Monitoring Ice Phenology in Lake Wetlands Based on Optical Satellite Data: A Case Study of Wuliangsu Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
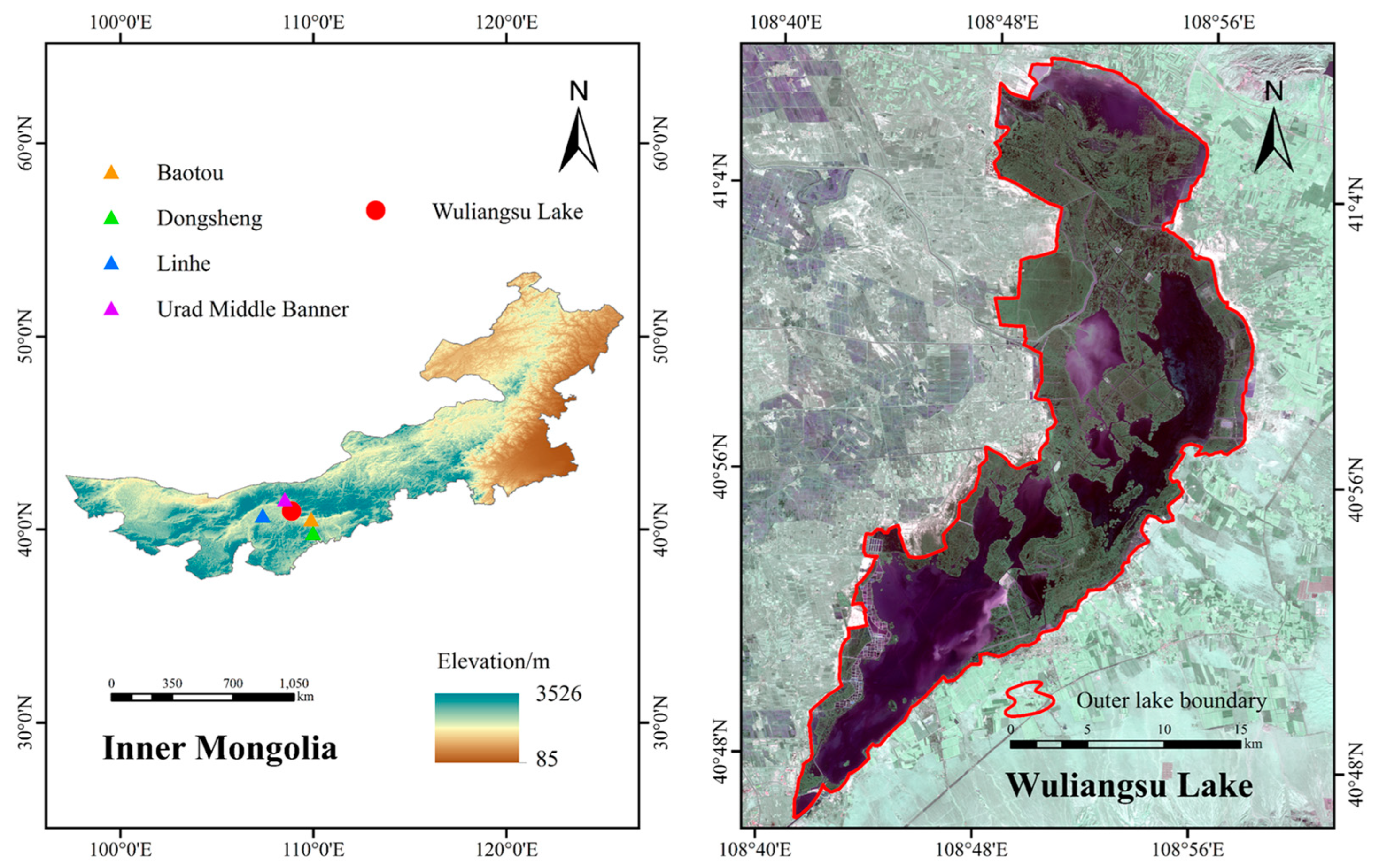
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Optical Satellite Data
2.2.1. MODIS Data
2.2.2. Landsat and Sentinel-2 Data
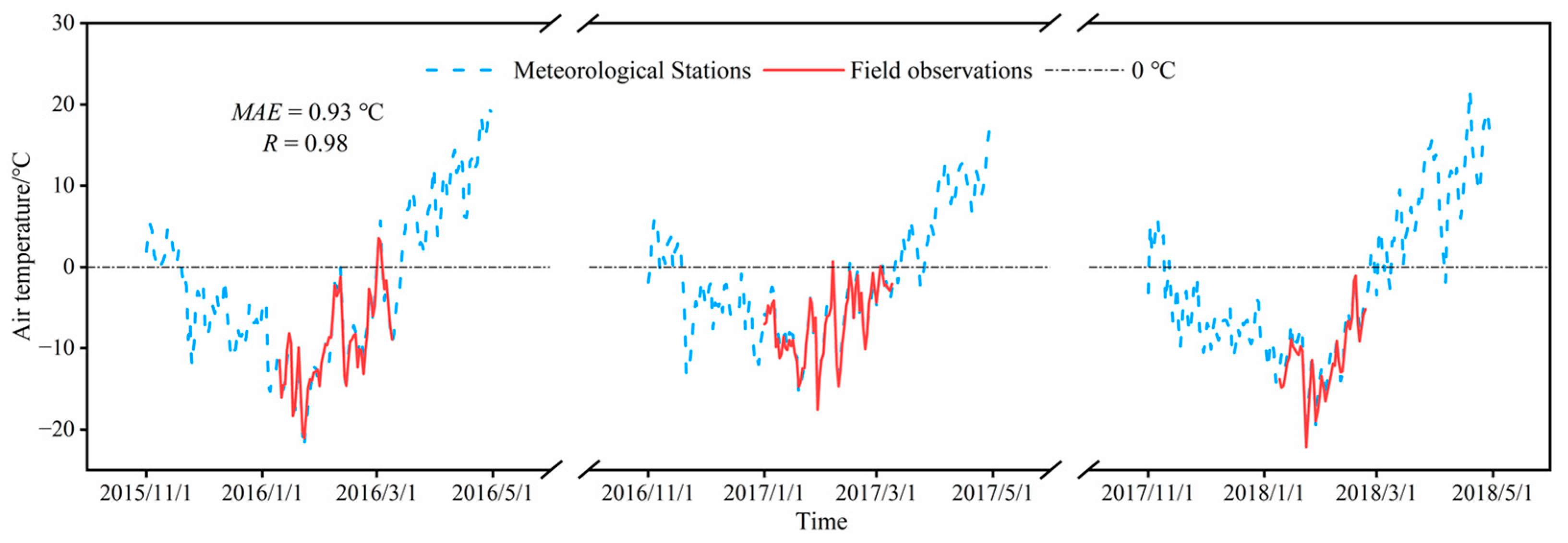
2.3. Meteorological Data
3. Methods
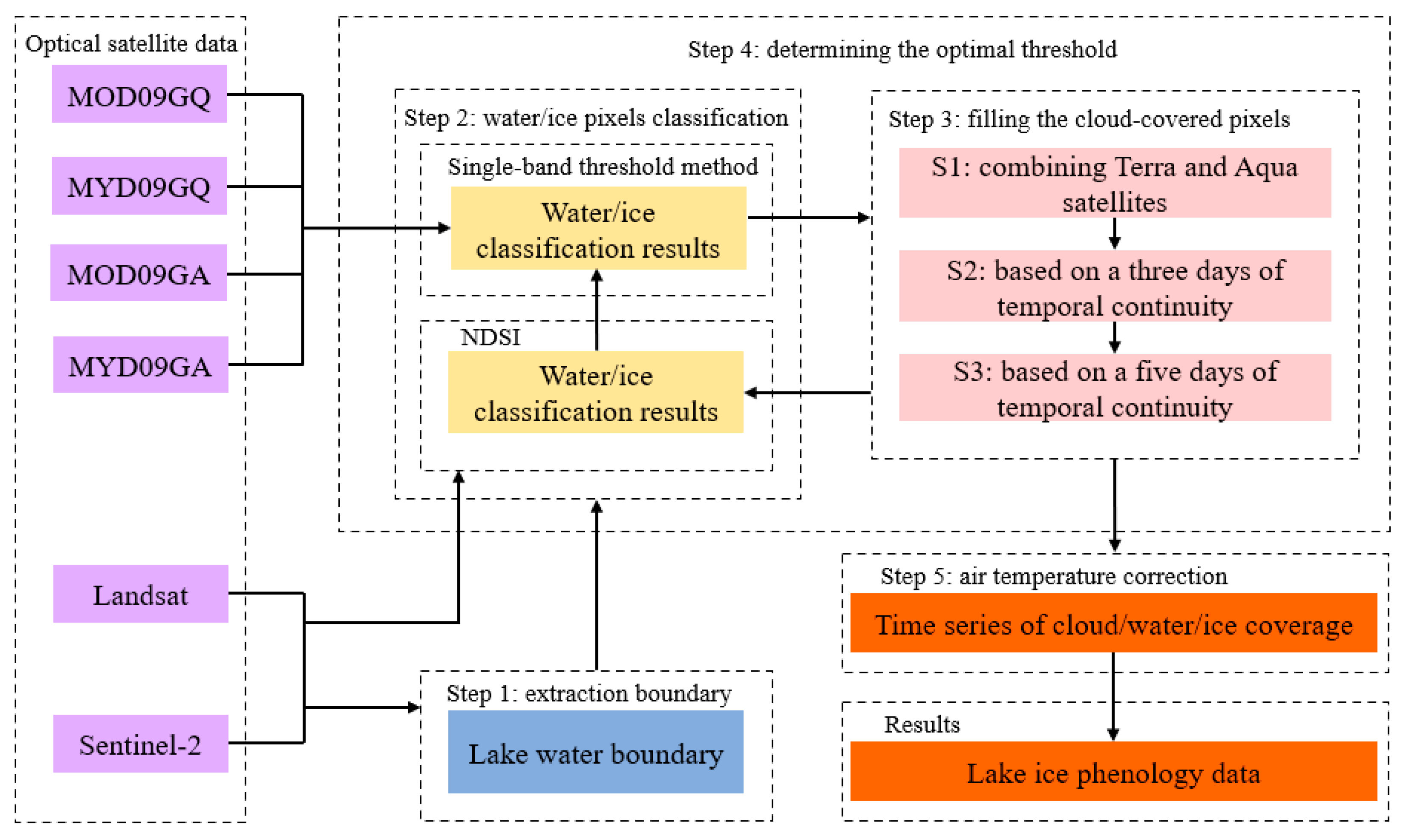
3.1. Lake Ice Phenology Extraction
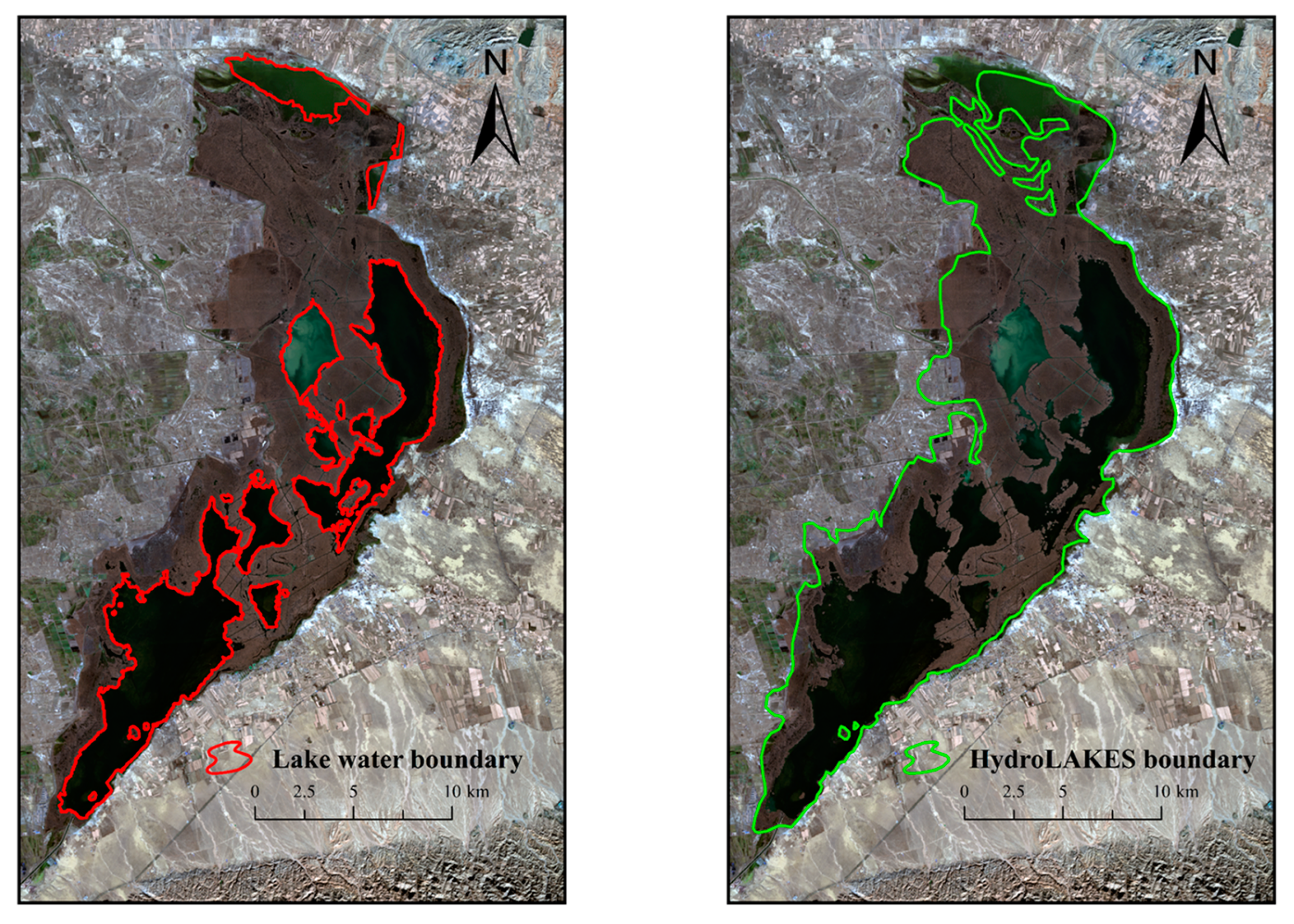
3.1.1. Extraction of Lake Water Boundary
3.1.2. Extraction of Water and Ice Pixels
3.1.3. Cloud Removal by Gap Filling
3.1.4. Air Temperature Calibration
3.1.5. Extraction of Lake Ice Phenology
3.2. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
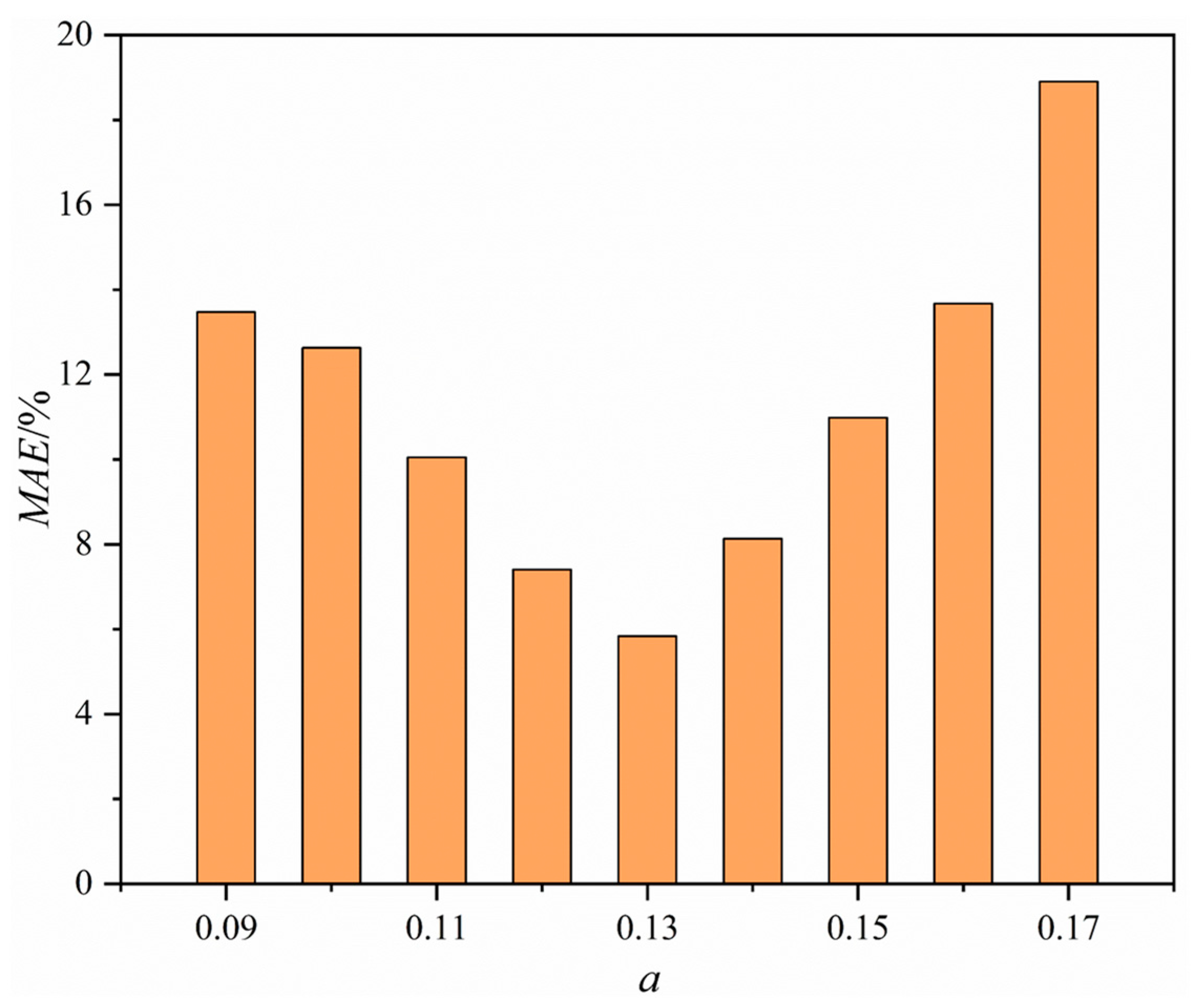
4.1. Determining the Optimal Threshold
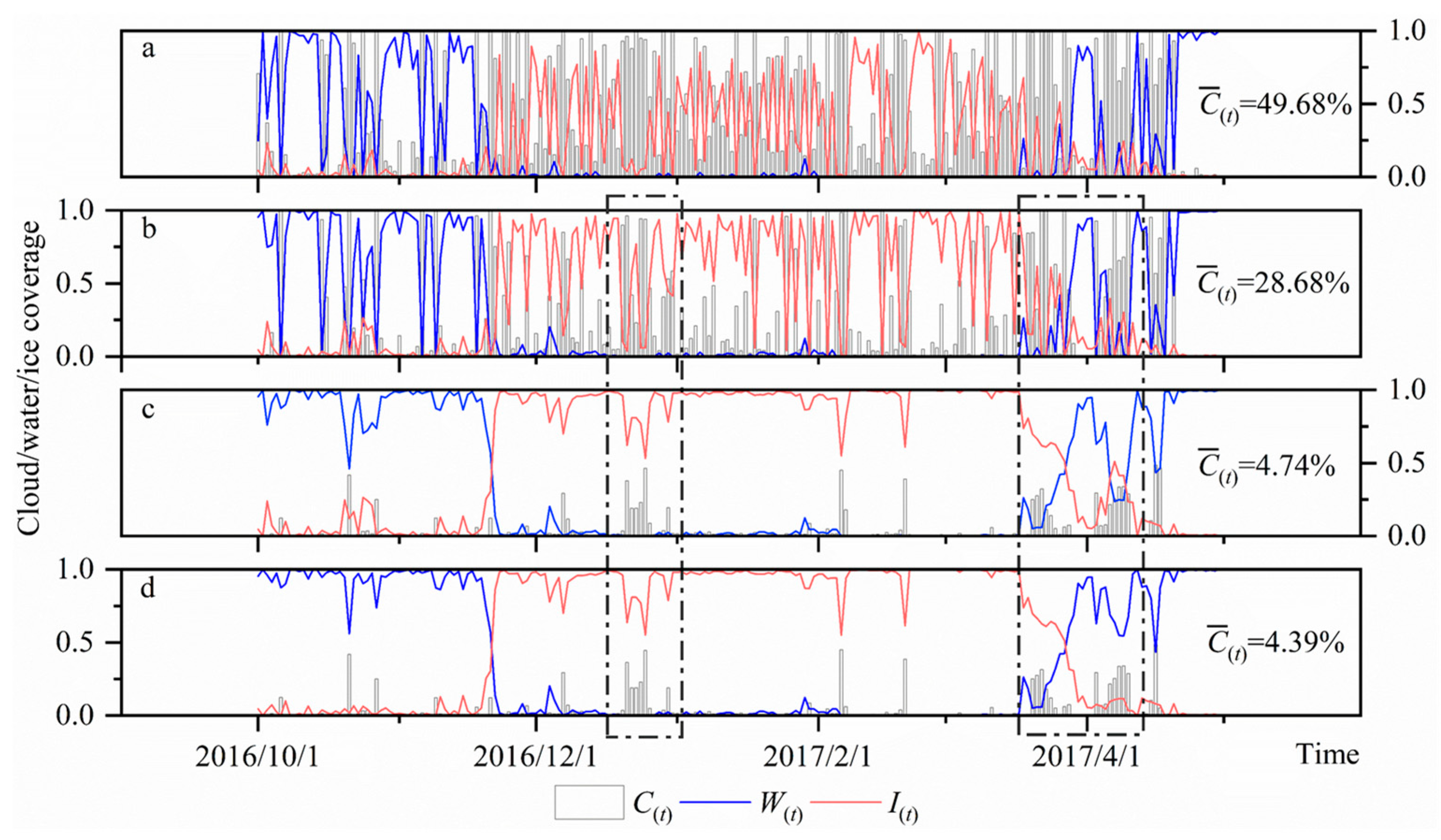
4.2. Cloud Removal and Filling
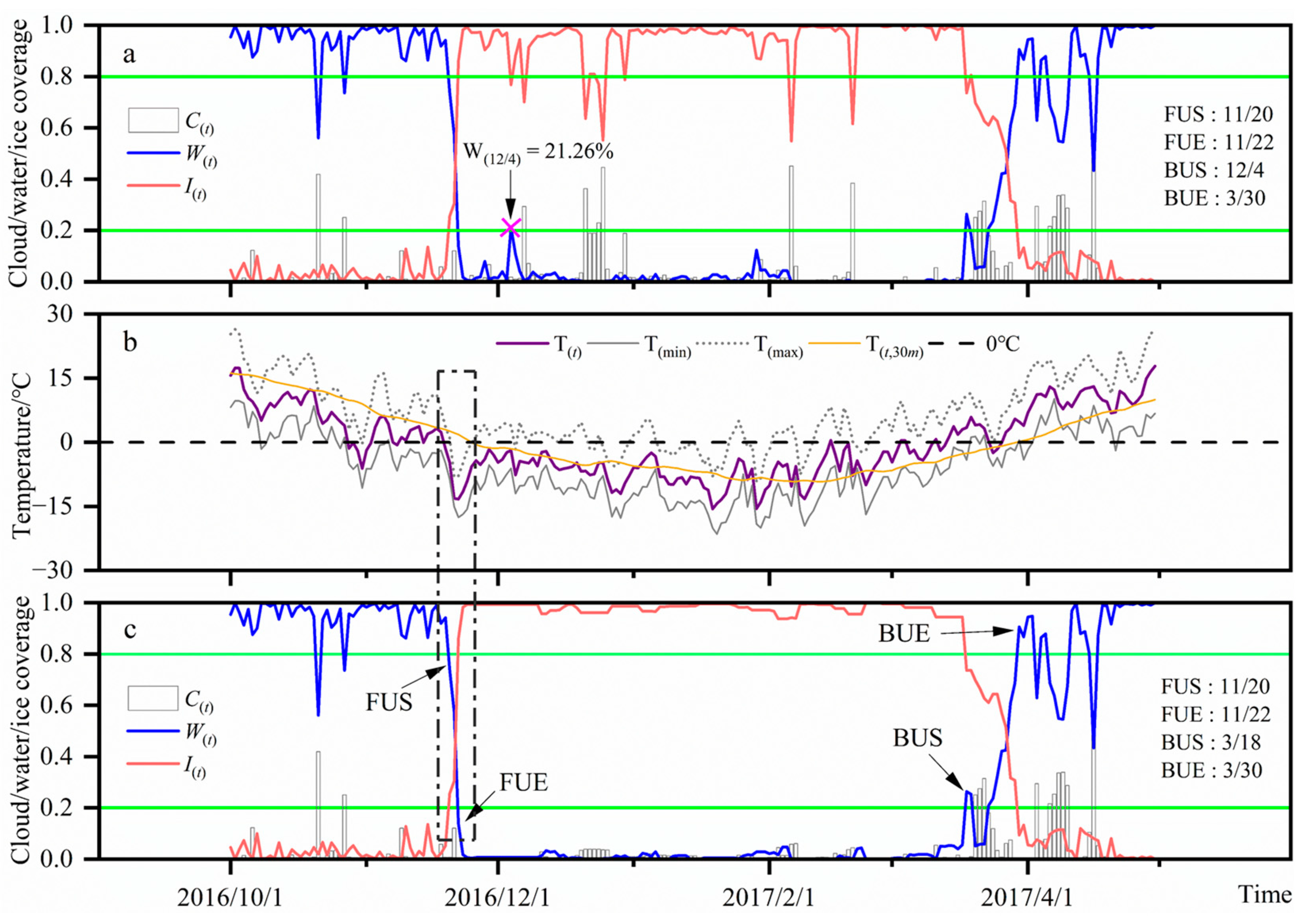
4.3. Air Temperature Correction
4.4. Lake Wetland Ice Phenology
4.4.1. Ice Phenology
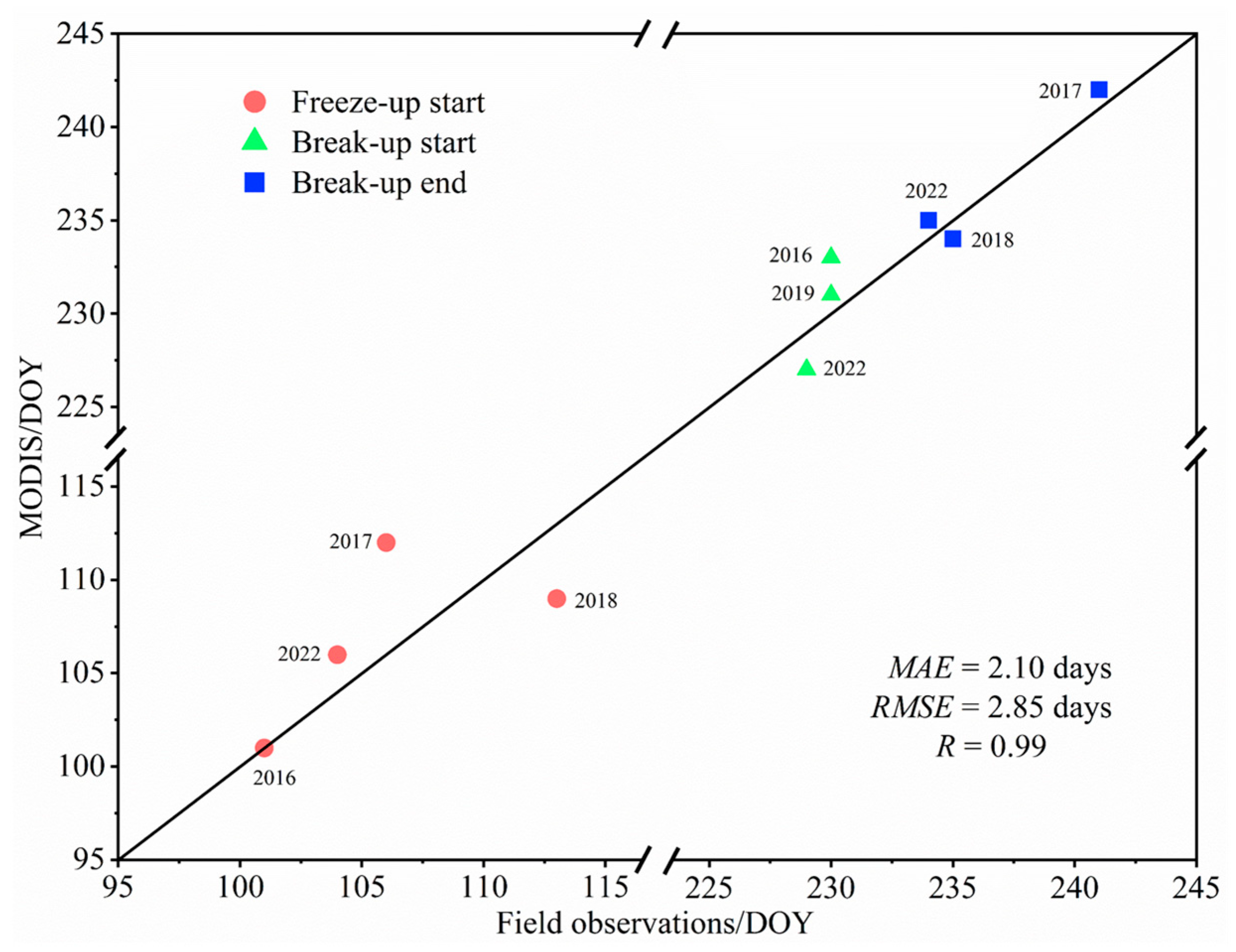
4.4.2. Verification of Ice Phenology Data
5. Discussion
5.1. Error Analysis
5.1.1. Satellite Products
5.1.2. Observation Principle
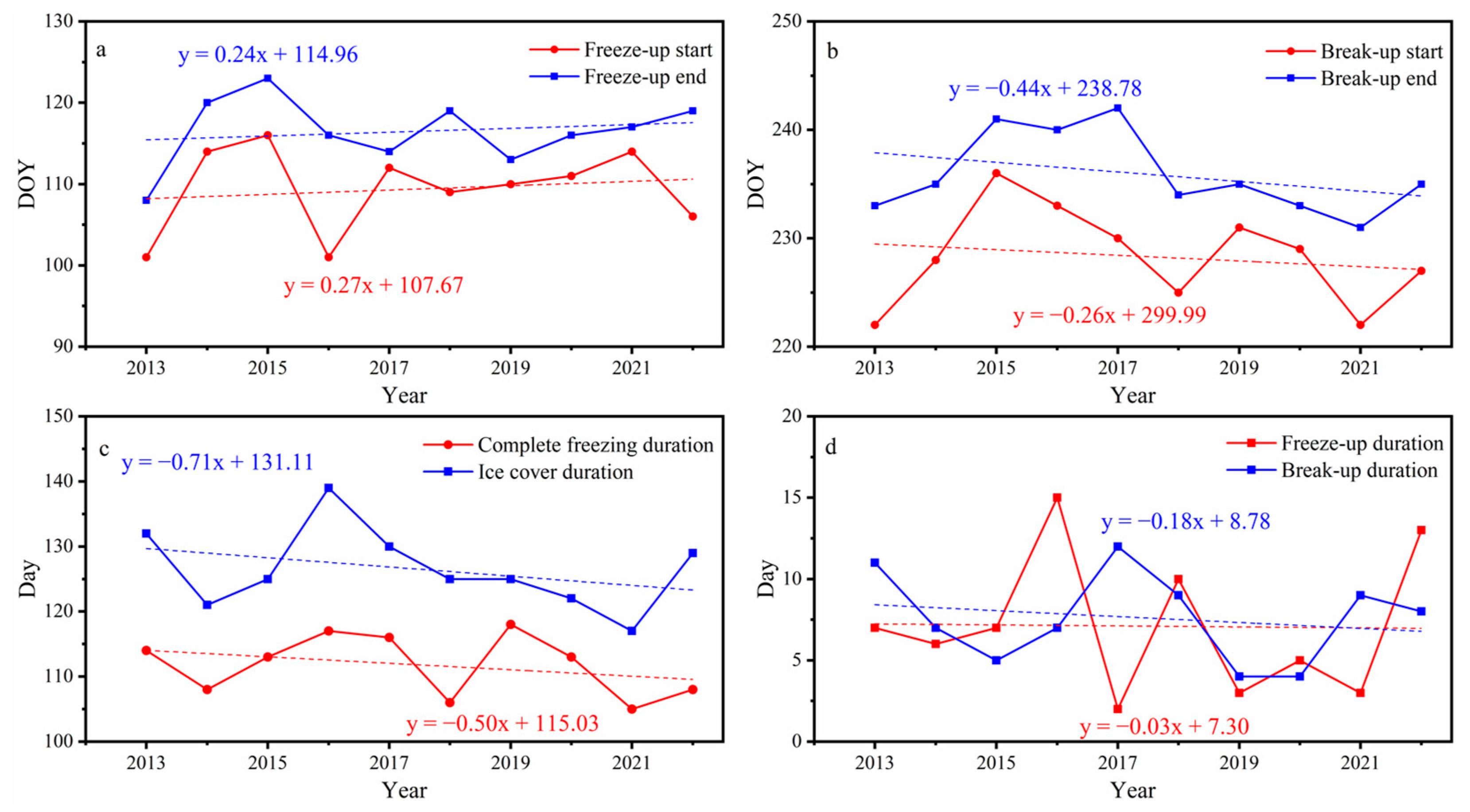
5.2. Trends of Ice Phenology
