Insights into the Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Attributes in Irrigated Farm Fields and Correlations with Management Practices: A Multivariate Statistical Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
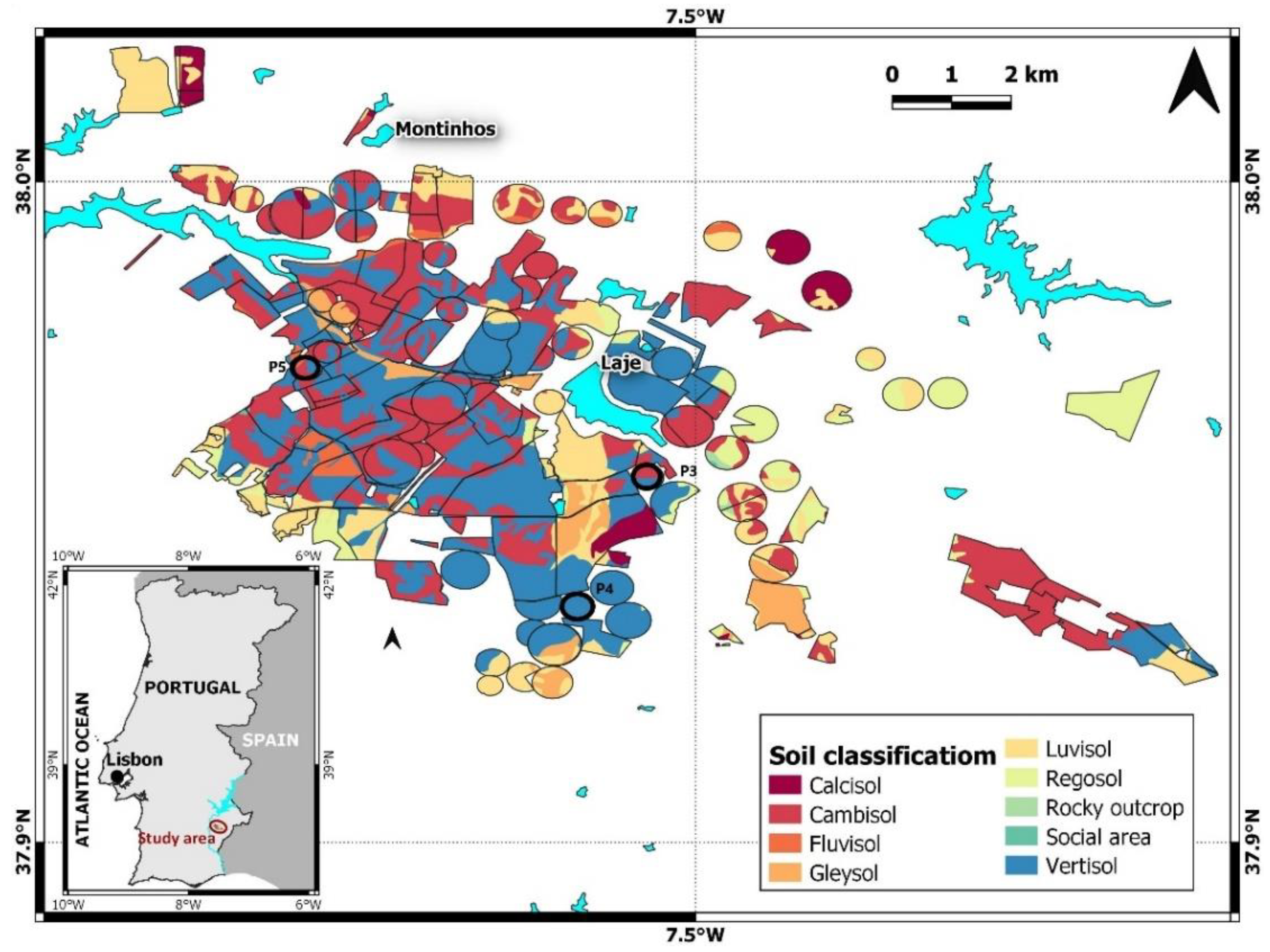
2.2. Sampling and Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Physical–Chemical Properties
3.2. Correlation and Data Structure
3.2.1. Layer 0–20 cm
3.2.2. Layer 20–40 cm
3.3. Discriminant Factors and Variables
3.3.1. Layer 0–20 cm
3.3.2. Layer 20–40 cm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adhikari, K.; Hartemink, A.E. Linking Soils to Ecosystem Services—A Global Review. Geoderma 2016, 262, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, W.E.; Pierce, F.J. The Dynamics of Soil Quality as a Measure of Sustainable Management. In Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Coleman, D.C., Bezdicek, D.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; SSSA Special Publication Number: Wisconsin, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Karlen, D.L.; Veum, K.S.; Sudduth, K.A.; Obrycki, J.F.; Nunes, M.R. Soil Health Assessment: Past Accomplishments, Current Activities, and Future Opportunities. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Water. Key Facts. Available online: http://www.fao.org/water/en/ (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Adejumobi, M.A.; Awe, G.O.; Abegunrin, T.P.; Oyetunji, O.M.; Kareem, T.S. Effect of Irrigation on Soil Health: A Case Study of the Ikere Irrigation Project in Oyo State, Southwest Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolskii, Y.; Aidarov, I.P.; Landeros-Sanchez, C.; Pchyolkin, V.V. Impact of Long-Term Freshwater Irrigation on Soil Fertility. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 68, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendra, B.; Fetouani, S.; Laffray, X.; Vanclooster, M.; Sbaa, M.; Aleya, L. Effects of Irrigation on Soil Physico-Chemistry: A Case Study of the Triffa Plain (Morocco). Irrig. Drain. 2012, 61, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.S.; Grant, C.D. The impact of irrigation on soil structure. Land & Water Australia; Land & Water Australia: Camberra, Australia, 2007; p. 31. Available online: https://library.dbca.wa.gov.au/static/FullTextFiles/070521.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Presley, D.R.; Ransom, M.D.; Kluitenberg, G.J.; Finnell, P.R. Effects of Thirty Years of Irrigation on the Genesis and Morphology of Two Semiarid Soils in Kansas. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadamma, S.; Lal, R.; Hoeft, R.G.; Nafziger, E.D.; Adee, E.A. Nitrogen Fertilization and Cropping System Impacts on Soil Properties and Their Relationship to Crop Yield in the Central Corn Belt, USA. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 98, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härdle, W.K.; Simar, L. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-3-662-45171-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yeater, K.; Villamil, M. Multivariate Methods for Agricultural Research. In Applied Statistics in Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Sciences; Glaz, B., Yeater, K.M., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.; Crop Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-89118-359-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, A.R.; Buschiazzo, D.E.; Peinemann, N. Management Discriminant Properties in Semiarid Soils. Soil Sci. 1998, 163, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, M.M.; Frighetto, R.T.S.; Valarini, P.J.; Tokeshi, H.; Poppi, R.J. Discrimination of Management Effects on Soil Parameters by Using Principal Component Analysis: A Multivariate Analysis Case Study. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 67, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, W.; Nascimento, C.; Silva, Y.; Silva, D.; Ferreira, H. Soil Fertility Changes in Vineyards of a Semiarid Region in Brazil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallarino, A.; Oyarzabal, E.; Hinz, P. Interpreting Within-Field Relationships Between Crop Yields and Soil and Plant Variables Using Factor Analysis. Precis. Agric. 1999, 1, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhos, K.; Szabó, S.; Ladányi, M. Influence of Soil Properties on Crop Yield: A Multivariate Statistical Approach. Int. Agrophys. 2015, 29, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.K.; Lal, R.; Ebinger, M. Determining Soil Quality Indicators by Factor Analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdous, S.; Begum, S.; Yasmin, A. Assessment of Soil Quality Parameters Using Multivariate Analysis in the Rawal Lake Watershed. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPMA Climate normal—1981–2010—Beja. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt/en/oclima/normais.clima/1981-2010/002/ (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- COTR SAGRA—Sistema Agrometeorológico Para a Gestão Da Rega No Alentejo (Agrometeorological System for Irrigation Management in Alentejo). Available online: http://www.cotr.pt/servicos/sagranet.php (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- IUSS Working Group WRB World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014; Update 2015; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014.
