Deformation Prediction System of Concrete Dam Based on IVM-SCSO-RF
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Indicator Variable Model
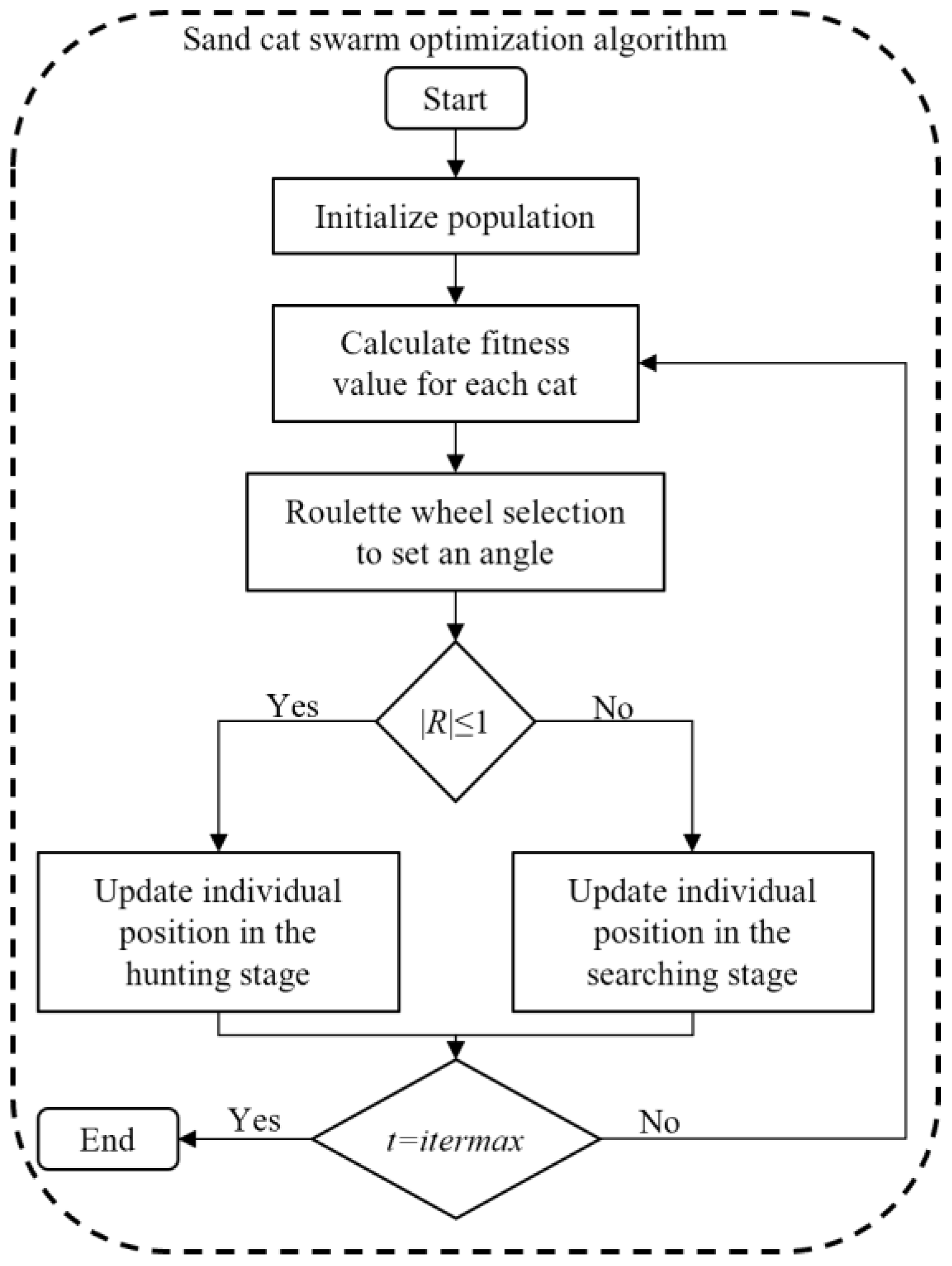
2.2. Sand Cat Swarm Optimization Algorithm
2.2.1. Initial Population
2.2.2. Searching the Prey
2.2.3. Attacking the Prey
2.2.4. Transition between Search and Hunting Stages
2.3. Random Forest Algorithm
2.3.1. Decision Tree Algorithm
2.3.2. Ensemble Learning
2.3.3. Out-of-Bag Error
2.3.4. Flow of Random Forest Algorithm
- Generate n groups of training samples randomly by bootstrap method, and construct decision trees based on the new sample sets.
- When selecting attributes for each internal node, select m attributes from all attributes randomly as the attribute set of the node. Based on CART algorithm, select the optimal attribute for splitting until the decision tree grows completely. During the growth of the decision tree, pruning is not required.
- Input the test sample set and obtain the final result on the basis of synthesizing the prediction results of all decision trees. For regression problems, the weighted average of prediction values of all decision trees is taken as the final prediction value.
