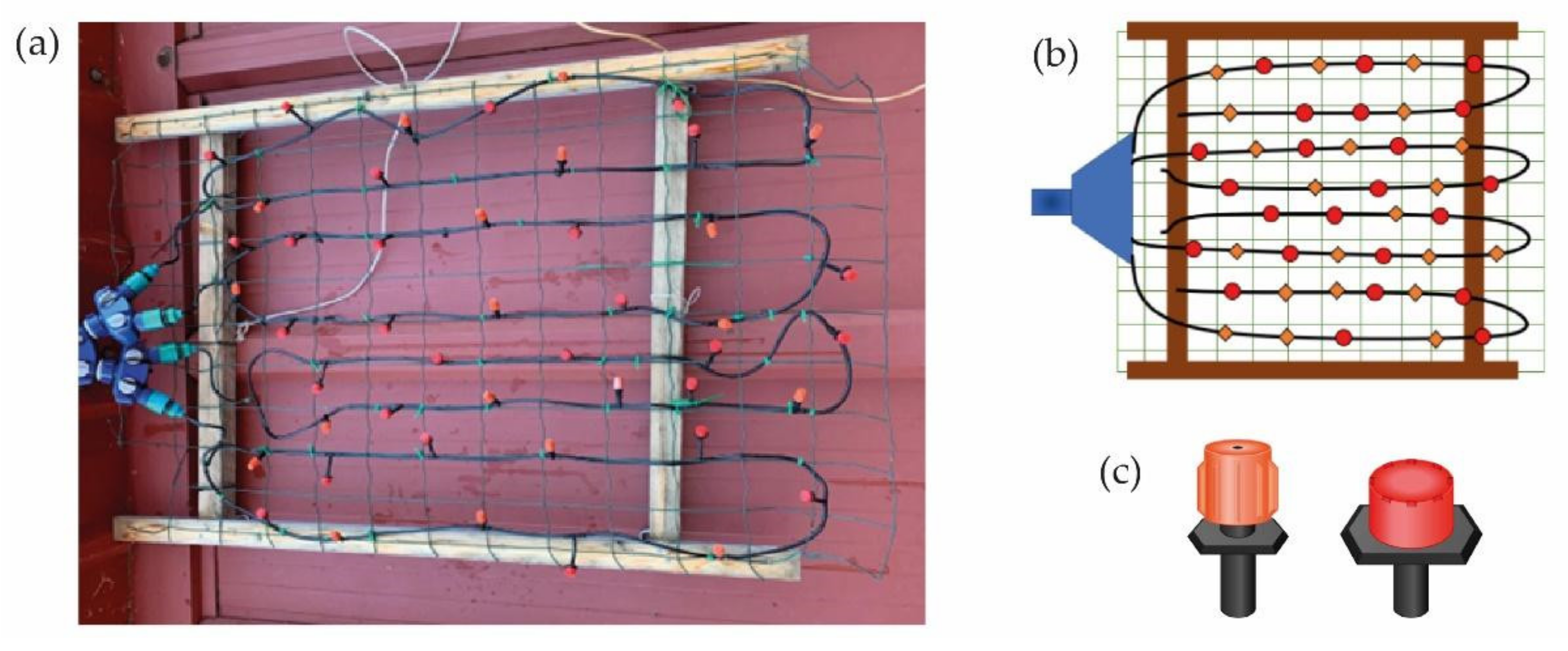
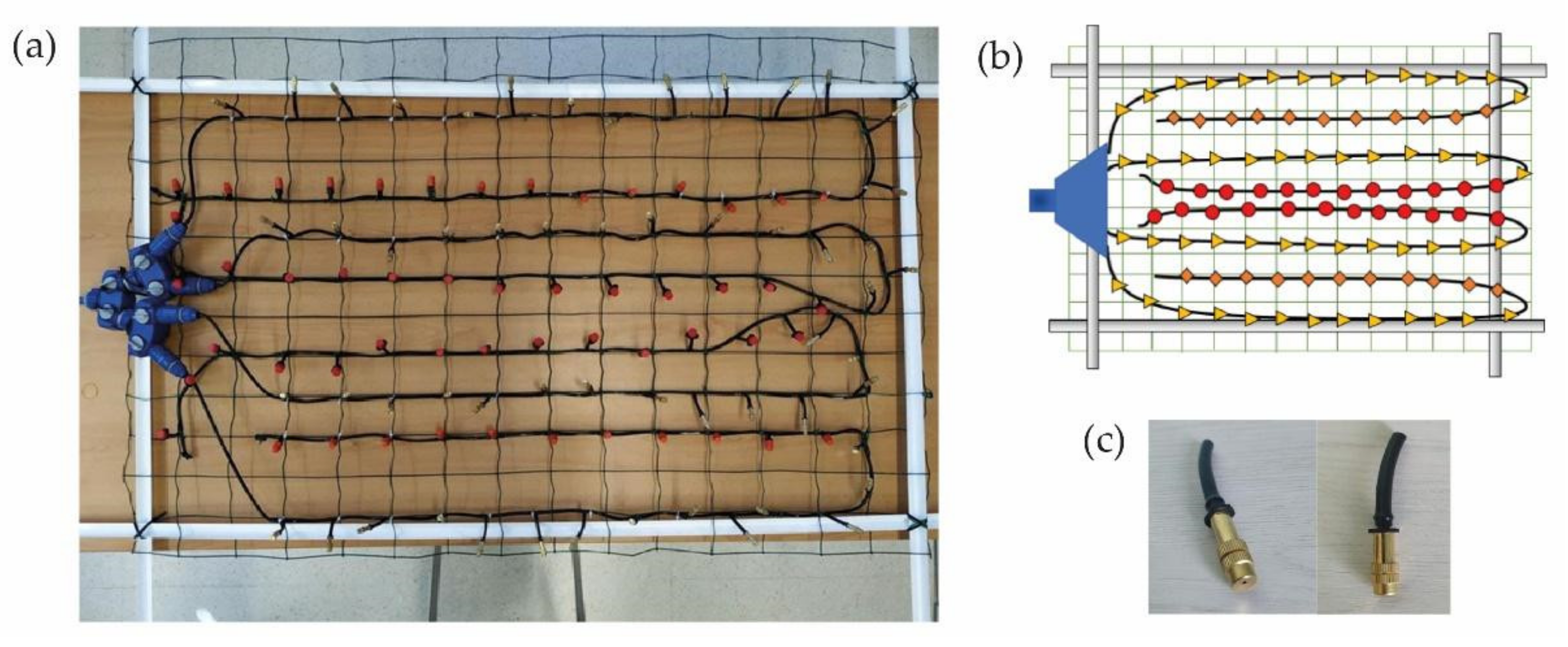
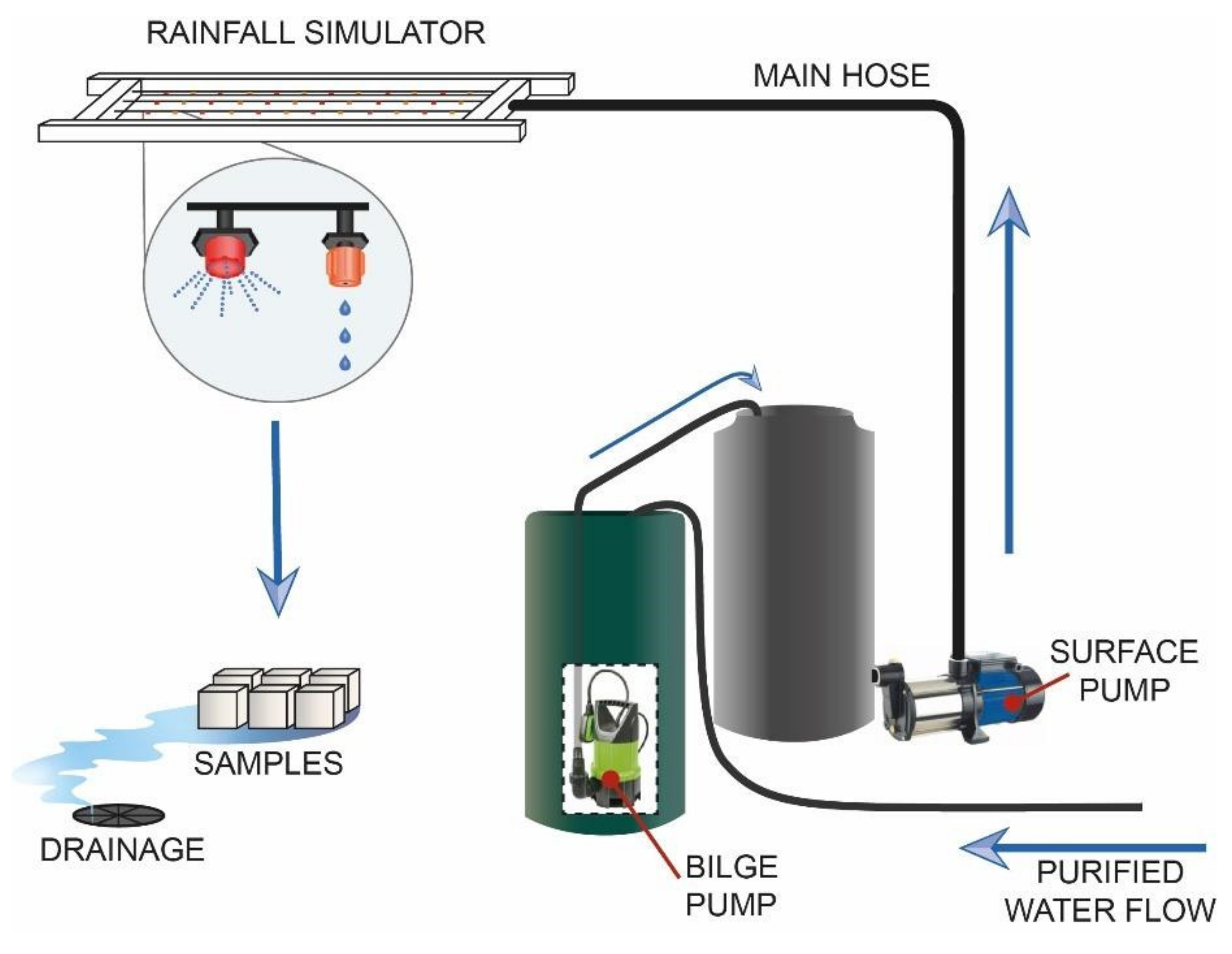
2.1. Simulator Structure Design
2.2. Rainfall Simulator Calibration
3. Results
Christiansen Uniformity Coefficient Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Achieving a spectrum of mini sprinklers with droppers that produce droplet sizes similar to natural droplet sizes.
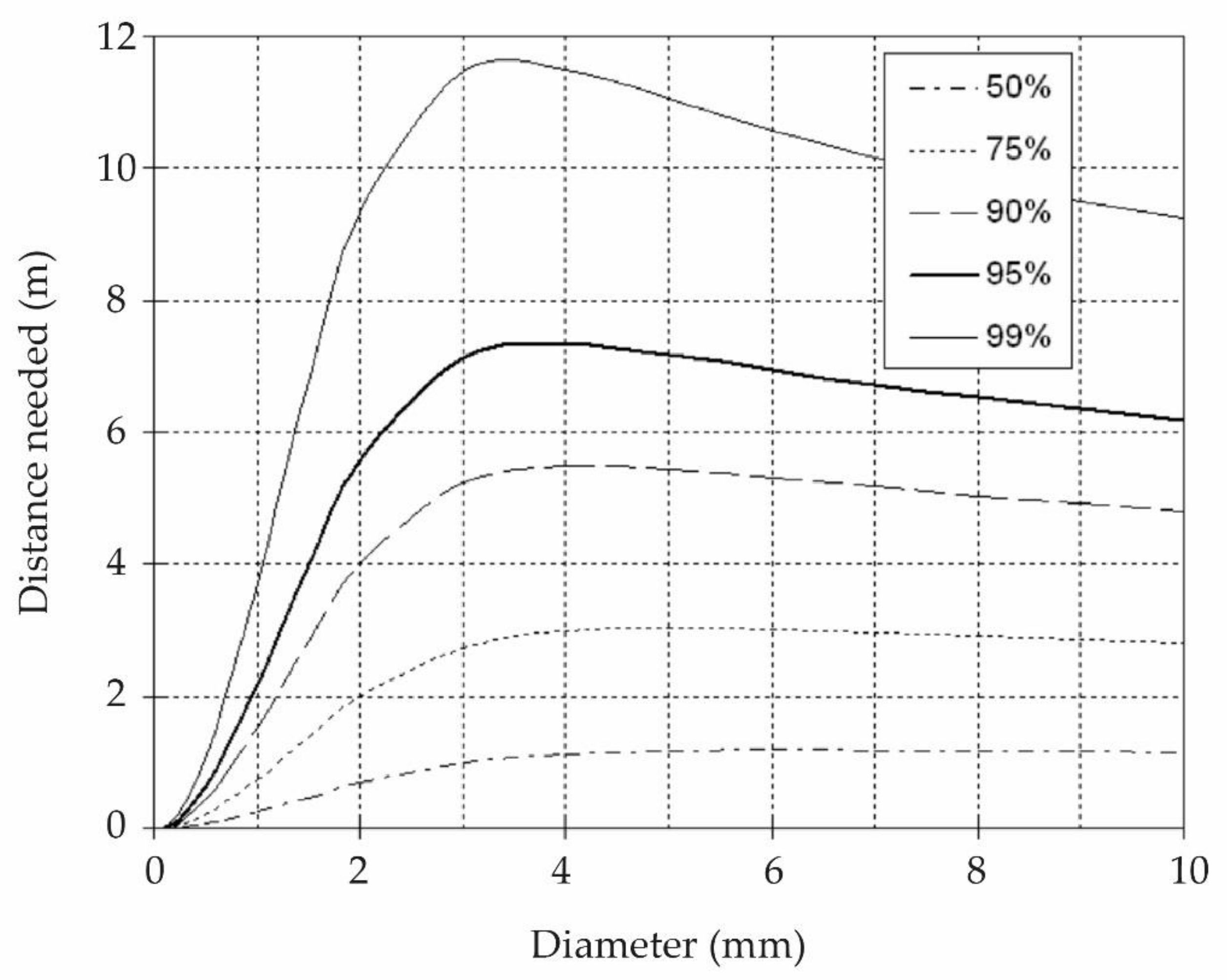
- Analyzing the distance required by a droplet to reach terminal velocity.
- Appropriate location that provides sufficient height to reach terminal velocity.
- Keeping the simulator sheltered from wind currents that may disperse water droplets.
- Versatility of the simulator to represent rainfall in different seasons, regions, or even in polluted atmospheres.
- Searching for homogeneity of results using the CUC.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mastoi, D. Design and Construction of Rainfall Simulator for Determination of Erosion. Doctoral Thesis, Sindh Agriculture University, Tando Jam, Pakistan, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaske, S.N.; Pathak, K.; Basak, A. A Comprehensive Design of Rainfall Simulator for the Assessment of Soil Erosion in the Laboratory. Catena 2019, 172, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergni, L.; Todisco, F.; Vinci, A. Setup and Calibration of the Rainfall Simulator of the Masse Experimental Station for Soil Erosion Studies. Catena 2018, 167, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassu, T.; Seeger, M.; Peters, P.; Keesstra, S.D. The