Coastal Soil Salinity Amelioration and Crop Yield Improvement by Biomaterial Addition in East China
Abstract
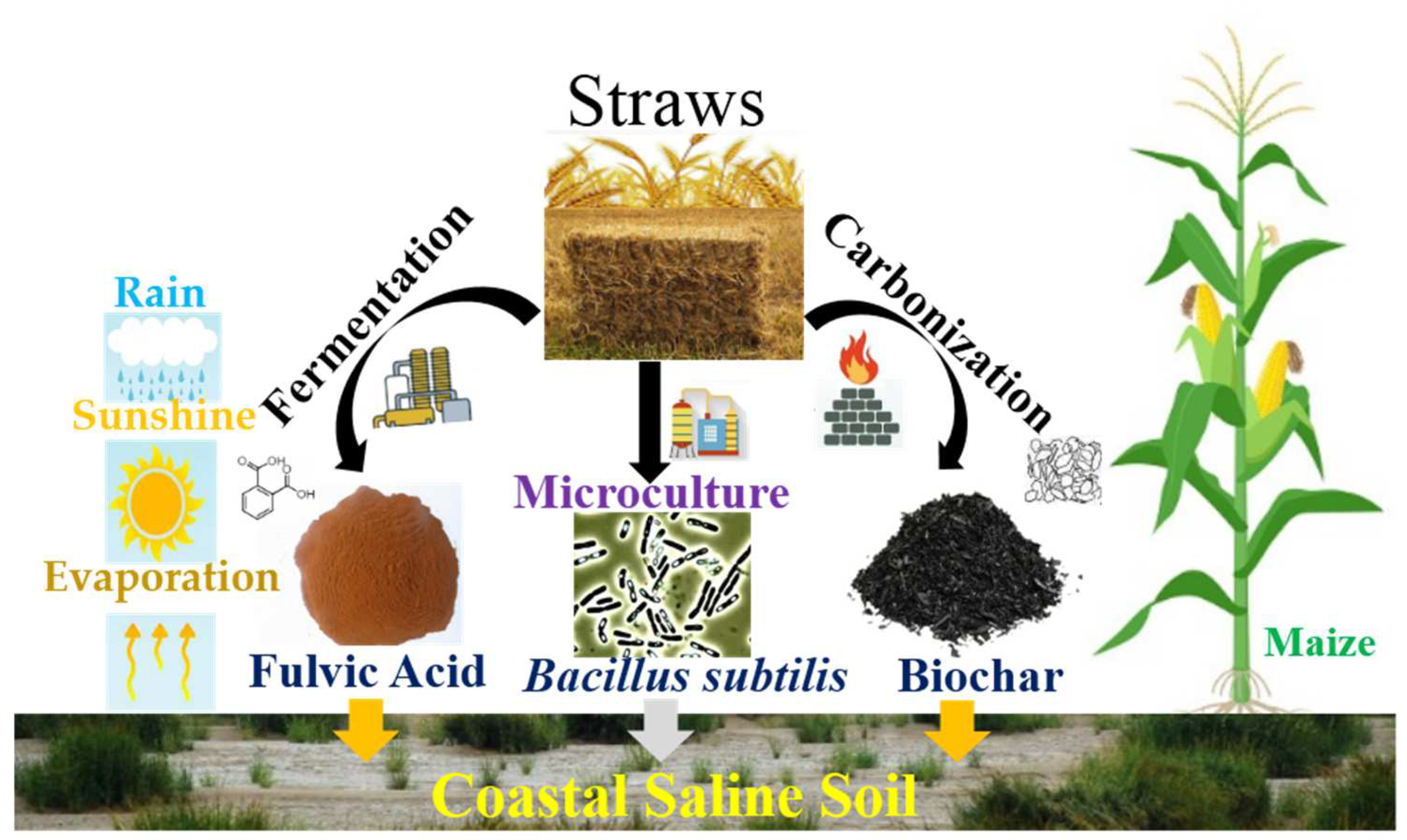
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Soil
2.2. Characterization of Biochar, Fulvic Acid and Bacillus Subtilis
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sampling, Measurements and Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties
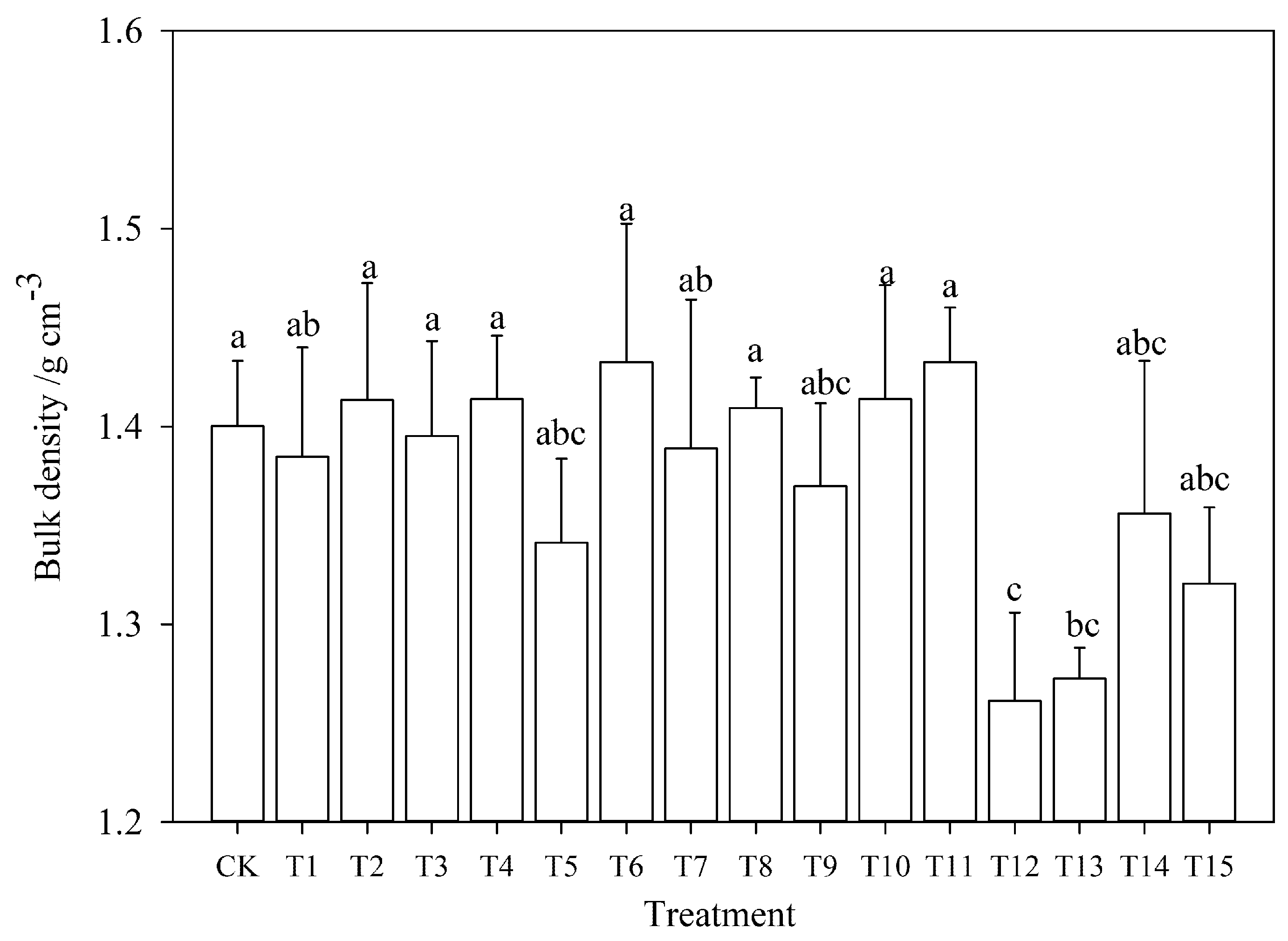
3.1.1. Soil Bulk Density
3.1.2. Soil Water Content, Saturated Water Content, Capillary Water Holding Capacity, Soil Porosity
3.1.3. EC, pH
3.2. SOC
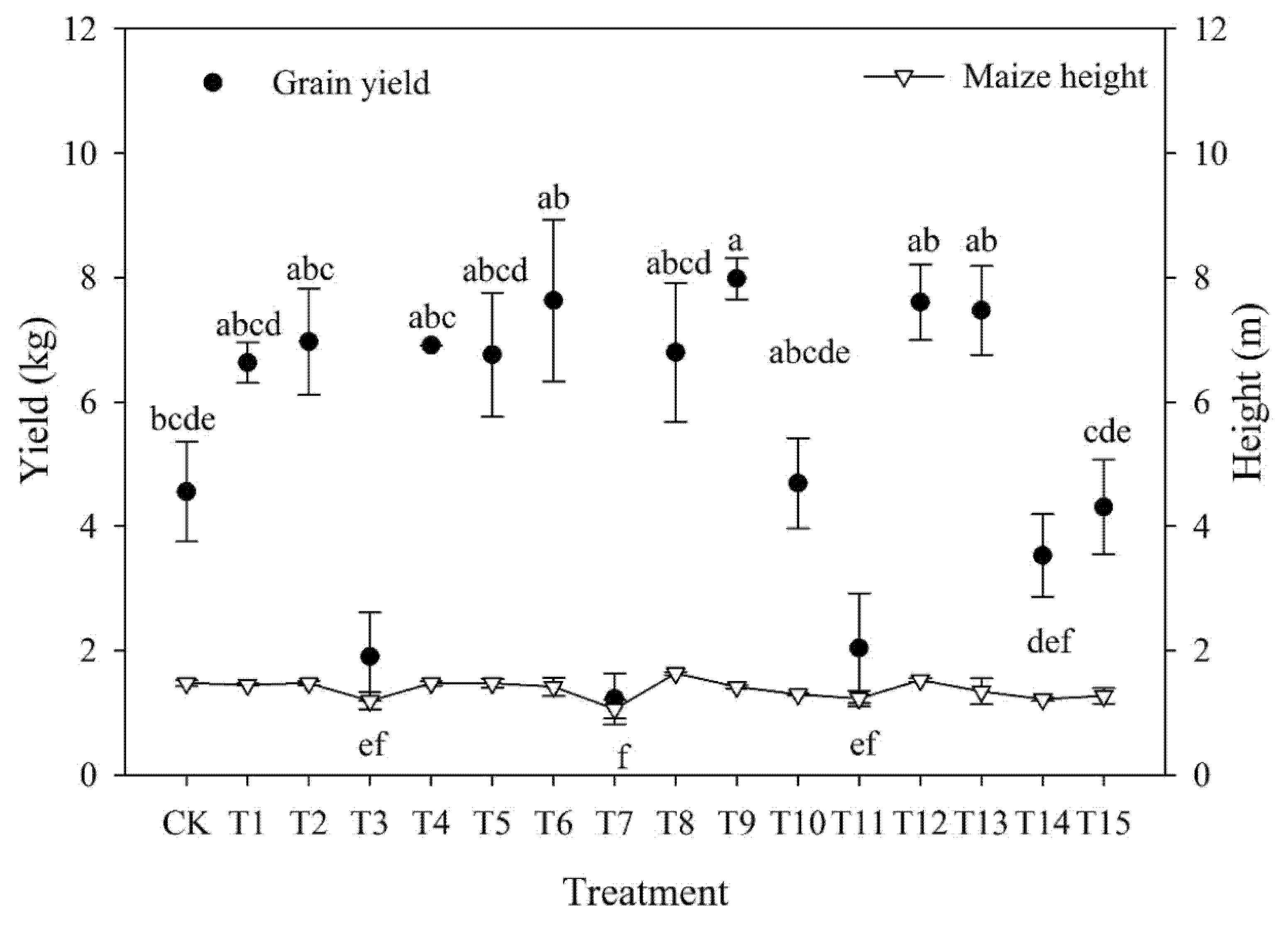
3.3. Plant Height and Grain Yield
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maomao, H.; Xiaohou, S.; Yaming, Z. Effects of Different Regulatory Methods on Improvement of Greenhouse Saline Soils, Tomato Quality, and Yield. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 953675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Effect of Soil Salinity and Sodicity with and Without Soil Conditioner (polyacrylamide) on the Seedling Emergence and Growth of Different Wheat Varieties. Pak. J. Appl. Sci. 2002, 2, 631–636. [CrossRef]
- Kant, C.; Aydin, A.; Turan, M. Ameliorative Effect of Hydro Gel Substrate on Growth, Inorganic Ions, Proline, and Nitrate Contents of Bean under Salinity Stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1420–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: An Introduction. In Biochar for Environmental Management: Science and Technology; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 1–9. ISBN 9781844076581. [Google Scholar]
- Slavich, P.G.; Sinclair, K.; Morris, S.G.; Kimber, S.W.L.; Downie, A.; Van Zwieten, L. Contrasting effects of manure and green waste biochars on the properties of an acidic ferralsol and productivity of a subtropical pasture. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Xu, R.-K.; Zhang, H. The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3488–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishchik, V.N.; Vorobyev, N.I.; Moiseev, K.G.; Sviridova, O.V.; Surin, V.G. Influence of Bacillus subtilis on the physiological state of wheat and the microbial community of the soil under different rates of nitrogen fertilizers. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Balaraju, K.; Park, K.-S.; Nam, K.-W.; Park, J.