Geochemical Characterization of the River Waters in the Pumqu Catchments, Central Himalayas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
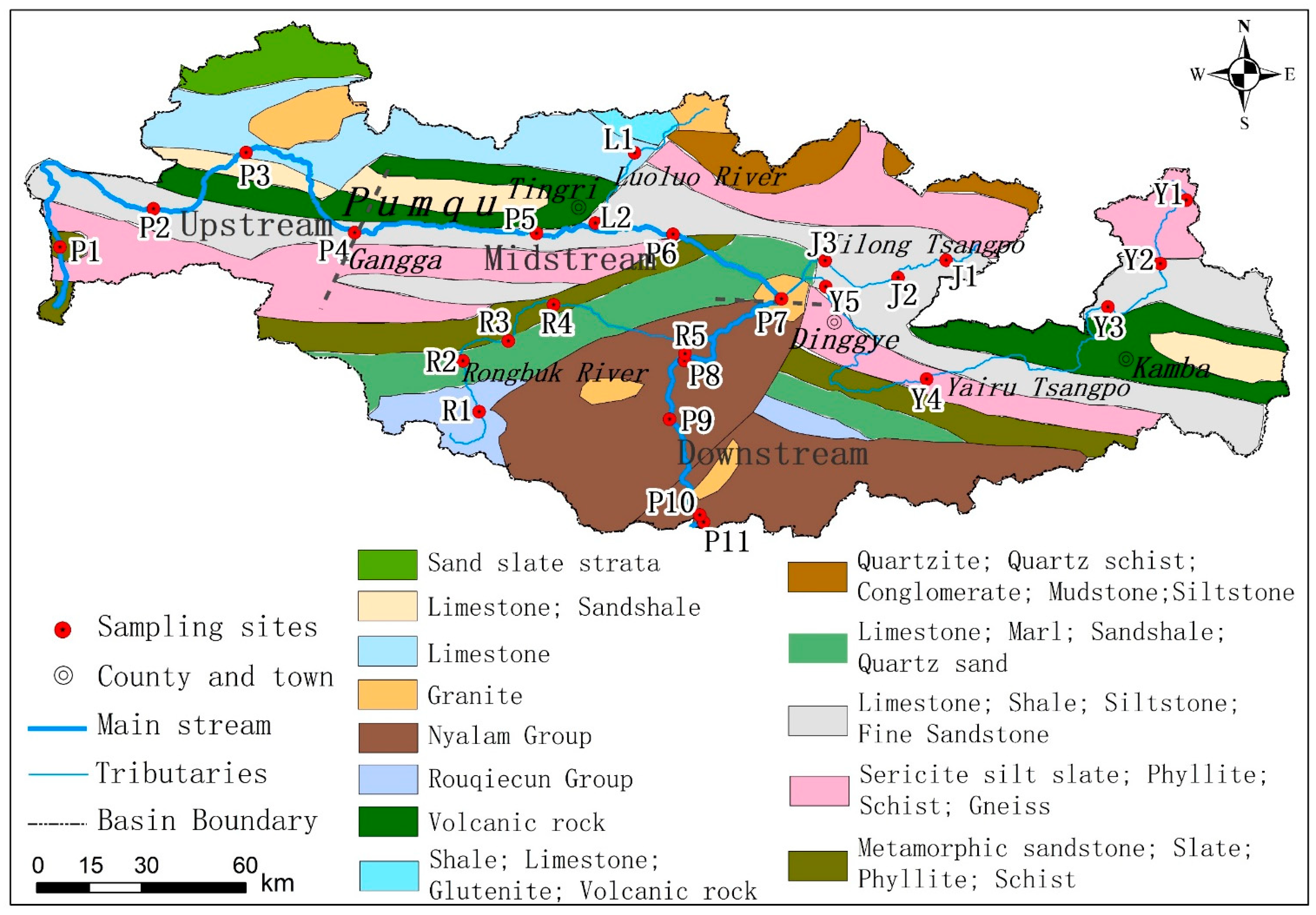
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Sample Analyses
2.3. Water Quality Index (WQI)
3. Results and Discussions
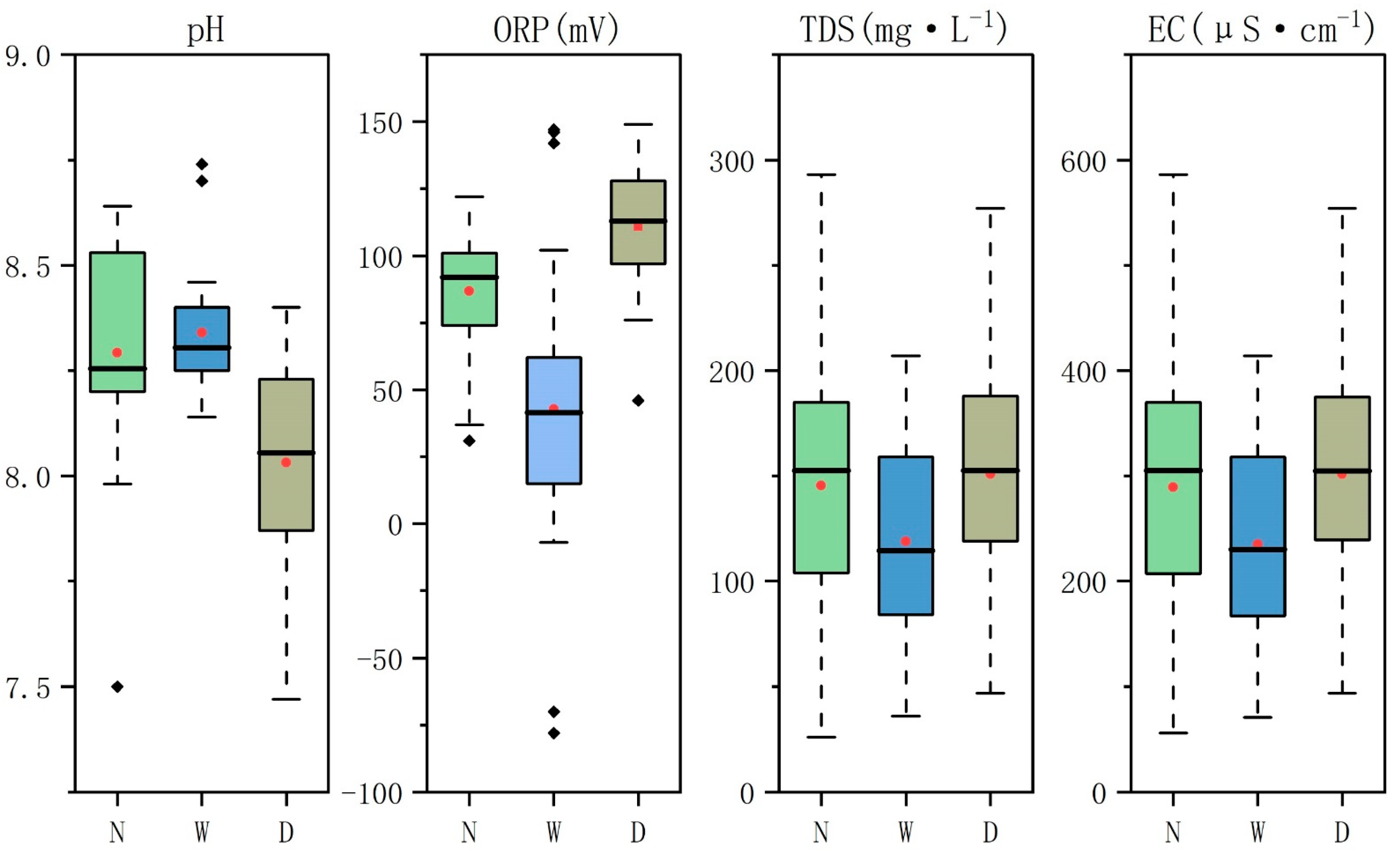
3.1. Status of In-Stream Physiochemical Parameters in the PC
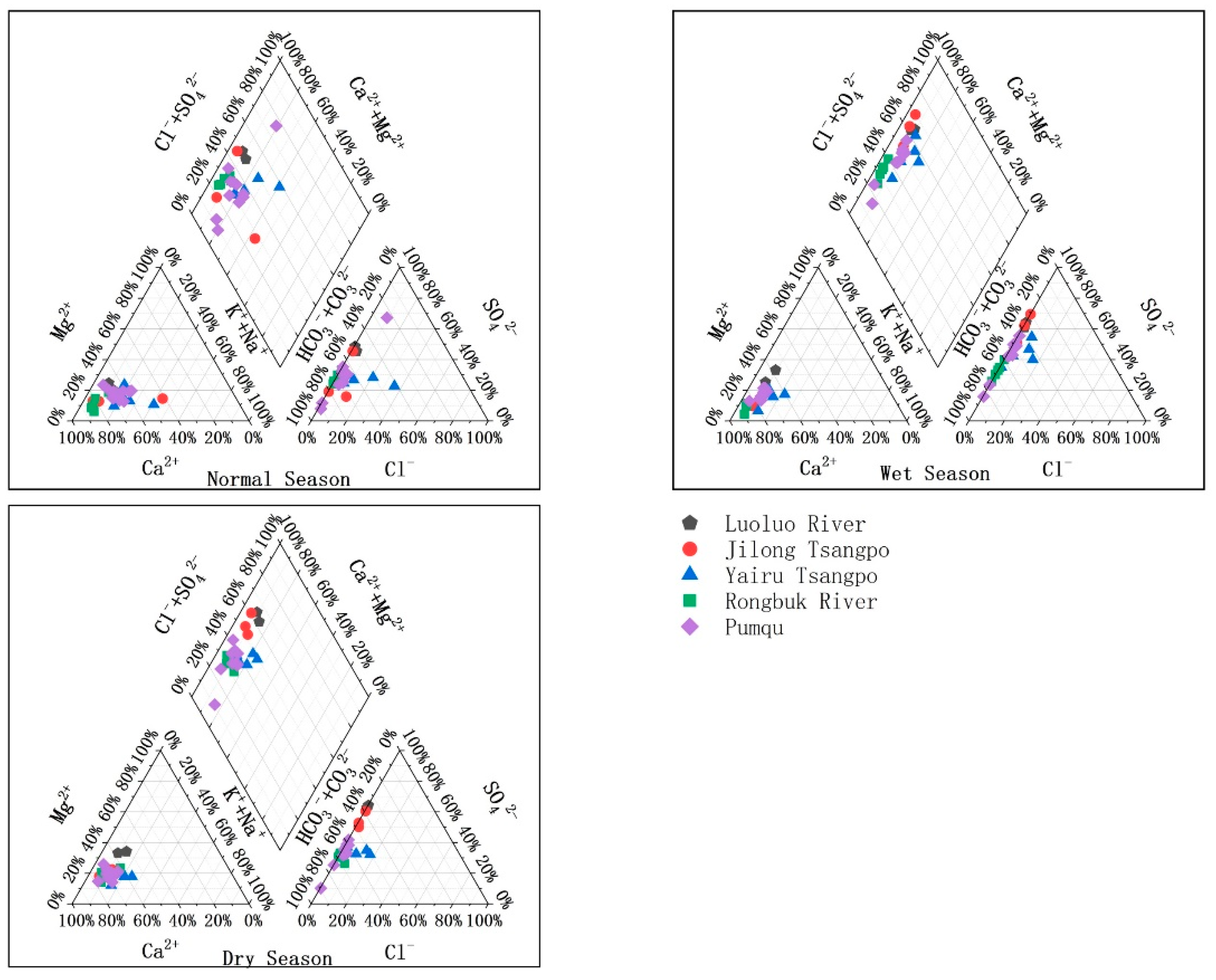
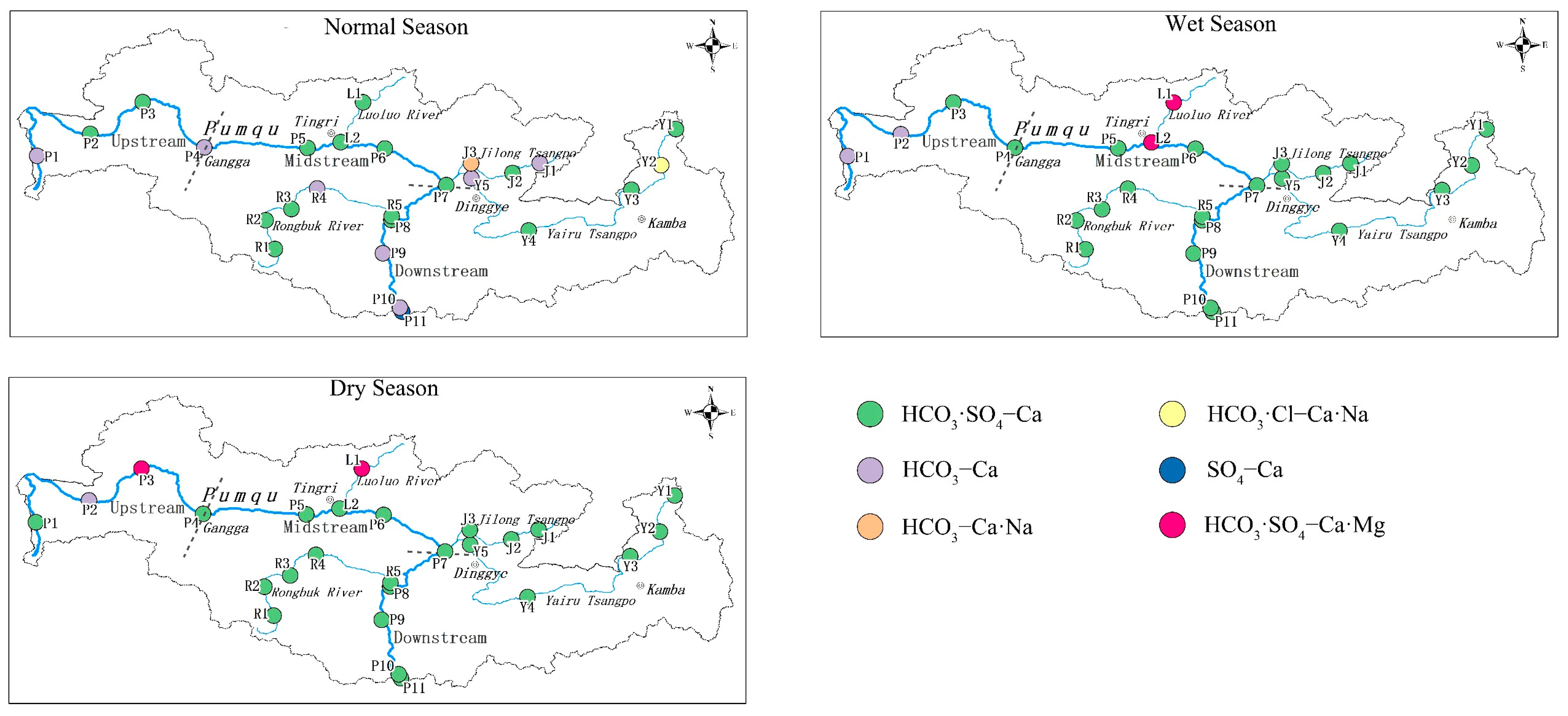
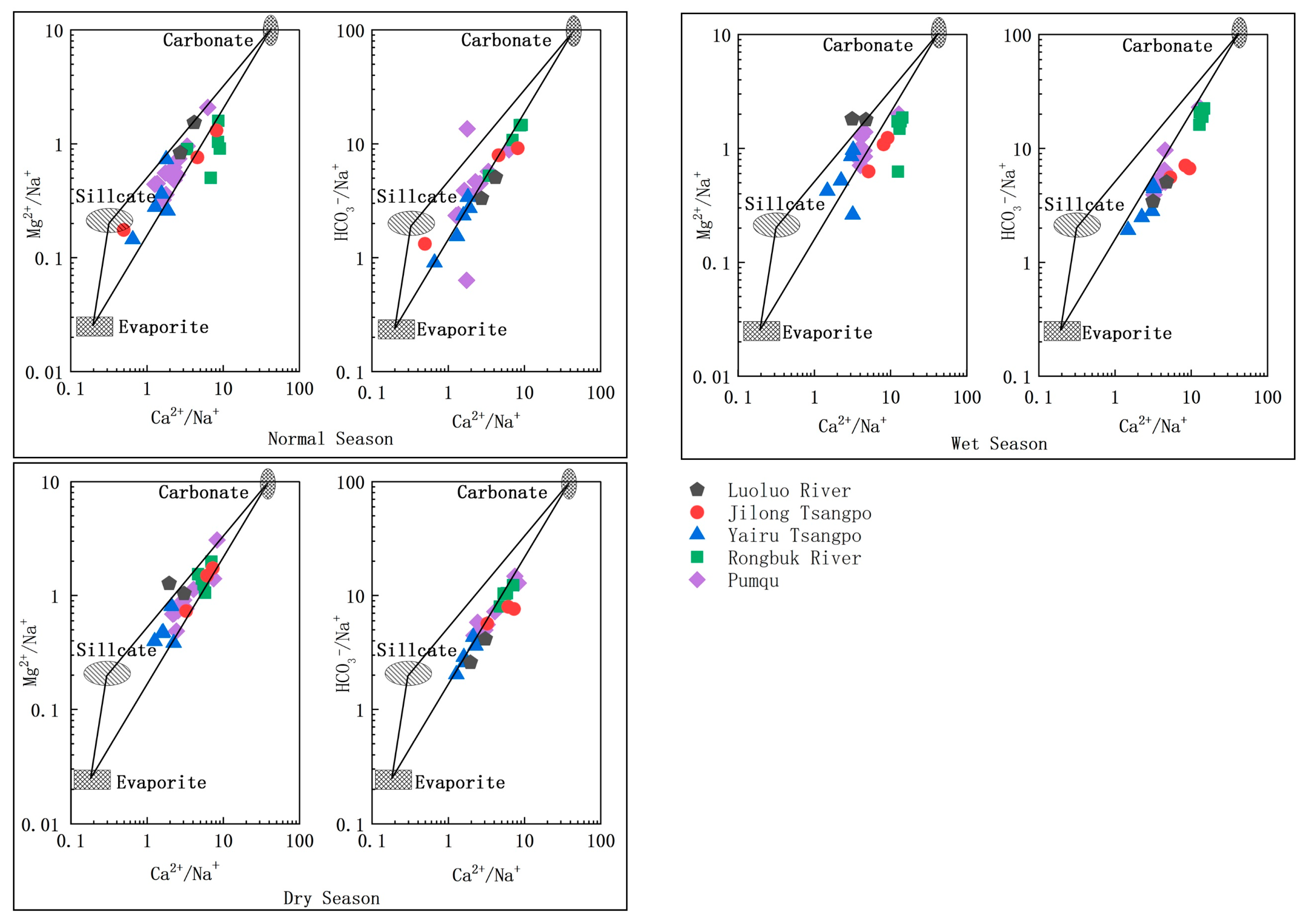
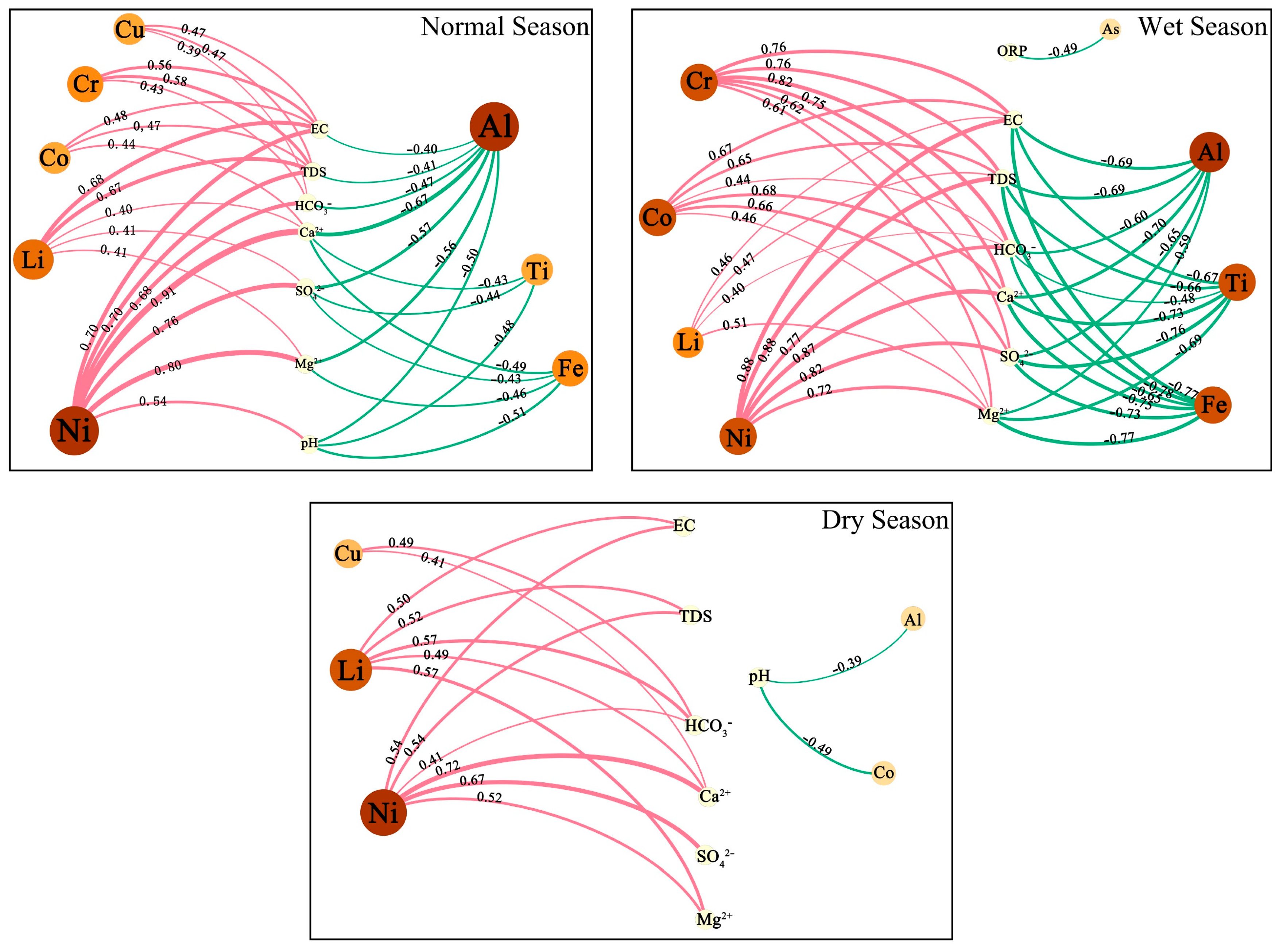
3.2. Hydrochemical Types and Their Controlling Factors in the PC
3.3. Contents of Trace Elements in the PC
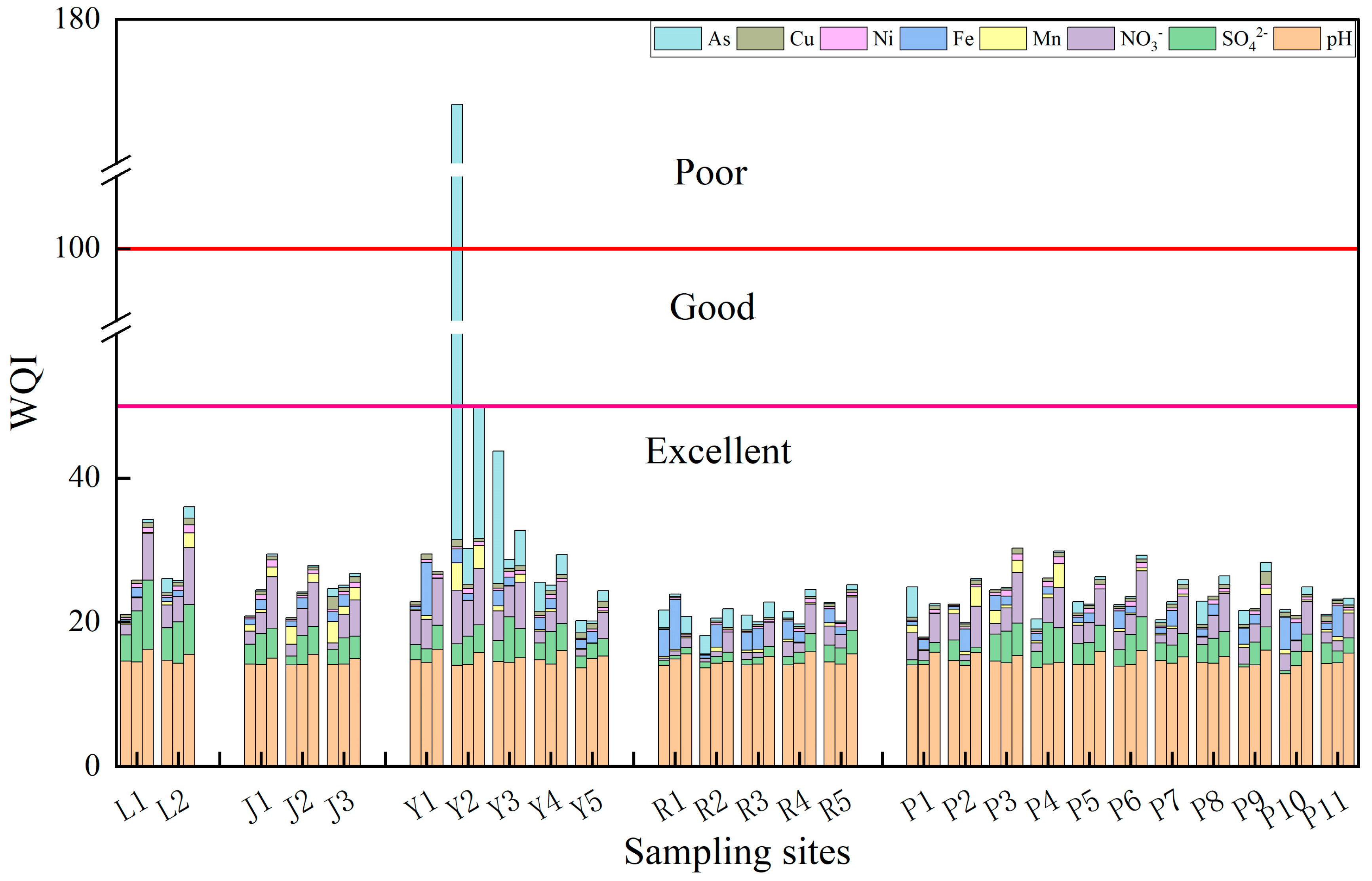
3.4. Evaluation of Water Quality of the PC by WQI
4. Conclusions and Prospect
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pant, R.R.; Zhang, F.; Rehman, F.U.; Wang, G.; Ye, M.; Zeng, C.; Tang, H. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xiao, J.; Evaristo, J.; Li, Z. Spatiotemporal variations in the hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of streamflow and groundwater in the Wei River of China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulikidis, N.T.; Amaxidis, Y.; Bertahas, I.; Laschou, S.; Gritzalis, K. Analysis of factors driving stream water composition and synthesis of management tools—A case study on small/medium Greek catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 362, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M.; Duo, B.; Gjessing, E.T. Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Metal contents of four selected rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M.; Gjessing, E.T.; Peräniemi, S.; Vogt, R.D. Environmental impact of mining activities on the surface water quality in Tibet: Gyama valley. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4177–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M.; Gjessing, E.; Peräniemi, S.; Vogt, R. Water quality in the southern Tibetan Plateau: Chemical evaluation of the Yarlung Tsangpo (Brahmaputra). River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Sillanpää, M. Water chemistry of the southern Tibetan Plateau: An assessment of the Yarlung Tsangpo river basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Major element chemistry of the Changjiang (Yangtze River). Chem. Geol. 2002, 187, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Riverine quality at the Anthropocene: Propositions for global space and time analysis, illustrated by the Seine River. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwar, R.T.; Utsev, J.T.; Hassan, M. Assessment of heavy metal and physico-chemical pollution loadings of River Benue water at Makurdi using water quality index (WQI) and multivariate statistics. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanidhi, D.; Aravinthasamy, P.; Subramani, T.; Muthusankar, G. Revealing drinking water quality issues and possible health risks based on water quality index (WQI) method in the Shanmuganadhi River basin of South India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 931–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, A.; Tiwari, S.K.; Pandey, H.K.; Chaurasia, A.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, Y.V. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index (WQI) under GIS framework. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, T.; Chai, C.; Cuo, L.; Su, F.; Zhang, F.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; et al. TP-River: Monitoring and Quantifying Total River Runoff from the Third Pole. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, E948–E965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Li, H.; Pan, X.; Ren, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W. Assessing glacier retreat and its impact on water resources in a headwater of Yangtze River based on CMIP6 projections. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzeng, l.; Luo, Z.; Ye, X.; Deqing, Q.; Huang, X. Hydrochemical Characteristics and environmental significance of hot spring waters in the Nyangchu River Basin, Tibet. J. Hydroecology 2022, 43, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Xiao, L.; Liou, Y.-A. Changes in glaciers and glacial lakes and the identification of dangerous glacial lakes in the Pumqu River Basin, Xizang (Tibet). Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 903709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Yan, J.; Cheng, X. Household perspective on cropland expansion on the Tibetan Plateau. Reg. Environ. Change 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ren, J.; Qin, D. Chemical characteristics at the head of Rongbuk River on Mt. Everest. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2000, 21, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Yao, X.; Yang, D.; Sun, M.; Qi, M.; Gong, P.; Li, X.; Gao, Y. Major ions and their controlling factors of surface water in the northern slope region in the middle Himalayas: A case study of Yairuzangbo Basin. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q. Basin-Scale Pollution Loads Analyzed Based on Coupled Empirical Models and Numerical Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CAS (Chinese Academy of Sciences). Report of a Scientific Expedition to the Everest Region: 1966–1968. Physical Geography; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- CAS (Chinese Academy of Sciences). Report of a Scientific Expedition to the Everest Region: 1966–1968. Modern Glaciers and Landforms; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- CAS (Chinese Academy of Sciences). Photo Collection of Scientific Expeditions in the Everest Region. 1966–1968. Geology; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Z.; You, M.; Zhu, M.; Guo, G.; Liu, S. Geothermal in Tibet; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Liao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; You, M.; Zhang, M. Thermal Spring in Tibet; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- CAS (Chinese Academy of Sciences). Tibet Water Conservancy; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Song, F.; Li, Z.; Yu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, D. A Value Assessment of Freshwater Ecosystem Services in the Pumqu River Basin, Tibet. J. Southwest Univ. 2018, 40, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Cheng, X.; He, X. Wetland Changes and Their Relation to Climate Change in the Pumqu Basin, Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L. Geological Atlas of China; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, K.; Xiao, J.; Li, S.; Li, Z. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and their controlling factors in the Fen River of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Kangabam, R.; Bhoominathan, S.D.; Kanagaraj, S.; Govindaraju, M. Development of a water quality index (WQI) for the Loktak Lake in India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şener, Ş.; Şener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, V.; Reddy, B.M. Geochemical characterization, deciphering groundwater quality using pollution index of groundwater (PIG), water quality index (WQI) and geographical information system (GIS) in hard rock aquifer, South India. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPEA & AQSIQ State Environmental Protection Administration of P.R. China & General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of P.R. China. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; China Academy of Environmental Science: Beijing, China, 2002; Volume GB 3838-2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yidana, S.M.; Yidana, A. Assessing water quality using water quality index and multivariate analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H. Hydrochemistry and Its Controlling Factors of Rivers in the Source Region of the Nujiang River on the Tibetan Plateau. Water 2019, 11, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Kuang, X.; Feng, Y.; Hao, Y.; He, Q.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, C. Hydrochemistry of the Lhasa River, Tibetan Plateau: Spatiotemporal Variations of Major Ions Compositions and Controlling Factors Using Multivariate Statistical Approaches. Water 2021, 13, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minch, M.J. An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding (Jeffrey, George A.); ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mazhar, S.N.; Ahmad, S. Assessment of water quality pollution indices and distribution of heavy metals in drinking water in Ramganga aquifer, Bareilly District Uttar Pradesh, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Lake and river ecosystems. In Limnology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M.; Gjessing, E.T.; Vogt, R.D. Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in the headwaters of four major Asian rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, B.Y.C.S.S.S.; Itoi, R.; Taguchi, S.; Saibi, H.; Yamashiro, R. Hydrogeochemical and isotope characterization of geothermal waters from the Cidanau geothermal field, West Java, Indonesia. Geothermics 2019, 78, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzeng, L.; Luo, Z.; Chen, H.; Huang, X. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Nyangchu River Basin in Tibet. Earth Environ. 2021, 49, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.; He, S.; Wen, H.; Liu, M.; Yu, S. Fate and origin of major ions in river water in the Lhasa River basin, Tibet. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yu, C.; Zha, X.; Gao, X.; Dai, E. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of natural water in the border areas of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1876–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Han, T.; Sillanpää, M.; Jing, Z.; You, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, C.; Yu, C.; Li, G. Seasonal and interannual changes of river chemistry in the source region of Yellow River, Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 119, 104638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hou, Z.; An, Z.; Liu, X.; Dong, J. Major ion chemistry of waters in Lake Qinghai catchments, NE Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Quat. Int. 2010, 212, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, C.; Thyne, G.D. Hydrologic and geologic factors controlling surface and groundwater chemistry in Indian Wells-Owens Valley area, southeastern California, USA. J. Hydrol. 2004, 285, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, R.R.; Qaiser, F.U.R.; Wang, G.; Adhikari, S.; Bishwakarma, K.; Baral, U.; Rimal, B.; Bhatta, Y.R.; Rijal, K. Hydrochemical appraisal and solute acquisitions in Seti River Basin, Central Himalaya, Nepal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, M.; Krishnaswami, S. Major ion chemistry of the Ganga–Brahmaputra river systems, India. Nature 1984, 312, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Khanna, P.; Chakrapani, G.J.; Balakrishnan, S. Geochemical characteristics of water and sediment of the Indus river, Trans-Himalaya, India: Constraints on weathering and erosion. J. Asian Earth Sci. 1998, 16, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-S.; Lee, K.