Pollution Evaluation of the El Pueblito River in Queretaro, Mexico, Using the Water Quality Index
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
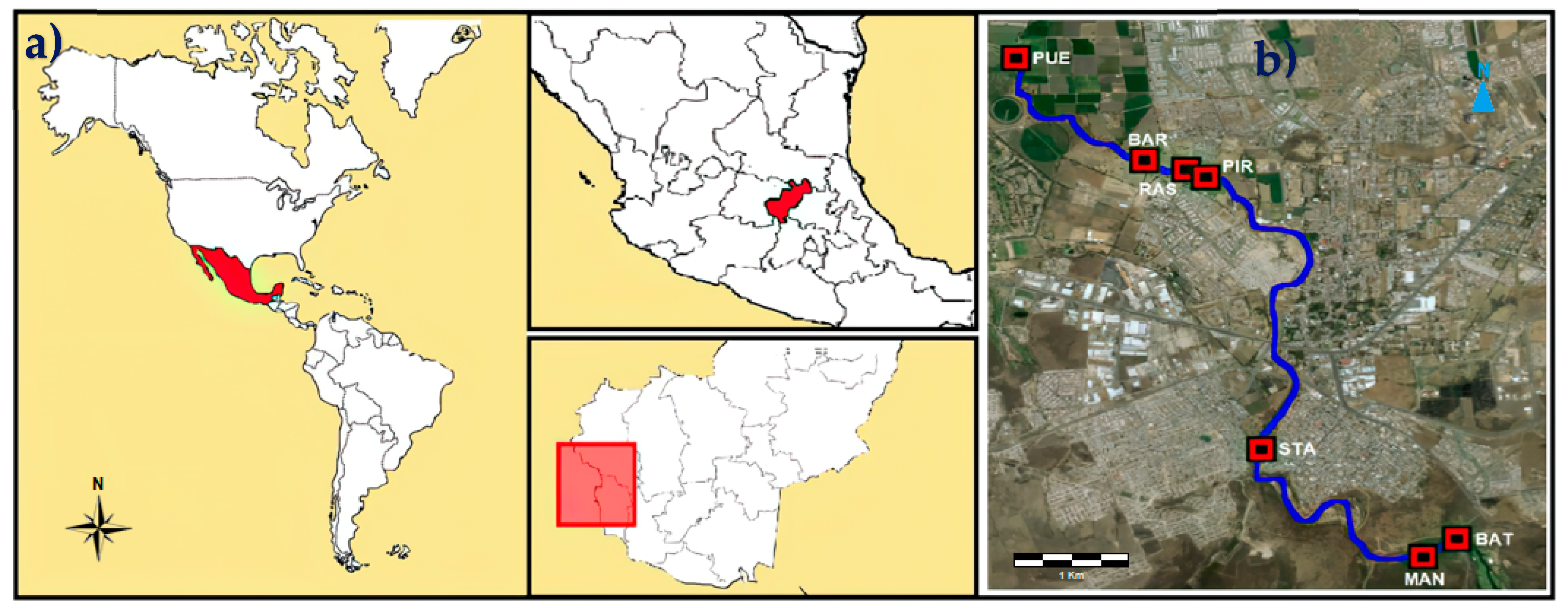
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampled Sites
2.3. Physicochemical Parameters
2.4. Biological Indicators
2.4.1. Daphnia Magna Assays
2.4.2. Bioassay with Sorghum Seed Base
2.5. Water Quality Index
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters
3.2. Biological Parameters and Bioassays
3.3. Parameters Correlation
3.4. Water Quality Index
4. Comparison of WQI and Biological Indicators
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, G.M.; Neary, J.P. Water Quality for Ecosystem and Human Health, 2nd ed.; United Nations Environment Programme, Global Environment Monitoring System (GEMS)/Water Programme: Ontario, ON, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Peña-Guzmán, C.; Ulloa-Sánchez, S.; Mora, K.; Helena-Bustos, R.; Lopez-Barrera, E.; Alvarez, J.; Rodriguez-Pinzón, M. Emerging Pollutants in the Urban Water Cycle in Latin America: A Review of the Current Literature. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Total Concentrations and Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution in Global River and Lake Water Bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathaniel, S.P.; Nwulu, N.; Bekun, F. Natural Resource, Globalization, Urbanization, Human Capital, and Environmental Degradation in Latin American and Caribbean Countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6207–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakre, G.; Shrivastava, N.; Mishra, P.K. Analytical Studies on Water Quality Index of River Tapti. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2011, 9, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Ober, J.; Karwot, J.; Rusakov, S. Tap Water Quality and Habits of Its Use: A Comparative Analysis in Poland and Ukraine. Energies 2022, 15, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Huang, T.; Yan, M.; Liu, K.; Miao, Y.; He, H.; Li, S.; Sekar, R. Combined Effects of Seasonality and Stagnation on Tap Water Quality: Changes in Chemical Parameters, Metabolic Activity and Co-Existence in Bacterial Community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroud, M.; Trolard, F.; Kefi, M.; Jebari, S.; Bourrié, G. Water Quality Indices: Challenges and Application Limits in the Literature. Water 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neachell, E. Book Review—Environmental Flows: Saving Rivers in the Thrid Millennium. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 132–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Elumalai, V.; Subramani, T. Seasonal Variation of Drinking Water Quality and Human Health Risk Assessment in Hancheng City of Guanzhong Plain, China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçer, M.A.T.; Sevgili, H. Parameters Selection for Water Quality Index in the Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Land-Based Trout Farms. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukate, S.; Wagh, V.; Panaskar, D.; Jacobs, J.A.; Sawant, A. Development of New Integrated Water Quality Index (IWQI) Model to Evaluate the Drinking Suitability of Water. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J. Evaluation of Water Quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China Using the Water Quality Index (WQI) Method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacioglu, H.; Boyacioglu, H. Surface Water Quality Assessment by Environmetric Methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debels, P.; Figueroa, R.; Urrutia, R.; Barra, R.; Niell, X. Evaluation of Water Quality in the Chillán River (Central Chile) Using Physicochemical Parameters and a Modified Water Quality Index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 110, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobjal, R. Water Quality Assessment in Terms of Water Quality Index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2014, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P. Application of Water Quality Indices and Dissolved Oxygen as Indicators for River Water Classification and Urban Impact Assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cude, C.G. Oregon Water Quality Index a Tool for Evaluating Water Quality Management Effectiveness. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Meta-Evaluation of Water Quality Indices. Application into Groundwater Resources. Water 2020, 12, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džeroski, S.; Demšar, D.; Grbović, J. Predicting Chemical Parameters of River Water Quality from Bioindicator Data. Appl. Intell. 2000, 13, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifinia, M.; Mahmoudifard, A.; Imanpour Namin, J.; Ramezanpour, Z.; Yap, C.K. Pollution Evaluation in the Shahrood River: Do Physico-Chemical and Macroinvertebrate-Based Indices Indicate Same Responses to Anthropogenic Activities? Chemosphere 2016, 159, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfanti, R.L.; Piccioni, D.E.; Handwerker, J.; Bahrami, N.; Krishnan, A.P.; Karunamuni, R.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.A.; Seibert, T.M.; Srikant, A.; Jones, K.A.; et al. The Structure of Health Factors among Community-dwelling Elderly People. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 372, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.L. Comparison between Water Quality Index (WQI) and Biological Indices, Based on Planktonic Diatom for Water Quality Assessment in the Dong Nai River, Vietnam. Pollution 2017, 3, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, K.E.; Cooper, T.F.; Humphrey, C.; Uthicke, S.; De’ath, G.; Davidson, J.; LeGrand, H.; Thompson, A.; Schaffelke, B. A Bioindicator System for Water Quality on Inshore Coral Reefs of the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T. A Generic Index of Diatom Assemblages as Bioindicator of Pollution in the Keelung River of Taiwan. Hydrobiologia 1999, 397, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.; Chopra, A.; Durgapal, N.; Kumar, A. Evaluation of Daphnia Magna as an Indicator of Toxicity and Treatment Efficacy of Municipal Sewage Treatment Plant. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2009, 11, 46835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuytema, G.S.; Nebeker, A.V.; Stutzman, T.W. Salinity Tolerance of Daphnia Magna and Potential Use for Estuarine Sediment Toxicity Tests. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 33, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deeb Ghazy, M.M.; Habashy, M.M.; Mohammady, E.Y. Effects of PH on Survival, Growth and Reproduction Rates of the Crustacean, Daphnia Magna. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gopi, R.A.; Ayyappan, S.; Chandrasehar, G.; Varma, K.K.; Goparaju, A. Effect of Potassium Dichromate on the Survival and Reproduction of Daphnia Magna. Bull. Environ. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 2012, 1, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ciencia Tecnología e Innovación En Querétaro. Casos Exitosos: Saneamiento de Las Aguas Río El Pueblito. Available online: http://www.concyteq.edu.mx/concyteq//uploads/publicacionArchivo/2017-06-742.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- NMX-AA-029-SCFI-2001. Determinación De Fósforo Total En Aguas Naturales, Residuales Y Residuales Tratadas. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166773/NMX-AA-029-SCFI-2001.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- NMX-AA-028-SCFI-2001. Análisis De Agua—Determinación de La Demanda Bioquímica de Oxígeno En Aguas Naturales, Residuales (DBO5) y Residuales Tratadas. Available online: http://www.economia-nmx.gob.mx/normas/nmx/2001/nmx-aa-028-scfi-2001.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- NMX-AA-030/2-SCFI-2011. Determinación de La Demanda Químia de Oxígeno En Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166775/NMX-AA-030-2-SCFI-2011.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- NMX-AA-034-SCFI-2015. Análisis de Agua- Medición de Sólidos y Sales Disueltas En Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Tratadas. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166146/nmx-aa-034-scfi-2015.