Coastal Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Hydrogeochemical Characterization Using Chemometric Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site Description and Procedure of Sampling
2.2. Water Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Major Cations, Anions, and Heavy Metal Analysis
2.4. Chemometric Analysis for Identification of Pollution Sources
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Heavy Metal Concentration in Groundwater
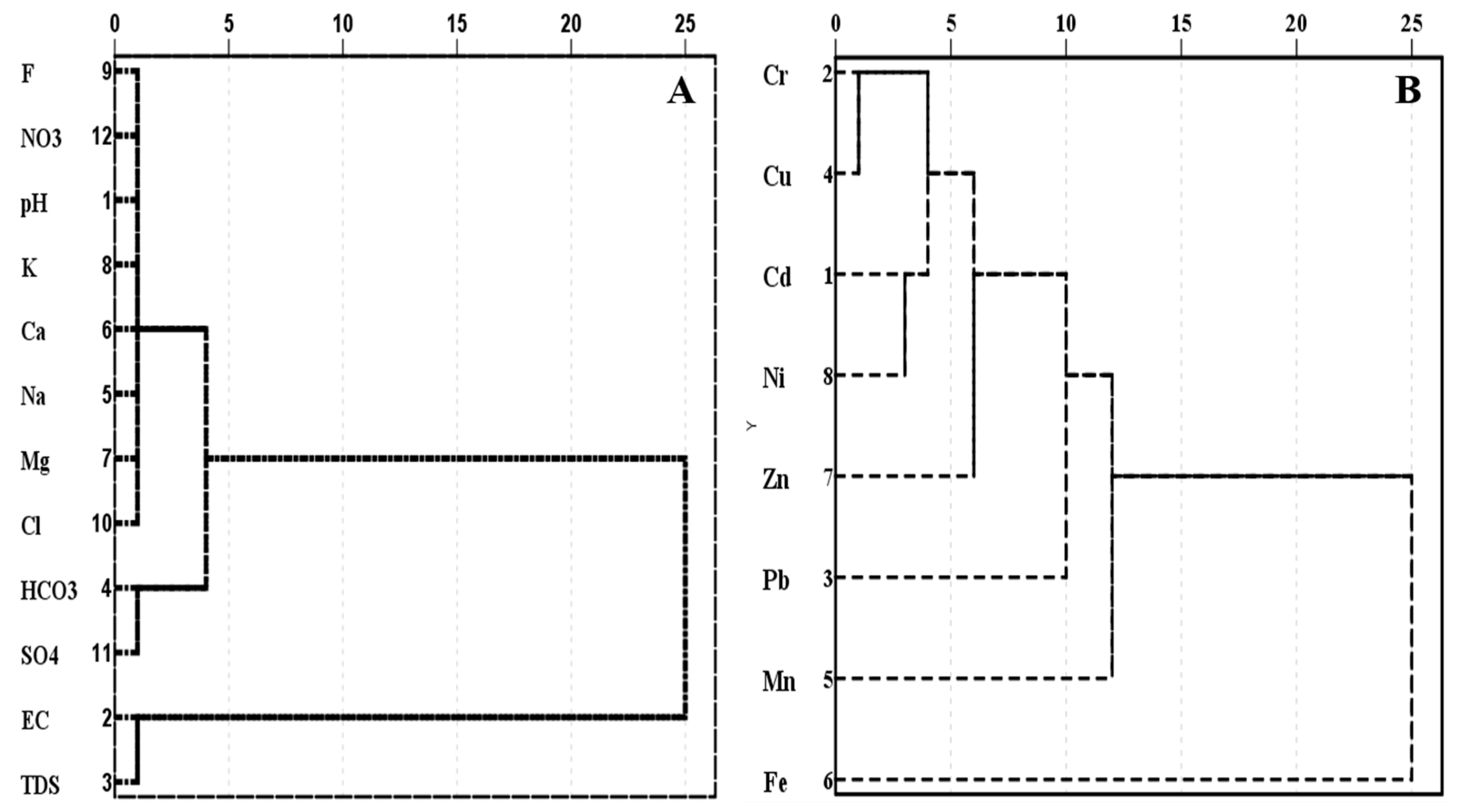
3.2. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saher, N.U.; Siddiqui, A.S. Occurrence of heavy metals in sediment and their bioaccumulation in sentinel crab (Macrophthalmus depressus) from highly impacted coastal zone. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.; Hewitt, J.; Pilditch, C.; Ellis, J. The development of a national approach to monitoring estuarine health based on multivariate analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saher, N.U.; Siddiqui, A.S. Comparison of heavy metal contamination during the last decade along the coastal sediment of Pakistan: Multiple pollution indices approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.L.; Ni, Q.Q.; Schoepf, U.J.; De Cecco, C.N.; Lin, H.; Duguay, T.M.; Zhang, L.J. Small intracranial aneurysms: Diagnostic accuracy of CT angiography. Radiology 2017, 285, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, N.U.; Asuquo, F.E.; Williams, A.B.; Essien, J.P.; Ekong, C.I.; Akpabio, O.; Olajire, A.A. Source evaluation and trace metal contamination in benthic sediments from equatorial ecosystems using multivariate statistical techniques. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Landesman, C.; Maanan, M.; Zourarah, B.; Fattal, P.; Sahabi, M. Evaluation of the anthropogenic influx of metal and metalloid contaminants into the Moulay Bousselham lagoon, Morocco, using chemometric methods coupled to geographical information systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4729–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, P.; Yu, W.; Shen, Z.; Feng, C. Spatial variation, environmental assessment and source identification of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian-Hong, L.; Zhi-Xun, Z.; Ri-Hui, L.; Zhong-Bei, W.; Xiao-Hui, C.; Fang-Hui, H. Geochemical characteristics of trace elements in the marine surface sediments outer Yangtze River Estuary. Geoscience 2011, 25, 1066. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Distribution of heavy metals and environmental assessment of surface sediment of typical estuaries in eastern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, X. Investigation on the catalytic behavior of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals on the biomass pyrolysis assisted with real-time monitoring. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 12654–12664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, D.; Wai, O.; Li, Y.S. Multivariate statistical study of heavy metal enrichment in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Meddah, R.; Afdali, M.; Touhami, F. Physicochemical and microbial assessment of spring water quality for drinking supply in Piedmont of Béni-Mellal Atlas (Morocco). Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2018, 104, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Akhter, G.; Jin, W. Delineation of saline-water intrusion using surface geoelectrical method in Jahanian Area, Pakistan. Water 2018, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, G.S.; Siyal, A.A.; Babar, M.M.; Siyal, P. Application of water quality index, synthetic pollution index, and geospatial tools for the assessment of drinking water quality in the Indus Delta, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasbela District Development Profile. 2011. Available online: https://pakistanalmanac.com/balochistan-lasbela/#_ftnref18 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Ahsan, S.N.; Malik, K.A. Geology and genesis of barite deposits of Lasbela and Khuzdar Districts, Balochistan, Pakistan. Resour. Geol. 1999, 49, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S. Groundwater hydrogeochemistry and probabilistic health risk assessment through exposure to arsenic-contaminated groundwater of Meghna floodplain, central-east Bangladesh. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. The varimax criterion for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika 1958, 23, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, south India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S. An assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes around brick kilns in three districts of Balochistan province, Pakistan, through water quality index and multivariate statistical approaches. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pak-EPA Government of Pakistan Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency (Ministry of Environment). National Standards for Drinking Water Quality; Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2008.
