Aquatic Macrophytes Shape the Foraging Efficiency, Trophic Niche Breadth, and Overlap among Small Fish in a Neotropical River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
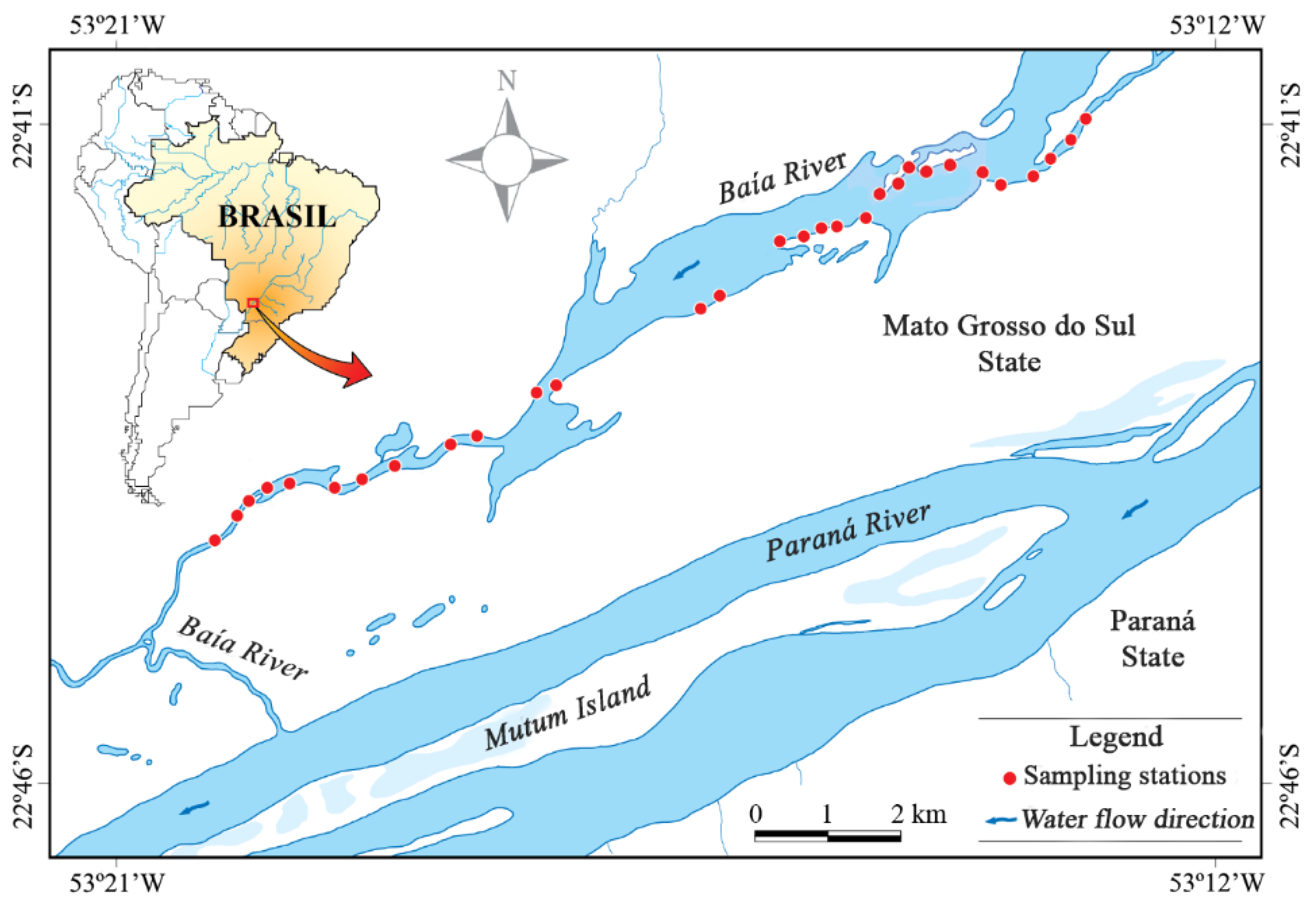
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Trophic Variables
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
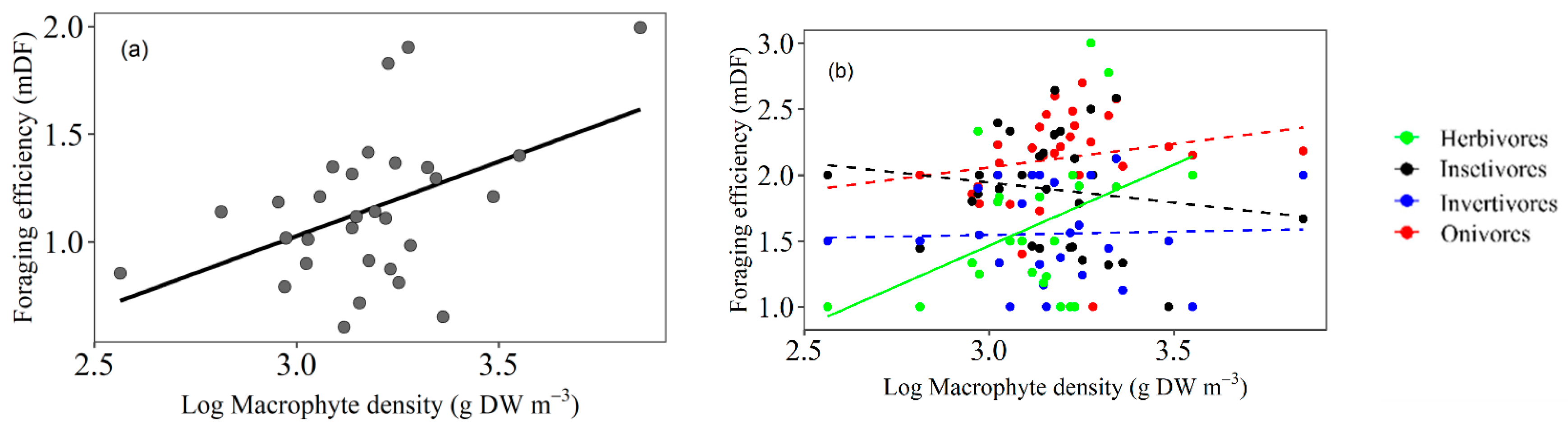
3.1. Foraging Efficiency
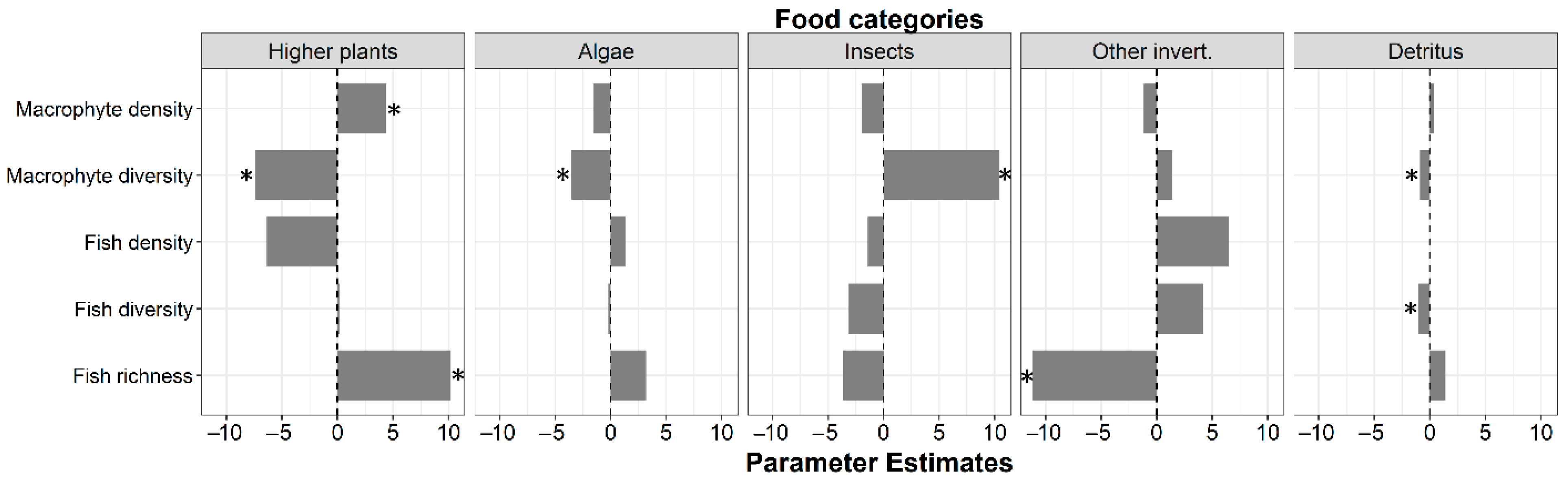
3.2. Food Categories
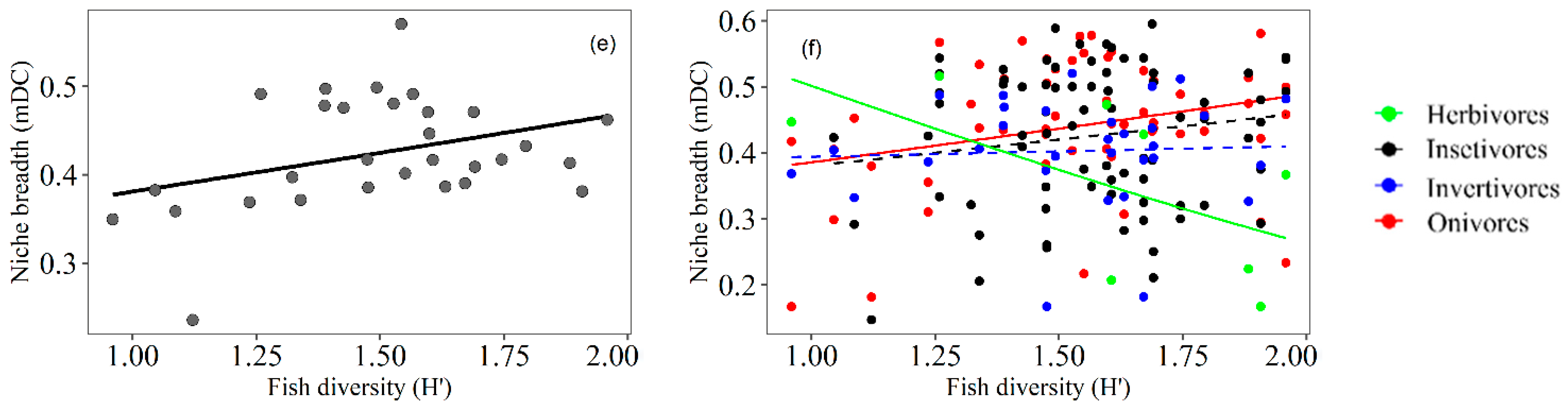
3.3. Trophic Niche Breadth
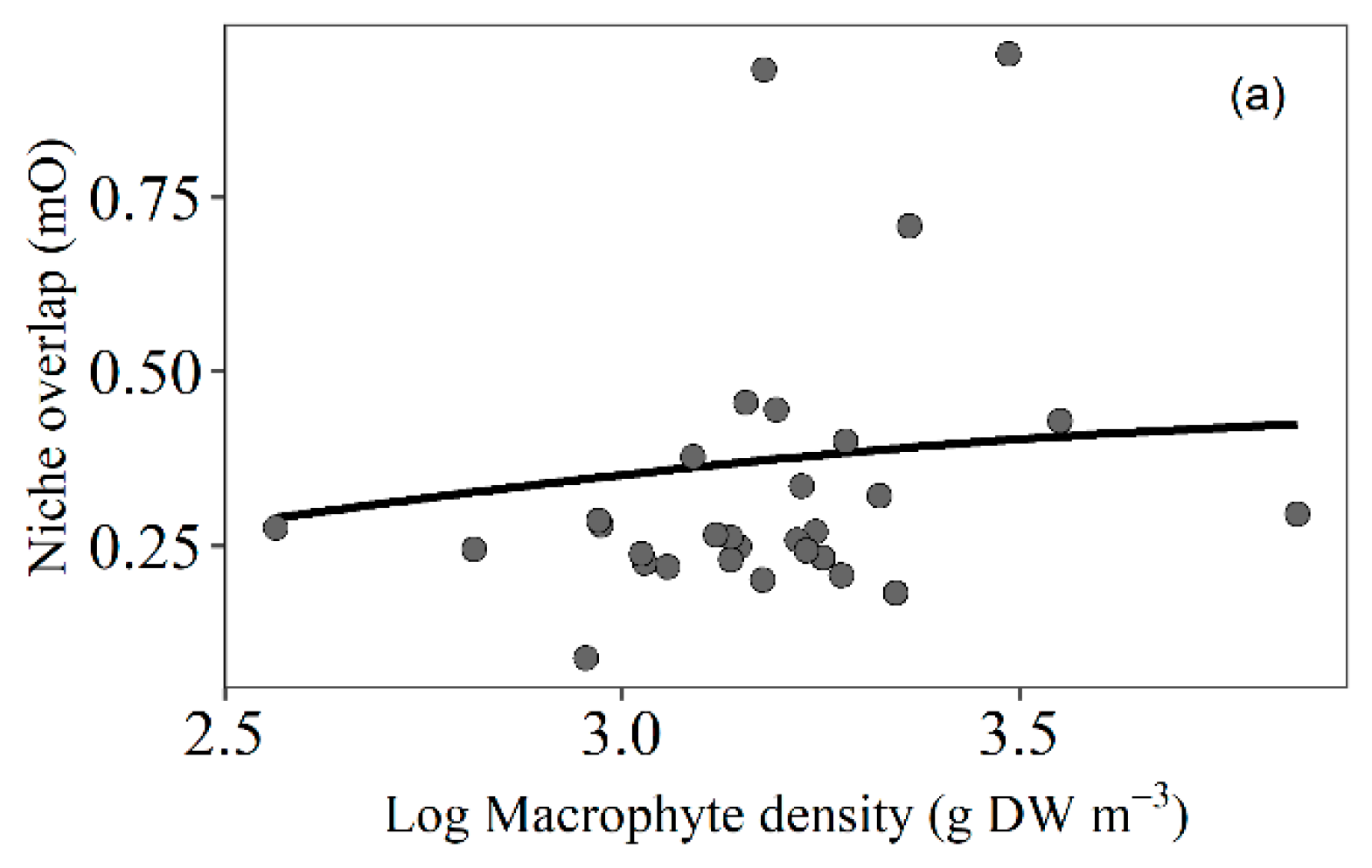
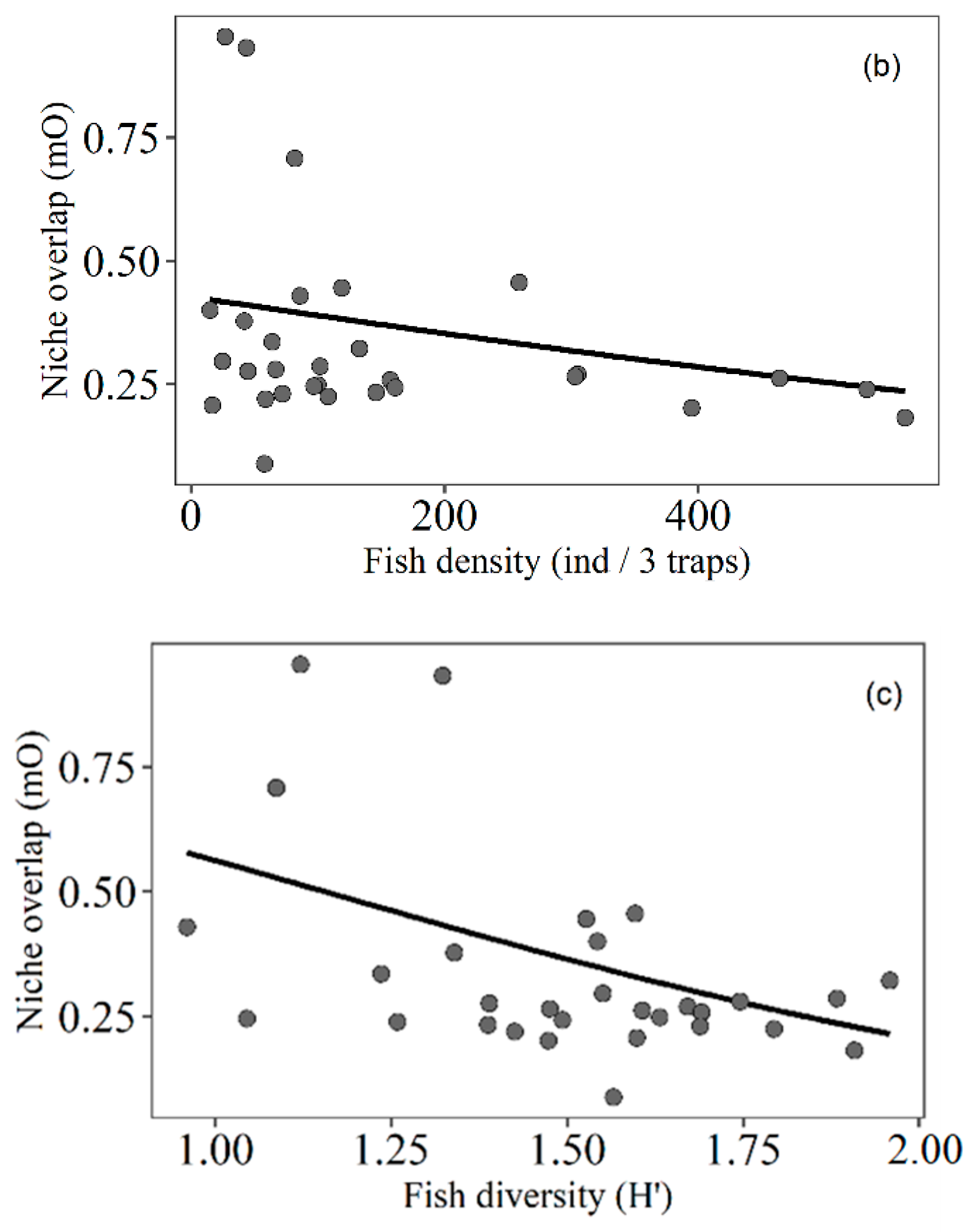
3.4. Trophic Niche Overlap
4. Discussion
4.1. Fish Foraging Efficiency Related to Macrophyte Density
4.2. Trophic Niche Breadth of Fish Related to Macrophyte Density
4.3. Trophic Niche Breadth of Fish Related to Macrophyte Diversity
4.4. Relationship between Fish Community Attributes and Fish Trophic Aspects
4.5. Trophic Niche Overlap of Fish Related to Macrophyte Density
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Kairesalo, T.; Perrow, M.R. Impact of Submerged Macrophytes on Fish-Zooplankton Interactions in Lakes. In The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Jeppesen, E., Søndergaard, M., Søndergaard, M., Christoffersen, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 131, pp. 91–114. [Google Scholar]
- Thomaz, S.M.; Cunha, E.R. The Role of Macrophytes in Habitat Structuring in Aquatic Ecosystems: Methods of Measurement, Causes and Consequences on Animal Assemblages’ Composition and Biodiversity. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2010, 22, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E.; Møller, P.H. Seasonal Dynamics in the Concentrations and Retention of Phosphorus in Shallow Danish Lakes after Reduced Loading. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2002, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Johansson, L.S.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jørgensen, T.B.; Liboriussen, L.; Jeppesen, E. Submerged Macrophytes as Indicators of the Ecological Quality of Lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M. Ecosystem Services Provided by Freshwater Macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, K.; Baumgartner, G.; Cavicchioli, M. Ecologia de Ovos e Larvas de Peixes. In A Planície de Inundação do Alto Rio Paraná: Aspectos Físicos, Biológicos e Socioeconômicos; Vazzoler, A., Agostinho, A., Hahn, N., Eds.; EDUEM/Nupélia: Maringá, Brazil, 1997; pp. 281–306. [Google Scholar]
- Carniatto, N.; Cunha, E.R.; Thomaz, S.M.; Quirino, B.A.; Fugi, R. Feeding of Fish Inhabiting Native and Non-Native Macrophyte Stands in a Neotropical Reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelicice, F.M.; Agostinho, A.A. Feeding Ecology of Fishes Associated with Egeria spp. Patches in a Tropical Reservoir, Brazil. