Assessments of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in Disctrict Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
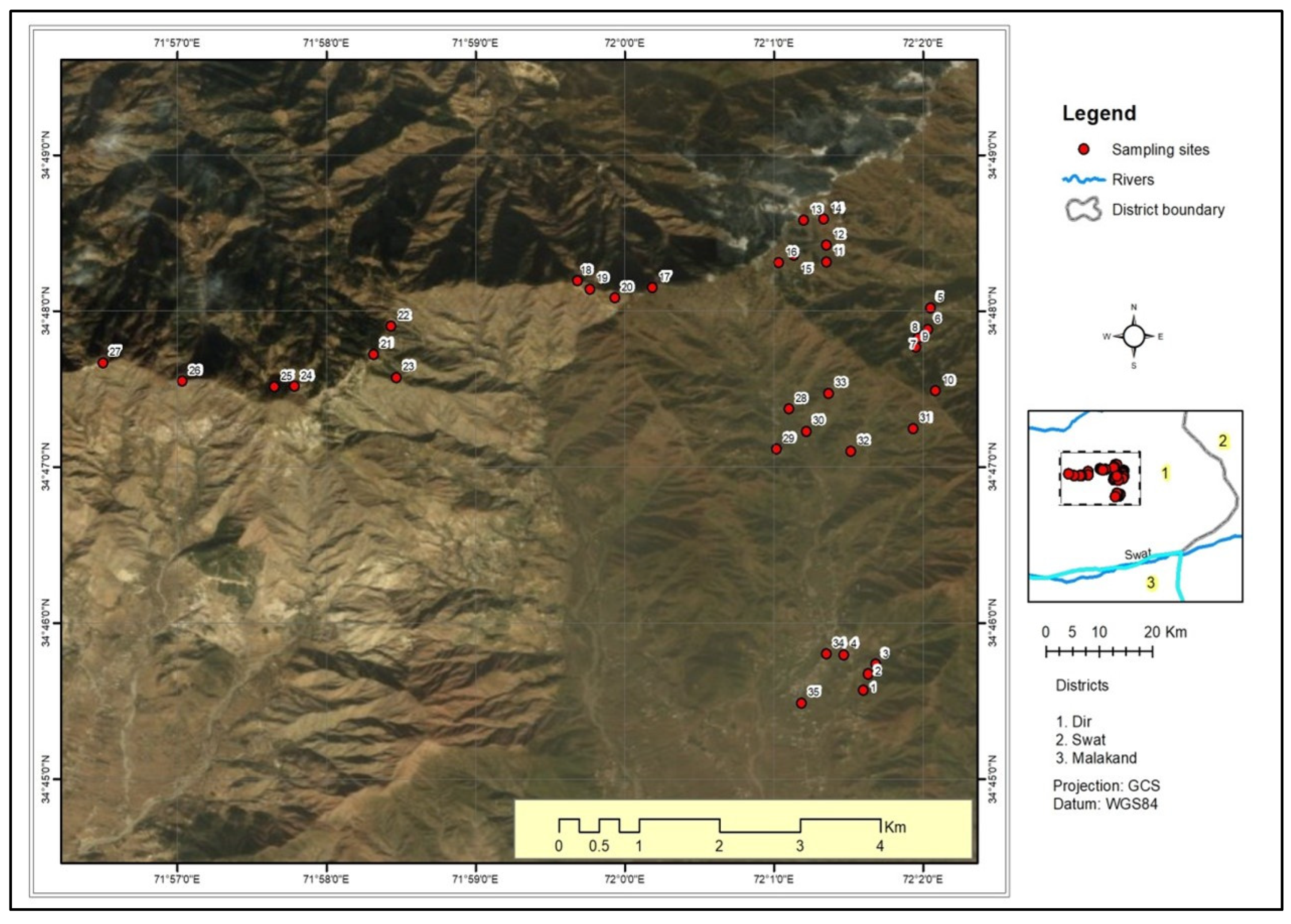
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Quantity Assessment
2.5. Health Risk
3. Results
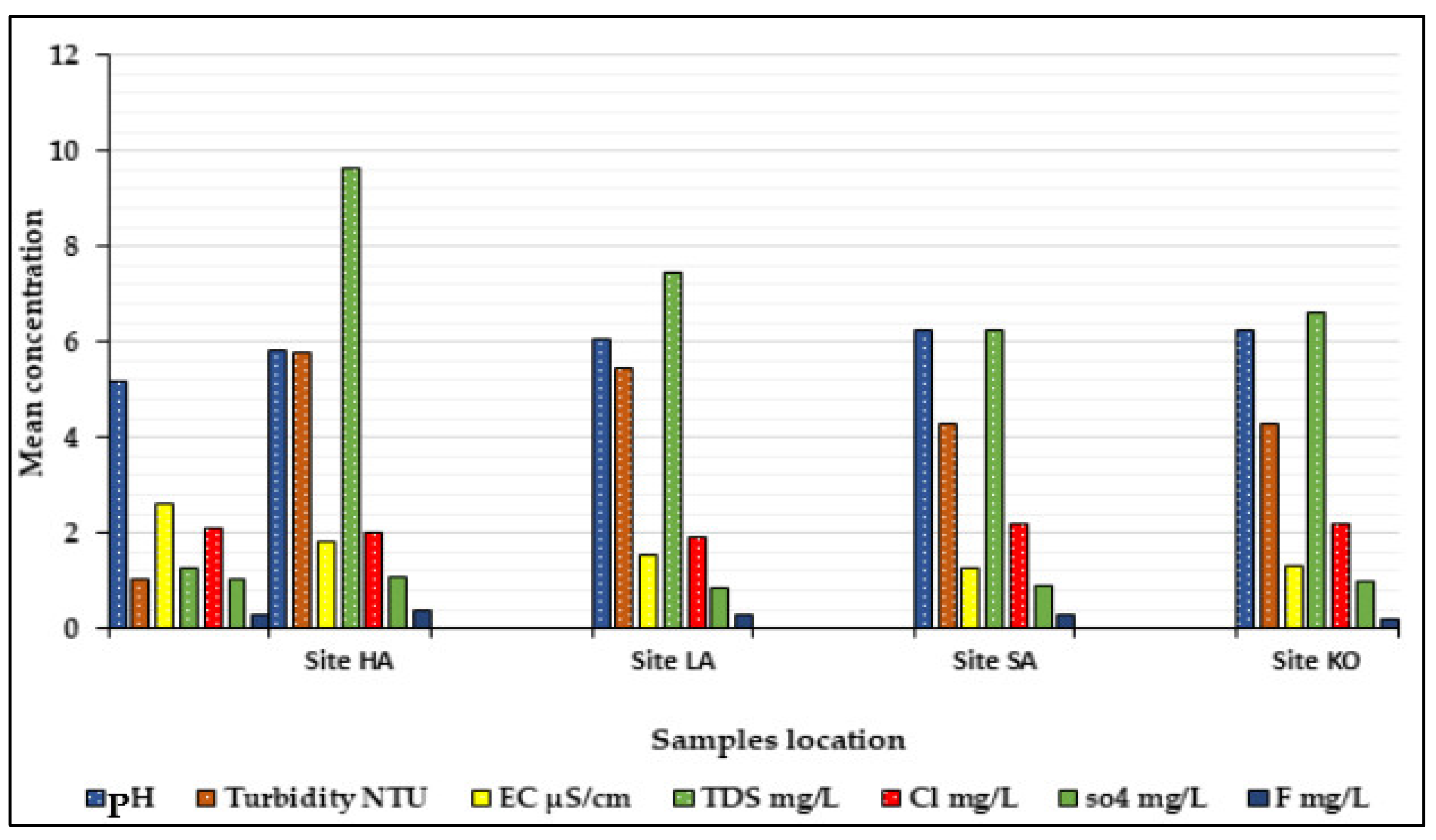
3.1. Qualitative Assessment
| Statistic | PH | Turbidity NTU | EC µS/cm | TDS mg/L | Cl mg/L | SO4 mg/L | F mg/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locations | WHO | 6.5–8.5 | 5 | 400 | 1000 | 250 | 250 | 1.5 |
| Site SI | Mean | 5.18 | 1.05 | 2.62 | 1.28 | 2.12 | 1.04 | 0.3 |
| SD | 1.27 | 6.17 | 2.66 | 1.26 | 8.58 | 0.12 | 0.14 | |
| Site HA | Mean | 5.82 | 5.77 | 1.82 | 9.62 | 2.01 | 1.07 | 0.39 |
| SD | 0.91 | 5.76 | 1.01 | 4.93 | 6.35 | 0.19 | 0.13 | |
| Site LA | Mean | 6.05 | 5.45 | 1.52 | 7.45 | 1.92 | 0.84 | 0.29 |
| SD | 0.88 | 6.95 | 1.23 | 5.78 | 1.01 | 0.16 | 0.13 | |
| Site SA | Mean | 6.22 | 4.27 | 1.25 | 6.26 | 2.18 | 0.91 | 0.3 |
| SD | 0.73 | 5.96 | 1.04 | 5.16 | 9.09 | 0.21 | 0.15 | |
| Site KO | Mean | 6.26 | 4.29 | 1.32 | 6.61 | 2.2 | 0.99 | 0.21 |
| SD | 0.39 | 4.68 | 2.11 | 8.32 | 4.72 | 0.19 | 0.12 |
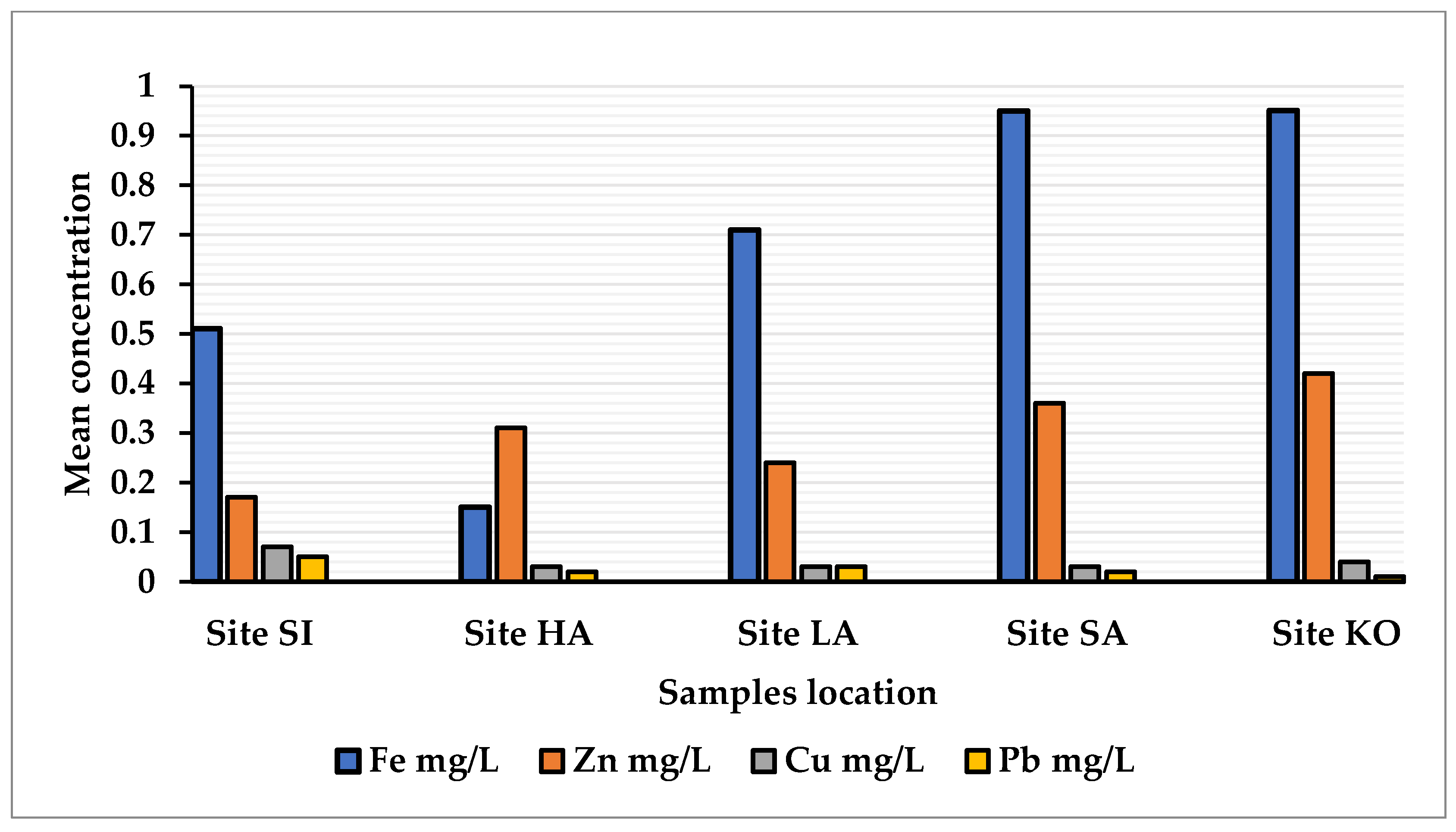
3.2. Heavy Metals Analysis
| Locations | Statistic | Fe mg/L | Zn mg/L | Cu mg/L | Pb mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO | 0.3 | 5 | 1.3 | 0.015 | |
| Site SI | Range | 0.16–0.93 | 0.08–0.29 | 0.03–0.01 | 0.01–0.10 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.51 ± 0.27 | 0.17 ± 0.074 | 0.07 ± 0.021 | 0.05 ± 0.035 | |
| Site HA | Range | 0.05–0.40 | 0.16–0.44 | 0.01–0.05 | 0.003–0.04 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.15 ± 0.11 | 0.31 ± 0.098 | 0.03 ± 0.014 | 0.02 ± 0.014 | |
| Site LA | Range | 0.49–1.20 | 0.12–0.40 | 0.01–0.05 | 0.01–0.08 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.71 ± 0.23 | 0.24 ± 0.097 | 0.03 ± 0.013 | 0.03 ± 0.022 | |
| Site SA | Range | 0.57–1.27 | 0.19–0.62 | 0.01–0.07 | 0.006–0.07 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.95 ± 0.24 | 0.36 ± 0.14 | 0.03 ± 0.021 | 0.02 ± 0.021 | |
| Site KO | Range | 0.91–0.97 | 0.29–0.48 | 0.02–0.06 | 0.01–0.03 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.95 ± 0.021 | 0.42 ± 0.066 | 0.04 ± 0.015 | 0.01 ± 0.005 |