-S.; Chang, H.-W.; Shin, H.S. Chemical weathering of carbonates and silicates in the Han River basin, South Korea. Chem. Geol. 2008, 247, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, S.; Jiang, P.-P.; Sun, P.-A. Water Chemical Characteristics and Influence of Exogenous Acids in the Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4687–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; He, J. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Possible Controls of the Surface Water in Ranwu Lake Basin. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4003–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, N.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Dürr, H.H.; Kempe, S.; Loos, S.; Middelkoop, H. Dissolved silica mobilization in the conterminous USA. Chem. Geol. 2010, 270, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Major ion chemistry of water and its controlling factors in the Yamzhog Yumco Basin, South Tibet. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pekey, H.; Karakaş, D.; Bakoglu, M. Source apportionment of trace metals in surface waters of a polluted stream using multivariate statistical analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5084-2021; Standard for Irrigation Water Quality. SEPA & SAMR State Environmental Protection Administration of P.R. China & State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB 5749-2006; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. MOH & SAC Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China & China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y. Impact of geothermal wastewater drainage on arsenic species in environmental media: A case study at the Yangbajing geothermal field, Tibet, China. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 7, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, X.; Xia, X.; Teng, Y. Identification of hydrochemical genesis and screening of typical groundwater pollutants impacting human health: A case study in Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, C.; Long, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wu, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, W.; Hu, X. Interaction