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2006, 15, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixo, M.H.F.; Quirino, B.A.; Yofukuji, K.Y.; Cardozo, A.L.P.; Fugi, R. Macrophyte Biomass Mediates Trophic Relationships between Congeneric Fishes and Invertebrate Communities. Limnologica 2022, 93, 125957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, S.B.; Winemiller, K.O. Niche Partitioning among Frugivorous Fishes in Response to Fluctuating Resources in the Amazonian Floodplain Forest. Ecology 2014, 95, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, L.; Ortega, J.; Mendes, A.; Penha, J. Nonlinear Effect of Density on Trophic Niche Width and between-Individual Variation in Diet in a Neotropical Cichlid. Austral Ecol. 2016, 41, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniatto, N.; Fugi, R.; Thomaz, S.M. Highly Segregated Trophic Niche of Two Congeneric Fish Species in Neotropical Floodplain Lakes. J. Fish Biol. 2017, 90, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey-Lee, R.N.; Gaiser, E.E.; Trexler, J.C. Relative Roles of Dispersal Dynamics and Competition in Determining the Isotopic Niche Breadth of a Wetland Fish. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.H.; Kluender, E.R.; Inebnit, T.E.; Reid Adams, S. Differences in Diet and Feeding Ecology of Similar-Sized Spotted (Lepisosteus oculatus) and Shortnose (Lepisosteus platostomus) Gars during Flooding of a South-Eastern US River. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2013, 22, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfe, D.M.; Barmuta, L.A. Habitat Structural Complexity Mediates Food Web Dynamics in a Freshwater Macrophyte Community. Oecologia 2006, 150, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianka, E.R. Niche Overlap and Diffuse Competition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 2141–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukowska, M.; Grzybkowska, M. Coexistence of Fish Species in a Large Lowland River: Food Niche Partitioning between Small-Sized Percids, Cyprinids and Sticklebacks in Submersed Macrophytes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacArthur, R.; Pianka, E. On Optimal Use of a Patchy Environment. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejříková, I.; Eloranta, A.P.; Vejřík, L.; Šmejkal, M.; Čech, M.; Sajdlová, Z.; Frouzová, J.; Kiljunen, M.; Peterka, J. Macrophytes Shape Trophic Niche Variation among Generalist Fishes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Bicudo, D.C.; Moschinicarlos, V. O Papel Do Perifíton em Áreas Alagáveis e nos Diagnósticos Ambientais. In Ecologia e Manejo de Macrófitas Aquáticas; Thomaz, S.M., Bini, L.M., Eds.; EDUEM: Maringá, Brazil, 2003; pp. 211–230. [Google Scholar]
- Schneck, F.; Schwarzbold, A.; Melo, A.S. Substrate Roughness Affects Stream Benthic Algal Diversity, Assemblage Composition, and Nestedness. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2011, 30, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M.; Dibble, E.D.; Evangelista, L.R.; Higuti, J.; Bini, L.M. Influence of Aquatic Macrophyte Habitat Complexity on Invertebrate Abundance and Richness in Tropical Lagoons. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.; Rosa, J.; Ferreira, V.G.; Conceição, E.d.O.; Martens, K.; Higuti, J. Macrophyte Life Forms Influence the Effects of Environmental and Spatial Factors on the Beta-Diversity of Associated Ostracod Communities (Crustacea). Aquat. Sci. 2021, 83, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Nakano, S.; Tokeshi, M. Influences of Habitat Complexity on the Diversity and Abundance of Epiphytic Invertebrates on Plants. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormul, R.P.; Thomaz, S.M.; Takeda, A.M.; Behrend, R.D. Structural Complexity and Distance from Source Habitat Determine Invertebrate Abundance and Diversity. Biotropica 2011, 43, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.D.; Wijnhoven, S.; van der Velde, G. Macrophyte Presence and Growth form Influence Macroinvertebrate Community Structure. Aquat. Bot. 2013, 104, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.L.; Poe, T.P.; Iii, J.R.P.F.; Schloesser, D.W. Relationships of Phytomacrofauna to Surface Area in Naturally Occurring Macrophyte Stands. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1988, 7, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotceitas, V. Plant Stem Density as a Cue in Patch Choice by Foraging Juvenile Bluegill Sunfish. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1990, 29, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, E.R.; Winemiller, K.O.; Silva, J.C.B.; Lopes, T.M.; Gomes, L.C.; Thomaz, S.M.; Agostinho, A.A. α and β Diversity of Fishes in Relation to a Gradient of Habitat Structural Complexity Supports the Role of Environmental Filtering in Community Assembly. Aquat. Sci 2019, 81, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirino, B.A.; Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Thomaz, S.M.; Heino, J.; Fugi, R. Macrophyte Stand Complexity Explains the Functional α and β Diversity of Fish in a Tropical River-Floodplain. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 83, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.E.; Hodges, K.B. Role of Aquatic Vegetation Coverage on Hypoxia and Sunfish Abundance in Bays of a Eutrophic Reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2000, 427, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, A.J.; Allen, M.S.; Gwinn, D.C. Influence of Macrophyte-Induced Hypoxia on Fish Communities in Lakes with Altered Hydrology. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2015, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrel, S.L.; Dibble, E.D. Foraging Efficiency of Juvenile Bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus, among Different Vegetated Habitats. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2001, 62, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, E.D.; Harrel, S.L. Largemouth Bass Diets in Two Aquatic Plant Communities. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 1997, 35, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Savino, J.F.; Stein, R.A. Predator-Prey Interaction between Largemouth Bass and Bluegills as Influenced by Simulated, Submersed Vegetation. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 1982, 111, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammons, S.M.; Maceina, M.J. Changes in Diet and Food Consumption of Largemouth Bass Following Large-Scale Hydrilla Reduction in Lake Seminole, Georgia. Hydrobiologia 2006, 560, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liversage, K.; Nurkse, K.; Kotta, J.; Järv, L. Environmental Heterogeneity Associated with European Perch (Perca fluviatilis) Predation on Invasive Round Goby (Neogobius melanostomus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 132, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarshana, T.; Asaeda, T.; Manatunge, J. Foraging Behaviour of Planktivorous Fish in Artificial Vegetation: The Effects on Swimming and Feeding. Hydrobiologia 2001, 442, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middaugh, C.R.; Foley, C.J.; Höök, T.O. Local and Lake-Scale Habitat Effects on Abundance, Lengths, and Diets of Age-0 Largemouth Bass and Bluegill in Indiana Temperate Lakes. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2013, 142, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohner, J.K.; Taylor, W.W.; Hayes, D.B.; Roth, B.M. Influence of Aquatic Macrophytes on Age-0 Largemouth Bass Growth and Diets. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2018, 147, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirino, B.A.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Deosti, S.; Bonecker, C.C.; Cardozo, A.L.P.; Yofukuji, K.Y.; Aleixo, M.H.F.; Fugi, R. Interactions between a Planktivorous Fish and Planktonic Microcrustaceans Mediated by the Biomass of Aquatic Macrophytes. J. Plankton Res. 2021, 43, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, L.B.; Cooper, W.E. Habitat Structural Complexity and the Interaction between Bluegills and Their Prey. Ecology 1982, 63, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenouillet, G.; Pont, D.; Seip, K.L. Abundance and Species Richness as a Function of Food Resources and Vegetation Structure: Juvenile Fish Assemblages in Rivers. Ecography 2002, 25, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloranta, A.P.; Vejříková, I.; Čech, M.; Vejřík, L.; Holubová, M.; Šmejkal, M.; Frouzová, J.; Kiljunen, M.; Jones, R.I.; Peterka, J. Some like It Deep: Intraspecific Niche Segregation in Ruffe (Gymnocephalus cernua). Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yofukuji, K.Y.; Cardozo, A.L.P.; Quirino, B.A.; Aleixo, M.H.F.; Fugi, R. Macrophyte Diversity Alters Invertebrate Community and Fish Diet. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.M.; Tófoli, R.M.; Silva, J.C.B.; Gomes, L.C.; Agostinho, A.A. Effects of Habitat Complexity on Trophic Interactions of Three Congeneric Fish Species. Aquat. Ecol. 2022, 56, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, A.L.P.; Quirino, B.A.; Yofukuji, K.Y.; Aleixo, M.H.F.; Fugi, R. Habitat Complexity and Individual Variation in Diet and Morphology of a Fish Species Associated with Macrophytes. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2021, 30, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Jeong, K.S.; Kim, S.K.; Joo, G.J. Impact of Habitat Heterogeneity on the Biodiversity and Density of the Zooplankton Community in Shallow Wetlands (Upo Wetlands, South Korea). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2016, 45, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianka, E.R. Competition and Niche Theory. In Theoretical Ecology: Principles and Applications; May, R.M., Ed.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1976; pp. 114–141. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, P.; Thomaz, S.M.; Kobayashi, J.T.; Bini, L.M. Species Richness Increases the Resilience of Wetland Plant Communities in a Tropical Floodplain. Austral Ecol. 2013, 38, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M.; Bini, L.M.; Pagioro, T.A.; Murphy, K.J.; dos Santos, A.M.; Souza, D.C. Aquatic Macrophytes of the Upper Paraná River Floodplain: Patterns of Diversity, Biomass and Decomposition. In The Upper Paraná River and Its Floodplain: Physical Aspects, Ecology and Conservation; Agostinho, A.A., Thomaz, S.M., Hahn, N.S., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 331–352. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, T.M.; Cunha, E.R.; Silva, J.C.B.; Behrend, R.D.L.; Gomes, L.C. Dense Macrophytes Influence the Horizontal Distribution of Fish in Floodplain Lakes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M.; Bini, L.M.; Bozelli, R.L. Floods Increase Similarity among Aquatic Habitats in River-Floodplain Systems. Hydrobiologia 2007, 579, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.C.; Bulla, C.K.; Agostinho, A.A.; Vasconcelos, L.P.; Miranda, L.E. Fish Assemblage Dynamics in a Neotropical Floodplain Relative to Aquatic Macrophytes and the Homogenizing Effect of a Flood Pulse. Hydrobiologia 2012, 685, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, E.D.; Pelicice, F.M. Influence of Aquatic Plant-Specific Habitat on an Assemblage of Small Neotropical Floodplain Fishes. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2010, 19, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, R.R.; Deprá, G.C.; Graça, W.J.; Pavanelli, C.S. Peixes Da Planície de Inundação Do Alto Rio Paraná e Áreas Adjacentes: Revised, Annotated and Updated. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2018, 16, e170094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, H. Plantas Daninhas Do Brasil: Terrestres, Aquáticas, Parasitas e Tóxicas, 3rd ed.; Instituto Plantarum: Nova Odessa, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pott, V.J.; Pott, A. Plantas Aquáticas Do Pantanal; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- McCafferty, W.P. Aquatic Entomology: The Fishermen’s and Ecologists’ Illustrated Guide to Insects and Their Relative; Jones and Bartlett Learning Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Elmoor-Loureiro, L.M.A. Manual de Identificação de Cladóceros Límnicos Do Brasil; Universa: Brasília, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach Contents Analysis—A Review of Methods and Their Application. J. Fish Biol. 1980, 17, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniatto, N.; Fugi, R.; Quirino, B.A.; Cunha, E.R.; Thomaz, S.M. An Invasive and a Native Macrophyte Species Provide Similar Feeding Habitat for Fish. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2020, 29, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeileis, A.; Hothorn, T. Diagnostic Checking in Regression Relationships. R. News 2002, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, S.L.P.; Cribari-Neto, F. Beta Regression for Modelling Rates and Proportions. J. Appl. Stat. 2004, 31, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeileis, A.; Cribari-Neto, F.; Gruen, B.; Kosmidis, I. Beta Regression. R Package Version 3.1-2. Available online: https://Cran.Rproject.Org/Web/Packages/Betareg/Betareg.Pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Hutchinson, G.E. An Introduction to Population Ecology; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Science BV: Amsterdam, CT, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Tokeshi, M.; Arakaki, S. Habitat Complexity in Aquatic Systems: Fractals and Beyond. Hydrobiologia 2012, 685, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniatto, N.; Thomaz, S.M.; Cunha, E.R.; Fugi, R.; Ota, R.R. Effects of an Invasive Alien Poaceae on Aquatic Macrophytes and Fish Communities in a Neotropical Reservoir. Biotropica 2013, 45, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.H.; Young, B.P.; Blinkoff, K.D. Mechanisms Underlying Habitat Use of Juvenile Largemouth Bass and Smallmouth Bass. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2003, 132, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Li, Z.F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, X.K.; Xie, J. Growth Responses of the Submerged Macrophyte Sago Pondweed (Potamogeton pectinatus) to Disturbance by Three Omnivorous Fishes. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, A.V.R.; Goulart, E.; Pagotto, J.P.A. Ecomorphology and Use of Food Resources: Inter- and Intraspecific Relationships of Fish Fauna Associated with Macrophyte Stands. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2016, 14, e150140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, E.D. Assessment of Fish-Plant Interactions. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 1996, 16, 357–372. [Google Scholar]
- Padial, A.A.; Thomaz, S.M.; Agostinho, A.A. Effects of Structural Heterogeneity Provided by the Floating Macrophyte Eichhornia azurea on the Predation Efficiency and Habitat Use of the Small Neotropical Fish Moenkhausia Sanctaefilomenae. Hydrobiologia 2009, 624, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Ning, J.; Zhong, P.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z. Size-Dependent Feeding of Omnivorous Nile Tilapia in a Macrophyte-Dominated Lake: Implications for Lake Management. Hydrobiologia 2015, 749, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhong, P.; Ning, J.; Liu, Z.; Jeppesen, E. Herbivory of Omnivorous Fish Shapes the Food Web Structure of a Chinese Tropical Eutrophic Lake: Evidence from Stable Isotope and Fish Gut Content Analyses. Water 2017, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisner, B.E.; McCauley, E.; Wrona, F.J. The Influence of Temperature and Food Chain Length on Plankton Predator-Prey Dynamics. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arim, M.; Bozinovic, F.; Marquet, P.A. On the Relationship between Trophic Position, Body Mass and Temperature: Reformulating the Energy Limitation Hypothesis. Oikos 2007, 116, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, F.; Maltchik, L.; Bianchini, I. Hydrologic Cycle and Dynamics of Aquatic Macrophytes in Two Intermittent Rivers of the Semi-Arid Region of Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2006, 66, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quirino, B.A.; Carniatto, N.; Guglielmetti, R.; Fugi, R. Changes in Diet and Niche Breadth of a Small Fish Species in Response to the Flood Pulse in a Neotropical Floodplain Lake. Limnologica 2017, 62, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Yousuf, A.R. Effect of Macrophytes on Phytophilous Macroinvertebrate Community: A Review. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2015, 3, 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, J.M.; Boll, T.