Wageningen Rainfall Simulator: Set-up and Calibration of an Indoor Nozzle-Type Rainfall Simulator for Soil Erosion Studies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, H.; Unal, N.E.; Cokgor, S.; Gedikli, A.; Yoon, J.; Koca, K.; Inci, S.B.; Eris, E. A Rainfall Simulator for Laboratory-Scale Assessment of Rainfall-Runoff-Sediment Transport Processes over a Two-Dimensional Flume. Catena 2012, 98, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iserloh, T.; Fister, W.; Seeger, M.; Willger, H.; Ries, J.B. A Small Portable Rainfall Simulator for Reproducible Experiments on Soil Erosion. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroosnijder, L. Measurement of Erosion: Is It Possible? Catena 2005, 64, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdá, A. Simuladores de Lluvia y Su Aplicación En Geomorfología: Estado de La Cuestión. Cuad. Investig. Geogr./Geogr. Res. Lett. 1999, 25, 45–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, A.; Alberto, F.; Machín, J.; Galán, A. Design and operation of a rainfall simulator for field studies of runoff and soil erosion. Soil Technol. 1990, 3, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.D. Simulation of Rainfall for Soil Erosion Research. Trans. ASAE 1965, 8, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Campelo, D.; Fernández-Raga, M.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, Á.; Guerra-Romero, M.I.; González-Domínguez, J.M. Extraordinary Protective Efficacy of Graphene Oxide over the Stone-Based Cultural Heritage. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakis, P.; Schellewald, C.; Kebremariam, K.F.; Theoharis, T. Simulating Erosion on Cultural Heritage Monuments. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Cultural Heritage and New Technologies (CHNT20), Vienna, Austria, 2–4 November 2015; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich, W.E.; Cox, J.R. Hydrologic Characteristics Immediately after Seasonal Burning on Introduced and Native Grasslands. J. Range Manag. 1992, 45, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H. Investigating Flood Impact on Crop Production under a Comprehensive and Spatially Explicit Risk Evaluation Framework. Agriculture 2022, 12, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.; Kleinman, P. Effect of Rainfall Simulator and Plot Scale on Overland Flow and Phosphorus Transport. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamošiūnaitė, M.; Tamošiūnas, S.; Daukšas, V.; Tamošiūnienė, M.; Žilinskas, M. Prediction of Electromagnetic Waves Attenuation Due to Rain in the Localities of Lithuania. Elektron. Elektrotech. 2010, 105, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nnadi, E.; Newman, A.; Duckers, L.; Coupe, S.; Charlesworth, S. Design and Validation of a Test Rig to Simulate High Rainfall Events for Infiltration Studies of Permeable Pavement Systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngezahayo, E.; Burrow, M.; Ghataora, G. Calibration of the Simple Rainfall Simulator for Investigating Soil Erodibility in Unpaved Roads. Int. J. Civ. Infrastruct. 