Zooplankton Compositions in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, a Water Source for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
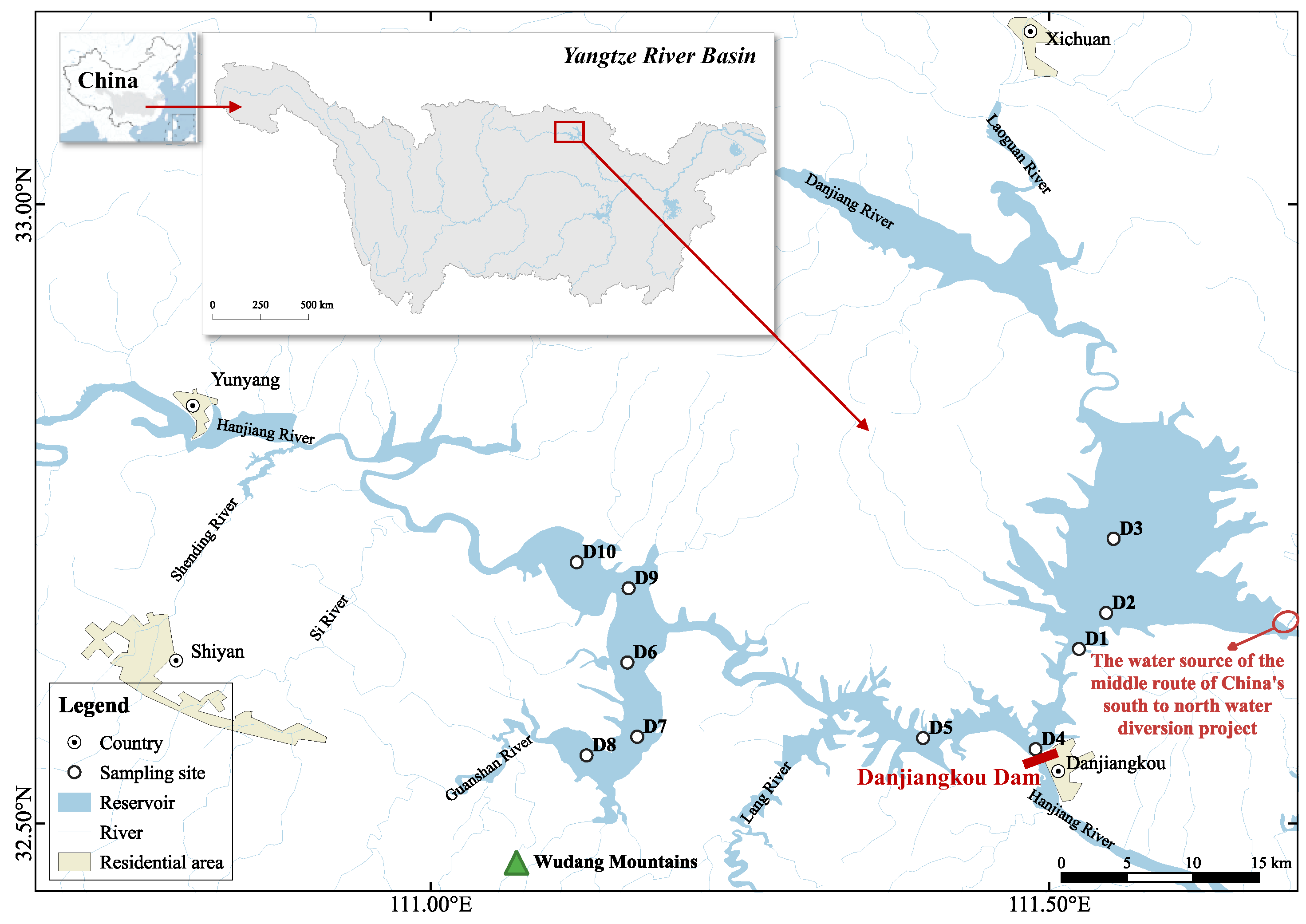
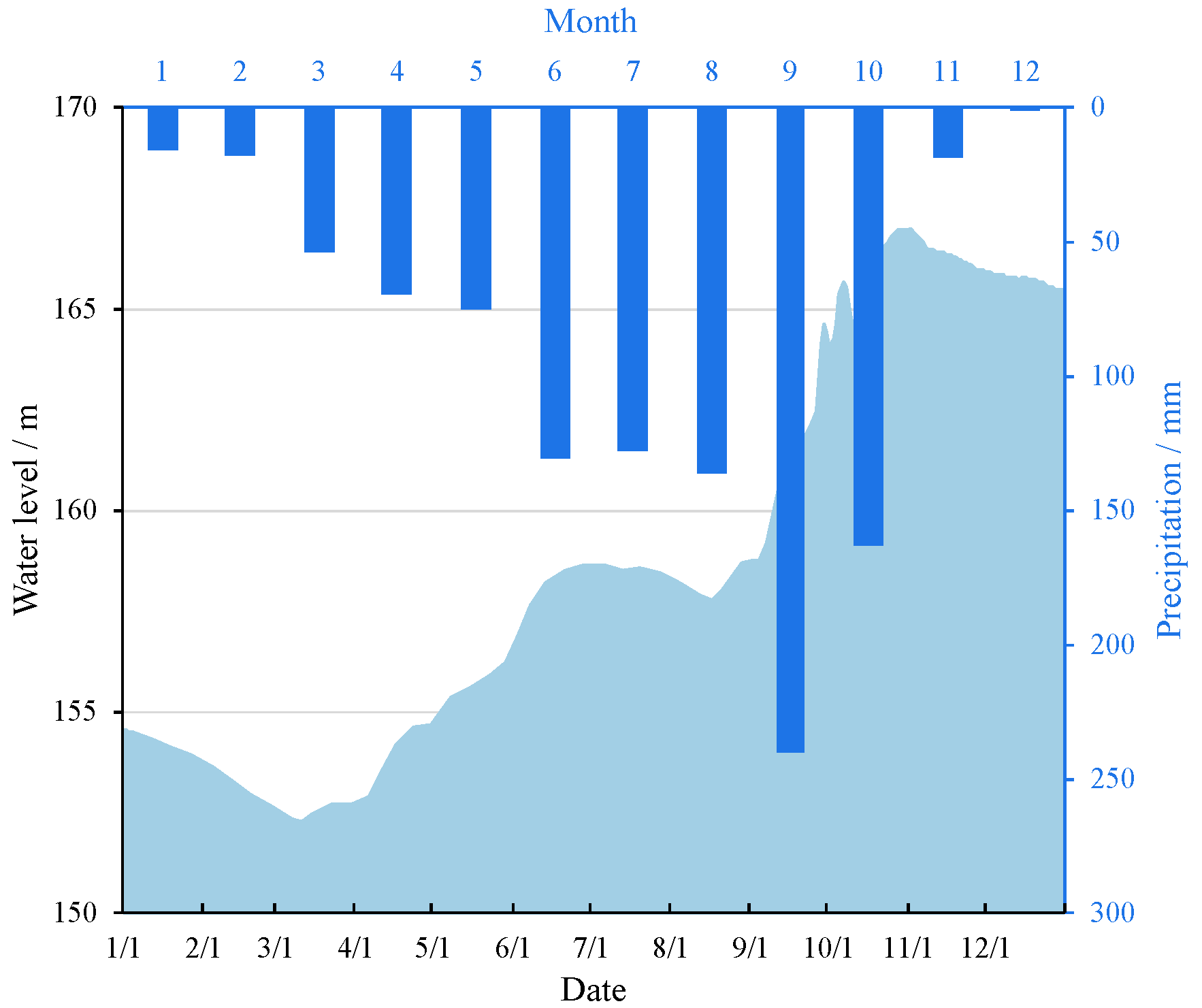
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.2. Sampling Methods and Analytical Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Zooplankton Composition and Biodiversity Indices
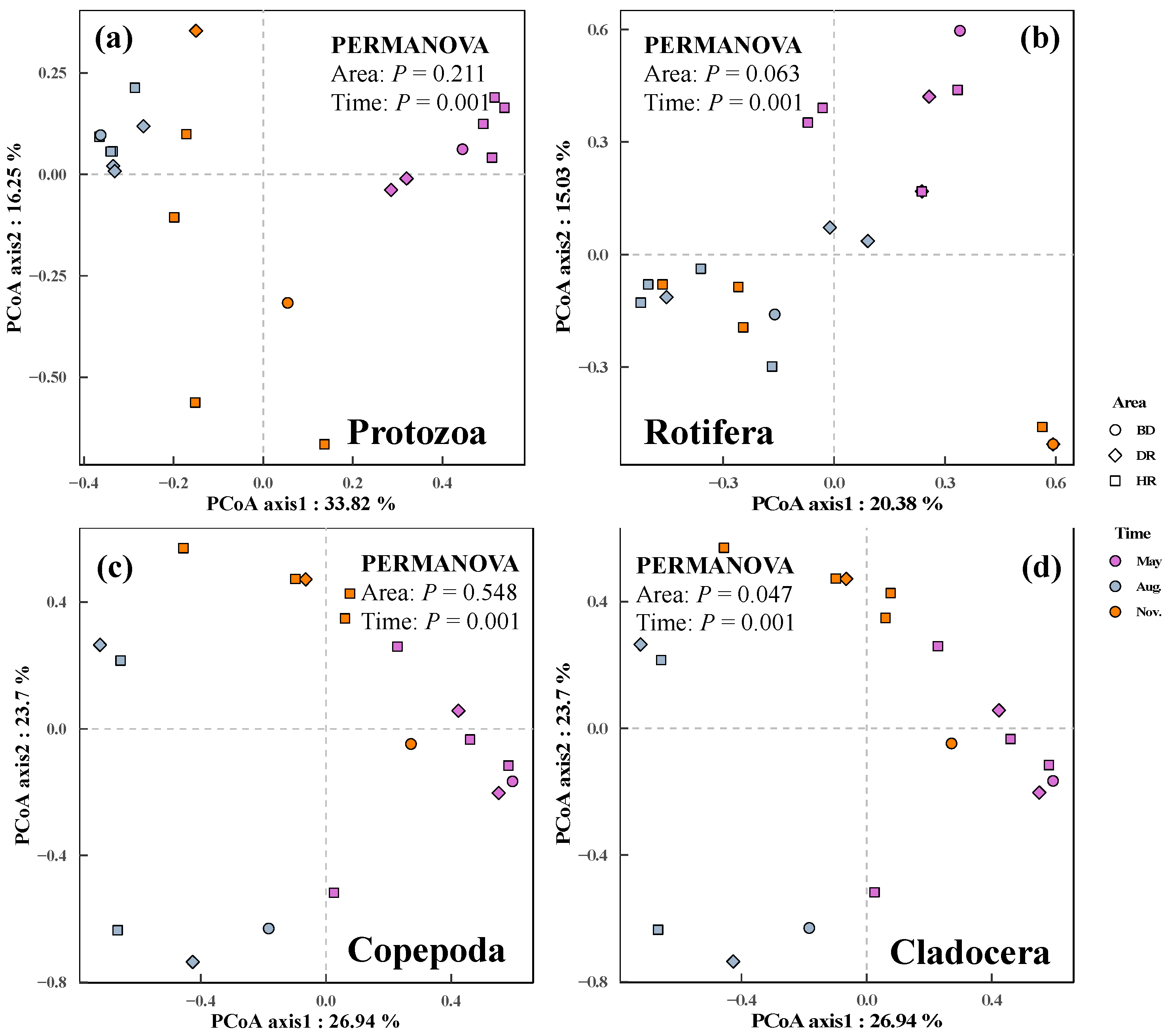
3.2. Changes in Zooplankton among Different Sampling Months and Areas
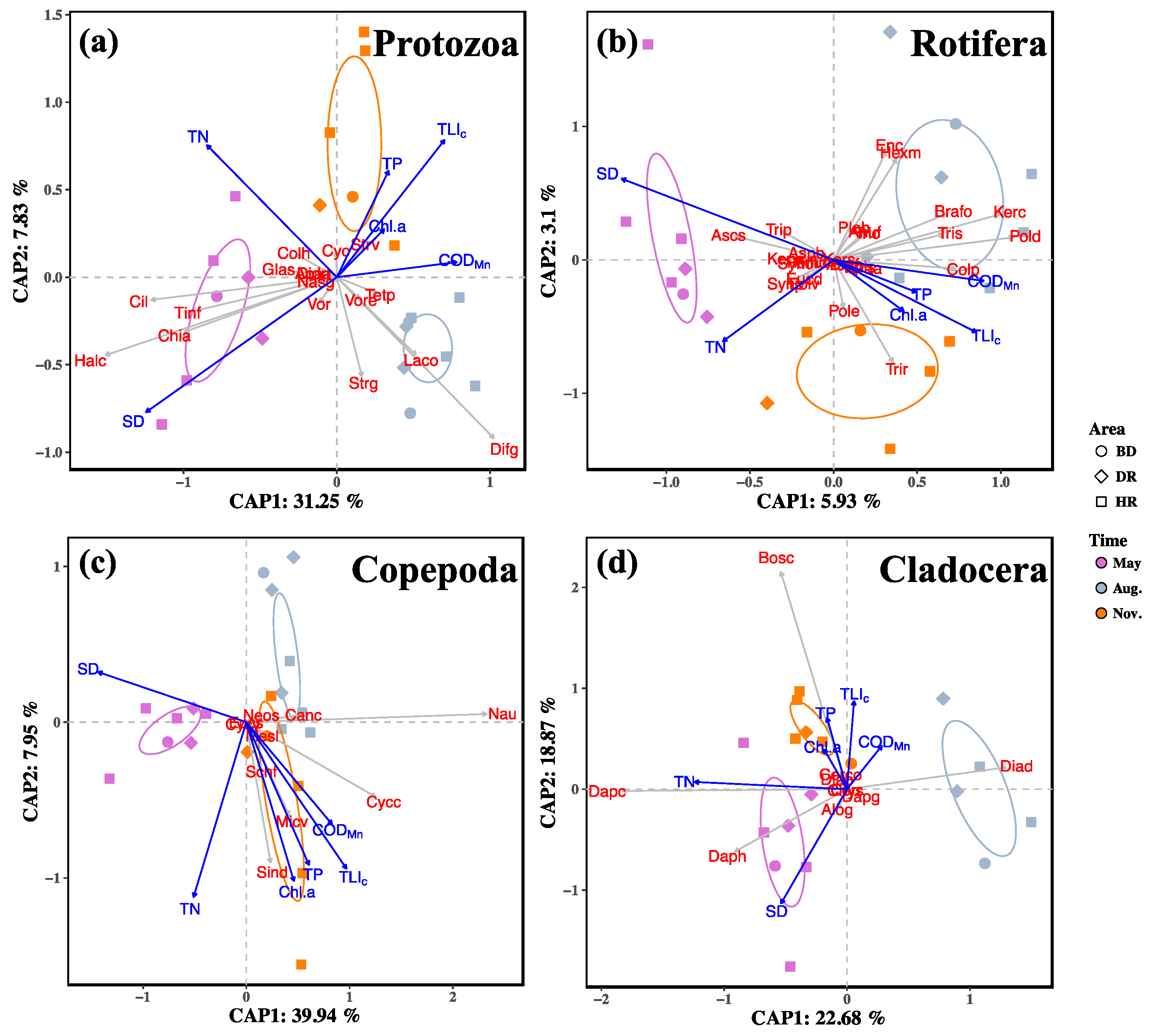
3.3. Zooplankton Functional Groups Composition
3.4. Relationships between Zooplankton and Water Trophic States
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of the Zooplankton Composition and Biodiversity
4.2. Changes of Zooplankton among the Sampling Months and Areas
4.3. Relationships of Zooplankton with Water Trophic States
4.4. Implications for Reservoir Ecological Conservation and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Functional Group | Abbreviation | Feeding Habits | Body Size/Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protozoan filter feeders | PF | Filter-feeding, feeding on bacteria, phytoplankton, and organic detritus | |
| Protozoan carnivores | PC | Carnivorous-feeding, feeding on small protozoans | |
| Rotifer filter feeders | RF | Filter-feeding, feeding on bacteria, phytoplankton, and organic detritus | |
| Rotifer carnivores | RC | Carnivorous-feeding, feeding on protozoans, other rotifers, and small crustacean | |
| Small copepod and cladoceran filter feeders | SCF | Filter-feeding, feeding on bacteria, phytoplankton, organic detritus, and protozoans | <0.7 mm |
| Small copepod and cladoceran carnivores | SCC | Carnivorous-feeding, feeding on rotifers, cladocerans, dipster (chironomidae larvae), and oligochaeta | <0.7 mm |
| Middle copepod and cladoceran filter feeders | MCF | Filter-feeding, feeding on bacteria, phytoplankton, organic detritus, and protozoans | 0.7–1.5 mm |
| Middle copepod and cladoceran carnivores | MCC | Carnivorous-feeding, feeding on rotifers, cladocerans, dipster (chironomidae larvae), and oligochaeta | 0.7–1.5 mm |
| Large copepod and cladoceran filter feeders | LCF | Filter-feeding, feeding on bacteria, phytoplankton, organic detritus, and protozoans | >1.5 mm |
| Large copepod and cladoceran carnivores | LCC | Carnivorous-feeding, feeding on rotifers, cladocerans, dipster (chironomidae larvae), and oligochaeta | >1.5 mm |
| Equation | Meaning of Abbreviation | Notes | Assessment Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLIc = (1) | m: number of indicators : coefficients of each parameters j : sub-index of TLIc | : Chl.a, 1; TP, 0.84; TN, 0.82; SD, −0.83; CODMn, 0.83 | Oligotrophic: <30 Mesotrophic: 30–50 Eutrophic: >50 (light-eutrophic: 50–60; medium-eutrophic: 60–70; hyper-eutrophic: >70) |
| TLI(Chl.a) = 10(2.5 + 1.086lnChl.a) (2) | Chl.a: chlorophyll a (μg/L) | ||
| TLI(TP) = 10(9.436 + 1.624lnTP) (3) | TP: Total phosphorus (mg/L) | ||
| TLI(TN) = 10(5.453 + 1.694lnTN) (4) | TN: Total nitrogen (mg/L) | ||
| TLI(SD) = 10(5.118 − 1.94lnSD) (5) | SD: Secchi disk depth (m) | ||
| TLI(CODMn) = 10(0.109 + 2.661lnCODMn) (6) | CODMn: Permanganate index (mg/L) |
| Taxonomic Groups | Months | Taxa Code | Average Dissimilarity | Standard Deviation | Contribution | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protozoa | May vs. Aug. | Halc | 0.1197 | 0.0317 | 0.1919 | 0.001 |
| Cil | 0.0950 | 0.0187 | 0.1523 | 0.001 | ||
| Difg | 0.0910 | 0.0164 | 0.1459 | 0.009 | ||
| Chia | 0.0636 | 0.0440 | 0.1019 | 0.002 | ||
| Tinf | 0.0582 | 0.0377 | 0.0933 | 0.001 | ||
| May vs. Nov. | Halc | 0.1457 | 0.0465 | 0.2243 | 0.001 | |
| Cil | 0.0922 | 0.0417 | 0.1419 | 0.003 | ||