- Tomaz, A.; Costa, M.J.; Coutinho, J.; Dôres, J.; Catarino, A.; Martins, I.; Mourinha, C.; Guerreiro, I.; Pereira, M.M.; Fabião, M.; et al. Applying Risk Indices to Assess and Manage Soil Salinization and Sodification in Crop Fields within a Mediterranean Hydro-Agricultural Area. Water 2021, 13, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varennes, A.D. Produtividade Dos Solos e Ambiente (Productivity of Soils and Environment); Escolar Editora: Lisboa, Portugal, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, L.A. An Examination of the Dgtjareff Method for Determining Soil Organic Matter, and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldahl, J. Neue Methode zur Bestimmung des Stickstoffs in organischen Körpern (New method for the determination of nitrogen in organic substances). Z. Für Anal. Chem. 1883, 22, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egner, H.; Riehm, H.; Domingo, W.R. Untersuchhungen Uber Die Chemische Boden: Analyse Als Grundlage Fur Die Beurteilung Der Nahrstoffzustandes Der Boden. II. Chemique Extractions, Methoden Zur Phosphor, Und Kalium-Bestimmung (Investiga-Tions on the Chemical Soil Analysis as a Basis for Assess-Ing the Soil Nutrient Status II: Chemical Extractionmethods for Phosphorus and Potassium Determination). K. Lantbr. Ann. 1960, 26, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System); StatSoft, Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2004; Available online: https://www.tibco.com/products/tibco-statistica (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Tomaz, A.; Palma, J.F.; Ramos, T.; Costa, M.N.; Rosa, E.; Santos, M.; Boteta, L.; Dôres, J.; Patanita, M. Yield, Technological Quality and Water Footprints of Wheat under Mediterranean Climate Conditions: A Field Experiment to Evaluate the Effects of Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization Strategies. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M.; Herrman, T.J.; Lingenfelser, J.; Jackson, D.S. Classification and Prediction of Maize Hardness-Associated Properties Using Multivariate Statistical Analyses. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 41, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIBCO TIBCO Statistica® User′s Guide, Version 14.0. Available online: https://docs.tibco.com/pub/stat/14.0.0/doc/html/UsersGuide/GUID-058F49FC-F4EF-4341-96FB-A785C2FA76E9-homepage.html (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- Foth, H.D. Fundamentals of Soil Science, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; ISBN 0-471-52279-1. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, R.; Giltrap, D.; Whitton, J. Contribution of Organic Matter and Clay Minerals to the Cation Exchange Capacity of Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1995, 26, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson: Columbus, OH, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-13-325448-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, D.; Datta, S.C.; Manjaiah, K.M. Fractions, Uptake and Fixation Capacity of Phosphorus and Potassium in Three Contrasting Soil Orders. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 14, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz, A.; Palma, P.; Fialho, S.; Lima, A.; Alvarenga, P.; Potes, M.; Costa, M.; Salgado, R. Risk Assessment of Irrigation-Related Soil Salinization and Sodification in Mediterranean Areas. Water 2020, 12, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, T.B.; Singh, L.K.; Yadav, A.K.; Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Jat, H.S.; Sharma, P.C.; Jat, M.L.; Stirling, C.M. Identifying Optimum Rates of Fertilizer Nitrogen Application to Maximize Economic Return and Minimize Nitrous Oxide Emission from Rice–Wheat Systems in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simfukwe, P.; Hill, P.W.; Emmett, B.A.; Jones, D.L. Identification and Predictability of Soil Quality Indicators from Conventional Soil and Vegetation Classifications. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity Measurements in Agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, R.; Millán, S.; Prieto, M.H.; Campillo, C. A Methodology Based on Apparent Electrical Conductivity and Guided Soil Samples to Improve Irrigation Zoning. Precis. Agric. 2015, 16, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral, F.J.; Terrón, J.M.; Silva, J.R.M. da Delineation of Management Zones Using Mobile Measurements of Soil Apparent Electrical Conductivity and Multivariate Geostatistical Techniques. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Field | Crop | Sowing (dd/mm) | Seasonal Irrigation Water (m3 ha−1) | First Irrigation (dd/mm) | Last Irrigation (dd/mm) | Fertilizer N (kg N ha−1) | Fertilizer P (kg P2O5 ha−1) | Fertilizer K (kg K2O ha−1) | Other Fertilizers (kg ha−1) | Pesticides (Active Substance) | Harvest (dd/mm) | Yield (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | P3 | Sunflower | 18/04 | 2517 | 19/04 | 01/08 | 127 | 34 | - | 16 SO3; 0.2 B | pre-emergence herbicide (pendimethalin); insecticide (deltamethrin) | 27/08 | 3470 |
| P4 | Sunflower | 27/04 | 4606 | 28/04 | 26/08 | 109 | 40 | 12 | 16 SO3 | pre-emergence herbicide (pendimethalin) | 18/09 | 4156 | |
| P5 | Maize | 18/07 | 4800 | 18/07 | 04/10 | 202 | 144 | 216 | 27 SO3 | post-emergence herbicide (foramsulfuron + isoxadifen-ethyl) | 17/01 1 | 5500 | |
| 2019 | P3 | Maize | 13/06 | 7500 | 2 | 2 | 253 | - | - | - | post-emergence herbicide (mesotrione + S-metolachlor + terbuthylazine); insecticide (lambda-cyhalothrin) | 17/11 | 11000 |
| P4 | Clover | 03/01 | 1510 | 18/04 | 24/06 | - | 88 | - | 0.2 SO3; 0.2 B; 0.1 MgO | - | 18/09 | 1703 | |
