Interplay between Asian Monsoon and Tides Affects the Plume Dispersal of the New Hu-Wei River off the Coast of Midwest Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
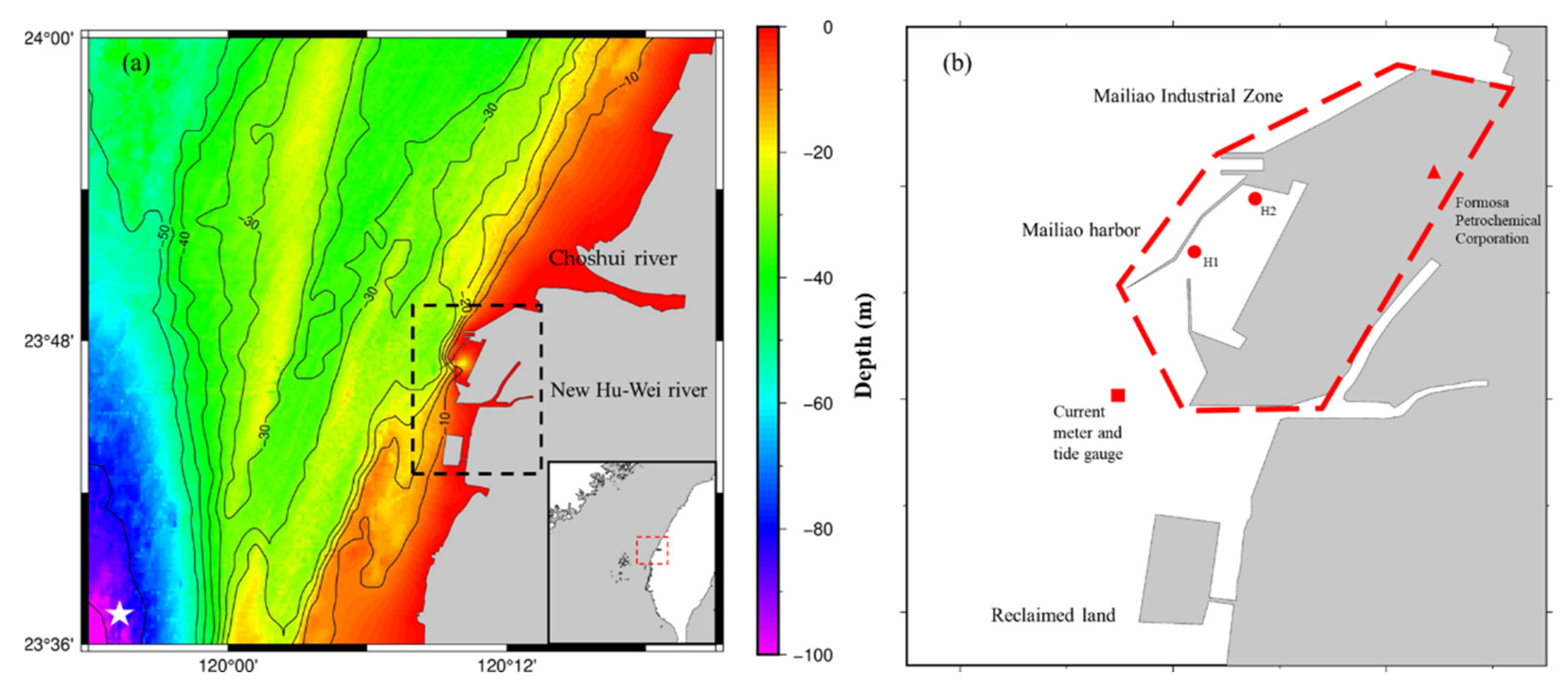
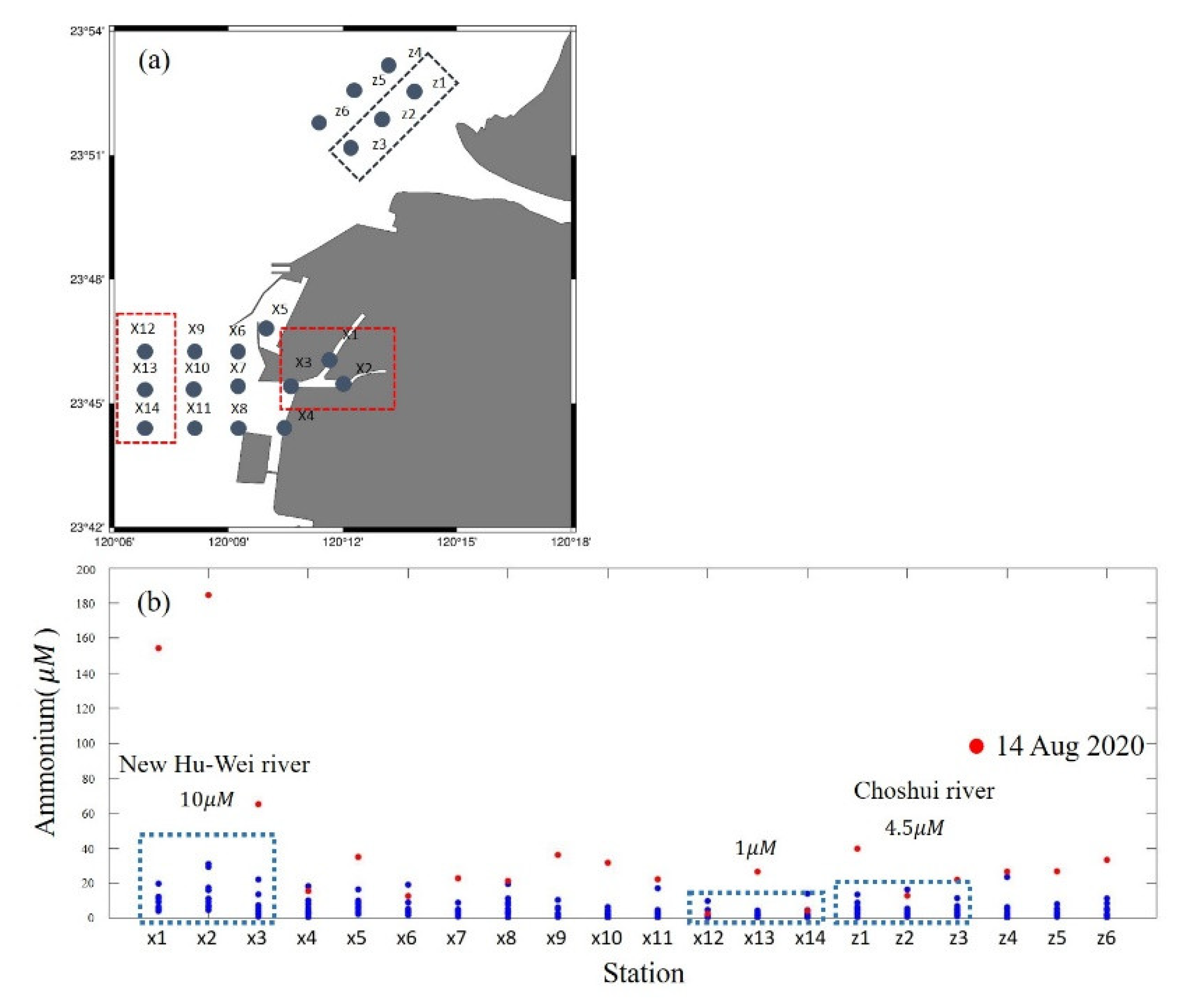
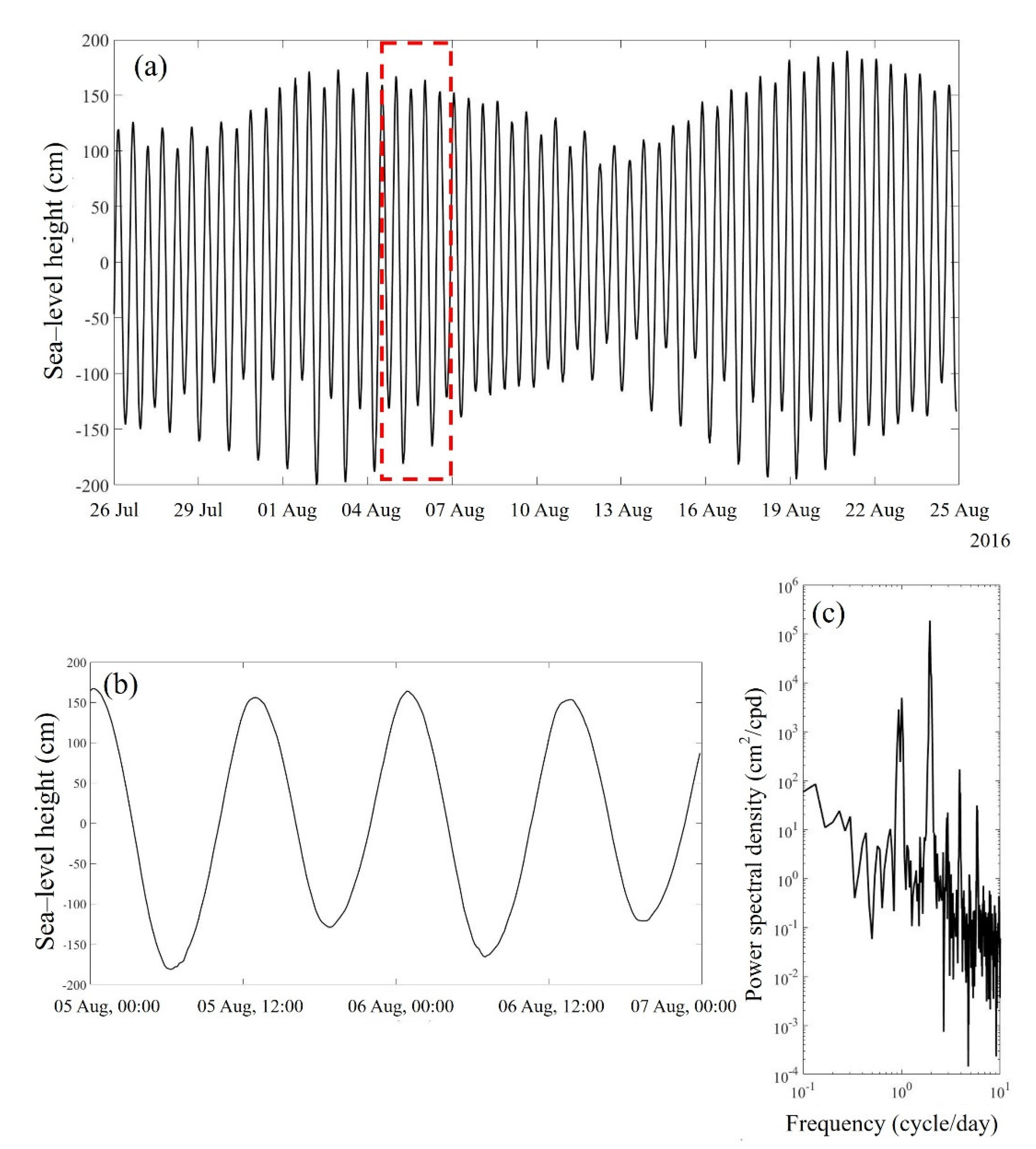
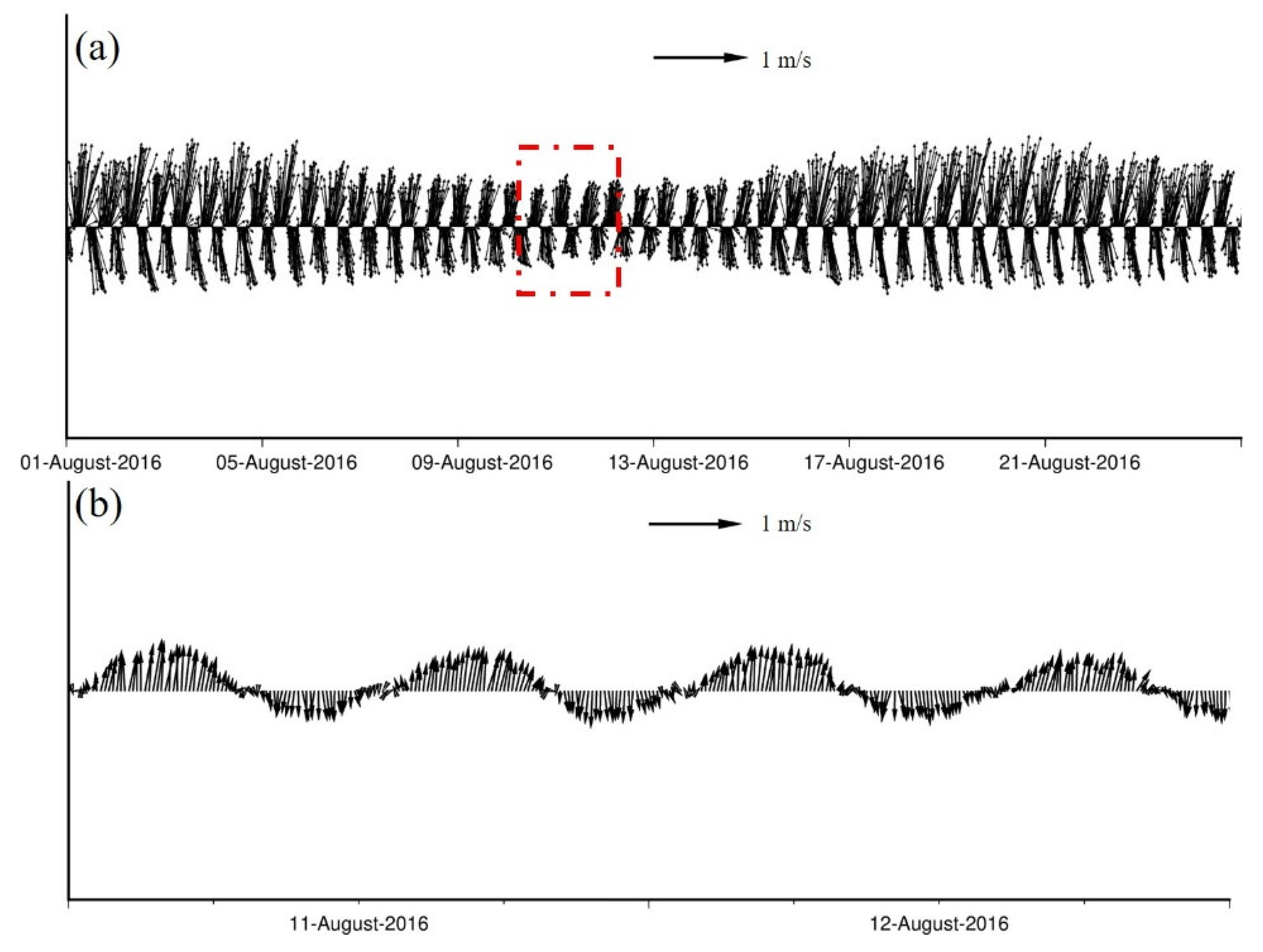
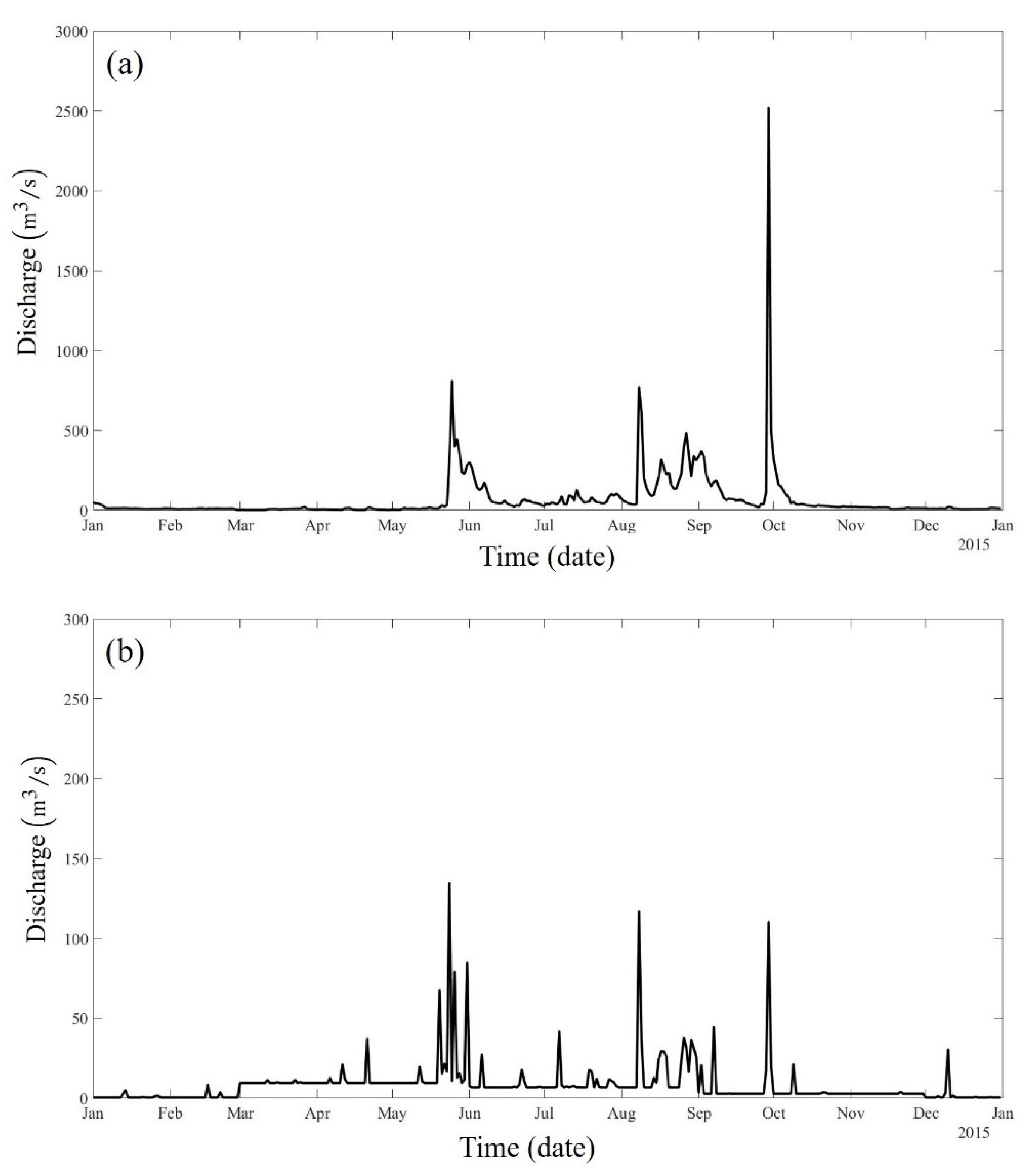
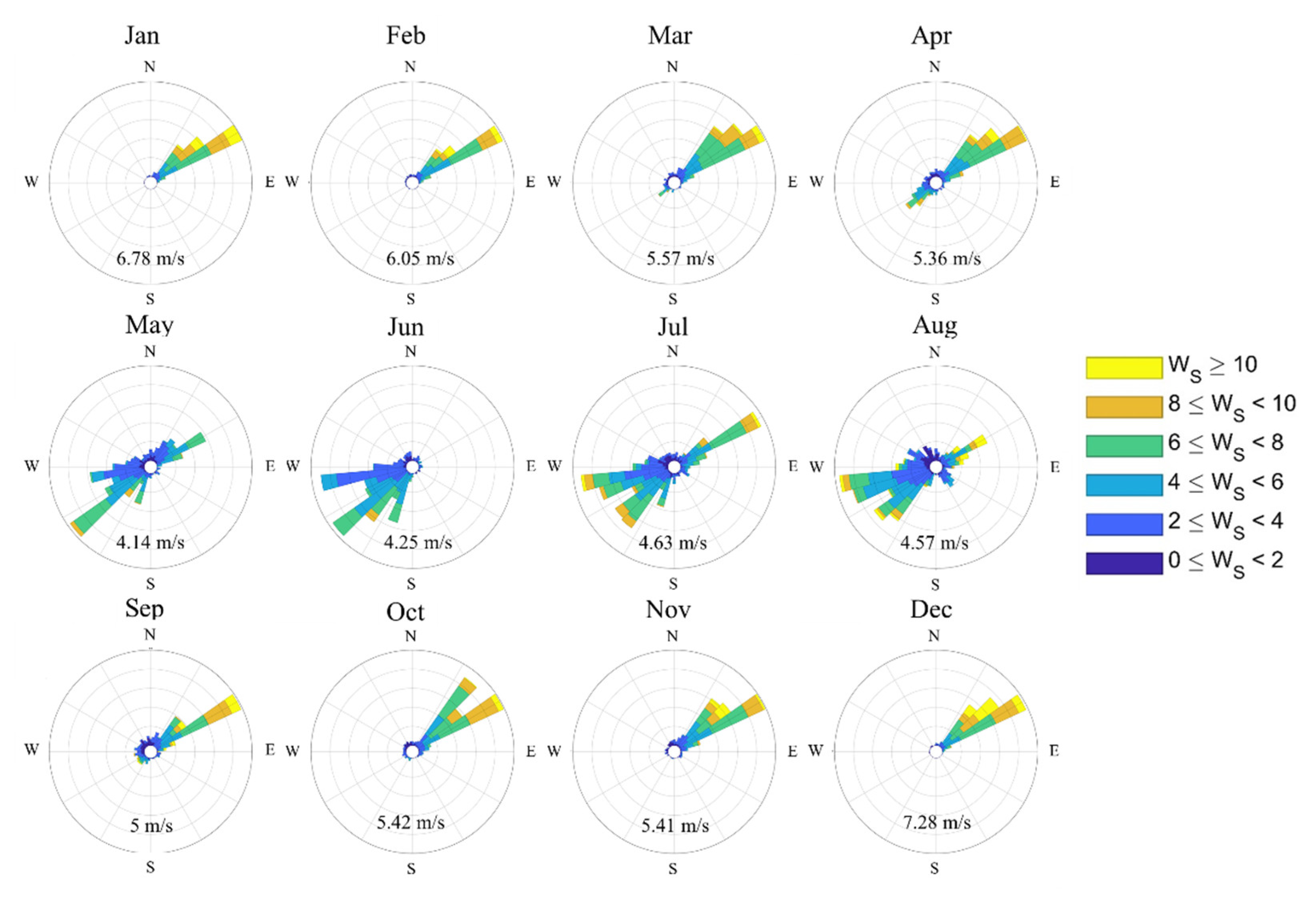
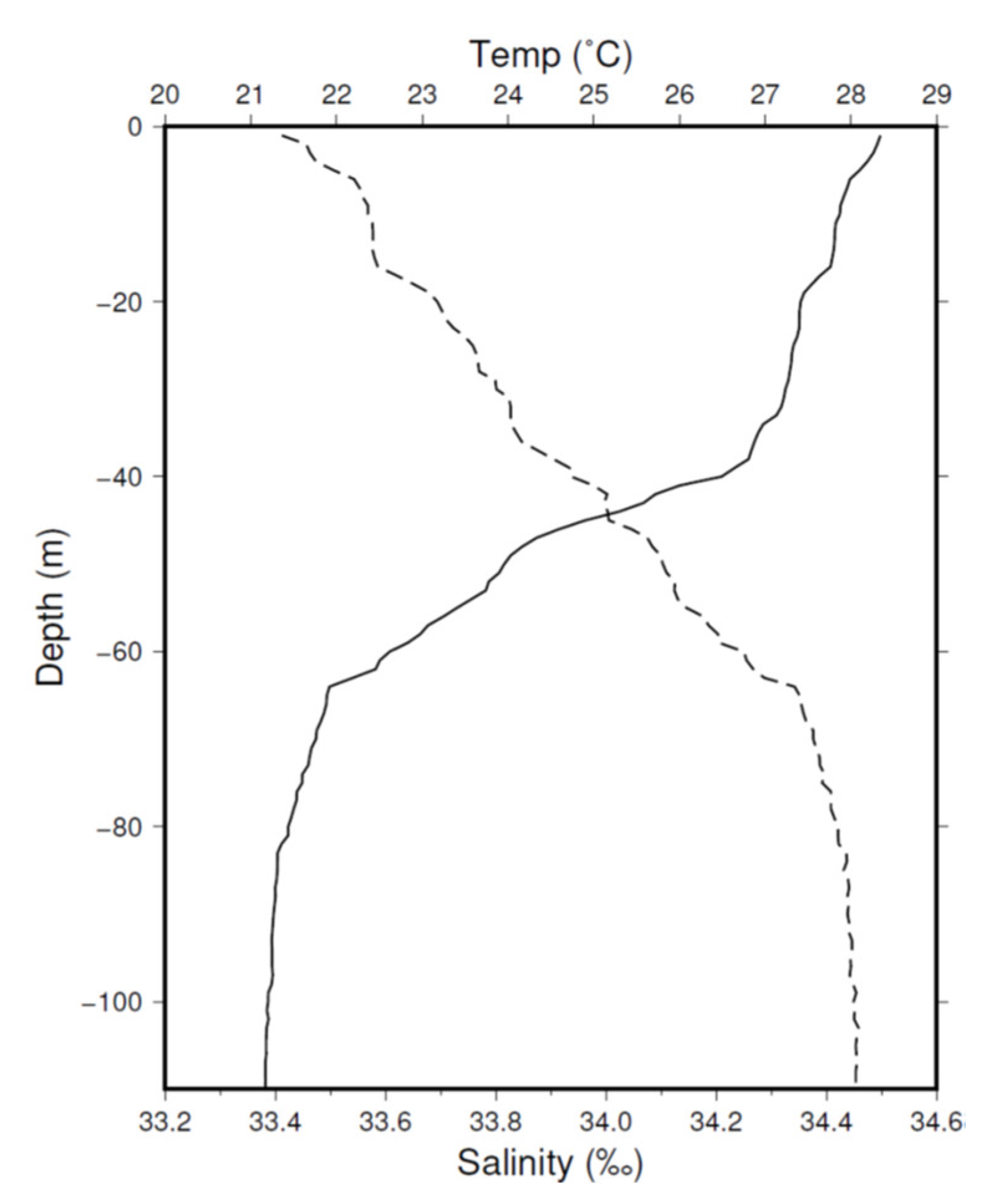
2. Observations
3. Model Formulation
4. Model Results
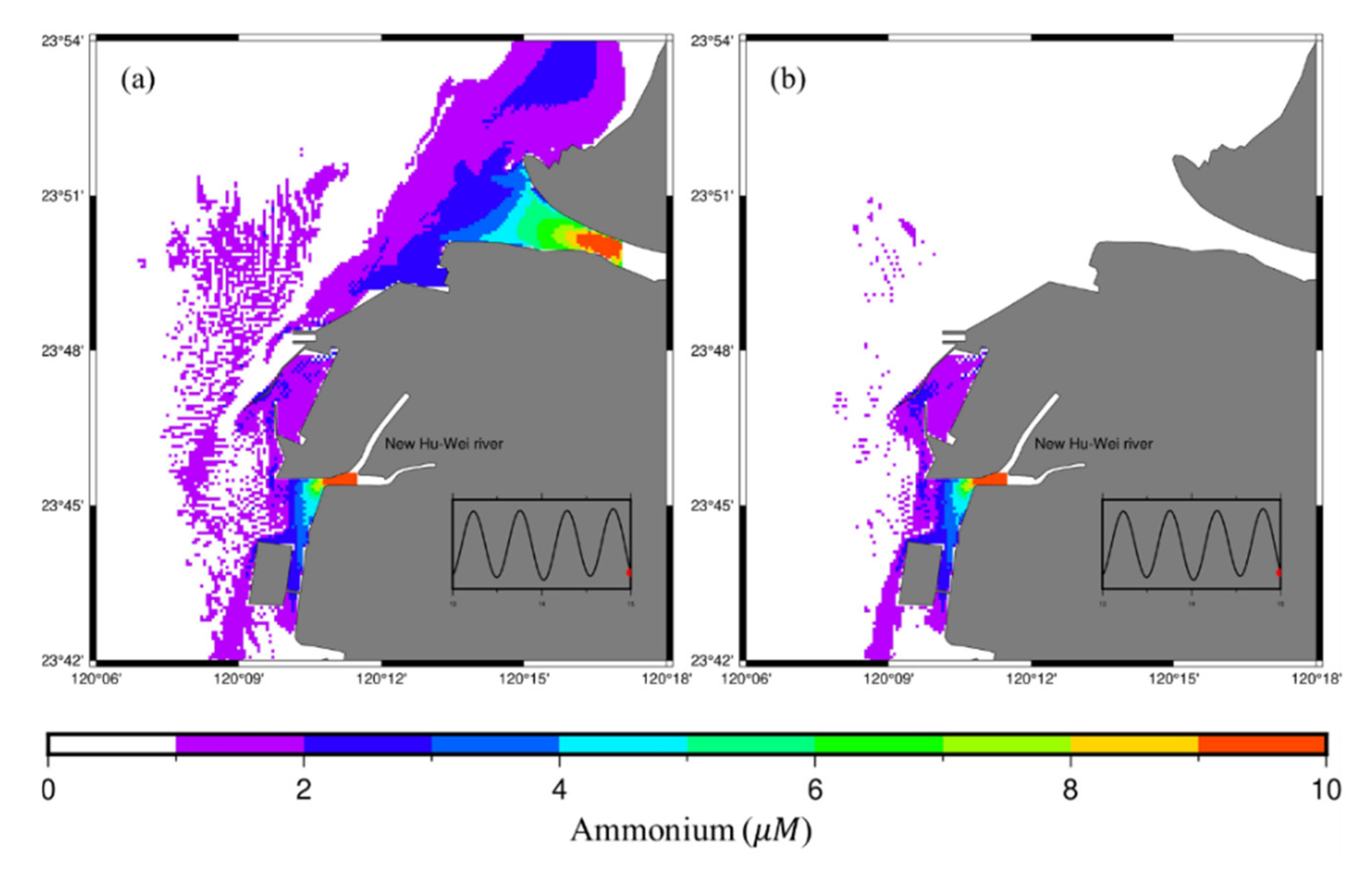
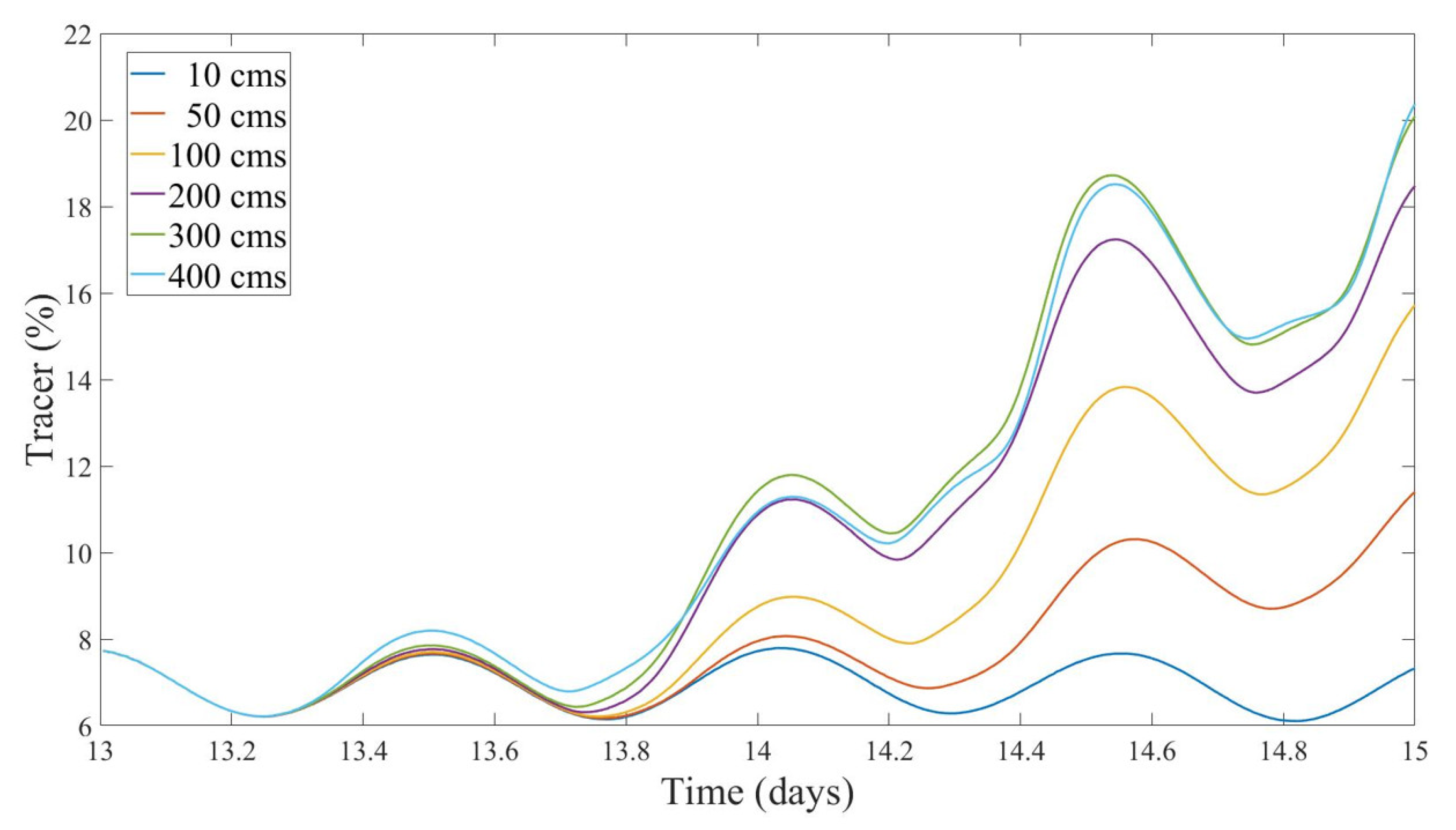
4.1. Plume of the Two Rivers Affects the Water Quality of the MIH
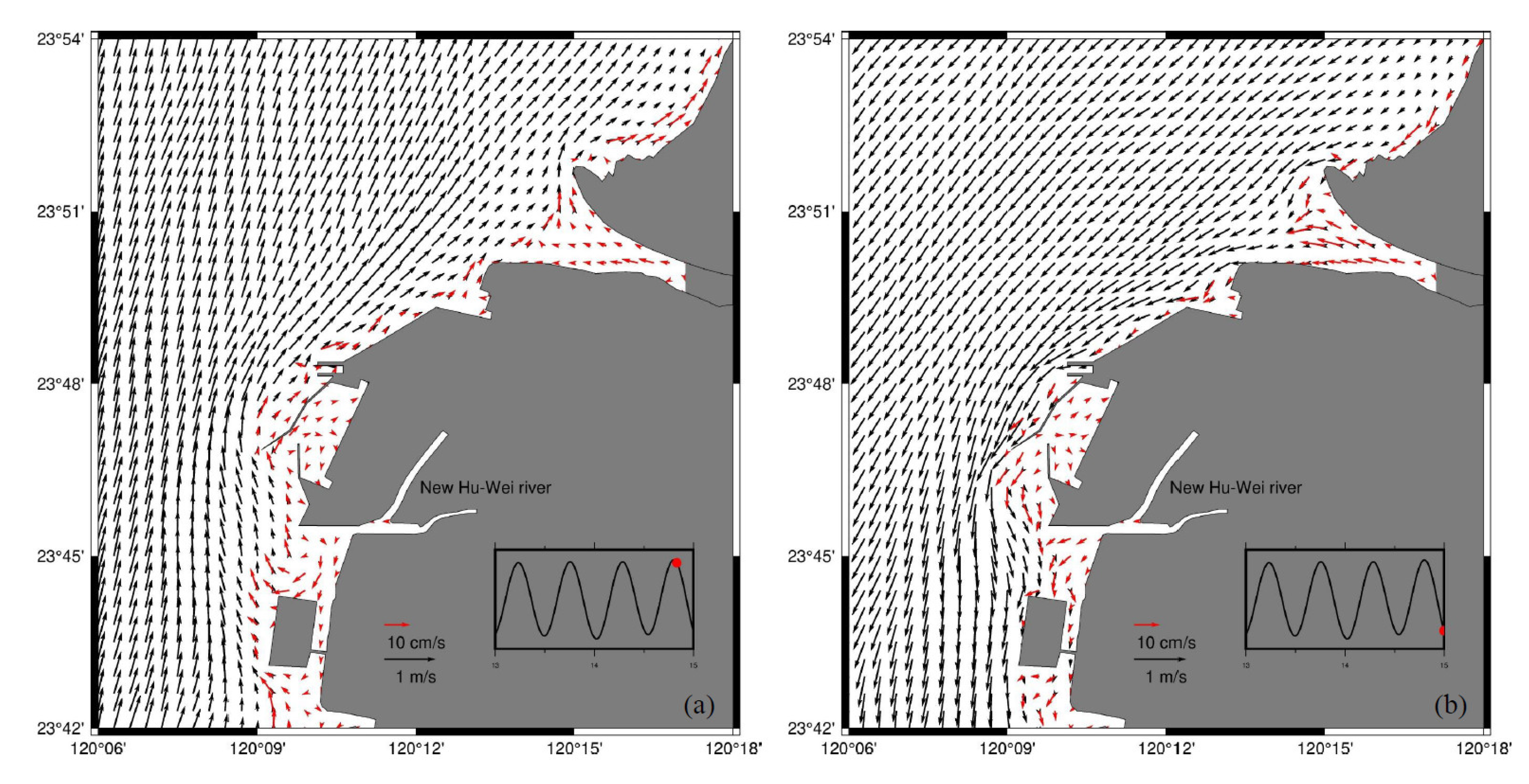
4.2. No Wind
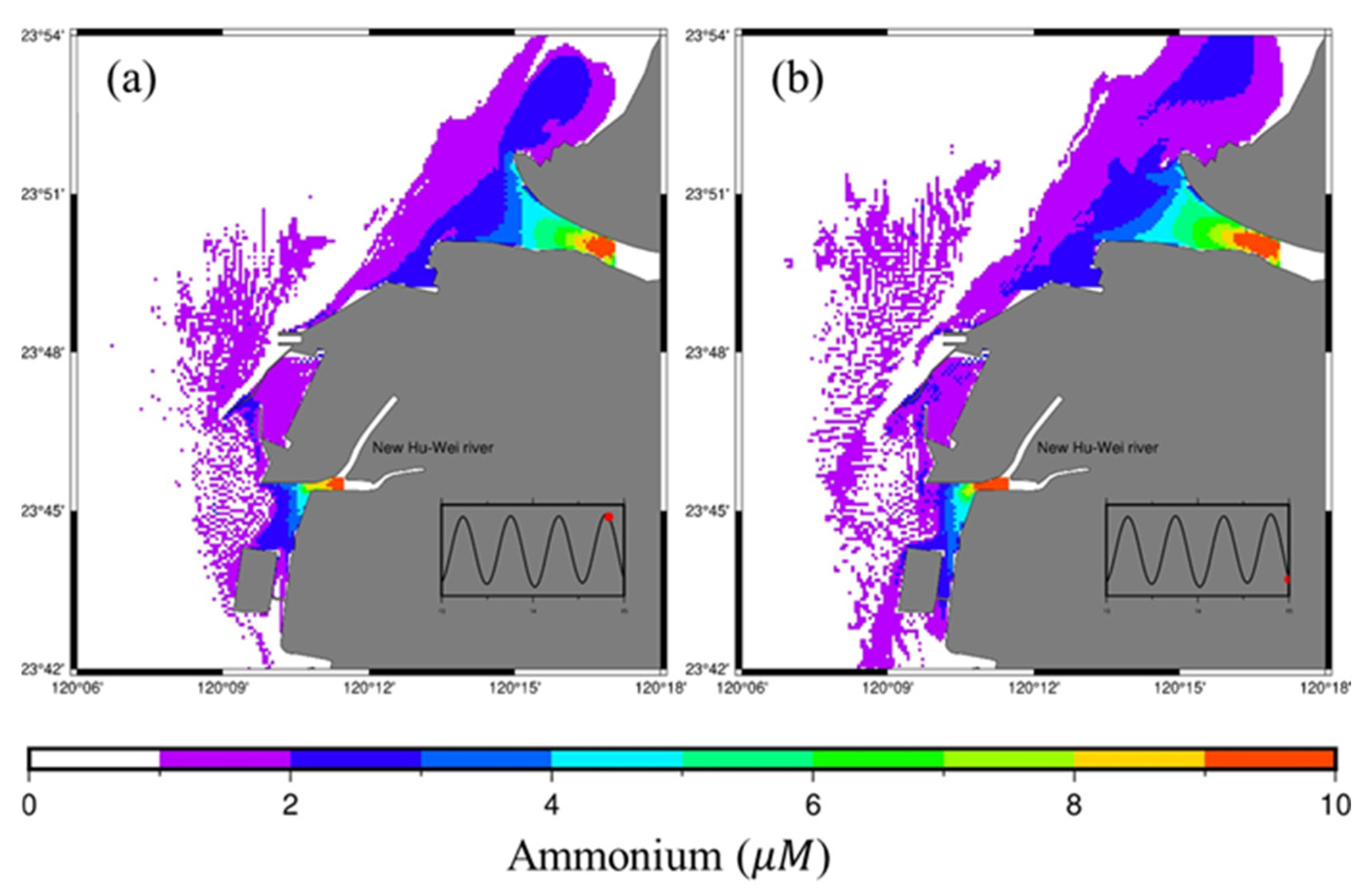
4.3. Southwesterly Winds