2.4. Construction of Deformation Prediction System of Concrete Dam Based on IVM-SCSO-RF
2.4.1. Input Variables
2.4.2. Parameters of RF
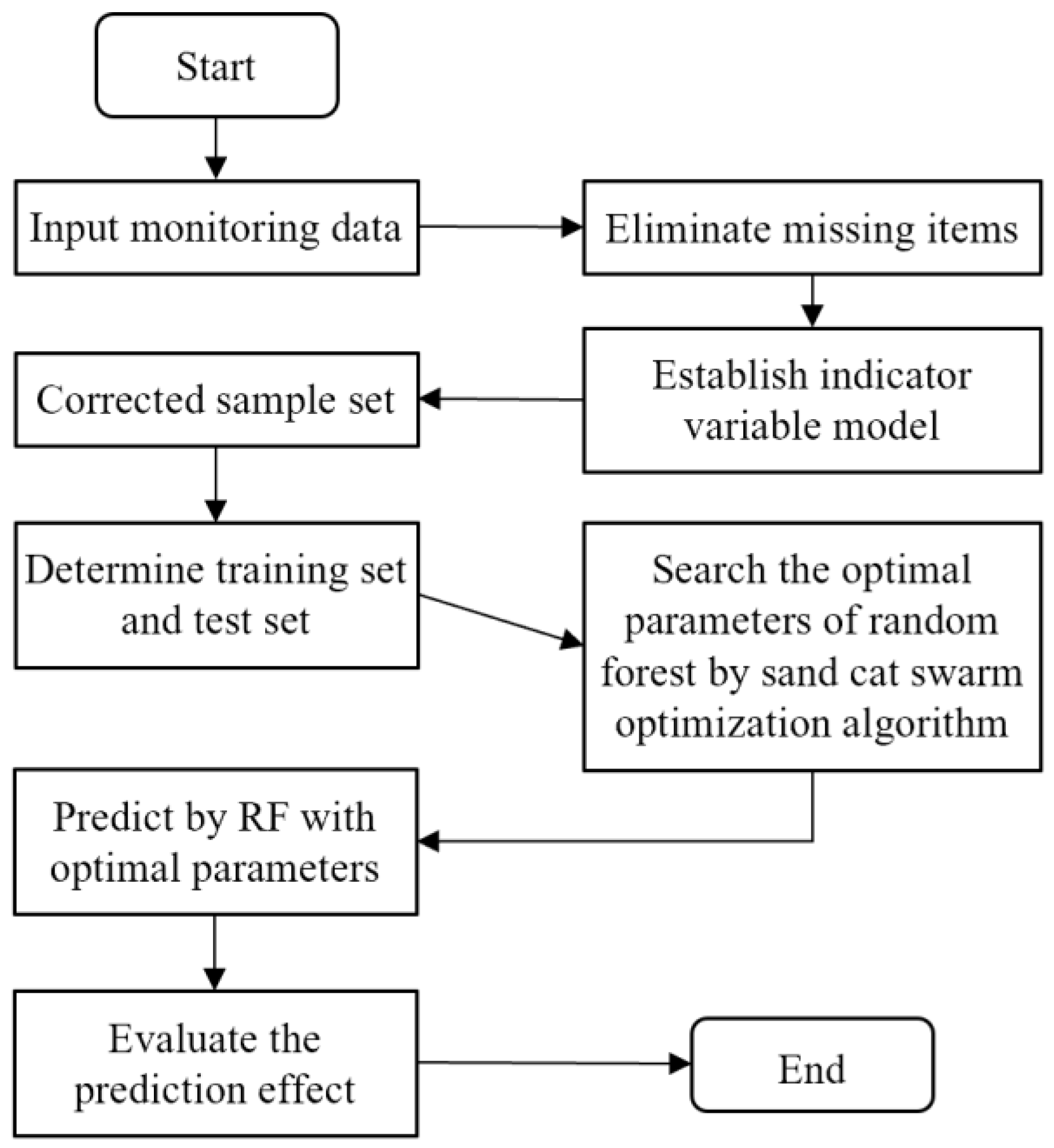
2.4.3. System Operation Process
- Read the original data, establish the IVM to eliminate system interference after removing the missing items in the monitoring values, and obtain the corrected sample set.
- Divide the sample set into training set and test set; the proportion of test set is generally 10%~20% of the total samples.