-W.; Park, K. Growth promotion and induced disease suppression of four vegetable crops by a selected plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) strain Bacillus subtilis 21-1 under two different soil conditions. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bauddh, K.; Barman, S.; Singh, R.P. Amendments of microbial biofertilizers and organic substances reduces requirement of urea and DAP with enhanced nutrient availability and productivity of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.B.; Istock, C.A. Gene Exchange and Natural Selection Cause Bacillus subtilis to Evolve in Soil Culture. Science 1979, 204, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashio, S.; Morishita, H. Salt-resistant Bacillusin Salty Natto. Jpn. J. Food Microbiol. 1997, 14, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, A.; Shackley, S.; Joseph, S.; Hammond, J.; Pan, G.; Bloom, A.A. Competing uses for China’s straw: The economic and carbon abatement potential of biochar. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Xiao, Z.; Xiao, H.; Xia, T.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, F. Revelation of the early responses of salt tolerance in maize via SSH libraries. Genes Genom. 2012, 34, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildrim, E.; Donmez, M.F.; Turan, M. Use of Bioinoculants in Ameliorative Effects on Radish Plants Under Salinity Stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Analytical Methods of Soil and Agricultural Chemistry; Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 30–32. ISBN 9787109066441. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Fan, F.; Liao, Y. Long-term effect of biochar application on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions in a rice paddy cropping system: A four-year case study in south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandian, K.; Subramaniayan, P.; Gnasekaran, P.; Chitraputhirapillai, S. Effect of biochar amendment on soil physical, chemical and biological properties and groundnut yield in rainfed Alfisol of semi-arid tropics. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 1293–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, L.D.; Zehetner, F.; Rampazzo, N.; Wimmer, B.; Soja, G. Long-term effects of biochar on soil physical properties. Geoderma 2016, 282, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, J.W.; Xu, H.J.; Zhou, C.J.; Wang, S.Q.; Xing, G.X. Effects of crop-straw biochar on crop growth and soil fertility over a wheat-millet rotation in soils of China. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, W.; Fu, J.; Pan, G.