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Volkmar, E.C.; Henson, S.S.; Dahlgren, R.A.; O’Geen, A.T.; Van Nieuwenhuyse, E.E. Diel Patterns of Algae and Water Quality Constituents in the San Joaquin River, California, USA. Chem. Geol. 2011, 283, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NMX-AA-042-SCFI-2015. Análisis de Agua - Enumeración de Organismos Coliformes Totales, Organismos Coliformes Fecales (Termotolerantes) y Escherichia Coli-Método Del Número Más Probable En Tubos Múltiples. D. Of. la Fed. 1–25. 2015. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166147/nmx-aa-042-scfi-2015.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- NMX-AA-087-SCFI-2010. Análisis de Agua- Evaluación de Toxicidad Aguada Con Daphnia Magna, Straus (Crustacea—Cladocera). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166797/NMX-AA-087-SCFI-2010.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- United States Enviromental Protection Agency. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms, 5th ed.; Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; ISBN EPA-821-R-02-012.
- Inc, A.B. Quest Grtaph TM. Available online: https://www.aatbio.com/tools/lc50-calculator (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Mitelut, A.A.C.; Popa, M.E. Seed Germination Bioassay for Toxicity Evaluation of Different Composting Biodegradable Materials. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 16, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of Water Quality Indices To Verify the Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquía River. Wat. Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagels, J.W.; Davies-Colley, R.J.; Smith, D.G. A Water Quality Index for Contact Recreation in New Zealand. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOM-003-SEMARNAT-1997; SEMARNAT Normas Oficiales Mexicanas Normas Oficiales Mexicanas. Comisión Nacional del Agua: Mexico City, Mexico, 2013; pp. 1–65.
- Enad, H.Y.; Jaeel, A.J. Water Quality Index of Tigris River on Waist Governorate for Aquatic Life. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 584, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. EPA Recreational Water Quality Criteria; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 1–69.
- Al-Rosyid, L.M.; Titah, H.S.; Santoso, I.B.; Mangkoedihardjo, S. Review on BOD/COD Ratio Toxicity to Daphnia Magna, Artemia Salina and Brachydanio Rerio. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2021, 20, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiga, W.; Boivin, P.; Ouarnier, N.; Fournier, F.; Fick, M. Quantification of the Inhibitory Effect of Steep Effluents on Barley Germination. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalkowski, T.; Zbytniewski, R.; Szpejna, J.; Buszewski, B. Application of Chemometrics in River Water Classification. Water Res. 2006, 40, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirin, S.; Yadav, A. Physico Chemical Analysis of Municipal Wastewater Discharge in Ganga River, Haridwar District of Uttarakhand, India. Curr. World Environ. 2014, 9, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorović, I.; Bečelić, M.; Planojević, I.; Ivančev-Tumbas, I.; Dalmacija, B. The Relationship between Whole Effluent Toxicity (WET) and Chemical-Based Effluent Quality Assessment in Vojvodina (Serbia). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 158, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Place | Coordinates | Altitude, ft | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | West | |||
| 1 | BAT | 20°30.845′ | 100°25.881′ | 6053 |
| 2 | MAN | 20°30.776′ | 100°26.065′ | 6047 |
| 3 | STA | 20°31.573′ | 100°26.774′ | 6023 |
| 4 | PIR | 20°32.951′ | 100°27.300′ | 6096 |
| 5 | RAS | 20°32.986′ | 100°27.336′ | 6096 |
| 6 | BAR | 20°30.827′ | 100°25.952′ | 6095 |
| 7 | PUE | 20°33582′ | 100°28.006′ | 6097 |
| Parameter | Weight Pi | Normalization Factor Ci | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 90 | 80 | 70 | 60 | 50 | 40 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 0 | ||
| BOD5 ac | 3 | 0.5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 18 |