- Input the training set data into the SCSO-RF algorithm and obtain the optimal parameter combination of the RF algorithm by SCSO algorithm.
- Input the test set data into the RF algorithm after parameter optimization and obtain the prediction results.
- Analyze the prediction effect by comparing the predicted value with the actual value and calculating the sum of squared error SSE, the mean-square error MSE, the mean absolute error MAE, the root-mean-square error RMSE, and the coefficient of determination R2.
3. Case Study
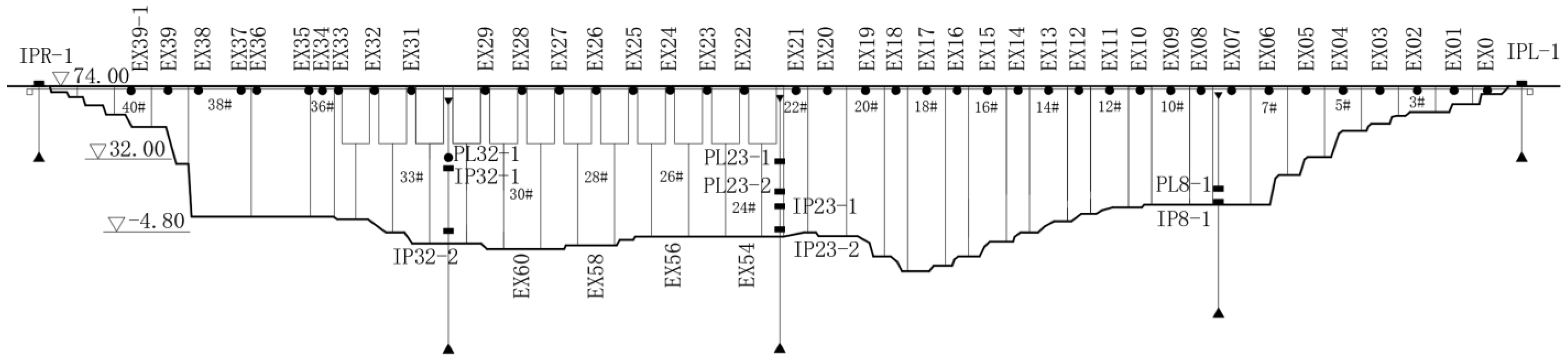
3.1. Project Overview
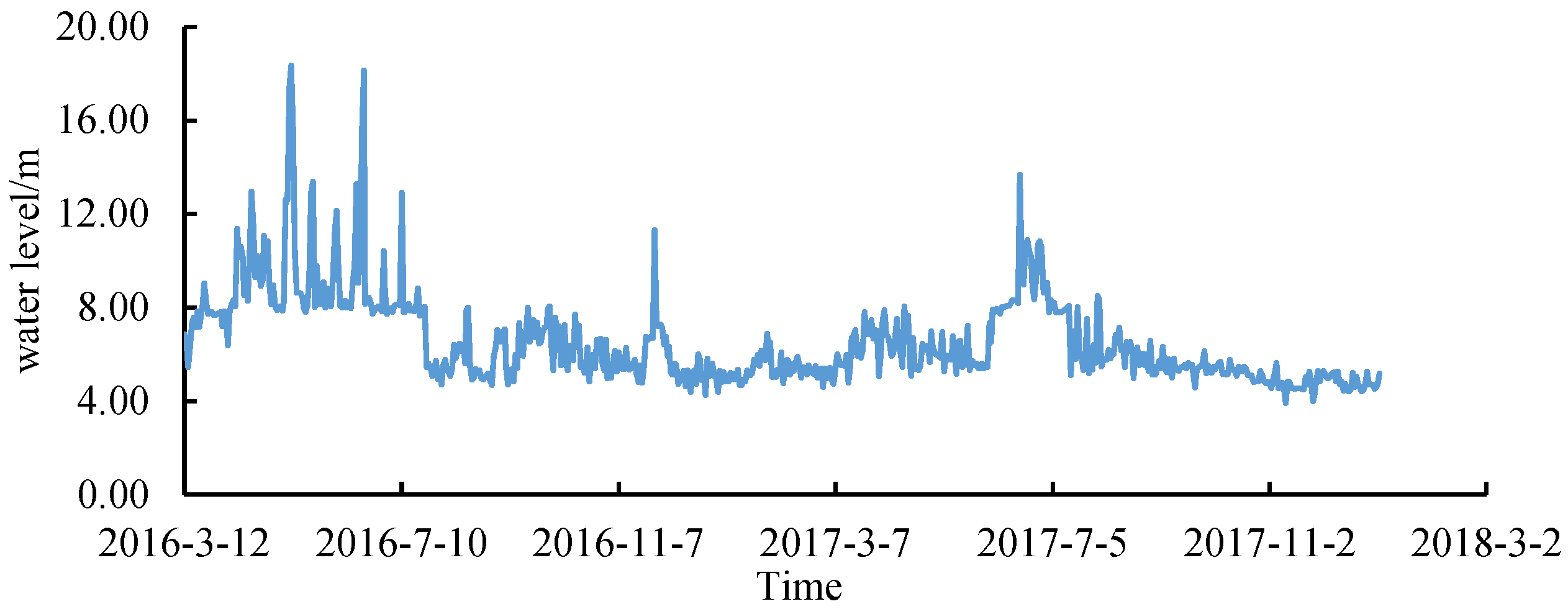
3.2. Performance Verification of IVM
3.3. Application of Deformation Prediction System of Concrete Dam Based on IVM-SCSO-RF
3.3.1. Correction of Measured Value by IVM
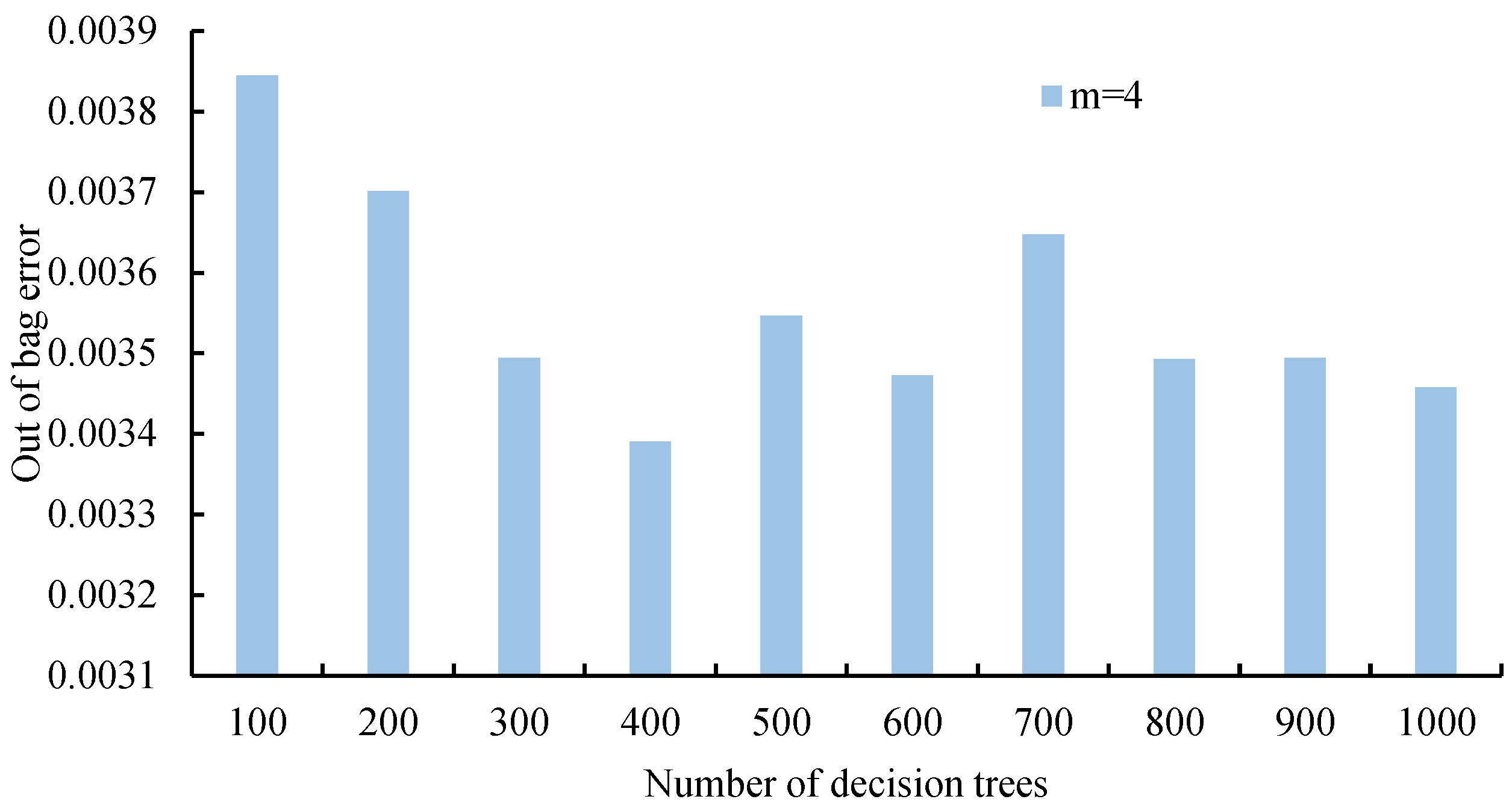
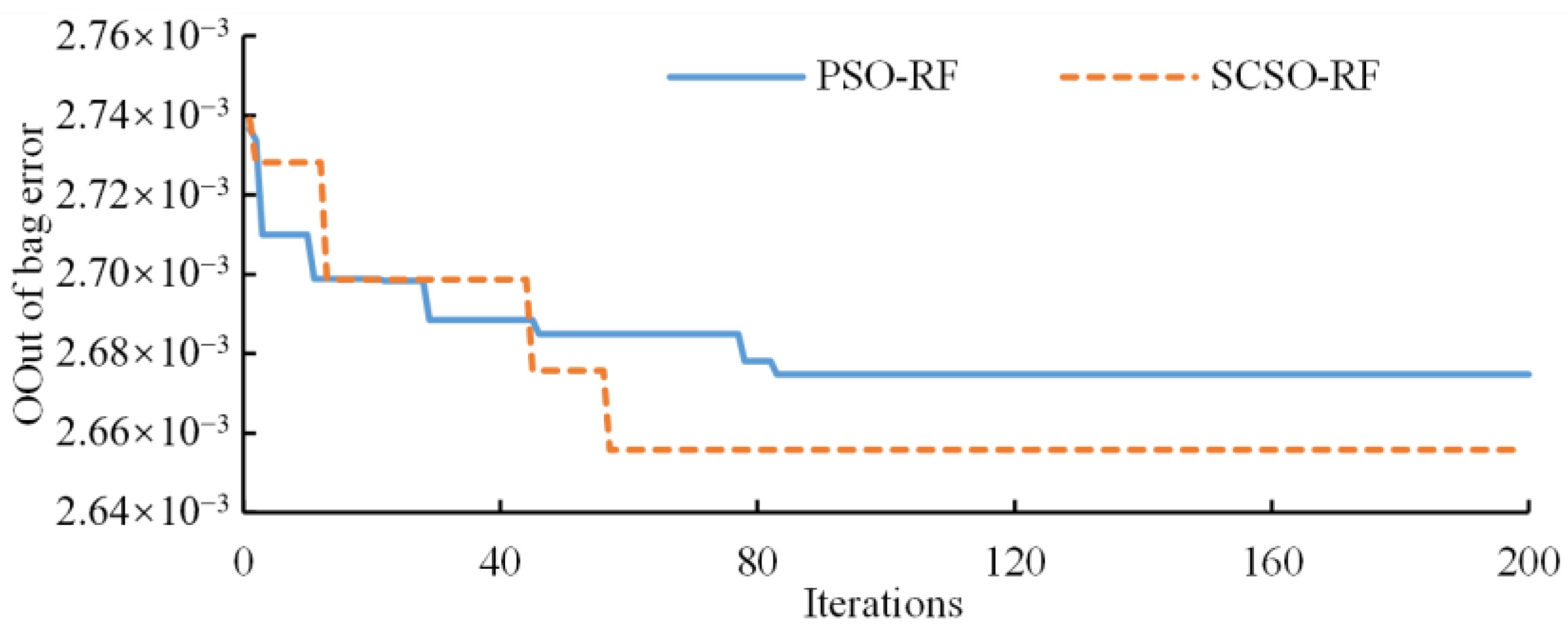
3.3.2. Parameter Optimization of RF Algorithm
- The trial-and-error method
- 2.
- Particle swarm optimization algorithm
- 3.