3.3. Health Risk Assessment
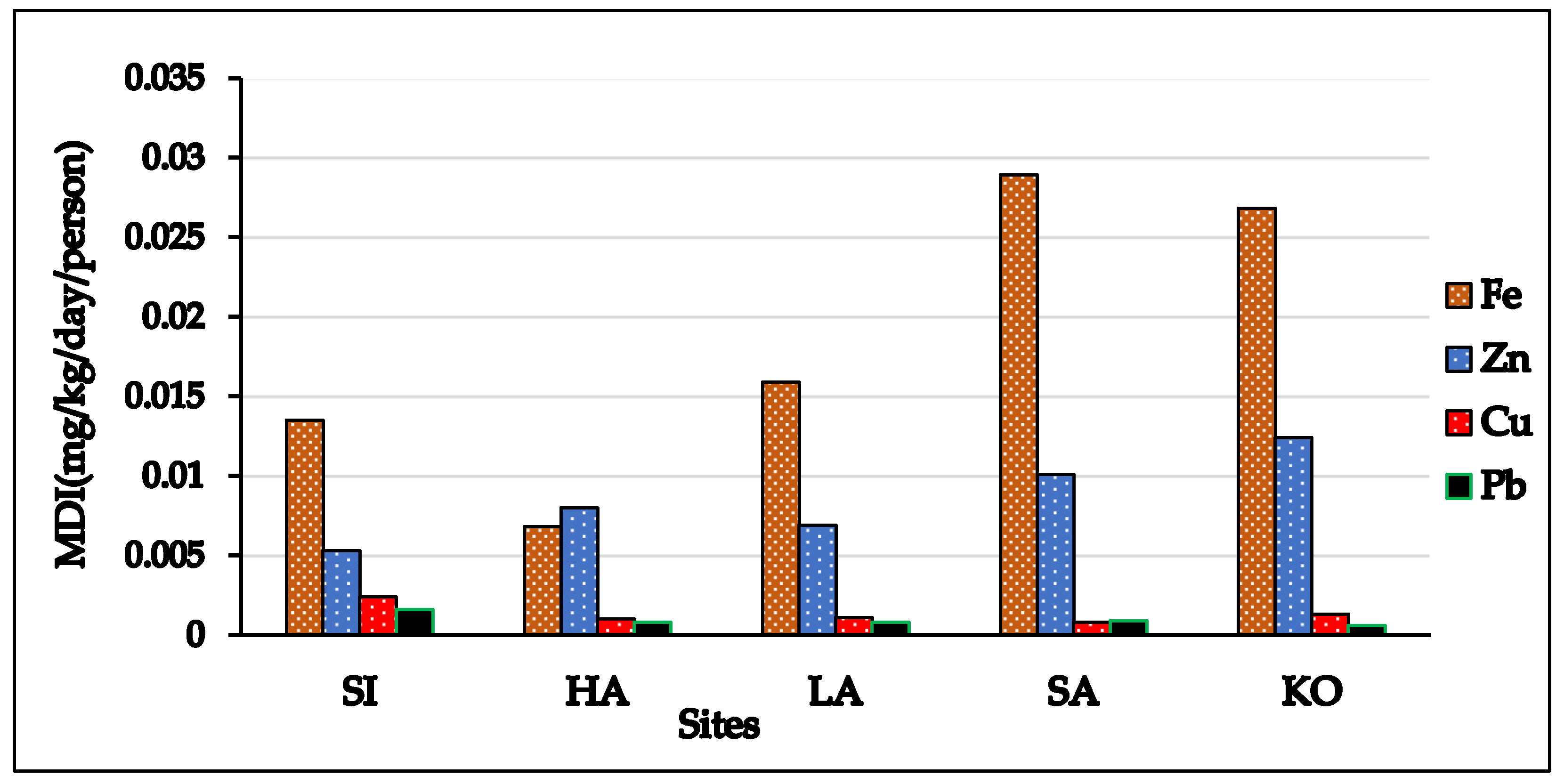
3.3.1. Maximum Daily Intake (MDI)
| Locations | Statistic | Fe | Zn | Cu | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site SI | Range | 0.004–0.02 | 0.002–0.008 | 0.001–0.003 | 0.0005–0.003 |
| Mean | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.001 | |
| Site HA | Range | 0.001–0.02 | 0.002–0.001 | 0.0004–0.001 | 0.0004–0.001 |
| Mean | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.0008 | |
| Site LA | Range | 0.003–0.021 | 0.003–0.01 | 0.0007–0.001 | 0.0001–0.002 |
| Mean | 0.01 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.0008 | |
| Site SA | Range | 0.01–0.03 | 0.005–0.01 | 0.0004–0.002 | 0.0002–0.002 |
| Mean | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.0008 | 0.0009 | |
| Site KO | Range | 0.02–0.028 | 0.008–0.01 | 0.0007–0.001 | 0.0004–0.0009 |
| Mean | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.0006 |
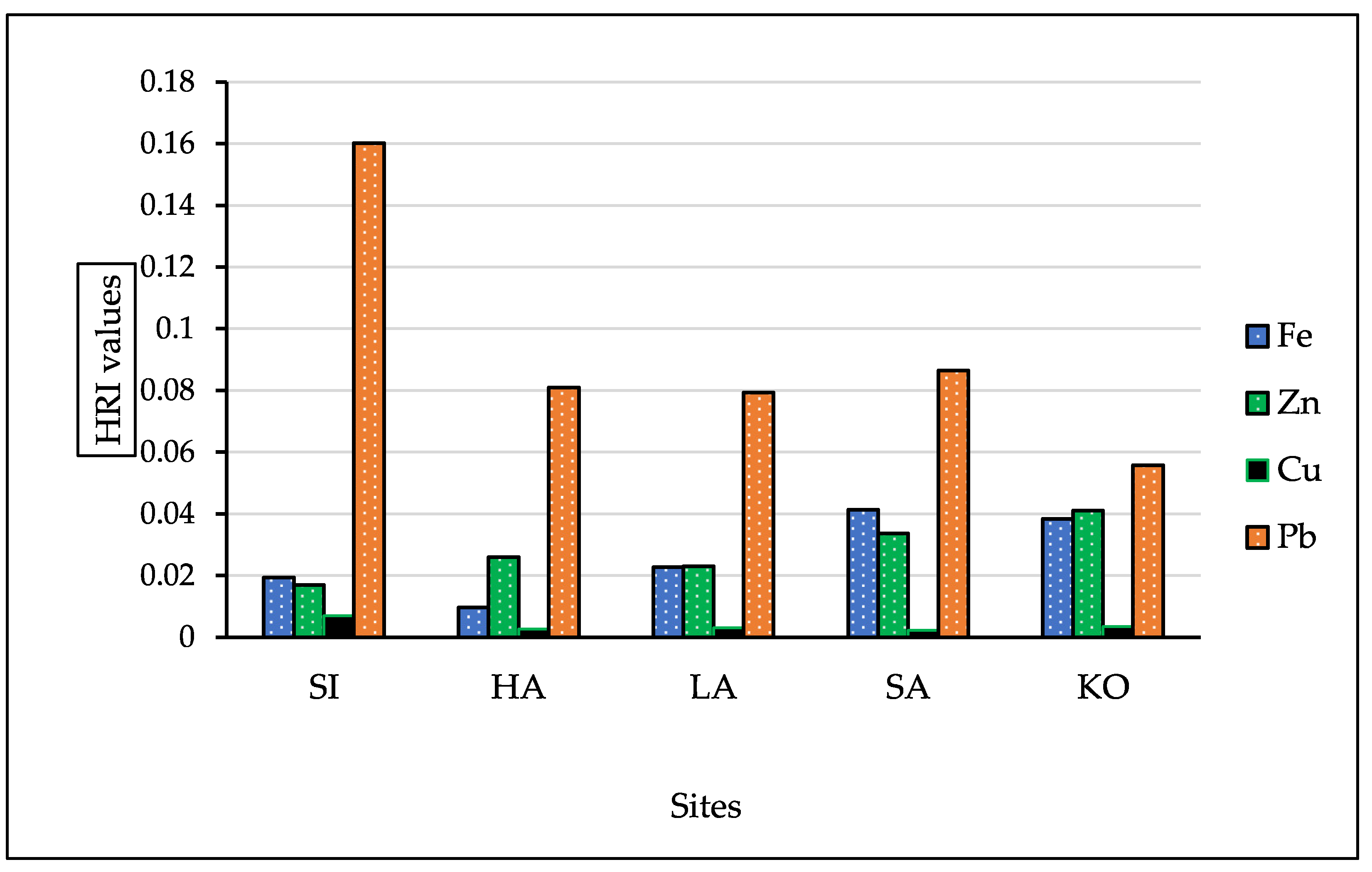
3.3.2. Health Risk Index (HRI)
| Locations | Statistic | Fe | Zn | Cu | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site SI | Range | 6.7 − 03–3.8 − 02 | 8.2 − 03–2.7 − 02 | 5.0 − 03–8.0 − 03 | 4.6 − 02–3.01 − 01 |
| Mean ± SD | 1.9 ± 02 | 1.7 ± 02 | 7.0 ± 03 | 1.6 ± 01 | |
| Site HA | Range | 2.4 − 03–3.0 − 02 | 9.6 − 03–4.2 − 02 | 1.2 − 03–3.7 − 03 | 3.7 − 02–1.3 − 01 |
| Mean ± SD | 9.7 ± 02 | 2.6 ± 02 | 2.7 ± 03 | 8.0 ± 02 | |
| Site LA | Range | 5.1 − 03–3.0 − 02 | 1.2 − 02–3.5 − 02 | 1.9 − 03–4.6 − 03 | 9.4 − 03–2.2 − 01 |
| Mean ± SD | 2.2 ± 02 | 2.3 ± 02 | 3.0 ± 03 | 7.9 ± 02 | |
| Site SA | Range | 2.3 − 02–5.2 − 02 | 1.8 − 02–5.9 − 02 | 1.0 − 03–5.9 − 03 | 1.8 − 02–1.9 − 01 |
| Mean ± SD | 4.1 ± 02 | 3.3 ± − 02 | 2.2 ± 03 | 8.6 ± 02 | |
| Site KO | Range | 3.3 − 02–3.9 − 02 | 2.8 − 02–4.6 − 02 | 1.9 − 03–5.2 − 03 | 3.9 − 02–8.5 − 02 |
| Mean ± SD | 3.8 ± 02 | 4.1 ± 02 | 3.4 ± 03 | 5.5 ± 02 |
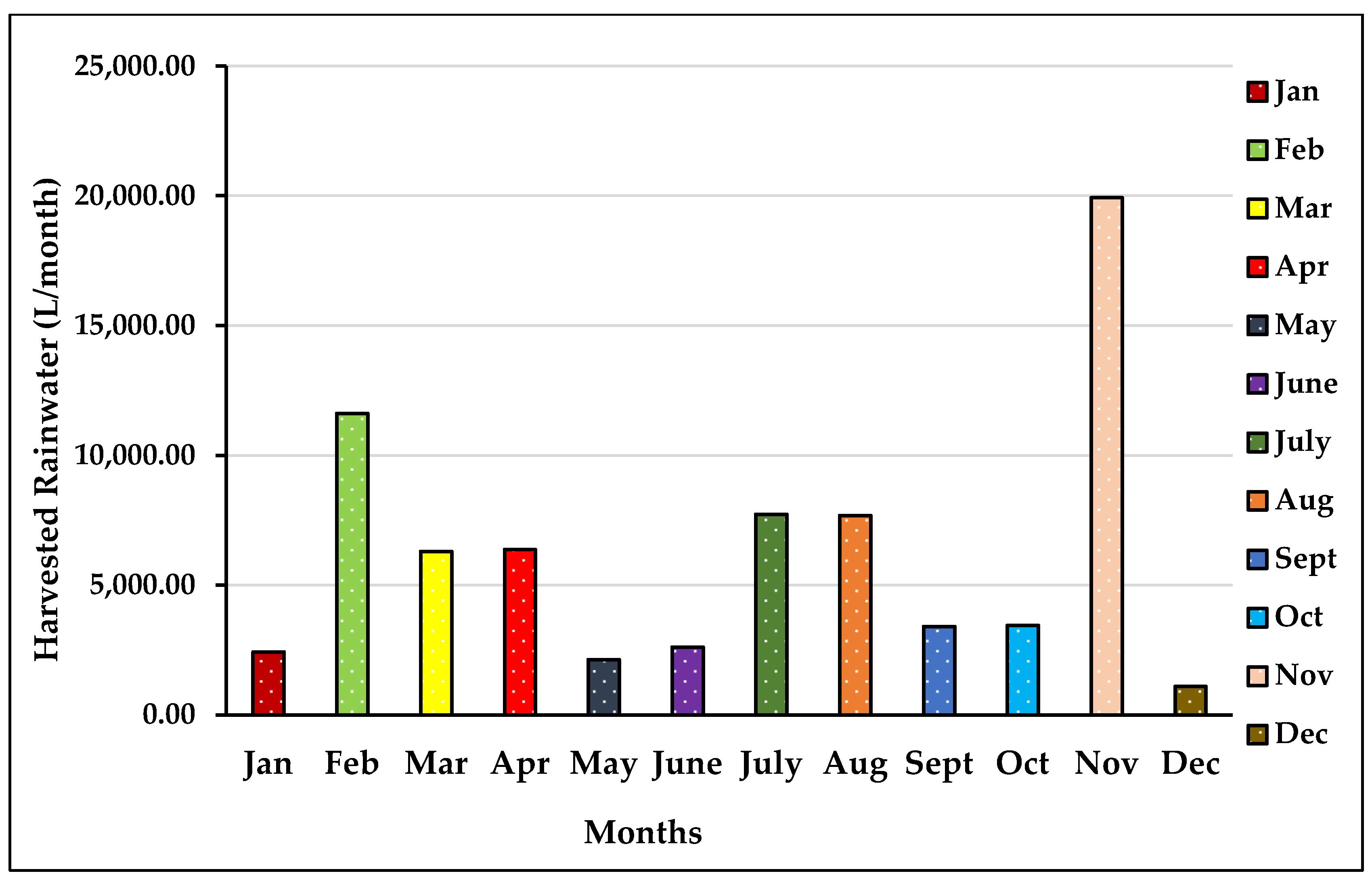
3.4. Quantitative Assessment
| Months | Average Monthly Rainfall (mm) | Average Roof Area (m2) | Runoff Coefficient | Monthly Harvested Rainwater (L/month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 38 | 80 | 0.8 | 2432 |
| Feb | 181.66 | 80 | 0.8 | 11,626.24 |
| Mar | 98.35 | 80 | 0.8 | 6294.4 |
| Apr | 99.66 | 80 | 0.8 | 6378.24 |