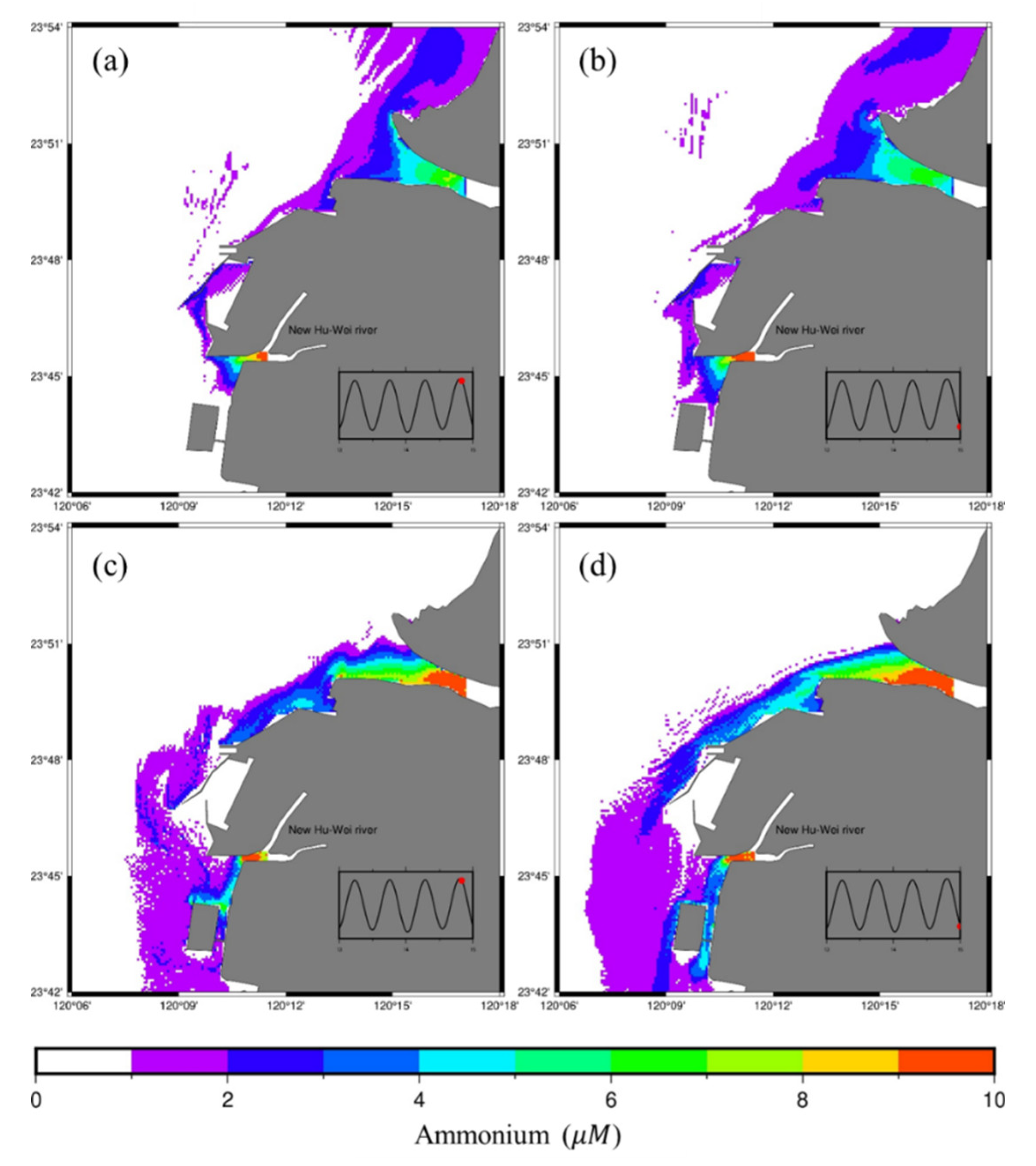
4.4. Northeasterly Winds
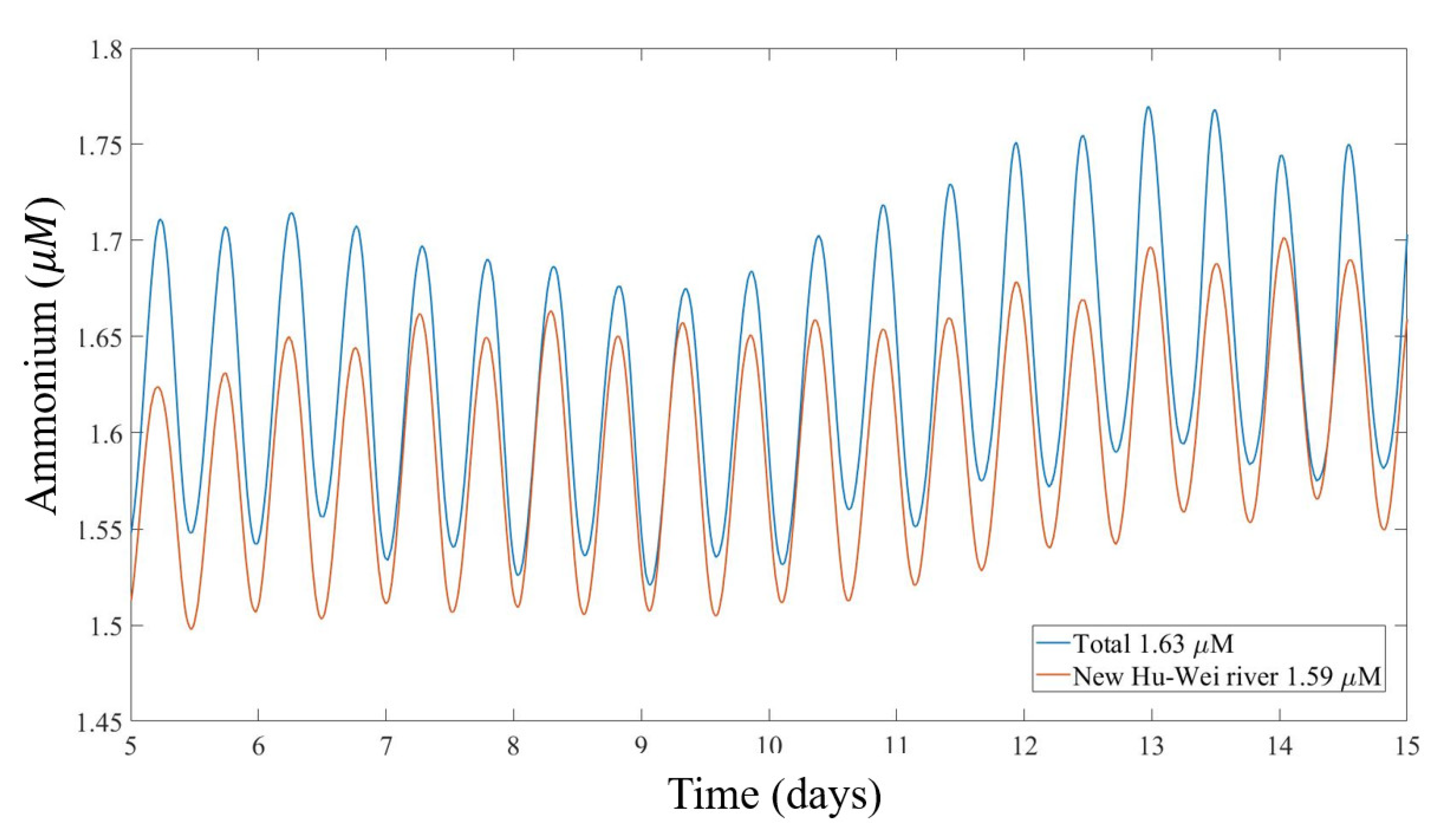
4.5. Relationship between Harbor Pollution and Discharge Flux
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The Generic Mapping Tools version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F. New, improved version of Generic Mapping Tools released. EOS Trans. AGU 1998, 79, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, S.M.; Lo, S.L.; Wang, S.H. A Generalized Water Quality Index for Taiwan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 96, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Meng, P.J.; Chen, C.C.; Tew, K.S. Monsoon effects on the residence time of a coastal lagoon in southwestern Taiwan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 233, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, M.S.A.; Lou, C.H.; Syai’in, M.; Ou, S.H.; Wang, Y.C. Long-Term River Water Quality Trends and Pollution Source Apportionment in Taiwan. Water 2018, 10, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, T.H.; Chen, J.L.; Huh, C.A. Sedimentary phosphorus species and sedimentation flux in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.Y. Tidal modulation of estuarine plumes. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.T.; Fan, K.L.; Chao, S.Y. Small-scale plumes from a semi-enclosed basin: Yin-Yang bay. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1994, 5, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.T.; Chao, S.Y.; Fan, K.L. Wind modulation of small-scale plumes from Yin-Yang bay. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1995, 6, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisma, D. Intertidal Deposits: River Mouths, Tidal Flats, and Coastal Lagoons; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; p. 525. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Chao, S.Y. A climatological description of circulation in and around the East China Sea. Deep-Sea Res. II 2003, 50, 1065–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chao, S.Y.; Liu, K.K. Effects of Reduced Yangtze River Discharge on the Circulation of Surrounding Seas. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2004, 15, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semtner, A.J. An oceanic general circulation model with bottom topography. Numer. Simul. Weather Clim. Tech. Rep. 1974, 9, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Chao, S.Y.; Fan, K.L. Flood-Ebb disparity of tidally Induced recirculation eddies in a semi-enclosed basin: Nan Wan Bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 1999, 19, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chao, S.Y.; Liu, K.K.; Huang, S.J.; Gong, G.C. Tidal effects on circulation in and near the East China Sea. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2014, 25, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, S.Y.; Paluszkiewicz, T. The hydraulics of density currents over estuarine sills. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 7065–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.Y.; Shaw, P.