- Sand cat swarm optimization algorithm
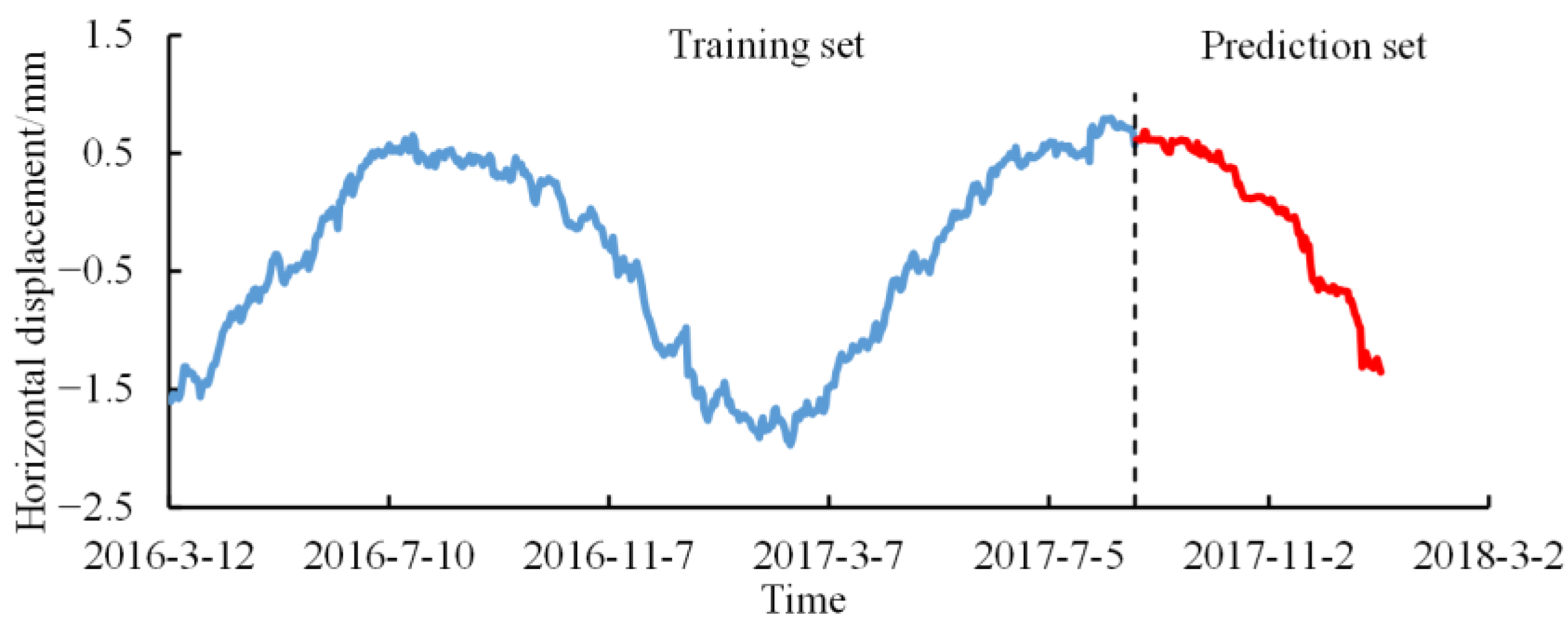
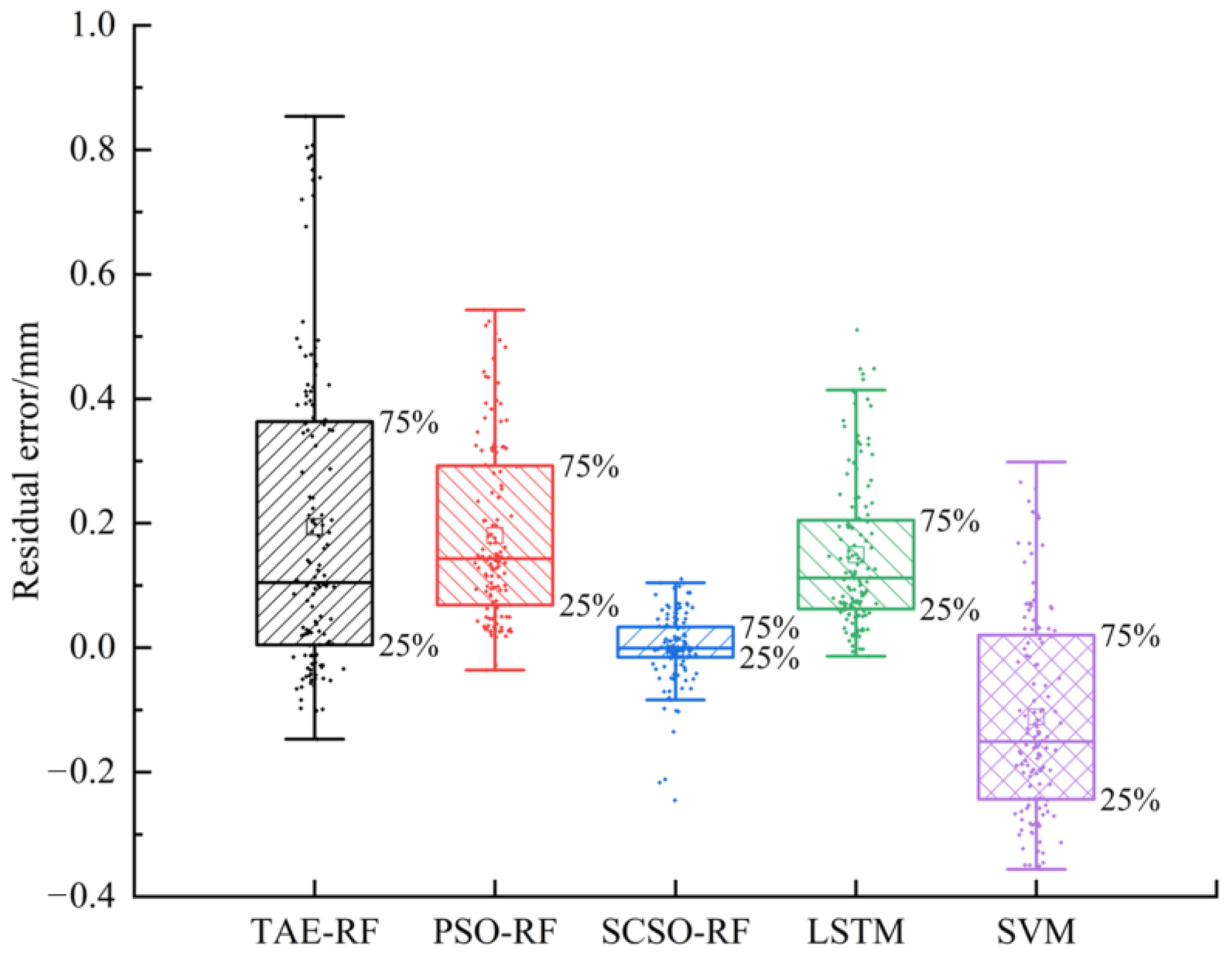
3.3.3. Training and Prediction of Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Georgakis, C.; Kabel, T.; Cao, E.; Wu, X.; Ma, J. Deformation Analysis of an Ultra-High Arch Dam under Different Water Level Conditions Based on Optimized Dynamic Panel Clustering. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K.; Bosshard, P.; Brewer, N. Exporting dams: China’s hydropower industry goes global. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, S294–S302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y.; Yu, S.; Liang, G. Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical analysis of valley narrowing deformation of high arch dam: A case study of the Xiluodu project in China. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, J. A technical review of hydro-project development in China. Engineering 2016, 2, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R. Key technologies in the design and construction of 300 m ultra-high arch dams. Engineering 2016, 2, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, C.; Su, H.; Wang, S. Advances in calculation models and monitoring methods for long-term deformation behavior of concrete dams. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2016, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chelidze, T.; Matcharashvili, T.; Mepharidze, E.; Mebonia, L.; Kalabegashvili, M.; Dovgal, N. Potential of Nonlinear Dynamics Tools in the Real-Time Monitoring of Large Dams: The Case of High Enguri Arc Dam. In Special Topics in Dam Engineering; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chongshi, G.; Huaizhi, S. Current status and prospects of long-term service and risk assessment of concrete dams. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2015, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Qu, X.; Hu, D.; Song, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, B. Research on singular value detection method of concrete dam deformation monitoring. Measurement 2021, 179, 109457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelidze, T.; Matcharashvili, T.; Abashidze, V.; Tsaguria, T.; Dovgal, N.; Zhukova, N. Complex dynamics of fault zone deformation under large dam at various time scales. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2019, 5, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Huang, Z.; Fang, C. A spatio-temporal clustering and diagnosis method for concrete arch dams using deformation monitoring data. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Shao, C.; Gu, C.; Xu, Y. An automatic data process line identification method for dam safety monitoring data outlier detection. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2022, 29, e2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Wu, B.; Yuan, J.; Li, S. LSTM-based deformation prediction model of concrete dams. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2022, 42, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Karimian, H.; Xiao, G.; Huang, J. A novel framework for prediction of dam deformation based on extreme learning machine and Lévy flight bat algorithm. J. Hydroinformatics 2021, 23, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.Y.; Loh, C.H. Monitoring of long-term static deformation data of Fei-Tsui arch dam using artificial neural network-based approaches. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2013, 20, 282–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Cao, E.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z. Cracking risk analysis of face slabs in concrete face rockfill dams during the operation period. Structures 2022, 40, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Wen, Z. Wavelet support vector machine-based prediction model of dam deformation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 110, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, H.; Fang, W.; Yu, T. LSTM-Based Deformation Prediction Model of the Embankment Dam of the Danjiangkou Hydropower Station. Water 2022, 14, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadiati, M.; Rajabi Yami, Z.; Eskandari, E.; Nakhaei, M.; Kisi, O. Application of artificial intelligence models for prediction of groundwater level fluctuations: Case study (Tehran-Karaj alluvial aquifer). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, S.; Vadiati, M.; Azizi, F.; Zamani, E.; Kisi, O. Groundwater Level Simulation Using Soft Computing Methods with Emphasis on Major Meteorological Components. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 3627–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baral, P.; Haq, M.A. Spatial prediction of permafrost occurrence in Sikkim Himalayas using logistic regression, random forests, support vector machines and neural networks. Geomorphology 2020, 371, 107331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, E.W.; Hill, R.A.; Leibowitz, S.G.; Olsen, A.R.; Thornbrugh, D.J.; Weber, M.H. Assessing the accuracy and stability of variable selection methods for random forest modeling in ecology. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, K.; Adeniyi, A.E.; DaSouza Jr, A.K.; Lim, D.; Nguyen, H.; Molina, N.R.; Xiong, L.; Weber, I.T.; Harrison, R.W. Machine learning methods accurately predict host specificity of coronaviruses based on spike sequences alone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Shen, W.; Wang, J.; Ali, A.; Li, M. Machine learning and geostatistical approaches for estimating aboveground biomass in Chinese subtropical forests. For. Ecosyst. 2020, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Gu, C.; Zhao, E.; Qin, X. Statistical model optimized random forest regression model for concrete dam deformation monitoring. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmokre, A.; Mihoubi, M.K.; Santillán, D. Analysis of dam behavior by statistical models: Application of the random forest approach. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 4800–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Weng, K.; Lin, C.; Zheng, Z. An improved random forest model for the prediction of dam displacement. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 9142–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Yang, M.; Gu, C.-S.; Huang, X.-f. A factor mining model with optimized random forest for concrete dam deformation monitoring. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinke, J.; Matcharashvili, T.; Chelidze, T.; Gogiashvili, J.; Nawroth, A.; Lursmanashvili, O.; Javakhishvili, Z. Influence of periodic variations in water level on regional seismic activity around a large reservoir: Field data and laboratory model. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2006, 156, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Matcharashvili, T.; Chelidze, T.; Zhukova, N.; Javakhishvili, Z. Investigating the dynamical features of the time distribution of the reservoir-induced seismicity in Enguri area (Georgia). Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelidze, T.; Matcharashvili, T.; Abashidze, V.; Dovgal, N.; Mepharidze, E.; Chelidze, L. Time Series Analysis of Fault Strain Accumulation around Large Dam: The Case of Enguri Dam, Greater Caucasus. In Building Knowledge for Geohazard Assessment and Management in the Caucasus and Other Orogenic Regions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Wu, Z.; Hong, Y. Adaptive model for dam automatic observation data analysis. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2001, 32, 34–36. Available online: https://mall.cnki.net/onlineread/Mall/MallIndex?sourceid=10&cover=1&fName=sjwj200106*1**1* (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Wu, Z. Safety Monitoring Theory and Its Application of Hydraulic Structures; Higher Education: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Seyyedabbasi, A.; Kiani, F. Sand Cat swarm optimization: A nature-inspired algorithm to solve global optimization problems. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, Z.; Su, H. An approach using random forest intelligent algorithm to construct a monitoring model for dam safety. Eng. Comput. 2021, 37, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, O.; Rokach, L. Ensemble learning: A survey. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyer, R.A.; Johnson, P.A. Nonlinear Mesoscopic Elasticity: The Complex Behaviour of Rocks, Soil, Concrete; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chelidze, T.; Matcharashvili, T.; Abashidze, V.; Kalabegishvili, M.; Zhukova, N. Real time monitoring for analysis of dam stability: Potential of nonlinear elasticity and nonlinear dynamics approaches. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2013, 7, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


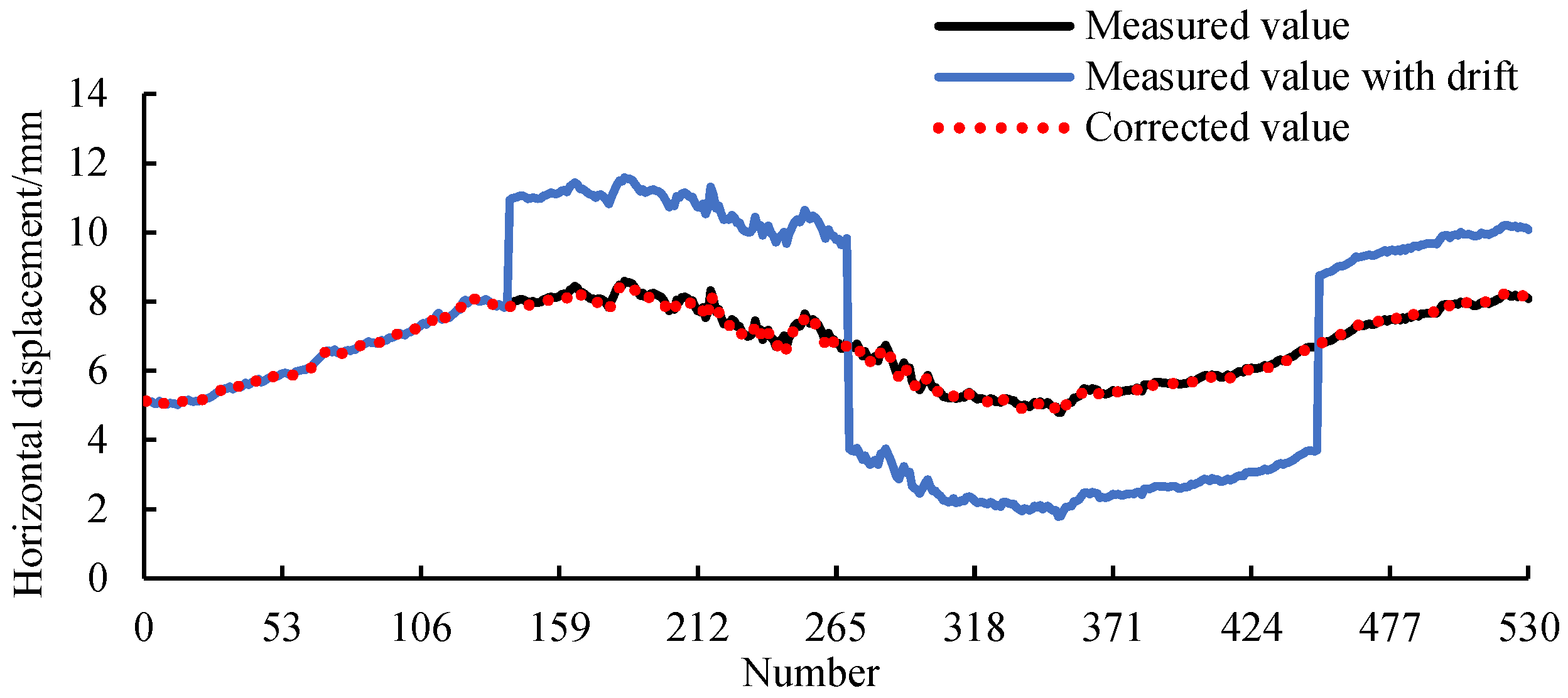

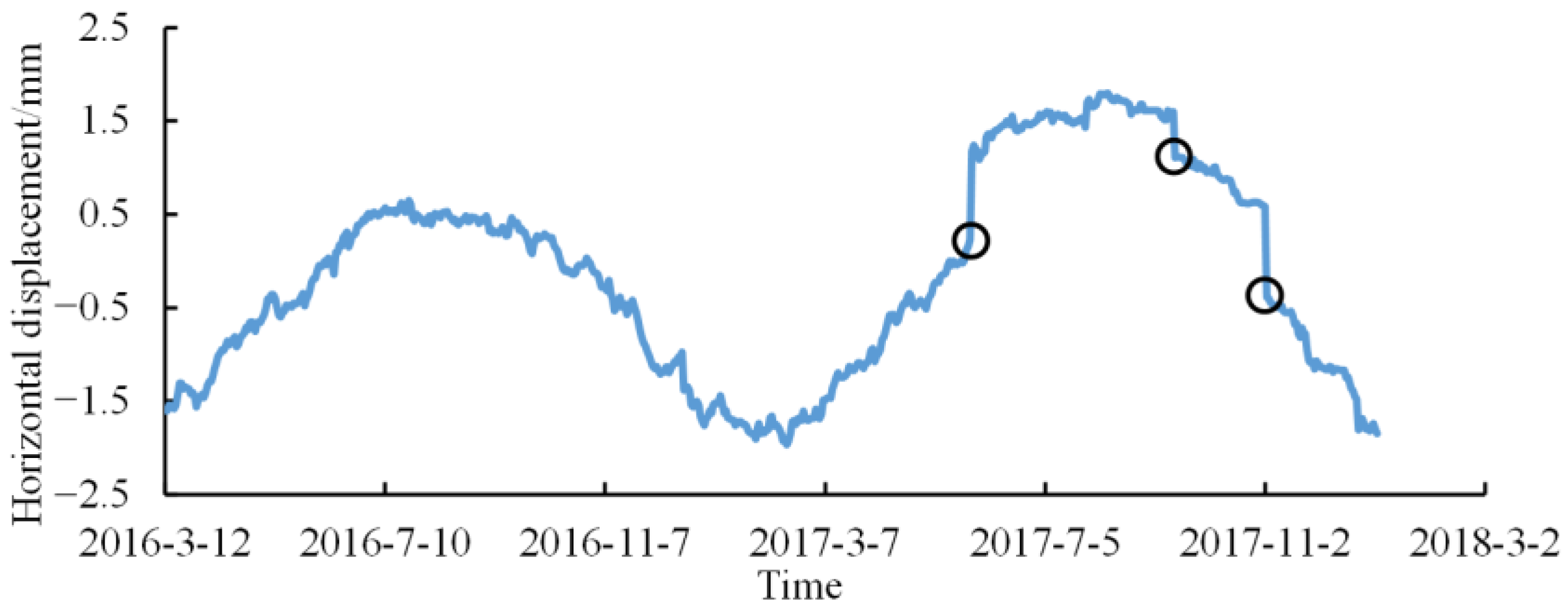

| Change Point | Actual Drift Value (mm) | Calculated Drift Value (mm) | Absolute Error (mm) | Error Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 140 | 3.00 | 3.078 | 0.078 | 2.6% |