analysis of hydrochemical factors and dissolved heavy metals in the karst Caohai Wetland based on PHREEQC, cooccurrence network and redundancy analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.T.; Laluraj, C.M.; Sharma, P.; Patel, L.K.; Thamban, M. Export fluxes of geochemical solutes in the meltwater stream of Sutri Dhaka Glacier, Chandra basin, Western Himalaya. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, R.T.; Gunduz, O. The impacts of geothermal fluid discharge on surface water quality with emphasis on arsenic. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Long, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wu, P. Influence of different land use types on hydrochemistry and heavy metals in surface water in the lakeshore zone of the Caohai wetland, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiller, A.M. Dissolved trace elements in the Mississippi River: Seasonal, interannual, and decadal variability. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 4321–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Planer-Friedrich, B.; Liu, M.; Yan, K.; Wu, G. Magmatic fluid input explaining the geochemical anomaly of very high arsenic in some southern Tibetan geothermal waters. Chem. Geol. 2019, 513, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Paraments | pH | SO42− | NO3− | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | — | mg·L−1 | mg·L−1 | μg·L−1 | μg·L−1 | μg·L−1 | μg·L−1 | μg·L−1 |
| Limit value [36] | 6~9 | 250 | 10 | 100 | 300 | 20 | 10 | 50 |
| wi | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| Wi for normal and wet season | 0.1538 | 0.1154 | 0.1823 | 0.1154 | 0.1154 | 0.0385 | 0.0769 | 0.1823 |
| Wi for dry season | 0.1793 | 0.1304 | 0.2174 | 0.1304 | — | 0.0435 | 0.0870 | 0.2174 |
| Season | Al | As | Co | Cr | Cu | Fe | Li | Mn | Mo | Ni | Ti | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main stream | ||||||||||||
| Pumqu | normal | 24.10 | 1.00 | 0.09 | 6.80 | 0.56 | 25.00 | 58.20 | 3.66 | 0.62 | 1.15 | 1.45 |
| wet | 37.20 | 0.41 | 0.19 | 18.30 | 0.58 | 36.00 | 23.80 | 1.91 | 0.73 | 2.59 | 1.68 | |
| dry | 12.00 | 1.23 | 0.38 | 9.45 | 0.68 | DL | 79.00 | 2.72 | 0.77 | 2.43 | 0.86 | |
| Tributary | ||||||||||||