| Chia | 0.0759 | 0.0543 | 0.1168 | 0.001 | ||
| Tinf | 0.0691 | 0.0456 | 0.1063 | 0.001 | ||
| Glas | 0.0369 | 0.0467 | 0.0568 | 0.01 | ||
| Aug. vs. Nov. | Difg | 0.1604 | 0.0365 | 0.2970 | 0.001 | |
| Strg | 0.0904 | 0.0698 | 0.1675 | 0.003 | ||
| Strv | 0.0858 | 0.0719 | 0.1589 | 0.005 | ||
| Laco | 0.0583 | 0.0709 | 0.1079 | 0.017 | ||
| Tetp | 0.0375 | 0.0671 | 0.0695 | 0.034 | ||
| Rotifera | May vs. Aug. | Colp | 0.0864 | 0.1095 | 0.0901 | 0.048 |
| Brafo | 0.0670 | 0.0744 | 0.0698 | 0.01 | ||
| Hexm | 0.0646 | 0.0868 | 0.0674 | 0.012 | ||
| Enc | 0.0550 | 0.0910 | 0.0573 | 0.043 | ||
| May vs. Nov. | Trir | 0.1788 | 0.1889 | 0.1845 | 0.002 | |
| Ascs | 0.1011 | 0.0976 | 0.1043 | 0.005 | ||
| Trip | 0.0854 | 0.1497 | 0.0882 | 0.02 | ||
| Synp | 0.0605 | 0.0841 | 0.0625 | 0.037 | ||
| Polv | 0.0487 | 0.0658 | 0.0503 | 0.037 | ||
| Aug. vs. Nov. | Colp | 0.0943 | 0.1116 | 0.1129 | 0.025 | |
| Brafo | 0.0700 | 0.0772 | 0.0838 | 0.007 | ||
| Hexm | 0.0675 | 0.0893 | 0.0808 | 0.023 | ||
| Enc | 0.0577 | 0.0937 | 0.0690 | 0.049 | ||
| Tris | 0.0553 | 0.0591 | 0.0661 | 0.038 | ||
| Cladocera | May vs. Aug. | Dapc | 0.3049 | 0.1408 | 0.3372 | 0.003 |
| Diad | 0.2099 | 0.1373 | 0.2321 | 0.001 | ||
| Daph | 0.1732 | 0.1262 | 0.1915 | 0.002 | ||
| May vs. Nov. | Bosc | 0.2718 | 0.1475 | 0.4133 | 0.018 | |
| Aug. vs. Nov. | Bosc | 0.2996 | 0.2189 | 0.3782 | 0.014 | |
| Diad | 0.1787 | 0.1152 | 0.2255 | 0.007 | ||
| Cerco | 0.0514 | 0.0795 | 0.0649 | 0.021 | ||
| Copepoda | May vs. Aug. | Nau | 0.2721 | 0.0801 | 0.4690 | 0.001 |
| Cycc | 0.1116 | 0.0544 | 0.1923 | 0.003 | ||
| May vs. Nov. | Nau | 0.2237 | 0.0803 | 0.3703 | 0.001 | |
| Cycc | 0.1287 | 0.0524 | 0.2131 | 0.002 | ||
| Sind | 0.0789 | 0.0478 | 0.1306 | 0.005 | ||
| Micv | 0.0542 | 0.0370 | 0.0897 | 0.009 |
References
- Stone, R. The Legacy of the Three Gorges Dam. Science 2011, 333, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; He, D.; Wang, H. Environmental Consequences of Damming the Mainstream Lancang-Mekong River: A Review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 146, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Cho, M.S.; Lin, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Qi, J.; Chen, J.; Moran, E.F. Recently Constructed Hydropower Dams Were Associated with Reduced Economic Production, Population, and Greenness in Nearby Areas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2108038119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, M.; van Soesbergen, A.; Sáenz, L. GOODD, a Global Dataset of More than 38,000 Georeferenced Dams. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, L.; Riseng, C.; Wehrly, K.; Pan, Y.; Song, K.; Da, L.; Pang, W.; You, Q.; Tian, H.; et al. Factors Determining Zooplankton Assemblage Difference among a Man-Made Lake, Connecting Canals, and the Water-Origin River. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J. Does the World Need Faunists? Based on Rotifer (Rotifera) Occurrence Reflections on the Role of Faunistic Research in Ecology. Internat. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2019, 104, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, S.; Kankaala, P.; Hämäläinen, H.; Jones, R.I. Seasonal Shifts in the Diet of Lake Zooplankton Revealed by Phospholipid Fatty Acid Analysis. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, U.A.D.; García-Berthou, E.