Assessment of Infiltration from Private Sewer Laterals: Case Study in Jurmala, Latvia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
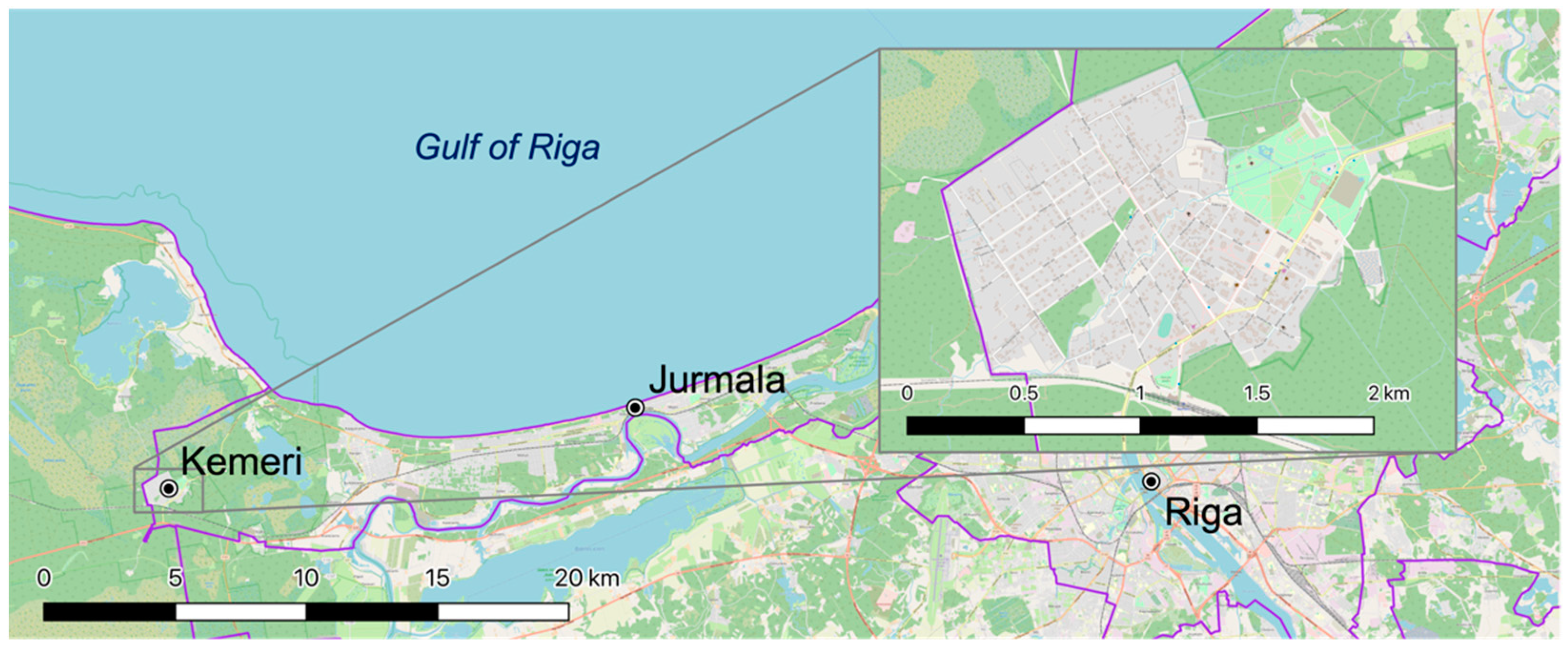
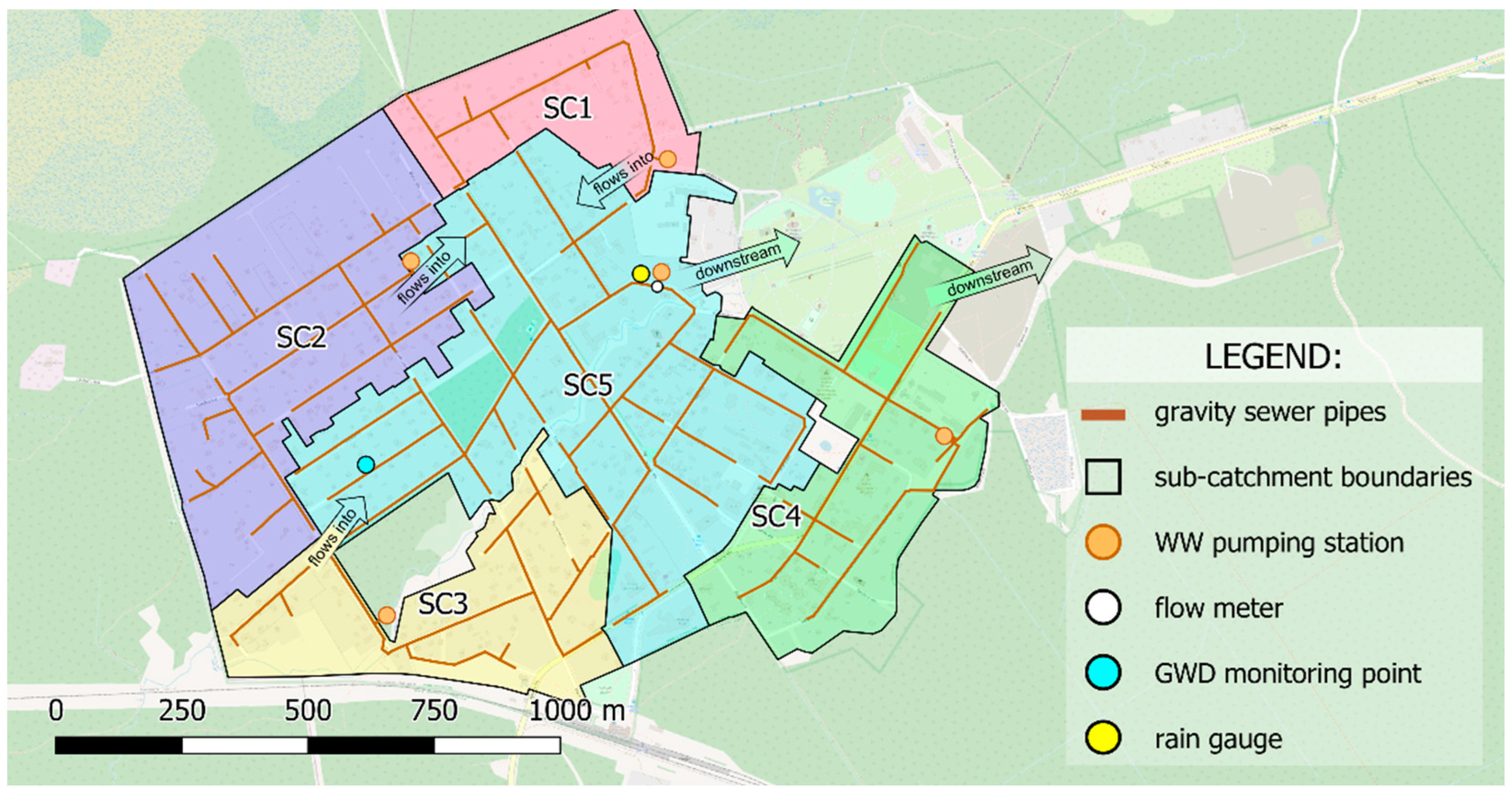
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sub-Catchment Description
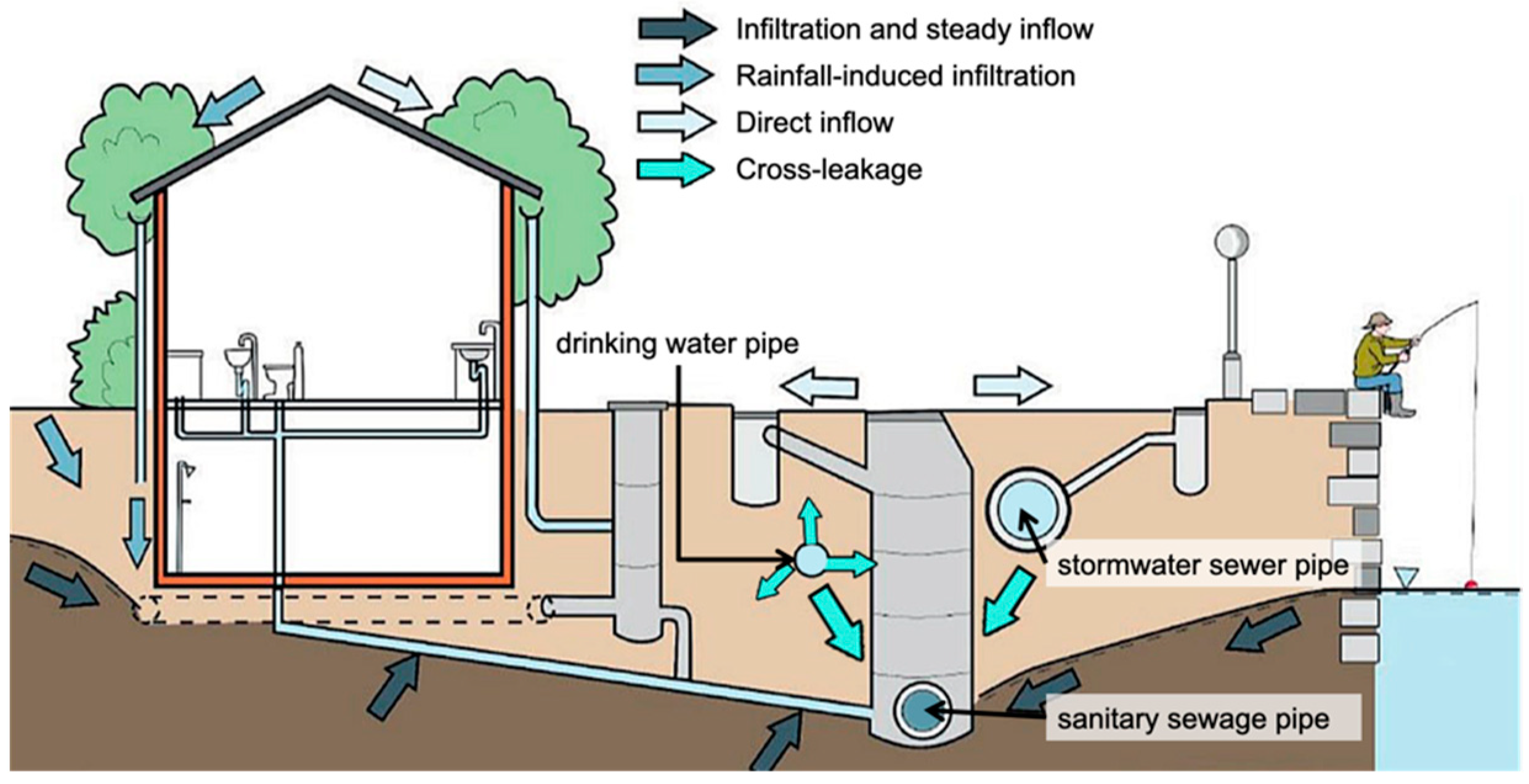
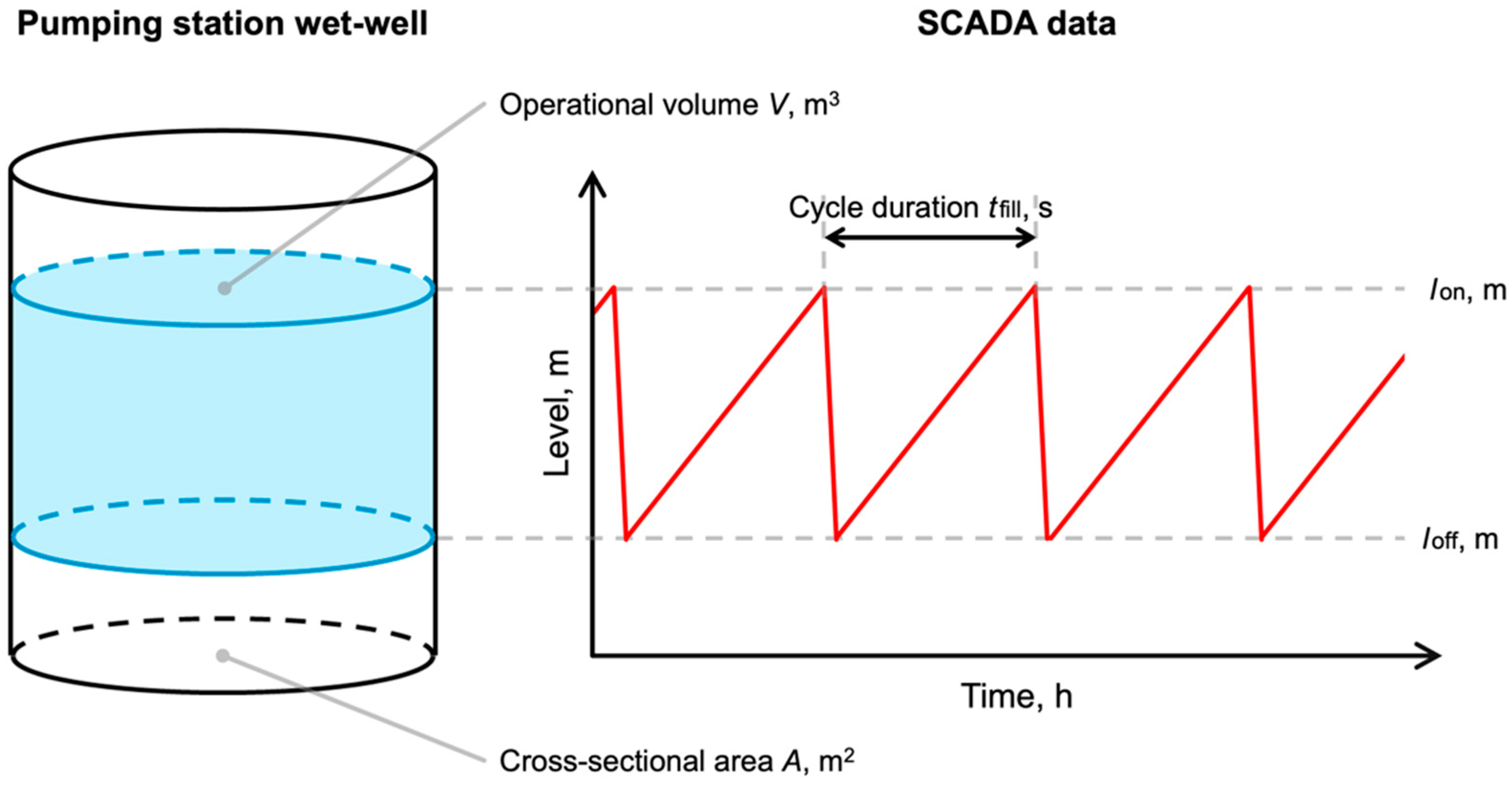
2.3. Method to Assess the I/I from Private Sewer Laterals
2.4. Measuring Equipment
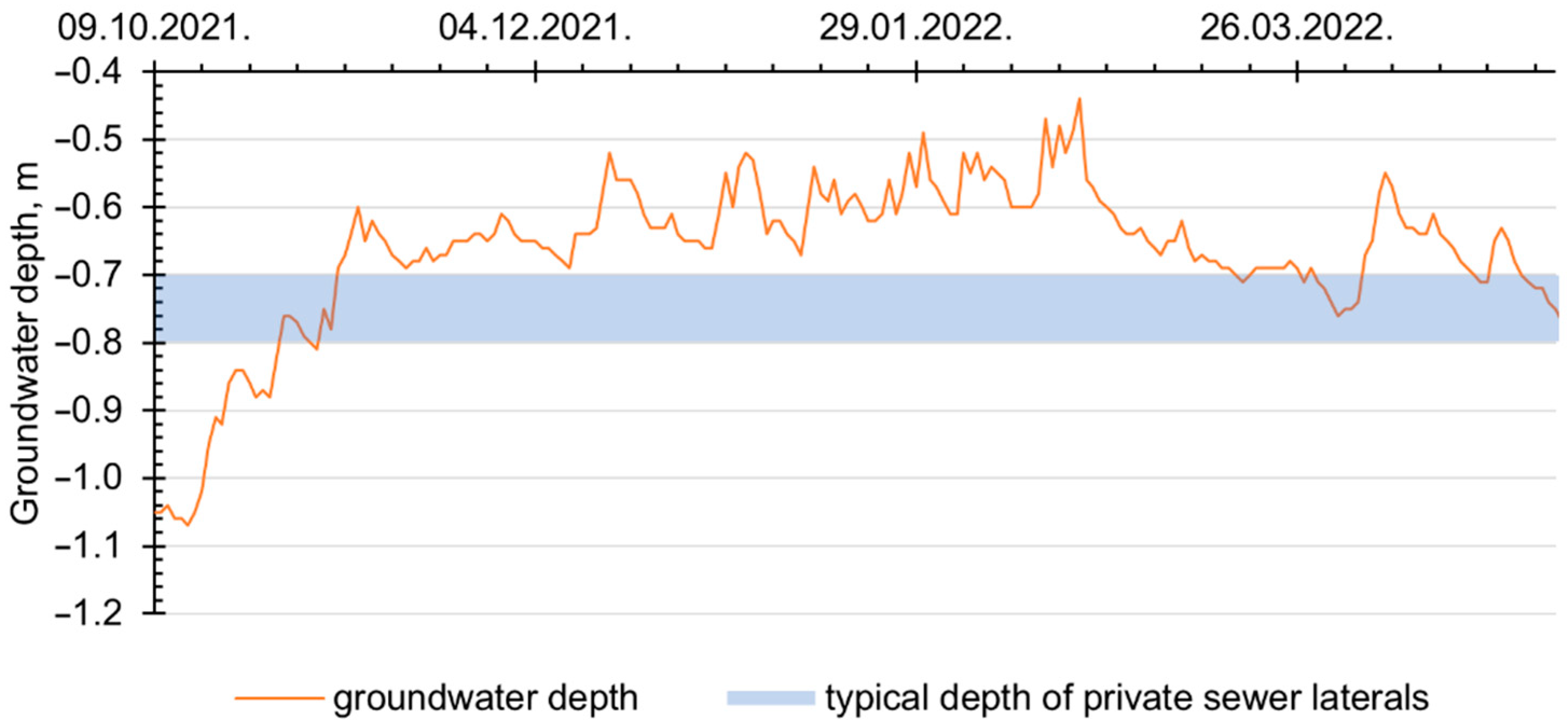
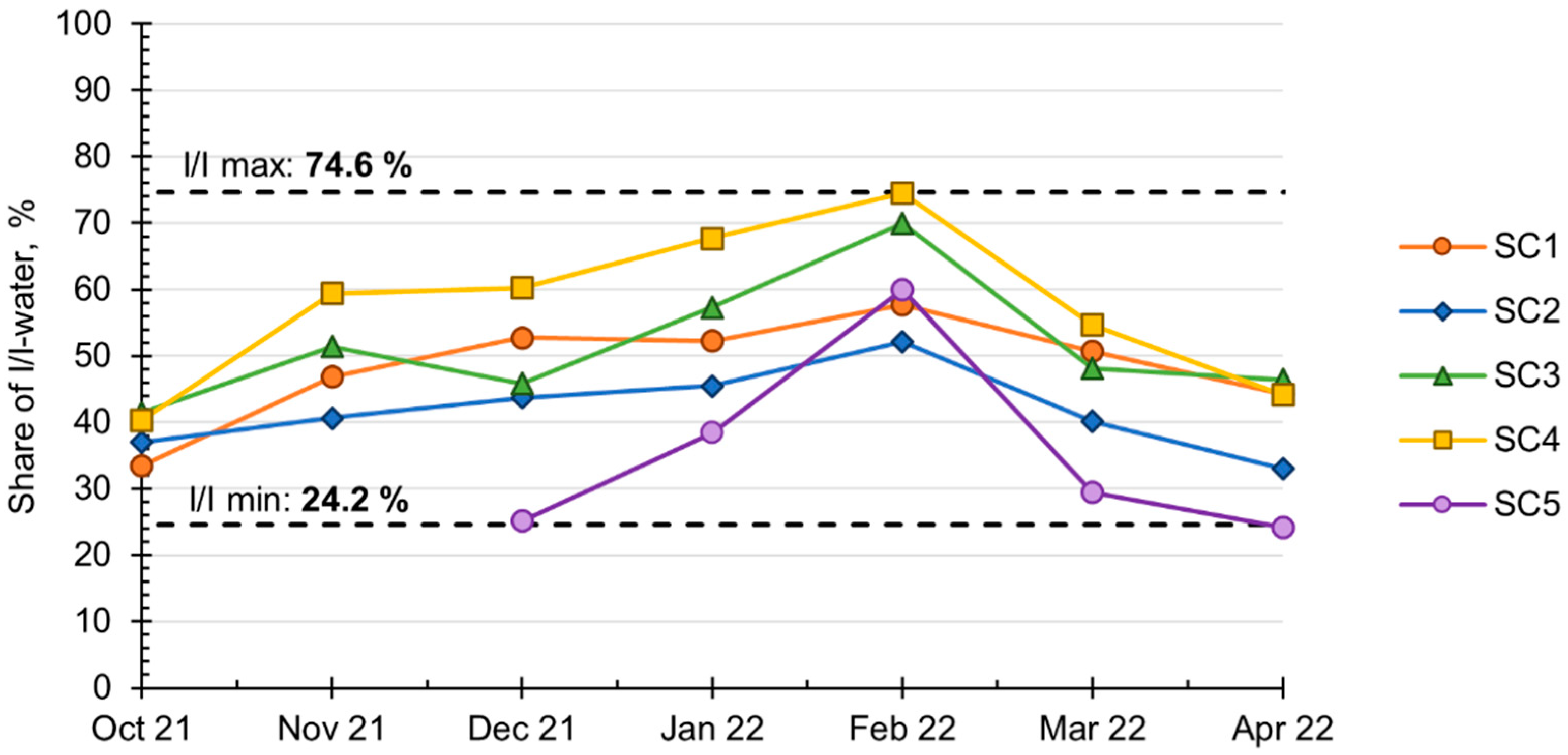
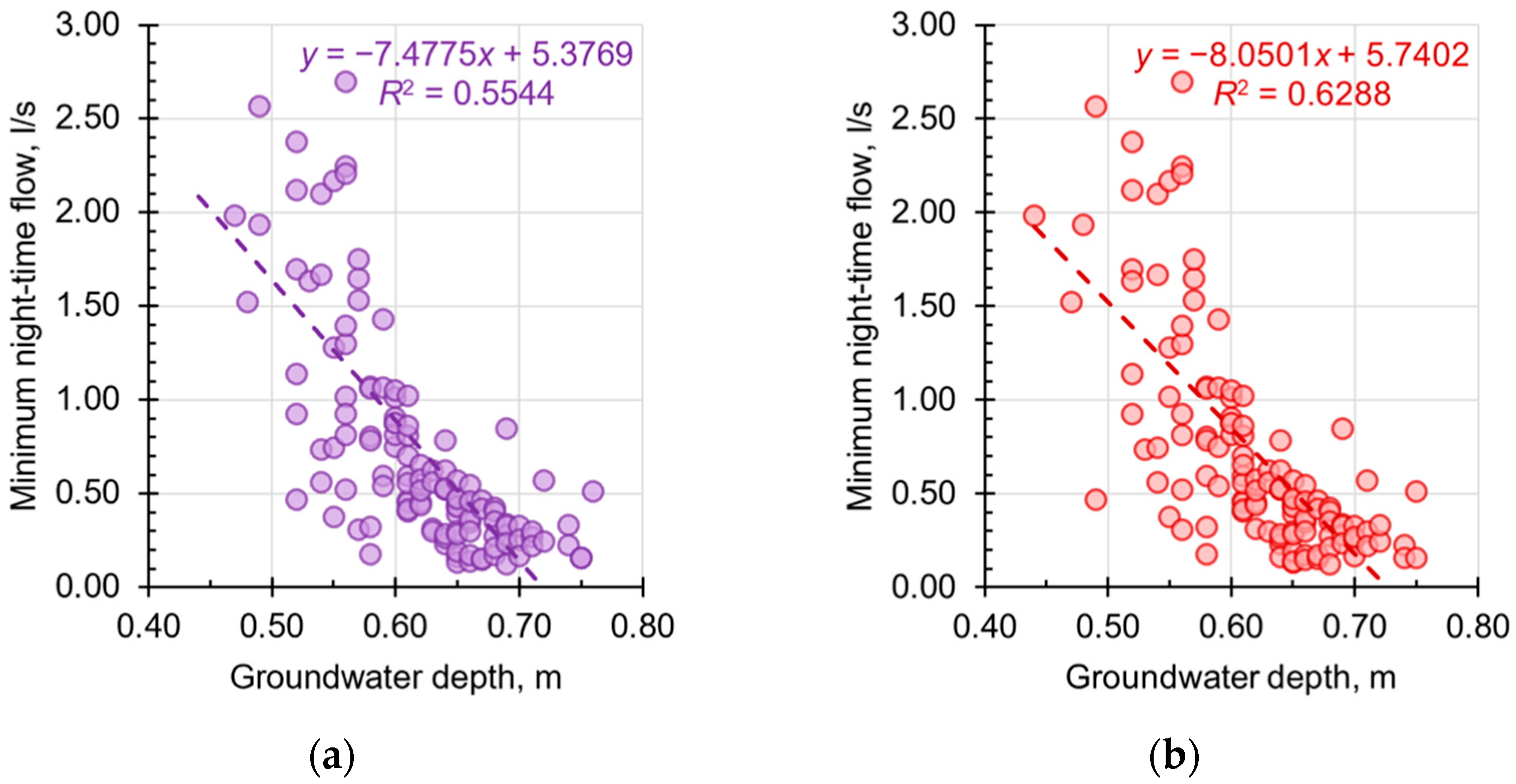
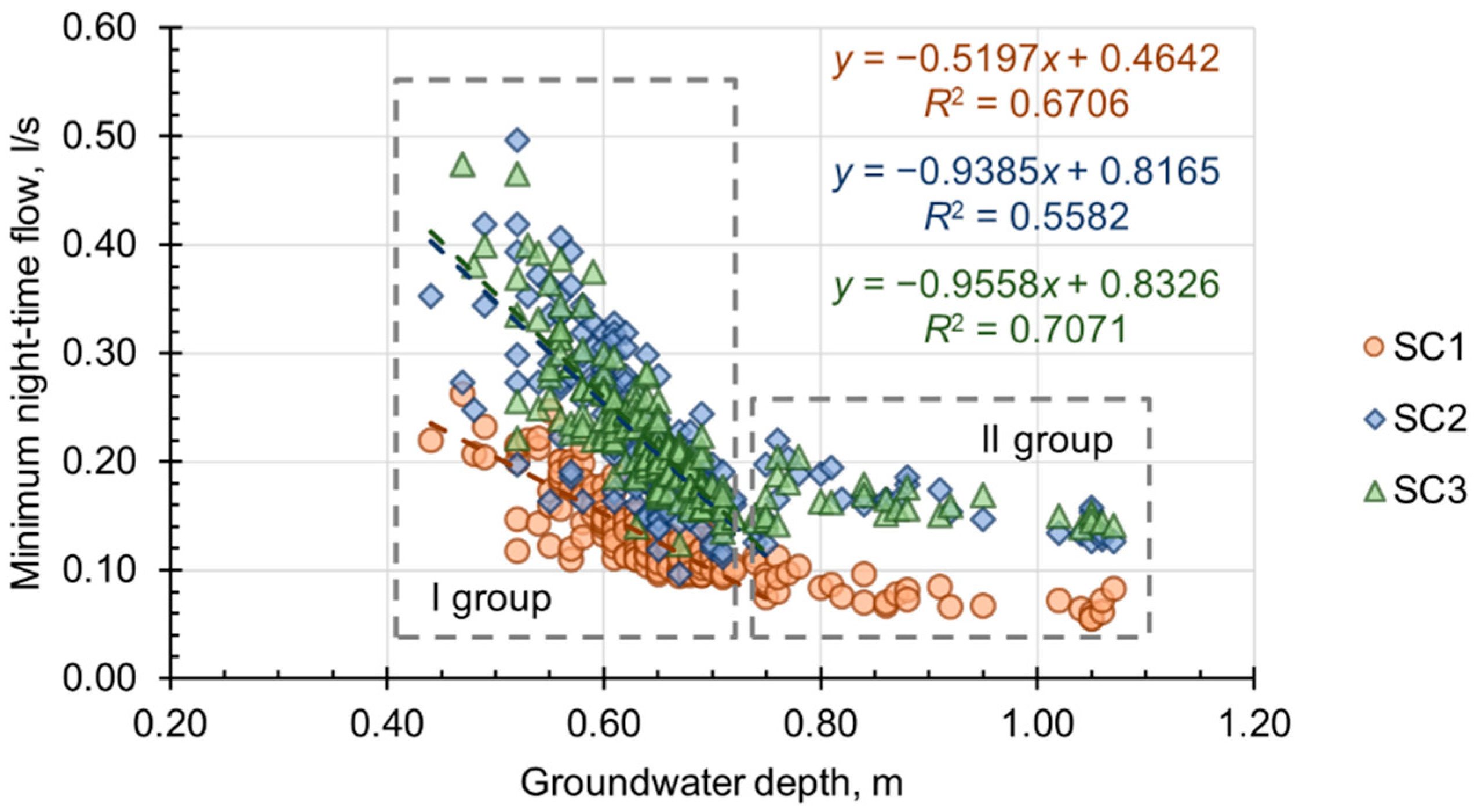
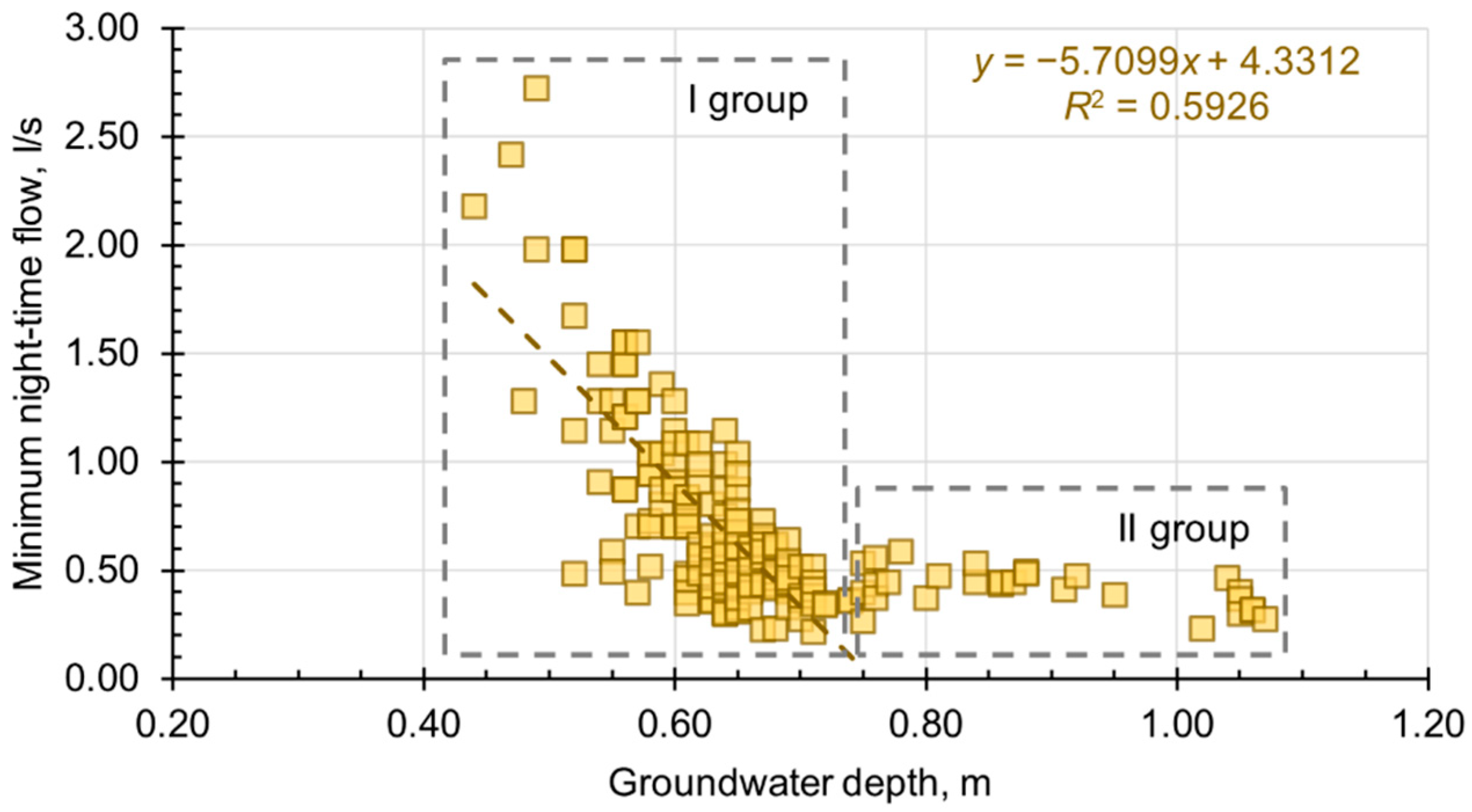