| Luoluo River | normal | 10.35 | 2.69 | 0.14 | 8.00 | 0.46 | 15.00 | 63.70 | 2.90 | 1.31 | 1.39 | 0.59 |
| wet | 15.35 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 18.85 | 0.66 | 27.00 | 18.24 | 0.51 | 1.28 | 3.17 | 0.75 | |
| dry | 5.45 | 2.41 | 0.44 | 8.59 | 0.90 | DL | 85.50 | 8.47 | 1.18 | 4.16 | 0.20 | |
| Jilong Tsangpo | normal | 3.68 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 8.50 | 0.33 | 21.00 | 2.87 | 21.40 | 0.53 | 1.24 | 0.20 |
| wet | 31.30 | 0.56 | 0.23 | 11.20 | 0.66 | 37.00 | 0.62 | 3.62 | 0.54 | 2.33 | 1.20 | |
| dry | 13.00 | 0.67 | 0.35 | 9.22 | 0.61 | DL | 3.10 | 10.00 | 0.40 | 3.52 | 0.20 | |
| Yairu Tsangpo | normal | 34.10 | 10.37 | 0.14 | 8.32 | 0.83 | 43.00 | 313.00 | 1.95 | 0.45 | 1.39 | 1.70 |
| wet | 30.00 | 1.74 | 0.24 | 20.70 | 0.79 | 36.00 | 250.00 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 3.13 | 1.56 | |
| dry | 12.00 | 6.45 | 0.21 | 6.77 | 0.63 | DL | 350.00 | 1.80 | 0.32 | 2.26 | 0.47 | |
| Rongbuk River | normal | 83.60 | 5.43 | 0.15 | 5.86 | 0.29 | 63.00 | 12.40 | 2.82 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 4.83 |
| wet | 104.00 | 0.97 | 0.13 | 14.40 | 0.26 | 76.00 | 10.50 | 2.12 | 0.62 | 1.69 | 7.04 | |
| dry | 14.00 | 5.08 | 0.37 | 7.82 | 0.33 | DL | 17.00 | 1.32 | 0.77 | 1.43 | 0.90 | |
| SEPA and AQSIQ [36] | - | 50 | - | 10 # | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MOH and SAC [62] | - | 10 | - | 50 # | 1000 | 300 | 200 | 100 | 70 | 20 | - | |
| SEPA and SAMR [61] | - | 100 | - | 100 # | 1000 | - | - | - | - | 200 | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Renzeng, L.; Huang, X. Geochemical Characterization of the River Waters in the Pumqu Catchments, Central Himalayas. Water 2022, 14, 3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223652
Yang Y, Chen H, Renzeng L, Huang X. Geochemical Characterization of the River Waters in the Pumqu Catchments, Central Himalayas. Water. 2022; 14(22):3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223652
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Hulin Chen, Lamu Renzeng, and Xiang Huang. 2022. "Geochemical Characterization of the River Waters in the Pumqu Catchments, Central Himalayas" Water 14, no. 22: 3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223652