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Effects of amendment of biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution on soil quality and wheat yield of a salt-stressed cropland from Central China Great Plain. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quin, P.; Cowie, A.; Flavel, R.; Keen, B.; Macdonald, L.; Morris, S.; Singh, B.; Young, I.; Van Zwieten, L. Oil mallee biochar improves soil structural properties—A study with x-ray micro-CT. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, L.R.; Reid, B.J.; Tang, X. Quantifying the influence of biochar on the physical and hydrological properties of dissimilar soils. Geoderma 2014, 235, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Caiji, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Ren, T.; Gai, X.; Xi, B.; Liu, H. Short-term effects of maize residue biochar on phosphorus availability in two soils with different phosphorus sorption capacities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, S.; Hottle, R.D.; Lal, R. Effects of Biochar and Anaerobic Digester Effluent on Soil Quality and Crop Growth in Karnataka, India. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jinghua, W.; Erda, L. The impacts of potential climate change and climate variability on simulated maize production in China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1996, 92, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, E.W.; Petersen, C.T.; Hansen, E.H.; Holm, J.K.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Biochar amendment to coarse sandy subsoil improves root growth and increases water retention. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.Y.; Kim, H.; Chen, J.J.; Kim, Y. Effects of Biochar Addition on Nitrogen Leaching and Soil Structure following Fertilizer Application to Rice Paddy Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 78, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, K.P.; George, D.; Swift, R.S.; Galea, V. The Influence of Biochar on Growth of Lettuce and Potato. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Li, G.-T.; Lin, Q.-M.; Zhao, X.-R. Crop Yield and Soil Properties in the First 3 Years After Biochar Application to a Calcareous Soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, B.; Chang, S.X.; Gong, J. Biochar addition affected the dynamics of ammonia oxidizers and nitrification in microcosms of a coastal alkaline soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, L.M.; Farrell, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Krull, E.S. Plant growth responses to biochar addition: An Australian soils perspective. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, M.; Clothier, B.; Bound, S.; Oliver, G.; Close, D. Does biochar influence soil physical properties and soil water availability? Plant Soil 2014, 376, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merante, P.; Dibari, C.; Ferrise, R.; Sánchez, B.; Iglesias, A.; Lesschen, J.P.; Kuikman, P.; Yeluripati, J.; Smith, P.; Bindi, M. Adopting soil organic carbon management practices in soils of varying quality: Implications and perspectives in Europe. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Priya, B.N.V.; Mahavishnan, K.; Gurumurthy, D.S.; Bindumadhava, H.; Ambika, P.U.; Navin, K.S. Fulvic Acid (FA) for Enhanced Nutrient Uptake and Growth: Insights from Biochemical and Genomic Studies. J. Crop Improv. 2014, 28, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutigliano, F.; Romano, M.; Marzaioli, R.; Baglivo, I.; Baronti, S.; Miglietta, F.; Castaldi, S. Effect of biochar addition on soil microbial community in a wheat crop. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 60, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X.-Y.; Tian, Y.; Gong, X.-Q. Biochar and humic acid amendments improve the quality of composted green waste as a growth medium for the ornamental plant Calathea insignis. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 176, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Pan, G.; Hussain, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X. Effect of biochar amendment on maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions from a soil organic carbon poor calcareous loamy soil from Central China Plain. Plant Soil 2012, 351, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, H.M.; Sharma, R.P. Long-Term Effect of Fertilizers and Amendments on Different Fractions of Organic Matter in an Acid Alfisol. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummadi, S.; Kadiyala, M.; Rao, K.; Athanasiadis, I.; Mulwa, R.; Kilavi, M.; Legesse, G.; Amede, T. Simulating adaptation strategies to offset potential impacts of climate variability and change on maize yields in Embu County, Kenya. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zheng, X.-Q.; Hu, F.; Li, H.-X.; Kong, B.; Wang, L.-L.; Sui, Y.