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, I.C.; Poole, C.; Giesen, W.; ValboJorgensen, J. Species diversity and ecology of Tonle Sap Great Lake, Cambodia. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 68, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G. Response of sediment chemistry and accumulation rates to recent environmental changes in the Clear Lake watershed, California, USA. Wetlands 2003, 23, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäranta, M.; Wen, L.J. Ice Phenology in Eurasian Lakes over Spatial Location and Altitude. Water 2022, 14, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, J.; Engelhardt, C.; Kirillin, G.; Matschullat, J. Lake ice phenology in Berlin-Brandenburg from 1947–2007: Observations and model hindcasts. Clim. Change 2012, 112, 791–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigosi, A.; Carey, C.C.; Ibelings, B.W.; Brookes, J.D. The interaction between climate warming and eutrophication to promote cyanobacteria is dependent on trophic state and varies among taxa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdorovennova, G.; Palshin, N.; Golosov, S.; Efremova, T.; Belashev, B.; Bogdanov, S.; Terzhevik, A. Dissolved Oxygen in a Shallow Ice-Covered Lake in Winter: Effect of Changes in Light, Thermal and Ice Regimes. Water 2021, 13, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, B.R.; Meester, L.D.; Bridge, T.C.L.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Pandolfi, J.M.; Corlett, R.T.