2021, 4, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.T.; Moldrup, P.; Thorndahl, S.; Nielsen, J.E.; Duus, L.B.; Rasmussen, S.H.; Uggerby, M.; Rasmussen, M.R. Automated Rainfall Simulator for Variable Rainfall on Urban Green Areas. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 3364–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, M.L.; Yusop, Z. Adaptability of Rainfall Simulators as a Research Tool on Urban Sealed Surfaces—A Review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 996–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes Sanchez Macedo, P.; Ferreira Pinto, M.; Alves Sobrinho, T.; Schultz, N.; Altamir Rodrigues Coutinho, T.; Fonseca de Carvalho, D. A Modified Portable Rainfall Simulator for Soil Erosion Assessment under Different Rainfall Patterns. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, N.; Johannsen, L.L.; Strauss, P.; Dostal, T.; Zumr, D.; Cochrane, T.A.; Klik, A. Splash Erosion Affected by Initial Soil Moisture and Surface Conditions under Simulated Rainfall. Catena 2021, 196, 104827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, T.P.; Thompson, A.L. Rainfall Simulator for Laboratory Studies. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2000, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjo, R. Measure of Rainfall Time Structure Using the Dimensionless N-Index. Clim. Res. 2016, 67, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Fraile, R.; Keizer, J.J.; Varela, M.E.; Castro, A.; Palencia, C.; Calvo, A.I.; Koenders, J.; Liliana, R.; Marqués, D.C. The Kinetic Energy of Rain Measured with an Optical Disdrometer: An Application to Splash Erosion. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.W. Soil Conservation; B.T. Batsford LTD: London, UK, 1971; ISBN 10: 0813823722. [Google Scholar]
- Laws, J.O. Measurements of the Fall-Velocity of Water-Drops and Raindrops. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1941, 22, 709–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živanović, N.; Rončević, V.; Spasić, M.; Ćorluka, S.; Polovina, S. Construction and Calibration of a Portable Rain Simulator Designed for the in Situ Research of Soil Resistance to Erosion. Soil Water Res. 2022, 17, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubenzer, G.D. Rainfall Characteristics Important for Simulation; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1979; Volume 10, pp. 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxel, J. Numerical Model for the Fall Speed of Rain Drops in a Rain Fall Simulator. I.C.E. Spec. Rep. 1998, 1, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, K.V.; Prupacher, H.R. A Determination of the Terminal Velocity and Drag of Small Water Drops by Means of a Wind Tunnel. J. Atmos. Sci. 1969, 26, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The Terminal Velocity of Fall for Water Droplets in Stagnant Air. J. Meteorol. 1949, 8, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASABE. Design and Installation of Micro-Irrigation Systems; American Society of Agricultural Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Palencia, C.; Keesstra, S.; Jordán, A.; Fraile, R.; Angulo-Martínez, M.; Cerdá, A. Splash Erosion: A Review with Unanswered Questions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossary of Meteorology Rain. Gloss. Meteorol. 2000. Available online: https://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Rain (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Fernandez-Raga, M.; Castro, A.; Marcos, E.; Palencia, C.; Fraile, R. Weather Types and Rainfall Microstructure in Leon, Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Castro, A.; Palencia, C.; Calvo, A.; Fraile, R. Rain Events on 22 October 2006 in León (Spain): Drop Size Spectra. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, A.; Todisco, F.; Vergni, L.; Torri, D. A Comparative Evaluation of Random Roughness Indices by Rainfall Simulator and Photogrammetry. Catena 2020, 188, 104468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, F.; Vergni, L.; Vinci, A.; Torri, D. Infiltration and Bulk Density Dynamics with Simulated Rainfall Sequences. Catena 2022, 218, 106542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

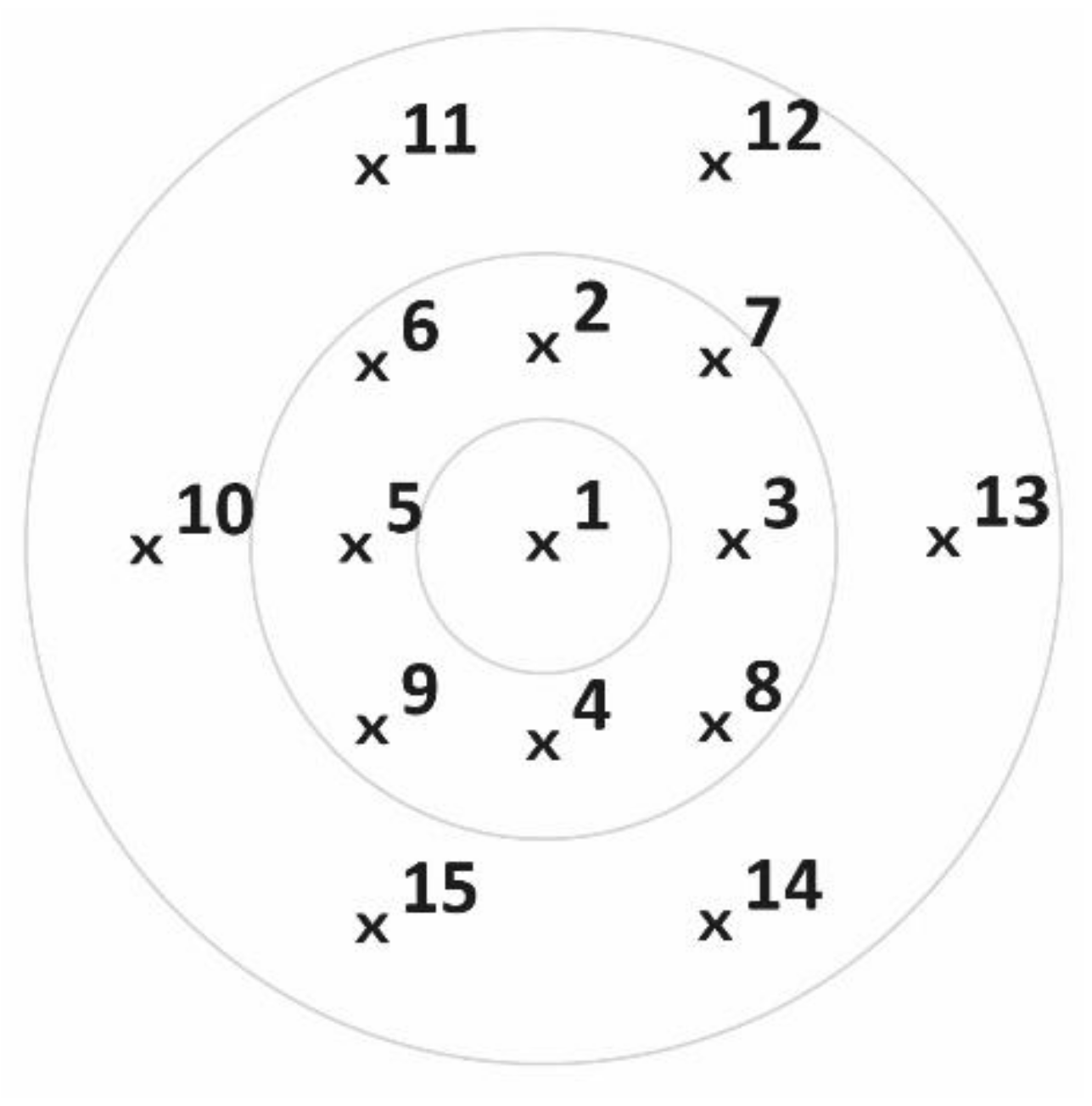

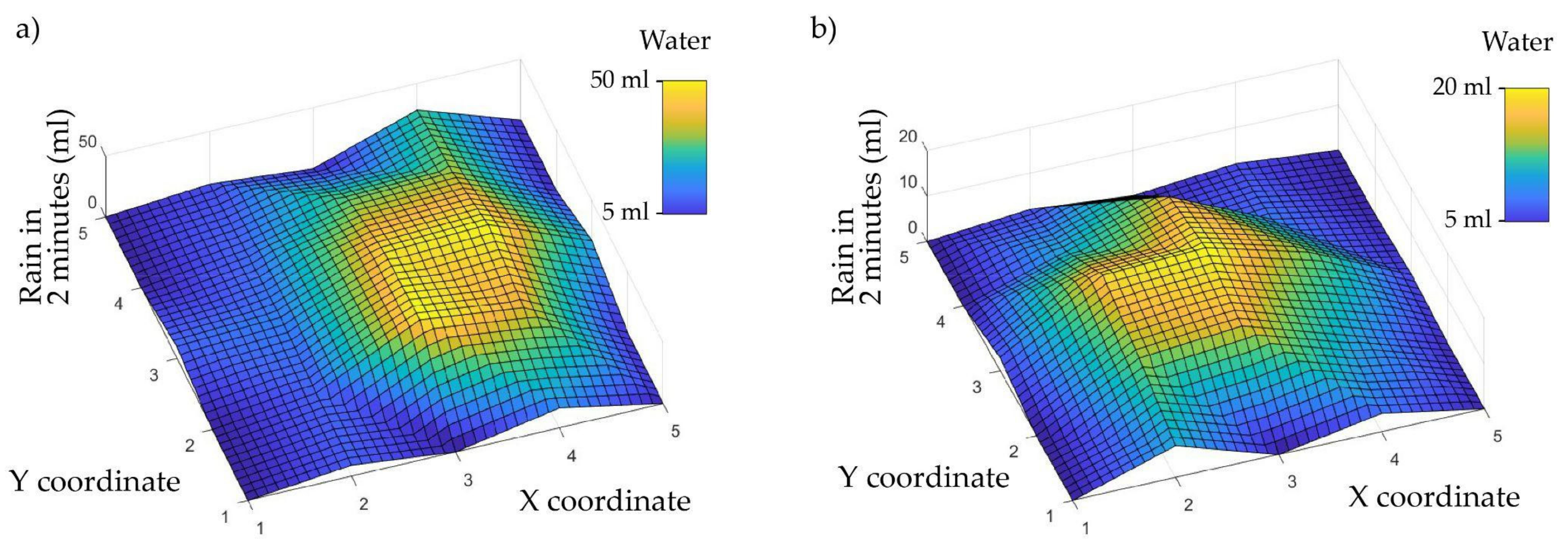
| Container No. | Test 1 (mL) | Test 2 (mL) | Test 3 (mL) | Test 4 (mL) | Mean (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41 | 44 | 51 | 53 | 47 |
| 2 | 46 | 40 | 57 | 58 | 50 |
| 3 | 52 | 39 | 55 | 55 | 50 |
| 4 | 36 | 22 | 38 | 32 | 32 |
| 5 | 14 | 11 | 13 | 16 | 14 |
| 6 | 8 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 7 | 37 | 43 | 41 | 38 | 40 |