- Masood, N.; Batool, S.; Farooqi, A. Groundwater Pollution in Pakistan. In Global Groundwater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Rume, T.; Azam, G. Hydrogeochemical investigation of groundwater in shallow coastal aquifer of Khulna District, Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4219–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Mondal, N.; Fauzia, F. Arsenic enrichment and its natural background in groundwater at the proximity of active floodplains of Ganga River, northern India. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahab, B.; Bashir, E.; Kaleem, M.; Naseem, S.; Rafique, T. Assessment of barite of Lasbela, Balochistan, Pakistan, as drilling mud and environmental impact of associated Pb, As, Hg, Cd and Sr. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 1115, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Hamza, S.; Nawaz-ul-Huda, S.; Bashir, E. Geochemistry of Cd in groundwater of Winder, Balochistan and suspected health problems. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Masoud, M.H.; Niyazi, B.A. Impact of evaporation on groundwater salinity in the arid coastal aquifer, Western Saudi Arabia. Catena 2021, 196, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houatmia, F.; Azouzi, R.; Charef, A.; Bédir, M. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical mechanisms evolution in Northeastern, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 746–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntunen, P.; Liukkonen, M.; Lehtola, M.; Hiltunen, Y. Cluster analysis by self-organizing maps: An application to the modelling of water quality in a treatment process. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, B.K.; Wang, P.; Saikia, A.; Song, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, J.; Gupta, U.N. Mineralogical and elemental analysis of some high-sulfur Indian Paleogene Coals: A statistical approach. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Mgbenu, C.N. Chemometric analysis for pollution source identification and human health risk assessment of water resources in Ojoto Province, southeast Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | S.D. | Variance | NWQS (Pak) | WHO (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (on scale) | 5.9 | 7.9 | 7.114 | 0.511 | 0.26 | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–8.0 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 689.0 | 981.0 | 826.88 | 81.46 | 6636.1 | 1200 | 1500 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 679.0 | 923.0 | 805.0 | 62.67 | 3927.3 | 1000 | 300 |
| HCO3−1 (mg/L) | 201.0 | 395.0 | 295.66 | 58.31 | 3400.1 | 500 | 500 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 44.0 | 172.0 | 90.05 | 27.20 | 740.2 | 200 | 200 |
| Ca+2 (mg/L) | 17.2 | 25.6 | 21.28 | 2.46 | 6.09 | 75 | 75 |
| Mg+2 (mg/L) | 70.0 | 153.0 | 105.72 | 23.59 | 556.4 | 150 | 50 |
| K+ (mg/L) | 1.9 | 7.9 | 4.65 | 1.69 | 2.85 | 12 | 12 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 41.0 | 88.0 | 64.63 | 12.02 | 144.52 | 250 | 250 |
| SO4−2 (mg/L) | 151.0 | 276.0 | 214.0 | 35.29 | 1246.05 | 250 | 250 |
| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | S.D. | Variance | Skewness | Kurtosis | WHO (2011) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.1 | 0.40 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 1.21 | 10 | (3 µg/L) |
| Cr | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.38 | −1.07 | 50 | 50 (µg/L) |
| Pb | 0.04 | 0.90 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 1.32 | 0.78 | 50 | 10 (µg/L) |
| Cu | 0.03 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 2.89 | 9.16 | 2000 | 2000 (µg/L) |
| Mn | 0.01 | 0.91 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.78 | 0.49 | 500 | 400 (µg/L) |
| Fe | 0.05 | 1.30 | 0.34 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 1.09 | −0.07 | 300 | 300 (µg/L) |
| Zn | 0.01 | 0.60 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 5000 | 3000 (ug/L) |
| Ni | 0.02 | 0.90 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 4.67 | 24.9 | 20 | (70 µg/L) |
| Para Meter | pH | EC | TDS | HCO3− | Na+ | Ca+2 | Mg+ | K+ | F− | Cl− | SO4−2 | NO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.0 | |||||||||||
| EC | 0.158 | 1.0 | ||||||||||