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Infrastructure to 2030 (Volume 2): Mapping Policy for Electricity, Water and Transport. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/futures/infrastructureto2030/40953164.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Semadeni-Davies, A.; Hernebring, C.; Svensson, G.; Gustafsson, L.-G. The Impacts of Climate Change and Urbanisation on Drainage in Helsingborg, Sweden: Combined Sewer System. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.B. (Ed.) Assessing Infiltration and Exfiltration on the Performance of Urban Sewer Systems (APUSS); IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-84339-149-4. [Google Scholar]
- Thorndahl, S.; Balling, J.D.; Larsen, U.B.B. Analysis and Integrated Modelling of Groundwater Infiltration to Sewer Networks: Integrated Modelling of Groundwater Infiltration to Sewer Networks. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3228–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödel, S.; Günthert, F.W.; Brüggemann, T. Investigating the Impacts of Extraneous Water on Wastewater Treatment Plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiß, G.; Brombach, H.; Haller, B. Infiltration and Inflow in Combined Sewer Systems: Long-Term Analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, K.J.; Bjerkholt, J.T.; Lindholm, O.G.; Ratnaweera, H. Analysing Consequences of Infiltration and Inflow Water (I/I-Water) Using Cost-Benefit Analyses. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, L.-G. Alternative Drainage Schemes for Reduction of Inflow/Infiltration-Prediction and Follow-Up of Effects with the Aid of an Integrated Sewer/Aquifer Model. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Urban Drainage, Internet, 21 September 2000; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Marleni, N.; Gray, S.; Sharma, A.; Burn, S.; Muttil, N. Impact of Water Management Practice Scenarios on Wastewater Flow and Contaminant Concentration. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saletti, A.O.; Rosén, L.; Lindhe, A. Framework for Risk-Based Decision Support on Infiltration and Inflow to Wastewater Sewer Systems. Water 2021, 13, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénédittis, J.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L. Infiltration in Sewer Systems: Comparison of Measurement Methods. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beheshti, M.; Sægrov, S.; Ugarelli, R. Infiltration/Inflow Assessment and Detection in Urban Sewer System. Vann 2015, 1, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, R.; International Water Association (Eds.) Performance Indicators for Wastewater Services; Manual of best practice; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2003; ISBN 978-1-900222-90-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kracht, O.; Gujer, W. Quantification of Infiltration into Sewers Based on Time Series of Pollutant Loads. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareš, V.; Krejčí, P.; Stránský, D.; Sýkora, P. Long-Term Monitoring of Infiltration/Inflow Based on Diurnal Variation of Pollutant Mass Flux. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Edinburgh, UK, 31 August–5 September 2008; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Dirckx, G.; Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C.; De Gueldre, G.; Van De Steene, B. Dilution of Sewage in Flanders Mapped with Mathematical and Tracer Methods. Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigiobbe, V.; Giulianelli, M. Quantification of Sewer System Infiltration Using Δ18O Hydrograph Separation. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ville, N.; Le, H.M.; Schmidt, L.; Verbanck, M.A. Data-Mining Analysis of in-Sewer Infiltration Patterns: Seasonal Characteristics of Clear Water Seepage into Brussels Main Sewers. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, K.J.; Bjerkholt, J.T.; Lindholm, O.G.; Ratnaweera, H. Infiltration and Inflow (I/I) to Wastewater Systems in Norway, Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. Water 2018, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczor, G.; Agnieszka, C. Analysis of the Proportion of Incidental Water in Annual Wastewater Inflows to a Selected Treatment Plant during a 15-Year Observation Period. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ūdenssaimniecības Nozares Rādītāji. Available online: https://www.sprk.gov.lv/content/nozares-raditaji-0 (accessed on 3 August 2022). (In Latvian)
- Relation: Jūrmala (13048687)-OpenStreetMap. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org/relation/13048687 (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Ziema, 2021. Available online: https://klimats.meteo.lv/laika_apstaklu_raksturojums/2022/ziema/ (accessed on 3 August 2022). (In Latvian).