| 8 | 39 | 29 | 34 | 39 | 35 |
| 9 | 9 | 10 | 14 | 11 | 11 |
| 10 | 11 | 10 | 13 | 6 | 10 |
| 11 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 9 |
| 12 | 18 | 10 | 18 | 16 | 16 |
| 13 | 18 | 12 | 19 | 18 | 17 |
| 14 | 35 | 20 | 29 | 26 | 28 |
| 15 | 5 | 4 | 10 | 9 | 7 |
| Container No. | Test 1 (mL) | Test 2 (mL) | Test 3 (mL) | Test 4 (mL) | Mean (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | 17 | 19 | 17 | 17 |
| 2 | 15 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 14 |
| 3 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 11 |
| 4 | 15 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 14 |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 15 | 16 |
| 6 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 10 | 12 |
| 7 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 7 |
| 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| 9 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 11 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| 12 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| 13 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 14 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 15 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| CLASSIFICATION | CUC (%) |
|---|---|
| Excellent | >90 |
| Good | 80–90 |
| Fair | 70–80 |
| Poor | 60–70 |
| Unacceptable | <60 |
| Cont.* 1 | Cont. 2 | Cont. 3 | Cont. 4 | Cont. 5 | Cont. 6 | Cont. 7 | Cont. 8 | Cont. 9 | Cont. 10 | Cont. 11 | Cont. 12 | Cont. 13 | Cont. 14 | Cont.15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUC-W | 89.9 | 85.6 | 88.8 | 84.4 | 88.9 | 91.0 | 94.3 | 89.4 | 86.4 | 80.0 | 91.4 | 87.5 | 85.8 | 83.6 | 64.3 |