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Co-Occurring Bighead and Silver Carps Show Similar Food Preference but Different Isotopic Niche Overlap in Different Lakes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, J.; Brett, M.T.; Vrede, T.; Ravet, J.L. Food Quantity and Quality Regulation of Trophic Transfer between Primary Producers and a Keystone Grazer (Daphnia) in Pelagic Freshwater Food Webs. Oikos 2007, 116, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.L.; Dodson, S.I. Predation, Body Size, and Composition of Plankton. Science 1965, 150, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, C.; Mazzeo, N.; Meerhoff, M.; Lacerot, G.; Clemente, J.M.; Scasso, F.; Kruk, C.; Goyenola, G.; García-Alonso, J.; Amsinck, S.L.; et al. High Predation Is of Key Importance for Dominance of Small-Bodied Zooplankton in Warm Shallow Lakes: Evidence from Lakes, Fish Exclosures and Surface Sediments. Hydrobiologia 2011, 667, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Chang, C.Y.; García-Comas, C.; Gong, G.C.; Hsieh, C. Increasing Zooplankton Size Diversity Enhances the Strength of Top-down Control on Phytoplankton through Diet Niche Partitioning. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.; Lamarra, V.; Lynch, M. Biomanipulation, an Ecosystem Approach to Lake Restoration. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Water Quality Management Through Biological Control, Gainesville, FL, USA, 23–30 January 1975; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rosińska, J.; Romanowicz-Brzozowska, W.; Kozak, A.; Gołdyn, R. Zooplankton Changes during Bottom-up and Top-down Control Due to Sustainable Restoration in a Shallow Urban Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19575–19587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wei, N.; Tang, C.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y. Biological Indicators of Ecological Quality in Typical Urban River-Lake Ecosystems: The Planktonic Rotifer Community and Its Response to Environmental Factors. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Johansson, L.S.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Chen, F.; Sh, T.; Jeppesen, E. Copepods as Environmental Indicator in Lakes: Special Focus on Changes in the Proportion of Calanoids along Nutrient and PH Gradients. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochocka, A. ZIPLAS: Zooplankton Index for Polish Lakes’ Assessment: A New Method to Assess the Ecological Status of Stratified Lakes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbiche-Neves, G.; Pomari, J.; Serafim-Júnior, M.; Nogueira, M.G. Cyclopoid Copepods as Indicators of Trophic Level in South American Reservoirs: A New Perspective at Species Level Based on a Wide Spatial-Temporal Scale. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, G.; Katsiapi, M.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Michaloudi, E. The Neglected Zooplankton Communities as Indicators of Ecological Water Quality of Mediterranean Lakes. Limnetica 2021, 40, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Chicote, J.; Armengol, X.; Rojo, C. Zooplankton Abundance: A Neglected Key Element in the Evaluation of Reservoir Water Quality. Limnologica 2018, 69, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, F. Are Zooplankton Useful Indicators of Water Quality in Subtropical Lakes with High Human Impacts? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Su, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, Z.; Shen, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Ding, G.; et al. Is Zooplankton Body Size an Indicator of Water Quality in (Sub)Tropical Reservoirs in China? Ecosystems 2022, 25, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, M. Spatial Gradient and Seasonal Variation of Trophic Status in a Large Water Supply Reservoir for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zheng, B.; Chang, S.; Fu, Q. Investigation of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Contents in Water in the Tributaries of Danjiangkou Reservoir. R Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 170624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.X.; Xu, J.F.; Yin, W.; Chen, Q.Z.