- Depth-to-Water Kartēšanas Dati. Available online: http://www.silava.lv/produkti/Kartografiskie-materiali.aspx (accessed on 3 August 2022). (In Latvian).
- Sola, K.J.; Bjerkholt, J.; Lindholm, O.; Ratnaweera, H. What Effect Does Rehabilitation of Wastewater Pipelines Have on the Share of Infiltration and Inflow Water (I/I-Water)? Water 2021, 13, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirckx, G.; Van Daele, S.; Hellinck, N. Groundwater Infiltration Potential (GWIP) as an Aid to Determining the Cause of Dilution of Waste Water. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.; Babcock, R. A Flow-Calibrated Method to Project Groundwater Infiltration into Coastal Sewers Affected by Sea Level Rise. Water 2020, 12, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, M.; Sægrov, S. Quantification Assessment of Extraneous Water Infiltration and Inflow by Analysis of the Thermal Behavior of the Sewer Network. Water 2018, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, M.; Sægrov, S. Detection of Extraneous Water Ingress into the Sewer System Using Tandem Methods—A Case Study in Trondheim City. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sub-Catchment | Network Length, m | Share of Old * Pipes, % | Average Depth, m | Connected Households, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC1 | 1120.3 | 0 | 2.47 | 85 |
| SC2 | 3144.8 | 0 | 2.48 | 60 |
| SC3 | 2067.1 | 0 | 2.72 | 64 |
| SC4 | 2486.7 | 82 | 2.78 | 46 |
| SC5 ** | 5648.2 | 31 | 2.60 | 58 |
| Measuring Device | Parameter Measured | Measurement Accuracy | Measurement Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| MACE FloPro XCi | Flow velocity | ±1% up to 3.0 m/s | Every minute |
| Flow depth | 0.2–1.0% of full scale | ||
| Campbell Scientific | Rainfall depth | ± 0.2 mm | Every 5 min |
| Kalyx-RG | Rainfall intensity | >98% up to 20 mm/h | |
| Measuring Rod | Groundwater level | ±0.01 m | Daily |
| Parameter | SC1 | SC2 | SC3 | SC4 | SC5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o offset | w/offset | |||||
| Correlation coeff. R | 0.8189 | 0.7471 | 0.8410 | 0.7698 | 0.7746 | 0.7930 |
| Regression coeff. R2 | 0.6706 | 0.5582 | 0.7071 | 0.5926 | 0.5544 | 0.6288 |
| y-intercept | 0.4642 | 0.8165 | 0.8326 | 4.3312 | 5.3769 | 5.7402 |
| Slope | −0.5197 | −0.9385 | −0.9558 | −5.7009 | −7.4775 | −8.0501 |
| p-value | 1.33 × 10−42 | 3.74 × 10−32 | 1.15 × 10−46 | 2.28 × 10−35 | 2.48 × 10−23 | 5.01 × 10−28 |
| Count | 171 | 173 | 173 | 174 | 125 | 124 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dakša, G.; Dejus, S.; Rubulis, J. Assessment of Infiltration from Private Sewer Laterals: Case Study in Jurmala, Latvia. Water 2022, 14, 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182870
Dakša G, Dejus S, Rubulis J. Assessment of Infiltration from Private Sewer Laterals: Case Study in Jurmala, Latvia. Water. 2022; 14(18):2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182870
Chicago/Turabian StyleDakša, Gints, Sandis Dejus, and Jānis Rubulis. 2022. "Assessment of Infiltration from Private Sewer Laterals: Case Study in Jurmala, Latvia" Water 14, no. 18: 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182870
APA StyleDakša, G., Dejus, S., & Rubulis, J. (2022). Assessment of Infiltration from Private Sewer Laterals: Case Study in Jurmala, Latvia. Water, 14(18), 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182870