| May | 33.25 | 80 | 0.8 | 2128 |
| June | 40.83 | 80 | 0.8 | 2613.12 |
| July | 120.86 | 80 | 0.8 | 7735.04 |
| Aug | 120.16 | 80 | 0.8 | 7690.24 |
| Sept | 53.3 | 80 | 0.8 | 3411.2 |
| Oct | 54 | 80 | 0.8 | 3456 |
| Nov | 30.33 | 80 | 0.8 | 1941.12 |
| Dec | 17.16 | 80 | 0.8 | 1098.24 |
| Total | 887.56 | - | - | 56,803.84 |
| Average | 73.96 | - | - | 4733.65 |
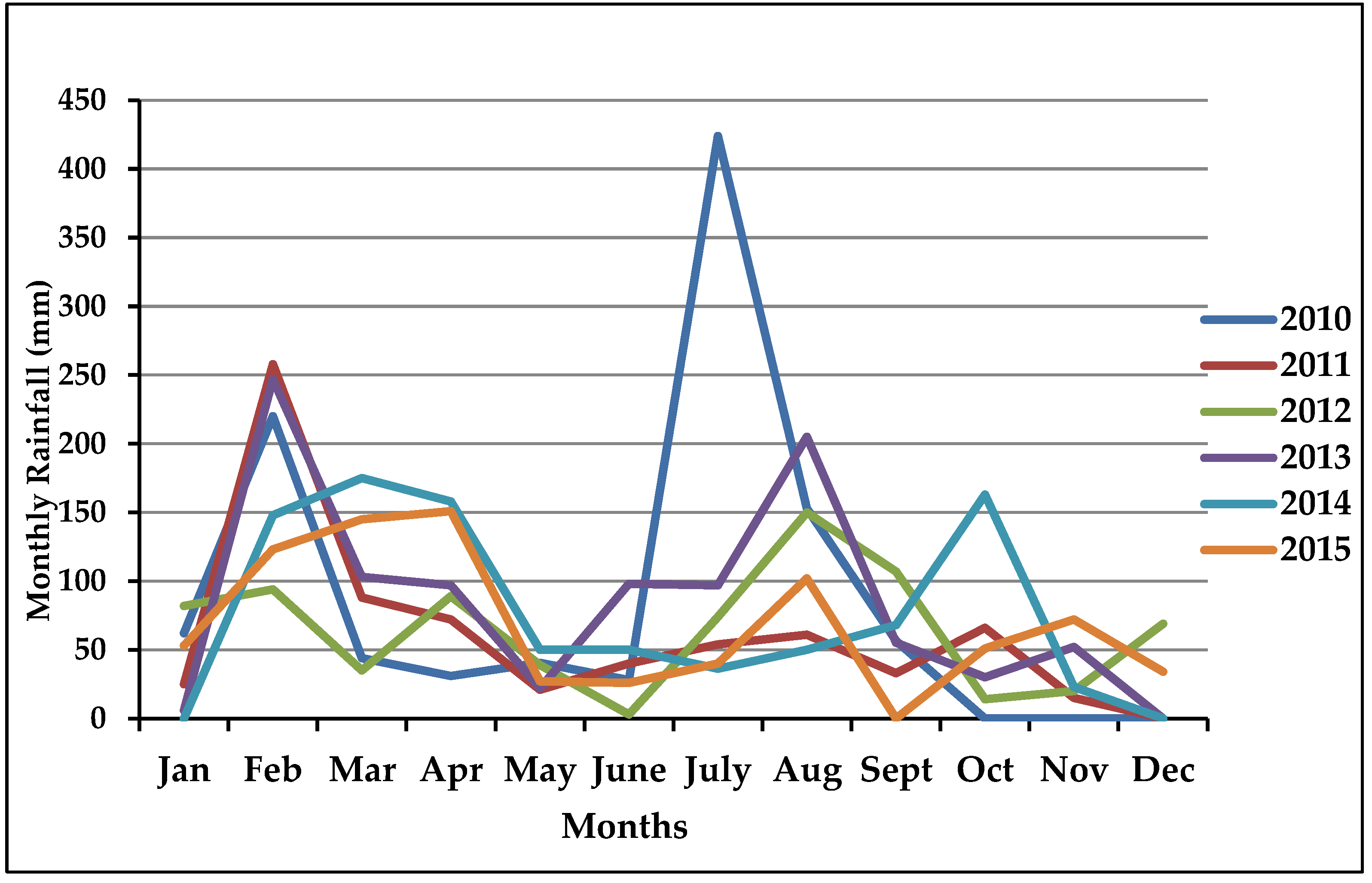
3.4.1. Monthly Rainfall
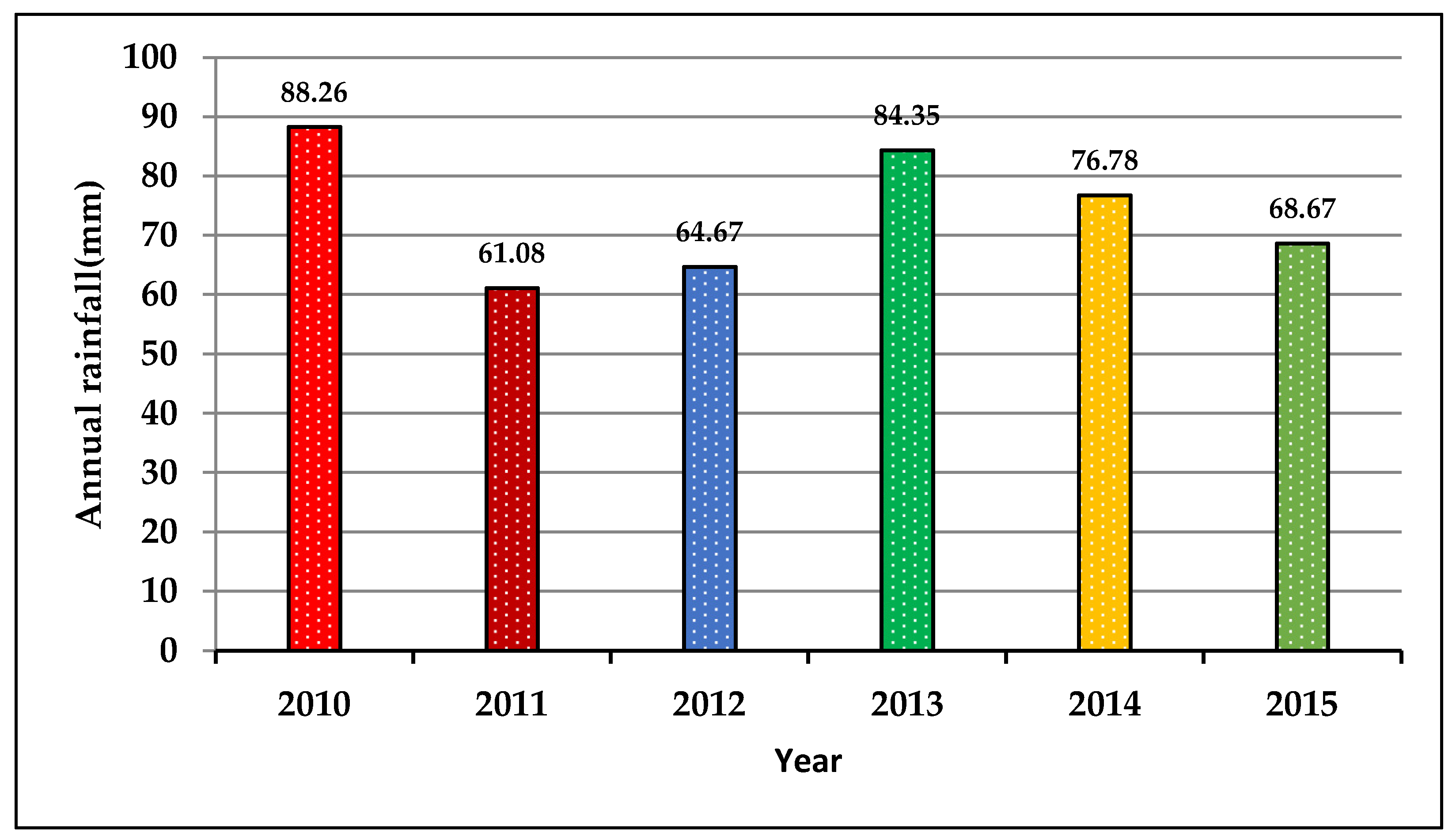
3.4.2. Annual Rainfall
3.4.3. Rainwater-Harvesting Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lasage, R.; Verburg, P.H. Evaluation of small scale water harvesting techniques for semi-arid environments. J. Arid Environ. 2015, 118, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisano, A.; Butler, D.; Ward, S.; Burns, M.J.; Friedler, E.; DeBusk, K.; Fisher-Jeffes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Rahman, A.; Furumai, H.; et al. Urban rainwater harvesting systems: Research, implementation and future perspectives. Water Res. 2017, 115, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, E.; Isazadeh, M.; Samadianfard, S.; Ramli, M.F.; Mosavi, A.; Nabipour, N.; Shamshirband, S.; Hajnal, E.; Chau, K.W. Groundwater quality assessment for sustainable drinking and irrigation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liaw, C.H.; Chiang, Y.C. Dimensionless analysis for designing domestic rainwater harvesting systems at the regional level in Northern Taiwan. Water 2014, 6, 3913–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mays, L.W. Survey of ancient water technologies in semi-arid and arid regions: Traditional knowledge for the future. Water Supply 2017, 17, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, W.; Gardner, T.; Toze, S. Microbiological quality of roof-harvested rainwater and health risks: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishna, H.J.; Brown, C.; Gerston, J.; Colley, S. The Texas Manual on Rainwater Harvesting, 3rd ed.; Texas Water Development Board: Austin, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kus, B.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S.; Shon, H.K. Analysis of first flush to improve the water quality in rainwater tanks. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, R.; Kamel, A.Z.; Adnan, A.H.; Rida, A.A. Quality Assessment of Harvested Roof Top Rainwater for Domestic Uses. Environ. Earth Sci. 2008, 6, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Quality_Assessment_of_Harvested_Rainwater_for_Domestic_Uses. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268047323_ (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Ubuoh, E.A. Susceptibility of Roofing Sheets to Atmospheric-Borne Corrosive Agents in Owerri, Nigeria. Int. People-Ware Appl. Gatew. Anal. Learn. 2012, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Susceptibility of Roofing Sheets to Atmospheric-Borne Corrosive Agents in Owerri, Nigeria. International People-ware Appliance for Gateway to Analytical Learning (Pakistan). Available online: https://www.bing.com/search?q=Ubuoh%2C+E.+A.+(2012).+Susceptibility+of+Roofing+Sheets+to+Atmospheric-Borne+Corrosive+Agents+in+Owerri%2C+Nigeria‖.+International+People-ware+Appliance+for+Gateway+to+Analytical+Learning+(Pakistan)%2C+1%2C+1-10.&cvid=bc3ae91 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Cheng, C.L.; Liao, M.C. Regional rainfall level zoning for rainwater harvesting systems in northern Taiwan. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 53, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbinosa, I.H.; Osemwengie, O.V. On-site assessment of environmental and sanitary qualities of Rainwater Harvesting System (RWH) in a rural community in Benin City, Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2016, 20, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meera, V.; Ahammed, M.M. Factors Affecting the Quality of Roof-Harvested Rainwater; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Boyle, F.; Reynolds, A. Rainwater harvesting and greywater treatment systems for domestic application in Ireland. Desalination 2010, 260, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S.A. Sources of pollution in rooftop rainwater harvesting systems and their control. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 2097–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flues, M.; Hama, P.; Lemes, M.J.L.; Dantas, E.S.K.; Fornaro, A. Evaluation of the rainwater acidity of a rural region due to a coal-fired power plant in Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyar, M.I.; Mitchell, V.G.; Ladson, A.; Diaper, C. Determining the sediment dynamics in a rainwater tank. In Novatech 2007-6ème Conférence sur les techniques et stratégies durables pour la gestion des eaux urbaines par temps de pluie/Sixth International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies in Urban Water Management; GRAIE: Lyon, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.Y.; Mun, J.S. Particle behaviour consideration to maximize the settling capacity of rainwater storage tanks. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schets, F.M.; Italiaander, R.; Van Den Berg, H.H.J.L.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Rainwater harvesting: Quality assessment and utilization in The Netherlands. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; McBroom, M.W.; Beasley, R.S. Roofing as a source of nonpoint water pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 73, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.A.; Parrish, K.; Ahmed, W.; Haas, C.N. Assessment of water quality in roof-harvested rainwater barrels in greater Philadelphia. Water 2018, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, X.; Chen, W.; Avand, M.; Janizadeh, S.; Kariminejad, N.; Shahabi, H.; Costache, R.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Mosavi, A. GIS-based machine learning algorithms for gully erosion susceptibility mapping in a semi-arid region of Iran. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, S.S.; Janizadeh, S.; Chandra Pal, S.; Saha, A.; Chakrabortty, R.; Melesse, A.M.; Mosavi, A. Flash flood susceptibility modeling using new approaches of hybrid and ensemble tree-based machine learning algorithms. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubin, B.; Mosavi, A.; Alamdarloo, E.H.; Hosseini, F.S.; Shamshirband, S.; Dashtekian, K.; Ghamisi, P. Earth fissure hazard prediction using machine learning models. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, S.N.; Samadianfard, S.; Sadri Nahand, H.; Mosavi, A.; Shamshirband, S.; Chau, K.W. Estimating daily dew point temperature using machine learning algorithms. Water 2019, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosavi, A.; Sajedi Hosseini, F.; Choubin, B.; Goodarzi, M.; Dineva, A.A.; Rafiei Sardooi, E. Ensemble boosting and bagging based machine learning models for groundwater potential prediction. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, S.; Samadianfard, S.; Sattari, M.T.; Mosavi, A.; Shamshirband, S.; Kmet, T.; Várkonyi-Kóczy, A.R. Modeling pan evaporation using Gaussian process regression K-nearest neighbors’ random forest and support vector machines; comparative analysis. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeniyi, I.F.; Olabanji, I.O. The physico-chemical and bacteriological quality of rainwater collected over different roofing materials in Ile-Ife, southwestern Nigeria. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 21, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.; Kim, N.D.; Johnston, D.M.; Nayyerloo, M. Health Hazards Associated with Consumption of Roof-Collected Rainwater in Urban Areas in Emergency Situations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gikas, G.D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Assessment of water quality of first-flush roof runoff and harvested rainwater. J. Hydrol. 2012, 466–467, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, F.A.; Al-Shareef, A.W. Roof rainwater harvesting systems for household water supply in Jordan. Desalination 2009, 243, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCuen, R.H. Hydrologic Analysis and Design; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004; p. 790. [Google Scholar]
- Viessman, W.J., Jr.; Lewis, G.L. (Eds.) Introduction to Hydrology; Harper Collins College: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 9780673993373. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Introduction-Hydrology-5th-Warren-Viessman/dp/067399337X (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Angrill, S.; Petit-Boix, A.; Morales-Pinzón, T.; Josa, A.; Rieradevall, J.; Gabarrell, X. Urban rainwater runoff quantity and quality—A potential endogenous resource in cities? J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 189, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aladenola, O.O.; Adeboye, O.B. Assessing the potential for rainwater harvesting. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, J.; Qamar, U.; Contijoch, M.; Amir, P.; Blackmore, D. Pakistan’s Water Economy: Running Dry; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.A.; Akber, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Kabir, M.P. Evaluation of harvested rainwater quality at primary schools of southwest coastal Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igbinosa, I.H.; Aighewi, I.T. Quality assessment and public health status of harvested rainwater in a peri-urban community in Edo State of Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguma, D.; Loiskandl, W.; Jung, H. Water Management, Rainwater Harvesting and Predictive Variables in Rural Households. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3333–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Hasan, Z.; Li, Z.; Zuberi, A.; Zorriehzahra, M.J.; Nabi, G. Diversity and community composition of ichthyofauna at Konhaye Stream, district Dir Lower, Pakistan. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2020, 19, 2322–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmal, M. Hand Pumps’ Water Quality Analysis for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes at District Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Eur. Acad. Res. 2014, 2, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; No. 6000; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisi, E.; Montibeller, A.; Schmidt, R.W. Potential for potable water savings by using rainwater: An analysis over 62 cities in southern Brazil. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bak, G.; Han, M. Quality of roof-harvested rainwater—Comparison of different roofing materials. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.H.; Martinson, D.B. Roofwater Harvesting: A Handbook for Practitioners; International Water and Sanitation Centre: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, S.; Shah, M.T.; Khan, S. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and their source apportionment in drinking water of Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchem. J. 2011, 98, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scope, C. Guidance for Performing Aggregate Exposure and Risk Assessments; No. 202; Office of Pesticide Programs-Environmental Protection Agency: Arlington, VA, USA, 1999.