| COD ac | 3 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 150 | 210 |
| Conductivity c | 1 | 750 | 1000 | 1250 | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 | 3000 | 5000 | 8000 | 12,000 | 16,000 |
| Phosphates ad | 1 | 0.16 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 6.4 | 9.6 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 96 | 160 | 240 |
| Ph d | 1 | 7 | 7.5 | 8 | 8.5 | 9 | 9.5 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| TDS a | 2 | 150 | 250 | 350 | 400 | 500 | 900 | 1100 | 1300 | 1600 | 1900 | 2500 |
| Total coliforms c | 4 | 50 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 | 5000 | 7000 | 10,000 | 14,000 | 19,000 |
| Total solids a | 1 | 100 | 171 | 249 | 338 | 441 | 564 | 712 | 905 | 1175 | 1526 | 1954 |
| Parameter | Average | Maximum | Minimum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 23.12 ± 1.40 | 24.80 | 21.10 |
| pH | 7.82 ± 0.32 | 8.39 | 7.24 |
| TDS (ng/L) | 786.27 ± 386.69 | 1570.00 | 360.00 |
| VSS (mg/L) | 279.54 ± 228.64 | 885.00 | 5.00 |
| TS (mg/L) | 722.35 ± 410.06 | 1575.00 | 5.00 |
| Conductivity (S/cm) | 1.11 ± 0.58 | 2.23 | 0.12 |
| CDO (mg/L) | 337.33 ± 395.53 * | 1289.00 * | ND |
| BOD (mg/L) | 352.97 ± 397.75 * | 1248.00 * | ND |
| Fecal coliforms (MPN/100 mL) | 1081.00 ± 1164.60 * | 2400.00 * | 0.3 |
| Parameter | Conductivity | COD | BOD | VSS | Sorghum | LC50 | TDS | PT | TS | Total Coliforms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | 1.00 | |||||||||
| COD | 0.69 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| BOD | 0.55 | 0.65 | 1.00 | |||||||
| VSS | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.51 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Sorghum | −0.19 | −0.32 | −0.35 | −0.22 | 1.00 | |||||
| LC50 | 0.37 | 0.68 | 0.36 | 0.38 | −0.19 | 1.00 | ||||
| TDS | 0.98 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 0.71 | −0.31 | 0.50 | 1.00 | |||
| PT | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.66 | −0.21 | 0.51 | 0.87 | 1.00 | ||
| TS | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 1.00 | |
| Total coliforms | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.82 | −0.21 | 0.46 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.19 | 1.00 |
| WQI Value Range | Rating of Water Quality |
|---|---|
| 91–100 | Excellent |
| 71–90 | Good |
| 51–70 | Medium |
| 26–50 | Bad |
| 0–25 | Very bad |
| Places/Week | RAS | PIR | PUE | STA | MAN | BAT | BAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27.12 | 36.53 | 42.65 | 78.90 | 76.65 | 79.30 | 31.29 |
| 2 | 26.80 | 29.95 | 38.47 | 89.65 | 90.45 | 90.93 | 29.34 |
| 3 | 26.29 | 32.62 | 42.12 | 89.46 | 89.62 | 73.36 | 30.59 |
| 4 | 28.78 | 35.29 | 38.90 | 61.12 | 82.86 | 89.62 | 32.77 |
| 5 | 27.01 | 31.52 | 38.80 | 68.02 | 71.29 | 67.89 | 31.57 |
| 6 | 27.58 | 30.51 | 38.63 | 78.86 | 82.90 | 73.04 | 30.81 |
| 7 | 25.39 | 28.61 | 34.95 | 83.65 | 87.20 | 81.86 | 31.52 |
| Average | 27.00 | 32.15 | 39.22 | 78.52 | 83.00 | 79.43 | 31.13 |
| SD | 0.85 | 2.65 | 1.92 | 11.42 | 7.40 | 9.44 | 1.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Nuñez, E.; Hernandez-Mendoza, C.; Perez-Moreno, V.; Cardenas, A. Pollution Evaluation of the El Pueblito River in Queretaro, Mexico, Using the Water Quality Index. Water 2022, 14, 3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193040
Rodriguez-Nuñez E, Hernandez-Mendoza C, Perez-Moreno V, Cardenas A. Pollution Evaluation of the El Pueblito River in Queretaro, Mexico, Using the Water Quality Index. Water. 2022; 14(19):3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193040
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Nuñez, Enrique, Christian Hernandez-Mendoza, Victor Perez-Moreno, and Arely Cardenas. 2022. "Pollution Evaluation of the El Pueblito River in Queretaro, Mexico, Using the Water Quality Index" Water 14, no. 19: 3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193040
APA StyleRodriguez-Nuñez, E., Hernandez-Mendoza, C., Perez-Moreno, V., & Cardenas, A. (2022). Pollution Evaluation of the El Pueblito River in Queretaro, Mexico, Using the Water Quality Index. Water, 14(19), 3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193040