-Y. Effect of temperature, rainfall and soil properties on farmland soil nitrification. Huanjing Kexue 2009, 30, 206–213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Feng, S.; Ma, J.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, C. Irrigation management for spring maize grown on saline soil based on SWAP model. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welde, K.; Gebremariam, H.L. Effect of different furrow and plant spacing on yield and water use efficiency of maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanckaert, J.; Pannecoucque, J.; VAN Waes, J.; DE Cauwer, B.; Latre, J.; Haesaert, G.; Reheul, D. Harvest date does not influence variety ranking in Belgian forage maize variety trials. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 154, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, B.A.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Eid, A.R.; Badr, E.A. Effect of Humic Acid, Mycorrhiza Inoculation, and Biochar on Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Flax under Newly Reclaimed Sandy Soil. Agric. Sci. 2014, 5, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Meng, J.; Liang, H.; Yang, E.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Jiang, L.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J. Effect of volatile organic compounds absorbed to fresh biochar on survival of Bacillus mucilaginosus and structure of soil microbial communities. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.N.; Martín, M.J.; Burguillo, F.J. A comparative study of the adsorption of humic acid, fulvic acid and phenol onto Bacillus subtilis and activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Medium | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar (t ha−1) | Fulvic Acid (1.5 t ha−1) | BS Suspension Soak Seed | |
| CK | 0 | N | N |
| T1 | 0 | N | Y |
| T2 | 0 | Y | N |
| T3 | 0 | Y | Y |
| T4 | 7.5 | N | N |
| T5 | 7.5 | N | Y |
| T6 | 7.5 | Y | N |
| T7 | 7.5 | Y | Y |
| T8 | 15 | N | N |
| T9 | 15 | N | Y |
| T10 | 15 | Y | N |
| T11 | 15 | Y | Y |
| T12 | 30 | N | N |
| T13 | 30 | N | Y |
| T14 | 30 | Y | N |
| T15 | 30 | Y | Y |
| Treatment | WC (%) | SWC (%) | CHC (%) | STP (%) | CP (%) | NP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 15.69 | 18.41 | 17.65 | 42.36 | 26.96 | 15.40 |
| T1 | 21.62 | 25.49 | 24.06 | 45.41 | 34.81 | 10.60 |
| T2 | 18.99 | 24.23 | 22.66 | 43.25 | 34.07 | 9.18 |
| T3 | 20.57 | 24.90 | 23.25 | 45.26 | 33.72 | 11.54 |
| T4 | 16.69 | 22.04 | 20.88 | 46.52 | 29.59 | 16.93 |
| T5 | 24.01 | 30.46 | 28.52 | 49.20 | 38.39 | 10.81 |