- Shittu, O.B.; Olaitan, J.O.; Amusa, T.S. Physico-chemical and bacteriological analyses of water used for drinking and swimming purposes in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2010, 11, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salam, M.; Alam, F.; Hossain, M.; Saeed, M.A.; Khan, T.; Zarin, K.; Rwan, B.; Ullah, W.; Khan, W.; Khan, O. Assessing the drinking water quality of educational institutions at selected locations of district Swat, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, C.B.; Klenzendorf, J.B.; Afshar, B.R.; Simmons, M.T.; Barrett, M.E.; Kinney, K.A.; Kirisits, M.J. The effect of roofing material on the quality of harvested rainwater. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggal, K.N. Element of Environmental Engineering Water Quality Analysis, Ram Nagar, New Delhi; Channel and Company Ltd.: Westborough, MA, USA, 2004; Available online: https://pdfgoal.com/downloads/elements_of_environmental_engineering_pdf_by_k_duggal (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Meera, V.; Ahammed, M.M. Water quality of rooftop rainwater harvesting systems: A review. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2006, 55, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhang, L.; Hart, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, H. Quality issues in harvested rainwater in arid and semi-arid Loess Plateau of northern China. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 57, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevondo, T.S.; Cloete, T.E. Bacterial and chemical quality of water supply in the Dertig village settlement. Water 1999, 25, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khatib, I.A.; Arafeh, G.A.; Al-Qutob, M.; Jodeh, S.; Hasan, A.R.; Jodeh, D.; van der Valk, M. Health risk associated with some trace and some heavy metals content of harvested rainwater in Yatta area, Palestine. Water 2019, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eletta, O.A.A.; Oyeyipo, J.O. Rainwater harvesting: Effect of age of roof on water quality. Int. J. Appl. Chem. 2008, 4, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Lamprea, K.; Ruban, V. Characterization of atmospheric deposition and runoff water in a small suburban catchment. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Ni, S. Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Chou, F.N.F.; Kabir, M.R.; Liaw, C.H. Rainwater: A Potential Alternative Source for Scarce Safe Drinking and Arsenic Contaminated Water in Bangladesh. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3987–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.P. Leaching of lead from new unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (uPVC) pipes into drinking water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 8405–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J. Is rainwater safe to drink? A review of recent findings. In Proceedings of the 9th International Rainwater Catchment Systems Conference, Petrolina, Brazil, 6–9 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Lead—ToxFAQs. 2007. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/dcs/ContactUs/Form (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Yousaf, S.; Begum, S.; Afridi, I.; Shakil, M.; Tariq, M. Assessment of drinking water quality and human health risks in the tehsils of Jamrud and Landikotal, Khyber Agency, Pakistan. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2016, 49, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Traboulsi, H.; Traboulsi, M. Rooftop level rainwater harvesting system. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taher, T.M. Quantity and Quality Considerations of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting as a Substantial Resource to Face Water Supply Shortages. Int. J. Water Resour. Arid Environ. 2014, 3, 1–10. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306058157_Quantity_and_Quality_Considerations_of_Rooftop_Rainwater_Harvesting_as_a_Substantial_Resource_to_Face_Water_Supply_Shortages (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Qin, M.M.; Chen, D.; Averyt, Z.R.; Miller, K.B.; Solomon, H.L.; Manning, S.C.; Marquis, M.R.; Tignor, M. IPCC, 2007: Summary for Policymakers. 2007. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/IPCC%2C-2007%3A-Summary-for-Policymakers-Qin-Chen/8109ccb13ca3c75354bbaaf9f7e0c825b438eb44 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Woltersdorf, L.; Liehr, S.; Döll, P. Rainwater Harvesting for Small-Holder Horticulture in Namibia: Design of garden variants and assessment of climate change impacts and adaptation. Water 2015, 7, 1402–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otti, V.I.; Ezenwaji, E.E. Enhancing community-driven initiative in rainwater harvesting in Nigeria. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 3, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, B.K.; Mandal, B.H. Construction and Evaluation of Rainwater Harvesting System for Domestic Use in a Remote and Rural Area of Khulna. Bangladesh ISRN Otolaryngol. 2014, 2014, 751952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmreich, B.; Horn, H. Opportunities in rainwater harvesting. Desalination 2009, 248, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shittu, O.I.; Okareh, O.T.; Coker, A.O. Development of rainwater harvesting technology for securing domestic water supply in Ibadan, Nigeria. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, L.F.S.; Terencio, D.P.S.; Racheco, F.A.L. Rainwater harvesting systems for low demanding applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 529, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rawan, B.; Ullah, W.; Ullah, R.; Akbar, T.A.; Ayaz, Z.; Javed, M.F.; Din, I.; Ullah, S.; Aziz, M.; Mohamed, A.; et al. Assessments of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in Disctrict Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Water 2022, 14, 3270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203270
Rawan B, Ullah W, Ullah R, Akbar TA, Ayaz Z, Javed MF, Din I, Ullah S, Aziz M, Mohamed A, et al. Assessments of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in Disctrict Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Water. 2022; 14(20):3270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203270
Chicago/Turabian StyleRawan, Bakht, Waheed Ullah, Rafi Ullah, Tahir Ali Akbar, Zainab Ayaz, Muhammad Faisal Javed, Islamud Din, Siddique Ullah, Mubashir Aziz, Abdullah Mohamed, and et al. 2022. "Assessments of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in Disctrict Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan" Water 14, no. 20: 3270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203270
APA StyleRawan, B., Ullah, W., Ullah, R., Akbar, T. A., Ayaz, Z., Javed, M. F., Din, I., Ullah, S., Aziz, M., Mohamed, A., Khan, N. A., & Khan, O. (2022). Assessments of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in Disctrict Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Water, 14(20), 3270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203270