-T.; Wu, S.Y. El Nio modulation of the South China Sea circulation. Prog. Oceanogr. 1996, 38, 51–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacanowski, R.C.; Philander, S.G.H. Parameterization of vertical mixing in numerical models of tropical ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, J.L.; Bryan, K. An ocean transport model for the North Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, M.G.G. Manual for Tidal Heights Analysis and Prediction; Institute of Ocean Sciences: Patricia Bay, BC, Canada, 1997; p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, D. Tides, Surges and Mean Sea Level: A Handbook for Engineers and Scientists; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1987; 472p. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, T.J. Verification of numerical models of Lake Ontario: Part I. Circulation in spring and early summer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1974, 4, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Tides | Tide Gauge Station | |
|---|---|---|
| Amplitude | Phase Lag | |
| Q1 | 0.0311 | 291.60 |
| O1 | 0.1526 | 114.83 |
| K1 | 0.1972 | 282.93 |
| N2 | 0.2509 | 27.37 |
| M2 | 1.3874 | 211.57 |
| S2 | 0.3432 | 359.72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, C.-Y.; Fang, T.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Lee, H.-J. Interplay between Asian Monsoon and Tides Affects the Plume Dispersal of the New Hu-Wei River off the Coast of Midwest Taiwan. Water 2022, 14, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020152
Ho C-Y, Fang T-H, Wu C-H, Lee H-J. Interplay between Asian Monsoon and Tides Affects the Plume Dispersal of the New Hu-Wei River off the Coast of Midwest Taiwan. Water. 2022; 14(2):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020152
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Chia-Ying, Tien-Hsi Fang, Cheng-Han Wu, and Hung-Jen Lee. 2022. "Interplay between Asian Monsoon and Tides Affects the Plume Dispersal of the New Hu-Wei River off the Coast of Midwest Taiwan" Water 14, no. 2: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020152
APA StyleHo, C.-Y., Fang, T.-H., Wu, C.-H., & Lee, H.-J. (2022). Interplay between Asian Monsoon and Tides Affects the Plume Dispersal of the New Hu-Wei River off the Coast of Midwest Taiwan. Water, 14(2), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020152







