A Joint Impact on Water Vapor Transport over South China during the Pre-Rainy Season by ENSO and PDO
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
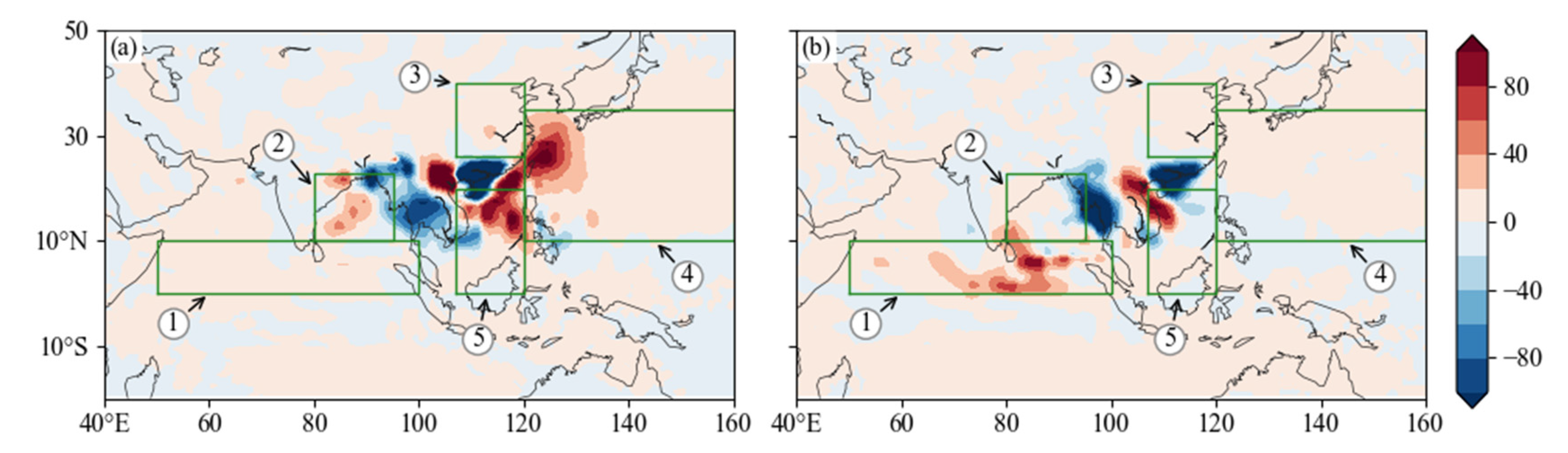
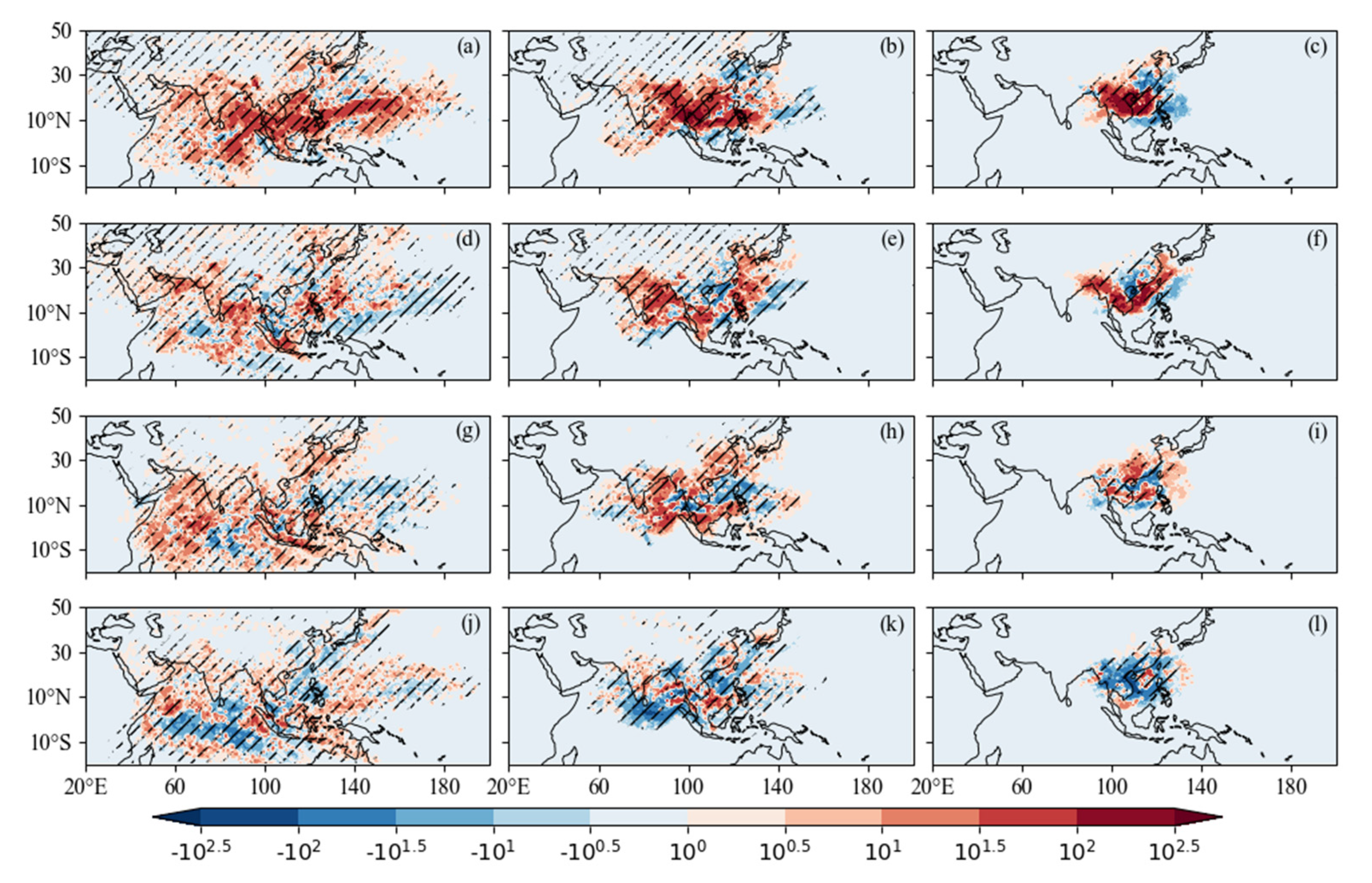
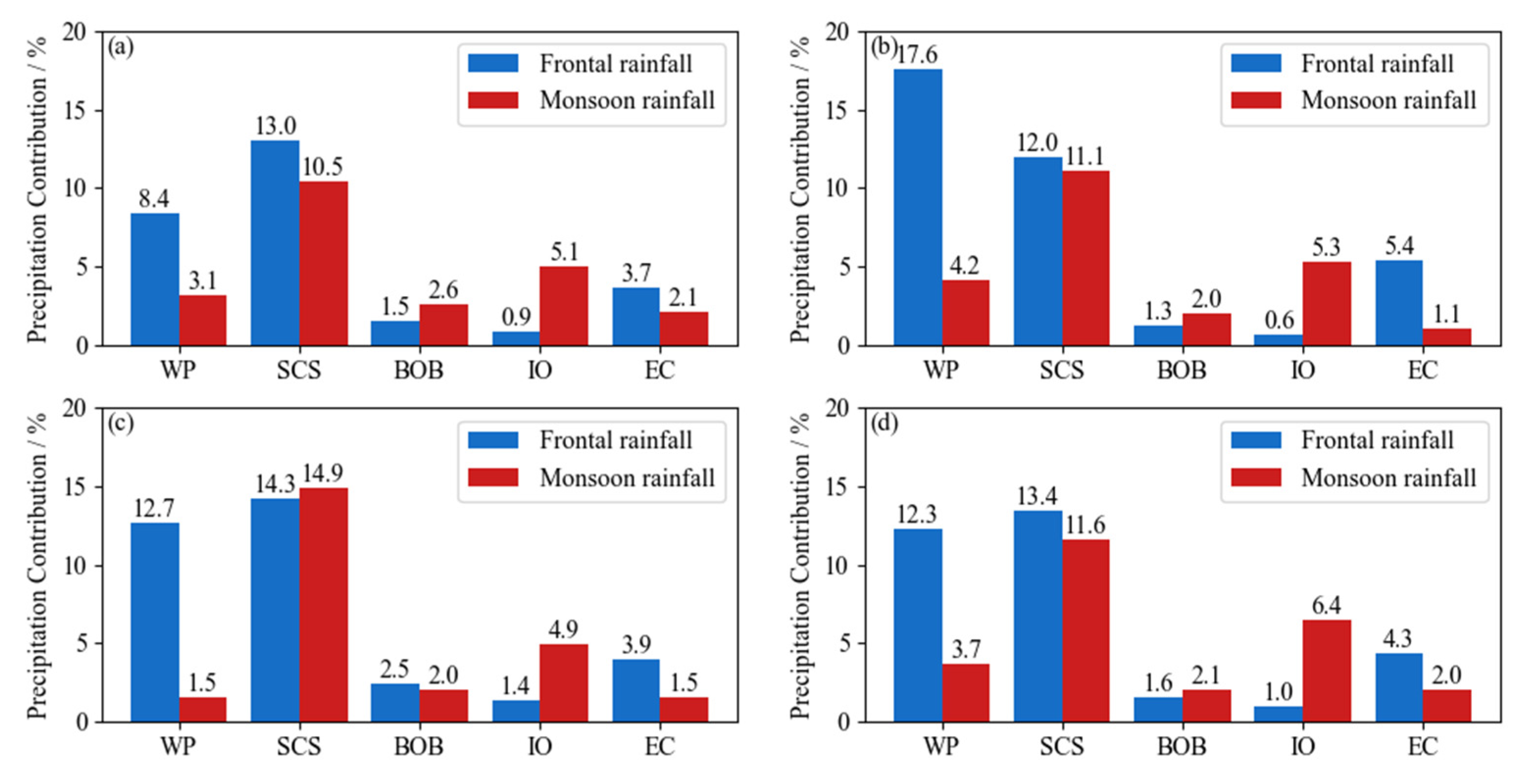
2.3. Division of Frontal Precipitation and Monsoon Precipitation in the Pre-Rainy Season over SC
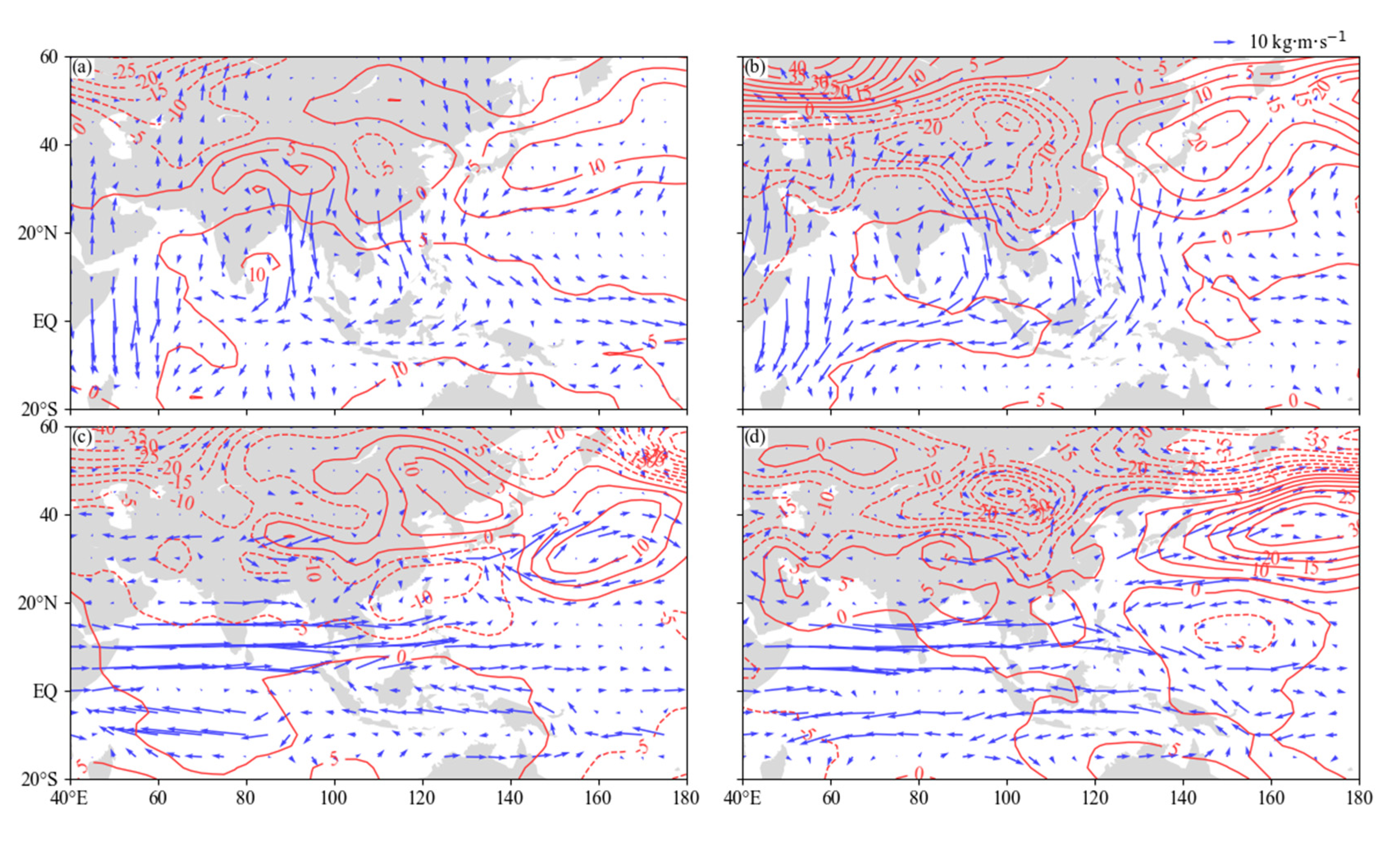
3. Results
3.1. ENSO Events in the Context of PDO
3.2. Impact of ENSO on the Water Vapor Transport Process of Precipitation in PFS over SC with PDO Context
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution of Water Vapor
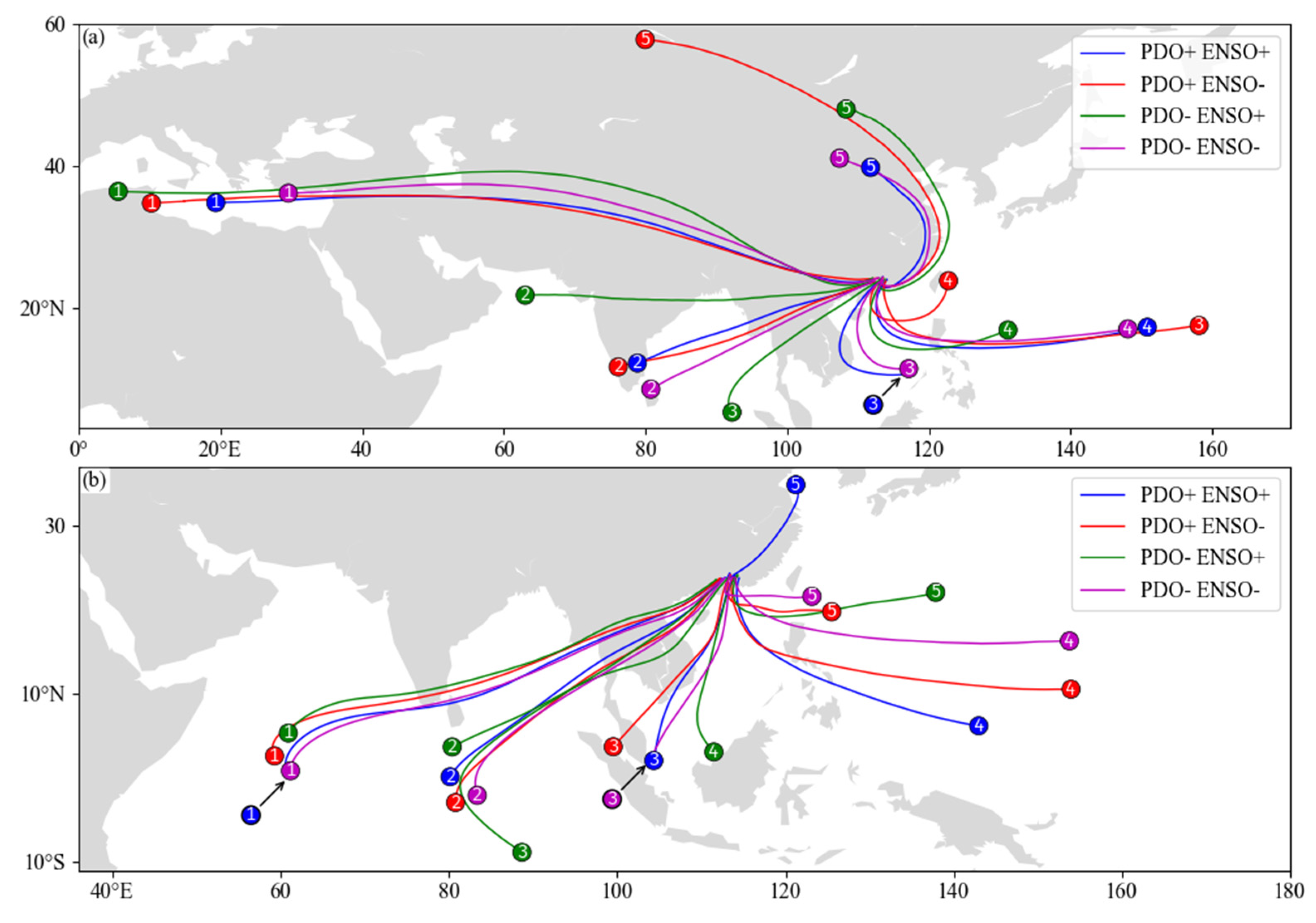
3.2.2. Water Vapor Transport Trajectory
3.2.3. Water Vapor Contribution of PFS Precipitation Sources over SC
3.2.4. Circulation Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Ent, R.J.; Wang-Erlandsson, L.; Keys, P.W.; Savenije, H.H.G. Contrasting roles of interception and transpiration in the hydrological cycle—Part 2: Moisture recycling. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2014, 5, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gimeno, L.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Stohl, A. On the origin of continental precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.M.; Eskridge, R.E. Atmospheric water vapor over china. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Huang, R.H. Characteristics of the interdecadal variations of heavy rain over china in the last 40 years. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 30, 1057. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, M. The statistical analysis of the persistent heavy rain in the last 50 years over China and their backgrounds on the large scale circulation. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 31, 779–792. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, C.Y.; Song, J. Comparison of the annual cycles of moisture supply over southwest and southeast China. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 10139–10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.M.; Ding, Y.H.; Guo, P.W.; Shen, H.F.; Fan, G.F. Linkage of the water vapor transport distribution with the rainy season and its precipitation in the southern regions south of the Yangtze River during the early summer. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2015, 73, 72–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.J.; Yu, R.C. Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in china. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newell, R.E.; Newell, N.E.; Zhu, Y.; Scott, C. Tropospheric rivers?—A pilot study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 2401–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wernli, B.H.; Davies, H.C. A lagrangian-based analysis of extratropical cyclones. I: The method and some applications. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 123, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle. Part I: Method description, validation, and demonstration for the August 2002 flooding in central Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle. Part II: Moisture Transports between Earth’s Ocean Basins and River Catchments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Forster, C.; Sodemann, H. Remote sources of water vapor forming precipitation on the Norwegian west coast at 600N—A tale of hurricanes and an atmospheric river. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D05102. [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno, L.; Stohl, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Dominguez, F.; Yoshimura, K.; Yu, L.; Drumond, A.; Durán-Quesada, A.M.; Nieto, R. Oceanic and terrestrial sources of continental precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Wang, H.J. Moisture sources of semi-arid grassland in China using the Lagrangian Particle Model FLEXPART. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2457–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. Description of the HYSPLIT_4 Modeling System. NOAA Tech. Memo. ERL ARL 1997, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system of trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Wang, H.J. Analysis of the major atmospheric moisture sources affecting three sub-regions of east China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.D. Detecting the origins of moisture over southeast China: Seasonal variation and heavy rainfall. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; He, X.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, T.; Wright, J.S.; Wang, B.; Lin, D. Moisture sources for wintertime extreme precipitation events over South China during 1979–2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6690–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.F.; Huang, W.Y.; Qiu, T.P.; He, X.S.; Wright, J.S.; Wang, B. Interannual variation and regime shift of the evaporative moisture sources for wintertime precipitation over southern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cai, R.H.; Lan, M.C.; Yao, R.; Yang, Y.Y. Analysis on the characteristics of low frequency oscillation in precipitation in flood season in Hunan Province. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2019, 39, 644–653. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chan, J.C.L.; Chen, W.; Ling, J.; Pinto, J.G.; Shao, Y.P. Synoptic-scale controls of persistent low temperature and icy weather over southern China in January 2008. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2009, 137, 3978–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.J.; Chen, H.P. Climate control for southeastern China moisture and precipitation: Indian or east asian monsoon? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y. Progress in research on the East Asian monsoon. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2006, 17, 711–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Liang, J.Y.; Lin, A.L.; Li, C.H.; Gu, D.J. Frontal Rain and Summer Monsoon Rain During Pre-rainy Season in South China. Part I: Determination of the Division Dates. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 30, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, R.H.; Wen, M. Severe rainfalls in south China during may 2013 and its relation to the onset of the south china sea summer monsoon. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2015, 73, 442–458. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Fan, L.; Zhang, G. Synergistic Effects of PDO and IOD on Water Vapor Transport in the Preflood Season over South China. Water 2022, 14, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.Z.; He, J.H.; Wu, Z.W. Features Analysis of the Different Precipitation Periods in the Pre-flood Season in South China. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteorol. 2005, 28, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Hu, Z.Z. Summer climate variability in china and its association with 500 hPa height an tropical convection. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1996, 74, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Sun, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in east China and its association with decreasing asian summer monsoon. part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 28, 1139–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.G.; Wen, Z.P.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.Q. An interdecadal change in southern China summer rainfall around 1992/93. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2389–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.C.; Wang, Q.G.; Feng, G.L. Determination of the major moisture sources of cumulative effect of torrential rain events during the preflood season over south China using a Lagrangian particle model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8369–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.S.; Song, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Mao, J.Y. Modulation of PDO on the predictability of the interannual variability of early summer rainfall over south China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13008–13021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.B.; Xu, Q.Z.; Ni, D.H. Interdecadal variation of spring precipitation in South China and its relationships with atmospheric circulation and SST. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 40, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.C.L.; Zhou, W. PDO, ENSO and the early summer monsoon rainfall over south China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L08810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.Q.; Qiao, Y.T.; Luo, H.B. The abrupt change of the circulation in Low-Latitudes during the period from April to June. Clim. Environ. Res. 2000, 5, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Chen, H. Characteristics of the interdecadal variability of precipitation in April and May over south China and possible relationship with the mid-west Pacific sst. Clim. Environ. Res. 2012, 17, 481–494. [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorological Administration. Available online: http://cmdp.ncc-cma.net/pred/cn_enso.php?product=cn_enso_pdo (accessed on 10 August 2022).

| PDO Positive Phase | PDO Negative Phase | |
|---|---|---|
| ENSO positive phase | 1977, 1982, 1987, 1992, 1994, 1997, 1998 | 1963, 1972, 2010 |
| ENSO negative phase | 1989, 1995, 1996 | 1964, 1971, 1974, 1975, 1999, 2006, 2007, 2011, 2012 |
| PDO Positive Phase | PDO Negative Phase | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Track Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Frontal precipitation | ENSO+ | Track amount | 15.38 | 31.16 | 4.58 | 23.79 | 25.09 | 15.61 | 16.56 | 3.64 | 27.73 | 36.47 |
| precipitation | 11.99 | 33.8 | 3.01 | 24.33 | 26.87 | 16.47 | 13.65 | 1.5 | 32.84 | 35.54 | ||
| ENSO− | Track amount | 41.37 | 26.78 | 12.99 | 10.8 | 8.06 | 7.6 | 14.34 | 28.27 | 20.79 | 28.99 | |
| precipitation | 44.67 | 28.58 | 16.22 | 6.68 | 3.85 | 5.74 | 10.74 | 29.97 | 22.99 | 30.57 | ||
| Monsoon precipitation | ENSO+ | Track amount | 7.27 | 20.63 | 35.35 | 8.03 | 28.71 | 19.07 | 23.44 | 18.32 | 25.76 | 13.41 |
| precipitation | 4.5 | 17.52 | 39.23 | 6.14 | 32.62 | 16.97 | 26.31 | 23.01 | 25.81 | 7.9 | ||
| ENSO− | Track amount | 13.24 | 10.65 | 23.72 | 17.32 | 35.07 | 25.65 | 18.31 | 6.6 | 37.84 | 11.6 | |
| precipitation | 9.25 | 7.95 | 25.81 | 14.85 | 42.14 | 29.35 | 17.06 | 4.88 | 39.56 | 9.15 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Fan, L. A Joint Impact on Water Vapor Transport over South China during the Pre-Rainy Season by ENSO and PDO. Water 2022, 14, 3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223639
Zhang G, Li J, Fan L. A Joint Impact on Water Vapor Transport over South China during the Pre-Rainy Season by ENSO and PDO. Water. 2022; 14(22):3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223639
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guangya, Junjie Li, and Lingli Fan. 2022. "A Joint Impact on Water Vapor Transport over South China during the Pre-Rainy Season by ENSO and PDO" Water 14, no. 22: 3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223639