| T6 | 20.11 | 21.82 | 20.95 | 42.91 | 31.70 | 11.21 |
| T7 | 23.50 | 26.68 | 24.58 | 45.38 | 35.57 | 9.81 |
| T8 | 25.19 | 29.45 | 28.04 | 46.98 | 39.39 | 7.59 |
| T9 | 23.60 | 26.58 | 24.80 | 46.94 | 34.87 | 12.07 |
| T10 | 25.85 | 30.40 | 23.05 | 49.00 | 31.15 | 17.85 |
| T11 | 23.20 | 26.28 | 25.24 | 44.74 | 36.96 | 7.78 |
| T12 | 26.47 | 38.31 | 35.03 | 54.32 | 42.40 | 11.92 |
| T13 | 22.16 | 30.11 | 26.79 | 50.39 | 35.22 | 15.17 |
| T14 | 22.69 | 26.07 | 24.57 | 45.53 | 35.47 | 10.06 |
| T15 | 25.32 | 33.36 | 28.96 | 51.85 | 36.95 | 14.90 |
| Initial Value | 28.12 | 33.29 | 32.36 | 48.31 | 44.30 | 4.00 |
| Treatment | SOC1st (g kg−1) | SOC2nd (g kg−1) | SOC2nd–SOC1st (g kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | ||
| CK | 5.20 a | 0.43 | 4.67 abc | 0.07 | −0.53 |
| T1 | 3.63 cde | 0.74 | 4.33 ab | 0.67 | 0.70 |
| T2 | 3.42 cde | 1.22 | 4.72 abc | 0.28 | 1.30 |
| T3 | 3.43 cde | 1.38 | 4.09 bc | 0.64 | 0.66 |
| T4 | 4.09 abcd | 0.27 | 4.66 abc | 0.30 | 0.57 |
| T5 | 3.71 cde | 0.76 | 4.98 abc | 0.85 | 1.27 |
| T6 | 5.09 ab | 0.14 | 4.38 abc | 1.12 | −0.71 |
| T7 | 3.48 cde | 0.52 | 3.30 c | 0.89 | −0.18 |
| T8 | 4.13 abcd | 0.61 | 5.86 ab | 1.28 | 1.73 |
| T9 | 3.26 cde | 0.27 | 4.86 abc | 0.89 | 1.60 |
| T10 | 3.32 cde | 1.09 | 4.41 abc | 1.26 | 1.09 |
| T11 | 2.86 de | 0.76 | 5.21 ab | 1.12 | 2.35 |
| T12 | 3.60 cde | 0.22 | 6.20 a | 0.87 | 2.60 |
| T13 | 4.24 abc | 0.73 | 5.96 ab | 1.79 | 1.72 |
| T14 | 2.66 e | 1.20 | 5.55 ab | 2.46 | 2.89 |
| T15 | 3.86 bcde | 0.58 | 5.46 ab | 1.40 | 1.61 |
| F probability | * | ns | |||
| LSD (0.05) | 1.29 | - | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Luo, Y.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Zhang, X. Coastal Soil Salinity Amelioration and Crop Yield Improvement by Biomaterial Addition in East China. Water 2022, 14, 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203266
Sun Y, Chen X, Yang J, Luo Y, Yao R, Wang X, Xie W, Zhang X. Coastal Soil Salinity Amelioration and Crop Yield Improvement by Biomaterial Addition in East China. Water. 2022; 14(20):3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203266
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yunpeng, Xiaobing Chen, Jingsong Yang, Yongming Luo, Rongjiang Yao, Xiangping Wang, Wenping Xie, and Xin Zhang. 2022. "Coastal Soil Salinity Amelioration and Crop Yield Improvement by Biomaterial Addition in East China" Water 14, no. 20: 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203266