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z.H. Effect of Local Watershed Landscapes on the Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations in the Waterbodies of Reservoir Bays. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, J.; Yin, W.; Jia, H.; Xu, J.; Hao, R.; Zhong, Z.; Shi, Z. Linking Water Environmental Factors and the Local Watershed Landscape to the Chlorophyll a Concentration in Reservoir Bays. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borutsky, E.B.; Wu, H.W.; Pai, K.T.; Ko, M.S.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, S.T.; Chen, S.T. Hydrobiological Survey of the Region of the Projected Dam-Reservoir of Danjiangkou, with Propositions for Fisheries Management. Acta Hydrobiol. Sinica 1959, 1, 33–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Yang, G.R.; Liu, J.L. Plankton Resource Survey of Dan Jiangkou Reservoir. J. Hubei Agric. Coll. 1996, 16, 38–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.J.; Pen, J.H.; Jian, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, H.J. The Assessment of Food Organism Resources and Trophic States of Danjiangkou Reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 1997, 09, 57–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.H.; Cai, Q.H.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M. Seasonal Change Features of Rotifer Community and Its Correlation with Environmental Factors in Danjiangkou Reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 941–949. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, W.J.; Zhu, L.Y.; Zhang, M.L. Community Structure of Planktonic Crustaceans in Danjiangkou Reservoir and Effects of Environmental Factors on It. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 77–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.S.; Zhang, L.Q.; Huang, Z.; Lin, L.; Wu, M.; Jin, H.Y. Analysis of Water Quality Changes and Pollution Countermeasures for Water Source Region of the Middle Route of South to North Water Diversion Project. China Water Resour. 2018, 27–30+58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, J.; Rogers, S.; Webber, M.; Finlayson, B.; Wang, M. Sustainability: Transfer Project Cannot Meet China’s Water Needs. Nature 2015, 527, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Wood, P.; van de Giesen, N.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Enhanced Potential Ecological Risk Induced by a Large Scale Water Diversion Project. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2020, 34, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y. Does Water Diversion Project Deteriorate the Water Quality of Reservoir and Downstream? A Case-Study in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhen, W. Relating Land-Use/Land-Cover Patterns to Water Quality in Watersheds Based on the Structural Equation Modeling. CATENA 2021, 206, 105566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, R.; Gan, L. Study on Spatial and Temporal Changes of Landscape Pattern in Danjiangkou Reservoir Wetland in Recent 20 Years. China Resour. Compr. Util. 2020, 38, 45–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J. The Freshwater Rotifers Fauna of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1961; pp. 1–343. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.R. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Copepoda; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 1–450. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.Z.; Du, N.S. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Cladocera; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 1–297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.X.; Chen, J.H. Atlas of Freshwater Microflora and Benthos (Second Edition); Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 1–410. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Huang, X.F. Research Methods of Freshwater Plankton; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991; pp. 1–414. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Huo, T.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Song, D.; Huang, X.; Zhao, C. Zooplankton Community and Its Environmental Driving Factors in Ulungur Lake, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2022, 37, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwagona, P.C.; Chengxue, M.; Hongxian, Y. Seasonal Dynamics of Zooplankton Functional Groups in Relation to Environmental Variables in Xiquanyan Reservoir, Northeast China. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2018, 54, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Information Theory in Ecology. Gen. Syst. 1958, 3, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communications; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. An Introduction to Mathematical Ecology; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, J.B. Nonmetric Multidimensional Scaling: A Numerical Method. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-Parametric Multivariate Analyses of Changes in Community Structure. Austral. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A New Method for Non-Parametric Multivariate Analysis of Variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Anderson, M.J. Distance-based redundancy analysis: Testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1999, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Oksanen, J.; Ter Braak, C.J.F. Testing the Significance of Canonical Axes in Redundancy Analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 2, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing Hierarchical and Variation Partitioning in Multiple Regression and Canonical Analyses Using the Rdacca.Hp R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, N. The Detection of Disease Clustering and a Generalized Regression Approach. Cancer Res. 1967, 27, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rcompanion: Functions to Support Extension Education Program Evaluation, R package version 2.4.6.; The Comprehensive R Archive Network: London, UK, 2016; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rcompanion (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- FSA: Fisheries Stock Analysis. R Package Version 0.9.1. Available online: https://github.com/droglenc/FSA (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.6-2. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Huang, H. LinkET: Everything Is Linkable. R Package Version 0.0.2.4. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/Hy4m/linkET (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- eulerr: Area-Proportional Euler and Venn Diagrams with Ellipses. R Package Version 6.1.1. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=eulerr (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Yu, G. Using ggtree to Visualize Data on Tree-Like Structures. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- aplot: Decorate a “ggplot” with Associated Information. R Package Version 0.1.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=aplot (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- ggpubr: “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots. R Package Version 0.4.0.999. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/ggpubr/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Thornton, K.W.; Kimmel, B.L.; Payne, F.E. Reservoir Limnology: Ecological Perspectives, 1st ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Havel, J.E.; Medley, K.A.; Dickerson, K.D.; Angradi, T.R.; Bolgrien, D.W.; Bukaveckas, P.A.; Jicha, T.M. Effect of Main-Stem Dams on Zooplankton Communities of the Missouri River (USA). Hydrobiologia 2009, 628, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, G.; Belmonte, G.; Marrone, F.; Naselli-Flores, L. Does Lake Age Affect Zooplankton Diversity in Mediterranean Lakes and Reservoirs? A Case Study from Southern Italy. Hydrobiologia 2010, 653, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Jiang, X.; Han, B.-P.; Jeppesen, E. Does Stocking of Filter-Feeding Fish for Production Have a Cascading Effect on Zooplankton and Ecological State? A Study of Fourteen (Sub)Tropical Chinese Reservoirs with Contrasting Nutrient Concentrations. Hydrobiologia 2014, 736, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Guo, L.; Wang, S. Diet and Feeding Ecology of Invasive Icefish Neosalanx Taihuensis in Erhai Lake, a Chinese Plateau Mesoeutrophicated Lake. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, Z.; Liu, J. Changes in Fisheries Resources in the Hanjiang River and Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. In Fishery Resources, Environment, and Conservation in the Mississippi and Yangtze (Changjiang) River Basins; Chen, Y., Chapman, D.C., Jackson, J.R., Chen, D., Li, Z., Killgore, K.J., Phelps, Q., Eggleton, M.A., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016; Volume 84, pp. 179–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ślusarczyk, M. Impact of fish predation on a small-bodied cladoceran: Limitation or Stimulation? Hydrobiologia 1997, 342–343, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.; Gyllstrom, M.; Stahl-Delbanco, A.; Svensson, M. Responses to Fish Predation and Nutrients by Plankton at Different Levels of Taxonomic Resolution. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havens, K.E.; Beaver, J.R.; Manis, E.E.; East, T.L. Inter-Lake Comparisons Indicate That Fish Predation, Rather than High Temperature, Is the Major Driver of Summer Decline in Daphnia and Other Changes among Cladoceran Zooplankton in Subtropical Florida Lakes. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.T.; Wang, P.Z.; Ye, S.W.; Yu, G.L.; Yuan, J.; Liu, J.S.; Zhang, T.L. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the Phytoplankton Community and Assessment of Fish Productivity in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, the Water Source for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 715–727. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.P.; Huang, G.; Jiang, C.J.; Zhang, W.C.; Wang, Q.D.; Yao, L.G. Characteristics and Historical Changes of the Fish Assemblage in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Biodivers. Sci. 2020, 28, 1202–1212. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.Y.; Zhao, X.F.; Gao, S.B.; Zhang, A.J.; Hu, J.; Li, S.X.; Hu, J.X.; Dong, F.Y. The Spatial Distribution Pattern of Autumn Macroinvertebrates in Relation to Environmental Factors in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1229–1241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dodson, S.I.; Everhart, W.R.; Jandl, A.K.; Krauskopf, S.J. Effect of Watershed Land Use and Lake Age on Zooplankton Species Richness. Hydrobiologia 2007, 579, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, E.P. The Strategy of Ecosystem Development. Science 1969, 164, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simões, N.R.; Nunes, A.H.; Dias, J.D.