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Iglesias, C.; Pedersen, A.R.; Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M. Role of Plant Architecture on Littoral Macroinvertebrates in Temperate and Subtropical Shallow Lakes: A Comparative Manipulative Field Experiment. Limnetica 2019, 38, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloranta, A.P.; Kahilainen, K.K.; Amundsen, P.A.; Knudsen, R.; Harrod, C.; Jones, R.I. Lake Size and Fish Diversity Determine Resource Use and Trophic Position of a Top Predator in High-Latitude Lakes. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, L. Food Consumption and the Significance of Detritus and Algae to Intraspecific Competition in Roach Rutilus rutilus in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake. Oikos 1983, 41, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabrand, A. Food of Roach (Rutilus rutilus) and Ide (Leusiscus idus): Significance of Diet Shift for Interspecific Competition in Omnivorous Fishes. Oecologia 1985, 66, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, J.A.; Fletcher, D.E.; Cooper, S.D.; Vaun McArthur, J. Fish Predation and Macroinvertebrate Abundance on Snags in Low-Gradient Blackwater Streams. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 36, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Ingram, T.; Stutz, W.E.; Snowberg, L.K.; Lau, O.L.; Pauli, J.S. Ecological Release from Interspecific Competition Leads to Decoupled Changes in Population and Individual Niche Width. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, C.E.; Albrecht, M.P.; Hahn, N.S. Patterns of Niche Breadth and Feeding Overlap of the Fish Fauna in the Seasonal Brazilian Pantanal, Cuiabá River Basin. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2011, 9, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinistro, R. Top-down and Bottom-up Regulation of Planktonic Communities in a Warm Temperate Wetland. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, K.E.; Thomaz, S.M.; Warfe, D.M. Habitat Complexity: Approaches and Future Directions. Hydrobiologia 2012, 685, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| R2 | General Mean | Trophic Guilds | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herb | Omni | Insect | Invert | |||||||||
| 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.25 | ||||||||
| Estimate | SE | t | p | t | p | t | p | t | p | t | p | |
| (Intercept) | 0.66 | 0.38 | 1.75 | 0.09 | −0.12 | 0.90 | 4.57 | <0.01 * | 3.31 | <0.01 * | 2.43 | <0.01 * |
| Macrophyte density | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.24 | <0.01 * | 2.17 | 0.04 * | 1.42 | 0.17 | −0.90 | 0.37 | 0.53 | 0.60 |
| Macrophyte diversity | −0.12 | 0.14 | −0.86 | 0.40 | −0.22 | 0.82 | −0.73 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.84 | −0.09 | 0.92 |
| Fish density | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.99 | 0.33 | −0.84 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.88 | 1.61 | 0.12 | 1.96 | 0.07 |
| Fish diversity | −0.04 | 0.30 | −0.13 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 0.51 | −1.03 | 0.31 | 1.05 | 0.30 | 1.86 | 0.06 |
| Fish richness | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 0.34 | 0.78 | 0.44 | 1.31 | 0.20 | −1.00 | 0.32 | −1.54 | 0.14 |
| R2 | Food Items | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher Plants | Algae | Insects | Other Invertebrates | Detritus | ||||||
| 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.42 | ||||||
| t | p | t | p | t | p | t | p | t | p | |
| (Intercept) | 11.2 | <0.01 * | 8.37 | <0.01 * | 18.2 | <0.01 * | 10.2 | <0.01 * | 3.45 | <0.01 * |