| 270 | −6.00 | −6.037 | 0.037 | 0.6% |
| 450 | 5.00 | 4.926 | 0.074 | 1.5% |
| Evaluation Criterion | TAE-RF | PSO-RF | SCSO-RF | LSTM | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSE/mm2 | 0.742 | 0.552 | 1.209 | 3.728 | 2.136 |
| MSE/mm2 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.004 |
| MAE/mm | 0.027 | 0.024 | 0.036 | 0.066 | 0.046 |
| RMSE/mm | 0.037 | 0.032 | 0.048 | 0.084 | 0.064 |
| R2 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.990 | 0.994 |
| Evaluation Criterion | TAE-RF | PSO-RF | SCSO-RF | LSTM | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSE/mm2 | 12.810 | 6.851 | 0.418 | 4.857 | 5.016 |
| MSE/mm2 | 0.097 | 0.052 | 0.003 | 0.037 | 0.038 |
| MAE/mm | 0.217 | 0.181 | 0.036 | 0.150 | 0.170 |
| RMSE/mm | 0.312 | 0.228 | 0.056 | 0.192 | 0.195 |
| R2 | 0.731 | 0.856 | 0.991 | 0.898 | 0.895 |
| Time | Measured Value/mm | Predicted Value/mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAE-RF | PSO-RF | SCSO-RF | LSTM | SVM | ||
| 9 September 2017 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.48 |
| 6 October 2017 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.16 |
| 16 October 2017 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.18 | 0.39 | −0.01 |
| 20 November 2017 | −0.28 | 0.05 | −0.04 | −0.24 | −0.01 | −0.39 |
| 21 November 2017 | −0.32 | 0.03 | −0.08 | −0.26 | −0.02 | −0.38 |
| 25 November 2017 | −0.46 | −0.04 | −0.14 | −0.36 | −0.10 | −0.43 |
| 26 November 2017 | −0.57 | −0.09 | −0.21 | −0.46 | −0.12 | −0.41 |
| 27 November 2017 | −0.59 | −0.11 | −0.22 | −0.49 | −0.15 | −0.45 |
| 28 November 2017 | −0.58 | −0.13 | −0.26 | −0.54 | −0.18 | −0.51 |
| 29 November 2017 | −0.66 | −0.14 | −0.27 | −0.57 | −0.21 | −0.56 |
| 16 December 2017 | −0.75 | −0.33 | −0.35 | −0.69 | −0.66 | −0.89 |
| 23 December 2017 | −1.31 | −0.50 | −0.78 | −1.32 | −0.80 | −1.01 |
| Evaluation Criterion | TAE-RF | PSO-RF | SCSO-RF | LSTM | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSE/mm2 | 2.189 | 1.204 | 0.060 | 1.359 | 0.365 |
| MSE/mm2 | 0.182 | 0.100 | 0.005 | 0.113 | 0.030 |
| MAE/mm | 0.369 | 0.287 | 0.062 | 0.297 | 0.144 |
| RMSE/mm | 0.427 | 0.317 | 0.071 | 0.337 | 0.174 |
| R2 | 0.307 | 0.619 | 0.981 | 0.570 | 0.884 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zheng, D.; Liu, Y. Deformation Prediction System of Concrete Dam Based on IVM-SCSO-RF. Water 2022, 14, 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223739
Zhang S, Zheng D, Liu Y. Deformation Prediction System of Concrete Dam Based on IVM-SCSO-RF. Water. 2022; 14(22):3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223739
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shi, Dongjian Zheng, and Yongtao Liu. 2022. "Deformation Prediction System of Concrete Dam Based on IVM-SCSO-RF" Water 14, no. 22: 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223739
APA StyleZhang, S., Zheng, D., & Liu, Y. (2022). Deformation Prediction System of Concrete Dam Based on IVM-SCSO-RF. Water, 14(22), 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223739