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A.; Velho, L.F.M.; Bonecker, C.C. Impact of Reservoirs on Zooplankton Diversity and Implications for the Conservation of Natural Aquatic Environments. Hydrobiologia 2015, 758, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, N.R.; Braghin, L.S.M.; Duré, G.A.V.; Santos, J.S.; Sonoda, S.L.; Bonecker, C.C. Changing Taxonomic and Functional β-Diversity of Cladoceran Communities in Northeastern and South Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 3845–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Nõges, P.; Davidson, T.A.; Haberman, J.; Nõges, T.; Blank, K.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Søndergaard, M.; Sayer, C.; Laugaste, R.; et al. Zooplankton as Indicators in Lakes: A Scientific-Based Plea for Including Zooplankton in the Ecological Quality Assessment of Lakes According to the European Water Framework Directive (WFD). Hydrobiologia 2011, 676, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, E.Z.C.; Liu, P.; Niu, H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Papa, R.D.S.; Dumont, H.J.; Han, B.-P. Zooplankton in a Continuous Waterscape: Environmental and Spatial Factors Shaping Spring Zooplankton Community Structure in a Large Canyon Reservoir at the Tropic of Cancer. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 3621–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Adrian, R.; De Senerpont Domis, L.; Elser, J.J.; Gaedke, U.; Ibelings, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Lürling, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Mooij, W.M.; et al. Beyond the Plankton Ecology Group (PEG) Model: Mechanisms Driving Plankton Succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.A.; Evans, A.; Coffin, B.; Arismendi, I.; Johnson, S.L. Resilience of Zooplankton Communities in Temperate Reservoirs with Extreme Water Level Fluctuations. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.C.; Ortega, J.C.G.; Vieira, L.C.G.; Velho, L.F.M.; Bini, L.M. Evidence That Dams Promote Biotic Differentiation of Zooplankton Communities in Two Brazilian Reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.H. The Crustacean Zooplankton in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 1995, 7, 240–248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Xu, S.; Lin, J.; Li, H.; Lin, Q.; Han, B.-P. Urbanization Increases Biotic Homogenization of Zooplankton Communities in Tropical Reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, A.; Hansson, L.-A.; Brodersen, J.; Nilsson, P.A.; Brönmark, C. Interactions between Predation and Resources Shape Zooplankton Population Dynamics. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arunjith, T.S.; Cheng, F.; Wang, Z.; Divya, K.R.; Xie, S. Diurnal Distribution of Fish Abundance and Size Composition in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Indian J. Fish. 2022, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Peder Jensen, J.; SØndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Landkildehus, F. Trophic Structure, Species Richness and Biodiversity in Danish Lakes: Changes along a Phosphorus Gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Jensen, C.; Faafeng, B.; Hessen, D.O.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Brettum, P.; Christoffersen, K. The Impact of Nutrient State and Lake Depth on Top-down Control in the Pelagic Zone of Lakes: A Study of 466 Lakes from the Temperate Zone to the Arctic. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

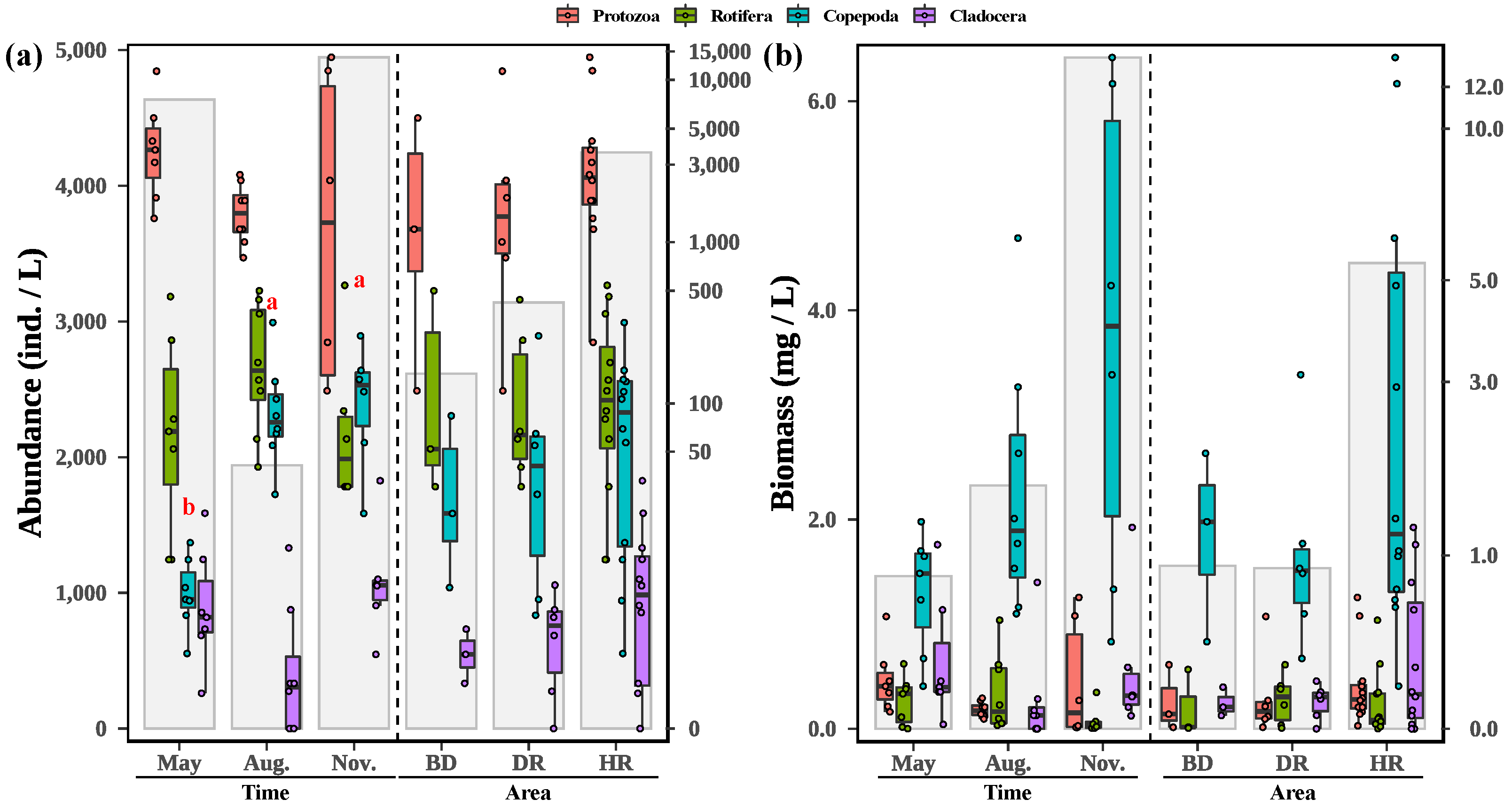
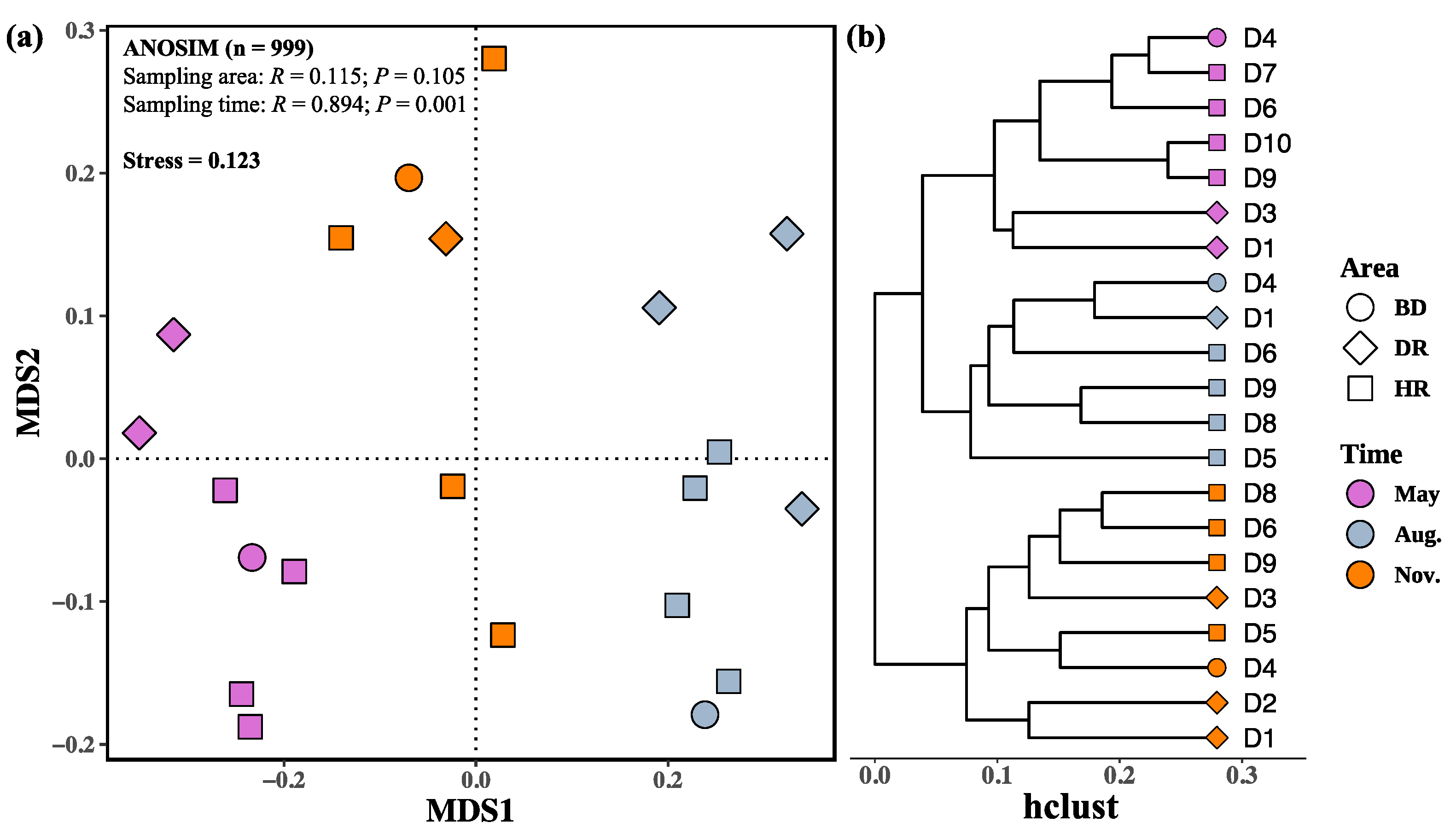

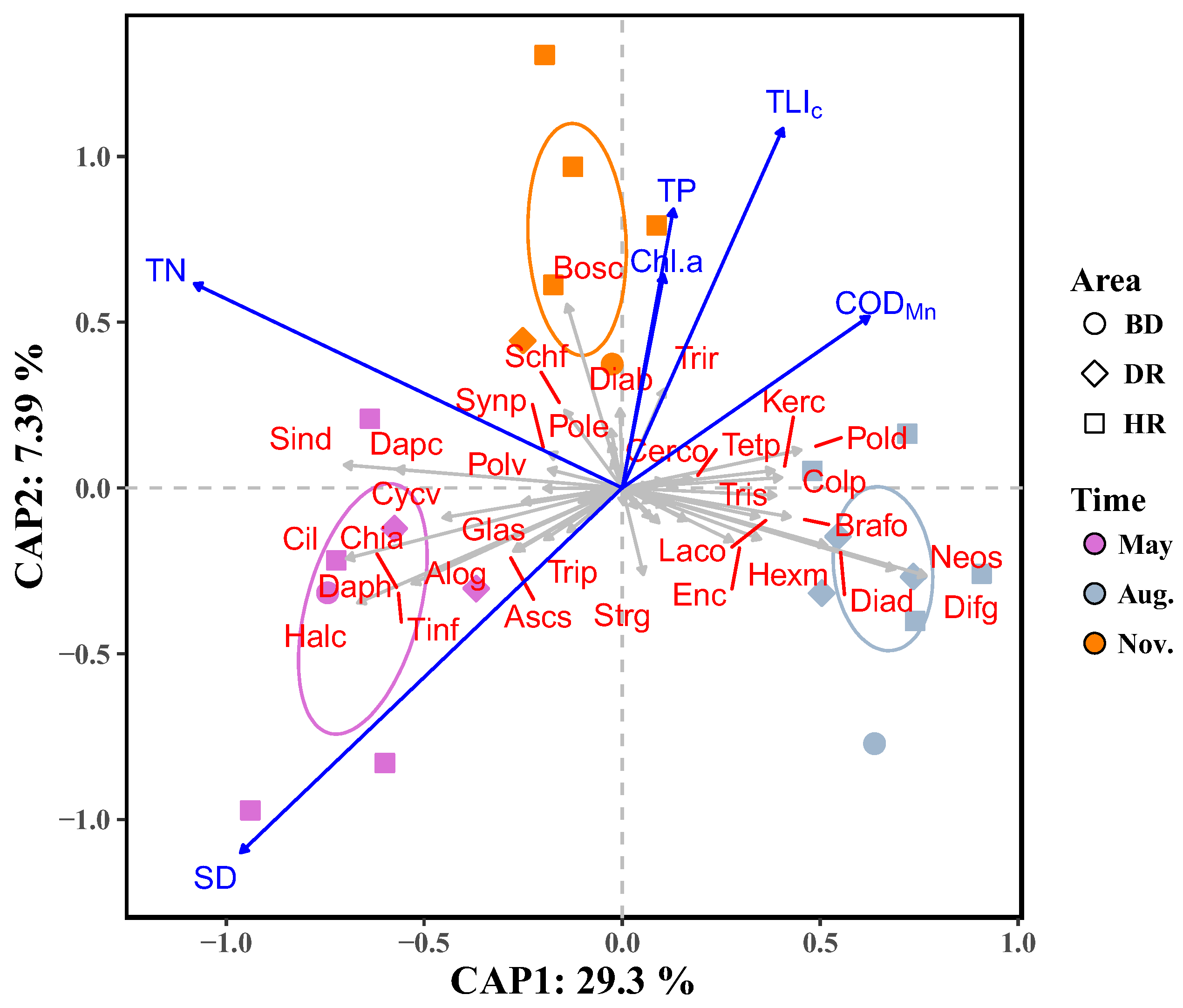

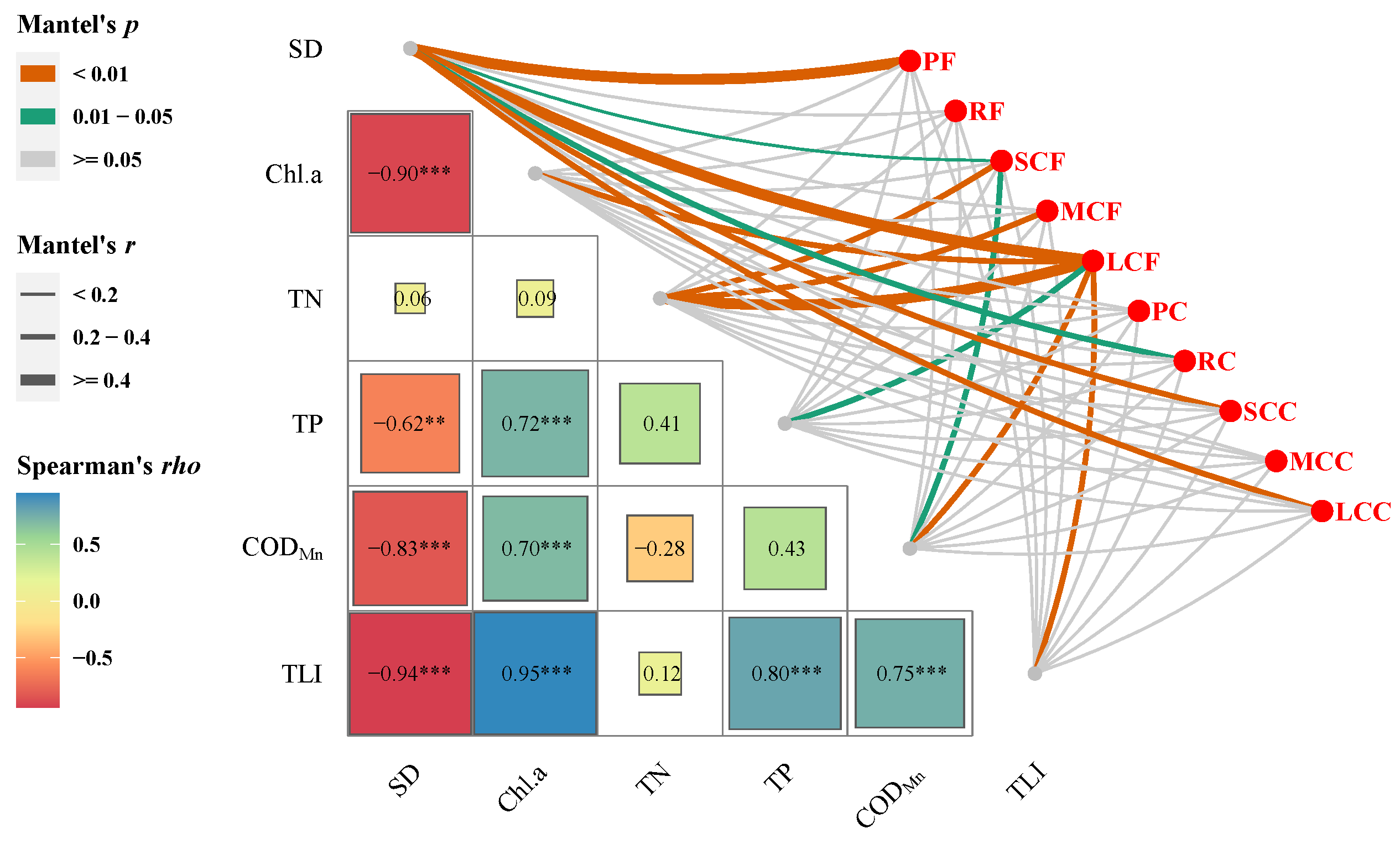
| Biodiversity Indices | Month | Area | Month: Area | Analysis Method | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May (N = 7) | Aug. (N = 8) | Nov. (N = 6) | F/H | p Value | BD (N = 3) | DR (N = 6) | HR (N = 12) | F/H | p Value | F/H | p Value | ||