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Pearce-Kelly, P.; Kovacs, K.M.; Dudgeon, D.; et al. The broad footprint of climate change from genes to biomes to people. Science 2016, 354, aaf7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropáček, J.; Maussion, F.; Chen, F.; Hoerz, S.; Hochschild, V. Analysis of ice phenology of lakes on the Tibetan Plateau from MODIS data. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.; Xie, P.; Leppäranta, M.; Wang, X.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Lin, H.; Shi, L. MODIS-based Daily Lake Ice Extent and Coverage dataset for Tibetan Plateau. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, S.E.; Vavrus, S.J.; Foley, J.A.; Fisher, V.A.; Wynne, R.H.; Lenters, J.D. Global patterns of lake ice phenology and climate: Model simulations and observations. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1998, 3, 28825–28837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Duguay, C.R. The response and role of ice cover in lake-climate interactions. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 671–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Huang, C.; Duan, H.; Gu, J.; Hou, J. Lake Phenology of Freeze-Thaw Cycles Using Random Forest: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pavelsky, T.M. Remote Sensing of Lake Ice Phenology across a Range of Lakes Sizes, ME, USA. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geldsetzer, T.; Sanden, J.V.D.; Brisco, B. Monitoring lake ice during spring melt using RADARSAT-2 SAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, S391–S400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, W.N.; Dai, M. High-resolution sea-ice motions from AMSR-E imagery. Ann. Glaciol. 2006, 44, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mack, S.; Padman, L.; Klinck, J. Extracting tidal variability of sea ice concentration from AMSR-E passive microwave single-swath data: A case study of the Ross Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tateyama, K.; Kameda, T.; Hutchings, J.K. Estimation of melt pond fraction over high-concentration Arctic sea ice using AMSR-E passive microwave data. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 7056–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, S.E.; Roof, S.R.; Retelle, M.J.; Werner, A.; Gunn, G.E.; Bunting, E.L. Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Estimates of Lake Ice Cover Timing on Linnévatnet, Kapp Linné, Svalbard Using In-Situ Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmejkalová, T.; Edwards, M.; Dash, J. Arctic lakes show strong decadal trend in earlier spring ice-out. Sci Rep. UK 2016, 6, 38449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ke, C.Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Duan, Z.; Lee, H. Variations of Lake Ice Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau From 2001 to 2017 Based on MODIS Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.G.; Banwell, A.F.; Willis, I.C.; Arnold, N.S. Dual-satellite (Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8) remote sensing of supraglacial lakes in Greenland. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 3045–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Kirillin, G. An Automatic Method to Detect Lake Ice Phenology Using MODIS Daily Temperature Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Duguay, C.R.; Xu, L.L. Assessment of machine learning classifiers for global lake ice cover mapping from MODIS TOA reflectance data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the volume and age of water stored in global lakes using a geo-statistical approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Blagrave, K.; Filazzola, A.; Imrit, M.A.; Hendricks Franssen, H.J. Forecasting the Permanent Loss of Lake Ice in the Northern Hemisphere Within the 21st Century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, X.N.; Wang, N.L.; Wu, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.J. Lake ice phenology variations and influencing factors of Selin Co from 2000 to 2020. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Cao, X.W.; Li, G.Y.; Huang, W.F.; Leppäranta, M.; Arvola, L.; Li, Z.J. Mass and Heat Balance of a Lake Ice Cover in the Central Asian Arid Climate Zone. Water 2020, 12, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.F.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, C.; Leppranta, M.; Li, Z.J.; Li, R.; Lin, Z.J. Radiative penetration dominates the thermal regime and energetics of a shallow ice-covered lake in an arid climate. Cryosphere 2021, 16, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Mu, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Seasonal and diurnal variations in methane emissions from Wuliangsu Lake in arid regions of China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4479–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Xie, F.; Lu, P.; Huo, P.Z.; Leppäranta, M. The role of lake heat flux in the growth and melting of ice. Adv. Polar Sci. 2021, 32, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) for the MODIS Snow and Sea Ice-Mapping Algorithms; NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2001. Available online: https://modis-snow-ice.gsfc.nasa.gov/?c=atbd&t=atbd (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Gafurov, A.; Bárdossy, A. Cloud removal methodology from MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Hao, X.; Fang, C. Recent trends of ice phenology for eight large lakes using MODIS products in Northeast China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 5388–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Song, K.; Ha, X.; Wen, Z.; Tan, Y.; Li, W. Investigation of spatial and temporal variability of river ice phenology and thickness across Songhua River Basin, northeast China. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 3581–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.R.; Bernier, M.; Gauthier, Y.; Kouraev, A. Remote Sensing of Lake and River Ice; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781118368909. [Google Scholar]

| Mean | Maximum | Minimum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original Terra | 38.67% | 42.30% (2015) | 31.54% (2014) |
| Original Aqua | 47.71% | 52.20% (2013) | 38.72% (2020) |
| S1 | 28.83% | 33.06% (2016) | 22.99% (2014) |
| S2 | 6.97% | 9.52% (2018) | 3.19% (2020) |
| S3 | 6.42% | 8.93% (2018) | 2.95% (2020) |
| FUS | FUE | BUS | BUE | FUD | BUD | CFD | ICD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 11/9 | 11/16 | 3/10 | 3/21 | 7 | 11 | 114 | 132 |
| 2014 | 11/22 | 11/28 | 3/17 | 3/24 | 6 | 7 | 108 | 121 |
| 2015 | 11/24 | 12/1 | 3/25 | 3/30 | 7 | 5 | 113 | 125 |
| 2016 | 11/9 | 11/24 | 3/22 | 3/29 | 15 | 7 | 117 | 139 |
| 2017 | 11/20 | 11/22 | 3/18 | 3/30 | 2 | 12 | 116 | 130 |
| 2018 | 11/17 | 11/27 | 3/14 | 3/23 | 10 | 9 | 106 | 125 |
| 2019 | 11/18 | 11/21 | 3/20 | 3/24 | 3 | 4 | 118 | 125 |
| 2020 | 11/19 | 11/24 | 3/18 | 3/22 | 5 | 4 | 113 | 122 |
| 2021 | 11/22 | 11/25 | 3/10 | 3/19 | 3 | 9 | 105 | 117 |