| CUC-A | 94.9 | 93.6 | 93.0 | 91.2 | 93.5 | 92.6 | 92.9 | 57.1 | 81.5 | 88.5 | 92.9 | 82.4 | 70.0 | 25.0 | 44.4 |
| CLASSIFICATION | L/m2/h |
|---|---|
| Light | <3.5 |
| Moderate | 2.5–7.6 |
| Heavy | 7.6–50 |
| Torrential | >50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Raga, M.; Rodríguez, I.; Caldevilla, P.; Búrdalo, G.; Ortiz, A.; Martínez-García, R. Optimization of a Laboratory Rainfall Simulator to Be Representative of Natural Rainfall. Water 2022, 14, 3831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233831
Fernández-Raga M, Rodríguez I, Caldevilla P, Búrdalo G, Ortiz A, Martínez-García R. Optimization of a Laboratory Rainfall Simulator to Be Representative of Natural Rainfall. Water. 2022; 14(23):3831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233831
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Raga, María, Indira Rodríguez, Pablo Caldevilla, Gabriel Búrdalo, Almudena Ortiz, and Rebeca Martínez-García. 2022. "Optimization of a Laboratory Rainfall Simulator to Be Representative of Natural Rainfall" Water 14, no. 23: 3831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233831
APA StyleFernández-Raga, M., Rodríguez, I., Caldevilla, P., Búrdalo, G., Ortiz, A., & Martínez-García, R. (2022). Optimization of a Laboratory Rainfall Simulator to Be Representative of Natural Rainfall. Water, 14(23), 3831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233831