| Macrophyte density | 2.38 | 0.03 * | −1.51 | 0.14 | −0.64 | 0.53 | −0.57 | 0.57 | 1.03 | 0.31 |
| Macrophyte diversity | −3.77 | <0.01 * | −3.20 | <0.01 * | 3.22 | <0.01 * | 0.62 | 0.54 | −2.64 | 0.01 * |
| Fish density | −1.91 | 0.07 | 0.73 | 0.47 | −0.26 | 0.80 | 1.71 | 0.10 | −0.08 | 0.94 |
| Fish diversity | 0.07 | 0.95 | −0.15 | 0.88 | −0.83 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.12 | −2.63 | 0.01 * |
| Fish richness | 2.49 | 0.02 * | 1.40 | 0.17 | −0.54 | 0.59 | −2.41 | 0.02 * | 2.01 | 0.06 |
| General Mean | Trophic Guilds | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herb | Omni | Insect | Invert | |||||||||
| Estimate | SE | z | p | z | p | z | p | z | p | z | p | |
| (Intercept) | −0.63 | 0.28 | −2.28 | 0.02 | 0.81 | 0.42 | −0.49 | 0.62 | −2.28 | 0.02 * | −0.69 | 0.49 |
| Macrophyte density | <−0.00 | 0.00 | −1.95 | 0.05 * | −0.07 | 0.94 | −2.90 | <0.01 * | −0.59 | 0.55 | −0.89 | 0.37 |
| Macrophyte diversity | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.54 | 0.56 | 2.40 | 0.01 * | 0.70 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 0.39 | −0.90 | 0.37 |
| Fish density | <0.00 | <0.00 | 0.68 | 0.50 | −1.20 | 0.23 | 2.27 | 0.08 | −0.38 | 0.70 | −1.35 | 0.18 |
| Fish diversity | 0.51 | 0.22 | 2.30 | 0.02 * | −2.44 | 0.01 * | 1.74 | <0.02 * | 0.82 | 0.41 | −0.42 | 0.67 |
| Fish richness | −0.04 | 0.04 | −1.17 | 0.24 | −0.68 | 0.49 | −1.92 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 1.15 | 0.25 |
| Estimate | SE | z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1.38 | 0.80 | 1.72 | 0.09 |
| Macrophyte density | 0.98 | 0.74 | 1.32 | 0.19 |
| Macrophyte density2 | −1.71 | 0.75 | −2.29 | 0.02 * |
| Macrophyte diversity | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0.94 |
| Fish density | <−0.00 | <0.00 | −2.65 | 0.05 * |
| Fish diversity | −1.85 | 0.70 | −1.95 | <0.01 * |
| Fish richness | 0.14 | 0.11 | 1.25 | 0.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quirino, B.A.; Thomaz, S.M.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Dainez-Filho, M.S.; Fugi, R. Aquatic Macrophytes Shape the Foraging Efficiency, Trophic Niche Breadth, and Overlap among Small Fish in a Neotropical River. Water 2022, 14, 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213543
Quirino BA, Thomaz SM, Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Dainez-Filho MS, Fugi R. Aquatic Macrophytes Shape the Foraging Efficiency, Trophic Niche Breadth, and Overlap among Small Fish in a Neotropical River. Water. 2022; 14(21):3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213543
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuirino, Bárbara Angélio, Sidinei Magela Thomaz, Erik Jeppesen, Martin Søndergaard, Mário Sérgio Dainez-Filho, and Rosemara Fugi. 2022. "Aquatic Macrophytes Shape the Foraging Efficiency, Trophic Niche Breadth, and Overlap among Small Fish in a Neotropical River" Water 14, no. 21: 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213543
APA StyleQuirino, B. A., Thomaz, S. M., Jeppesen, E., Søndergaard, M., Dainez-Filho, M. S., & Fugi, R. (2022). Aquatic Macrophytes Shape the Foraging Efficiency, Trophic Niche Breadth, and Overlap among Small Fish in a Neotropical River. Water, 14(21), 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213543