| 2022 | 11/14 | 11/27 | 3/16 | 3/24 | 13 | 8 | 108 | 129 |
| Average | 11/17 | 11/25 | 3/17 | 3/25 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 111.8 | 126.5 |
| Max | 11/24 | 12/1 | 3/25 | 3/30 | 15 | 12 | 118 | 139 |
| Min | 11/9 | 11/16 | 3/10 | 3/19 | 2 | 4 | 105 | 117 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, P.; Lu, P.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z. Monitoring Ice Phenology in Lake Wetlands Based on Optical Satellite Data: A Case Study of Wuliangsu Lake. Water 2022, 14, 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203307
Huo P, Lu P, Cheng B, Zhang L, Wang Q, Li Z. Monitoring Ice Phenology in Lake Wetlands Based on Optical Satellite Data: A Case Study of Wuliangsu Lake. Water. 2022; 14(20):3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203307
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Puzhen, Peng Lu, Bin Cheng, Limin Zhang, Qingkai Wang, and Zhijun Li. 2022. "Monitoring Ice Phenology in Lake Wetlands Based on Optical Satellite Data: A Case Study of Wuliangsu Lake" Water 14, no. 20: 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203307
APA StyleHuo, P., Lu, P., Cheng, B., Zhang, L., Wang, Q., & Li, Z. (2022). Monitoring Ice Phenology in Lake Wetlands Based on Optical Satellite Data: A Case Study of Wuliangsu Lake. Water, 14(20), 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203307