| P5 | Sunflower | 16/05 | 3570 | 20/05 | 30/08 | 81 | 19 | 20 | 7 SO3 | pre-emergence herbicides (pendimethalin, glyphosate) | 15/09 | 3257 | |
| 2020 | P3 | Sunflower | 09/03 | 5420 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 13/08 | 8660 |
| P4 | Onion | 11/01 | 3210 | 11/01 | 24/08 | 113 | 1 | 0.1 | 210 SO3; 65 CaO; 2 Zn; 1 Mn; 0.1 MgO | pre- and post-emergence herbicides (aclonifen, clethodime) | 21/08 | 26,848 | |
| P5 | Maize | 15/06 | 5160 | 15/06 | 15/09 | 82 | 59 | 121 | 5 SO3; 3 Zn | pre- and post-emergence herbicides (glyphosate, MCPA, 2,4-D + florasulam, mesotrione + S-metolachlor + terbuthylazine); insecticides (lambda-cyhalothrin, chlorantraniliprole) | 15/10 | 9182 |
| Site | C. Sand (g kg−1) | F. Sand (g kg−1) | Silt (g kg−1) | Clay (g kg−1) | CEC (cmol (+) kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 | 197.6 (±10.0) | 230.7 (±6.0) | 192.1 (±15.5) | 379.6 (±1.8) | 56.5 (±0.3) |
| P4 | 160.5 (±11.1) | 159.2 (±6.5) | 248.3 (±1.4) | 432.0 (±16.1) | 57.0 (±0.8) |
| P5 | 163.7 (±9.8) | 177.5 (±14.2) | 287.6 (±19.1) | 371.2 (±25.9) | 53.6 (±2.1) |
| Site | C. Sand (g kg−1) | F. Sand (g kg−1) | Silt (g kg−1) | Clay (g kg−1) | CEC (cmol (+) kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 | 192.2 (±11.00) | 232.4 (±5.6) | 192.7 (±15.7) | 375.7 (±2.3) | 58.1 (±0.6) |
| P4 | 164.1 (±19.08) | 167.2 (±6.4) | 246.7 (±9.5) | 422.0 (±17.0) | 57.9 (±1.2) |
| P5 | 176.0 (±9.82) | 173.3 (±12.6) | 243.8 (±5.8) | 406.9 (±17.4) | 53.9 (±1.4) |
| Date | Site | pH | EC (dS m−1) | SOM (g kg−1) | N (%) | P (mg P2O5 kg−1) | K (mg K2O kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | P3 | 8.39 (±0.03) | 0.16 (±0.00) | 15.8 (±0.5) | 0.08 (±0.00) | 248.61 (±31.32) | 115.07 (±9.21) |
| P4 | 8.28 (±0.06) | 0.13 (±0.00) | 12.8 (±0.4) | 0.06 (±0.00) | 221.34 (±19.07) | 206.59 (±14.06) | |
| P5 | 8.02 (±0.03) | 0.18 (±0.01) | 11.4 (±0.6) | 0.08 (±0.00) | 418.63 (±88.63) | 236.78 (±14.02) | |
| T2 | P3 | 8.34 (±0.03) | 0.35 (±0.01) | 12.2 (±0.6) | 0.09 (±0.00) | 124.46 (±17.60) | 106.57 (±7.30) |
| P4 | 7.89 (±0.03) | 0.35 (±0.02) | 19.6 (±2.4) | 0.07 (±0.00) | 143.64 (±10.22) | 149.26 (±4.68) | |
| P5 | 8.45 (±0.02) | 0.24 (±0.01) | 19.1 (±1.8) | 0.08 (±0.01) | 326.53 (±32.45) | 367.04 (±16.31) | |
| T3 | P3 | 8.40 (±0.01) | 0.28 (±0.02) | 10.6 (±0.8) | 0.09 (±0.00) | 145.24 (±12.73) | 102.62 (±13.52) |
| P4 | 1 | ||||||
| P5 | 1 | ||||||
| T4 | P3 | 8.08 (±0.02) | 0.29 (±0.01) | 10.0 (±0.4) | 0.10 (±0.00) | 148.57 (±14.68) | 94.98 (±6.93) |
| P4 | 8.25 (±0.02) | 0.26 (±0.01) | 6.9 (±0.4) | 0.08 (±0.00) | 115.81 (±6.99) | 145.16 (±5.96) | |
| P5 | 8.06 (±0.04) | 0.30 (±0.01) | 16.0 (±0.6) | 0.10 (±0.00) | 239.86 (±21.76) | 226.06 (±14.34) | |
| T5 | P3 | 7.92 (±0.01) | 0.58 (±0.01) | 15.0 (±0.2) | 0.10 (±0.00) | 180.82 (±18.98) | 147.75 (±18.55) |
| P4 | 7.80 (±0.01) | 0.46 (±0.02) | 10.4 (±0.2) | 0.09 (±0.01) | 106.32 (±6.64) | 261.43 (±48.24) | |