| TDS | 0.144 | 0.178 | 1.0 | |||||||||
| HCO3− | 0.161 | 0.49 * | 0.405 * | 1.0 | ||||||||
| Na+ | 0.107 | 0.404 * | 0.304 | 0.427 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Ca+2 | 0.052 | 0.227 | −0.207 | 0.097 | 0.118 | 1.0 | ||||||
| Mg+ | −0.04 | 0.273 | 0.361 * | 0.226 | 0.105 | 0.100 | 1.0 | |||||
| K+ | 0.41 * | 0.271 | 0.003 | 0.148 | 0.223 | 0.102 | 0.043 | 1.0 | ||||
| F− | 0.358 * | 0.507 ** | 0.271 | 0.398 * | 0.443 ** | 0.114 | 0.006 | 0.475 ** | 1.0 | |||
| Cl− | 0.66 | −0.142 | −0.297 | −0.183 | 0.140 | 0.010 | −0.158 | 0.229 | 0.068 | 1.0 | ||
| SO4−2 | 0.158 | 0.091 | 0.299 | 0.164 | 0.423 | 0.247 | 0.165 | −0.027 | 0.033 | 0.065 | 1.0 | |
| NO3− | 0.222 | 0.554 ** | −0.016 | 0.202 | 0.147 | 0.085 | −0.314 | −0.019 | 0.498 ** | −0.039 | −0.016 | 1.0 |
| Parameter | Cd | Cr | Pb | Cu | Mn | Fe | Zn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | |||||||
| Cr | −0.083 | 1 | ||||||
| Pb | −0.122 | 0.286 | 1 | |||||
| Cu | −0.317 | 0.090 | −0.122 | 1 | ||||
| Mn | 0.143 | 0.191 | 0.374 * | 0.186 | 1 | |||
| Fe | 0.050 | 0.286 | 0.417 * | −0.028 | 0.138 | 1 | ||
| Zn | 0.039 | 0.060 | 0.133 | 0.305 | 0.088 | 0.064 | 1 | |
| Ni | 0.097 | 0.130 | 0.085 | −0.082 | 0.434 ** | 0.176 | −0.067 | 1 |
| Element | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 5 | Factor 6 | Factor 7 | Factor 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.341 | −0.356 | −0.312 | 0.198 | 0.604 | −0.101 | 0.198 | 0.062 |
| EC | 0.731 | 0.068 | 0.144 | 0.157 | −0.182 | 0.008 | 0.039 | 0.147 |
| TDS | 0.352 | 0.537 | −0.558 | 0.093 | 0.037 | −0.049 | −0.097 | −0.005 |
| HCO3 | 0.605 | 0.378 | −0.132 | 0.287 | −0.024 | 0.056 | −0.118 | −0.186 |
| Na | 0.616 | 0.350 | 0.000 | −0.196 | 0.251 | 0.270 | −0.065 | 0.055 |
| Ca | 0.197 | −0.173 | 0.339 | 0.389 | −0.126 | 0.385 | 0.486 | −0.184 |
| Mg | 0.160 | 0.522 | −0.020 | 0.541 | −0.130 | −0.096 | 0.055 | 0.191 |
| K | 0.547 | −0.0168 | 0.343 | 0.113 | 0.485 | −0.138 | 0.038 | −0.081 |
| F | 0.839 | −0.185 | −0.126 | −0.093 | 0.121 | −0.024 | −0.099 | −0.064 |
| Cl | −0.178 | −0.020 | 0.500 | −0.070 | 0.650 | 0.297 | −0.295 | 0.087 |
| SO4−2 | 0.155 | 0.634 | 0.033 | −0.406 | 0.113 | −0.001 | 0.103 | 0.538 |
| Cd | 0.000 | 0.670 | 0.401 | −0.057 | −0.032 | 0.211 | 0.060 | −0.340 |
| Cr | 0.461 | −0.082 | −0.106 | −0.481 | −0.004 | −0.213 | 0.574 | 0.082 |
| Pb | 0.408 | −0.363 | 0.359 | −0.415 | −0.316 | −0.273 | −0.122 | 0.099 |
| Cu | 0.179 | −0.383 | −0.663 | −0.025 | 0.003 | 0.438 | −0.044 | −0.095 |
| Mn | 0.442 | 0.042 | −0.041 | −0.550 | −0.171 | 0.240 | −0.339 | −0.355 |
| Fe | 0.745 | −0.095 | 0.268 | 0.190 | −0.166 | −0.211 | 0.071 | −0.159 |
| Zn | 0.166 | −0.216 | 0.083 | −0.035 | −0.234 | 0.703 | 0.198 | 0.371 |
| Ni | 0.385 | −0.320 | 0.108 | 0.361 | −0.212 | −0.002 | −0.529 | 0.364 |
| Eigenvalue | 3.98 | 2.34 | 1.77 | 1.70 | 1.43 | 1.30 | 1.20 | 1.10 |
| Total variance | 20.95 | 12.35 | 9.36 | 8.97 | 7.56 | 6.87 | 6.34 | 5.27 |
| Cumulative variance | 20.95 | 33.30 | 42.66 | 51.64 | 659.21 | 66.09 | 72.43 | 77.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, H.; Naz, I.; Alhodaib, A.; Abdullah, M.; Muddassar, M. Coastal Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Hydrogeochemical Characterization Using Chemometric Techniques. Water 2022, 14, 3583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213583
Ullah H, Naz I, Alhodaib A, Abdullah M, Muddassar M. Coastal Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Hydrogeochemical Characterization Using Chemometric Techniques. Water. 2022; 14(21):3583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213583
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Hidayat, Iffat Naz, Aiyeshah Alhodaib, Muhammad Abdullah, and Muhammad Muddassar. 2022. "Coastal Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Hydrogeochemical Characterization Using Chemometric Techniques" Water 14, no. 21: 3583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213583
APA StyleUllah, H., Naz, I., Alhodaib, A., Abdullah, M., & Muddassar, M. (2022). Coastal Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Hydrogeochemical Characterization Using Chemometric Techniques. Water, 14(21), 3583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213583