| Margalef richness index (Dm) | 1.71~3.18 (2.30 ± 0.18) a | 1.43~2.94 (2.04 ± 0.19) a | 1.27~2.13 (1.64 ± 0.14) a | 5.71 | 0.018 | 1.94~2.94 (2.32 ± 0.31) a | 1.32~2.35 (1.67 ± 0.15) a | 1.27~3.18 (2.11 ± 0.15) a | 4.63 | 0.032 | 1.19 | 0.363 | Anova |
| Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H′N) | 0.61~2.38 (1.58 ± 0.20) ab | 1.40~2.23 (1.77 ± 0.11) a | 0.41~1.68 (1.03 ± 0.21) b | 6.72 | 0.011 | 1.43~2.23 (1.78 ± 0.24) a | 0.61~1.80 (1.34 ± 0.16) a | 0.41~2.38 (1.50 ± 0.18) a | 2.09 | 0.167 | 1.49 | 0.266 | Anova |
| Pielou evenness index (J′N) | 0.22~0.72 (0.53 ± 0.06) a | 0.58~0.71 (0.64 ± 0.02) a | 0.17~0.70 (0.42 ± 0.09) a | 5.30 | 0.071 | 0.48~0.71 (0.63 ± 0.07) a | 0.22~0.61 (0.52 ± 0.06) a | 0.17~0.72 (0.52 ± 0.06) a | 1.30 | 0.522 | 4.70 | 0.320 | Scheirer–Ray–Hare test |
| Parameters | Month | Area | Month: Area | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May (N = 7) | Aug. (N = 8) | Nov. (N = 6) | H | p Value | BD (N = 3) | DR (N = 6) | HR (N = 12) | H | p Value | H | p Value | |
| SD (m) | 6.10~10.20 (7.75 ± 0.57) a | 2.70~4.30 (3.71 ± 0.21) b | 0.90~4.50 (2.48 ± 0.59) b | 13.97 | <0.001 | 3.50~7.40 (5.07 ± 1.19) a | 3.90~7.30 (5.11 ± 0.60) a | 0.90~10.20 (4.42 ± 0.90) a | 2.12 | 0.346 | 2.14 | 0.711 |
| Chl.a (μg/L) | 1.28~2.68 (1.96 ± 0.17) b | 1.66~5.91 (4.18 ± 0.60) ab | 3.31~91.29 (21.42 ± 14.10) a | 9.86 | 0.007 | 1.84~4.74 (2.81 ± 0.96) a | 1.61~5.58 (2.96 ± 0.61) a | 1.28~91.29 (12.46 ± 7.25) a | 3.42 | 0.181 | 1.44 | 0.837 |
| TN (mg/L) | 1.45~1.95 (1.79 ± 0.06) a | 0.83~1.19 (1.05 ± 0.04) b | 1.50~2.69 (1.91 ± 0.18) a | 12.82 | 0.002 | 1.12~1.86 (1.52 ± 0.22) a | 0.96~1.73 (1.32 ± 0.12) a | 0.83~2.69 (1.65 ± 0.16) a | 2.34 | 0.310 | 2.02 | 0.732 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.01~0.04 (0.02 ± 0.00) a | 0.01~0.04 (0.03 ± 0.00) a | 0.02~0.10 (0.05 ± 0.01) a | 4.36 | 0.113 | 0.02~0.03 (0.02 ± 0.00) a | 0.01~0.04 (0.02 ± 0.00) a | 0.01~0.10 (0.04 ± 0.01) a | 3.34 | 0.188 | 3.79 | 0.436 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 1.63~1.80 (1.72 ± 0.03) b | 2.14~2.77 (2.45 ± 0.07) a | 1.82~5.48 (2.72 ± 0.56) a | 14.07 | <0.001 | 1.79~2.68 (2.21 ± 0.26) a | 1.68~2.40 (2.06 ± 0.13) a | 1.63~5.48 (2.42 ± 0.30) a | 0.45 | 0.800 | 1.20 | 0.878 |
| TLIc | 26.99~33.86 (30.95 ± 0.90) b | 30.12~38.85 (36.08 ± 1.04) a | 33.75~61.53 (44.29 ± 4.06) a | 10.68 | 0.005 | 30.85~38.24 (34.30 ± 2.15) a | 28.72~38.32 (33.22 ± 1.56) a | 26.99~61.53 (39.07 ± 2.63) a | 3.80 | 0.150 | 1.07 | 0.899 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, T.; Liao, C.; Yu, G.; Yuan, J.; Liu, J.; Ye, S. Zooplankton Compositions in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, a Water Source for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. Water 2022, 14, 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203253
Xiong M, Li R, Zhang T, Liao C, Yu G, Yuan J, Liu J, Ye S. Zooplankton Compositions in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, a Water Source for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. Water. 2022; 14(20):3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203253
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Mantang, Ruojing Li, Tanglin Zhang, Chuansong Liao, Gongliang Yu, Jing Yuan, Jiashou Liu, and Shaowen Ye. 2022. "Zooplankton Compositions in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, a Water Source for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China" Water 14, no. 20: 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203253
APA StyleXiong, M., Li, R., Zhang, T., Liao, C., Yu, G., Yuan, J., Liu, J., & Ye, S. (2022). Zooplankton Compositions in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, a Water Source for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. Water, 14(20), 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203253