| P5 | 1 |
| Date | Site | pH | EC (dS m−1) | SOM (g kg−1) | N (%) | P (mg P2O5 kg−1) | K (mg K2O kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | P3 | 8.49 (±0.02) | 0.15 (±0.00) | 16.9 (±1.4) | 0.07 (±0.00) | 144.85 (±7.02) | 94.82 (±7.05) |
| P4 | 8.19 (±0.05) | 0.16 (±0.00) | 8.2 (±0.2) | 0.05 (±0.00) | 131.13 (±4.44) | 139.03 (±3.62) | |
| P5 | 8.09 (±0.07) | 0.14 (±0.01) | 7.9 (±0.6) | 0.06 (±0.00) | 258.99 (±67.76) | 150.23 (±11.43) | |
| T2 | P3 | 8.40 (±0.03) | 0.30 (±0.02) | 11.2 (±0.4) | 0.08 (±0.00) | 106.20 (±15.77) | 96.99 (±6.14) |
| P4 | 7.97 (±0.02) | 0.29 (±0.02) | 18.5 (±3.1) | 0.07 (±0.00) | 83.74 (±1.71) | 139.38 (±3.09) | |
| P5 | 8.49 (±0.02) | 0.30 (±0.02) | 16.8 (±1.5) | 0.07 (±0.00) | 197.73 (±18.97) | 183.27 (±9.77) | |
| T3 | P3 | 8.35 (±0.02) | 0.29 (±0.01) | 10.2 (±0.9) | 0.08 (±0.01) | 148.44 (±12.28) | 121.46 (±19.84) |
| P4 | 1 | ||||||
| P5 | 1 | ||||||
| T4 | P3 | 8.10 (±0.01) | 0.32 (±0.01) | 9.8 (±0.8) | 0.10 (±0.00) | 118.42 (±11.96) | 86.27 (±7.98) |
| P4 | 1 | ||||||
| P5 | 7.98 (±0.01) | 0.37 (±0.01) | 15.1 (±0.8) | 0.09 (±0.00) | 192.95 (±16.97) | 195.35 (±16.83) | |
| T5 | P3 | 8.11 (±0.01) | 0.28 (±0.00) | 13.3 (±0.4) | 0.09 (±0.00) | 133.02 (±14.65) | 73.48 (±9.30) |
| P4 | 7.83 (±0.05) | 0.41 (±0.04) | 9.0 (±0.4) | 0.09 (±0.01) | 74.64 (±4.27) | 164.78 (±11.08) | |
| P5 | 1 |
| pH | EC | SOM | N | P | K | C. Sand | F. Sand | Silt | Clay | CEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| EC | −0.487 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| SOM | 0.093 | 0.011 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| N | −0.270 | 0.591 | 0.150 | 1.000 | |||||||
| P | 0.273 | −0.461 | 0.426 | 0.021 | 1.000 | ||||||
| K | −0.108 | −0.124 | 0.348 | 0.020 | 0.538 | 1.000 | |||||
| C. Sand | 0.068 | 0.050 | −0.075 | 0.047 | −0.162 | −0.449 | 1.000 | ||||
| F. Sand | 0.103 | 0.108 | −0.025 | 0.178 | −0.119 | −0.441 | 0.920 | 1.000 | |||
| Silt | −0.078 | −0.117 | 0.198 | −0.030 | 0.119 | 0.447 | −0.556 | −0.396 | 1.000 | ||
| Clay | −0.123 | 0.086 | −0.180 | −0.086 | 0.088 | 0.155 | −0.554 | −0.564 | −0.197 | 1.000 | |
| CEC | −0.170 | 0.164 | −0.245 | 0.043 | −0.196 | −0.151 | −0.033 | −0.097 | −0.302 | 0.434 | 1.000 |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.215 | 0.043 | −0.719 | −0.186 |
| EC | 0.093 | 0.111 | 0.893 | 0.070 |
| SOM | −0.061 | −0.195 | 0.100 | −0.542 |
| N | 0.198 | 0.035 | 0.753 | −0.251 |
| P | 0.015 | 0.068 | −0.257 | −0.799 |
| K | −0.323 | −0.092 | 0.073 | −0.741 |
| C. Sand | 0.897 | −0.259 | 0.004 | 0.152 |
| F. Sand | 0.943 | −0.256 | 0.053 | 0.100 |
| Silt | −0.793 | −0.527 | −0.042 | −0.169 |
| Clay | −0.413 | 0.861 | 0.001 | 0.008 |
| CEC | 0.008 | 0.830 | 0.088 | 0.183 |
| Eigenvalues | 2.988 | 2.224 | 1.837 | 1.206 |
| % Total variance | 27.16 | 20.22 | 16.70 | 10.97 |
| %. Accumulated variance | 27.16 | 47.38 | 64.08 | 75.04 |
| pH | EC | SOM | N | P | K | C. Sand | F. Sand | Silt | Clay | CEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| EC | −0.301 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| SOM | 0.234 | 0.124 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| N | −0.172 | 0.672 | 0.326 | 1.000 | |||||||
| P | 0.397 | −0.111 | 0.224 | −0.042 | 1.000 | ||||||
| K | −0.232 | 0.209 | 0.183 | −0.036 | 0.302 | 1.000 | |||||
| C. Sand | 0.019 | 0.092 | 0.135 | 0.054 | 0.082 | −0.073 | 1.000 | ||||
| F. Sand | 0.266 | 0.001 | 0.062 | 0.176 | −0.013 | −0.541 | 0.712 | 1.000 | |||
| Silt | −0.181 | −0.064 | −0.065 | −0.118 | −0.105 | 0.405 | −0.868 | −0.820 | 1.000 | ||
| Clay | −0.130 | −0.022 | −0.120 | −0.157 | 0.103 | 0.286 | −0.800 | −0.894 | 0.691 | 1.000 | |
| CEC | −0.026 | −0.147 | −0.178 | −0.023 | −0.134 | −0.190 | −0.517 | −0.121 | 0.278 | 0.289 | 1.000 |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.195 | −0.288 | 0.241 | 0.752 |
| EC | 0.038 | 0.863 | −0.148 | −0.200 |
| SOM | 0.063 | 0.363 | −0.092 | 0.562 |
| N | 0.032 | 0.894 | 0.124 | 0.066 |
| P | −0.141 | −0.211 | −0.443 | 0.594 |
| K | −0.464 | 0.233 | −0.695 | 0.228 |
| C. Sand | 0.929 | 0.024 | −0.275 | 0.005 |
| F. Sand | 0.925 | 0.041 | 0.237 | 0.085 |
| Silt | −0.869 | −0.007 | −0.099 | −0.050 |
| Clay | −0.869 | −0.052 | 0.127 | −0.034 |
| CEC | −0.302 | 0.043 | 0.758 | 0.094 |
| Eigenvalues | 3.614 | 1.953 | 1.611 | 1.152 |
| % Total variance | 32.85 | 17.75 | 14.65 | 10.47 |
| %. Accumulated variance | 32.85 | 50.60 | 65.25 | 75.72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomaz, A.; Martins, I.; Catarino, A.; Mourinha, C.; Dôres, J.; Fabião, M.; Boteta, L.; Coutinho, J.; Patanita, M.; Palma, P. Insights into the Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Attributes in Irrigated Farm Fields and Correlations with Management Practices: A Multivariate Statistical Approach. Water 2022, 14, 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203216
Tomaz A, Martins I, Catarino A, Mourinha C, Dôres J, Fabião M, Boteta L, Coutinho J, Patanita M, Palma P. Insights into the Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Attributes in Irrigated Farm Fields and Correlations with Management Practices: A Multivariate Statistical Approach. Water. 2022; 14(20):3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203216
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomaz, Alexandra, Inês Martins, Adriana Catarino, Clarisse Mourinha, José Dôres, Marta Fabião, Luís Boteta, João Coutinho, Manuel Patanita, and Patrícia Palma. 2022. "Insights into the Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Attributes in Irrigated Farm Fields and Correlations with Management Practices: A Multivariate Statistical Approach" Water 14, no. 20: 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203216








